THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS
|
|
|
- Oliver Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AgroLife Scientific Journal - Volume 6, Number 2, 2017 ISSN ; ISSN CD-ROM ; ISSN ONLINE ; ISSN-L THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS Alexandra Mihaela POPA, Valentina SIMION, Iuliana CODREANU Cristina FERNOAGĂ, Mihai CORNILĂ, Mario CODREANU University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Bucharest, 59 Mărăşti Blvd., District 1, , Bucharest, Romania, Phone: , Fax: , alexandrapopa613@gmail.com Abstract Corresponding author alexandrapopa613@gmail.com This paper briefly reviews the basic definitions of hematuria, the common causes and the prevalence of this simptom on dogs and cats. This study was conducted in the Clinic of Faculty of Veterinary Medicine in the period between using IDEXX UA dipstick, IDEXX VetLab UA, Refractometer RHCN-200ATC and Grant Bio PCV Combined Centrifuge.Data collected recorded 65 animals,with felines obtaining a precentage of 42% and canine 28% in regard of hematuria prevlance by species.in case of hematuria prevalence based on gender we registered 62% males and 38% females.in hematuria prevalence by age we listed 32% of animales cu age range between 6-10 years, 31% with 1-5 years, and also 31% over 10 years, and 6% less than a year. From a total of 51 urinary dipstick who tested positive, we discovered on the examination of urine sediment that 46 samples confirms, and 5 samples offered a false - positive. Of the 71 samples analyzed 76% were within the macroscopic hematuria and 24% to microscopic hematuria, and 28% of the samples showed no hematuria. As a conlcusion hematuria is a common finding of urological pathology and it is important to known the risk factors of every species. Key words: hematuria, prevalence, gross hematuria, microhematuria. INTRODUCTION Hematuria is defined as the presence of five or more RBCs per high-power (40x) field in a fresh, centrifuged specimens obtained by eithermanual compression of the bladder catheterisation, or cystocentesis (Reine at al.,2005). Healthy animals can excrete as many as 3 red blood cells per high-power field (Chew, 2011). Hematuria is commonly subdivided according to its type asmacroscopic hematuria (i.e., visible, named gross hematuria) and microscopic hematuria (Figure 1, Figure 3) (i.e., nonvisible detected with a microscope), time of micturition (initial, terminal or total), duration (intermittent or persistent) and the clinical form - symptomatic or asymptomatic (Costache, 2005). Initial hematuria indicates the origin in urethra or prostate (males), total hematuria in bladder, ureter, and kidneys, and terminal hematuria, bladder or prostate (Mazhari, 2002) (Figure 2). Gross hematuria is suspected when urine is has an abnormal color, usually red or tea-colored. In evaluating gross hematuria, it is 155 important to confirm the presence of RBCs by microscopy (Massengill, 2008) Microhematuria is often detected during investigation of symptoms such as dysuria, urinary frequency, or flank pain (Massengill, 2008) Gross hematuria Microscopic hematuria Figure 1. Gross hematuria vs. Microhematuria Initial hematuria Terminal hematuria Total hematuria Figure 2. Hematuria. Time of micturition
2 a b c Figure 3. a Normal urine; b microscopic hematuria (+++); c macroscopic hematuria (Barrat, 2007). Dipstick hematuria and dipstick microhematuria is a nondiagnostic screening test offering a positive result due to oxidation of a test-strip reagent (Rao and Jones, 2008). This paper briefly reviews thebasic definitions of hematuria, the common causes and the prevalence of this simptom on dogs and cats. There are many causes of hematuria, and is a priority in the medical act for the doctor to discover the origin of hematuria by establishing whether its nature is renal or non-renal (Table 1). A reagent strip, also called a dipstick, is a narrow strip of plastic with small pads attached to it. Each pad contains reagents for a different reaction, thus allowing for the simultaneous determination of several tests. The colors generated on each reagent pad vary according to the concentration of the analyte present. Colors generated by each pad are visually compared against a range of colors on brandspecific color charts (Bataille et al., 2016). Urine dipstick is used to test for the peroxidase activity of erythrocytes (Robert, 2007). Table 2. Substances tested for by urine dipsticks Commonly assessed Less commonly assessed Blood Ketones Protein Urobilinogen Glucose Bilirubin Leukocyte esterase Specific gravity (After: Barrat, 2007) Commonly assessed Less commonly assessed Blood Ketones Protein Urobilinogen Glucose Bilirubin Leukocyte esterase Specific gravity Intrinsic Renal Disease Glomerulonephropathy Cystic disease Renal tumors Interstitial disease Interstitial nephritispapillary necrosis/analgesics Stones or crystals Acute infection Atrioventricular malformation (After: Fine, 2002) Table 1. Causes of hematuria Non-Renal Disease Ureteric (stones,tumor) Bladder - Cystitis) - tumors - stones Prostate (carcinoma - Prostatitis) Urethral lesions Diagnosis of hematuria can be pronounced easily by using urine strips which evaluates for pyuria, proteinuria, heme positivity, and urinary concentrating defects (Table 2) and using microscopic examination of urine sediment by evaluating for white blood cells and clumps, RBC morphology, crystals, and casts. Crystalluria can be