Radiological Assessment of Children with Pectus Excavatum
|
|
|
- Henry Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 51 Original Article Radiological Assessment of Children with Pectus Excavatum Arturas Kilda 1, Algidas Basevicius 2, Vidmantas Barauskas 1, Saulius Lukosevicius 2 and Donatas Ragaisis 2 1 Department of Pediatric Surgery, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania, 2 Department of Radiology, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania ABSTRACT Objective. To assess what degree of chest wall deformation changes statistically reliably after surgery, using pre- and postoperative radiological examination data. Methods. Radiological chest examinations were performed for 88 children before and after remedial operations. Pre- and postoperative chest radiograph and CT were performed to measure transversal chest width; sagittal left chest side depth, sagittal right chest side depth, sternovertebral distance, and vertebral body length. Derivative indices were also estimated: Vertebral index (VI), Frontosagittal index (FI), Haller index (HI) and asymmetry index. Computerized assessment of data was used. For statistical analysis, the software Statistica 6.0 was used. Results. Postoperatively VI increased approximately by 2.37±2.72, FI decreased by 4.60±4.34, and HI value increased approximately up by 0.45±0.49. Statistically significant deformation index difference before and after surgery was not detected when VI was below 26.2 (p=0.08), FI was above 32.9 (p=0.079) and HI was less than 3.12 (p=0.098). Conclusion. Preoperative CT and X-ray assessment of chest wall deformation degree is important for pediatric patients. The following deformation indices are indications for surgical treatment: VI>26, FSI<33 and HI>3.1. [Indian J Pediatr 2007; 74 (2) : ] slu@delfi.lt Key words : Funnel chest; Pectus excavatum; Preoperative radiological assessment; Chest wall deformation indices; Children Funnel chest (pectus excavatum) is among the most prevalent congenital chest wall deformities, with incidence of 1/300 children, which causes various disturbances. 1,2, 3,4,5 Funnel chest compresses chest organs and causes cardio-respiratory disorders (heart palpitations, tachycardia, disturbed comprehensive inspiration, etc.). These problems lead to impaired child development and physical exercise limitation. 2,4,6 Recently, more evidence has appeared that only severe chest wall deformation can cause malfunctioning of chest organs. 4,7,8 It is claimed that depressed chest wall influences child s psychological state, which, in turn, inflict psychosomatic disturbances and physical exercise limitations. 8,9 Cosmetic and psychological indications for surgical treatment gained more importance after minimally invasive and providing better cosmetic results Nuss operation for pectus excavatum had been introduced For assessment of indications for surgically corrective treatment, radiological examination is of great significance. Even in cases of moderate chest wall deformation with no signs of chest organ compression, indications for surgery can be determined by size of deformation seen on chest radiograph or CT. 13 Therefore, surgical treatment can solve cosmetic and/or psychological problems, as well as remedy smaller scale deformations Precise radiological assessment parameters delineating the limits of norm and pathology have not yet been defined. Authors aim to report the experience of our departments regarding treatment of pediatric patients with pectus excavatum and to suggest an algorithm for radiological examination along with radiological indications for surgery. Correspondence and Reprint requests : Dr. Lukosevicius Saulius, Eiveniu St. 2, P.O. Box 1010, Department of Radiology, Kaunas University of Medicine, Kaunas LT-50009, Lithuania. Fax : MATERIALS AND METHODS 88 children with pectus excavatum were examined and Indian Journal of Pediatrics, Volume 74 February,
2 52 A. Kilda et al operated during in the Department of Pediatric Surgery of our Medical University Hospital. For all patients radiograph was performed before and one month after the operation. Informed consent has been obtained from patients/ their representatives, as well as all the followed procedures were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee of Kaunas University of Medicine and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, revised in Before surgery, all of the 88 children underwent frontal and left lateral chest X-ray examination in the vertical position. A regular viewing-box and a ferule, calibrated to 1 mm accuracy, were used to evaluate radiographs. CT scanning was performed for 58 children appointed to the investigation by a reffering physician. Investigation was performed by Siemens Somatom Plus 4 (Siemens AG) spiral CT scanner. During the examination, the patient was in the typical chest scanning position, breathing withheld. To avoid excessive exposure to X-rays, a single CT slice was performed in the most concave chest part on inhalation and exhalation. The distances were measured to the accuracy of 1 mm. The following values were measured: transverse distance of the chest wall, sagittal length of the chest left and right side, sternovertebral distance and vertebral body length (Fig. 1). Arithmetic mean of values measured on inspiration and expiration was calculated in order to reduce error probability. Deformation indices were calculated according to K.Ohno s method. 8 VI, FSI and HI were evaluated on X-ray and CT images. The obtained data had strong correlation (correlation coefficient r=0.96, p<0.0001). As supplementary dimensions, chest flatness and chest asymmetry index were assessed on CT scans. Chest flatness index = 2a/b+b 1. If chest flatness index is below 2, chest is considered flat. If this value is 2 or higher, chest is regarded as normal. In assessment of chest asymmetry, left and right side chest depth ratio was calculated, according to the following equation: Asymmetry index = 1 (b/b 1 ), where b/b 1 is left and right side chest depth ratio on inspiration and expiration. Chest wall is considered asymmetric if asymmetry index is < 0.05 (left side of the chest is more convex) or >0.05 (right side of the chest is more convex). Critical range [0.05] is set in accordance with the 5% error probability. If VI 30, FSI 30 and HI 3.3, deformation indices are considered as high. If VI<30, FSI>30 and HI<3.3, deformation indices are low. 13 If at least one of the indices (VI, FSI or HI) is identified as high, a pediatric patient is ascribed to a group of roentgenologically severe deformation. If the indices are low, deformation roentgenologically is regarded as moderate. Severe deformation was diagnosed in 34 (38.6%), moderate in 54 children (61.4%). Statistical analysis was performed by STATISTICA 6.0 software. Parametric data were compared according to the t-student method. Mean values were compared by the method of two independent samples. Postoperative results were assessed by analyzing the same data according to the pair (dependent) sample method. If sample contained less than 30 values or if these values did not match normal distribution law, mean values were compared using methods of non-parametrical statistics (Mann-Whitney-U method for parametric values and Wilcoxson method for the range values). RESULTS Fig Axial CT scan indicating value assessments. Here: a transversal chest dimension; b and b 1 sagittal right and left chest size dimensions; c sternovertebral distance; v vertebral body length v Vertebral Index(VI):VI = *100 v + c c Frontosagittal Index (FSI) : FSI = *100 a Haller Index (HI): HI = a/c 67 children were operated by Ravitch method, attaching the sternum by external tractive suture. 21 children were operated by the minimally invasive Nuss method. Statistically significant differences with regard to age, sex, or degree of the deformation were not detected in both groups. Postoperatively, deformation indices exhibited the same changes in both groups. The sternovertebral distance increased to 1.49±1.23 cm in the group where Nuss method was applied, whereas the distance increased to 1.02±0.98 (p=0.258) in the group where Ravitch method was applied, indicating that the change in the sternovertebral distance is independent of the operation method. Comparison of index changes before and after the surgery is presented in Table 1. Postoperatively VI decreased by 2.73±2.72 on average (range from 0 to 12.32), FSI increased by 4.60±4.34 on Indian Journal of Pediatrics, Volume 74 February, 2007
