CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1. Urinanalysis
|
|
|
- Tyler Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1 Urinanalysis PLEASE NOTE: The actual urinanalysis goes rather quickly. You may want to skip directly to the Lab Exercise, collect data, and read the Introduction outside of lab. I. Introduction This document provides instruction for performing a chemical analysis using a urine dipstick. The testing may consist of any or all of the following: ph, protein (as a semiquantitative analysis), glucose, bilirubin, ketones, hemoglobin (blood), urobilinogen, nitrite, leukocytes (leukocyte esterase) and specific gravity. These test require an order from primary care provider (Physician, Nurse Practitioner, Physician Assistant). At the discretion of the provider, test results where clinical indication or departmental protocol suggest confirmatory testing, the urine specimen may be sent to the laboratory. Urine test depend on these 7 principles:! Urine is a physiological fluid of widely varying composition formed by the kidney from the blood. The principle constituent of urine is water (92-99% in normal urine).! Thousands of compounds have been identified in normal urine and the vast majority are derived from the blood. The major urine components are creatinine, urea, uric acid, sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, phosphates, sulfates, and ammonia.! A considerable portion of the urine solids is waste products which have been filtered through the kidneys and are being excreted from the body. Some of the constituents are considered to be regulatory substances, which may be either retained or excreted by the kidney. Urine is a principle pathway for excretion of body waste and for homeostatic regulations of body water and body electrolytes.! A fresh early morning specimen after overnight fasting gives the most valuable information concerning renal function and Genitourinary disease. Therefore, whenever feasible, collect specimen routinely in early A.M.! A mid-stream collection enhances the stability of the specimen.! A randomly voided specimen may also be tested.! The urine specimen should be examined within 1 hour of collection, or it should be refrigerated.
2 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 2! If urine is unusually dark (brown or blackish), send laboratory for testing. Most likely specimen contains one or more of the following metabolites: myoglobin, bile porphyrins, homogentisic acid. This should be brought to the attention of the attending physician. The chemical principles of the reagent pads on the strips are (do not memorize the colors): 1. ph - this test is based on a double indicator principle that gives a broad range of colors covering the urinary ph range from 5 to 9. Colors range from orange through yellow and green to blue. 2. Protein - This test is based on the protein-error-of-indicators principle. At a constant buffered ph, the development of any green color is due to the presence of protein. Colors range from yellow for "Negative" through yellow-green and green to green-blue for "Positive" reactions. 3. Glucose - This test is based on a double sequential enzyme reaction to colors ranging from green to brown 4. Ketone - This test is based on the development of colors ranging from buff-pink, for a negative reading, to purple when acetoacetic acid reacts with nitroprusside. 5. Bilirubin - This test is based on the coupling of bilirubin with diazotized dichloraniline in a strongly acid medium. The color ranges through various shades of tan. 6. Blood - This test is based on the peroxidase-like activity of hemoglobin with resulting color ranges from orange through green to dark blue. 7. Urobilinogen - This test is based on the Ehrlich reaction in which p- diethylaminobenzaldehyde reacts with urobilinogen in a strongly acid medium to produce a pink-red color. 8. Nitrite - This test depends upon the conversion of nitrate (derived from the diet) to nitrite by the action of Gram negative bacteria in the urine. At the acid ph of the reagent area, nitrite in the urine reacts to produce a pink color. 9. Leukocytes Granulocytic leukocytes contain esterases that produce a purple product. 10. Specific gravity-- In the presence of cations, protons are released by a complexing agent in the test and produce a color change of the indicator, (bromthymol blue) from blue to yellow.