determined by calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, or cystine crystals. Hypercalciuria isthe most common cause of crystalluria (Massengill, 2008). Urine culture is performed in cases that have clinical symptoms or laboratory evidence (pyuria, hematuria, bacteriuria, positive nitrites) of a urinary tract infection (Bataille et al., 2016). Also in the assessment of patients that express hematuria, complementary tests should be performed such as blood pressure, evaluation of renal functional parameters and proteinuria (Van Der Molen et al., 2012). If the test is positive for hematuria unaccompanied by urine abnormality it is necessary to determine serum creatinine. If it has a high value more tests will be done. The normal values of serum creatinine indicates the need for an ultrasound (Fine, 2002). MATERIALS AND METHODS This study was conducted in the Clinic of Faculty of Veterinary Medicine in the period between In order to establish the prevalence of hematuria in dogs and cats, fresh midstream urine samples (5-10 ml) were obtained from animals with urologic signs. 156
3 We evaluated 71 samples, 27 from feline and 18 from canine, 40 being males and 25 females, with age range between 4.5 months and 17 years. The urine samples were first evaluated macroscopically, and its color and clarity were recorded; than we used IDEXX UA dipstick for detecting the blood in IDEXX VetLab UA Analyzer and Clinical Refractometer RHCN- 200ATC for measuring the urine specific gravity. The change in the color were noted an compared with standard provided. After the macroscopic evaluation the samples were prepared for urine sediment examination by centrifugation for 10 minutes at 6000x in a Grant Bio PCV-2400 Combined Centrifuge. The supernatant fluid was decanted and a drop of sediment was transferred to a glass slide and a coverslip was placed on the specimen. The slides were examined at 400 magnification for red blood cells. Hematuria was considered to be present at five or more RBCs per high-power (40x) field. Hematuria prevalence by species 28% 42% Feline Canine Figure 4. Hematuria prevalence by species (Original) The males who participated in this survey most were diagnosticated with urinary lithiasis and FUS. Females who manifested hematuria were diagnosticated majority of them with cystitis, microlithiasis and just one case with glomerulonephritis and FUS. Hematuria prevalence by gender RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS In the study prevalence of hematuria on dogs and cats, we have taken in consideration parametres that influence the result and conclusion, such as species, age and gender. In regard of hematuria prevalence survey considering species, our result was that 65 animals participated, and felines obtained a precentage of 42% and canine 28%. Giving this result and from the diagnosis established, the felines are more prone to express hematuria, being liable to develop FUS (feline urological syndrome), urinary lithiasis and cystitis (Figure 4). In case of hematuria prevalence based on gender we recorded a significant proportion of males which have registered a percentage of 62% followed by 38% females. Based on the diagnosis discovered the percentage 62% males with hematuria is slightly predictable being well known the frequency of urological pathology in males due to anatomical features of lower urinary tract (Figure 5). 38% 62% Males Females Figure 5. Hematuria prevalence by gender (Original) Hematuria was encountred in different ages of the subjects, in a prevalence of 32% of animales cu age range between 6-10 years, 31% with 1-5 years, and also 31% over 10 years, and 6% less than a year (Figure 6). Other studies have concluded that risk-factors for stone formation, are age, gender and breed, together with influences such as geographical location, presence of UTI and dietary history (Syme, 2012). Cystine urolithiasis occurs preponderantly (98%) in male dogs and are not common in very young dogs but tend to occur in middleage (Syme, 2012). 157
4 The prevalence of cystine calculi is highly dependent on geographical location, with a higher reported prevalence in dogs in Europe than dogs from the USA (Syme, 2012). Figure 6. Hematuria prevalence by age (Original) We evaluated 65 animals from which we colected 71 samples on a period of 5 months; the result we obtained using urinary dipstick IDEXX UA, was 51 tested positive for RBC/ hemoglobin/ myoglobin - urine is discolored but no RBC are noted on microscopic examination (Figure 7) Hematuria prevalence by age 31% 32% 6% % > 1 year 1-5 years 6-10 years < 10 years Numbers of dipstick tests Positive samples for hematuria Figure 7. Numbers of dipstick test and positive samples for hematuria (Original) Table 3 summarizes the main causes in appearance of urine strips errors (Fine, 2002). Table 3. Reasons in appearance of urine strips errors* Reasons blood shows on dipstick urinalysis but not on microscopic exam (false positive) Exercise Reasons blood doesn t show on dipstick urinalysis but is present on microscopic exam (false negative) Captopril Vitamin C Dehydration Acidic urine (ph <1.5) Hemoglobin (part of red blood cell) Myoglobin (break down product of red blood cell) (After: O Brien et al., 2014). Concentrated urine Protein in the urine dipstick exposed to air The protocol in the diagnosis of hematuria includes first testing with urinary strip and if it is positive urine should be sent for urinalysis. If