Design Philosophy Abdominal
|
|
|
- Herbert Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Abdominal Abd/Pelvis Abdominal 6.1/6.2/6.3 Abd/Pelvis R/O Hernia High Image Quality Cancer Follow Up Abd/Pelvis Abd/Pelvis Flank Pain Abd/Pelvis Pre IVC Filter Removal Low Dose Renal Stone (including limited follow up) Abd/Pelvis Colonography Chest/Abd/Pelvis with IV Contrast Chest/Abd/Pelvis without IV Contrast Abd/Pelvis Urography Abdominal (Use routine abd/pelvis protocol) Abdominal 6.7/6.8/6.9 Abdominal 6.10/6.11/6.12 Abdominal 6.73/6.74/6.75 Abdominal 6.13/6.14/6.15 Abdominal 6.16/6.17/6.18 Abdominal 5.4/5.5/5.6 Abdominal 5.7/5.8/5.9 Abdominal 6.22/6.23/6.24 This is standard abdomen pelvis protocol. It is the default protocol for the vast majority of studies. This one is useful when a general screening protocol is needed. This protocol is intended for the evaluation of hernias. It asks the patient to perform a Valsalva maneuver during the scan to enhance the prominence of any hernia. Higher image quality version of the routine abdomen pelvis protocol. This protocol is to be used for cancer follow up on patients with pathology known to be of a subtle nature. The order should specifically ask for this version of the abdomen pelvis routine protocol at the time of placing the order. Typically, a determination would be made based on age and disease process (usually dependent on whether they could have metastatic disease to the liver). This protocol is primarily targeted for the first time evaluation of obstructing renal calculus. It is a non contrast study; therefore, not optimal for imaging other causes of abdominal pain. However, it may suffice in situations where the disease processes are not subtle. We discourage it for appendicitis. This protocol is used to assess for both the position and for the presence of clot in an IVC filter prior to removal. IV contrast is used and images are obtained 180 seconds after contrast injection to optimize opacification of the inferior vena cava and iliac veins. This protocol is intended for follow up of patients with known kidney stones; those status post lithotripsy; or those presenting to the emergency department with typical flank pain and are known to have kidney stones. Image resolution is satisfactory for identifying calculi, but not optimal for other pathology. This protocol is used to screen the colon for polyps or colonic mass disease. Patients undergo bowel preparation prior to the scan, and are then scanned in the supine and prone positions following colonic CO2 insufflation via rectal balloon tipped catheter. The supine prone positioning is meant to displace any retained fluid and fully expose all parts of the colon between the two views. A right lateral decubitus view can be added if distention is suboptimal in a colonic segment. The study is performed without IV contrast and at low dose as it is used in screening asymptomatic patients in most cases. If a patient has a known colon cancer and the referrer desires screening of the colon combined with assessment for metastatic disease, IV contrast can be administered on the supine view. This protocol is most commonly applied to patients with neoplasm that may affect the entire torso, but is not expected to affect the head and neck. This scan is usually performed for the evaluation of tumor or other conditions that may affect the entire torso in patients who cannot get IV contrast due to allergy or renal failure. This protocol is optimized for viewing the kidneys and the renal collecting system. The most common indication is hematuria.
2 Urothelial tumor follow up Abdominal 6.70/6.71/6.72 This protocol will be for patients with known urothelial cancer (bladder or ureters) and NO current evidence of or suspected metastatic disease. Also, some of these patients will not have a bladder (so no need for those to void as they will have a urostomy) If they have metastatic disease, routine CT A/P will suffice. Abd Liver Biphasic Abdominal 6.25/6.26/6.27 Abd Liver Triphasic Abdominal 6.28/6.29/6.30 Abd Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Abd Adrenal Gland Adenoma Abd Pancreas Pancreas Cancer (Neoplasm Screening) Abdominal 6.82/6.83/6.84 Abdominal 6.31/6.32/6.33 Abdominal 6.40/6.41/6.42 This protocol is optimized to evaluate cirrhotic patients and suspected liver tumors. It is also applied for the evaluation of hypervascular metastatic disease to the liver. This protocol is optimized for the work up of a potential liver transplant recipient. It has a high resolution arterial phase for precise hepatic arterial anatomy; a late arterial phase for the detection of tumor; and a portal/ parenchymal phase for the demonstration of varices and other possible pathology. Finally, a three minute delayed phase is performed to satisfy the UNOS requirement for HCC detection. This protocol, which is used to rule out HCC, is similar to the biphasic liver protocol, except it includes an additional delayed phase as mandated by UNOS. This protocol is optimized for the characterization of adrenal enlargement specifically for a suspect adenoma. It would not be protocol of choice to rule out pheocromocytoma. This scan is used in patients where there is suspicion of pancreas mass. The first phase is scanned in the late arterial phase. Since pancreatic adenocarcinoma is hypovascular, it is best detected at 40 seconds post contrast when the normal glandular tissue enhances optimally and the hypovascular tumor does not (optimizes contrast between the lesion and the background pancreas). The second phase is portal venous, to evaluate the solid organs, particularly the liver, for metastatic disease and for routine evaluation of the abdomen and pelvis. Abd/Pelvis Kidney Tumor Abdominal 6.49/6.50/6.51 CTA Abd Renal Donor Abdominal 6.52/6.53/6.54 Abd Small Bowel Enterography CTA Abd Obscure GI Bleed CTA Abd Mesenteric Ischemia Abdominal 6.55/6.56/6.57 Abdominal 6.58/6.59/6.60 Also for preoperative evaluation of known pancreatic neoplasm. It is optimized to detect vascular compromise. This protocol is optimized to evaluate patients with suspicion or evaluation of small renal neoplasm. This protocol is optimized to evaluate the potential renal transplant donor. This protocol is optimized for the evaluation of the small bowel. It is specifically designed for inflammatory bowel disease. This protocol is optimized to evaluate the source of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Abdominal 