abdominal pain In another noncontrolled follow-up study comprising We have carried out a controlled investigation of
|
|
|
- Emmeline Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1975, 50, 110. Long-term prognosis in children with recurrent abdominal pain M. FJORD CHRISTENSEN and 0. MORTENSEN From the University Clinic of Paediatrics, Arhus Municipal Hospital, Denmark Christensen, M. F., and Mortensen, 0. (1975). Archives of Disease in Childhood, 50, 110. Long-term prognosis in children with recurrent abdominal pain. The present study is a follow-up of 34 cases admitted to a paediatric department with recurrent abdominal pain (RAP) in 1942 and persons without a history of RAP were selected at random and included as controls. Using a questionnaire, there was a higher incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms among persons with a history of RAP during childhood than among controls (P < 0 05). 18 of the original 34 cases who still had symptoms were re-examined; 11 had a clinical picture consistent with a diagnosis of irritable colon, 5 had a picture compatible with both irritable colon and peptic ulcer/gastritis, and 2 had duodenal ulcer. Abdominal pains occurred no more frequentlyamong children ofparents who had had RAP during childhood than among children of parents without such a history. However, there was a higher incidence of abdominal pain among children of parents who were complaining of abdominal discomfort at the time of the investigation than among children whose parents were without such symptoms (P < 0 005). It has been generally held that the prognosis for children with recurrent abdominal pain (RAP) is good, though this point of view is not supported by the few published follow-up studies. Apley (1959) examined 30 persons who had been in hospital as children with RAP 8-20 years earlier. The patients had received no or inadequate treatment. 9 were free from symptoms. In 9 cases the episodes of abdominal pain had ceased only to be replaced by other symptoms, especially headache. In 12 cases abdominal pains persisted, mostly accompanied by 'nervous' complaints. Among 18 controls, one had severe headache, 4 had occasional slight headache, 3 had occasional abdominal discomfort, and one suffered from nervousness. Apley and Hale (1973) reported a follow-up of 30 persons years after they had been referred to a children's hospital on account of RAP and treated with reassurance and explanation. The results were similar to those of the first study except for the following points: the children who responded to treatment recovered more quickly than those described in the first study; relapse did not occur in treated patients; and in the treated group fewer nonabdominal disorders developed. Received 29 July In another noncontrolled follow-up study comprising 116 children with abdominal pains, Dahl and Haahr (1969) reported that 48% had obtained relief of their symptoms, while 36% were still suffering from abdominal pains. In 16% the abdominal symptoms had ceased, but other complaints had appeared. This study was carried out between one and 10 years after discharge from hospital. A fourth study, that of Papatheophilou, Jeavons, and Disney (1972), was incomplete, since information was only obtained from 14 of 100 patients; in these the abdominal pains had disappeared by the age of years. We have carried out a controlled investigation of the long-term prognosis of 34 children with RAP, partly in order to supplement previous studies, and partly for the purpose of elucidating the type of abdominal discomfort in adults with continued symptoms. In addition, there was an opportunity to obtain information about abdominal pains in the original patients' children. Patients and methods From 1 April 1942 to 31 December 1943 a total of 38 children, aged between 2 years 11 months and 13 years, with an average age of 7 years 10 months, were referred to the paediatric department of the Arhus 110
2 Long-term prognosis in children with recurrent abdominal pain Municipal Hospital with RAP. All children were subjected to inpatient hospital evaluation as part of a research project concerning children with RAP. Routine studies included ESR and Hb concentration, urine analysis, tuberculin test, examination of gastric juice by test meal, barium meal, examination of the stool for blood, and assessment of the intelligence quotient. The 38 children had typical histories of RAP and fulfilled the following diagnostic criteria. They had complained of at least three episodes of abdominal pain in a period longer than 3 months. No organic diseases were found to account for the pain. The type of treatment applied was reassurance based on explanation of the character of the condition. The follow-up investigation had two purposes. (1) To compare these original 38 patients as adults with controls, and look for possible differences in the frequency of both abdominal and nonabdominal symptoms, in social status and in the frequency of abdominal pains in their offspring. This part of the investigation was based on a questionnaire. (2) To elucidate the type of abdominal discomfort in adults with continued symptoms. This part of the investigation was based on interview and examination. From 1970 to 1972, all 38 persons were located through the public registration office. Elaborate questionnaires relating to their social status and health and also to the health of their children were forwarded by mail. Complete answers were received from 20 females and 14 males. The average age of these 34 persons at the time of the follow-up study was 35 years 11 months. Those complaining of persistent abdominal symptoms were contacted by one of the authors (M.F.C.), a detailed interview and thorough clinical examination took place, and relevant information concerning previous hospitalization and examinations in outpatient clinics was provided. The control material consisted of 59 persons born between 1 January 1930 and 31 December 1940, selected at random on the basis of their registration number in the public registration office in Arhus. They received a similar questionnaire and this was completed by who appeared to have had abdominal pains as children were excluded. The remaining 45 included 25 males and 20 females with an average age of 36 years 5 months. A tentative diagnosis of irritable colon was accepted in the presence of colonic pain accompanied by at least one of the following symptoms: periods with constipation and/or diarrhoea, and meteorism, in the absence of other recognized colonic disease. A diagnosis of peptic ulcer/gastritis