the patient has more than five RBCs/hpf, microscopic hematuria is present. The American Urologic Association declares evaluation should be based solely on findings from microscopic examination of urine sediment and not on a dipstick reading. (O Brien et al., 2014). From a total of 51 urinary dipstick who tested positive, we discovered on the examination of urine sediment that 46 samples confirms the presence of more five red blood cells (RBCs)/high power field, and 5 samples offered a false - positive (Figure 8). Positive dipstick for hematuria with negative microscopy are often due to false negative microscopy. With bright field microscopy, negative results may occur as a result of spontaneous lysis of red cells or by failure to detect ghost forms (Choi, 2003). It is been noted that microscopic hematuria is present when more than five red blood cells (RBCs)/high power field are found (Fine, 2002). Dipstick testing is the initial test for detecting hematuria. It is very sensitive and will pick up one to two RBCs/hpf (Fine, 2002). Dipstick testing will register positive in a urine that has microscopic hematuria allowed to stand for too long (i.e., with hemolyzed RBCs) in spite of few or no red cells being seen on the film. In some cases, dipstick tests provides a false negative or false positive (Choi, 2003) ,00 40,00 20,00 0,00 51 Red blood cells 46 Urinary dipstick positive Urine sediment microscope positive Figure 8. Urine dipstick positive vs. Urine sediment microscope positive (Original) Of the 71 samples analyzed it was determined that 76% were within the macroscopic
5 hematuria and 24% to microscopic hematuria, and 28% of the samples showed no hematuria (Figure 9). In assessing gross hematuria, it is important to verify the presence of RBCs by microscopy. After centrifugation of the urine, the finding of red urinary sediment with a positive strip test for hemoglobin it suggest hematuria, whereas red supernatant with negative dipstick testing for hemoglobin is indicative of myoglobinuria, hemoglobinuria, or other causes of discolored urine (Veerreddy, 2013). The overwhelming result in which macrohematuria is triple to microscopic hematuria is probably due to the fact that most of the diagnosis established implies o advanced pathological disorder in which bleeding is a common sign. Concerning the micturition moment, terminal hematuria records a higher proportion, being an element suggesting the involvement of the lower urinary tract. urolithiasis and cystitis, can help the clinician to pursue a reduced number of methods of investigation offering a fast diagnosis. More often than not, owners, demand an immediate diagnosis, particularly when there is macroscopic hematuria due to the impact of blood in the urine that alarms them. A simple and practical approach to the animal who presents hematuria should consists in a fewer invasive studies, a less costly evaluation, and a accurate diagnosis. Our results suggest that asymptomatic microscopic hematuria in dogs and cats is rarely associated withclinically significant disease of the urinary tract, but is mandatory to keep under observations the animals. Gross hematuria is more commonly and is associated with urinary tract disease, such that a thorough evaluation for determination of the bleeding origin is justified and recommended. REFERENCES 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Figure 9. Gross hematuria and microhematuria (Original) CONCLUSIONS 76% 24% 28% Gross hematuria Microscopic hematuria Hematuria is a common finding of urological pathology as we discovered in our study. Hematuria in dogs and cats has a wide differential diagnosis, with different therapeutic approaches compared to human patients. It is important that in the first evaluation of the animals the clinician takes account of the risk factors of every species. Knowing that felines with male gender are prone to develop urological disorders that express macroscopic hematuria such as FUS, 159 Barratt J., What to do with patients with abnormal dipstick urinalysis. Medicine, 35(7), p Bataille A., Wetzstein M., Hertig A., Vimont S., Rondeau E. & Galichon P., Evidence of dipstick superiority over urine microscopy analysis for detection of hematuria. BMC Research Notes, 9(1), Chew D.J., DiBartola S.P., & Schenck P.A., Urinalysis. Canine and Feline Nephrology and Urology, p Choi K., Approach to Proteinuria and Hematuria in General Practice Urine microscopy the Liquid Biopsy. Hematuria, p. 1 7 Costache C., Hematuria - algoritm de diagnostic. 1(3), p Fine B. A., Hematuria. p Massengill S.F.,2008. Hematuria. Pediatrics in Review, 29(10), p Mazhari R. & Kimmel P.L., Hematuria: An algorithmic.69(11). O Brien W., O Connor K., Lailas N., Schenk G., Young J., Pruna C., Starks C., Spencer J., Tamburro K., age K., Parker M., The urology group, 30, Rao P.K. & Jones J.S., How to evaluate dipstick hematuria : What to do before you refer. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 75(3), p Syme H.M., Stones in cats and dogs: What can be learnt from them? Arab Journal of Urology, 10(3), p Reine N.J.& Langston C.E., Urinalysis interpretation: How to squeeze out the maximum
