Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol ABNORMAL VULVAL LESIONS: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
|
|
|
- Georgina Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol ABNORMAL VULVAL LESIONS: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Journal Name : International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology For your questions please send message to editorijrcog@gmail.com
2 TITLE PAGE Type of Article: Case Series Abnormal vulval lesions: Diagnosis and management. Dr. Aarti Kothari 1*, Dr. Usha Parekh 1, Dr. Rashmi Mahajan 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Dhiraj General Hospital, Waghodia Vadodara, Gujarat, India 2 Department of Dermatology, Dhiraj General Hospital, Waghodia Vadodara, Gujarat, India *Corresponding author: Dr. Aarti Kothari Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Dhiraj General Hospital, Room 22, Gargi Hostel, Sumandeep Vidyapeeth, Piparia, Waghodia, Vadodara , Guajarat Mobile No.: aartikothari13@gmail.com
3 ABSTRACT Background: Vulval symptoms are commonly found and cause considerable distress for women. Symptoms are often chronic and can significantly affect the quality of women's lives including sexual function and well being. Despite the frequency of vulval symptoms, women often find it difficult to seek medical advice due to multiple reasons, mostly cultural and emotional. This part is not easily self observable neither are women aware of the fact that a vulvar lesion could also be a manifestation of a systemic disease. The idea behind this study was to identify whether presenting vulval lesion is dermatological or non dermatological & to control the symptoms, to identify nature of the various vulvar lesions (inflammatory or neoplastic) and to identify those skin lesions not responding to treatment which require biopsy &further management. Methods: It was a clinical descriptive study. Cases included women with vulvar lesions who attended Gynaec OPD at Dhiraj General Hospital affiliated to S.B.K.S. Medical Institute and Research Centre of Vadodara. After taking their informed consent,all the women who had symptoms like vaginal discharge, itching or discomfort associated a with vulvar lesion, visible lesion or growth over vulva were thoroughly investigated to rule out any systemic illness causing vulvar lesion following which biopsy was taken if solid growth or a non healing lesion was present. Treatment was done according to the lesions. Conclusions: In the presence of vulvar complains, a diagnostic pathway including systematic physical examination is always mandatory to detect SCC early. A non healing lesion must be subjected to biopsy mandatorily. Women should be educated to avoid ODC drugs or creams when they face Vulval lesions. Keywords: Vulvar lesions, Haemangioma, Behcet's disease, Tuberculosis cutis orificialis
4 INTRODUCTION Vulval symptoms are common and cause considerable distress for women. Symptoms are often chronic and can significantly affect the quality of women's lives including sexual function and well being. Anatomically it is a part of genitalia, composed of several folds including clitoral hood, labia majora and minora, hymen, and anal margin 1. Despite the frequency of vulval symptoms, women often find it difficult to seek medical advice. Research has shown that there are many reasons as to why women do not ask for help including: That for cultural or emotional reasons as this part of the body is not much debated or discussed about in Indian women. That this region is not easily self-observable. The feeling that it is an embarrassing, uncomfortable or private matter. The belief that it is a normal part of getting older. Not being aware that there are treatments available. Not knowing how to initiate a conversation about these issues. Lack of knowledge that that signs can be observed elsewhere on the body, such as in lichen sclerosus or psoriasis when the lesion could be in Vulva. Lack of knowledge that many vulval lesions can be secondary to large variety of diseases, such as digestive, hematological, immunological, and endocrine disorders. Pathologically vulva, as a part of genitalia, can be involved by specific disorders such as multifocal HPV lesions of or vaginal infection Vulva can also exhibit specific dermatological diseases 2. In addition, vulva can also exhibit signs of a large variety of diseases, such as digestive, hematological, immunological, and endocrine disorders 3. Hence any vulvar disorder could be a presentation of not only dermatological but also non dermatological condition.
5 AIM To diagnose and treat abnormal vulvar lesions in women who attended Gynaec OPD of Dhiraj general hospital. OBJECTIVES Identify whether presenting vulval lesion is dermatological or non dermatological & to control the symptoms. Identify nature of the lesion. (Whether it is inflammatory or neoplastic). Identify those Skin lesions not responding to treatment which require biopsy &further management. MATERIALS AND METHODS It was a clinical descriptive study. Cases included women with vulvar lesions who attended Gynaec OPD at Dhiraj General Hospital affiliated to S.B.K.S. Medical Institute and Research Centre of Vadodara. After taking their informed consent,all the women with vulvar lesions were thoroughly investigated to rule out any systemic illness causing vulvar lesion following biopsy was taken if solid growth or a non healing lesion was present. Treatment was done according to the lesions. INCLUSION CRITERIA All females who had symptoms like vaginal discharge, itching or discomfort associated a with vulvar lesion All females with visible lesion over vulva. All females with visible growth over vulva. EXCLUSION CRITERIA Women who had vaginitis or cervicitis. Women with diagnosed or recurrent vulval cancer. Women with asymptomatic or nonvisible lesions.