3 53 Radiological Assessment of Children with Pectus Excavatum TABLE 1. The Assessment of Deformation Index Changes According to t Student Pair (dependent) Sample Method. Deformative Mean Error 95% reliability Index probability Limits of difference reliability min max VI preoperatively p< VI postoperatively FSI preoperatively p< FSI postoperatively HI preoperatively 3.35 p< HI postoperatively Here: VI vertebral index, FSI frontosagittal index, HI-Haller Index. average (range from 0 to 20.00). The mean value of increase of HI was 0.45±0.49 (maximum increase was 2.33). Increase of sternovertebral distance was directly dependent on roentgenologically severe and moderate deformation difference. In case of moderate deformation, sternovertebral distance increased to 11.23±10.91% whereas, in case of severe deformation, the distance increased to 28.3±26.82%, p=0.014 (Fig. 2). Statistically significant differences between deformation indices pre- and post surgery were missing when VI <26.2 (p=0.08), FSI >32.9 (p=0.079) and HI < 3.12 (p=0.098) were detected preoperatively. Increase of SV distance (%) n=34 n=54 Severe Moderate Degree of chest deformation Fig. 2. The percent value of increase of sternovertebral distance with respect to roentgenologically assessed degree of chest deformation (p=0.014). Here: SV sternovertebral distance. DISCUSSION Since changes of chest wall bones constitute the main anatomic component of chest wall deformities, radiological chest examination enables assessment of chest condition, deformation degree and shape. It also allows planning the operation, predicting its results and treatment outcome. 1,3,8,13-15 Frontal and lateral chest radiograph helps to reveal the severity of deformation. For a comprehensive chest wall assessment, however, chest CT scanning is essential. The latter enables us to visualize not only chest shape but also presents exact topography of chest organs. 13, 16, 17 Authors believe that radiological examination gives precise objective assessment of and postoperative results and adds substantially to subjective criteria, the opinion of a child or family. It has been reported that the majority of patients give a positive evaluation of corrective surgery right after the operation. After some time, however, they become dissatisfied with its cosmetic or functional results. 8, 13 In addition, after a prolonged period of time, more people become disappointed with surgical results. 8 Radiological examination data enable us to determine exact indications for surgery, to select a relevant surgical technique and to envisage changes in the sternum location, as well as in the shape of chest. Basing on our results suggest that, preoperative frontal and lateral chest radiograph and CT scanning should be performed for all children. If deformation is visually severe and surgery is inevitable, CT scanning can substitute chest radiograph. CT allows a more accurate assessment of relevant deformation indices, evaluation of chest shape and asymmetry. If full CT scanning is performed, a child is exposed to large doses of radiation. Therefore, after scout scanning, it is recommended to perform only single-slice scanning in the most concave level of the chest. CT scanning on inspiration and expiration is recommended in order to diminish error caused by chest wall excursion during breathing. Such CT scans do not provide lung pattern, nor Mediastinum configuration. For this reason, authors perform singleslice CT for children with no respiratory and cardiovascular disturbances or for children who underwent X-ray examination for other reasons that same year. Although chest radiograph enables assessment of main deformation indices, it is not sufficient to evaluate chest flatness and asymmetry. These values are essential for surgery planning and choosing the type of sternum 2, 4, 6, 8, 13, 14, 16, 17 stabilization. The increase of sternovertebral distance was directly dependent on preoperatively assessed deformation index: the more severe deformation before operation, the bigger is the change. It was authors objective to find when the deformation index postoperatively remains reliably stable, i.e. what the deformation index limit is when the operation does not increase sternovertebral distance. The analysis revealed that sternovertebral distance increases below 5% if preoperatively VI mean value was <26.2, FSI>32.9, and HI<3.12. The findings are very close to those reported in the literature on the subject, specifically, in the description of cases when chest is considered to be of 2, 6, 8, 13, regular configuration, if VI<28. FSI>28 and HI< , 16 Chest deformation indices are closely interrelated. VI Indian Journal of Pediatrics, Volume 74 February,
4 54 A. Kilda et al characterizes skeletal and funnel depth ratio. FSI reveals chest width, but does not depend on the vertebra size. FSI demonstrates statistically significant correlation with child s age. Consequently, it may be misleading to rely only on this index for the assessment of relation between sternum and spine. FSI also depends on child s age: higher VI was found in younger children. 8, 18 For the evaluation of deformation, it is important to consider not only separate deformation indices but also the totality of those indices. Precise evaluation is possible only by computed analysis whereas manual calculation of all deformation indices and their assessment is inaccurate and time consuming. It is recommended to classify roentgenologically tested deformation as severe or moderate. If a single deformation index exceeds critical value (VI>28, FSI<33, HI >3.2), deformation is regarded as severe. If all indices are below critical value, it is moderate. Other authors present similar deformation index limits. 2,4,5,7,8,13,14,16 Such method of assessment allows establishing precise indications for surgery since, in cases of severe deformation; there is a statistically reliable increase of sternovertebral distance, as well as other deformation indices. Such a classification is important for practical purposes, too. Authors results demonstrated that the ranges of critical deformation index values corresponded to statistically reliable increase of chest volume. In cases of moderate chest wall deformation, the sternum position does not change significantly with respect to spine. However, if VI<26, FSI>33 and HI is <3.1, it is very likely that sternum position will remain unchanged with respect to spine, especially in cases of flat chest. In such cases it is important to evaluate the child s posture initially: if it is incorrect, chest often visually looks deformed. 15, 19, 20 This is different in cases with asymmetric chest, when it should be immediately corrected to avoid the development of scoliosis. 20 The study has certain limitations. One of them is that due to insufficient number of investigations we could not evaluate statistical significance of postoperative shape of chest. Chest flatness and chest asymmetry were not assessed in postoperative period because only a few children passed postoperative CT evaluation yet. Also correlation between the imaging data with the clinical data is beyond the scope of this article. Authors did not present evaluation of imaging indices for pectus excavatum with other possible outcomes of repair of pectus excavatum, such as post operative short and long term patient's satisfaction, clinical evaluation of the residual chest wall deformity and lung function test in severe cases of pectus excavatum. In the present study we tried to establish the first step to an overall preoperative chest wall evaluation system, basing not on separate indices but on interaction of various postoperative indices. Using this evaluation it could be possible to determine whether the alteration of bony cage of chest wall will be statistically significant 146 after operation. CONCLUSION When preparing a pediatric patient for a surgical pectus excavatum correction, it is important to perform CT scanning and give an overall evaluation of the chest shape and deformation degree. The following deformation indices are considered indications for surgically corrective treatment: VI>26, FSI<33 and HI>3.1. REFERENCES 1. Donnelly LF, Frush DP. Abnormalities of the chest wall in pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999 December; 173(6): Fonkalsrud EW, Dunn JC, Atkinson JB. Repair of pectus excavatum deformities: 30 years of experience with 375 patients. Ann Surg 2000 March; 231(3) : Golladay ES, Golladay GJ. Chest wall deformities. Indian J Pediatr 1997 May; 64(3) : Saxena AK, Schaarschmidt K, Schleef J, Morcate JJ, Willital GH. Surgical correction of pectus excavatum: the Munster experience. Langenbecks Arch Surg 1999 April; 384(2) : Suita S, Taguchi T, Masumoto K, Kubota M, Kamimura T. Funnel chest: treatment strategy and follow-up. Pediatr Surg Int 2001 July;17(5-6) : Haller JA, Jr., Scherer LR, Turner CS, Colombani PM. Evolving management of pectus excavatum based on a single institutional experience of 664 patients. Ann Surg 1989 May; 209(5) : Kaguraoka H, Ohnuki T, Itaoka T, Kei J, Yokoyama M, Nitta S. Degree of severity of pectus excavatum and pulmonary function in preoperative and postoperative periods. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1992 November; 104(5) : Ohno K, Nakahira M, Takeuchi S, Shiokawa C, Moriuchi T, Harumoto K, Nakaoka T, Ueda M, Yoshida T, Tsujimoto K, Kinoshita H. Indications for surgical treatment of funnel chest by chest radiograph. Pediatr Surg Int 2001 November; 17(8) : Einsiedel E, Clausner A. Funnel chest. Psychological and psychosomatic aspects in children, youngsters, and young adults. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1999 October;40(5) : Croitoru DP, Kelly RE, Jr., Goretsky MJ, Lawson ML, Swoveland B, Nuss D. Experience and modification update for the minimally invasive Nuss technique for pectus excavatum repair in 303 patients. J Pediatr Surg 2002 March; 37(3) : Hosie S, Sitkiewicz T, Petersen C, Gobel P, Schaarschmidt K, Till H, Noatnick M, Winiker H, Hagl C, Schmedding A, Waag KL. Minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum the Nuss procedure. A European multicentre experience. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2002 August; 12(4) : Miller KA, Woods RK, Sharp RJ, Gittes GK, Wade K, Ashcraft KW, Snyder CL, Andrews WM, Murphy JP, Holcomb GW, III. Minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum: a single institution s experience. Surgery 2001 October;130(4) : Ohno K, Morotomi Y, Nakahira M, Takeuchi S, Shiokawa C, Moriuchi T, Harumoto K, Nakaoka T, Ueda M, Yoshida T, Yamada H, Tsujimoto K, Kinoshita H. Indications for surgical repair of funnel chest based on indices of chest wall deformity and psychological state. Surg Today 2003; 33(9) : de Matos AC, Bernardo JE, Fernandes LE, Antunes MJ. Indian Journal of Pediatrics, Volume 74 February, 2007
5 55 Radiological Assessment of Children with Pectus Excavatum Surgery of chest wall deformities. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg September; 12(3) : Ohno K, Morotomi Y, Ueda M, Yamada H, Shiokawa C, 15. Donnelly LF, Frush DP, Foss JN, O Hara SM, Bisset GS, III. Nakaoka T, Tsujimoto K, Nakahira M, Moriuchi T, Harumoto Anterior chest wall: frequency of anatomic variations in K, Yoshida T. Comparison of the Nuss procedure for pectus children. Radiology 1999 September; 212(3) : excavatum by age and uncommon complications. Osaka City 16. Nakahara K, Ohno K, Miyoshi S, Maeda H, Monden Y, Med J 2003 December; 49(2) : Kawashima Y. An evaluation of operative outcome in patients 19. Frick SL. Scoliosis in children with anterior chest wall with funnel chest diagnosed by means of the computed deformities. Chest Surg Clin N Am 2000 May; 10(2) : tomogram. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1987 April; 93(4) : Waters P, Welch K, Micheli LJ, Shamberger R, Hall JE. Scoliosis 17. Willital GH. [Indication and operative technique in chest in children with pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum. J deformities (author s transl)]. Z Kinderchir 1981 July;33(3) : Pediatr Orthop 1989 September; 9(5) : Indian Journal of Pediatrics, Volume 74 February,
The Comparison Of Measurements On Chest X-Ray For Patients With Pectus Deformity. S Gurkok, O Genc, M Dakak, A Gozubuyuk, R Gorur, K Balkanli
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 The Comparison Of Measurements On Chest X-Ray For Patients With Pectus Deformity S Gurkok, O Genc, M Dakak, A Gozubuyuk,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 The Comparison Of Measurements On Chest X-Ray For Patients With Pectus Deformity S Gurkok, O Genc, M Dakak, A Gozubuyuk,
Pectus excavatum (PE) is one of the most common
 Analysis of the Nuss Procedure for Pectus Excavatum in Different Age Groups Do Hyung Kim, MD, Jung Joo Hwang, MD, Mi Kyeong Lee, RN, Doo Yun Lee, MD, and Hyo Chae Paik, MD Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
Analysis of the Nuss Procedure for Pectus Excavatum in Different Age Groups Do Hyung Kim, MD, Jung Joo Hwang, MD, Mi Kyeong Lee, RN, Doo Yun Lee, MD, and Hyo Chae Paik, MD Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
MODIFICATION OF THE NUSS PROCEDURE-PREVENTION OF INJURIES OF THE HEART AND MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS
 . Bali Medical Journal (BMJ) 20, Volume 1, Number 3: 88-92 MODIFICATION OF THE NUSS PROCEDURE-PREVENTION OF INJURIES OF THE HEART AND MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS Mirko Žganjer Children s Hospital Zagreb, Department
. Bali Medical Journal (BMJ) 20, Volume 1, Number 3: 88-92 MODIFICATION OF THE NUSS PROCEDURE-PREVENTION OF INJURIES OF THE HEART AND MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS Mirko Žganjer Children s Hospital Zagreb, Department
Optoelectronic plethysmography demonstrates abrogation of regional chest wall motion dysfunction in patients with pectus excavatum after Nuss repair
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 160 164 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Optoelectronic plethysmography demonstrates abrogation of regional chest wall motion dysfunction in patients with pectus
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 160 164 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Optoelectronic plethysmography demonstrates abrogation of regional chest wall motion dysfunction in patients with pectus
Correlation Between Sternal Depression and Cardiac Rotation in Pectus Excavatum: Evaluation With Helical CT
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Chu et al. CT of Pectus Excavatum Pediatric Imaging Original Research Zhi-gang Chu 1 Jian-qun Yu Zhi-gang Yang Li-qing Peng Hong-li Bai Xue-ming Li Chu ZG, Yu JQ, Yang
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Chu et al. CT of Pectus Excavatum Pediatric Imaging Original Research Zhi-gang Chu 1 Jian-qun Yu Zhi-gang Yang Li-qing Peng Hong-li Bai Xue-ming Li Chu ZG, Yu JQ, Yang
Initial results with minimally invasive repair of pectus carinatum
 Initial results with minimally invasive repair of pectus carinatum Attila, MD Objective: Pectus carinatum is traditionally repaired by using some modification of the open Ravitch procedure, with its possible
Initial results with minimally invasive repair of pectus carinatum Attila, MD Objective: Pectus carinatum is traditionally repaired by using some modification of the open Ravitch procedure, with its possible
Pectus Excavatum Reconstruction With Silicone Implants. Long-Term Results and a Review of the English-Language Literature
 REVIEW ARTICLES Pectus Excavatum Reconstruction With Silicone Implants Long-Term Results and a Review of the English-Language Literature Bart Jorrit Snel, MD,* Cees A. Spronk, MD, Paul M. N. Werker, MD,
REVIEW ARTICLES Pectus Excavatum Reconstruction With Silicone Implants Long-Term Results and a Review of the English-Language Literature Bart Jorrit Snel, MD,* Cees A. Spronk, MD, Paul M. N. Werker, MD,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Surgical Treatment of Chest Wall Deformities (Congenital or File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgical_treatment_of_chest_wall_deformities_congenital_or_acquired
Corporate Medical Policy Surgical Treatment of Chest Wall Deformities (Congenital or File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgical_treatment_of_chest_wall_deformities_congenital_or_acquired
Nuss procedure for repair of pectus excavatum after failed Ravitch procedure in adults: indications and caveats
 Original Article Nuss procedure for repair of pectus excavatum after failed Ravitch procedure in adults: indications and caveats Gregor J. Kocher 1, Nathalie Gstrein 1, Dawn E. Jaroszewski 2, Mennatallah
Original Article Nuss procedure for repair of pectus excavatum after failed Ravitch procedure in adults: indications and caveats Gregor J. Kocher 1, Nathalie Gstrein 1, Dawn E. Jaroszewski 2, Mennatallah
Pectus chest deformities are among the most common
 Repair of Pectus Chest Deformities in 320 Adult Patients: 21 Year Experience Dawn E. Jaroszewski, MD, and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD Department of Surgery and Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, David Geffen