6 information from a small sample. Clinical Techniques in Small Animal Practice, 20(1 SPEC.ISS.), p Roberts J.R., Urine Dipstick Testing : Everything You Need to Know Urinalysis: A Comprehensive Review. Emergency Med. News, 29(June), p Van Der Molen A.J. & Hovius M.C., Hematuria: A problem-based imaging algorithm illustrating the recent Dutch Guidelines on Hematuria. American Journal of Roentgenology, 198(6), p Veerreddy P., Hemoglobinuria misidentified as hematuria: Review of discolored urine and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Clinical Medicine Insights: Blood Disorders, 6, p
THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS
 Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (2) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS Alexandra
Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (2) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS Alexandra
Taking a dip into urinalysis
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS)
 GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
It s not just water! What is Urinalysis?
 It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
Application Note. Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1
 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Lecture 7. The Urinary System
 Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
URINANLYSIS. Pre-Lab Guide
 URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
Hematuria. Ramzi El-Baroudy (ESPNT)
 Hematuria Ramzi El-Baroudy (ESPNT) Hematuria is the presence of RBCs in urine. If the amount of blood in urine is big enough, the urine will, then, look red. Something which is, undoubtedly, terrifying.
Hematuria Ramzi El-Baroudy (ESPNT) Hematuria is the presence of RBCs in urine. If the amount of blood in urine is big enough, the urine will, then, look red. Something which is, undoubtedly, terrifying.
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST. Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
H(a)ematuria. FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute
 H(a)ematuria FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute From Philadelphia to Bristol, England Southmead Hospital, 1916 Southmead Hospital, 2013 Southmead Hospital, 2014 H(a)ematuria Blood
H(a)ematuria FX Keeley Consultant Urologist Bristol Urological Institute From Philadelphia to Bristol, England Southmead Hospital, 1916 Southmead Hospital, 2013 Southmead Hospital, 2014 H(a)ematuria Blood
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis
 The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis
 Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012
 Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012 Introduction Haematuria Positive blood on urine dipstick 5 red blood cells/ microliter of urine Prevalence Gross haematuria ( macroscopic) 0.13 % Microscopic- 1.5% Haematuria +
Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012 Introduction Haematuria Positive blood on urine dipstick 5 red blood cells/ microliter of urine Prevalence Gross haematuria ( macroscopic) 0.13 % Microscopic- 1.5% Haematuria +
Paediatrica Indonesiana. Urine dipstick test for diagnosing urinary tract infection
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Urine dipstick test for diagnosing urinary tract infection Syarifah Julinawati, Oke Rina, Rosmayanti, Rafita Ramayati, Rusdidjas Abstract
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Urine dipstick test for diagnosing urinary tract infection Syarifah Julinawati, Oke Rina, Rosmayanti, Rafita Ramayati, Rusdidjas Abstract
Assessment of urine of a bovine patient
 Commonwealth of Australia Copyright regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Adelaide pursuant of Part VB of the Copyright Act
Commonwealth of Australia Copyright regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Adelaide pursuant of Part VB of the Copyright Act
URINARY CRYSTALS. by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown
 URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5
 Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
Urologic investigations
 Urologic investigations د. Laboratory studies EXAMINATION OF URINE Urinalysis: Urinalysis is one of the most important and useful urologic tests available. Reasons for inadequate urinalyses include: (1)
Urologic investigations د. Laboratory studies EXAMINATION OF URINE Urinalysis: Urinalysis is one of the most important and useful urologic tests available. Reasons for inadequate urinalyses include: (1)
Science of Veterinary Medicine. Urinary System Unit Handouts
 Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Urinalysis (UA) provides information about the urinary
 Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University
Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Outline Introduction of diabetic nephropathy Manifestations of diabetic nephropathy Staging of diabetic nephropathy Microalbuminuria Diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy Treatment of
Diabetic Nephropathy Outline Introduction of diabetic nephropathy Manifestations of diabetic nephropathy Staging of diabetic nephropathy Microalbuminuria Diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy Treatment of
Urinalysis Made Easy: The Complete Urinalysis with Images from a Fully Automated Analyzer
 Urinalysis Made Easy: The Complete Urinalysis with Images from a Fully Automated Analyzer A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP Lighthouse Veterinary Consultants, LLC Gainesville, FL Ideal conditions
Urinalysis Made Easy: The Complete Urinalysis with Images from a Fully Automated Analyzer A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP Lighthouse Veterinary Consultants, LLC Gainesville, FL Ideal conditions