6 METHODOLOGY The importance of history taking cannot be emphasized enough. The following points were considered while eliciting the history. Whether symptoms were sudden or gradual in onset was asked. Complaints of pain, discomfort, irritation, itching were commonly encountered. Complaints of dyspareunia, discharge and whether the partner had any similar complaints were enquired about. Since we dealt mostly with women from rural backgrounds who are not very good at accurate localisation of that part of their anatomy, whether the lesion was vulval or vaginal was ascertained. Some women who had made close inspection with a hand mirror could describe the lesion whilst others did not contemplate looking down there. Complaints of dysuria and increased urinary frequency too were looked out for as even in absence of urinary tract infection, it is painful to pass urine through an inflamed area. Questions about any other concurrent problems such as psoriasis, chickenpox, history of trauma or recent use of antibiotics were asked. Also, whether or not the problem was recurrent was kept in mind. Details of any personal or family history of atopic conditions (hay fever, asthma, eczema) were elicited. History of weight loss or prolonged cough helped us to conclude a tuberculous affection. History of diabetes was asked for in cases of recurrent vulvitis. Also, that Crohn's disease might as well have vulvar cutaneous involvement was kept in mind. A thorough examination with adequate lighting was done, as changes can be subtle. Pelvic floor muscle tone was assessed if penetration was painful. Examination of the rest of the body, including the mouth, for signs of lichen planus and the scalp, elbows, knees and nails for psoriasis was done.eczema may be seen at any site. The conjunctiva was examined as its affected in cases of Behcet s disease. Thorough examination of
7 the lymph nodes was done keeping in mind possibility of TB or malignancy. Lower eyelids, malar area, upper lips were examined as they may be involved in Syringomas. When confronted with a vulvar lesion, it is helpful to "categorize" the lesion using a systematic pathway which decreases the chance of missing a diagnosis. Dermatological and neoplastic classification is beyond the scope of this paper and only unususal cases have been the focus.thus the colour and presentation of the lesion was used to broadly classify the lesion and to reach a provisional diagnosis. Outline 4 Visible White Lesions Lichen sclerosus Squamous cell hyperplasia Leukoplakia HPV VIN Squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva Red or Dark Lesions Seborrheid dermatitis Psoriasis Lichen planus Lentigo Paget's disease
8 Nevi VIN or cancer Malignant melanoma When the diagnosis was not readily apparent by unaided (ie, naked-eye) or colposcopic examination of the vulva,vulvar biopsies were performed for acetowhite changes and visible vulvar lesions such as ulceration or hyperpigmentation. Mostly the diagnosis was done by inspection and clinical presentation. It was remembered that Patch testing may be necessary in cases of vulvar detmatitis. Serology: CRP and ESR was done in patients who appeared to have tuberculous affection of the vulva. CBC was routinely done in all cases. ANA and HLA-B51 was done where if Behçet's disease was a possibility. RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin) was done in solitary, raised, firm, red papules with regional non tender lymphadenopathy. HIV testing was done in all cases routinely. Urine: PCR for Chlamydia (First pass urine test) PCR for Gonorrhea (First pass urine test) For Non healing lesions the patient was referred for biopsy of lesion.the mainstay of diagnosis is vulvar biopsy. Furthermore, all patients with a nonneoplastic vulvar epithelial disorder were checked at regular intervals. Areas of ulceration or foci of granulation or nodularity that developed were biopsied to exclude malignant change. The formation of hyperkeratotic plaques or erosions that do not respond to treatment aroused suspicions of malignancy.
