ABDOMINAL PAIN, CHRONIC
|
|
|
- Candace Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more bouts of pain severe enough to affect activities (usually school attendance) over a period of not less than three months. For some, the duration of three months is too long and intervention may need to occur earlier. Most children with this syndrome have a poorly understood yet easily recognisable condition for which an organic cause remains elusive. The approach adopted must be based on a thorough clinical assessment of the child. Incidence About forty years ago it was suggested that this condition affected 10 to 15 % of school children in Britain. A more recent community survey in North America found a prevalence of about 20%.The precise incidence in New Zealand is unknown but experience suggests that it is probably similar to overseas estimates. Chronic abdominal pain is one of the three common pain syndromes of childhood; the other two are headaches and recurrent limb pains. Aetiology Attempts to clearly distinguish organic from functional abdominal pain are fraught with difficulty as these two influences are not mutually exclusive in children. Psychological complications of organic disease are common and even in children with purely functional disorders, organic factors may contribute to symptomatology. Despite many studies, the causes of the chronic abdominal pain syndrome in children remain unknown. The pain is not simply due to social modelling or a means to avoid school although in some cases either or both of these factors may be important. Studies examining intestinal permeability, dysmotility, abnormal autonomic responses, H. pylori infection and carbohydrate (lactose and sorbitol) malabsorption have not produced consistent results. They are plagued by selection bias (most subjects coming from tertiary institutions), lack of controls, and the use of techniques that cannot be reproduced. Even when a putative cause is identified it is clear that other factors must be involved. An example of this is carbohydrate malabsorption. Though lactose malabsorption is common only a minority of subjects appear to be affected symptomatically. Defining the role of psychological factors has been even more difficult. Though some studies have suggested that environmental stressors are responsible, others have indicated the opposite. Clearly, other factors must be involved because not all children who suffer adverse life events develop abdominal pain. It is not surprising therefore that the most useful approach is a biopsychosocial one where the recurrent abdominal pain is viewed as the child s response to biological factors, influenced by temperament (the child s developing personality) and reinforced by the family and school environment. Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood hur är en prostata gjort Page: biopsi? 1 of 7
2 Clinical Assessment The logical approach to the child with chronic abdominal pain begins with a detailed history and physical examination. With encouragement even young children are able to indicate by pointing with one finger the site of maximal intensity of the pain. John Apley (the paediatrician who first described this syndrome) observed that the further the site of maximal pain is from the umbilicus, the greater the likelihood of organic disease. Children often have difficulty describing the character of the pain but are usually able to describe any radiation. Night-waking suggests peptic ulcer disease as does pain that is aggravated by meals.the latter may also be a symptom of gastro-oesophageal reflux particularly when associated with vomiting. It is important to obtain a detailed history of the frequency and character of the child s bowel motions. Older children are often embarrassed to discuss their bowel motions and it may be necessary to keep a diary. Blood in the bowel motions, fever, weight loss, arthritis and skin rashes are indicators of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Sudden onset of abdominal pain associated with nausea, vomiting or pallor suggests abdominal migraine If the child s diet contains excessive amounts of lactose or sorbitol (as an artificial sweetener) restricting these should result in an improvement in symptoms if their malabsorption is responsible for pain and flatulence. Drugs that produce abdominal pain include tetracyclines (oesophagitis) and non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents (gastritis). Specific enquiry should be made for a family history of irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcer, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease and migraine. The best way to assess the severity of the pain is to find out how much it interferes with the child s daily activities. In younger children chronic abdominal pain may be a manifestation of separation anxiety. With older children and adolescents, time should always be taken to interview the patient alone. During this interview concerns regarding the cause of the pain are explored and stressors in the home and school environments are discussed. Parental conflict, concerns regarding academic achievement, peer relationships, bullying, substance abuse, and sexuality are all potential areas of concern for older children and adolescents (HEADSS assessment). The possibility that the child or adolescent is depressed should always be considered. It is always helpful to ask the parents and the child what they think may be causing the abdominal pain.it is not uncommon for them to be worried that the pain might be due to a serious disease e.g. leukaemia which can easily be excluded on clinical assessment and a blood count. Physical examination must include an assessment of growth and general nutrition. A complete physical examination may detect other clues to underlying disease processes (e.g. clubbing in chronic inflammatory bowel disease) and always provides reassurance to the child and family that their concerns are being taken seriously. Abdominal examination focuses on areas of tenderness, organomegaly and masses. Rectal examination is useful in detecting faecal impaction but is not always indicated. However, it is always important to inspect the perianal area for the presence of fissures and skin tags. Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood Page: 2 of 7