Repair of Pectus Chest Deformities in 320 Adult Patients: 21 Year Experience Dawn E. Jaroszewski, MD, and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD Department of Surgery and Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, David Geffen
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1
 Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
married to Dr. med. Elke Gützlaff 3 children University of Kiel, Lübeck and Hannover ( `80)
 Curriculum Vitae Name: Date and Place of Birth: Family: Present Adress Medical Training: Prof. Dr. med. Claus Petersen July 14, 1954, in Kiel, Germany married to Dr. med. Elke Gützlaff 3 children Dept.
Curriculum Vitae Name: Date and Place of Birth: Family: Present Adress Medical Training: Prof. Dr. med. Claus Petersen July 14, 1954, in Kiel, Germany married to Dr. med. Elke Gützlaff 3 children Dept.
Ten year experience of bioabsorbable mesh support in pectus excavatum repair
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 733 740 Ten year experience of bioabsorbable mesh support in pectus excavatum repair L. Luzzi a, *, L. Voltolini a, J. Zacharias b, A. Campione a,
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 733 740 Ten year experience of bioabsorbable mesh support in pectus excavatum repair L. Luzzi a, *, L. Voltolini a, J. Zacharias b, A. Campione a,
Surgical Treatment of the Funnel Chest Deformation at the Children
 American Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 3(2): 8-12 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajp doi: 10.11648/j.ajp.20170302.12 ISSN: 2472-0887 (Print); ISSN: 2472-0909 (Online) Surgical Treatment of the Funnel
American Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 3(2): 8-12 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajp doi: 10.11648/j.ajp.20170302.12 ISSN: 2472-0887 (Print); ISSN: 2472-0909 (Online) Surgical Treatment of the Funnel
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT
 Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Single centre experience on short bar technique for pectus excavatum
 Featured Article Single centre experience on short bar technique for pectus excavatum Hans Kristian Pilegaard 1,2 1 Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus,
Featured Article Single centre experience on short bar technique for pectus excavatum Hans Kristian Pilegaard 1,2 1 Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus,
Management of postoperative infections after the minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2005) 40, 1004 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Management of postoperative infections after the minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair Casey M. Calkins, Stephen
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2005) 40, 1004 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Management of postoperative infections after the minimally invasive pectus excavatum repair Casey M. Calkins, Stephen
Reliability of a standardized protocol to calculate cross-sectional chest area and severity indices to evaluate pectus excavatum
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2006) 41, 1219 1225 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Reliability of a standardized protocol to calculate cross-sectional chest area and severity indices to evaluate pectus
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2006) 41, 1219 1225 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Reliability of a standardized protocol to calculate cross-sectional chest area and severity indices to evaluate pectus
Minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum: A novel morphology-tailored, patient-specific approach
 Park et al General Thoracic Surgery Minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum: A novel morphology-tailored, patient-specific approach Hyung Joo Park, MD, a Jin Yong Jeong, MD, a Won Min Jo, MD, a Jae
Park et al General Thoracic Surgery Minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum: A novel morphology-tailored, patient-specific approach Hyung Joo Park, MD, a Jin Yong Jeong, MD, a Won Min Jo, MD, a Jae
What's new in pediatric surgery? A minimally invasive technique to correct pectus excavatum
 BUMC Proceedings 1999;12:25-28 What's new in pediatric surgery? A minimally invasive technique to correct pectus excavatum DALE COLN, MD Department of Surgery, BUMC An effective method for surgically repairing
BUMC Proceedings 1999;12:25-28 What's new in pediatric surgery? A minimally invasive technique to correct pectus excavatum DALE COLN, MD Department of Surgery, BUMC An effective method for surgically repairing
INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 J Korean Med Sci 2003; 18: 360-4 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The aim of this study was to compare clinical outcomes in pectus excavatum patients undergoing a Ravitch
J Korean Med Sci 2003; 18: 360-4 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The aim of this study was to compare clinical outcomes in pectus excavatum patients undergoing a Ravitch
 The double rib contour sign (DRCS) in lateral spinal radiographs. Aetiologic implications for scoliosis Theodoros B GRIVAS, Spyros DANGAS, Basil D POLYZOIS, Panagiotis SAMELIS Orthopaedic Department, Thriasio
The double rib contour sign (DRCS) in lateral spinal radiographs. Aetiologic implications for scoliosis Theodoros B GRIVAS, Spyros DANGAS, Basil D POLYZOIS, Panagiotis SAMELIS Orthopaedic Department, Thriasio
Short Nuss bar procedure
 Art of Operative Techniques Short Nuss bar procedure Hans Kristian Pilegaard 1,2 1 Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby, Aarhus, Denmark; 2 Department of
Art of Operative Techniques Short Nuss bar procedure Hans Kristian Pilegaard 1,2 1 Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby, Aarhus, Denmark; 2 Department of
Pectus excavatum is a chest wall deformity characterized
 Minimally Invasive Repair for Pectus Excavatum in Adults Swee H. Teh, MD, Angela M. Hanna, MD, Tuan H. Pham, MD, PhD, Adriana Lee, MD, Claude Deschamps, MD, Penny Stavlo, RN, and Christopher Moir, MD Divisions
Minimally Invasive Repair for Pectus Excavatum in Adults Swee H. Teh, MD, Angela M. Hanna, MD, Tuan H. Pham, MD, PhD, Adriana Lee, MD, Claude Deschamps, MD, Penny Stavlo, RN, and Christopher Moir, MD Divisions
Research Article Effects of Pectus Excavatum on the Spine of Pectus Excavatum Patients with Scoliosis
 Hindawi Healthcare Engineering Volume 2017, Article ID 5048625, 6 ages htts://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5048625 Research Article Effects of Pectus Excavatum on the Sine of Pectus Excavatum Patients with Scoliosis
Hindawi Healthcare Engineering Volume 2017, Article ID 5048625, 6 ages htts://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5048625 Research Article Effects of Pectus Excavatum on the Sine of Pectus Excavatum Patients with Scoliosis
Paediatric Dose Reduction and Image Quality
 Paediatric Dose Reduction and Image Quality Alan Whiteside The majority of this work was undertaken as part of MSc Thesis of Helen Dixon. Introduction Paediatric CT protocols result in a higher effective
Paediatric Dose Reduction and Image Quality Alan Whiteside The majority of this work was undertaken as part of MSc Thesis of Helen Dixon. Introduction Paediatric CT protocols result in a higher effective
Current Management of Pectus Deformities. George W. Holcomb, III, M.D., MBA Surgeon-in-Chief Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Missouri
 Current Management of Pectus Deformities George W. Holcomb, III, M.D., MBA Surgeon-in-Chief Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Missouri Pectus Deformities Pectus Excavatum Pectus Carinatum Mixed Excavatum/Carinatum
Current Management of Pectus Deformities George W. Holcomb, III, M.D., MBA Surgeon-in-Chief Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, Missouri Pectus Deformities Pectus Excavatum Pectus Carinatum Mixed Excavatum/Carinatum
Nonoperative management of pectus carinatum
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2006) 41, 40 45 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Nonoperative management of pectus carinatum Ala Stanford Frey, Victor F. Garcia, Rebeccah L. Brown, Thomas H. Inge, Frederick
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2006) 41, 40 45 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Nonoperative management of pectus carinatum Ala Stanford Frey, Victor F. Garcia, Rebeccah L. Brown, Thomas H. Inge, Frederick
Breathe In... Breathe Out... Stop Breathing: Does Phase of Respiration Affect the Haller Index in Patients With Pectus Excavatum?