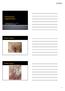
9 CASE PRESENTATIONS: CASE 1 : A 23 year old female, nulligravida came with complaints of growth on medial region of the right vulva for 6 years, when she had first noticed it as a reddish subcutaneous nodule. She ignored it despite its gradual clinical enlargement. There was no significant past or family history. Local examination revealed a pedunculated growth of 6 cm x 3cm,non tender with irregular margins. It was soft in consistency. There was no lymphadenopathy. Transillumination test was positive. Differential diagnosis were labial cyst, and mesenchymal tumors such as lipoma and liposarcoma. USG showed ill-defined hypoechoic mass of heterogeneous echotexture with multiple cystic spaces within. Colour Doppler was done which showed no feeder vessel from large vessel and slow venous flow. Treatment : Simple tumor excision was done at the level of the stalk. Histopathology report was suggestive of a HEMANGIOMA. ( Image 1 : Haemangioma vulva.) CASE 2 :A 65 year old Para 4 Live 4 female presented with complaints of dysuria and ulceration over external genitalia for 1 year. It had grown slightly in size over the past year. She had no significant past, personal or family history. The patient had initially been given antibiotics elsewhere classifying it as an inflammatory lesion. Local examination revealed a growth with an ulcerated area of 4 x 3 cm which involved the left labia minora, labia majora and clitoris. It was irregular, non tender, soft with erosions over the surface. Inguinal lymphadenopathy was palpable Differential diagnosis: Squamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, adenocarcinoma
10 Old age with a non healing ulcer with nontender lymphadenopathy led us to suspect that it could be malignant and biopsy was done.biopsy report suggested Well differentiated Squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva and nodes were evaluated by FNAC.staging workup, including chest X-rays, and abdominal CT scan, did not show any sign of distant sites of disease. Radical vulvectomy with bilateral inguinal lymphadenectomy with vulvar reconstruction was done. The patient was referred to a higher centre for further treatment. (Image 2 :Squamous cell carcinoma ) CASE 3 :A 25 years old G2P1L1 at 33 weeks of gestation with fever and rashes over left foot, hand, genital n oral lesions that developed over a month. There were episodes of simlar ulcerations last year. On clinical intraoral exam, multiple ulcers were observed, measuring approximately cm in diameter, with the presence of an erythematous halo. On examination of vulva Multiple bluish red ulcers necrotic ulcers which were painful during palpation were seen, which had irregular margins were present over right labia, clitoris and fourchette. The labia was swollen and pushed the left labia to one side, rendering a distorted appearance. Bilateral cervical, axillary and inguinal non tender lymphadenopathy was present. Differential diagnosis : Malignancy,HIV / AIDS, MAGIC Syndrome ( mouth and Genital ulcers with inflamed cartilages), Sarcoidosis, PFAPA Syndrome (Periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis and adenitis syndrome) Histopathology from skin biopsy showed acute on chronic inflammation with necrotic areas and areas of leucocytoclastic vasculitis and was consistent with findings of BEHCET S DIEASE Management: Erythromycin (500mg) QID and Clotrimazole mouth paint was given. Fluticasone ointment for local application was given. Patient went into spontaneous labour at 36 weeks and delivered a female child of 1.9 kgs her post partum period was uneventful and the rashes healed over the next 2 weeks. (Image 3 :Behcets disease afflicting vulva.)
11 CASE 4 : A 33 year old female P2,L2 came with complaints of a swelling over the vulva which was associated with mild pain. This swelling had grown in size over 1 year. Local Examination showed a cyst of 1 x 2 cms. over the right labia minora. It was soft, cystic, non tender. No lymphadenopathy was present. Differential Diagnosis: Inclusion cyst, sebaceous cyst, Bartholin s cyst. Diagnosis of Bartholin s cyst made by clinical evaluation and physical evaluation. Marsupialisation was done and antibiotics were given. (Image 4 : BARTHOLINS CYST) CASE 5 : A 22 year old female patient presented with chronic painful ulcers of over genitalia and weight loss since 12 months. There was no history of persistent cough, though there were episodes of mild evening rise in temperature. On examination: There were multiple painful ulcers involving the labia majora, minora and fourchette which were associated with seropurulent discharge. Multiple, enlarged, non tender, mobile inguinal lymph nodes could be palpated. (Image 5 (a):tuberculous cutis orificialis) (Image 5 (b) Tuberculoid granulomas) Differential diagnosis: Tuberculous cutis orificialis, syphilis, deep fungal infections Mantoux test was positive. erythrocyte sedimentation rate (80 mm/h; normal 1 20) and low haemoglobin (Hb 10 g/dl; normal 12 16). Liver function, renal function and blood
12 sugar were normal. Serology for sex transmitted diseases including syphilis, human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B, C was negative. Histopathology revealed tuberculoid granulomas with necrosis in the deeper dermis. Acid-fast bacilli were seen in the granuloma and necrotic area by Ziehl-Neelsen stain Diagnosis Tuberculous cutis orificialis The patient was started on standard anti-tb therapy, consisting of isoniazid 300 mg, rifampicin 600 mg, pyrazinamide 1000 mg, and sethambutol 900 mg daily for 2 months, followed by an additional 4 months therapy with isoniazid and rifampicin. CASE 6:A 45 year old female patient presented with large verrucous plaque over suprapubic region extending to right labia majora for past 5 years. H/O occasional fluid discharge from lesions. On examination indurated non tender bilateral inguinal lymph nodes present. FNAC revealed features of tuberculous lymphadenitis Histopathology from the lesion revealed multiple dilated cystic spaces in the papillary dermis Diagnosis Lymphedema of vulva secondary to tuberculosis (Image 6 (a): Lymphedema vulva) (Image 6 (b) : Multiple dilated cystic spaces in the papillary dermis.)