6.61/6.62/6.63 This protocol is optimized to evaluate for mesenteric ischemia. Trauma Chest Abdominal 5.22/5.23/5.24 Trauma Chest/Abd/Pelvis Abdominal 5.25/5.26/5.27 Trauma Abd/Pelvis Abdominal 6.4/6.5/6.6 Cystogram Abdominal 8.10/8.11/8.12 This protocol is optimized for the emergency evaluation for aortic injury, as well as any other sequel of trauma. This is tailored for rapid deceleration injury. Note: Routine creatinine cut off for IV contrast administration does not apply in a trauma. Emergency evaluation for aortic injury and/or organ disruption. Note: Routine creatinine cut off for IV contrast administration does not apply in a trauma. Emergency evaluation for traumatic organ disruption. This is usually reserved for a direct blow to the abdomen or low velocity MVA. Note: Routine creatinine cut off for IV contrast administration does not apply in a trauma. In the trauma setting, to evaluate bladder for trauma induced leak. (Typically performed when the standard trauma scan is inconclusive for a bladder leak.) In the non trauma setting, specifically for the evaluation of bladder tumor and to evaluate for non traumatic or post operative bladder leak. Body Pelvis Abdominal 8.16/8.17/8.18 This is a standard or routine examination of the pelvis meant to assess for pelvic pathologies that are not hypervascular.
3 Chest Chest Standard (Routine & High Resolution) Chest Low Dose Follow up Chest Low Dose Screening Chest 5.1/5.2/5.3 Chest 5.10/5.11/5.12 Chest 5.13/5.14/5.15 Chest CTA for PE Chest 5.16/5.17/5.18 Chest Dynamic 3D Airway Chest 5.70/5.71/5.72 This protocol is designed to address nearly all indications for chest CT while maintaining very low radiation exposure levels. It includes detailed information on the lungs, airways, and soft tissues. High resolution images for evaluating the lungs are a central part of this protocol, avoiding the need to rescan patients who have diffuse lung disease. Although intravenous contrast material can be administered at the discretion of the protocolling radiologist, for the vast majority of indications, contrast is not needed. This protocol was designed for follow up of nodules, pleural effusions, and other abnormalities using significantly lower dose than the standard CT. For nearly all patients, the effective dose will be below 3 msv, typically in the 1 2 msv range. This protocol is designed to be used exclusively for lung cancer screening. It meets the technical standards put forth by the American College of Radiology and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). This protocol is nearly identical to the routine chest CT protocol, and reconstructed axial images are identical. Multiplanar MIPs are included to meet CPT code requirements. The contrast injection protocol is designed to limit the number of bolus failures and maximize opacification of the pulmonary vasculature. This protocol is designed to evaluate the central airways, particularly to assess for tracheobronchomalacia or excessive dynamic airway collapse. In addition to standard high resolution images of the lungs, the forced expiratory images accentuate collapsibility of the trachea and central bronchi. This protocol includes additional reformations including minimum intensity projections (MinIPs) and optional 3 D virtual bronchoscopic images, which referring providers might find informative. For patients who have a recent volumetric thin section CT of the chest, the expiratory sequence of this protocol performed alone may be sufficient, minimizing additional radiation exposure. Because the breathing technique is different than traditional end expiratory chest CT, proper training of technologists and coaching of patients with close radiologist oversight will maximize the utility of this protocol.
4 Cardiovascular Non Gated CTA (Chest/Abd/Pelvis) Retrospectively Gated CTA Chest Gated Chest and Non Gated Abd/Pelvis CTA Prospectively Gated Coronary CTA Retrospectively Gated Coronary CTA CV 5.28/5.29/5.30 CV 5.31/5.32/5.33 CV 5.34/5.35/5.36 CV 5.37/5.38/5.39 CV 5.40/5.41/5.42 TAVI CTA CV 5.43/5.44/5.45 Prospectively Gated CTA Chest (Non Coronary) CV 5.46/5.47/5.48 Upper Extremity CTA CV 5.49/5.50/5.51 Lower Extremity CTA CV 5.52/5.53/5.54 Post Endostent Non Con Volume Change (Abd/Pelvis only) Prospectively Gated Left Atrial Appendage CV 5.58/5.59/5.60 CV 5.73/5.74/5.75 Evaluate for known or suspected type B (descending) aortic dissection, intramural hematoma (IMH), aneurysm, leak, tear, or vasculitis. Used to evaluate the heart and great vessels (aorta and pulmonary arteries) in patients with higher rates or in patients in which cardiac function is also being assessed. This is frequently used in patients with congenital heart disease that have contra indication for MRI. Used to evaluate patients with ascending aorta aneurysm in addition thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. Retrospective gating is used to minimize the delay between the gated chest and the non gated abdomen and pelvis sections. Used to evaluate the coronary arteries in patients with appropriate heart rates. Used to evaluate the coronary arteries in patients with higher rates or in patients in which cardiac function is also being assessed. Evaluation of patients being considered for trans catheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). This includes a retrospectively gated CTA of the heart to evaluate the aortic root for implantation of the valve and a nongated CTA chest abdomen and pelvis to evaluate the aorta and iliofemoral arteries to assess access. Evaluate for ascending aortic aneurysm, dissection, or injury. Evaluate cardiac or vascular abnormality without cardiac motion. (Note: A prospectively gated chest CTA cannot be combined with a non gated CTA abdomen/pelvis. If gated chest is need along with CTA abdomen/pelvis, use retrospective gating.) To evaluate upper extremity ischemia. The scan includes vascular imaging from the aortic arch to the finger tips. For iliac occlusive disease, peripheral vascular disease, and patients with a cold foot. Measure abdominal aortic aneurysm volume after endovascular repair. If the volume is stable or has decreased since the prior examination, no hemodynamically significant endoleak is present. Evaluation for left atrial thrombus, pre op for device (Watchman (TM)) implant. Includes two scan phases, a CTA on expiration and a 1 minute delay. Both phases are prospectively gated.