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research irkemeier et al. Haller Index in Patients With Pectus Excavatum Pediatric Imaging Original Research Krista L. irkemeier 1 Daniel J. Podberesky 1 Shelia Salisbury 2 Suraj
Pediatric Imaging Original Research irkemeier et al. Haller Index in Patients With Pectus Excavatum Pediatric Imaging Original Research Krista L. irkemeier 1 Daniel J. Podberesky 1 Shelia Salisbury 2 Suraj
CT-Densitometry A structure-based quantitative analysis of lung-ct in emphysema
 CT-Densitometry A structure-based quantitative analysis of lung-ct in emphysema R.A. Blechschmidt and U. Lörcher Department of Radiology, Deutsche Klinik für Diagnostik Aukammallee 33, 65191 Wiesbaden,
CT-Densitometry A structure-based quantitative analysis of lung-ct in emphysema R.A. Blechschmidt and U. Lörcher Department of Radiology, Deutsche Klinik für Diagnostik Aukammallee 33, 65191 Wiesbaden,
Pulmonary function before and after the Nuss procedure in adolescents with pectus excavatum: correlation with morphological subtypes
 Jeong et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2015) 10:37 DOI 10.1186/s13019-015-0236-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pulmonary function before and after the Nuss procedure in adolescents with pectus
Jeong et al. Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2015) 10:37 DOI 10.1186/s13019-015-0236-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pulmonary function before and after the Nuss procedure in adolescents with pectus
Forces to be overcome in correction of pectus excavatum
 Forces to be overcome in correction of pectus excavatum Peter G. Weber, MD, Hans P. Huemmer, MD, and Bertram Reingruber, MD Objective: The Erlangen technique of funnel chest correction is carried out through
Forces to be overcome in correction of pectus excavatum Peter G. Weber, MD, Hans P. Huemmer, MD, and Bertram Reingruber, MD Objective: The Erlangen technique of funnel chest correction is carried out through
Citation for published version (APA): Eijkelkamp, M. F. (2002). On the development of an artificial intervertebral disc s.n.
 University of Groningen On the development of an artificial intervertebral disc Eijkelkamp, Marcus Franciscus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen On the development of an artificial intervertebral disc Eijkelkamp, Marcus Franciscus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Minimally Invasive Repair of Pectus Carinatum in Patients Unsuited to Bracing Therapy
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2016;49:92-98 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Minimally Invasive Repair of Pectus Carinatum in Patients Unsuited to Bracing Therapy Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2016.49.2.92
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2016;49:92-98 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Minimally Invasive Repair of Pectus Carinatum in Patients Unsuited to Bracing Therapy Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2016.49.2.92
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
P chondrosternal depression), the most common congenital
 Pectus Excavaturn Repair Claude Deschamps, MD ectus excavatum (also known as funnel chest or P chondrosternal depression), the most common congenital chest wall deformity, involves depression or inward
Pectus Excavaturn Repair Claude Deschamps, MD ectus excavatum (also known as funnel chest or P chondrosternal depression), the most common congenital chest wall deformity, involves depression or inward
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
Pectus excavatum is the most common congenital
 Nonprosthetic Surgical Repair of Pectus Excavatum Hiroshi Iida, MD, PhD, Yoshio Sudo, MD, PhD, Yasuyuki Yamada, MD, PhD, Yasushi Matsushita, MD, PhD, Kunihiro Eda, MD, PhD, and Yuho Inoue MD, PhD GENERAL
Nonprosthetic Surgical Repair of Pectus Excavatum Hiroshi Iida, MD, PhD, Yoshio Sudo, MD, PhD, Yasuyuki Yamada, MD, PhD, Yasushi Matsushita, MD, PhD, Kunihiro Eda, MD, PhD, and Yuho Inoue MD, PhD GENERAL
7th CONFERENCE on DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Łódź, December 8-11, 2003
 7th CONFERENCE on DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Łódź, December 8-11, 2003 1. Introduction NUMERICAL MODEL OF A THORAX Jan Awrejcewicz and Bartosz Łuczak Abstract. Finite element analysis of
7th CONFERENCE on DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Łódź, December 8-11, 2003 1. Introduction NUMERICAL MODEL OF A THORAX Jan Awrejcewicz and Bartosz Łuczak Abstract. Finite element analysis of
Original Report. Imaging Findings in Pediatric Patients with Persistent Airway Symptoms After Surgery for Double Aortic Arch
 Robert J. Fleck 1,2 Preeyacha Pacharn 1,3 Bradley L. Fricke 1 Matthew A. Ziegler 1 Robin T. Cotton 4 Lane F. Donnelly 1 Received August 30, 2001; accepted after revision October 22, 2001. 1 Department
Robert J. Fleck 1,2 Preeyacha Pacharn 1,3 Bradley L. Fricke 1 Matthew A. Ziegler 1 Robin T. Cotton 4 Lane F. Donnelly 1 Received August 30, 2001; accepted after revision October 22, 2001. 1 Department
Grading of Vertebral Rotation
 Chapter 5 Grading of Vertebral Rotation The measurement of vertebral rotation has become increasingly prominent in the study of scoliosis. Apical vertebral deformity demonstrates significance in both preoperative
Chapter 5 Grading of Vertebral Rotation The measurement of vertebral rotation has become increasingly prominent in the study of scoliosis. Apical vertebral deformity demonstrates significance in both preoperative
Moderators: Malgorzata Lutwin-Kawalec, MD, Dinesh K Choudhry, MD, FRCA. Institution: Nemours/AI DuPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, DE
 PBLD Table # 17 A teenager with Factor V Leiden and pectus excavatum for a Nuss procedure: navigating recommendations for testing, perioperative risk of thrombosis and post-operative pain management. Moderators:
PBLD Table # 17 A teenager with Factor V Leiden and pectus excavatum for a Nuss procedure: navigating recommendations for testing, perioperative risk of thrombosis and post-operative pain management. Moderators:
P keel ), or pigeon breast, is the term applied to
 Surgical Management of Pectus Carinatum Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD ectus carinatum (from the Latin, chest with a P keel ), or pigeon breast, is the term applied to various protrusion deformities of the anterior
Surgical Management of Pectus Carinatum Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD ectus carinatum (from the Latin, chest with a P keel ), or pigeon breast, is the term applied to various protrusion deformities of the anterior
IN 1997 we reported our 10 years of experience with a
 Experience and Modification Update for the Minimally Invasive Nuss Technique for Pectus Excavatum Repair in 303 Patients By Daniel P. Croitoru, Robert E. Kelly, Jr, Michael J. Goretsky, M. Louise Lawson,
Experience and Modification Update for the Minimally Invasive Nuss Technique for Pectus Excavatum Repair in 303 Patients By Daniel P. Croitoru, Robert E. Kelly, Jr, Michael J. Goretsky, M. Louise Lawson,
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use?
 Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Lorenz Bar Repair of Pectus Excavatum in the Adult Population: Should it be Done?
 Lorenz Bar Repair of Pectus Excavatum in the Adult Population: Should it be Done? Vanessa A. Olbrecht, MD, Meghan A. Arnold, MD, Rosemary Nabaweesi, MPH, MBChB, David C. Chang, PhD, MPH, Kimberly H. McIltrot,
Lorenz Bar Repair of Pectus Excavatum in the Adult Population: Should it be Done? Vanessa A. Olbrecht, MD, Meghan A. Arnold, MD, Rosemary Nabaweesi, MPH, MBChB, David C. Chang, PhD, MPH, Kimberly H. McIltrot,
Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of Anterior Chest Wall Joint and Bone Disorders
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Uchiyama, Takayoshi; Nakao, Susumu; Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1978, 23
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Surgical Repair for P Function Tomita, Masao; Koga, Yasunori; Shib Onitsuka, Toshio; Sakoda, Koichiro; Shigehito; Nakamura, Yuzuru; Ayabe,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Surgical Repair for P Function Tomita, Masao; Koga, Yasunori; Shib Onitsuka, Toshio; Sakoda, Koichiro; Shigehito; Nakamura, Yuzuru; Ayabe,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Costochondral Abnormalities in Children Presenting With Anterior Chest Wall Mass
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Supakul and Karmazyn Ultrasound of ostochondral bnormalities Pediatric Imaging Original Research Nucharin Supakul 1 oaz Karmazyn Supakul N, Karmazyn Keywords: anterior
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Supakul and Karmazyn Ultrasound of ostochondral bnormalities Pediatric Imaging Original Research Nucharin Supakul 1 oaz Karmazyn Supakul N, Karmazyn Keywords: anterior
Radiation Dose To Pediatric Patients in Computed Tomography in Sudan
 Radiation Dose To Pediatric Patients in Computed Tomography in Sudan Omer Osman,Saeed Medical Physics Department, ALNeelain University, Sudan Presentation outlines Introduction Objectives Materials and
Radiation Dose To Pediatric Patients in Computed Tomography in Sudan Omer Osman,Saeed Medical Physics Department, ALNeelain University, Sudan Presentation outlines Introduction Objectives Materials and
studies Pectus excavatum and cardiac dysfunction: a case report with pre- and post-operative haemodynamic
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 74-78 Pectus excavatum and cardiac dysfunction: a case report with pre- and post-operative haemodynamic studies P A MAJID,1 B S ZIENKOCICZ,' AND J P ROOS1 From the Department of Cardiology,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 74-78 Pectus excavatum and cardiac dysfunction: a case report with pre- and post-operative haemodynamic studies P A MAJID,1 B S ZIENKOCICZ,' AND J P ROOS1 From the Department of Cardiology,
Thoracic Kyphosis: Range in
 979 Downloaded from wwwajronlineorg by 463199 on 02/13/18 from IP address 463199 Copyright ARRS For personal use only; all rights reserved Thoracic Kyphosis: Range in Normal Subjects Gerald T Fon1 2 Thoracic
979 Downloaded from wwwajronlineorg by 463199 on 02/13/18 from IP address 463199 Copyright ARRS For personal use only; all rights reserved Thoracic Kyphosis: Range in Normal Subjects Gerald T Fon1 2 Thoracic
Indications for the surgical treatment of the funnel chest
 555 Indications for the surgical treatment of the funnel chest Clinic of Pediatric Surgery, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania Key words: funnel chest, chest wall deformities. Summary. Aim of the
555 Indications for the surgical treatment of the funnel chest Clinic of Pediatric Surgery, Kaunas University of Medicine, Lithuania Key words: funnel chest, chest wall deformities. Summary. Aim of the
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CHEST CTA Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 71275 Last Review Date: August 2014 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CHEST CTA Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 71275 Last Review Date: August 2014 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
Chest Wall Deformities
 CHAPTER 53 Chest Wall Deformities Michael Singh Dakshesh Parikh Brian Kenney Pectus Carinatum Pectus carinatum (PC), or pigeon chest, is a spectrum of anterior chest wall anomalies characterised by protrusion
CHAPTER 53 Chest Wall Deformities Michael Singh Dakshesh Parikh Brian Kenney Pectus Carinatum Pectus carinatum (PC), or pigeon chest, is a spectrum of anterior chest wall anomalies characterised by protrusion
Porcine model for early onset scoliosis created with a posterior mini-invasive method
 E-Poster #P72 Porcine model for early onset scoliosis created with a posterior mini-invasive method WANG Bin, ZHENG Xin, QIU Yong*, QIAN Bang-ping, SUN Xu, ZHU Zezhang, YU Yang Spine surgery, the Affiliated
E-Poster #P72 Porcine model for early onset scoliosis created with a posterior mini-invasive method WANG Bin, ZHENG Xin, QIU Yong*, QIAN Bang-ping, SUN Xu, ZHU Zezhang, YU Yang Spine surgery, the Affiliated
Novel Approaches for Assessing the Chest Wall and Spine in the Treatment of SMA
 Center for Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome Novel Approaches for Assessing the Chest Wall and Spine in the Treatment of SMA RM Campbell, MD Director, Center for Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome Division
Center for Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome Novel Approaches for Assessing the Chest Wall and Spine in the Treatment of SMA RM Campbell, MD Director, Center for Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome Division
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Instruction for healthcare professionals
 Materials needed Computer with DVD capability LCD projector "Curve Checks" DVD Pretest forms one per participant (see appendix) Evaluation forms one per participant (see appendix) Curve Checks Reference
Materials needed Computer with DVD capability LCD projector "Curve Checks" DVD Pretest forms one per participant (see appendix) Evaluation forms one per participant (see appendix) Curve Checks Reference
Acknowledgments. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Lung Nodule Detection. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Chest CT Protocols. Chest CT Protocols
 Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Natural history of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a tool for guidance in decision of surgery of curves above 50