13 DISCUSSION The vulva is the part of the female genital tract located between the genitocrural folds laterally, the mons pubis anteriorly, and the anus posteriorly. This hollow structure contains the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal orifice, hymen, Bartholin glands, and Skene ducts. Microscopically, vulva is covered by different types of epithelia, depending on the area of interest, including, from its lateral to medial region, keratinized hair bearing skin, partially keratinized hairless skin, and, beyond Hart s line, mucous membrane of the vestibule. A large number and variety of adnexal structures are associated with vulvar skin in its different sections, such as pilosebaceous units, sebaceous and sweat glands, mucous secretory glands, muscle fibers, and deeper major or minor vestibular glands. Vicinity of underlying vascular structures can also modify vulvar aspects. Therefore, any component of blood and lymphatic vessels can be affected through malformations, tumors, or dystrophic changes.the epithelium of the vestibule is neither pigmented nor keratinized and contains eccrine gland. Considering anatomy and patient s own point of view, this region is of course not easily self-observable. 2 From the above cases we can understand that the women coming with vulvar lesions to the OPD are few. To come to a reasonable diagnosis, it is very important that we follow a protocol or an outline, based on color, symptoms, concurrent lesions elsewhere and assessment of lymph nodes. The history may be difficult to elicit because of anxiety about the diagnosis, frustration about ineffective treatment, secondary sexual dysfunction or resultant and often underrecognised depression. When child presents with a condition that is usually sexually transmitted (such as genital warts or HSV), sexual activity needs to be considered, but it is not the only cause. Evidence of trauma, especially with a spurious explanation, is also suggestive. Other features may include behavioural disorders and inappropriate sexual behavior Infectious disorders include diseases caused by known transmissible agents, such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. Non neoplastic epithelial disorders like Acanthosis nigricans, Behcet s disease, Contact dermatitis, Lichen sclerosis, Paget s disease, atopic dermatitis can also affect vulva. Cystic lesions of vulva include bartholin gland cyst, skene duct cyst, epithelial inclusion cyst. Other than cancer vulva, solid Nonneoplastic lesions includes fibroma, hemangioma, lipoma etc.
14 Too often, women suffering from vulvar complains, especially itching, are still nowadays offered symptomatic treatment without even examination or diagnostic process, such as over-the-counter delivery of any cream. This may, in some cases, lead, even in young people, to delayed diagnosis of life-threatening diseases, such as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). 2 No screening strategies have been developed for the prevention of vulvar cancer through early detection of VIN. Diagnosis is limited to visual assessment. Biopsy is indicated for most pigmented and non healing vulvar lesions 5. Vulval cancer is a aggressive cancer with poor prognosis and few treatment options hence by thoroughly diagnosing and treating these premalignant and benign lesions we can prevent cancer. CONCLUSIONS: Vulva can also exhibit signs of a large variety of diseases, such as digestive, hematological, immunological, and endocrine disorders. Hence consider any vulvar disorder as a potential expression of a very large panel of diseases. In the presence of vulvar complains, a diagnostic pathway including systematic physical examination is always mandatory to detect SCC early. Important to note localization, boarder asymmetry, number, color &distribution of abnormal lesion on examination. A biopsy always indicated in a non healing ulcerative or hypertrophied lesion not responding to medical treatmen Women should be educated to avoid ODC drugs or creams when they face Vulval lesions.
15 REFERENCES 1. S. K. Fistarol and P. H. Itin, Diagnosis and treatment of lichen sclerosus, American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, vol. 14, no. 1, pp , Jean Doyen et al., Vulvar Skin Disorders throughout Lifetime: About Some Representative Dermatoses, BioMed Research International Volume 2014 (2014), Article ID Marzano AV, Borghi A, Stadnicki A, Crosti C, Cugno M. Cutaneous manifestations in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: pathophysiology, clinical features, and therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis Jan. 20 (1): D. Ashley Hill, M.D, Vulvar Diseases in Primary Care The Visible Lesion: Is it Cancer?, Retrieved from 5. Management of Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Committee Opinion No American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2011;118:
16 Article Images
17 Article Images
18 Article Images
19 Article Images
20 Article Images
21 Article Images
22 Article Images
23 Article Images
Disorders of the vulva
 Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Meet the ISSVD. President ISSVD. Jacob Bornstein, MD
 Meet the ISSVD Jacob Bornstein, MD President ISSVD Chairman, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Western Galilee Hospital Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Medicine Nahariya, Israel ISSVD Symposium: The
Meet the ISSVD Jacob Bornstein, MD President ISSVD Chairman, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Western Galilee Hospital Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Medicine Nahariya, Israel ISSVD Symposium: The
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
Clinical Scoring System to Detect Malignant and Premalignant Vulval Lesions
 The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 DOI 10.1007/s13224-013-0458-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Scoring System to Detect Malignant and Premalignant Vulval
The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (January February 2014) 64(1):41 46 DOI 10.1007/s13224-013-0458-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Scoring System to Detect Malignant and Premalignant Vulval
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver, Canada
 Case title: Case authors: Case synopsis: The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Dr. Leslie A. Sadownik Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver,