5 Musculoskeletal Bony Pelvis/Hips/SI/Femur/FAI (Without Metal) and Bony Pelvis/Hips/SI/Femur/FAI (With Metal) Knee/Tibia (Without Metal) and Knee/Tibia (With Metal) Ankle/Foot/Distal Tibia (Without Metal) and Ankle/Foot/Distal Tibia (With Metal) MSK 8.1/8.2/8.3 and 8.4/8.5/8.6 MSK 9.3 and 9.4 MSK 9.1 and 9.2 Femoral Anteversion MSK 9.8/9.9/9.10 Shoulder/Humerus (With or Without Metal) Elbow/Forearm (Without Metal) and Elbow/Forearm (With Metal) Wrist (Without Metal) and Wrist (With Metal) Soft Tissue Extremity with IV Contrast Chest Wall/Clavicle/AC Joint/SC Joint/Sternum/Ribs MSK 4.1/4.2/4.3 MSK 4.6 and 4.7 MSK 4.8 and 4.9 MSK 9.13/9.14/9.15 MSK 4.11/4.12/4.13 This protocol is designed to examine the cortex of the pelvic ring and acetabuli. Scans of the Bony Pelvis are most often obtained in the setting of acute trauma, or in the evaluation of fracture, SI joints, and prosthesis. Orthopedic surgeons may request post operative scans to assess healing, hardware, or osteolysis. The primary indication for a knee CT is to assess the alignment and degree of displacement of fracture fragments, particularly at the articular surfaces. These can also be used to assess the integrity of the bone around prosthesis. On rare occasions, a CT will be done immediately after an arthrogram of the knee. There is one single scanning protocol for all ankles and feet, which is typically used to evaluate for trauma. In most cases it is desirable to scan both ankles/feet at the same time. This protocol is a non contrast CT through bilateral hips, knees, and ankles (excluding the femur, tibia, and fibula shafts) to allow for measurement of the version angles of the femora and, if desired, tibiae. A routine shoulder CT (non arthogram) is used to evaluate for fractures of the scapula and/or proximal humerus, dislocation, shoulder prosthesis, or masses/infection in a patient who is not MR compatible. The primary indication for a shoulder arthrogram CT is to evaluate the rotator cuff and labrum in a patient who is not MR compatible. This primary indication is to evaluate for fracture, dislocation, or osteochrondritis. The elbow is the most difficult joint to scan as it is usually difficult to optimally position the elbow, particularly when it is in a cast. This scan is used to evaluate for wrist fracture, and similar to the elbow, it is important to position the arm over the head, with the arm as straight as possible. This protocol is used for detection or characterization of mass or infection. Bony detail is not important for these scans which use a dose level similar to an extremity CTA. Detection or characterization of fractures, evaluation of treated fractures to evaluate the progress of osseous healing or adequacy of fracture fixation. Also for the evaluation of arthritis, mineralized bone and soft tissue lesions, and to evaluate osteoarthritis. For infection, contrast will likely be needed.