A. SAP is the D-Lab's name for a specific set of serum biochemical tests.
 Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Hey Doc, there s blood in my urine Evaluation of hematuria. Christian S. Kuhr, MD FACS May 4, 2018
 Hey Doc, there s blood in my urine Evaluation of hematuria Christian S. Kuhr, MD FACS May 4, 2018 Objectives Understand the algorithm for hematuria evaluation Know the differential diagnosis for hematuria
Hey Doc, there s blood in my urine Evaluation of hematuria Christian S. Kuhr, MD FACS May 4, 2018 Objectives Understand the algorithm for hematuria evaluation Know the differential diagnosis for hematuria
Poor Predictive Ability of Urinalysis and Microscopic Examination to Detect Urinary Tract Infection
 Microbiology and Infectious Disease / POOR PREDICTIVE ABILITY OF URINALYSIS Poor Predictive Ability of Urinalysis and Microscopic Examination to Detect Urinary Tract Infection Joy D. Van Nostrand, MS,
Microbiology and Infectious Disease / POOR PREDICTIVE ABILITY OF URINALYSIS Poor Predictive Ability of Urinalysis and Microscopic Examination to Detect Urinary Tract Infection Joy D. Van Nostrand, MS,
BCH472 [Practical] 1
![BCH472 [Practical] 1 BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/89/98494556.jpg) BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
VetScan UA Urine Analyzer Clinical Performance Larry Lem, PhD & Andrew Rosenfeld, DVM, ABVP
 VetScan UA Urine Analyzer Clinical Performance Larry Lem, PhD & Andrew Rosenfeld, DVM, ABVP Abstract Background: The VetScan UA urine strip reader is an analyzer designed to provide semi-quantitative and
VetScan UA Urine Analyzer Clinical Performance Larry Lem, PhD & Andrew Rosenfeld, DVM, ABVP Abstract Background: The VetScan UA urine strip reader is an analyzer designed to provide semi-quantitative and
Guidelines for the management of a child with haematuria
 Guidelines for the management of a child with haematuria Children s Kidney Centre University Hospital of Wales Cardiff CF14 4XW DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were produced in good faith by the author(s)
Guidelines for the management of a child with haematuria Children s Kidney Centre University Hospital of Wales Cardiff CF14 4XW DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were produced in good faith by the author(s)
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
The Urinary System. Lab Exercise 38. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Michelle Moy, MAd Ed, MT(ASCP)SC Program Director Clinical Laboratory Science Program Loyola University Chicago, Illinois
 Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Unit Outline. Chemical Exam of Urine. Unit 3. Reagent strip manufactures
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 1 Overview of Procedure & ph Unit Outline Introduction to reagent strip testing ph Glucose & Carbohydrates Ketones Protein Bilirubin
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 1 Overview of Procedure & ph Unit Outline Introduction to reagent strip testing ph Glucose & Carbohydrates Ketones Protein Bilirubin
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review
 31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical Pathologist Urinalysis A Review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical
31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical Pathologist Urinalysis A Review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents. Amal Alamri
 Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Controls (positive and negative) for quality assessment-located in central laboratory Note: See central lab UA procedure for QC. Read strips visually.
 ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
Urine analysis. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Urine analysis By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Functions of Renal system Excretory functions Metabolic waste Drug clearance Toxin clearance Urea, Creatinin Regulatory functions Water balance Blood / urine
Urine analysis By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Functions of Renal system Excretory functions Metabolic waste Drug clearance Toxin clearance Urea, Creatinin Regulatory functions Water balance Blood / urine
RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture
 #Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
#Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان
 4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
Dipstick Urinalysis as a Test for Microhematuria and Occult Bladder Cancer
 Bladder Cancer 3 (2017) 45 49 DOI 10.3233/BLC-160068 IOS Press Research Report 45 Dipstick Urinalysis as a Test for Microhematuria and Occult Bladder Cancer Richard S. Matulewicz a,b,, John Oliver DeLancey
Bladder Cancer 3 (2017) 45 49 DOI 10.3233/BLC-160068 IOS Press Research Report 45 Dipstick Urinalysis as a Test for Microhematuria and Occult Bladder Cancer Richard S. Matulewicz a,b,, John Oliver DeLancey
CLINICAL AND ULTRASOUND FEATURES IN DYSURIC DOGS
 AgroLife Scientific Journal - Volume 6, Number 2, 2017 ISSN 2285-5718; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5726; ISSN ONLINE 2286-0126; ISSN-L 2285-5718 CLINICAL AND ULTRASOUND FEATURES IN DYSURIC DOGS Mario CODREANU, Alexandra
AgroLife Scientific Journal - Volume 6, Number 2, 2017 ISSN 2285-5718; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5726; ISSN ONLINE 2286-0126; ISSN-L 2285-5718 CLINICAL AND ULTRASOUND FEATURES IN DYSURIC DOGS Mario CODREANU, Alexandra
Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
SCBM343- Urinalysis. Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul. Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
 SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
Urinalysis Review and Case Studies
 Urinalysis Review and Case Studies A Complete Urinalysis John H. Landis, MS, MLS(ASCP) Adjunct Professor, University of Cincinnati Adjunct Professor, Oakland University Professor Emeritus, Ferris State
Urinalysis Review and Case Studies A Complete Urinalysis John H. Landis, MS, MLS(ASCP) Adjunct Professor, University of Cincinnati Adjunct Professor, Oakland University Professor Emeritus, Ferris State
AUCKLAND REGIONAL UROLOGY GUIDELINES AND REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
 AUCKLAND REGIONAL UROLOGY GUIDELINES AND REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS This document outlines the urological conditions currently funded at Auckland District Health Board (ADHB), Counties Manukau District Health
AUCKLAND REGIONAL UROLOGY GUIDELINES AND REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS This document outlines the urological conditions currently funded at Auckland District Health Board (ADHB), Counties Manukau District Health
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today
 III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview
 Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview In-Lab Exercises Read Me This is a very diverse lab. We will be looking at the gross anatomy of the urinary tract, the microscopic anatomy on both models and slides,
Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview In-Lab Exercises Read Me This is a very diverse lab. We will be looking at the gross anatomy of the urinary tract, the microscopic anatomy on both models and slides,
URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES
 Deborah Burgess, M.D. Nephrology Department 16 Oct 90 URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES The kidney regulates the internal environment of the body by controlling electrolyte and water balance; and establishes
Deborah Burgess, M.D. Nephrology Department 16 Oct 90 URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES The kidney regulates the internal environment of the body by controlling electrolyte and water balance; and establishes
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Case studies. Stephen Mark Rob Walker
 Case studies Stephen Mark Rob Walker Case 1 31 yr old woman with 3 rd UTI. E coli Frequency and dysuria Asymptomatic after treatment Recurrent UTI Lower tract symptoms Coliforms Asymptomatic after treatment
Case studies Stephen Mark Rob Walker Case 1 31 yr old woman with 3 rd UTI. E coli Frequency and dysuria Asymptomatic after treatment Recurrent UTI Lower tract symptoms Coliforms Asymptomatic after treatment
Bacterial urinary tract infections
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
How to interpret your urine sample results
 How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
Urine bench. Urine test for: SARAH Sugar
 Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1. Urinanalysis
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1 Urinanalysis PLEASE NOTE: The actual urinanalysis goes rather quickly. You may want to skip directly to the Lab Exercise, collect data, and read the Introduction
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1 Urinanalysis PLEASE NOTE: The actual urinanalysis goes rather quickly. You may want to skip directly to the Lab Exercise, collect data, and read the Introduction