Case title: Case authors: Case synopsis: The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Dr. Leslie A. Sadownik Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver,
3/25/2019. J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse
 J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse 1 4 th most common GYN cancer 5% of malignancies of GYN type. 4850 new cases annually 1030 deaths Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (Lichen
J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse 1 4 th most common GYN cancer 5% of malignancies of GYN type. 4850 new cases annually 1030 deaths Cigarette smoking Vulvar dystrophy (Lichen
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
HOW TO DIAGNOSE VULVAR DISEASES:
 HOW TO DIAGNOSE VULVAR DISEASES: Diagnostic approach. Normal findings. Maria Sol Peremateu, MD A wide spectrum of benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions may occur on the vulva. Some of the disorders
HOW TO DIAGNOSE VULVAR DISEASES: Diagnostic approach. Normal findings. Maria Sol Peremateu, MD A wide spectrum of benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions may occur on the vulva. Some of the disorders
Giant Acrochordon of Vulva
 Giant Madhusudan Dey, Reema Kumar, Raghu Sriram Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Abstract Giant acrochordon or fibroepithelial stromal polyps usually occur
Giant Madhusudan Dey, Reema Kumar, Raghu Sriram Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Abstract Giant acrochordon or fibroepithelial stromal polyps usually occur
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
MYTHS OF STIs True or False
 MYTHS OF STIs True or False 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Birth control pills prevent the spread of STDs. 3. Douching will cure and STD. 4. Abstinence is the best way to prevent
MYTHS OF STIs True or False 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Birth control pills prevent the spread of STDs. 3. Douching will cure and STD. 4. Abstinence is the best way to prevent
Lesions & Lifestyles
 Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
III CONGRESO INTERNACIONAL EN GINECOESTÉTICA Y CIRUGÍA ÍNTIMA
 28 OCTUBRE 2017 MADRID, ESPAÑA III CONGRESO INTERNACIONAL EN GINECOESTÉTICA Y CIRUGÍA ÍNTIMA PLASTIA DE LOS LABIOS MAYORES DRA. ANA LÚCIA NOGUEIRA www.clinicasabeanas.pt ABOUT ME BOUT Dra. Ana Lúcia Nogueira,
28 OCTUBRE 2017 MADRID, ESPAÑA III CONGRESO INTERNACIONAL EN GINECOESTÉTICA Y CIRUGÍA ÍNTIMA PLASTIA DE LOS LABIOS MAYORES DRA. ANA LÚCIA NOGUEIRA www.clinicasabeanas.pt ABOUT ME BOUT Dra. Ana Lúcia Nogueira,
Clinical Pathological Conference. Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva
 Clinical Pathological Conference Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva History F/48 Chinese Married Para 1 Presented in September 2004 Vulval mass for 2 months Associated with watery and blood stained discharge
Clinical Pathological Conference Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva History F/48 Chinese Married Para 1 Presented in September 2004 Vulval mass for 2 months Associated with watery and blood stained discharge
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Treatment of Bowenoid and Basaloid Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 with Imiquimod 5% Cream DO NOT DUPLICATE
 The Journal of Reproductive Medicine Treatment of Bowenoid and Basaloid Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 with Imiquimod 5% Cream Claudia Marchitelli, M.D., Graciela Secco, M.D., Myriam Perrotta, M.D.,
The Journal of Reproductive Medicine Treatment of Bowenoid and Basaloid Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2/3 with Imiquimod 5% Cream Claudia Marchitelli, M.D., Graciela Secco, M.D., Myriam Perrotta, M.D.,
Dr. Maliheh Keshvari
 1 Dr. Maliheh Keshvari Assistant professor of Urology Fellowship in Female Urology Mashhad University of Medical Sciences 2 Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction 3 It was not until recently that urologists
1 Dr. Maliheh Keshvari Assistant professor of Urology Fellowship in Female Urology Mashhad University of Medical Sciences 2 Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction 3 It was not until recently that urologists
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Timby/Smith: Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9/e
 Timby/Smith: Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9/e Chapter 62: Caring for Clients With Sexually Transmitted Diseases Slide 1 Epidemiology Introduction Study of the occurrence, distribution, and causes
Timby/Smith: Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9/e Chapter 62: Caring for Clients With Sexually Transmitted Diseases Slide 1 Epidemiology Introduction Study of the occurrence, distribution, and causes
How to Prevent Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
Collar stud abscess an interesting case report
 Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
What are the symptoms of a vulval skin condition?
 Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad. Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
4Ps LUMPS AND BUMPS B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS. Most Common BUMP in the oral cavity Fibroma INTERDENTAL PAPILLAE LESIONS
 B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
Periocular Malignancies
 Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Icd 10 code for enlarged inguinal lymph nodes
 Cari untuk: Cari Cari Icd 10 code for enlarged inguinal lymph nodes 22-2-2012 AMERICAN JOINT COMMITTEE ON CANCER AJCC CANCER STAGING AT L A S EDITORS FREDERICK L. GREENE, m.d. Chair, Department of General
Cari untuk: Cari Cari Icd 10 code for enlarged inguinal lymph nodes 22-2-2012 AMERICAN JOINT COMMITTEE ON CANCER AJCC CANCER STAGING AT L A S EDITORS FREDERICK L. GREENE, m.d. Chair, Department of General
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
Sexually Transmitted. Diseases
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases How can I get an STD? Many STDs are carried and transmitted through semen and vaginal fluids. Some STDs can be spread through skin to skin contact Mother to child STDs: Signs
Sexually Transmitted Diseases How can I get an STD? Many STDs are carried and transmitted through semen and vaginal fluids. Some STDs can be spread through skin to skin contact Mother to child STDs: Signs
What's the problem? - click where appropriate.