6 Neuroradiology Brain Routine and Pediatric NAT/Trauma (Helical Mode) Brain Helical Scan with Angled Axial Reformations Neuro 1.1/11.1/11.2 Neuro 1.2/11.3/11.4 Brain (Axial Mode) Neuro 1.3/11.5/11.6 Stealth Stereotactic Head (Whole Brain Treatment Planning) Neuro 1.10/11.11/11.12 Orbit Routine Neuro 2.1/12.1/12.2 Facial Trauma Routine Neuro 2.5/12.9/12.10 Sinuses Diagnostic Neuro 2.7/12.13/12.14 Temporal Bone (without Contrast) Temporal Bone (with Contrast Only or with & without Contrast) Neuro 2.10/12.18/12.19 Neuro 2.11/12.20/12.21 For routine head imaging and emergent imaging including trauma, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, tumor, and preliminary stroke screening. May need to add contrast for more sensitive evaluation of tumor or infection. Use this protocol when the head cannot be properly positioned for a routine helical head scan. Example: when you cannot move the patient s head into proper position (trauma, cervical collar, rigid neck). For routine head imaging and emergent imaging including trauma, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, tumor, and preliminary stroke screening. May need to add contrast for more sensitive evaluation of tumor or infection. Helical mode should be used routinely for adult head CT scans. Only use axial mode when you cannot move the patient s head into proper position (trauma, cervical collar, rigid neck), and do not wish to perform a helical scan with angled axial reformats. This axial mode can also be used in unstable patients in the ED when the CT scan time must be expedited. This is a protocol which delivers thin section images for use in whole brain radiation treatment planning, intraoperative neuronavigation, and cranioplasty planning. Image requirements for the software associated with these uses varies, and verification of compatibility is recommended. For evaluation of infection, inflammatory, or neoplastic processes may add contrast as needed to increase sensitivity. May also be used for trauma, blunt or penetrating, localized to the orbit. Not to evaluate diffuse facial trauma or infection/inflammatory processes, as this requires a CT maxillofacial. Maxillofacial CT done for evaluation of facial trauma, blunt or penetrating, facial infections or inflammation, as well as assessment of congenital abnormalities. Contrast may be added for sensitivity, particularly in infection, as warranted. 3D reconstructions may be performed if requested by clinical service. For evaluation of routine sinus inflammatory disease, assessment of bone involvement from infectious, inflammatory, or neoplastic processes, and sinonasal neoplasms. May add contrast as needed typically for non routine sinus inflammatory disease. Not for evaluation of facial trauma or orbital processes. For evaluation of hearing loss, congenital abnormalities, infection, trauma, and neoplasms. Contrast may be added as needed for infection or neoplasms. Used in conjunction with MRI to evaluate neoplasms typically unless contraindication to MRI. This protocol adds contrast to the standard CT temporal bone, for use in cases of inflammation / infection or concern for sigmoid sinus compromise. This protocol is also used for cases in which there is a concern for a cerebellopontine angle mass causing sensorineural hearing loss.
7 Adult Neck Routine Neuro 3.1/3.2/3.3 Pediatric Neck Routine Neck (Parathyroid Adenoma) Adult Adult Cervical Spine (without Metal) and Adult Cervical Spine (With Metal) Adult Thoracic Spine (without Metal) and Adult Thoracic Spine (with Metal) Adult Lumbar Spine (without Metal) and Adult Lumbar Spine (with Metal) Stroke Deluxe Total Cerebrovascular CTA Head Only (Stenosis, Aneurysm, Unknown Bleed) CTA Neck Only (Cerebrovascular Disease) Neuro /13.2.1/13.4.1/13.6.1/ Neuro 3.5/3.6/3.7/13.1.9/ Neuro 3.16/3.17/3.18 and 3.19/3.20/3.21 Neuro 7.4/7.5/7.6 and 7.19/7.20/7.21 Neuro 7.1/7.2/7.3 and 7.16/7.17/7.18 Neuro 1.6/1.13/11.16/11.17 Neuro 1.7/11.18/11.19 Neuro 3.11/11.22/11.23 CT Venography Neuro 1.9/11.24/11.25 For evaluation of head and neck cancer (pre and post treatment), infection, soft tissue trauma, or inflammatory processes. Not for evaluation of cervical spine trauma or suspected vascular injury. This is an age specific protocol designed to give a diagnostic and appropriately low dose examination through the neck. This protocol is for evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy, developmental anomalies (such a branchial cleft cysts), as well as infectious, and inflammatory conditions within the pediatric neck. Indications include hypercalcemia, parathryoid adenoma (suspected or confirmed), and parathyroid surgical planning. On early arterial and delayed contrast enhanced images the enhancement of parathyroid adenomas can be confused with the intrinsically CT hyperdense thyroid gland. This protocol includes an additional non contrast phase to enable more confident detection and discrimination of parathyroid adenomas from the adjacent thyroid tissue. For evaluation of spine trauma, degenerative disease, infection, and bone tumors. May add contrast as needed. Not for primary evaluation of soft tissues. For evaluation of trauma, degenerative disease, infection, and bone tumors. May add contrast as needed. For evaluation of trauma, degenerative disease, infection, and bone tumors. May add contrast as needed. For evaluation of stroke, vascular trauma, aneurysm, vasospasm, and atherosclerotic disease. Requires administration of IV contrast. For evaluation of intracranial stenosis, aneurysm, vascular malformation, unknown bleed, vasospasm. Assessment of atherosclerotic disease, trauma with suspected vascular injury, or vascular neoplasms. Requires administration of IV contrast. This protocol consists of a slightly delayed phase of vascular imaging, for use in cases of suspected venous sinus thrombosis or occlusion..