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi
 Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinalysis Competition Dr. Katharine Dahl Dr. Brenda Shinar
 Urinalysis Competition 2017 Dr. Katharine Dahl Dr. Brenda Shinar Question 1. (PGY-1) An appropriate collection technique must be used in order to interpret urinalysis correctly. Which of the following
Urinalysis Competition 2017 Dr. Katharine Dahl Dr. Brenda Shinar Question 1. (PGY-1) An appropriate collection technique must be used in order to interpret urinalysis correctly. Which of the following
Pediatric Nephrology Consult and Referral Guidelines
 Pediatric Nephrology Consult and Referral Guidelines Introduction We see children and teens from birth to 21 years. The most common reasons patients are referred to pediatric nephrology services include:
Pediatric Nephrology Consult and Referral Guidelines Introduction We see children and teens from birth to 21 years. The most common reasons patients are referred to pediatric nephrology services include:
ASYMPTOMATIC MICROSCOPIC HEMATURIA IN WOMEN JOLYN HILL, MD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, CLINICAL UROGYNECOLOGY FEBRUARY14, 2017
 ASYMPTOMATIC MICROSCOPIC HEMATURIA IN WOMEN JOLYN HILL, MD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, CLINICAL UROGYNECOLOGY FEBRUARY14, 2017 DISCLOSURES No financial disclosures Urogynecologist via Ob/Gyn pathway ASYMPTOMATIC
ASYMPTOMATIC MICROSCOPIC HEMATURIA IN WOMEN JOLYN HILL, MD ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, CLINICAL UROGYNECOLOGY FEBRUARY14, 2017 DISCLOSURES No financial disclosures Urogynecologist via Ob/Gyn pathway ASYMPTOMATIC
CLINITEK Novus Automated Urine Chemistry Analyzer
 CLINITEK, Atlas, Novus, Status+, and all associated marks are trademarks of Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc. or its affiliates. All other trademarks are properties of their respective owners. Product
CLINITEK, Atlas, Novus, Status+, and all associated marks are trademarks of Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc. or its affiliates. All other trademarks are properties of their respective owners. Product
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I
 Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE
 EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
UROLOGIC SYSTEM. Objectives 3/7/2016. Nursing Assessment/Monitoring. Nursing Assessment/Monitoring. Diagnostic Studies. Physical Assessment
 UROLOGIC SYSTEM Mary Susan Goodrich, RN, BSN, MSN, MBA, CMSRN, COS-C Saint Luke s Health System SPRING 2016 Objectives Describe a complete nursing assessment of the urologic system Document a nursing plan
UROLOGIC SYSTEM Mary Susan Goodrich, RN, BSN, MSN, MBA, CMSRN, COS-C Saint Luke s Health System SPRING 2016 Objectives Describe a complete nursing assessment of the urologic system Document a nursing plan
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
Identification and qualitative Analysis. of Renal Calculi
 Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
How to interpret your urine sample results
 How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
Dipstick Testing of Urine Can It Replace Urine Microscopy?
 Dipstick Testing of Urine Can It Replace Urine Microscopy? MARY C. MORRISON, M.D. AND GIFFORD LUM, M.D. One thousand consecutive urine specimens were studied to assess the sensitivity of a commercially
Dipstick Testing of Urine Can It Replace Urine Microscopy? MARY C. MORRISON, M.D. AND GIFFORD LUM, M.D. One thousand consecutive urine specimens were studied to assess the sensitivity of a commercially
This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics
 This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories Hot Topics. These presentations provide short discussion
This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories Hot Topics. These presentations provide short discussion
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice
 Print PDF Save PDF Sign Up for Newsletter Past Editions August/September 2012 Focus: Renal Disease Diagnostics Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice Interview with Brenda Harai, DVM, MS,
Print PDF Save PDF Sign Up for Newsletter Past Editions August/September 2012 Focus: Renal Disease Diagnostics Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice Interview with Brenda Harai, DVM, MS,
Examination by dipstick: (Orthotoluidine & organic peroxidase) Hemoglobin free in urine. Hemoglobin from red blood cells in urine.
 Examination by dipstick: (Orthotoluidine & organic peroxidase) Hemoglobin free in urine Hemoglobin from red blood cells in urine Myoglobin Normal erythrocyte excretion rate * 0 425.000/12 h. ( mean 65.750
Examination by dipstick: (Orthotoluidine & organic peroxidase) Hemoglobin free in urine Hemoglobin from red blood cells in urine Myoglobin Normal erythrocyte excretion rate * 0 425.000/12 h. ( mean 65.750
Management of common uroliths through diet
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of common uroliths through diet Author : Marge Chandler Categories : Canine, Companion animal, Feline, Vets Date
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
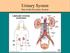 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