 J Child Orthop (2013) 7:37 41 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0462-7 CURRENT CONCEPT REVIEW Natural history of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a tool for guidance in decision of surgery of curves above 50 Aina
J Child Orthop (2013) 7:37 41 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0462-7 CURRENT CONCEPT REVIEW Natural history of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a tool for guidance in decision of surgery of curves above 50 Aina
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Occipital flattening in the infant skull
 Occipital flattening in the infant skull Kant Y. Lin, M.D., Richard S. Polin, M.D., Thomas Gampper, M.D., and John A. Jane, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Plastic Surgery and Neurological Surgery, University
Occipital flattening in the infant skull Kant Y. Lin, M.D., Richard S. Polin, M.D., Thomas Gampper, M.D., and John A. Jane, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Plastic Surgery and Neurological Surgery, University
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications
 Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in Radiology Juxtadiaphragmatic lesions
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in Radiology Juxtadiaphragmatic lesions
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Hemivertebra Resection Combined With Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Rigid Congenital Kyphoscoliosis in Adolescence
 Hemivertebra Resection Combined With Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Rigid Congenital Kyphoscoliosis in Adolescence Comparison of Clinical, Radiographic, and Health-Related Quality of Life
Hemivertebra Resection Combined With Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Rigid Congenital Kyphoscoliosis in Adolescence Comparison of Clinical, Radiographic, and Health-Related Quality of Life
Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
A Comparison of Cobb Angle: Standing Versus Supine Images of Late-Onset Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 216; 81: 27-276 DOI: 1.12659/PJR.895949 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 215.9.13 Accepted: 215.11.22 Published: 216.6.1 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 216; 81: 27-276 DOI: 1.12659/PJR.895949 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 215.9.13 Accepted: 215.11.22 Published: 216.6.1 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical
Chest wall deformities and coincidence of additional anomalies, screening results of the Turkish children with the review of the literature
 Current Thoracic Surgery To cite this article: Tokur M, Demiröz ŞM, Sayan M, Tokur N, Arpağ H. Chest wall deformities and coincidence of additional anomalies, screening results of the 25.000 Turkish children
Current Thoracic Surgery To cite this article: Tokur M, Demiröz ŞM, Sayan M, Tokur N, Arpağ H. Chest wall deformities and coincidence of additional anomalies, screening results of the 25.000 Turkish children
Vacuum bell therapy. Frank-Martin Haecker, Sergio Sesia. Introduction
 Featured Article Vacuum bell therapy Frank-Martin Haecker, Sergio Sesia Department of Pediatric Surgery, University Children s Hospital, Basel, Switzerland Correspondence to: Frank-Martin Haecker, MD,
Featured Article Vacuum bell therapy Frank-Martin Haecker, Sergio Sesia Department of Pediatric Surgery, University Children s Hospital, Basel, Switzerland Correspondence to: Frank-Martin Haecker, MD,
Nuss Ravitch modified CPT Codes repair repair modify CPT Code repair repair Nuss codes repair modified Nuss modified Ravitch procedure
 Sep 1, 2013. Nuss procedure or the Ravitch technique (original or modified), typically requiring the removal of a portion of damaged.. CPT Codes. Description: Codes Covered When Medically Necessary. 21740.
Sep 1, 2013. Nuss procedure or the Ravitch technique (original or modified), typically requiring the removal of a portion of damaged.. CPT Codes. Description: Codes Covered When Medically Necessary. 21740.
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
A thesis submitted to the. Graduate School. of the University of Cincinnati. in partial fulfillment of the. requirements for the degree of
 Virtual Implantation Of Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices A thesis submitted to the Graduate School of the University of Cincinnati in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master
Virtual Implantation Of Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices A thesis submitted to the Graduate School of the University of Cincinnati in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master
After the Chest X-Ray:
 After the Chest X-Ray: What To Do Next Alan S. Brody Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief of Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio USA What Should We Do Next? CT scan?
After the Chest X-Ray: What To Do Next Alan S. Brody Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief of Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio USA What Should We Do Next? CT scan?
Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments
 Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments Scoliosis Spinal Deformity 3-dimensional deformity affecting all 3 planes Can be difficult to visualize with 2-dimensional radiographs Kyphosis Deformity affecting
Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments Scoliosis Spinal Deformity 3-dimensional deformity affecting all 3 planes Can be difficult to visualize with 2-dimensional radiographs Kyphosis Deformity affecting
3/28/18. Navigating the Bumps and Dips: The Ins and Outs of Pectus Excavatum and Pectus Carinatum. Disclosure Information.
 Navigating the Bumps and Dips: The Ins and Outs of Pectus Excavatum and Pectus Carinatum Beth Orrick, MSN, APRN, FNP-BC Amy Pierce, MSN, APRN, PPCNP-BC Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, MO Disclosure
Navigating the Bumps and Dips: The Ins and Outs of Pectus Excavatum and Pectus Carinatum Beth Orrick, MSN, APRN, FNP-BC Amy Pierce, MSN, APRN, PPCNP-BC Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City, MO Disclosure
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.90 Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/20135:2012 Return
MP 7.01.90 Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/20135:2012 Return
The Nuss procedure brought innovation to surgical treatment of pectus excavatum.