3 Formulation By the end of the clinical assessment it is usually possible to classify the child s presentation into one of six categories. 1. Chronic or Recurent Abdominal Pain Syndrome This is the commonest of the five syndromes and occurs in children between the ages of 5 and 12 years. The pain is ill-defined, periumbilical and is unrelated to meals or the passage of bowel motions. It may be accompanied by pallor, nausea and headache. The physical examination and screening tests are entirely normal. 2. Constipation Pain is a feature of constipation throughout childhood and adolescence. Older children are often reluctant to discuss their bowel motions and once toilet- trained many parents do not pay much attention to the frequency of their child s bowel motions. If uncertainty remains then including their frequency as part of a pain diary is helpful. Anal fissures manifesting as fresh blood on a constipated stool may lead to reluctance to the passage of further motions and result in abdominal pain 3. Peptic Ulcer Disease Clues that the pain may be due to peptic ulcer disease are night-waking, pain related to meals and a positive family history. The pain is usually epigastric but may be periumbilical. The underlying pathology is either frank ulceration or gastritis. Functional dyspepsia is only diagnosed after endoscopy. 4. Irritable Bowel Syndrome This diagnosis is more common in adolescence and initially only a few suggestive features may be present making the diagnosis difficult until further symptoms arise. It should be entertained when abdominal pain is relieved by defaecation or associated with a change in stool frequency or consistency. The stools may vary in consistency from hard to loose and watery. Straining at stool, urgency, the passage of mucus, bloating and a sensation of abdominal distension are all features of this syndrome. The pain is often cramping and though it may be located anywhere in the abdomen it is usually maximal in the lower quadrants. Physical examination is usually normal but sometimes there is tenderness in the lower quandrants. 5. Abdominal migraine This is likely in children who have a sudden onset of episodic midline abdominal pain lasting between 1 and 72 hours. Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, pallor and other vasomotor symptoms are common and least 2 should be present to make the diagnosis. 6. Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Recurrent abdominal pain is a prominent feature of Crohn s disease, whilst in ulcerative colitis it is less prominent; it is usually associated with the passage of stool and more likely to be associated with bloody diarrhoea. Fatigue, weight loss, night-waking and a positive family history (in 30 % of cases) are all further pointers to these diseases. Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood Page: 3 of 7
4 Investigations These follow logically from the history and examination and can be divided into screening investigations and those that are used to confirm or exclude specific diagnoses (Table1). A full blood count and ESR (or c-reactive protein) should always be performed. Faeces should be tested for occult blood and examined for the presence of red or white cells, bacteria and parasites. A normal urinalysis helps exclude atypical presentations of urinary tract infections. An abdominal x- ray may help confirm the clinical impression of constipation by demonstrating faecal loading. The presence of anaemia, thrombocytosis, iron deficiency, elevated ESR or C-reactive protein and reduced serum albumin, may all indicate chronic inflammatory bowel disease. An ultrasound is useful in excluding suspected gallbladder, renal or pelvic (ovarian cysts) disease but has a very low yield when used indiscriminately in all children with chronic abdominal pain. Endoscopy is the investigation of choice to confirm or exclude peptic ulcer disease, antral gastritis or oesophagitis. Biopsies may show evidence of H. pylori infection. Colonoscopy is indicated if chronic inflammatory bowel disease is suspected. Biopsies will help clinch the diagnosis. Barium contrast studies are helpful in defining the extent of the disease. Table 1: Investigations In Children With Chronic Abdominal Pain: Screening: Full blood count ESR (or C-reactive protein) Stool examination (including occult blood) Urinalysis In selected cases: Abdominal X-ray Abdominal ultrasound Endoscopy (and biopsy) Barium contrast studies Management Successful management is dependant on an accurate diagnosis. Not surprisingly the greatest difficulty is encountered with the non-specific recurrent abdominal pain syndrome. There is no place for rigid guidelines and one depends on clinical judgement in deciding on the most effective approach, which is based on thorough clinical assessment. One of the most important aspects of management is parental reassurance. Fears of specific underlying diseases need to be confidently allayed. Parents need to know that this is a common well-recognised but poorly understood condition. A diary kept by the child with parental assistance is an easy way to confirm the frequency, duration and associations of the pain. Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood Page: 4 of 7