AN APPROACH TO HEMATURIA. Dr Saima Ali
 AN APPROACH TO HEMATURIA Dr Saima Ali Definition Microscopic hematuria hematuria is defined as the presence of 5 or more RBCs per high-power field in 3 of 3 consecutive centrifuged specimens obtained at
AN APPROACH TO HEMATURIA Dr Saima Ali Definition Microscopic hematuria hematuria is defined as the presence of 5 or more RBCs per high-power field in 3 of 3 consecutive centrifuged specimens obtained at
EMPIRICAL TREATMENT OF SELECT INFECTIONS ADULT GUIDELINES. Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection
 URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
URINARY TRACT Refer to VIHA Algorithm for the empiric treatment of Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria on the VIHA Intranet: https://intranet.viha.ca/departments/pharmacy/clinical_pharmacy/pages/infec
Chronic Kidney Disease Early Diagnosis is Key. Bill Saxon DACVIM, DACVECC
 Chronic Kidney Disease Early Diagnosis is Key Bill Saxon DACVIM, DACVECC Chronic kidney disease can be defined as an abnormality in kidney function that persists for 3 months or longer or imaging findings
Chronic Kidney Disease Early Diagnosis is Key Bill Saxon DACVIM, DACVECC Chronic kidney disease can be defined as an abnormality in kidney function that persists for 3 months or longer or imaging findings
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Investigating the recheck rules for urine analysis in children
 Investigating the recheck rules for urine analysis in children Y.M. He*, S.W. Yao*, Y.J. Huang, B.S. Liang and H.Y. Liu Clinical Laboratory, Guangzhou Women and Children s Medical Center, Guangzhou Medical
Investigating the recheck rules for urine analysis in children Y.M. He*, S.W. Yao*, Y.J. Huang, B.S. Liang and H.Y. Liu Clinical Laboratory, Guangzhou Women and Children s Medical Center, Guangzhou Medical
Urine. Dr.Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Urine 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry (Tietz) Sixth edition 2 Urine: Sterile fluid (in
Urine 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry (Tietz) Sixth edition 2 Urine: Sterile fluid (in
A general approach to canine urinary tract disorders: origin to treatment
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A general approach to canine urinary tract disorders: origin to treatment Author : Fernando Reina Categories : RVNs Date :
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A general approach to canine urinary tract disorders: origin to treatment Author : Fernando Reina Categories : RVNs Date :
RED URINE. 24 th June 2016 Dr Amrit Kaur
 RED URINE 24 th June 2016 Dr Amrit Kaur 4 year old male with macroscopic haematuria 5 month h/o intermittent MaH 12 episodes, coca-cola urine Treated for UTIs, urine cultures negative Urine dipstick always
RED URINE 24 th June 2016 Dr Amrit Kaur 4 year old male with macroscopic haematuria 5 month h/o intermittent MaH 12 episodes, coca-cola urine Treated for UTIs, urine cultures negative Urine dipstick always
Clinical Test Report. of DUS10 (Urine Reagent Strips) Effective Date: April DFI Lab. Dong-Ai Hospital Medical Center: Clinical Pathology
 Page 1 / 8 APPROVED Clinical Test Report of DUS10 (Urine Reagent Strips) Effective Date: April. 13. 2010 DFI Lab Dong-Ai Hospital Medical Center: Clinical Pathology Page 2 / 8 The evaluation followed Method
Page 1 / 8 APPROVED Clinical Test Report of DUS10 (Urine Reagent Strips) Effective Date: April. 13. 2010 DFI Lab Dong-Ai Hospital Medical Center: Clinical Pathology Page 2 / 8 The evaluation followed Method
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Crystalluria in a dog E. Hooijberg, J. Leidinger and E. Leidinger Labor invitro, Vienna, Austria
 File 2 Crystalluria in a dog E. Hooijberg, J. Leidinger and E. Leidinger Labor invitro, Vienna, Austria Interpretation and Diagnosis The sediment, shown in Figure 1 below, contained small globular yellow-brown
File 2 Crystalluria in a dog E. Hooijberg, J. Leidinger and E. Leidinger Labor invitro, Vienna, Austria Interpretation and Diagnosis The sediment, shown in Figure 1 below, contained small globular yellow-brown
Diagnosis and Management of UTI s in Care Home Settings. To Dip or Not to Dip?
 Diagnosis and Management of UTI s in Care Home Settings To Dip or Not to Dip? 1 Key Summary Points: Treat the patient NOT the urine In people 65 years, asymptomatic bacteriuria is common. Treating does
Diagnosis and Management of UTI s in Care Home Settings To Dip or Not to Dip? 1 Key Summary Points: Treat the patient NOT the urine In people 65 years, asymptomatic bacteriuria is common. Treating does
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
ACTIVITY DISCLAIMER DISCLOSURE. Charles Carter, MD, FAAFP. Audience Engagement System Step 1 Step 2 Step 3. Learning Objectives
 ACTIVITY DISCLAIMER Hematuria: Organizing Your Approach Charles Carter, MD, FAAFP The material presented here is being made available by the American Academy of Family Physicians for educational purposes
ACTIVITY DISCLAIMER Hematuria: Organizing Your Approach Charles Carter, MD, FAAFP The material presented here is being made available by the American Academy of Family Physicians for educational purposes
Urinary. Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine. Figure Slide 15.21a
 Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