 General Thoracic Surgery Nagasao et al Stress distribution on the thorax after the Nuss procedure for pectus excavatum results in different patterns between adult and child patients Tomohisa Nagasao, MD,
General Thoracic Surgery Nagasao et al Stress distribution on the thorax after the Nuss procedure for pectus excavatum results in different patterns between adult and child patients Tomohisa Nagasao, MD,
Disclosures. Introduction. Purpose. Morphologic Variation in Lumbar Spinal Canal Dimensions by Gender, Race and Age
 Disclosures Morphologic Variation in Lumbar Spinal Canal Dimensions by Gender, Race and Age Jeremy D. Shaw, MD, MS; Daniel L. Shaw, BA; Daniel R. Cooperman, MD; Jason D. Eubanks, MD; Ling Li, MSPH; David
Disclosures Morphologic Variation in Lumbar Spinal Canal Dimensions by Gender, Race and Age Jeremy D. Shaw, MD, MS; Daniel L. Shaw, BA; Daniel R. Cooperman, MD; Jason D. Eubanks, MD; Ling Li, MSPH; David
Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib. Description
 Subject: Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib Description The vertical expandable prosthetic titanium
Subject: Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib Description The vertical expandable prosthetic titanium
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY. Evidence Review: Surgical correction for pectus deformity (all ages)
 Evidence Review: Surgical correction for pectus deformity (all ages) NHS England Evidence Review: Surgical correction for pectus deformity (all ages) First published: November 2015 Updated: Prepared by
Evidence Review: Surgical correction for pectus deformity (all ages) NHS England Evidence Review: Surgical correction for pectus deformity (all ages) First published: November 2015 Updated: Prepared by
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
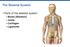 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
New Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Machines (idxa) and Vertebral Fracture Assessment
 Case 1 New Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Machines (idxa) and Vertebral Fracture Assessment (VFA) History and Examination Your wealthy friend who is a banker brings his 62-year-old mother to your office
Case 1 New Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Machines (idxa) and Vertebral Fracture Assessment (VFA) History and Examination Your wealthy friend who is a banker brings his 62-year-old mother to your office
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
MEASUREMENTS OF THE STERNUM FOR BETTER CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION
 MEASUREMENTS OF THE STERNUM FOR BETTER CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION Pedersen I.M.G.¹,Hermans J.J.²,Molenbroek J.F.M.¹ 1 Delft University of Technology, Faculty Industrial Design Engineering, Landbergstraat
MEASUREMENTS OF THE STERNUM FOR BETTER CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION Pedersen I.M.G.¹,Hermans J.J.²,Molenbroek J.F.M.¹ 1 Delft University of Technology, Faculty Industrial Design Engineering, Landbergstraat
CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis
 CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis Poster No.: C-1503 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Buchberger, B. von Rahden, J. Schmid, W. Kenn, C.-T. Germer, D. Hahn; Würzburg/DE Keywords:
CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis Poster No.: C-1503 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Buchberger, B. von Rahden, J. Schmid, W. Kenn, C.-T. Germer, D. Hahn; Würzburg/DE Keywords:
Pain and Anxiety Management in Minimally Invasive Repair of Pectus Excavatum
 Brief Report Korean J Pain 2012 October; Vol. 25, No. 4: 267-271 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.267 Pain and Anxiety Management in Minimally Invasive Repair of
Brief Report Korean J Pain 2012 October; Vol. 25, No. 4: 267-271 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.267 Pain and Anxiety Management in Minimally Invasive Repair of
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Laser Doppler imaging as a tool in the burn wound treatment protocol
 Original paper Videosurgery Laser Doppler imaging as a tool in the burn wound treatment protocol Algirda Venclauskiene 1, Algidas Basevicius 2, Ernest Zacharevskij 3, Vytautas Vaicekauskas 4, Rytis Rimdeika
Original paper Videosurgery Laser Doppler imaging as a tool in the burn wound treatment protocol Algirda Venclauskiene 1, Algidas Basevicius 2, Ernest Zacharevskij 3, Vytautas Vaicekauskas 4, Rytis Rimdeika
Pediatric Severe OSAHS with a Funnel Chest W Ma, J Wang, P Hui, L Zhao, X Wei, Y Xie ABSTRACT
 Pediatric Severe OSAHS with a Funnel Chest W Ma, J Wang, P Hui, L Zhao, X Wei, Y Xie ABSTRACT The primary etiopathology of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) includes tonsil or
Pediatric Severe OSAHS with a Funnel Chest W Ma, J Wang, P Hui, L Zhao, X Wei, Y Xie ABSTRACT The primary etiopathology of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) includes tonsil or
A prospective study on quality of life in youths after pectus excavatum correction
 Featured Article A prospective study on quality of life in youths after pectus excavatum correction Johanne Jeppesen Lomholt 1, Elisabeth Brammer Jacobsen 2, Mikael Thastum 1, Hans Pilegaard 3,4 1 Department
Featured Article A prospective study on quality of life in youths after pectus excavatum correction Johanne Jeppesen Lomholt 1, Elisabeth Brammer Jacobsen 2, Mikael Thastum 1, Hans Pilegaard 3,4 1 Department
Thoracic Surgery. Treating a wide range of chest disorders
 Thoracic Surgery Treating a wide range of chest disorders Thoracic Surgery at UCLA The UCLA Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery is among the nation s leaders in providing care for a wide range of chest
Thoracic Surgery Treating a wide range of chest disorders Thoracic Surgery at UCLA The UCLA Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery is among the nation s leaders in providing care for a wide range of chest
Institutional review board approval was obtained prior to the start of this study.
 Lower Limb Alignment and Length Measurements - Comparison of Computed Tomography, Upright Full-Length Conventional Radiography and Upright Biplanar Linear-Low Dose X-ray Scanner Poster No.: C-1382 Congress:
Lower Limb Alignment and Length Measurements - Comparison of Computed Tomography, Upright Full-Length Conventional Radiography and Upright Biplanar Linear-Low Dose X-ray Scanner Poster No.: C-1382 Congress:
A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels
 A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels Takao Nakajima 1, Yong Kim 2, Masabumi Miyamoto 3 Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Nippon Medical School, Chiba Hokusoh Hospital 1 Dept. of Orthop.
A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels Takao Nakajima 1, Yong Kim 2, Masabumi Miyamoto 3 Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Nippon Medical School, Chiba Hokusoh Hospital 1 Dept. of Orthop.
Class Time: 9/12,10-10,11-21 Days: Listed Saturdays 1p-4p Room:HS208. Office Phone: Home Phone:
 Semester/Year: FALL 2015 CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS RDTK 1920 H1 Computed Tomography Procedures I Lecture Hours: 3 Lab Hours: 0 Credit Hours: 3 Class Time: 9/12,10-10,11-21 Days: Listed Saturdays 1p-4p
Semester/Year: FALL 2015 CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS RDTK 1920 H1 Computed Tomography Procedures I Lecture Hours: 3 Lab Hours: 0 Credit Hours: 3 Class Time: 9/12,10-10,11-21 Days: Listed Saturdays 1p-4p
LIVING ANATOMY: IMPLICATIONS OF RESPIRATION CONVOCATION MARCH 16, 2019 PAMELA L. WILSON, D.O.
 LIVING ANATOMY: IMPLICATIONS OF RESPIRATION CONVOCATION MARCH 16, 2019 PAMELA L. WILSON, D.O. I believe you are taught anatomy in our school more thoroughly than any other school to date, because we want
LIVING ANATOMY: IMPLICATIONS OF RESPIRATION CONVOCATION MARCH 16, 2019 PAMELA L. WILSON, D.O. I believe you are taught anatomy in our school more thoroughly than any other school to date, because we want
Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010
 Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010 Self Assessment Module on Nuclear Medicine and PET/CT Case Review FDG PET/CT IN LYMPHOMA AND MELANOMA Submitted
Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010 Self Assessment Module on Nuclear Medicine and PET/CT Case Review FDG PET/CT IN LYMPHOMA AND MELANOMA Submitted
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
What Are the Best Exercises for Scoliosis? Lise Stolze Polestar Educator, Physical Therapist, and certified C2 Schroth Scoliosis Therapist
 What Are the Best Exercises for Scoliosis? Lise Stolze Polestar Educator, Physical Therapist, and certified C2 Schroth Scoliosis Therapist I will be brief since this is a whole course in itself! We know
What Are the Best Exercises for Scoliosis? Lise Stolze Polestar Educator, Physical Therapist, and certified C2 Schroth Scoliosis Therapist I will be brief since this is a whole course in itself! We know