5 Diary for recording the frequency and associations of the pain Date: Time: What I was doing when the pain started How bad my pain was (1 to 3 1= mild 3= the worst pain) How long my pain lasted What made my pain better The role of environmental stressors need to be discussed in a non-judgmental way. Most parents are aware that stress can produce real pain. It makes sense to ensure that any bullying at school, concerns regarding academic progress or poor peer relationships are all sympathetically addressed. Any pain is much easier to cope with when the home and school environments are perceived as supportive. School attendance has to be actively managed in its own right as absenteeism is much more difficult to address once it has become entrenched and affected the child s self-confidence. The non-specific abdominal pain is often most severe in the morning but rarely lasts more than an hour it is important to take the child to school once the pain starts settling. Similarly any sick bay attendances should be as short as possible and sending the child home from school is always the last resort. It is helpful to gain the support of teachers to ensure that the child and the pain are appropriately managed. With regular follow-up and support from their GP most children with recurrent abdominal pain syndrome will improve or at least reach a stage where they can cope with daily activities. Cognitive behavioural therapy may be helpful. When to refer the child with Chronic Abdominal Pain to a Paediatric Clinic: Diagnostic uncertainty Excessive parental anxiety School absenteeism Suspicion of serious gastrointestinal disease (persistent vomiting, weight loss, dysphagia) Night-waking Pain localized away from the umbilicus Poor growth or weight loss Extra-intestinal symptoms e.g. fever, rash, mouth ulcers, joint pain) Blood in stools Anaemia Raised ESR Family history of peptic ulcer or inflammatory bowel disease The management of the other conditions responsible for recurrent abdominal pain is as below: Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood Page: 5 of 7
6 Management of specific conditions causing chronic abdominal pain Constipation: see constipation guideline Laxatives (e.g. Movicol, Lactulose, bulking agents) Increase dietary fibre Regular toileting (5 minutes on toilet 20 minutes after breakfast and evening meal) Star chart for younger children Irritable Bowel Syndrome Explanation Avoiding /managing psychosocial triggers High fibre diet may be helpful Peptic Ulcer Disease H 2 blockers Proton pump inhibitors Abdominal migraine Pizotifen may be effective as prophylaxis Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nutritional support Anti-inflammatory /immunomodulatory drugs Prognosis Most studies show that organic disease is rarely missed in children with chronic abdominal pain. Thirty to fifty percent of children with chronic abdominal pain settle within 6 weeks with the rest taking somewhat longer. Factors associated with a poorer prognosis are shown in Table 2. Table 2: Prognostic Indicators in Children with Chronic Abdominal Pain Factor Better prognosis Worse prognosis Family No family history of chronic pain Family members with chronic pain Gender Girls Boys Age Of Onset Older than 6 years Younger than 6 years Duration of pain before Treatment Less than 6 months More than 6 months Adults who as children had chronic abdominal pain are at increased risk of having functional abdominal pain (as well as headaches and back pain) but in the vast majority of cases this does not interfere with their daily activities. Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood Page: 6 of 7
7 Conclusion Recurrent abdominal pain of childhood is a common condition of childhood. The vast number of children with this condition do not have serious underlying gastro-intestinal disease and those that do can be readily distinguished by clinical assessment and a few basic screening investigations. References Up to date; Evaluation of the child and adolescent with chronic abdominal pain. Last literature review 19.1: January Contains details of Rome III diagnostic criteria for functional gastrointestinal disorders at childhood (ages 4-18 years). Clinical Report: New recommendations for treating children with chronic abdominal pain. Subcommittee on Chronic Abdominal Pain of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics March 2006 Cochrane database of systematic reviews has ongoing reviews of psychosocial, dietary and pharmacological interventions. Abdominal Pain, Recurrent in Childhood Page: 7 of 7
ABDOMINAL PAIN, CHRONIC
 Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Introduction Incidence Aetiology Clinical Assessment Formulation Investigations Management Prognosis Conclusion References Introduction The generally accepted definition of this condition is three or more
Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Chronic Abdominal Pain in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. What Is IBS?