8 Pediatrics Routine Abdomen/Pelvis Acute Appendicitis Abdomen/Pelvis Renal Stone/Flank Pain Triphasic Liver Trauma Abdomen/Pelvis /16.2.1/16.4.1/16.6.1/ for /16.2.6/16.4.6/16.6.6/ /16.2.1/16.4.1/16.6.1/ for /16.2.6/16.4.6/16.6.6/ /16.2.2/16.4.2/16.6.2/ for /16.2.7/16.4.7/16.6.7/ /16.2.3/16.4.3/16.6.3/ for /16.2.8/16.4.8/16.6.8/ /16.2.4/16.4.4/16.6.4/ for /16.2.9/16.4.9/16.6.9/ For evaluation of nonspecific abdominal pain, abscesses in postoperative patients or acutely ill inflammatory bowel disease patients, fever of unknown origin, as well as for appendicitis in outpatients. Additionally used for initial diagnosis and follow up of abdominal neoplasm when concurrent chest CT imaging is not indicated. A low dose protocol for patients in whom the only clinical concern is to rule out appendicitis. This will not image the lung bases and will minimally image the inferior aspects of the solid organs. This protocol aims to evaluate patients with renal colic or hematuria in whom renal and bladder ultrasound has been unable to identify a source for the symptoms or on whom renal and bladder ultrasound cannot be performed. This protocol should only be ordered by surgeons for liver tumor evaluation prior to surgical resection in order to fully assess the tumor s relationship to the hepatic arteries, portal veins, and hepatic veins. This will also assess for variant arterial or venous anatomy. This protocol is designed to evaluate patients who have suffered from blunt or penetrating trauma for possible internal injuries. Delayed images may be required at the radiologist s discretion to evaluate for active bleeding, but the field of view should be limited to the area of concern only so as to keep radiation dose as low as possible. This protocol should always be done following administration of IV contrast as evaluation for solid organ injuries, and to a lesser extent bowel/mesenteric injuries is significantly limited on non contrast examinations. This is especially true in pediatric patients with little mesenteric fat.
9 Chest Standard (Routine & High Resolution) /15.2.1/15.4.1/15.6.1/ for /15.2.8/15.4.8/15.6.8/ Chest with IV Contrast XXX for xxxxx Chest Pectus CTA Chest for PE Routine Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis Trauma Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis Chest Dynamic 3D Airway /15.2.3/15.4.3/15.6.3/ for / / / / /15.2.4/15.4.4/15.6.4/ for / / / / /15.2.5/15.4.5/15.6.5/ for / / / / /15.2.6/15.4.6/15.6.6/ for / / / / /15.2.2/15.4.2/15.6.2/ No higher image quality version of this protocol This non contrast protocol is performed to evaluate the lung parenchyma for evidence of interstitial lung disease, bronchiectasis, or aspiration. As pediatric patients have little mediastinal fat, evaluation for mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, as well as mediastinal pathology in general, would be limited. This protocol is designed to further evaluate patients with chest infections such as pneumonia with or without empyema, neoplasm, fever of unknown origin, vascular rings and slings, as well as mass lesions such as congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation and sequestration. Additionally, this could be used in evaluation of patients who have suffered blunt or penetrating trauma to the chest only. Technique for the pectus excavatum protocol was optimized for evaluating the bony thorax. These images allow for precise calculation of the Haller and correction indices, as well as for pre surgical planning. This protocol is designed to evaluate patients who are suspected of having pulmonary embolism. This protocol is intended to initially diagnose and followup malignancy and to evaluate for infection/fever of unknown origin in patients with nonspecific symptoms or who are immunocompromised. This protocol is designed to evaluate patients who have suffered from blunt or penetrating trauma for possible internal injuries. Delayed images may be required at the radiologist s discretion to evaluate for active bleeding, but the field of view should be limited to the area of concern only so as to keep radiation dose as low as possible. This protocol should always be done following administration of IV contrast as evaluation for vascular and solid organ injuries, and to a lesser extent bowel/ mesenteric injuries is significantly limited on non contrast examinations. This is especially true in pediatric patients who have little mediastinal and mesenteric fat. This protocol is designed to evaluate the central airways, particularly to assess for tracheobronchomalacia or excessive dynamic airway collapse. In addition to standard high resolution images of the lungs, the forced expiratory images accentuate collapsibility of the trachea and central bronchi. This protocol includes additional reformations including minimum intensity projections (MinIPs) and optional 3 D virtual bronchoscopic images, which referring providers might find informative. For patients who have a recent volumetric thin section CT of the chest, the expiratory sequence of this protocol performed alone may be sufficient, minimizing additional radiation exposure. Because the breathing technique is different than traditional end expiratory chest CT, proper training of technologists and coaching of patients with close radiologist oversight will maximize the utility of this protocol.