 STI Tool v 1.9 @ 16/11/2017 What's the problem? - click where appropriate. Male problems: screening urethral symptoms proctitis in gay men lumps or swellings ulcers or sores skin rash and/or itch Female
STI Tool v 1.9 @ 16/11/2017 What's the problem? - click where appropriate. Male problems: screening urethral symptoms proctitis in gay men lumps or swellings ulcers or sores skin rash and/or itch Female
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3
 PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
Lichen sclerosus. Lichen planus
 Lichen sclerosus Lichen planus Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist, Heatherwood and Wexham Park NHS Foundation Trust & St John s Institute of Dermatology, GSTT Outline Typical features of lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus Lichen planus Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist, Heatherwood and Wexham Park NHS Foundation Trust & St John s Institute of Dermatology, GSTT Outline Typical features of lichen sclerosus
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 37/Aug 21, 2014 Page 9580
 THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
Spectrum of Vulvar Lesions in an Obstetrics and Gynecology Outpatient Clinic
 in an Obstetrics and Gynecology Outpatient Clinic Ozhan Ozdemir, Mustafa Erkan Sari, Funda Arpaci Ertugrul, Ertugrul Sen, Bunyamin Ugur Ilgin, Cemal Atalay Ankara Numune Education and Research Hospital,
in an Obstetrics and Gynecology Outpatient Clinic Ozhan Ozdemir, Mustafa Erkan Sari, Funda Arpaci Ertugrul, Ertugrul Sen, Bunyamin Ugur Ilgin, Cemal Atalay Ankara Numune Education and Research Hospital,
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN)
 Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is it? Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is a condition where there are pre-cancerous cells in the skin of
Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is it? Vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is a condition where there are pre-cancerous cells in the skin of
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA
 CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA Report of two Cases with Clinical and Diagnostic Implications Presented By Dr. Amar Sholapurkar Under the guidance of Dr.Ausaf Ahsan Department of Oral Medicine & Radiology, MCODS,
CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA Report of two Cases with Clinical and Diagnostic Implications Presented By Dr. Amar Sholapurkar Under the guidance of Dr.Ausaf Ahsan Department of Oral Medicine & Radiology, MCODS,
Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis
 Home Search Browse Resources Help What's New About Purpose Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis This study is currently recruiting patients. Sponsors and Collaborators: University of Pennsylvania Amgen
Home Search Browse Resources Help What's New About Purpose Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis This study is currently recruiting patients. Sponsors and Collaborators: University of Pennsylvania Amgen
Clinicopathologic Self-Assessment
 Clinicopathologic Self-Assessment Handout Symposium (S003), July 27 th 2017 Maija Kiuru MD PhD Assistant Professor, Departments of Dermatology & Pathology University of California Davis CASE 1: History
Clinicopathologic Self-Assessment Handout Symposium (S003), July 27 th 2017 Maija Kiuru MD PhD Assistant Professor, Departments of Dermatology & Pathology University of California Davis CASE 1: History
Objectives. 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions. 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
 The Joy of Pediatric Skin Dr. Claire Sanger University of Kentucky Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Objectives 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
The Joy of Pediatric Skin Dr. Claire Sanger University of Kentucky Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Objectives 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
11/1/18. Age and Vulvar Pathology ANATOMY. Prepuce Clitoris Vestibule Hart line. Labia. minora. Labia. majora. Fourchette.
 Age and Vulvar Pathology Maria Angelica Selim, MD Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Director Dermatopathology Unit Duke University Medical Center Labia minora Labia majora Bartholin s duct Prepuce
Age and Vulvar Pathology Maria Angelica Selim, MD Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Director Dermatopathology Unit Duke University Medical Center Labia minora Labia majora Bartholin s duct Prepuce
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD J M O R G A N
 VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
Sexual Abuse. Dr Burke Baird
 Sexual Abuse Dr Burke Baird Unlike physical abuse, where you are typically faced with a suspicious injury and you go looking for an explanation, with sexual abuse, you usually start with a verbal disclosure
Sexual Abuse Dr Burke Baird Unlike physical abuse, where you are typically faced with a suspicious injury and you go looking for an explanation, with sexual abuse, you usually start with a verbal disclosure
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers
 Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
SCORE 0 SCORE 1 SCORE 2 SCORE 3 Asymptomatic and fully active (ECOG 0; KPS or LPS 100%)
 Organ Scoring of Chronic GVHD PERFORMANCE SCORE: KPS ECOG LPS SKIN SCORE % BSA GVHD features to be scored by BSA: applies: Maculopapular rash/erythema Lichen planus-like features Sclerotic features Papulosquamous
Organ Scoring of Chronic GVHD PERFORMANCE SCORE: KPS ECOG LPS SKIN SCORE % BSA GVHD features to be scored by BSA: applies: Maculopapular rash/erythema Lichen planus-like features Sclerotic features Papulosquamous
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY
 Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Chancroid Table of Contents
 Subsection: Chancroid Page 1 of 8 Chancroid Table of Contents Chancroid Fact Sheet Subsection: Chancroid Page 2 of 8 Chancroid (Haemophilus ducreyi) Overview (1,2) For a more complete description of chancroid,
Subsection: Chancroid Page 1 of 8 Chancroid Table of Contents Chancroid Fact Sheet Subsection: Chancroid Page 2 of 8 Chancroid (Haemophilus ducreyi) Overview (1,2) For a more complete description of chancroid,
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Clinical Education Initiative CHANCROID: CLINICAL UPDATE. Speaker: Patricia Coury-Doniger, FNP-C, ANC
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org CHANCROID: CLINICAL UPDATE Speaker: Patricia Coury-Doniger, FNP-C, ANC 2/8/2017 Chancroid: Clinical Update [video transcript] 00:00:11 I have no disclosures.