 1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
1 What Is IBS? At the outset, we want to clear up some terminology issues. IBS is the abbreviation that doctors use for irritable bowel syndrome, often when they are talking about people with IBS. We will
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
 Original citation: Macdougall, Colin. (2009) Food intolerance in children (non-allergenic food hypersensitivity). Paediatrics and Child Health, Vol.19 (No.8). pp. 388-390. ISSN 1751-7222 Permanent WRAP
Original citation: Macdougall, Colin. (2009) Food intolerance in children (non-allergenic food hypersensitivity). Paediatrics and Child Health, Vol.19 (No.8). pp. 388-390. ISSN 1751-7222 Permanent WRAP
IBS - Definition. Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by:
 IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
IBS - Definition Chronic functional disorder of GI generally characterized by: 3500 3000 No. of Publications 2500 2000 1500 1000 Irritable Bowel syndrome Irritable Bowel Syndrome 500 0 1968-1977 1978-1987
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 2. DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT 2.1 How is it diagnosed? Generally the following approach is followed: Clinical
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 2. DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT 2.1 How is it diagnosed? Generally the following approach is followed: Clinical
Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s. Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care
 Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care Prevalence of GI problems in the consulting population Thompson et al, Gut 2000 Number of patients % of patients
Bowel cancer risk in the under 50s Greg Rubin Professor of General Practice and Primary Care Prevalence of GI problems in the consulting population Thompson et al, Gut 2000 Number of patients % of patients
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
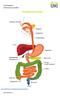 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
MOVICOL HALF PI December MOVICOL-Half. Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Potassium 5.4 mmol/l. Bicarbonate 17 mmol/l
 MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
MOVICOL -Half Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: Product Description: MOVICOL-Half Each sachet of MOVICOL-Half contains: Macrogol 3350 6.563 g Sodium chloride 175.4 mg Sodium bicarbonate
CHRONIC DIARRHEA DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE THAN 4 WEEKS
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults
 Irritable bowel syndrome in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Welcome In February 2008, NICE published a clinical guideline on
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised Welcome In February 2008, NICE published a clinical guideline on
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Associated with
 Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Certain genes passed on from parent to child increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease, if the right trigger occurs.
 Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Topic Page: Crohn's disease Definition: Crohn's disease from Benders' Dictionary of Nutrition and Food Technology Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, commonly the terminal ileum, of unknown aetiology,
Loyola University Medical Center Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery
 Loyola University Medical Center Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Medical History Questionnaire Name: Date: Age: D.O.B. Race: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical
Loyola University Medical Center Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Medical History Questionnaire Name: Date: Age: D.O.B. Race: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children
 Providing care together in York, Scarborough, Bridlington, Malton, Selby and Easingwold Communities Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children Information for parents, relatives and carers For more information,
Providing care together in York, Scarborough, Bridlington, Malton, Selby and Easingwold Communities Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children Information for parents, relatives and carers For more information,
MOVICOL Junior Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350)
 MOVICOL Junior Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: MOVICOL Junior Product Description: Each sachet of MOVICOL Junior contains: Macrogol 3350 Sodium chloride Sodium bicarbonate Potassium chloride
MOVICOL Junior Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: MOVICOL Junior Product Description: Each sachet of MOVICOL Junior contains: Macrogol 3350 Sodium chloride Sodium bicarbonate Potassium chloride
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Rex J Polson 17 th January 2018 Overview Description of the condition Discussion of symptoms and investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Dr Rex J Polson 17 th January 2018 Overview Description of the condition Discussion of symptoms and investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment
There are clues to help to decide if the bellyache is a medical problem:
 Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Objectives. Pain Types Brief Review. Referred Pain. Chronic/Recurrent Abdominal Pain 1/12/2017. I have no conflicts of interest to disclose
 Joshua D Noe, MD Associate Professor of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition Medical College of Wisconsin I have no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Differentiate functional
Joshua D Noe, MD Associate Professor of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition Medical College of Wisconsin I have no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Differentiate functional
The Primary Functional Diagnosis of the G.I. & Biliary System
 Functional Physiology, Dysfunctions, and Assessments of the G.I. and Gallbladder a 3-part Webinar Series The Functional Diagnosis Webinars With DR. DICKEN WEATHERBY Creator of the Blood Chemistry Software
Functional Physiology, Dysfunctions, and Assessments of the G.I. and Gallbladder a 3-part Webinar Series The Functional Diagnosis Webinars With DR. DICKEN WEATHERBY Creator of the Blood Chemistry Software
fever a persistent unexplained change in bowel habit in somebody over 50 years of age a family history of bowel or ovarian cancer.