was accepted when supported by x-ray study, or suggested by epigastric pain provoked by hunger, in the absense of other recognized relevant abdominal disorder. A diagnosis of abdominal pains in children of the original patients and the control subjects was accepted if the children were 3-15 years old, and if the point in the questionnaire asking whether they suffered from abdominal pains was answered in the affirmative. For statistical evaluation the X2 test was used. 3 ill Results According to the questionnaire 18 of the original 34 patients, 11 females and 7 males, had suffered from chronic or recurrent abdominal symptoms as adults. In the controls 13 of 45, 8 females and 5 males, had also experienced this (Table I). The TABLE I Frequency of abdominal symptoms in adults with and without recurrent abdominal pain in childhood 34 Adults with 45 Adults without recurrent abdominal recurrent abdominal pain in childhood pain in childhood Abdoninal symptoms No abdominal symptoms difference is significant (P <0 05). 11 of the 18 persons with continual symptoms had experienced a symptom-free period during adolescence. A further study of the 18 adults with recurrent or persistent abdominal symptoms showed that 11, 8 females and 3 males, had a clinical picture consistent with the diagnosis of irritable colon. 5, 3 females and 2 males, had a picture compatible with both irritable colon and peptic ulcer/gastritis. The remaining 2 patients, both males, had duodenal ulcer, verified by barium meal (Table II). Twelve patients had mild symptoms, but 5 had more pronounced discomfort which limited normal activities. One was sufficiently severely affected to have been admitted to hospital on several occasions. Nongastrointestinal symptoms were also significantly commoner in the original patients than the controls. Among the 34 patients 11 had other complaints, especially headache, often migrainous, back pain, 'bad nerves', or gynaecological symptoms. Among the 45 controls, only 6 had nongastrointestinal symptoms (Table III). The difference is significant (P <0 05). Social assessment with respect to occupation and marital status showed no difference between the two groups. Neither was there any demonstrable difference in the incidence of abdominal pains among the offspring of these groups (P >0 05) (Table IV). The average age of the original patients' children between 3 and 15 was 8 years 6 months; the corresponding figure for the children of the control subjects was 9 years 4 months. A total of 86 adults, patients and controls, answered the questionnaire. Of these, 37 had
3 112 Christensen and Mortensen TABLI Type of abdominal discomfort in 18 adult. Attacks Case no. Pain Pain Estimated attacks especially in Stress localization description per year spring and autumn provocation 5 Periumbilical Colicky 50 No Yes 10 Epigastric Burning, 1 No Yes 11 Epigastric, Burning, 75 Yes Yes 12 Periumbilical I Colicky 50 No Yes 13 Epigastric Colicky, Daily No Yes left of umbilicus grumbling 15 Whole abdominal Colicky 50 No Yes region 16 Periumbilical Colicky 12 Yes Yes 17 Periumbilical Grumbling, Daily No Yes 18 Infraumbilical Colicky 50 No Yes 19 Epigastric Burning 60 Yes No 20 Periumbilical Squeezing 10 No Yes 22 Left of umbilicus Colicky 2 No Yes 23 Right epigastric Burning 2 Yes No 24 Epigastric, Burning, 25 Yes Yes 25 Epigastric Hunger,, 50 No Yes left of umbilicus 26 Left of umbilicus Grumbling 2 No Yes 27 Epigastric, Hunger, 6 No Yes 34 Periumbilical Colicky 4 No Yes TABLE III Frequency of nonabdominal symptoms in adults with and without recurrent abdominal pain in childhood 34 Adults with 45 Adults without recurrent abdominal recurrent abdominal pain in childhood pain in childhood Nonabdominal symptoms present 11 6 Nonabdominal symptoms absent ~~~~~ abdominal complaints and 49 were symptom free. In the children of the former group abdominal pains occurred definitely more frequently (P <0 005) than in children whose parents were without symptoms (Table V). Discussion Even if the nature of the condition of RAP is not fully understood there seems to be some agreement on the following points. The pain tends to occur in 'sensitive' children (Apley, 1959; Moro, 1913; Stone and Barbero, 1970) when they are exposed to emotional tension (Apley, 1959; British Medical Journal, 1970; Green, 1967; Mac Keith and O'Neill, 1951; Moro, 1913; Singh, Gupta, and Agrawal, 1972; Stone and Barbero, 1970), and in whose TABLE IV Abdominal pains in children of adults with and without recurrent abdominal pain in childhood 47 Children of adults with recurrent 58 Children of adults without recurrent abdominal pain in childhood abdominal pain in childhood Abdominal pains present 9 7 Abdominal pains absent 38 51
4 with recurrent abdominal pain in childhood Long-term prognosis in children with recurrent abdominal pain 113 Hunger Diarrhoea and/or Meteorism Tender X-ray Tentative provocation constipation colon diagnosis No No Yes No Irritable colon No No Yes Yes Gastritis Irritable colon, gastritis Yes Yes Yes Yes Irritable colon, gastritis/ peptic ulcer No Yes Yes Yes Barium meal, enema, Irritable colon and pyelography negative No Yes Yes Yes Barium enema Irritable colon negative No No Yes Yes Irritable colon Yes No Yes No Duodenal ulcer Duodenal ulcer No No Yes Yes Irritable colon No Yes Yes Yes Spastic colon with Irritable colon sigmoidal diverticula No No No No Duodenal ulcer Duodenal ulcer Yes Yes Yes Yes Duodenal ulcer Irritable colon, duodenal ulcer Yes Yes Yes Yes Barium meal and Irritable colon, enema negative gastritis No Yes No Yes Irritable colon Yes No Yes Yes Irritable colon, gastritis/peptic ulcer families other members also have symptoms of abdominal pain (Apley, 1959; Stone and Barbero, 1970; 0ster, 1972). There is evidence to suggest that the site of the condition is in the colon (Dimson, 1971; Kopel, Kim, and Barbero, 1967; Stone and Barbero, 1970), the autonomic innervation of which is altered with resulting increased motility (Kopel et al., 1967). The present investigation supports some of the above points, by throwing light upon certain aspects of the long-term facts about children with RAP. In previous investigations about one-third of children with RAP, apparently unaffected by treatment with reassurance and explanation, had abdominal symptoms as adults (Apley, 1959; Apley and Hale, 1973; Dahl and Haahr, 1969). From our investigation it seems that about half the children with this disorder, treated with reassurance and explanation, will be likely to suffer from abdominal symptoms as adults, as opposed to between one-third and one-fourth of children without RAP. The present follow-up took place as late as 28 to 30 years after hospitalization of the patients, which may account for the difference between the present and previous studies as to the frequency of continued symptoms. Further, a number of our patients with symptoms in the adult stage had experienced a symptom-free period during adolescence. The investigation does not explain why some TABLE V Abdominal pains in children of adults with and without abdominal symptoms 46 Children of adults with 70 Children of adults without abdominal symptoms abdominal symptoms Abdominal pains present 13 5 Abdominal pains absent 33 65