Effective Utilization of Imaging. John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging
 Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
W/ (2) (3) (4) (5) (5) (6) (6) CTA
 Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS
 JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Body CT Protocols General tips:
 Body CT Protocols General tips: -Check the list of protocol types on Intrad -Look at prior studies for help -Look up clinical info in Epic or Powerchart -Call ordering clinician if you have unanswered
Body CT Protocols General tips: -Check the list of protocol types on Intrad -Look at prior studies for help -Look up clinical info in Epic or Powerchart -Call ordering clinician if you have unanswered
PREAMBLE GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
 PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
Special Instructions
 FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
73725x2 MRA Pelvis Runoff (to ankle) CTA Abdomen with & without CTA Cardiac Brain without 70551
 CT CT Myelogram MRI Abdomen without 74150 Cervical 62302 Abdomen / MRCP 74181 Abdomen with 74160 Thoracic 62303 Abdomen / MRCP with & without 74183 Abdomen with & without 74170 Lumbar 62304 Abdomen / Pelvis
CT CT Myelogram MRI Abdomen without 74150 Cervical 62302 Abdomen / MRCP 74181 Abdomen with 74160 Thoracic 62303 Abdomen / MRCP with & without 74183 Abdomen with & without 74170 Lumbar 62304 Abdomen / Pelvis
HONG KONG COLLEGE OF RADIOLOGISTS. Higher Training (Radiology) Subspecialty Training in Computed Tomography
 HONG KONG COLLEGE OF RADIOLOGISTS Higher Training (Radiology) Subspecialty Training in Computed Tomography [The following guidelines should be read in conjunction with the General Guidelines on Higher
HONG KONG COLLEGE OF RADIOLOGISTS Higher Training (Radiology) Subspecialty Training in Computed Tomography [The following guidelines should be read in conjunction with the General Guidelines on Higher
Appropriate Imaging Tests Lead to Meaningful Results. Dr. Richard Wasley May 2011
 Appropriate Imaging Tests Lead to Meaningful Results Dr. Richard Wasley May 2011 Summarize the advantages and limitations of specific imaging tests and why clinical information is so important to radiologists
Appropriate Imaging Tests Lead to Meaningful Results Dr. Richard Wasley May 2011 Summarize the advantages and limitations of specific imaging tests and why clinical information is so important to radiologists
GUIDELINES FOR. Advanced. Imaging Studies
 GUIDELINES FOR Advanced Imaging Studies Locations Herrin Hospital Memorial Hospital of Carbondale St. Joseph Memorial Hospital 201 S 14th Street Herrin, IL 62948 618.942.2171 ext 35400 General Radiography*
GUIDELINES FOR Advanced Imaging Studies Locations Herrin Hospital Memorial Hospital of Carbondale St. Joseph Memorial Hospital 201 S 14th Street Herrin, IL 62948 618.942.2171 ext 35400 General Radiography*
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Vascular CT Protocols
 Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
CPT CODES. Ph: (307) Fax: (307) CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00
 Ph: (307) 382-4282 Fax: (307) 382-4291 CPT CODES CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00 74150 Abdomen w/o contrast $ 809.00 74160 Abdomen w/ contrast $1175.00 w/ contrast: $1262.00 74170 Abdomen w_w/o contrast $1324.00
Ph: (307) 382-4282 Fax: (307) 382-4291 CPT CODES CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00 74150 Abdomen w/o contrast $ 809.00 74160 Abdomen w/ contrast $1175.00 w/ contrast: $1262.00 74170 Abdomen w_w/o contrast $1324.00
CT PROCEDURE REFERENCE GUIDE 2017
 Head CT PROCEDURE REFERENCE GUIDE 2017 Procedure Contrast Scan Field Preparatio n Base of Skull to Vertex Sinuses Orbits Mastoids/IAC/ Temporal Bones Facial Bones ST Neck Low Dose Lung Screening Routine
Head CT PROCEDURE REFERENCE GUIDE 2017 Procedure Contrast Scan Field Preparatio n Base of Skull to Vertex Sinuses Orbits Mastoids/IAC/ Temporal Bones Facial Bones ST Neck Low Dose Lung Screening Routine
Stroke / CVA TIA Trauma Dizziness Headaches. Acoustic Neuroma Syrinx Visual Change Vascular Lesions (AVM) Elevated Prolactin Vertigo Bell s palsy
 Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Communication of Critical and/or Discrepant Findings. Stephen Alden, Lorie Cavalli and Bobby Kalb, MD Effective Date: 08/01/08
 DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL IMAGING POLICIES, PROCEDURES AND PROTOCOLS Subject: Policy: Communication of Critical and/or Discrepant Findings RR003 Author: Stephen Alden, Lorie Cavalli and Bobby Kalb, MD Effective
DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL IMAGING POLICIES, PROCEDURES AND PROTOCOLS Subject: Policy: Communication of Critical and/or Discrepant Findings RR003 Author: Stephen Alden, Lorie Cavalli and Bobby Kalb, MD Effective
CT Scan Reference Guide
 Diagnostic Imaging A Department of Rutland Regional Medical Center CT Scan Reference Guide 10/01/2017 Safety Questions for Exams with IV Contrast...Page 3 CPT Code Scan Ranges: Head...Pages 4-5 Neck/Spine...Pages
Diagnostic Imaging A Department of Rutland Regional Medical Center CT Scan Reference Guide 10/01/2017 Safety Questions for Exams with IV Contrast...Page 3 CPT Code Scan Ranges: Head...Pages 4-5 Neck/Spine...Pages
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest
 (Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to:
 RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
Acute Aortic Syndromes
 Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline
 Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Normal Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Evaluate normal anatomy, perfusion, function 2 Pathology, Perfusion,
Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Normal Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Evaluate normal anatomy, perfusion, function 2 Pathology, Perfusion,
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less)
 Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review
 AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review Modality Body Part CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT
AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review Modality Body Part CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT
Radiography. 1. Introduction. 2. Documentation of Compliance. 3. Didactic Competency Requirements. 4. Clinical Competency Requirements
 PRIMARY CERTIFICATION AND REGISTRATION Radiography 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet the Professional Education Requirements specified in the ARRT Rules
PRIMARY CERTIFICATION AND REGISTRATION Radiography 1. Introduction Candidates for certification and registration are required to meet the Professional Education Requirements specified in the ARRT Rules
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
EXAMS_ Page 1/5 SORTED - NUMERIC
 BIOPSY 19103L-MR MV MR Guided Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77021, 10022, 19295, 90772, A4550, 99000 19103L-ST MV Stereotactic Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77031, 10022, 19295, 90772,
BIOPSY 19103L-MR MV MR Guided Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77021, 10022, 19295, 90772, A4550, 99000 19103L-ST MV Stereotactic Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77031, 10022, 19295, 90772,
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Cine loop of tomosynthesis slice images through the chest. 14 Standard PA chest radiograph (left) and single slice from the tomosynthesis image dataset (right) of a patient
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Cine loop of tomosynthesis slice images through the chest. 14 Standard PA chest radiograph (left) and single slice from the tomosynthesis image dataset (right) of a patient
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D.
 CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
11/1/2014. Radiologic incidentalomas Ordering pitfalls Newer technology and applications
 Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
CT: Common Protocols. Michael Steigner, M.D. Director, Vascular CT/MR Assistant Professor of Radiology
 CT: Common Protocols BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Heart & Vascular Center Harvard Medical School Teaching Hospital Michael Steigner, M.D. Director, Vascular CT/MR Assistant Professor of Radiology msteigner@bwh.harvard.edu
CT: Common Protocols BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Heart & Vascular Center Harvard Medical School Teaching Hospital Michael Steigner, M.D. Director, Vascular CT/MR Assistant Professor of Radiology msteigner@bwh.harvard.edu
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
We Accept Care Credit
 We Accept Care Credit Standard Fee Schedule Valid 1-Jan-18 to 1-July-18 **Prices Subject to Change, Call 702-222-3544 For Verification** Exam CPT PAYMENT IN FULL AT TIME OF SERVICE EKG 93000 35 TREADMILL
We Accept Care Credit Standard Fee Schedule Valid 1-Jan-18 to 1-July-18 **Prices Subject to Change, Call 702-222-3544 For Verification** Exam CPT PAYMENT IN FULL AT TIME OF SERVICE EKG 93000 35 TREADMILL
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma
 Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
CT Chest. Verification of an opacity seen on the straight chest X ray
 CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Routine Guide EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION. 14x17 CW* 14x17LW 14x17LW. 14x17LW 14x17LW 14x17LW
 EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous)
 CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
NYU School of Medicine Department of Radiology Rotation-Specific House Staff Evaluation
 Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Radiology Codes Requiring Authorization*
 70336 Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 Computed tomography, head or brain; with contrast material(s)
70336 Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 Computed tomography, head or brain; with contrast material(s)
Anesthesia Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes
 Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2009 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Code
Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2009 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Code
Diagnostic Imaging
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
RADIOLOGY (Management)
 ULTRASOUND BETA SCAN/ U/S ORBITAL 1600 Daily U/S WHOLE ABDOMEN (Abd + Pelvis) 1200 Daily U/S PELVIS 1200 Daily U/S ABDOMEN 1200 Daily U/S BREAST 1800 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR STUDY 3000 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR
ULTRASOUND BETA SCAN/ U/S ORBITAL 1600 Daily U/S WHOLE ABDOMEN (Abd + Pelvis) 1200 Daily U/S PELVIS 1200 Daily U/S ABDOMEN 1200 Daily U/S BREAST 1800 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR STUDY 3000 Daily U/S FOLLICULAR
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D
 Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo
 Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Radiological Investigations of Abdominal Trauma
 76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies
 Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
2012 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 2012 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana CT Head 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o CT Head 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT Head 70482
2012 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana CT Head 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o CT Head 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT Head 70482
Reduce Exposure Eyes. CT Imaging Procedures. Head Positioning. Head Pathology 5/16/2008. CT Head & Posterior Fossa
 CT Head & Posterior Fossa CT Imaging Procedures Scoutview = Lateral OML ( 10 to 20 degrees) 15 degrees ( above OML) Time (fastest obtain info) Slide # 1 Slide # 2 2 CT Head & Posterior Fossa Reduce Exposure
CT Head & Posterior Fossa CT Imaging Procedures Scoutview = Lateral OML ( 10 to 20 degrees) 15 degrees ( above OML) Time (fastest obtain info) Slide # 1 Slide # 2 2 CT Head & Posterior Fossa Reduce Exposure
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V
 CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
Multislice CT. - fast scanning - submilimeter slices
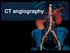 CT angiography Multislice CT - fast scanning - submilimeter slices CT angiography - Minimal invasivity - High resolution (similar to DSA, higher than MRI) - Cannot assess hemodynamics (contrary to DSA)
CT angiography Multislice CT - fast scanning - submilimeter slices CT angiography - Minimal invasivity - High resolution (similar to DSA, higher than MRI) - Cannot assess hemodynamics (contrary to DSA)
COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS for the CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
 COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS for the 10/2013 CERTIFICATION BOARD FOR RADIOLOGY PRACTITIONER ASSISTANTS CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION Note: The competency requirements contained in this document will be in effect
COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS for the 10/2013 CERTIFICATION BOARD FOR RADIOLOGY PRACTITIONER ASSISTANTS CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION Note: The competency requirements contained in this document will be in effect
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
CT Chest HRCT CT Chest WO
 CT Chest HRCT CT Chest WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
CT Chest HRCT CT Chest WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
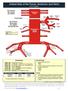 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
2014 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review
 CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast CT Head 1 70482 followed by
CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast CT Head 1 70482 followed by
Contributors. Thanks to Peter Miller, MD; LCDR Kevin Preston, MD; and Keith Newbrough, MD for their generous contribution of images:
 Contributors Thanks to Peter Miller, MD; LCDR Kevin Preston, MD; and Keith Newbrough, MD for their generous contribution of images: Peter Miller, MD, Indiana University School of Medicine Chapter 1: Figure
Contributors Thanks to Peter Miller, MD; LCDR Kevin Preston, MD; and Keith Newbrough, MD for their generous contribution of images: Peter Miller, MD, Indiana University School of Medicine Chapter 1: Figure
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial)
 CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Smith D, Chudgar A, Daly B, Cooper M. Evaluation of potential renal transplant recipients with computed tomography angiography. Arch Intern Med. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2012.1466.