 If you have had these symptoms for some time, if they come and go but never completely go away, then go and see your doctor. In practice, IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion. There is no test or marker that
If you have had these symptoms for some time, if they come and go but never completely go away, then go and see your doctor. In practice, IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion. There is no test or marker that
abdominal pain In another noncontrolled follow-up study comprising We have carried out a controlled investigation of
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1975, 50, 110. Long-term prognosis in children with recurrent abdominal pain M. FJORD CHRISTENSEN and 0. MORTENSEN From the University Clinic of Paediatrics, Arhus Municipal
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1975, 50, 110. Long-term prognosis in children with recurrent abdominal pain M. FJORD CHRISTENSEN and 0. MORTENSEN From the University Clinic of Paediatrics, Arhus Municipal
190 Index Case studies, abdominal pain, 2 Crohn s disease, 2 3, cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), 2 fecal incontinence (FI), 2 medical c
 Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions
 PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
PELVIC PAIN : Gastroenterological Conditions Departman Tarih Prof. A. Melih OZEL, MD Department of Gastroenterology Anadolu Medical Center Hospital Gebze Kocaeli - TURKEY Presentation plan 15 min. Introduction
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Lacrofarm Junior, powder for oral solution, sachet 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each sachet of contains the following active
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Lacrofarm Junior, powder for oral solution, sachet 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each sachet of contains the following active
MOVICOL Junior Chocolate Flavour Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350)
 MOVICOL Junior Chocolate Flavour Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: MOVICOL Junior Chocolate Flavour Product Description: Each sachet of MOVICOL Junior Chocolate contains: Macrogol 3350
MOVICOL Junior Chocolate Flavour Powder for Solution (macrogol 3350) Product Name: MOVICOL Junior Chocolate Flavour Product Description: Each sachet of MOVICOL Junior Chocolate contains: Macrogol 3350
2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each sachet of Macrovic Junior powder for oral solution contains the following active ingredients:
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Macrovic Junior powder for oral solution 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each sachet of Macrovic Junior powder for oral solution
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Macrovic Junior powder for oral solution 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each sachet of Macrovic Junior powder for oral solution
IBS. Patient INFO. A Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Patient INFO IBS A Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome The information provided by the AGA Institute is not medical advice and should not be considered a replacement for seeing a medical professional. About
Patient INFO IBS A Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome The information provided by the AGA Institute is not medical advice and should not be considered a replacement for seeing a medical professional. About
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mustafa Giaffer March 2017
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Functional Dyspepsia. Norbert Welkovics Heine van der Walt
 Norbert Welkovics Heine van der Walt Characteristics: Central abdomen Pain or discomfort Not associated with bowel movements No structural or biochemical abnormalty Definition Part of Gastroduodenal disorders
Norbert Welkovics Heine van der Walt Characteristics: Central abdomen Pain or discomfort Not associated with bowel movements No structural or biochemical abnormalty Definition Part of Gastroduodenal disorders
An Approach to Abdominal Pain
 An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
An Approach to Abdominal Pain objectives Should know the different types of abd pain Is acute or chronic? Hx taking skills with knowing the key questions Important abdominal pain signs A good differential
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
Tana's Habitat - Vim and Vigor - They Don t Call Them High Bars For Nothin
 http://www.tanashabitat.com/vim/0404151of6.asp Do you have a tummy ache that ver seems to go away? Do you wish your gu would just calm down and let you live your life? If so, you re not alo. You may suffer
http://www.tanashabitat.com/vim/0404151of6.asp Do you have a tummy ache that ver seems to go away? Do you wish your gu would just calm down and let you live your life? If so, you re not alo. You may suffer
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Colon Hydrotherapy Questionnaire
 Colon Hydrotherapy Questionnaire Full Name: Address: Telephone: Occupation: How did you hear about us? Email: Date of Birth: Please list any conditions for which you are currently being treated: Women
Colon Hydrotherapy Questionnaire Full Name: Address: Telephone: Occupation: How did you hear about us? Email: Date of Birth: Please list any conditions for which you are currently being treated: Women
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES
 OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