5 114 Christensen and Mortensen children with RAP will have symptoms as adults and others not. The majority of adults with continued abdominal discomfort had symptoms suggesting the diagnosis of irritable colon. This may support the assumption that RAP in children is a result of a colonic disturbance, but does not prove it. The frequency of presumed psychosomatic symptoms in these patients as compared with controls is in keeping with the findings of Apley (1959) and Apley and Hale (1973), and with the view that children with RAP are vulnerable to emotional tension. Although about half the children with RAP will develop abdominal disorders as adults, their symptoms do not greatly affect their social life or their normal life. In Apley and Hale's study also only 2 out of 11 with continued abdominal pains had symptoms severe enough to restrict their normal activities. We were surprised to find that the children of persons with a history of RAP during childhood apparently did not suffer from abdominal pain more frequently than children of persons without RAP during childhood. Conway (1951) found the opposite. We and others (Apley, 1959; Stone and Barbero, 1970; 0ster, 1972) have shown that the children of adults with abdominal symptoms currently are likely to suffer from abdominal pains more frequently than the children of adults with no such symptoms. The present investigation thus emphasizes parental abdominal symptoms occurring currently as a significant factor in childhood abdominal pains. The best form of therapy remains to be settled. Apparently, the conventional reassurance and explanation is not sufficient, but we do not know whether more intense psychiatric treatment might prevent some little bellyachers from growing up to become big bellyachers. This work was made possible by a grant from 'B0rnefonden ved professor Bent Andersen, Arhus'. REFERENCES Apley, J. (1959). The Child with Abdominal Pains. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. Apley, J., and Hale, B. (1973). Children with recurrent abdominal pain: how do they grow up? British Medical Journal, 3, 7. British Medical Journal. (1970). Leading article. Recurrent abdominal pain in children, 4, 66. Conway, D. J. (1951). A study of abdominal pain in childhood. Great Ormond Street Journal, 2, 99. Dahl, L., and Haahr, J. (1969). Recidiverende mavesmerter barnealderen. Ugeskrift for Laeger, 131, Dimson, S. B. (1971). Transit time related to clinical findings in children with recurrent abdominal pain. Pediatrics, 47, 666. Green, M. (1967). Diagnosis and treatment: psychogenic, recurrent, abdominal pain. Pediatrics, 40, 84. Kopel, F. B., Kim, I. C., and Barbero, G. J. (1967). Comparison of rectosigmoid motility in normal children, children with recurrent abdominal pain, and children with ulcerative colitis. Pediatrics, 39, 539. Mac Keith, R., and O'Neill, D. (1951). Recurrent abdominal pain in children. Lancet, 2, 278. Moro, E. (1913). Ueber rezidivierende Nabelkoliken bei alteren Kindern. Muenchener Medizinische Wochenschrift, 60, ster, J. (1972). Recurrent abdominal pain, headache and limb pains in children and adolescents. Pediatrics, 50, 429. Papatheophilou, R., Jeavons, P. M., and Disney, M. E. (1972). Recurrent abdominal pain: a clinical and electroencephalographic study. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 14, 31. Singh, M. V., Gupta, S., and Agrawall, H. C. (1972). Sociopsychological basis of abdominal pain in children. Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 39, 33. Stone, R. T., and Barbero, G. J. (1970). Recurrent abdominal pain in childhood. Pediatrics, 45, 732. Correspondence to Dr. M. Fjord Christensen, Department of Paediatrics, Heming Central Hospital, 7400 Herning, Denmark. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 February Downloaded from on 26 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
ABDOMINAL PAIN, CHRONIC
 Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
ABDOMINAL PAIN, CHRONIC
 Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. What Is IBS?
 1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
There are clues to help to decide if the bellyache is a medical problem:
 Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Upper stomach pain that comes and goes
 P ford residence southampton, ny Upper stomach pain that comes and goes 10-3-2018 Find out what might be causing your upper or lower stomach pain and when you should consult a doctor using our trusted
P ford residence southampton, ny Upper stomach pain that comes and goes 10-3-2018 Find out what might be causing your upper or lower stomach pain and when you should consult a doctor using our trusted
190 Index Case studies, abdominal pain, 2 Crohn s disease, 2 3, cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), 2 fecal incontinence (FI), 2 medical c
 Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Recurrent Abdominal Pain: an Etiological Study among in a Referreal Children's Medical Center in Iran
 Original Article Iran J Ped Sep 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:235-240 Recurrent Abdominal Pain: an Etiological Study among in a Referreal Children's Medical Center in Iran Touran shahraki 1, Fatemeh Farahmand
Original Article Iran J Ped Sep 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:235-240 Recurrent Abdominal Pain: an Etiological Study among in a Referreal Children's Medical Center in Iran Touran shahraki 1, Fatemeh Farahmand
 Original citation: Macdougall, Colin. (2009) Food intolerance in children (non-allergenic food hypersensitivity). Paediatrics and Child Health, Vol.19 (No.8). pp. 388-390. ISSN 1751-7222 Permanent WRAP
Original citation: Macdougall, Colin. (2009) Food intolerance in children (non-allergenic food hypersensitivity). Paediatrics and Child Health, Vol.19 (No.8). pp. 388-390. ISSN 1751-7222 Permanent WRAP
and compared in 98 patients with the irritable colon syndrome and in 90 control subjects.