3 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 3 II. Lab Exercises A. Using the strips Take a strip from each jar. The following is a list of what we might have in the lab: (NOTE: as of the writting of this document, all we have available is Chemstrips 6, 7, 8, and 9 with SG. Ignore any that we do not have n the lsit below) 1. ChemStrip UGK strip for Diabetes Testing, MM # 32141, (glucose and ketones) 2. ChemStrip 4OB strip, Fisher, Cat. No. BC , (blood, glucose, leukocytes, and protein) 3. ChemStrip 7 strip, MM# 32150, (Blood, Nitrite, Glucose, Ketones, Leukocytes, Protein, ph) 4. ChemStrip 9 strip, Fisher, Cat. No. BC , (Blood, Bilirubin, Glucose, Ketones, Leukocytes, Protein, ph, Nitrite, Urobilinogen) 5. ChemStrip 10 strip, MM# 32230, (Blood, Bilirubin, Glucose, Ketones, Leukocytes, Protein, ph, Nitrite, Urobilinogen, Specific Gravity) 6. Multistix 10SG, PSS# 2161 (Multistix 9 plus specific gravity)! Careful attention must be paid to time limits set for each reagent pad.! Be aware that darkly colored urines may have substances that interfere with reading color test pads. Avoid testing of samples heavily pigmented by pyridium drugs. Follow these steps: 1. Thoroughly mix urine specimens by inverting 10X. 2. Remove one strip from the vial and replace cap. 3. Hold the strip against vial to observe proper reading format. 4. Completely immerse reagent areas of the strip in the urine specimen and remove immediately. Start the timer and touch (blot) the edge of the strip on an absorbent material to remove the excess urine. This prevents the run-off phenomenon which can lead to erroneous or inaccurate results. 5. Hold the strip in a horizontal position to prevent possible mixing of chemicals from adjacent reagent areas and/or contaminating the hands with urine. 6. Compare reagent areas to corresponding Color Chart on the bottle label at the time
4 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 4 specified. HOLD STRIP CLOSE TO COLOR BLOCKS AND MATCH CAREFULLY. Avoid laying the strip directly on the Color Chart as this will result in the urine soiling the chart. 7. After dipping the strip, check the ph area. If the color on the pad is not uniform, read the ph reagent area immediately, comparing the darkest color to the appropriate Color Chart. 8. Refer to specific manufacturer s instructions on package insert or on vial for permitted reading time. A positive reaction (small or greater) at or less than 2 minutes on the leukocyte test may be regarded as a positive indication of leukocytes in urine. Color changes that occur after 2 minutes are of no diagnostic value. 9. Record results on patient chart (Analysis Sheet below). 10. Discard used reagent strip. Reseal specimen & set aside for possible further testing. CAUTION doing the ph test:: If proper procedure is not followed and excess urine remains on the strip, a phenomenon known as "runover" may occur in which the acid buffer from the protein reagent area will run onto the ph area, causing a false lowering in the ph result. ANOTHER CAUTION: Urobilinogen: The absence of urobilinogen cannot be determined with this test. For best results, samples should be at room temperature when tested since reactivity is influenced by specimen temperature. B. Microscopic Exam There is a chart in lab showing common bodies found in a urine specimen. Red Blood Cells Hematuria is the presence of abnormal numbers of red cells in urine due to: glomerular damage, tumors which erode the urinary tract anywhere along its length, kidney trauma, urinary tract stones, etc. This will be confirmed with the urinanalysis sticks. White Blood Cells Pyuria refers to the presence of abnormal numbers of leukocytes that may appear with infection in either the upper or lower urinary tract or with acute glomerulonephritis.
5 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 5 Usually, the WBC's are granulocytes. White cells from the vagina, especially in the presence of vaginal and cervical infections, or the external urethral meatus in men and women may contaminate the urine. Casts LOTS of substances can clump together or crystalize and form casts in the urine. Urinary casts are formed only in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) or the collecting duct (distal nephron). The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and loop of Henle are not locations for cast formation. An absence of casts does not rule out renal disease. Casts may be absent or very few in cases of chronic, progressive, generalized nephritis. Even in cases of acute renal disease, casts can be few or absent in a single sample since they tend be shed intermittently. Furthermore, casts are unstable in urine and are prone to dissolution with time, especially in dilute and/or alkaline urine. Although the presence of numerous casts is solid evidence of generalized (usually acute) renal disease, it is not a reliable indicator of prognosis. If the underlying cause can be removed or diminished, regeneration of renal tubular epithelium can occur (provided the basement membrane remains intact). Look at these cast on the wall charts: RBC: The presence of this red blood cell cast in on urine microscopic analysis suggests a glomerular or renal tubular injury. WBC: Pus in the urine. Possibly from a reproductive tract infection in women. Hyaline or Protein casts: The factors which favor protein cast formation are low flow rate, high salt concentration, and low ph, all of which favor protein denaturation and precipitation, particularly that of the Tamm-Horsfall protein. Protein casts with long, thin tails formed at the junction of Henle's loop and the distal convoluted tubule are called cylindroids. Hyaline casts can be seen even in healthy patients.