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org CHANCROID: CLINICAL UPDATE Speaker: Patricia Coury-Doniger, FNP-C, ANC 2/8/2017 Chancroid: Clinical Update [video transcript] 00:00:11 I have no disclosures.
Photo Diagnosis. An illustrated quiz on problems seen in everyday practice ANSWERS ON PAGE 52. Provided by Dr. Benjamin Barankin, Edmonton, Alberta.
 An illustrated quiz on problems seen in everyday practice Case 1 A 67-year-old man had surgery on the chest two years ago after significant weight loss and night sweats. 2. What factors can increase the
An illustrated quiz on problems seen in everyday practice Case 1 A 67-year-old man had surgery on the chest two years ago after significant weight loss and night sweats. 2. What factors can increase the
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Take out CST test corrections What do you know about STDs?
 Assignment #5 STDs LO: To understand sexually transmitted diseases. EQ: What are all of the ways to contract STDs? (4-5 sentences underlining key words) AGENDA 5/12-5/13 1. Group work 2. Notes Homework
Assignment #5 STDs LO: To understand sexually transmitted diseases. EQ: What are all of the ways to contract STDs? (4-5 sentences underlining key words) AGENDA 5/12-5/13 1. Group work 2. Notes Homework
OCCG SERVICE SPECIFICATION (2017/18)
 OCCG SERVICE SPECIFICATION (2017/18) Primary Care Service for Skin Cancers: Dermatology Shared Care Monitoring for Melanoma, Lichen Sclerosus and Squamos Cell Carcinoma 1. Background For patients who have
OCCG SERVICE SPECIFICATION (2017/18) Primary Care Service for Skin Cancers: Dermatology Shared Care Monitoring for Melanoma, Lichen Sclerosus and Squamos Cell Carcinoma 1. Background For patients who have
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II SESSION VI. Friday, MARCH 20, 2015 STUDENT COPY
 MHD II, Session VI, STUDENT Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II SESSION VI Friday, MARCH 20, 2015 STUDENT COPY Resource for cases: ACP Medicine (Scientific American Medicine) - Vaginitis
MHD II, Session VI, STUDENT Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II SESSION VI Friday, MARCH 20, 2015 STUDENT COPY Resource for cases: ACP Medicine (Scientific American Medicine) - Vaginitis
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive abdominal distension 3 months Failure
 Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS
 LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
How is it transferred?
 STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
Fever in Lupus. 21 st April 2014
 Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Swelling. Size: measure exact size in cm using a tape measure (measure longitudinal and transverse axis and if possible the depth)
 Swelling Inspection Site: exact anatomic position Number: single or multiple Shape: spherical, oval, kidney-shaped or irregular Size: measure exact size in cm using a tape measure (measure longitudinal
Swelling Inspection Site: exact anatomic position Number: single or multiple Shape: spherical, oval, kidney-shaped or irregular Size: measure exact size in cm using a tape measure (measure longitudinal
Malignant Melanoma Early Stage. A guide for patients
 This melanoma patient brochure is designed to help educate melanoma patients and their caregivers. It was developed under the guidance of Dr. Michael Smylie, Professor, Department of Oncology, University
This melanoma patient brochure is designed to help educate melanoma patients and their caregivers. It was developed under the guidance of Dr. Michael Smylie, Professor, Department of Oncology, University
Lichen planus. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Lichen planus Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 8 What is lichen planus? Lichen planus is a non-cancerous, inflammatory skin condition that causes an itchy, non-infectious rash (small purple
Lichen planus Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 8 What is lichen planus? Lichen planus is a non-cancerous, inflammatory skin condition that causes an itchy, non-infectious rash (small purple
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II SESSION 6. Friday, MARCH 18, 2016 STUDENT COPY
 MHD II, Session 6, STUDENT Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II SESSION 6 Friday, MARCH 18, 2016 STUDENT COPY Resource for cases: ACP Medicine (Scientific American Medicine) - Vaginitis
MHD II, Session 6, STUDENT Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II SESSION 6 Friday, MARCH 18, 2016 STUDENT COPY Resource for cases: ACP Medicine (Scientific American Medicine) - Vaginitis
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system?
 Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect
 Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE!
 What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE! What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? How are they spread? What are the different types of STDs? How do I protect myself? STDs are infections or diseases
What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE! What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? How are they spread? What are the different types of STDs? How do I protect myself? STDs are infections or diseases
Preventing Sexual Transmitted Diseases
 Preventing Sexual Transmitted Diseases Chapter 12 Card game Lie Sexually Transmitted Diseases Sexuality is an intrinsic part of human nature and affects many things People are not always honest about their
Preventing Sexual Transmitted Diseases Chapter 12 Card game Lie Sexually Transmitted Diseases Sexuality is an intrinsic part of human nature and affects many things People are not always honest about their
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Cervical Cancer 3/25/2019. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
 Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
BCCCP Approved ICD-9 Code List Fiscal Year 2010
 BCCCP Approved ICD-9 List Fiscal Year 2010 Diagnosis Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Central portion 174.2 Malignant
BCCCP Approved ICD-9 List Fiscal Year 2010 Diagnosis Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Central portion 174.2 Malignant
Chief complaint. A mass at right chest
 Chief complaint A mass at right chest Present illness This 1-year-5-month-old girl had a mass at right side chest since one month ago. flat and not tender at first In the recent 2 days, the mass enlarged
Chief complaint A mass at right chest Present illness This 1-year-5-month-old girl had a mass at right side chest since one month ago. flat and not tender at first In the recent 2 days, the mass enlarged
Mousa. Lina Al-Lawama. Enas Ajarma. 0 P a g e
 3 Mousa Lina Al-Lawama Enas Ajarma 0 P a g e رب اشرح لي صدري ويسر لي أمري واحلل عقدة من لساني يفقهوا قولي -Last time we were talking about vulvar pathology (non neoplastic epithelial disorder :lichen chronicus
3 Mousa Lina Al-Lawama Enas Ajarma 0 P a g e رب اشرح لي صدري ويسر لي أمري واحلل عقدة من لساني يفقهوا قولي -Last time we were talking about vulvar pathology (non neoplastic epithelial disorder :lichen chronicus
That. Name QUIZ. 60 SEPTEMBER 2017 // dentaltown.com
 QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview Q: What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? A: It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. Q: How many people have STDs?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview Q: What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? A: It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. Q: How many people have STDs?
WOMENCARE. Herpes. Source: PDR.net Page 1 of 8. A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407)
 WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Herpes Basics: Herpes is a common viral disease characterized by painful blisters of the mouth or genitals. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Herpes Basics: Herpes is a common viral disease characterized by painful blisters of the mouth or genitals. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes
Oral Tumors in Dogs Gingival Enlargement
 Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Non venereal benign dermatoses of vulva in sexually active women: a clinical study
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Singh G et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2016 Jun;2(2):25-29 http://www.ijord.com Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20162419
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Singh G et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2016 Jun;2(2):25-29 http://www.ijord.com Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20162419
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 5 No 2:16, December Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris Pathak D.* and Thapa A** Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 5 (2): 16 * Consultant Dermatologist, Delhi Dermatology Group Kubba,
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris Pathak D.* and Thapa A** Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 5 (2): 16 * Consultant Dermatologist, Delhi Dermatology Group Kubba,
ASCCP 2016 Annual Meeting. Post Test. Hope K. Haefner, MD The University of Michigan Center for Vulvar Diseases
 ASCCP 2016 Annual Meeting Post Test Hope K. Haefner, MD The University of Michigan Center for Vulvar Diseases haefner@umich.edu Disclosure Hope Haefner, MD was previously on the advisory board of Merck
ASCCP 2016 Annual Meeting Post Test Hope K. Haefner, MD The University of Michigan Center for Vulvar Diseases haefner@umich.edu Disclosure Hope Haefner, MD was previously on the advisory board of Merck
Vulvar Disease Clinical Cases
 Vulvar Disease Clinical Cases Hope K. Haefner, MD Professor University of Michigan Health System February 27, 2015 Cartagena Conflicts of Interest Hope Haefner, MD is on the Advisory Board of Merck Co.,
Vulvar Disease Clinical Cases Hope K. Haefner, MD Professor University of Michigan Health System February 27, 2015 Cartagena Conflicts of Interest Hope Haefner, MD is on the Advisory Board of Merck Co.,
STI Review. CALM: STI/HIV - Lesson One (Handout 3) Bacteria/ Transmission. Symptoms. Disease. Virus
 STI Review Bacteria/ Virus? Transmission Chlamydia Bacteria Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with a person who has Chlamydia Genital Herpes Virus By direct contact with the sores or blisters of an infected
STI Review Bacteria/ Virus? Transmission Chlamydia Bacteria Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with a person who has Chlamydia Genital Herpes Virus By direct contact with the sores or blisters of an infected
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