 Gut, 1970, 11, 668-672 The transport of colonic contents in the irritable colon syndrome J. A. RITCHIE From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, The Radcliffe Infirmary, and the Nuffield Institute
Gut, 1970, 11, 668-672 The transport of colonic contents in the irritable colon syndrome J. A. RITCHIE From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, The Radcliffe Infirmary, and the Nuffield Institute
Prevalence of Migraine and Other Headaches in Early Puberty
 Scand J Prim Health Care 194;2: 2-32 2 Prevalence of Migraine and Other Headaches in Early Puberty by mm SILLANPM PAULA PIEKKALA Scand J Prim Health Care Downloaded from informahealthcare.com by 13.9.1.220
Scand J Prim Health Care 194;2: 2-32 2 Prevalence of Migraine and Other Headaches in Early Puberty by mm SILLANPM PAULA PIEKKALA Scand J Prim Health Care Downloaded from informahealthcare.com by 13.9.1.220
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Februarv, I947 CALCULUS IN THE APPENDIX 93
 Februarv, I947 CALCULUS IN THE APPENDIX 93 Illustrations CALCULUS IN THE APPENDIX SIMULATING URETERIC CALCULUS BY R. S. HUNT, F.R.C.S.E., LIEUT.-COL., R.A.M.C. * inesbe ;9ll -* - i...f :0'1 :,Oil Postgrad
Februarv, I947 CALCULUS IN THE APPENDIX 93 Illustrations CALCULUS IN THE APPENDIX SIMULATING URETERIC CALCULUS BY R. S. HUNT, F.R.C.S.E., LIEUT.-COL., R.A.M.C. * inesbe ;9ll -* - i...f :0'1 :,Oil Postgrad
Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children
 Providing care together in York, Scarborough, Bridlington, Malton, Selby and Easingwold Communities Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children Information for parents, relatives and carers For more information,
Providing care together in York, Scarborough, Bridlington, Malton, Selby and Easingwold Communities Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children Information for parents, relatives and carers For more information,
Downloaded from by guest on August 19, 2018
 Pediatrics VOLUME 25 JANUARY 1960 NUMBER 1 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS PROCEEDINGS ABDOMINAL EPILEPSY IN CHILDHOOD George H. Schade, M.D., and Helen Gofman, M.D. Department of Pediatrics and Mental
Pediatrics VOLUME 25 JANUARY 1960 NUMBER 1 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS PROCEEDINGS ABDOMINAL EPILEPSY IN CHILDHOOD George H. Schade, M.D., and Helen Gofman, M.D. Department of Pediatrics and Mental
migraine compared with those of migraine
 Archives of Disease in Childhood 1995; 72: 413-417 Department of Medical Paediatrics, Royal Aberdeen Children's Hospital I Abu-Arafeh G Russell Correspondence to: Dr I Abu-Arafeh, Department of Child Health,
Archives of Disease in Childhood 1995; 72: 413-417 Department of Medical Paediatrics, Royal Aberdeen Children's Hospital I Abu-Arafeh G Russell Correspondence to: Dr I Abu-Arafeh, Department of Child Health,
Johns Hopkins Hospital Division of Gastroenterology Patient Questionnaire
 Johns Hopkins Hospital Division of Gastroenterology Patient Questionnaire Please complete this questionnaire before your scheduled appointment and bring this form with you the day of your visit. Patient
Johns Hopkins Hospital Division of Gastroenterology Patient Questionnaire Please complete this questionnaire before your scheduled appointment and bring this form with you the day of your visit. Patient
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 2. DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT 2.1 How is it diagnosed? Generally the following approach is followed: Clinical
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 2. DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT 2.1 How is it diagnosed? Generally the following approach is followed: Clinical
Preschool wheezing and prognosis at 10
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 642-646 Original articles Preschool wheezing and prognosis E S PARK, J GOLDING, F CARSWELL, AND S STEWART-BROWN Department of Child Health, University of Bristol
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 642-646 Original articles Preschool wheezing and prognosis E S PARK, J GOLDING, F CARSWELL, AND S STEWART-BROWN Department of Child Health, University of Bristol
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
... PRESENTATION... Defining and Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on a presentation by Marvin M. Schuster, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 20% of the general population has irritable bowel
Tension-Type Headache
 Chronic Headache Tension-Type Headache Its mechanism and treatment JMAJ 47(3): 130 134, 2004 Manabu SAKUTA Chief Professor, First Internal Medicine (Neurology), Kyorin University Abstract: Tension-type
Chronic Headache Tension-Type Headache Its mechanism and treatment JMAJ 47(3): 130 134, 2004 Manabu SAKUTA Chief Professor, First Internal Medicine (Neurology), Kyorin University Abstract: Tension-type
Emotional Relationships Social Life Sexually Recreation
 Name Date Address City State Zip Married Single Partner Divorced Widowed Date of Birth SS# Email Work Phone Home Phone Cell Phone Occupation Referred by Emergency Contact Family Physician Contact May we
Name Date Address City State Zip Married Single Partner Divorced Widowed Date of Birth SS# Email Work Phone Home Phone Cell Phone Occupation Referred by Emergency Contact Family Physician Contact May we
PATIENT INFORMATION Please print clearly and complete all blanks
 PATIENT INFORMATION Please print clearly and complete all blanks DATE: REFERRED BY: SEX: NAME: LAST FIRST MIDDLE BIRTHDATE: MAILING ADDRESS: CITY STATE ZIP TELEPHONE: CELL PHONE: WORK NUMBER: SS # MARITAL
PATIENT INFORMATION Please print clearly and complete all blanks DATE: REFERRED BY: SEX: NAME: LAST FIRST MIDDLE BIRTHDATE: MAILING ADDRESS: CITY STATE ZIP TELEPHONE: CELL PHONE: WORK NUMBER: SS # MARITAL
Recurrent Abdominal Pain
 Article gastroenterology Recurrent Abdominal Pain Paul N. Thiessen, MD* Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to: 1. Characterize the epidemiology and classification of. 2. List
Article gastroenterology Recurrent Abdominal Pain Paul N. Thiessen, MD* Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to: 1. Characterize the epidemiology and classification of. 2. List
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
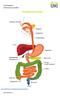 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
PATIENT REGISTRATION
 P Account# PATIENT REGISTRATION Please answer all questions completely. PAYMENT IS EXPECTED WHEN SERVICES ARE RENDERED Date New Update Name Date of Birth Male Last First Middle Female Home Address City/State/Zip
P Account# PATIENT REGISTRATION Please answer all questions completely. PAYMENT IS EXPECTED WHEN SERVICES ARE RENDERED Date New Update Name Date of Birth Male Last First Middle Female Home Address City/State/Zip
REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* SYRACUSE, NEW YORK
 VOL. 115, No. 2 REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* By SEUK KY KIM, M.D.,t LLOYD S. ROGERS, M.D.,t and ROBERT E. HEITZMAN, M.D. SYRACUSE, NEW YORK E ARLY physiologists thought that gastric acid was partly controlled
VOL. 115, No. 2 REFLUX ALKALINE GASTRITIS* By SEUK KY KIM, M.D.,t LLOYD S. ROGERS, M.D.,t and ROBERT E. HEITZMAN, M.D. SYRACUSE, NEW YORK E ARLY physiologists thought that gastric acid was partly controlled
PERSONAL INJURY QUESTIONNAIRE
 PERSONAL INJURY QUESTIONNAIRE Name Phone ( ) Age Birth Date Sex S.S.N. Employer Address Did you report this to YOUR Car Insurance? Yes No (Circle One) Your Car Insurance Co. is Claim # Claims Adjuster
PERSONAL INJURY QUESTIONNAIRE Name Phone ( ) Age Birth Date Sex S.S.N. Employer Address Did you report this to YOUR Car Insurance? Yes No (Circle One) Your Car Insurance Co. is Claim # Claims Adjuster
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
Background. Background. Headache Examination. Headache History. Primary vs. Secondary Headaches. Headaches In Children: Why Worry?