Supplementary Online Content Smith D, Chudgar A, Daly B, Cooper M. Evaluation of potential renal transplant recipients with computed tomography angiography. Arch Intern Med. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2012.1466.
Memory Loss, Confusion Shunt check Stroke/Bleed Trauma. Meningioma Infection Metastatic Staging. Foreign Body Trauma. Mass, swelling Pain
 CT Anatomical Guide Area of Concern Body Part Most common indications Contrast Procedure to Pre-Cert CPT Codes Head Brain Alzheimer s Change in mental status CVA TIA Hydrocephalus Cerebral Aneurysm (MRI
CT Anatomical Guide Area of Concern Body Part Most common indications Contrast Procedure to Pre-Cert CPT Codes Head Brain Alzheimer s Change in mental status CVA TIA Hydrocephalus Cerebral Aneurysm (MRI
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
05/02/ CPT Preauthorization Groupings Effective May 2, Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6. CPT Description SEGR CT01
 Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Preauthorization Groupings CPT
Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Preauthorization Groupings CPT
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Emerging Applications in Musculoskeletal CT Imaging
 Emerging pplications in Musculoskeletal CT Imaging y K Murali MD(RD), PDCC, Director of Interventional Radiology, G. Francis DMRD, DN (RD), Consultant Radiologist, and R. Madan, MS, MD, Consultant Radiologist,
Emerging pplications in Musculoskeletal CT Imaging y K Murali MD(RD), PDCC, Director of Interventional Radiology, G. Francis DMRD, DN (RD), Consultant Radiologist, and R. Madan, MS, MD, Consultant Radiologist,
ADI Procedure Codes. August 2016 Revised April 2017 Page 1 of 7 ADI Procedure Codes
 Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR. Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum. YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024)
 SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024) Course Directors: David W. Trost, MD, Franz Kainberger, MD Faculty: Gerd Bodner, MD, Marius
SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024) Course Directors: David W. Trost, MD, Franz Kainberger, MD Faculty: Gerd Bodner, MD, Marius
ADDITIONS. The following codes have been added.
 ADDITIONS The following codes have been added. 99446 Interprofessional telephone/internet assessment and management service provided by treating/requesting physician or other qualified health care professional;
ADDITIONS The following codes have been added. 99446 Interprofessional telephone/internet assessment and management service provided by treating/requesting physician or other qualified health care professional;
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
CT & PET/CT Scheduling Guidelines LVHN (5846) Fax:
 www.lvhn.org CHEST CT (x-ray is almost always required) 71250 Nodules Abnormal cxr, ancillary finding, f/u study WO No 71250 HRCT: Interstitial lung disease, i.e. asbestosis, sarcoidosis, TB SOBOE, dry
www.lvhn.org CHEST CT (x-ray is almost always required) 71250 Nodules Abnormal cxr, ancillary finding, f/u study WO No 71250 HRCT: Interstitial lung disease, i.e. asbestosis, sarcoidosis, TB SOBOE, dry
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN
 CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND METHODS SUPPLEMENT Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database MAY 2017 Minnesota Department of Health Health Economics Program 85 E. 7th
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND METHODS SUPPLEMENT Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database MAY 2017 Minnesota Department of Health Health Economics Program 85 E. 7th
Codes Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (MSI): Updated 3/2014
 s Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (): Updated 3/2014 0042T Cerebral Perfusion Analysis using CT with contrast 0159T CAD, including computer algorithm analysis, BREAST MRI 0195T prepare interspace,
s Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (): Updated 3/2014 0042T Cerebral Perfusion Analysis using CT with contrast 0159T CAD, including computer algorithm analysis, BREAST MRI 0195T prepare interspace,
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V
 CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
Are extra-colonic findings on CT colonogram clinically significant? A review of 758 consecutive cases
 Are extra-colonic findings on CT colonogram clinically significant? A review of 758 consecutive cases Lynn WR 1, Vadhwana B 1, Borgstein R 2, Demetriou G 1, Nair MS 1, Meleagros L 1, Bell DJ 2 1 Department
Are extra-colonic findings on CT colonogram clinically significant? A review of 758 consecutive cases Lynn WR 1, Vadhwana B 1, Borgstein R 2, Demetriou G 1, Nair MS 1, Meleagros L 1, Bell DJ 2 1 Department
Ultrasound ICD-10-CM
 Ultrasound ICD-10-CM Clinical Documentation Guides Brought to you by www.codingstrategies.com The Resource for Physician and Outpatient Coding, Compliance & ICD-10-CM OTHER CLINICAL DOCUMENTATION GUIDES
Ultrasound ICD-10-CM Clinical Documentation Guides Brought to you by www.codingstrategies.com The Resource for Physician and Outpatient Coding, Compliance & ICD-10-CM OTHER CLINICAL DOCUMENTATION GUIDES
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CHEST CTA Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 71275 Last Review Date: August 2014 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CHEST CTA Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 71275 Last Review Date: August 2014 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