Crohn's disease CAUSES COURSE OF CROHN'S DISEASE TREATMENT. Sulfasalazine
 Crohn's disease Crohn's disease is an inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that affects children and adults. Common features of Crohn's disease include mouth sores, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight
Crohn's disease Crohn's disease is an inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that affects children and adults. Common features of Crohn's disease include mouth sores, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight
6/25/ % 20% 50% 19% Functional Dyspepsia Peptic Ulcer GERD Cancer Other
 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
PATIENT HISTORY FORM
 PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date: Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Middle Initial: Referred By: Age: Primary Care Doctor: Please provide name(s) of other physician(s) that you have visited within the last year:
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Michael Weiss MD, FACG
 Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD
 GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
children Crohn s disease in MR enterography for GI Complications Microscopy Characterization Primary sclerosing cholangitis Anorectal fistulae
 MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
Bloating, Flatulence, and
 A 45-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Flatulence, and Intermittent Loose Stools Anthony J. Lembo, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Laboratory
A 45-Year-Old Man With Recurrent Abdominal Pain, Bloating, Flatulence, and Intermittent Loose Stools Anthony J. Lembo, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Motility Laboratory
migraine compared with those of migraine
 Archives of Disease in Childhood 1995; 72: 413-417 Department of Medical Paediatrics, Royal Aberdeen Children's Hospital I Abu-Arafeh G Russell Correspondence to: Dr I Abu-Arafeh, Department of Child Health,
Archives of Disease in Childhood 1995; 72: 413-417 Department of Medical Paediatrics, Royal Aberdeen Children's Hospital I Abu-Arafeh G Russell Correspondence to: Dr I Abu-Arafeh, Department of Child Health,
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery)
 Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Preparing For Colonoscopy
 Preparing For Colonoscopy COLONOSCOPY OVERVIEW A colonoscopy is an exam of the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract, which is called the colon or large intestine (bowel). Colonoscopy is a safe procedure
Preparing For Colonoscopy COLONOSCOPY OVERVIEW A colonoscopy is an exam of the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract, which is called the colon or large intestine (bowel). Colonoscopy is a safe procedure
Pediatric Gastroenterology Referral Guidelines
 Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Patient guidance. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Patient guidance uk Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome is a disease/condition characterized by abdominal bloating, pain and changed bowel movements. Irritable bowel syndrome may have a serious
Patient guidance uk Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome is a disease/condition characterized by abdominal bloating, pain and changed bowel movements. Irritable bowel syndrome may have a serious
Male Symptom Monitor
 Male Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Have you had any of the following
Male Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Have you had any of the following
Candida stool test What is Candida? What causes Candida? What are the symptoms of Candida? Why take the test?
 Candida stool test What is Candida? Candida albicans can exist in a benign form in various parts of the body the skin, genitals and especially the digestive tract. It is an integral part of our body ecology.
Candida stool test What is Candida? Candida albicans can exist in a benign form in various parts of the body the skin, genitals and especially the digestive tract. It is an integral part of our body ecology.
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview
 Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
 What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
Prepared by: Dr Katherine Brown Fir Lea House Whitecross Newquay Cornwall TR8 4LW. Date: 17/10/2016
 EXPERT MEDICAL REPORT FOR THE COURT ON BREACH OF DUTY Prepared by: Dr Katherine Brown Fir Lea House Whitecross Newquay Cornwall TR8 4LW Date: 17/10/2016 -------------------------------------------------------------------
EXPERT MEDICAL REPORT FOR THE COURT ON BREACH OF DUTY Prepared by: Dr Katherine Brown Fir Lea House Whitecross Newquay Cornwall TR8 4LW Date: 17/10/2016 -------------------------------------------------------------------
Inflammatory or Irritable? (the bowel, not the speaker)
 South GP CME Edgar Centre, Dunedin August 2014 Inflammatory or Irritable? (the bowel, not the speaker) Dr Jason Hill MBChB FRACP FRCP Edin Department of Gastroenterology, Southern DHB Dunedin School Of
South GP CME Edgar Centre, Dunedin August 2014 Inflammatory or Irritable? (the bowel, not the speaker) Dr Jason Hill MBChB FRACP FRCP Edin Department of Gastroenterology, Southern DHB Dunedin School Of
Unit 4: Contemporary Nutrition Issues. Malnutrition (Undernutrition)
 Unit 4: Contemporary Nutrition Issues Malnutrition (Undernutrition) Syllabus Link: What is Undernutrition? Undernutrition: A condition that occurs when an individual s diet is lacking one or more nutrients.