 Background Headaches In Children: Why Worry? Marcy Yonker MD FAHS Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Arizona Director, Pediatric Headache Program Phoenix Children s Hospital Headaches are
Background Headaches In Children: Why Worry? Marcy Yonker MD FAHS Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Arizona Director, Pediatric Headache Program Phoenix Children s Hospital Headaches are
Dr. Hall New Patient Paperwork Please fill out these forms completely
 Dr. Hall New Patient Paperwork Please fill out these forms completely Date of Appointment Complete the enclosed packet and bring it to the appointment along with all X Rays, MRI disc and reports. Please
Dr. Hall New Patient Paperwork Please fill out these forms completely Date of Appointment Complete the enclosed packet and bring it to the appointment along with all X Rays, MRI disc and reports. Please
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
PATIENT HEALTH HISTORY
 Name DOB Sex Age Date MR# PLACE CHARGE TICKET LABEL IN THE DASHED SPACE OR COMPLETE THE ABOVE: PLEASE ANSWER EACH QUESTION AS CORRECTLY AS YOU CAN BY PLACING AN "X" IN APPROPRIATE BOX What is the reason
Name DOB Sex Age Date MR# PLACE CHARGE TICKET LABEL IN THE DASHED SPACE OR COMPLETE THE ABOVE: PLEASE ANSWER EACH QUESTION AS CORRECTLY AS YOU CAN BY PLACING AN "X" IN APPROPRIATE BOX What is the reason
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Physicians: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Physicians: Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Ashwani Kapoor, MD Pathologist:
Page 1 of 5 Physicians: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Physicians: Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Ashwani Kapoor, MD Pathologist:
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 ... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
Health screening questionnaire
 Health screening questionnaire High Road Buckhurst Hill Essex IG9 5HX Tel: 020 8936 1202 Fax: 020 8936 1191 Visit: theholly.com Title: Surname: Forenames: Date of birth: Age: Address: Tel no. (Home): Tel
Health screening questionnaire High Road Buckhurst Hill Essex IG9 5HX Tel: 020 8936 1202 Fax: 020 8936 1191 Visit: theholly.com Title: Surname: Forenames: Date of birth: Age: Address: Tel no. (Home): Tel
Association between diabetes, severe hypoglycaemia, and electroencephalographic abnormalities
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 992-996 Association between diabetes, severe hypoglycaemia, and electroencephalographic abnormalities G SOLT.tSZ AND G ACSADI Department of Paediatrics, University
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 992-996 Association between diabetes, severe hypoglycaemia, and electroencephalographic abnormalities G SOLT.tSZ AND G ACSADI Department of Paediatrics, University
Recurrent abdominal pain and consulting behaviour among children in a rural community in Malaysia
 University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Christopher Boey Chiong Meng March, 2001 Recurrent abdominal pain and consulting behaviour among children in a rural community in Malaysia Christopher Boey
University of Malaya From the SelectedWorks of Christopher Boey Chiong Meng March, 2001 Recurrent abdominal pain and consulting behaviour among children in a rural community in Malaysia Christopher Boey
Low FODMAP Dietary Approach For FGD/IBS. Our Experience. Charlotte McCamphill 19 th February 2015
 Low FODMAP Dietary Approach For FGD/IBS Our Experience Charlotte McCamphill 19 th February 2015 CONTENTS What Is IBS What are FODMAPs Service Provision Audit Results Future Work WHAT IS IBS The Rome III
Low FODMAP Dietary Approach For FGD/IBS Our Experience Charlotte McCamphill 19 th February 2015 CONTENTS What Is IBS What are FODMAPs Service Provision Audit Results Future Work WHAT IS IBS The Rome III
The late prognosis of perforated duodenal ulcer
 Gut, 1962, 3, 6 The late prognosis of perforated duodenal ulcer A. C. B. DEAN,1 C. G. CLARK, AND A. H. SINCLAIR-GIEBEN From Aberdeen Royal Infirmary and the Department of Mental Health, niversity of Aberdeen
Gut, 1962, 3, 6 The late prognosis of perforated duodenal ulcer A. C. B. DEAN,1 C. G. CLARK, AND A. H. SINCLAIR-GIEBEN From Aberdeen Royal Infirmary and the Department of Mental Health, niversity of Aberdeen
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders.
 Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Prof. Dr. Mufti Munsurar Rahman Dept. of Medicine Enam Medical College Hospital
 Prof. Dr. Mufti Munsurar Rahman Dept. of Medicine Enam Medical College Hospital Functional constipation : prevalence and life style factors in a district of Bangladesh Perveen I, Rahman MM, Saha M, Parvin
Prof. Dr. Mufti Munsurar Rahman Dept. of Medicine Enam Medical College Hospital Functional constipation : prevalence and life style factors in a district of Bangladesh Perveen I, Rahman MM, Saha M, Parvin
Prevalence of dysmenorrhea in young women (16 25 years): A cross-sectional study
 Prevalence of dysmenorrhea in young women (16 25 years): A cross-sectional study Henna Haris 1 *, Jameel Ummar 1, Mohammad Maaz 1, Mohammad Mustafa 1, Shazia Aslam 1, Rizwana B Shaikh 2, Shatha Al Sharbatti
Prevalence of dysmenorrhea in young women (16 25 years): A cross-sectional study Henna Haris 1 *, Jameel Ummar 1, Mohammad Maaz 1, Mohammad Mustafa 1, Shazia Aslam 1, Rizwana B Shaikh 2, Shatha Al Sharbatti
SICKNESS ABSENCE BEFORE THE FIRST CLINICAL
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 20. SICKNESS ABSENCE BEFORE THE FIRST CLINICAL EPISODE OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE BY J. A. HEADY, J. N. MORRIS, F. J. LLOYD, and P. A. B. RAFFLE From the Social Medicine
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 20. SICKNESS ABSENCE BEFORE THE FIRST CLINICAL EPISODE OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE BY J. A. HEADY, J. N. MORRIS, F. J. LLOYD, and P. A. B. RAFFLE From the Social Medicine
florida child neurology
 Headaches florida child neurology You re sitting at your desk, working on a difficult task, when it suddenly feels as if a belt or vice is being tightened around the top of your head. Or you have periodic
Headaches florida child neurology You re sitting at your desk, working on a difficult task, when it suddenly feels as if a belt or vice is being tightened around the top of your head. Or you have periodic
Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/za_gb/intro Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PFAPA 1.1 What is it? PFAPA stands for Periodic Fever Adenitis Pharyngitis
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/za_gb/intro Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PFAPA 1.1 What is it? PFAPA stands for Periodic Fever Adenitis Pharyngitis
Failure to thrive: diagnostic yield of hospitalisation
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1982, 57, 347-351 Failure to thrive: diagnostic yield of hospitalisation DONALD M BERWICK, JANICE C LEVY, AND RUTH KLEINERMAN Center for the Analysis of Health Practices,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1982, 57, 347-351 Failure to thrive: diagnostic yield of hospitalisation DONALD M BERWICK, JANICE C LEVY, AND RUTH KLEINERMAN Center for the Analysis of Health Practices,
MEDICAL HISTORY RECORD
 MEDICAL HISTORY RECORD Please print and complete all information. Case. Male Female Medicare. Medicaid. Today s Date Birthdate Last Name First Middle Daytime Phone Home Phone Address City Marital Status
MEDICAL HISTORY RECORD Please print and complete all information. Case. Male Female Medicare. Medicaid. Today s Date Birthdate Last Name First Middle Daytime Phone Home Phone Address City Marital Status
Columbus Oncology and Hematology Associates 810 Jasonway Ave. Columbus, OH 43214, Ph: , Fax:
 Columbus Oncology and Hematology Associates 810 Jasonway Ave. Columbus, OH 43214, www.coainc.cc Ph: 614.442.3130, Fax: 614.442.3145 Name (Last, First, Middle) Birth Date Age Social Security # Appointment
Columbus Oncology and Hematology Associates 810 Jasonway Ave. Columbus, OH 43214, www.coainc.cc Ph: 614.442.3130, Fax: 614.442.3145 Name (Last, First, Middle) Birth Date Age Social Security # Appointment
Acknowledgements. Illness Behavior A cognitive and behavioral phenomenon. Seeking medical care. Communicating pain to others
 Acknowledgements Parent Training to Address Pediatric Functional Abdominal Pain: A Researcher s Perspective Dr. Kim Swanson National Institutes of Health Rona L. Levy, MSW, PhD, MPH Professor and Director
Acknowledgements Parent Training to Address Pediatric Functional Abdominal Pain: A Researcher s Perspective Dr. Kim Swanson National Institutes of Health Rona L. Levy, MSW, PhD, MPH Professor and Director
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
International Conference on Treatment Modalities for Eating Disorders: Consensus and Controversy Jerusalem - February 2013
 International Conference on Treatment Modalities for Eating Disorders: Consensus and Controversy Jerusalem - February 2013 FOOD AVOIDANT EMOTIONAL DISORDERS (FAED) Rose Geist, MD Chief of Mental Health
International Conference on Treatment Modalities for Eating Disorders: Consensus and Controversy Jerusalem - February 2013 FOOD AVOIDANT EMOTIONAL DISORDERS (FAED) Rose Geist, MD Chief of Mental Health
ESULTS OF PARTIAL GASTRECTOMY
 ESULTS OF PARTIAL GASTRECTOMY FOR PEPTIC ULCER By J. S. STAFFURTH, M.D., M.R.C.P. Resident Assistant Physician, St. Thomas's Hospital, London Numerous reports are available of the long-term results of
ESULTS OF PARTIAL GASTRECTOMY FOR PEPTIC ULCER By J. S. STAFFURTH, M.D., M.R.C.P. Resident Assistant Physician, St. Thomas's Hospital, London Numerous reports are available of the long-term results of
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
PATIENT HISTORY FORM
 PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Residual Functional Capacity Questionnaire SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 Residual Functional Capacity Questionnaire SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Patient: DOB: Physician completing this form: Please complete the following questions regarding this patient's impairments and attach
Residual Functional Capacity Questionnaire SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Patient: DOB: Physician completing this form: Please complete the following questions regarding this patient's impairments and attach
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Gastroenterologists: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Gastroenterologists: Marc L.
Page 1 of 5 Gastroenterologists: D.F. Jackson, III, MD William D. McLaughlin, MD Robert P. Albares, MD Jeffrey J. Crittenden, MD Samuel J. Tarwater, MD Travis J. Rutland, MD Gastroenterologists: Marc L.
An Approach to Abdominal Pain
 An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
Patient History (Please Print)
 Patient History (Please Print) Date: Name: Email: Phone: (Home) (Mobile) (Work) Address: City: Zip: Birth Date: / / Male Female Spouse/Parent Name: # of Children: Married Single Divorced Widowed Are you
Patient History (Please Print) Date: Name: Email: Phone: (Home) (Mobile) (Work) Address: City: Zip: Birth Date: / / Male Female Spouse/Parent Name: # of Children: Married Single Divorced Widowed Are you
634 N. STATE STREET, WESTERVILLE OH, (614) 901-WELL
 eas 634 N. STATE STREET, WESTERVILLE OH, 43082 (614) 901-WELL www.abilitychiro.com Name: Age: Date: Address: City: State: Zip Code: Alternate Address: City: State: Zip Code: Cell Phone: ( ) Cell Phone
eas 634 N. STATE STREET, WESTERVILLE OH, 43082 (614) 901-WELL www.abilitychiro.com Name: Age: Date: Address: City: State: Zip Code: Alternate Address: City: State: Zip Code: Cell Phone: ( ) Cell Phone
A Study of Severity of Depression in Thalassemia Patients
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 2, No. 85, DIP: 18.01.005/20170402 ISBN: 978-1-365-68608-5 http://www.ijip.in January-March, 2017 A
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 2, No. 85, DIP: 18.01.005/20170402 ISBN: 978-1-365-68608-5 http://www.ijip.in January-March, 2017 A
Motility of the pelvic colon
 Part IV Motility of the pelvic colon Gut, 1965, 6, 105 Abdominal pain associated with colonic hypermotility after meals' A. M. CONNELL, F. AVERY JONES, AND E. N. ROWLANDS From the Medical Research Council
Part IV Motility of the pelvic colon Gut, 1965, 6, 105 Abdominal pain associated with colonic hypermotility after meals' A. M. CONNELL, F. AVERY JONES, AND E. N. ROWLANDS From the Medical Research Council
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s. Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care
 Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care Prevalence of GI problems in the consulting population Thompson et al, Gut 2000 Number of patients % of patients
Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care Prevalence of GI problems in the consulting population Thompson et al, Gut 2000 Number of patients % of patients
Home Address. City Postal Code Home Telephone # Business Telephone # Address. Emergency Contact Name, Address, Phone#
 Date Name / / last first middle initial Personal Health # - Male Female Home Address City Postal Code Home Telephone # Business Telephone # Cell # E-Mail Address Best way to contact you: Home # Work #
Date Name / / last first middle initial Personal Health # - Male Female Home Address City Postal Code Home Telephone # Business Telephone # Cell # E-Mail Address Best way to contact you: Home # Work #
St Andrew s College Medical Questionnaire.
 Page 1 of 5 St Andrew s College Medical Questionnaire. It is important that you answer all questions in full. Where possible any supporting medical documents should be sent with this form. Failure to disclose
Page 1 of 5 St Andrew s College Medical Questionnaire. It is important that you answer all questions in full. Where possible any supporting medical documents should be sent with this form. Failure to disclose
Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
Case Presentation: Mr. S
 Case Presentation: Mr. S History Seen as inpatient in May, but has significant prior history and is a poor historian 53 y.o. Male no PMH, has been out of contact with medicine for years aside from hernia
Case Presentation: Mr. S History Seen as inpatient in May, but has significant prior history and is a poor historian 53 y.o. Male no PMH, has been out of contact with medicine for years aside from hernia
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 Patient information Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) i Important information for all patients experiencing irritable bowel syndrome. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (:
Patient information Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) i Important information for all patients experiencing irritable bowel syndrome. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (:
This article attempts to answer the questions asked by many parents about their children s spinal health. Appearing in Issue #18. Order A Copy Today
 Chiropractors have been caring for children for more than a 100 years. Many common childhood ailments will respond to this safe, natural form of health care. More and more parents especially those who
Chiropractors have been caring for children for more than a 100 years. Many common childhood ailments will respond to this safe, natural form of health care. More and more parents especially those who
GASTROCARE, P.C. Contact Preference: HOME: Cell #: Office #: REASON FOR VISIT: Allergies: Current Medications (Name/Dose/How taken):
 GASTROCARE, P.C. DR. A.B. REDDY, M.D., F.A.C.G. DR. REKHA KHURANA, M.D. Referring Physician: First Name: Date of Birth: Last name: Age: Pharmacy (include location): Fax Number: Email Address: Gender: Male
GASTROCARE, P.C. DR. A.B. REDDY, M.D., F.A.C.G. DR. REKHA KHURANA, M.D. Referring Physician: First Name: Date of Birth: Last name: Age: Pharmacy (include location): Fax Number: Email Address: Gender: Male
supplementary antacids. Radiological evidence of healing or marked improvement was seen
 Gut, 1970, 11, 171-175 Clinical study of Duogastrone in the treatment of duodenal ulcers B. 0. AMURE From the University of Ibadan, Nigeria SUMMARY This study confirms the preliminary reports that Duogastrone
Gut, 1970, 11, 171-175 Clinical study of Duogastrone in the treatment of duodenal ulcers B. 0. AMURE From the University of Ibadan, Nigeria SUMMARY This study confirms the preliminary reports that Duogastrone
ACTIVE EDGE CHIROPRACTIC
 ACTIVE EDGE CHIROPRACTIC HEALTH HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE PERSONAL INFORMATION Name: Female Male Alberta Health Care# Address: City: Province: Postal Code: Telephone: Home: Work: Cell: Email: Occupation: Birth
ACTIVE EDGE CHIROPRACTIC HEALTH HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE PERSONAL INFORMATION Name: Female Male Alberta Health Care# Address: City: Province: Postal Code: Telephone: Home: Work: Cell: Email: Occupation: Birth
A new website is underconstruction with the latesest updated information. Please us ethe below as a general guide only.
 Important Note A new website is underconstruction with the latesest updated information. Please us ethe below as a general guide only. The Below has become of historical interest only. Reproduced verbatim
Important Note A new website is underconstruction with the latesest updated information. Please us ethe below as a general guide only. The Below has become of historical interest only. Reproduced verbatim
MICHAEL PRITCHARD. most of the high figures for psychiatric morbidity. assuming that a diagnosis of psychiatric disorder has
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (November 1972) 48, 645-651. Who sees a psychiatrist? A study of factors related to psychiatric referral in the general hospital Summary A retrospective study was made of all
Postgraduate Medical Journal (November 1972) 48, 645-651. Who sees a psychiatrist? A study of factors related to psychiatric referral in the general hospital Summary A retrospective study was made of all
1.0 Presenting complaint: Onset 1.1 When it started? 1.2 How did it start? Progress 1.3 Has the problem increased /decreased so far?
 Case history Sr. No. Name Sex M / F Age Marital Status B / S / M / W Occupation Date 1.0 Presenting complaint: Onset 1.1 When it started? 1.2 How did it start? Progress 1.3 Has the problem increased /decreased
Case history Sr. No. Name Sex M / F Age Marital Status B / S / M / W Occupation Date 1.0 Presenting complaint: Onset 1.1 When it started? 1.2 How did it start? Progress 1.3 Has the problem increased /decreased
History of Present Illness Please answer the following questions
 Last Name First Name Date of Birth: / / What is the main reason for your visit today? Social Security Number: History of Present Illness Please answer the following questions Bladder Cancer Urinary Tract
Last Name First Name Date of Birth: / / What is the main reason for your visit today? Social Security Number: History of Present Illness Please answer the following questions Bladder Cancer Urinary Tract
Non Cardiac Chest Pain or Angina like Chest Pain. Wafaa El-Aroussy, MD Prof of Cardiovascular Medicine Cardiology Department Cairo University
 Non Cardiac Chest Pain or Angina like Chest Pain By Wafaa El-Aroussy, MD Prof of Cardiovascular Medicine Cardiology Department Cairo University Prevalence of CP 7-11 % in primary practice 25% in a life
Non Cardiac Chest Pain or Angina like Chest Pain By Wafaa El-Aroussy, MD Prof of Cardiovascular Medicine Cardiology Department Cairo University Prevalence of CP 7-11 % in primary practice 25% in a life
Emory Clinic Department of Neurological Surgery Second Opinion Questionnaire
 Emory Clinic Department of Neurological Surgery Second Opinion Questionnaire First Name: M.I. Last Name: Date of Birth: Phone: Marital Status: Married Divorced Separated Widowed Single Work Status: Employed
Emory Clinic Department of Neurological Surgery Second Opinion Questionnaire First Name: M.I. Last Name: Date of Birth: Phone: Marital Status: Married Divorced Separated Widowed Single Work Status: Employed
58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain
 Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
DOWNLOAD OR READ : IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME ONE DISEASE SEVERAL OR NONE PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES VOL 5 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME ONE DISEASE SEVERAL OR NONE PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES VOL 5 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 irritable bowel syndrome one disease several or none perspectives
DOWNLOAD OR READ : IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME ONE DISEASE SEVERAL OR NONE PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES VOL 5 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 irritable bowel syndrome one disease several or none perspectives
Patient Interview Form
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Interview Form Patient Information First Name: MRN: Last Name: Date Of Birth: Contact Preference Email Telephone call- Work Telephone call - Home Email Please check one as your preferred
Page 1 of 5 Patient Interview Form Patient Information First Name: MRN: Last Name: Date Of Birth: Contact Preference Email Telephone call- Work Telephone call - Home Email Please check one as your preferred
Internet-Based Self-Help Training for Children and Adolescents with Recurrent Headache: A Pilot Study
 Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 2008, 36, 241 245 Printed in the United Kingdom doi:10.1017/s1352465808004219 Internet-Based Self-Help Training for Children and Adolescents with Recurrent Headache:
Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 2008, 36, 241 245 Printed in the United Kingdom doi:10.1017/s1352465808004219 Internet-Based Self-Help Training for Children and Adolescents with Recurrent Headache:
CONSULTATION ADMITTANCE FORM
 CONSULTATION ADMITTANCE FORM Last Name: First Name: Address: City Postal Code: Home Phone: Work Phone: Age: Birth date (dd/mm/yr): Sex: M / F Height Weight Occupation: Alberta Health Care #: PLEASE CHECK
CONSULTATION ADMITTANCE FORM Last Name: First Name: Address: City Postal Code: Home Phone: Work Phone: Age: Birth date (dd/mm/yr): Sex: M / F Height Weight Occupation: Alberta Health Care #: PLEASE CHECK
A: PARTICIPANT INFORMATION
 A: PARTICIPANT INFMATION 1. What is your age today? Years of age 2. What is the date of your birth? Month: Day: Most of the questions we will be asking you in this follow-up questionnaire are about the
A: PARTICIPANT INFMATION 1. What is your age today? Years of age 2. What is the date of your birth? Month: Day: Most of the questions we will be asking you in this follow-up questionnaire are about the
MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (female)
 MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (female) Slievemore Clinic, Old Dublin Road, Stillorgan, Co. Dublin. Tel 01-2000501 The appointment comprises of a discussion about this questionnaire and a subsequent medical examination.
MEDICAL QUESTIONNAIRE (female) Slievemore Clinic, Old Dublin Road, Stillorgan, Co. Dublin. Tel 01-2000501 The appointment comprises of a discussion about this questionnaire and a subsequent medical examination.
Abdominal pain with back pain dark stools
 Abdominal pain with back pain dark stools Black (tar) colored stools, frequent dark urination,. An abdominal aortic dissection is a medical emergency and causes sudden abdominal or back pain. List of 25
Abdominal pain with back pain dark stools Black (tar) colored stools, frequent dark urination,. An abdominal aortic dissection is a medical emergency and causes sudden abdominal or back pain. List of 25
HEADACHE: Types, Tips & Treatment Suggestions
 Headaches are one of the most common complaints patients present with in primary care settings. They are often correlated with stress, tension and a litany of existing medical conditions. Often, patients
Headaches are one of the most common complaints patients present with in primary care settings. They are often correlated with stress, tension and a litany of existing medical conditions. Often, patients
Health History Questionaire
 Patient DOB: Patient Name: Date: Health History Questionaire Who referred your consultation? If no one referred you, how did you hear about us? Who is your primary care physician? Have you ever seen a
Patient DOB: Patient Name: Date: Health History Questionaire Who referred your consultation? If no one referred you, how did you hear about us? Who is your primary care physician? Have you ever seen a
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE*
 RESULTS WITH ABDOMINAL RESECTION IN HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE* BY F. REHBEIN and H. VON ZIMMERMANN From the Surgical Department of the Children's Hospital, Bremen For six years we have been practising abdominal
RESULTS WITH ABDOMINAL RESECTION IN HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE* BY F. REHBEIN and H. VON ZIMMERMANN From the Surgical Department of the Children's Hospital, Bremen For six years we have been practising abdominal
CASE SCENARIO EXERCISE
 påçííáëü=pìêîéáää~ååé=çñ=eé~äíüå~êé ^ëëçåá~íéç=fåñéåíáçå=mêçöê~ããé CASE SCENARIO EXERCISE CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION SURVEILLANCE SCOTTISH SURVEILLANCE OF HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED INFECTION
påçííáëü=pìêîéáää~ååé=çñ=eé~äíüå~êé ^ëëçåá~íéç=fåñéåíáçå=mêçöê~ããé CASE SCENARIO EXERCISE CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION SURVEILLANCE SCOTTISH SURVEILLANCE OF HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED INFECTION
TNF Receptor Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS)
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro TNF Receptor Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS TRAPS 1.1 What is it? TRAPS is an inflammatory disease characterised by
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro TNF Receptor Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS TRAPS 1.1 What is it? TRAPS is an inflammatory disease characterised by
When the Stomach loses the Head
 When the Stomach loses the Head Creative dealing with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) The V European Congress of Ericksonian Hypnosis and Psychotherapy Krakow June 12-15, 2014 Brigitta Loretan-Meier Master
When the Stomach loses the Head Creative dealing with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) The V European Congress of Ericksonian Hypnosis and Psychotherapy Krakow June 12-15, 2014 Brigitta Loretan-Meier Master
THE INCIDENCE OF INCOMPLETE DESCENT OF THE TESTICLE AT BIRTH
 THE INCIDENCE OF INCOMPLETE DESCENT OF THE TESTICLE AT BIRTH BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge (RECEIo-ED FOR PUBUCATION JANUARY 17. 19) Descent of the testicle from the abdomen into meaning
THE INCIDENCE OF INCOMPLETE DESCENT OF THE TESTICLE AT BIRTH BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge (RECEIo-ED FOR PUBUCATION JANUARY 17. 19) Descent of the testicle from the abdomen into meaning