6 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 6 DATA/ANALYSIS SHEET Name Format CHEMSTRIP TestStrip ONLY (Ignore Multistix) Results: There are 5 data sheets for 5 samples. Then, do the questions in the ANALYSIS section. HOW TO READ THE Specific Gravity reader: The reader has 3 graphs...the 1st 2 on the left are not to be used. Just use the one that says "UG". It reads sort of awkwardly: So..if the reading goes to "-20", that reads as (added together).
7 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 7 SAMPLE 1 1. Color: See Strip Jar for chart Colorless pale yellow yellow amber red brown 2. Turbidity: Clear slightly hazy hazy slightly cloudy cloudy 3. Glucose (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Normal Multistix: Negative Bilirubin Chemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Ketone (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative small moderate large Multistix: Negative Blood BloodChemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Trace ph Chemstrip: Multistix: Normal Range: 5 9 Normal Range: Protein (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Uro-bilinogen Chemstrip: normal Multistix: Nitrite: Negative Positive 11. Leukocytes Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Specific gravity Chemstrip: Multistix:
8 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 8 SAMPLE 2 1. Color: See Strip Jar for chart Colorless pale yellow yellow amber red brown 2. Turbidity: Clear slightly hazy hazy slightly cloudy cloudy 3. Glucose (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Normal Multistix: Negative Bilirubin Chemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Ketone (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative small moderate large Multistix: Negative Blood BloodChemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Trace ph Chemstrip: Multistix: Normal Range: 5 9 Normal Range: Protein (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Uro-bilinogen Chemstrip: normal Multistix: Nitrite: Negative Positive 11. Leukocytes Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Specific gravity Chemstrip: Multistix:
9 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 9 SAMPLE 3 1. Color: See Strip Jar for chart Colorless pale yellow yellow amber red brown 2. Turbidity: Clear slightly hazy hazy slightly cloudy cloudy 3. Glucose (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Normal Multistix: Negative Bilirubin Chemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Ketone (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative small moderate large Multistix: Negative Blood BloodChemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Trace ph Chemstrip: Multistix: Normal Range: 5 9 Normal Range: Protein (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Uro-bilinogen Chemstrip: normal Multistix: Nitrite: Negative Positive 11. Leukocytes Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Specific gravity Chemstrip: Multistix:
10 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 10 SAMPLE 4 1. Color: See Strip Jar for chart Colorless pale yellow yellow amber red brown 2. Turbidity: Clear slightly hazy hazy slightly cloudy cloudy 3. Glucose (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Normal Multistix: Negative Bilirubin Chemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Ketone (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative small moderate large Multistix: Negative Blood BloodChemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Trace ph Chemstrip: Multistix: Normal Range: 5 9 Normal Range: Protein (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Uro-bilinogen Chemstrip: normal Multistix: Nitrite: Negative Positive 11. Leukocytes Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Specific gravity Chemstrip: Multistix:
11 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 11 SAMPLE 5 1. Color: See Strip Jar for chart Colorless pale yellow yellow amber red brown 2. Turbidity: Clear slightly hazy hazy slightly cloudy cloudy 3. Glucose (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Normal Multistix: Negative Bilirubin Chemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Ketone (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative small moderate large Multistix: Negative Blood BloodChemstrip: Negative Multistix: Negative Trace ph Chemstrip: Multistix: Normal Range: 5 9 Normal Range: Protein (mg/dl) Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Uro-bilinogen Chemstrip: normal Multistix: Nitrite: Negative Positive 11. Leukocytes Chemstrip: Negative trace Multistix: Negative trace Specific gravity Chemstrip: Multistix:
12 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 12 Analysis Findings in Disease: Answer the questions below. There is a sheet with each strip jar that describes what might be expected with certain readings. Also, I have added some notes of my own: Glucose: Diabetes mellitus is the chief cause of glucosuria. The sugar content of a diabetic urine may reach as high as 10%, but 2-5% values are more commonly found. Bilirubin: Bilirubin may often appear in the urine before other signs of liver dysfunction are apparent. Blood: Hemoglobinuria may indicate a hematologic disorder such as haemolytic anemia, hemolytic transfusion reaction, etc. In these, the RBCs are destroyed and release their hemoglobin. It is also found in poisonings with strong acids or mushrooms, following burns, or in renal infection. A significant amount of free hemoglobin is found in the urine whenever red blood cells are present in excessive numbers. Another cause may be bleeding in the urinary tract. Protein: Please Note: the test strips are giving their readings in mg; 500 mg =.5 grams 1. Marked proteinuria (more than 4 gm per day) is typical of the several renal disease: nephrotic syndrome, glomerulonephritis, nephrosclerosis, amyloid disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and severe venous congestion of the kidney produced by renal vein thrombosis, congestive heart failure, or constrictive pericarditis. 2. Moderate proteinuria (0.5 to 4.0 gm per day) is found in the vast majority of renal diseases (see above) as well as preeclampsia and any inflammatory, malignant, degenerative, or irritative condition of the lower urinary tract, including the presence of calculi. 3. Minimal proteinuria (less than 0.5 gm per day) is associated with chronic glomerulonephritis, renal tubular disorders and various disorders of the lower urinary tratc leading to bleeding. Urobilinogen: Urinary bilinogen is increased by any condition that causes an increase in the production of bilirubin (that is, increased destruction of RBCs: hemolytic anemia, pernicious anemia, and malaria are examples) or by any disease that prevents the liver from normally removing the reabsorbed urobilinogen from the portal circulation (infectious hepatitis, toxic
13 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 13 hepatitis, portal cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, and infectious mononucleosis being examples). 1. Describe what diseases, disorders or conditions you expect with each sample: 2. Name all the substances we tested for: 3. Describe, in your own words, what runover is. Why would the ph be lowerd?
14 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis Would you expect a lot of lipid-soluble substance in urine? Why or why not? 5. When should a urine analysis be preformed for optimal conditions? Which other conditions are optimal? 6. Draw a hyaline, RBC, and WBC cast in the space below:
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis
 Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
URINANLYSIS. Pre-Lab Guide
 URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS)
 GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
Controls (positive and negative) for quality assessment-located in central laboratory Note: See central lab UA procedure for QC. Read strips visually.
 ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents. Amal Alamri
 Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
It s not just water! What is Urinalysis?
 It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
Routine urine examination
 Routine urine examination 尿常规检查 Huawei Liang, PhD E-mail: hwliang99@163.com Objectives To examine urine for the presence of normal and abnormal constituents by routine urine analysis Principles Urine formation
Routine urine examination 尿常规检查 Huawei Liang, PhD E-mail: hwliang99@163.com Objectives To examine urine for the presence of normal and abnormal constituents by routine urine analysis Principles Urine formation
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE
 EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
BCH472 [Practical] 1
![BCH472 [Practical] 1 BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/89/98494556.jpg) BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview
 Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview In-Lab Exercises Read Me This is a very diverse lab. We will be looking at the gross anatomy of the urinary tract, the microscopic anatomy on both models and slides,
Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview In-Lab Exercises Read Me This is a very diverse lab. We will be looking at the gross anatomy of the urinary tract, the microscopic anatomy on both models and slides,
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
The Urinary System. Lab Exercise 38. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST. Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
Science of Veterinary Medicine. Urinary System Unit Handouts
 Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Unit Outline. Chemical Exam of Urine. Unit 3. Reagent strip manufactures
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 1 Overview of Procedure & ph Unit Outline Introduction to reagent strip testing ph Glucose & Carbohydrates Ketones Protein Bilirubin
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 1 Overview of Procedure & ph Unit Outline Introduction to reagent strip testing ph Glucose & Carbohydrates Ketones Protein Bilirubin
Taking a dip into urinalysis
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis
 The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today
 III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
Physical Characteristics of
 Physical Characteristics of Urine Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The urinary system s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries the glomeruli distributed more or
Physical Characteristics of Urine Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The urinary system s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries the glomeruli distributed more or