Unit 4: Contemporary Nutrition Issues Malnutrition (Undernutrition) Syllabus Link: What is Undernutrition? Undernutrition: A condition that occurs when an individual s diet is lacking one or more nutrients.
What is Crohn's disease?
 What is Crohn's disease? Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most
What is Crohn's disease? Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most
Bleeding in the Digestive Tract
 Bleeding in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Bleeding in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health
Guideline scope Diverticular disease: diagnosis and management
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Diverticular disease: diagnosis and management The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a clinical guideline on diverticular
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Diverticular disease: diagnosis and management The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a clinical guideline on diverticular
Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology
 Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health
Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health
study was undertaken to assess the epidemiology, course and outcome of UC patients attending a hospital in Jordan.
 Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a relatively uncommon, chronic, recurrent inflammatory disease of the colon or rectal mucosa [1]. Often a lifelong illness, the condition can have a profound emotional and social
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a relatively uncommon, chronic, recurrent inflammatory disease of the colon or rectal mucosa [1]. Often a lifelong illness, the condition can have a profound emotional and social
Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61
 Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 February 2008 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg61 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Recurrent Abdominal Pain: an Etiological Study among in a Referreal Children's Medical Center in Iran
 Original Article Iran J Ped Sep 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:235-240 Recurrent Abdominal Pain: an Etiological Study among in a Referreal Children's Medical Center in Iran Touran shahraki 1, Fatemeh Farahmand
Original Article Iran J Ped Sep 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:235-240 Recurrent Abdominal Pain: an Etiological Study among in a Referreal Children's Medical Center in Iran Touran shahraki 1, Fatemeh Farahmand
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
The London Gastroenterology Partnership CROHN S DISEASE
 CROHN S DISEASE What is Crohn s disease? Crohn s disease is a condition, in which inflammation develops in parts of the gut leading to symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal pain and tiredness. The inflammation
CROHN S DISEASE What is Crohn s disease? Crohn s disease is a condition, in which inflammation develops in parts of the gut leading to symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal pain and tiredness. The inflammation
Functional Diagnosis of the GI Dicken Weatherby, N.D.
 Functional Diagnosis Gastrointestinal System The Application of FDM Testing Identifying and Assessing for Dysfunctions in the GI NAQ - Upper Digestion 51. Belching or gas within 1 hr. of a meal 60. Do
Functional Diagnosis Gastrointestinal System The Application of FDM Testing Identifying and Assessing for Dysfunctions in the GI NAQ - Upper Digestion 51. Belching or gas within 1 hr. of a meal 60. Do
Late effects of treatment for colorectal cancer. Claire Taylor Macmillan Nurse Consultant St Mark s Hospital
 Late effects of treatment for colorectal cancer Claire Taylor Macmillan Nurse Consultant St Mark s Hospital The number of people living with cancer is set to double from 2m to 4m by 2030 Source: Maddams
Late effects of treatment for colorectal cancer Claire Taylor Macmillan Nurse Consultant St Mark s Hospital The number of people living with cancer is set to double from 2m to 4m by 2030 Source: Maddams
Eosinophilic Disease. E.g.i.d. group. An Introduction written by parents
 www.egid.org.uk Our facebook group link: http://www.facebook.com/home.php?#!/group.php? gid=28072826009 Eosinophilic Disease E.G.I.D. Group E.g.i.d. group An Introduction written by parents 0 Table of
www.egid.org.uk Our facebook group link: http://www.facebook.com/home.php?#!/group.php? gid=28072826009 Eosinophilic Disease E.G.I.D. Group E.g.i.d. group An Introduction written by parents 0 Table of
Ovarian cyst, indigestion, constipation, back pain bloating
 P ford residence southampton, ny Ovarian cyst, indigestion, constipation, back pain bloating 14-11-2017 Read about causes of symptoms and treatment of abdominal pain in adults and when to seek medical
P ford residence southampton, ny Ovarian cyst, indigestion, constipation, back pain bloating 14-11-2017 Read about causes of symptoms and treatment of abdominal pain in adults and when to seek medical
Understanding your take home medications from the surgical ward. Information for Patients