Urine Reagent Strip (Blood - Ketone - Glucose - Protein - ph - Bilirubin)
 Urine Reagent Strip (Blood - Ketone - Glucose - Protein - ph - Bilirubin) Cat. No.:DTS411 Pkg.Size: Intended use CD Diagnostics Urine Reagent Strips (URS) for Urinalysis are firm plastic strips to which
Urine Reagent Strip (Blood - Ketone - Glucose - Protein - ph - Bilirubin) Cat. No.:DTS411 Pkg.Size: Intended use CD Diagnostics Urine Reagent Strips (URS) for Urinalysis are firm plastic strips to which
Urine. Dr.Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Urine 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry (Tietz) Sixth edition 2 Urine: Sterile fluid (in
Urine 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry (Tietz) Sixth edition 2 Urine: Sterile fluid (in
CHEMSTRIP 7 - URINE TEST STRIP
 University of California, San Francisco -- Department of Laboratory Medicine San Francisco General Hospital 1001 Potrero Avenue, San Francisco CA 94110 Clinical Laboratory- Eberhard Fiebig, MD, Director
University of California, San Francisco -- Department of Laboratory Medicine San Francisco General Hospital 1001 Potrero Avenue, San Francisco CA 94110 Clinical Laboratory- Eberhard Fiebig, MD, Director
Urinalysis (Macroscopic( Chemical Tests) ) Background. Ishihara Color Blindness Tests 12/22/2012. Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD
 Urinalysis (Macroscopic( Chemical Tests) ) Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD Background Routine chemical examination of urine has changed dramatically since the early days of urine testing, owing to the
Urinalysis (Macroscopic( Chemical Tests) ) Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD Background Routine chemical examination of urine has changed dramatically since the early days of urine testing, owing to the
Urine analysis. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Urine analysis By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Functions of Renal system Excretory functions Metabolic waste Drug clearance Toxin clearance Urea, Creatinin Regulatory functions Water balance Blood / urine
Urine analysis By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Functions of Renal system Excretory functions Metabolic waste Drug clearance Toxin clearance Urea, Creatinin Regulatory functions Water balance Blood / urine
Topic Objectives. Physical Examination LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE. Appearance. Odor Specific Gravity Volume
 LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Urine Casts. Microscopic Sediment Casts. Unit 2; Session 6
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Urine Dipstick Medical Mobile Unit: Patient Test Procedure
 Urine Dipstick Medical Mobile Unit: Patient Test Procedure Children s Hospital: Emergency Department Medical Mobile Unit PURPOSE To provide instruction in performing a manual Routine Urine Test using urine
Urine Dipstick Medical Mobile Unit: Patient Test Procedure Children s Hospital: Emergency Department Medical Mobile Unit PURPOSE To provide instruction in performing a manual Routine Urine Test using urine
SCBM343- Urinalysis. Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul. Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
 SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
By Sandipkumar Kanazariya. Tuesday, December 11,
 By Sandipkumar Kanazariya Tuesday, December 11, 2018 1 Under pathological conditions urine excreted by patient shows the presence of abnormal constituents along with normal constituents. Abnormal constituents
By Sandipkumar Kanazariya Tuesday, December 11, 2018 1 Under pathological conditions urine excreted by patient shows the presence of abnormal constituents along with normal constituents. Abnormal constituents
Application Note. Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1
 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood
LABORATORY 2: Macroscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 2: Macroscopic Urinalysis Points: Points are awarded for the skills demonstrated in the laboratory, as well as successful and timely completion of study questions. Objectives: According to the
LABORATORY 2: Macroscopic Urinalysis Points: Points are awarded for the skills demonstrated in the laboratory, as well as successful and timely completion of study questions. Objectives: According to the
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Urinary system. Lab-7
 Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
URINE REAGENT STRIPS FOR URINALYSIS
 CORTEZ DIAGNOSTICS, INC. 20521 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116 Woodland Hills, CA, 91367 USA Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 E-mail: onestep@rapidtest.com Web site: www.rapidtest.com See external
CORTEZ DIAGNOSTICS, INC. 20521 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116 Woodland Hills, CA, 91367 USA Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 E-mail: onestep@rapidtest.com Web site: www.rapidtest.com See external
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models: pelvis
 159 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1: Urinary System Anatomy,
159 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1: Urinary System Anatomy,
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
LABORATORY 6: The Complete Urinalysis with Automation
 LABORATORY 6: The Complete Urinalysis with Automation PreLab Preparation: 1. Review YouTube videos on Clinitek Status Principle & Operation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-8loszd-u8&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1tpqqh9m88&feature=endscreen&nr=1
LABORATORY 6: The Complete Urinalysis with Automation PreLab Preparation: 1. Review YouTube videos on Clinitek Status Principle & Operation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-8loszd-u8&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1tpqqh9m88&feature=endscreen&nr=1
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture
 #Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
#Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Urinalysis Review and Case Studies
 Urinalysis Review and Case Studies A Complete Urinalysis John H. Landis, MS, MLS(ASCP) Adjunct Professor, University of Cincinnati Adjunct Professor, Oakland University Professor Emeritus, Ferris State
Urinalysis Review and Case Studies A Complete Urinalysis John H. Landis, MS, MLS(ASCP) Adjunct Professor, University of Cincinnati Adjunct Professor, Oakland University Professor Emeritus, Ferris State
References Required document for Laboratory Accreditation by the College of American Pathologists.
 Subject Urinalysis Clinitek Advantus Regional Index Number Lab-1589 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional Clinic / Affiliate Hospital Laboratories Category Departmental Contact Elizabeth A Kamprud Last
Subject Urinalysis Clinitek Advantus Regional Index Number Lab-1589 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional Clinic / Affiliate Hospital Laboratories Category Departmental Contact Elizabeth A Kamprud Last
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
*Function maintains homeostasis by regulating the water balance and by removing harmful substances
 The Excretory System GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND DEFINITIONS: *Function maintains homeostasis by regulating the water balance and by removing harmful substances *Homeostasis (homeo: constant; stasis: state)
The Excretory System GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND DEFINITIONS: *Function maintains homeostasis by regulating the water balance and by removing harmful substances *Homeostasis (homeo: constant; stasis: state)
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System. Short Answer. Figure 15.1
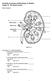 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System Short Answer Figure 15.1 Using Figure 15.1, identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter. Answer: B Diff:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System Short Answer Figure 15.1 Using Figure 15.1, identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter. Answer: B Diff:
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #8: ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM and CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #8: ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM and CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 7 th ed. (2015)
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #8: ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM and CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 7 th ed. (2015)
Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5
 Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES
 Deborah Burgess, M.D. Nephrology Department 16 Oct 90 URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES The kidney regulates the internal environment of the body by controlling electrolyte and water balance; and establishes
Deborah Burgess, M.D. Nephrology Department 16 Oct 90 URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES The kidney regulates the internal environment of the body by controlling electrolyte and water balance; and establishes
LAB 10: RENAL FUNCTION
 Page 10.1 LAB 10: RENAL FUNCTION The renal system is comprised of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. This system has many functions, the most obvious are the creation, storage and excretion
Page 10.1 LAB 10: RENAL FUNCTION The renal system is comprised of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. This system has many functions, the most obvious are the creation, storage and excretion
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Biomarkers of renal diseases. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Microscopic Examination of Urine
 Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Department of Laboratories St. Louis, MO 63110
 Page 1 of 8 PROCEDURE: URINALYSIS ON THE CLINITEK STATUS+ ISSUE DATE: August 2010 REVISION DATE: REVIEWED DATE: May 2017 PRINCIPLE: The Siemens Clinitek Status Analyzer is a portable instrument powered
Page 1 of 8 PROCEDURE: URINALYSIS ON THE CLINITEK STATUS+ ISSUE DATE: August 2010 REVISION DATE: REVIEWED DATE: May 2017 PRINCIPLE: The Siemens Clinitek Status Analyzer is a portable instrument powered
Excretory Physiology
 Excretory Physiology Urine production and eliminations are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis composition of blood is determined more by kidney function than by diet all body systems
Excretory Physiology Urine production and eliminations are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis composition of blood is determined more by kidney function than by diet all body systems
RELEASES TOXIC FUMES!
 Name(s): Block: Date: Urinary System Lab Activity: Urinalysis Background: Urinalysis, the physical, chemical, and microscopic analysis or examination of urine can provide information about a person s carbohydrate
Name(s): Block: Date: Urinary System Lab Activity: Urinalysis Background: Urinalysis, the physical, chemical, and microscopic analysis or examination of urine can provide information about a person s carbohydrate
A. SAP is the D-Lab's name for a specific set of serum biochemical tests.
 Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Urine bench. Urine test for: SARAH Sugar
 Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urinalysis (Testing Urine Samples)
 Name: Date: Period: Urinalysis (Testing Urine Samples) Case Studies: Patient 1: Patient 2: Patient 3: Patient 4: Mr. Bob has normal looking urine. He has regular yearly checkups and has no visible symptoms.
Name: Date: Period: Urinalysis (Testing Urine Samples) Case Studies: Patient 1: Patient 2: Patient 3: Patient 4: Mr. Bob has normal looking urine. He has regular yearly checkups and has no visible symptoms.
How do we detect PEDs?
 How do we detect PEDs? Drug Testing https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dq5pvabzpxq Urine sample Blood sample Detection of drug metabolites The Excretory System Urine is excreted from bladder via the urethra
How do we detect PEDs? Drug Testing https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dq5pvabzpxq Urine sample Blood sample Detection of drug metabolites The Excretory System Urine is excreted from bladder via the urethra
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Fal Fal P h y s i o l o g y 6 1 1, S a n F r a n c i s c o S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y
 Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Type Description Date Version Performed By Notes
 Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and Trauma Center Clinical Laboratory 1001 Potrero Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94110 Barbara Haller, MD, PhD, Director 48667.266 CHEMSTRIP 2 GP - URINE TEST STRIP
Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and Trauma Center Clinical Laboratory 1001 Potrero Avenue, San Francisco, CA 94110 Barbara Haller, MD, PhD, Director 48667.266 CHEMSTRIP 2 GP - URINE TEST STRIP
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
A&P of the Urinary System
 A&P of the Urinary System Week 44 1 Objectives Identify the organs of the urinary system, from a Identify the parts of the nephron (the functional unit List the characteristics of a normal urine specimen.
A&P of the Urinary System Week 44 1 Objectives Identify the organs of the urinary system, from a Identify the parts of the nephron (the functional unit List the characteristics of a normal urine specimen.
Lecture 7. The Urinary System
 Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
5/10/2014. Observation, control of blood pressure. Observation, control of blood pressure and risk factors.
 Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Outline Introduction of diabetic nephropathy Manifestations of diabetic nephropathy Staging of diabetic nephropathy Microalbuminuria Diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy Treatment of
Diabetic Nephropathy Outline Introduction of diabetic nephropathy Manifestations of diabetic nephropathy Staging of diabetic nephropathy Microalbuminuria Diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy Treatment of
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
How to interpret your urine sample results
 How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
How to interpret your urine sample results
 How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Clinical Test Report. of DUS10 (Urine Reagent Strips) Effective Date: April DFI Lab. Dong-Ai Hospital Medical Center: Clinical Pathology
 Page 1 / 8 APPROVED Clinical Test Report of DUS10 (Urine Reagent Strips) Effective Date: April. 13. 2010 DFI Lab Dong-Ai Hospital Medical Center: Clinical Pathology Page 2 / 8 The evaluation followed Method
Page 1 / 8 APPROVED Clinical Test Report of DUS10 (Urine Reagent Strips) Effective Date: April. 13. 2010 DFI Lab Dong-Ai Hospital Medical Center: Clinical Pathology Page 2 / 8 The evaluation followed Method
510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY ASSAY AND INSTRUMENT COMBINATION TEMPLATE
 510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY ASSAY AND INSTRUMENT COMBINATION TEMPLATE A. 510(k) Number: k063276 B. Purpose for Submission: New device C. Measurand: Urinary Glucose, Blood,
510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY ASSAY AND INSTRUMENT COMBINATION TEMPLATE A. 510(k) Number: k063276 B. Purpose for Submission: New device C. Measurand: Urinary Glucose, Blood,
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