 Understanding your take home medications from the surgical ward Information for Patients i Information for Patients Please read this leaflet before taking the medications that have been prescribed for
Understanding your take home medications from the surgical ward Information for Patients i Information for Patients Please read this leaflet before taking the medications that have been prescribed for
Kids Get Chronic Pain Too
 Kids Get Chronic Pain Too DR. Kathleen Cooke Anaesthetist and pain medicine specialist, St Vincent s Hospital, Qld A holistic plan is essential, including physical, emotional and social support, to manage
Kids Get Chronic Pain Too DR. Kathleen Cooke Anaesthetist and pain medicine specialist, St Vincent s Hospital, Qld A holistic plan is essential, including physical, emotional and social support, to manage
Indigestion (dyspepsia)
 Commissioning pathways Indigestion (dyspepsia) Supplementary information to be read in conjunction with the pathway Reference Supplementary Information 1.1 Symptom Description Annual incidence 40%. Prevalence
Commissioning pathways Indigestion (dyspepsia) Supplementary information to be read in conjunction with the pathway Reference Supplementary Information 1.1 Symptom Description Annual incidence 40%. Prevalence
Treatment of haemorrhoids. Mr Rowan Collinson FRACS Colorectal and General Surgeon Auckland
 Treatment of haemorrhoids Mr Rowan Collinson FRACS Colorectal and General Surgeon Auckland Much overlap of haemorrhoidal symptoms with other conditions Is it just the haemorrhoids? what type of haemorrhoidal
Treatment of haemorrhoids Mr Rowan Collinson FRACS Colorectal and General Surgeon Auckland Much overlap of haemorrhoidal symptoms with other conditions Is it just the haemorrhoids? what type of haemorrhoidal
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now. George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, :35 4:05 PM
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, 2017 3:35 4:05 PM Dr. Logan indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. He does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Now George M. Logan, MD Friday, May 5, 2017 3:35 4:05 PM Dr. Logan indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. He does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
F A M N O P R S ! D !
 A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
RABEPRAZOL 10mg and 20mg Gastro-resistant Tablets
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER RABEPRAZOL 10mg and 20mg Gastro-resistant Tablets RABEPRAZOLE This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER RABEPRAZOL 10mg and 20mg Gastro-resistant Tablets RABEPRAZOLE This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS
 ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT CONSTIPATION Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CONSTIPATION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT CONSTIPATION Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different
Low FODMAP Dietary Approach For FGD/IBS. Our Experience. Charlotte McCamphill 19 th February 2015
 Low FODMAP Dietary Approach For FGD/IBS Our Experience Charlotte McCamphill 19 th February 2015 CONTENTS What Is IBS What are FODMAPs Service Provision Audit Results Future Work WHAT IS IBS The Rome III
Low FODMAP Dietary Approach For FGD/IBS Our Experience Charlotte McCamphill 19 th February 2015 CONTENTS What Is IBS What are FODMAPs Service Provision Audit Results Future Work WHAT IS IBS The Rome III
Medical History Form
 Medical History Form Full Name Title: Mr/Mrs/Ms/Miss Address Date of Birth Date Telephone: Mobile: Email: How did you hear about the Garden of health? G.P s Name and Address Are you currently seeing your
Medical History Form Full Name Title: Mr/Mrs/Ms/Miss Address Date of Birth Date Telephone: Mobile: Email: How did you hear about the Garden of health? G.P s Name and Address Are you currently seeing your
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Patient Information Leaflet MOVICOL Paediatric Plain 6.9g sachet, powder for oral solution
 Patient Information Leaflet MOVICOL Paediatric Plain 6.9g sachet, powder for oral solution Read all of this leaflet carefully before you give this medicine to your child. Keep this leaflet. You may need
Patient Information Leaflet MOVICOL Paediatric Plain 6.9g sachet, powder for oral solution Read all of this leaflet carefully before you give this medicine to your child. Keep this leaflet. You may need
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
Professional Hypnotherapy & Hypnosis Training. Hypnotherapy & Hypnosis For IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
 Professional Hypnotherapy & Hypnosis Training Hypnotherapy & Hypnosis For IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) What Is IBS? (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) IBS is the term for a collection of symptoms that may include:
Professional Hypnotherapy & Hypnosis Training Hypnotherapy & Hypnosis For IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) What Is IBS? (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) IBS is the term for a collection of symptoms that may include:
