Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis
|
|
|
- Jeffry Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spine Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis J. S. Lee, K. T. Suh From the Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan, Korea There are few reports on the treatment of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis through the posterior approach using a single incision. Between October 1999 and March 2003 we operated on 18 patients with pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis. All underwent posterior lumbar interbody fusion using an autogenous bone graft from the iliac crest and pedicle screws via a posterior approach. The clinical outcome was assessed using the Frankel neurological classification and the criteria of Kirkaldy-Willis. Under the Frankel classification, two patients improved by two grades (C to E), 11 by one grade, and five showed no change. The Kirkaldy-Willis functional outcome was excellent in five patients, good in ten and fair in three. Bony union was confirmed six months after surgery in 17 patients, but in one patient this was not achieved until two years after operation. The mean lordotic angle before operation was 20 (-2 to 42 ) and the mean lordotic angle at the final follow-up was 32.5 (17 to 44 ). Two patients had a superficial wound infection and two a transient root injury. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous iliac crest bone graft and pedicle screw fixation via a posterior approach can provide satisfactory results in pyogenic spondylodiscitis. J. S. Lee, MD, Assistant Professor K. T. Suh, MD, PhD, Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Pusan National University, College of Medicine, 1-10 Ami- Dong, Seo-Gu, Pusan , Korea. Correspondence should be sent to Professor K. T. Suh; kuentak@pusan.ac.kr 2006 British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery doi: / x.88b $2.00 J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2006;88-B: Received 6 October 2005; Accepted after revision 5 January 2006 Surgical treatment for pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis may be required for those who do not respond to antibiotic treatment or in the presence of a collapsed lumbar body, an epidural abscess or a neurological deficit. 1-7 Although various approaches to the surgical management of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis have been described, 1,3,6,8-12 many patients in whom medical management has failed have been treated by debridement, followed several weeks later by internal fixation. 1,2,13-15 Some have found percutaneous transpedicular discectomy to be an excellent treatment in the early stages of uncomplicated spondylodiscitis. 16,17 Others have suggested that internal fixation can be left in place if debridement is performed and a prolonged course of intravenous antibiotics given. 8,11,18 Others have used antibioticimpregnated methylmethacrylate 8 and continuous suction/irrigation systems. 10 However, there are few reports on the treatment of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis using posterior lumbar interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixation. 19,20 The aims of this procedure are to remove the infected disc, promote natural wound healing by firm fixation and to facilitate early mobilisation and rehabilitation. Patients and Methods This study was a retrospective review of 18 patients treated by one surgeon (JSL) for pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis between October 1999 and March Their details are shown in Table I. The medical records were reviewed and the patients recalled for followup. There were ten women and eight men. Their mean age at the time of surgery was 57.7 years (44 to 71), and the mean period of follow-up was 32 months (24 to 48). Most complained of severe lower back pain and disturbance of gait over a period of one to eight months. Of these, 16 had neurological deficits (Frankel 21 B to D) which included motor weakness, sensory changes, pain radiating to the lower limbs, and urinary symptoms. There were five patients with diabetes mellitus, three were hypertensive, two had a gastric ulcer and one was in chronic renal failure. The L2-L3 level was affected in one patient, L3-L4 in six, L4-L5 in eight and L5-S1 in three. Between one and three levels were fused. The presumed cause of the infection was an epidural injection in nine patients, a post-laminectomy infection in four, and in five the cause was unknown. Operation was indicated when the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels did not return to normal VOL. 88-B, No. 6, JUNE
2 766 J. S. LEE, K. T. SUH Table I. Details of the patients Case Age (yrs) Gender Medical problem * Spinal stenosis Epidural abscess Level Area for instrumentation Duration of symptoms (mths) Presumed cause Organism Post-operative antibiotics (wks) 1 68 M L3-L4 L3-L4 3 Epidural injection S. aureus 6 IV/12 PO 2 54 F GU + - L4-L5 L4-L5 2 Epidural injection No growth 6 IV/8 PO 3 52 F DM - + L5-S1 L4-S1 3 Post-laminectomy S. aureus 6 IV/8 PO 4 49 M L4-L5 L4-L5 5 Unknown C. luteola 6 IV/8 PO 5 71 M L3-L4 L3-L4 6 Post-laminectomy S. aureus 6 IV/6 PO 6 62 F DM + + L3-L4 L3-L4 2 Epidural injection No growth 7 IV/6 PO 7 53 F HT - + L4-L5 L4-L5 3 Epidural injection MRSA 8 IV/12 PO 8 51 F HT - + L4-L5 L4-S1 1 Unknown No growth 6 IV/12 PO 9 66 M L2-L3 L2-L3 2 Post-laminectomy No growth 6 IV/6 PO F HT - + L3-L4 L2-L5 5 Epidural injection S. aureus 6 IV/4 PO M L4-L5 L4-L5 4 Unknown No growth 6 IV/8 PO F DM - - L4-L5 L4-S1 1 Epidural injection MRSA 12 IV/24 PO M CRF + + L3-L4 L3-L5 5 Epidural injection B. cepacia 4 IV/6 PO F L5-S1 L4-S1 2 Post laminectomy No growth 6 IV/6 PO M DM - + L4-L5 L4-L5 1 Epidural injection S. aureus 6 IV/8 PO F GU + - L3-L4 L3-L5 4 Unknown No growth 6 IV/8 PO M L4-L5 L4-S1 8 Unknown No growth 6 IV/6 PO F DM + + L5-S1 L5-S1 2 Epidural injection No growth 6 IV/6 PO * GU, gastric ulcer; DM, diabetes mellitus; HT, hypertension; CRF, chronic renal failure +, present; -, absent IV, intravenously; PO, orally and pain persisted after the administration of antibiotics for more than three weeks, or when neurological changes were noted as a result of an abscess compressing the dura. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior fixation was indicated in patients with a small abscess in the anterior portion of the vertebral body connected to a disc, so that drainage could be accomplished through the posterior approach. It was also indicated in those with spinal stenosis and those in whom the anterior approach could not be used because the abscess was in the posterior portion of the dura. The white blood cell, ESR and CRP levels were determined and plain radiographs, radionucleide studies and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were undertaken before surgery. A computed tomography (CT)-guided fine-needle biopsy of the infected disc space was performed in all patients. The disc material and infected end-plate removed during surgery were sent for culture and histology. Plain and dynamic radiographs were obtained in all patients 3, 6 and 12 months after surgery. At the final follow-up evaluation, the fusion and measurements of the lordotic angle were carried out by two surgeons (JSL, KTS). CT was also used to assess the fusion and the formation of a bone bridge. The radiographs were graded according to the criteria of Lee, Vessa and Lee 22 (Table II). In our study we classified both definitive and probable fusion as a fusion. The lumbar lordotic angle was measured from the upper end-plate of T12 to the upper end-plate of S1 preoperatively, post-operatively, and at the final follow-up. The functional outcome was classified according to the Frankel classification 21 and the criteria of Kirkaldy-Willis (Table III). 23 Operative technique. A posterior laminectomy and pedicle screw fixation was performed under general anaesthesia. When possible, a pedicle screw was not applied directly to the infected vertebral body. When the infection and destruction of the vertebral body was severe, we fixed one level above or below the segment. After pedicle screw fixation, the disc space was distracted and the infected endplate, disc and soft tissue removed. The space created after Table II. The criteria of Lee et al 22 for results of radiographic fusion Grade Description Definitive fusion Definitive bony trabecular bridging across the graft-host interface, no motion (< 3 ) on flexionextension radiograph, and no gap at interface Probable fusion No definitive bony trabecular crossing, but no detectable motion and no identifiable gap at the interface Possible pseudarthrosis No bony trabecular crossing, no movement but identifiable gap at the interface Definite pseudarthrosis No traversing trabecular bone, definitive gap, and movement > 3 Table III. The criteria of Kirkaldy-Willis et al 23 for functional outcome Grade Description Excellent The patient has returned to his normal work and other activities with little or no complaint Good The patient has returned to his normal work but may have some restriction in other activities, and may on occasion after heavy work have recurrent back pain requiring a few days rest Fair The patient has to reduce his working capacity, taking a lighter job or working part-time, and may occasionally have recurrence of pain requiring absence from work for one to two weeks, once or twice a year Poor The patient does not return to work THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
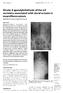
3 POSTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION WITH AN AUTOGENOUS ILIAC CREST BONE GRAFT 767 Fig. 1a Fig. 1b Case 3 A 52-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus developed an L5-S1 staphylococcal spondylodiscitis. She underwent posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous strut iliac graft. a) pre-operative anteroposterior and lateral radiographs show L5-S1 disc interspace narrowing and irregular end-plates (arrow); b) T2-weighted sagittal and contrastenhanced T1-weighted axial images show an epidural abscess (arrow) and destruction of the L5-S1 disc interspace; c) lateral radiograph taken two years after surgery shows radiolucency around the pedicle screw. The functional outcome was excellent. The autogenous strut iliac graft has united (arrow). Fig. 1c meticulous debridement was filled with an autogenous iliac bone graft. A tricortical iliac graft was used in all patients. After this graft had been firmly fixed by compression of the space, a posterolateral graft was performed in order to obtain a 360 fusion. The patients were mobilised three days after surgery and wore a lumbosacral orthosis for three months. The appropriate antibiotics were administered intravenously for a mean of 6.4 weeks (4 to 12) after operation, followed by oral administration for a mean of 8.6 weeks (4 to 24). Statistical analysis. Serial changes of white blood cell, ESR, and CRP levels and lordotic angle were assessed using the Friedman test with Dunn s post-multiple comparison test. The differences in these measurements between the stenotic and the non-stenotic groups and the patients with and without an epidural abscess were analysed using the Mann- Whitney U test. The final results at follow-up between these groups of patients were compared using Fisher s exact test as appropriate. A value of p < 0.05 was defined as statistically significant. Results Bony union and change in lordotic angle. Bony union was obtained by six months after operation in 17 patients (Fig. 1). In one patient union was not achieved until two years after surgery (Fig. 2). The mean lordotic angle before operation was 20 (-2 to 42 ), improving after the procedure to 34.3 (19 to 47 ). At the final follow-up it was 32.5 (17 to 44 ) (Table IV). These changes were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Clinical. Although a pre-operative needle biopsy was performed in all patients, bacterial growth was obtained in only three cases. Bacteria were cultured from material removed from the disc and the infected end-plate in nine patients, including Staphylococcus aureus in five, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in two, Cheryscomonas luteola in one, and Burkholderia cepacia in one. Histological examination of the material removed from the disc and the infected end-plate confirmed the presence of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis in all patients. VOL. 88-B, No. 6, JUNE 2006
4 768 J. S. LEE, K. T. SUH Fig. 2a Case 11 A 65-year-old man with spinal stenosis developed L4-L5 spondylodiscitis and underwent posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an autogenous strut iliac graft. a) contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sagittal and axial images show destruction of the L4-L5 disc interspace and extension along the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments; b) pre-operative (left) and postoperative lateral radiographs at one (centre) and two years (right), showing that bony union has been achieved (arrows). Fig. 2b On admission, the mean white blood cell count was 9041 ml (5120 to ), the mean ESR was 71 mm/h (12 to 113), and the mean CRP level was 6.18 mg/dl (1.02 to 14.40). The ESR was reduced after surgery, became normal in seven patients (39%) by six weeks and was normal in 12 patients (67%) at the final follow-up. The CRP became normal within five months after surgery in 17 patients (94%). The mean white blood cell count decreased by six weeks after surgery to 6361 ml (3700 to ; p < 0.01) and at the last follow-up to 6277 ml (3960 to 8370; p < 0.01). With regard to the presence or absence of stenosis and epidural abscess, there was no statistically significant difference in white blood cell count, ESR, CRP level or lordotic angle between patients with stenosis and those with an abscess (p > 0.05). There were post-operative complications in four patients, comprising a superficial wound infection in two and a transient nerve root palsy in two. As assessed by the Frankel neurological classification, 21 two patients improved by two grades (C to E), 11 improved by one grade, and five showed no change. The functional outcome as assessed using the Kirkaldy-Willis criteria 23 was excellent in five patients, good in ten and fair in three. Table V shows the differences in outcome at final follow-up in the presence or absence of stenosis and epidural abscess. They were not statistically significant. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 POSTERIOR LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION WITH AN AUTOGENOUS ILIAC CREST BONE GRAFT 769 Table IV. Radiological and clinical results in the 18 patients Case Lordotic angle ( ) Frankel scale 21 Pre-operative Immediate post-operative Final follow-up Pre-operative Final follow-up Post-operative complication Follow-up period (mths) Outcome (Kirkaldy-Willis 23 ) B C 25 Fair D D 48 Good D E 26 Excellent D E 36 Good E E 27 Excellent C D Superficial 36 Good infection D E Transient root 36 Good injury D E 24 Excellent E E 25 Good D E 36 Good C D Transient root 28 Fair injury C C Superficial 29 Fair infection D E 24 Good C D 36 Good C E 24 Excellent D D 31 Good D E 37 Good C E 48 Excellent Table V. Final clinical outcomes according to the presence or absence of the stenosis and epidural abscess Result Stenosis Present (n = 10) Absent (n = 8) p value Epidural abscess Present (n = 10) Absent (n = 8) p value Excellent Good Fair Discussion The incidence of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis after discectomy has been reported to be 0.7% to 0.8% even when prophylactic antibiotic treatment is given. 24,25 The number of spinal procedures for either diagnostic or therapeutic purposes has increased significantly in recent years, which has increased the incidence of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis. The major cause in our patients was an epidural root block carried out in those who were immunocompromised or who had comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus. A total of nine of our 18 patients had received an epidural root block before the infection developed. In the natural course of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis, granulation tissue invades the disc from the subchondral tissue and absorbs disc tissue to suppress the infection. 26 This process would finally result in fusion. Pseudarthrosis would be induced when no interbody fusion occurred. Kyphotic deformity results when the disc becomes malaligned. Although it has been stated that fibrous or osseous union occurs by between six and 24 months after conservative treatment for discitis, Fredrickson et al 4 reported an incidence of osseous union of only 35% of patients. The objectives of surgery are to debride the necrotic material, decompress the neural structures, stabilise the unstable segments by a bone graft and increase the chances of faster wound healing by restoring spinal alignment. 3,9 The anterior approach is used because the infection begins in the anterior part of the spine. An abscess usually involves the anterior spine and an epidural abscess or sequestrated bone compresses the anterior dura. Following an anterior approach an anterior strut graft is used after debridement. However, an anterior interbody fusion performed without internal fixation requires long-term bed rest, a body cast or additional posterior surgery. 27,28 Although Eysel et al 29 have reported good clinical outcomes, including bony union and normal haematological findings following anterior interbody fusion with firm internal fixation, there is a risk of recurrent infection because the metal is at the site of infection. There is also an increased risk of post-operative complications, such as neurological damage, hernia, and injury to the gastrointestinal and genitourinary systems as a result of adhesions around the infected spine. It is difficult to apply this procedure to the lower lumbar spine. There are few reports on the treatment of pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis with posterior lumbar interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixation. 19,20 The benefits are early mobilisation because of sound internal fixation, earlier rehabilitation because of reduced morbidity and adequate removal of the abscess in the posterior and anterior dura, sequestrated bone, and any small abscesses in the anterior spine. Posterior instrumentation can be used to correct the spinal deformity, while spinal stenosis, which is usually observed in elderly patients, can be treated simultaneously. The mean age of the 18 patients we studied was 57.7 years VOL. 88-B, No. 6, JUNE 2006
6 770 J. S. LEE, K. T. SUH (44 to 71) and ten had spinal stenosis. There was an epidural abscess in ten patients; it was found in the anterior dura in seven and in the posterior dura in three. If the anterior approach is used in the presence of spinal stenosis, posterior decompression is needed as a secondary procedure. Firm fixation helps to control infection in long bones. We felt that firm internal fixation could help control the pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis. However, the presence of an artificial implant where inflammatory tissue is present can induce bacterial attachment and the formation of a biofilm. 30,31 By placing an implant in the cancellous bone of the vertebral body where the blood flow is good and by performing meticulous debridement of necrotic tissue before inserting the implant, the autoimmune system can treat inflammation by preventing bacterial attachment as well as the formation of a biofilm. This can be influenced by preoperative treatment with antibiotics. 29,31 Internal fixation for tuberculous spondylitis is safe 31 and the risk of a recurrence in pyogenic lumbar spondylodiscitis is not high. 29 If possible, in our patients the pedicle screw was not applied directly to the vertebral body causing the infection. When the infection and destruction of the vertebral body was severe, the chance of contact with the infection could be reduced by fixation one level above or below the segment. Compared with anterior debridement and the use of a strut bone graft, the disadvantage of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixation is that fixation may be needed for one, two, or more segments when vertebral body destruction is severe. However, we have found that this did not influence the return of our patients to an active life. This study has limitations. The number of patients included was relatively small and studies with larger numbers of patients are required. However, posterior lumbar interbody fusion with an accompanying bone graft can be considered for patients with an adjacent small abscess in the anterior spine and slight vertebral body destruction, those with an epidural abscess in the posterior dura, patients with spinal stenosis, and those with an abscess in the lower lumbar spine. Supplementary Material A further opinion by Mr Brad Williamson is available with the electronic version of this article on our website at This study was supported by Medical Research Institute Grant (2006-9), Pusan National University. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. References 1. Abramovitz JN, Batson RA, Yablon JS. Vertebral osteomyelitis: the surgical management of neurologic complications. Spine 1986;11: Arnold PM, Baek PN, Bernardi RJ, Luck EA, Larson SJ. Surgical management of nontuberculous thoracic and lumbar vertebral osteomyelitis: report of 33 cases. Surg Neurol 1997;47: Eismont FJ, Bohlman HH, Soni PL, Goldberg VM, Freehafer AA. Pyogenic and fungal vertebral osteomyelitis with paralysis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1983;65-A: Fredrickson B, Yuan H, Olans R. Management and outcome of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Clin Orthop 1978;131: Gepstein R, Folman Y, Lidor C, et al. Management of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with spinal cord compression in the elderly. Paraplegia 1992;30: Kemp HB, Jackson JW, Jeremiah JD, Hall AJ. Pyogenic infections occurring primarily in intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1973;55-B: Osenbach RK, Hitchon PW, Menezes AH. Diagnosis and management of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis in adults. Surg Neurol 1990;33: Dietze DD, Haid RW Jr. Antibiotic-impregnated methylmethacrylate in the treatment of infections with spinal instrumentation: case report and technical note. Spine 1992;17: Emery SE, Chan DP, Woodward HR. Treatment of hematogenous pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with anterior debridement and primary bone grafting. Spine 1989; 14: Garrido E, Rosenwasser RH. Experience with suction-irrigation technique in the management of spinal epidural infection. Neurosurgery 1983;12: Levi AD, Dickman CA, Sonntag VK. Management of postoperative infections after spinal instrumentation. J Neurosurg 1997;86: Mann S, Schutze M, Sola S, Piek J. Nonspecific pyogenic spondylodiscitis: clinical manifestations, surgical treatment, and outcome in 24 patients. Neurosurg Focus 2004;17: Graziano GP, Sidhu KS. Salvage reconstruction in acute and late sequelae from pyogenic thoracolumbar infection. J Spinal Disord 1993;6: Liebergall M, Chaimsky G, Lowe J, Robin GC, Floman Y. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with paralysis: prognosis and treatment. Clin Orthop 1991;269: Rea GL, McGregor JM, Miller CA, Miner ME. Surgical treatment of the spontaneous spinal epidural abscess. Surg Neurol 1992;37: Hadjipavlou AG, Katomis PK, Gaitanis IN, et al. Percutaneous transpedicular discectomy and drainage in pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J 2004;13: Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, Muffoletto AJ. Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine 2000;25: Thalgott JS, Cotler HB, Sasso RC, LaRocca H, Gardner V. Postoperative infections in spinal implants: classification and analysis. Spine 1991;16: Przybylski GJ, Sharan AD. Single-stage autogenous bone grafting and internal fixation in the surgical management of pyogenic discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis. J Neurosurg 2001;94: Rath SA, Neff U, Schneider O, Richter HP. Neurosurgical management of thoracic and lumbar vertebral osteomyelitis and discitis in adults: a review of 43 consecutive surgically treated patients. Neurosurgery 1996;38: Frankel HL, Hancock DO, Hyslop G, et al. The value of postural reduction in the initial management of the closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. Paraplegia 1969;7: Lee CK, Vessa P, Lee JK. Chronic disabling low back pain syndrome caused by internal disc derangement: the results of disc excision and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 1995;20: Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KW, Cauchoix J, McIvor G. Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop 1974;99: Leung PC. Complication in the first 40 cases of microdiscectomy. J Spinal Disord 1988;1: Lindholm TS, Pylkkanen P. Discitis following removal of intervertebral disc. Spine 1982;7: Fraser RD, Osti OL, Vernon-Roberts B. Iatrogenic discitis: the role of intravenous antibiotics in prevention and treatment. Spine 1989;14: Fukuta S, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, et al. Two-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for pyogenic and tuberculotic spondylitis. Spine 2003;28: Ha KY, Kim YH. Postoperative spondylitis after posterior lumbar interbody fusion using cages. Eur Spine J 2004;13: Eysel P, Hopf C, Vogel I, Rompe JD. Primary stable anterior instrumentation or dorsoventral spondylodesis in spondylodiscitis?: results of a comparative study. Eur Spine J 1997;6: Costerton JW, Irvin RT, Cheng KJ. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Ann Rev Microbiol 1981;35: Oga M, Arizono T, Takasita M, Sugioka Y. Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis: clinical and biological study. Spine 1993; 18: THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
For pyogenic spondylitis, conservative management
 SPINE Volume 41, Number 17, pp E1022 E1029 ß 2016 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved CLINICAL CASE SERIES Posterior Only Approach for Lumbar Pyogenic Spondylitis With Short Instrumentation
SPINE Volume 41, Number 17, pp E1022 E1029 ß 2016 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved CLINICAL CASE SERIES Posterior Only Approach for Lumbar Pyogenic Spondylitis With Short Instrumentation
Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion and Posterior Instrumentation
 Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2003;12:92 96 DOI: 10.1159/000069113 Received: April 21, 2002 Revised: August 3, 2002 Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion
Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2003;12:92 96 DOI: 10.1159/000069113 Received: April 21, 2002 Revised: August 3, 2002 Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion
Pyogenic spinal infection can be thought of as a
 Case Report 651 Pyogenic Spondylitis Presenting with Skip Lesions Po-Liang Lai, MD; Hsieh-Shong Leu 1, MD MSc; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Wen-Jer Chen, MD; Lih-Huei Chen, MD We report on a 65-year-old man who
Case Report 651 Pyogenic Spondylitis Presenting with Skip Lesions Po-Liang Lai, MD; Hsieh-Shong Leu 1, MD MSc; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Wen-Jer Chen, MD; Lih-Huei Chen, MD We report on a 65-year-old man who
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture: Severe Canal Compromise but Neurologically Intact Cases
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
In the adult population, vertebral discitis and osteomyelitis. Posterior fixation without debridement for vertebral body osteomyelitis and discitis
 Posterior fixation without debridement for vertebral body osteomyelitis and discitis Neurosurg Focus 37 (2):E6, 2014 AANS, 2014 Ahmed S. Mohamed, M.D., 1 Jung Yoo, M.D., 1 Robert Hart, M.D., 1 Brian T.
Posterior fixation without debridement for vertebral body osteomyelitis and discitis Neurosurg Focus 37 (2):E6, 2014 AANS, 2014 Ahmed S. Mohamed, M.D., 1 Jung Yoo, M.D., 1 Robert Hart, M.D., 1 Brian T.
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis
 Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
Surgical outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar lesions in rheumatoid arthritis Fujiwara H*, Kaito T**, Makino T**, Ishii T*, Yonenobu K*** Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, *National
Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity. Department of Spine, General Hospital of Lanzhou Command, Gansu, China
 Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit
 Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2016 Sep;23(3): Originally published online September 30, 2016;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Multifocal Extensive Spinal Tuberculosis Accompanying Isolated Involvement of Posterior Elements - A Case Report - Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Young
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Multifocal Extensive Spinal Tuberculosis Accompanying Isolated Involvement of Posterior Elements - A Case Report - Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Young
POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS IN OPERATED CASES OF PYOGENIC SPONDYLODISCITIS
 Original Article Orthopaedics POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS IN OPERATED CASES OF PYOGENIC SPONDYLODISCITIS Ravikumar T V 1, Shivprasad M S 2, Yashavatha Kumar 1, Vinay Jain K 3, Mahesh 1 1 -Assistant Professor,
Original Article Orthopaedics POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS IN OPERATED CASES OF PYOGENIC SPONDYLODISCITIS Ravikumar T V 1, Shivprasad M S 2, Yashavatha Kumar 1, Vinay Jain K 3, Mahesh 1 1 -Assistant Professor,
Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up
 Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up Janek Frantzén M.D., Neurosurgeon Turku University Hospital, Finland ROME SPINE 2011 7.12.2011 1 Clinical Development
Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up Janek Frantzén M.D., Neurosurgeon Turku University Hospital, Finland ROME SPINE 2011 7.12.2011 1 Clinical Development
Serum C-reactive protein levels correlate with clinical response in patients treated with antibiotics for wound infections after spinal surgery
 The Spine Journal 6 (2006) 311 315 Serum C-reactive protein levels correlate with clinical response in patients treated with antibiotics for wound infections after spinal surgery Mustafa H. Khan, MD a,
The Spine Journal 6 (2006) 311 315 Serum C-reactive protein levels correlate with clinical response in patients treated with antibiotics for wound infections after spinal surgery Mustafa H. Khan, MD a,
ASJ. Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular Decompression and Instrumented Fusion in Thoracic and Thoracolumbar Tuberculosis. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(1):31-36 Transpedicular decompression https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.31 in potts spine Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(1):31-36 Transpedicular decompression https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.31 in potts spine Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular
Increased Fusion Rates With Cervical Plating for Two- Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
 Increased Fusion Rates With Cervical Plating for Two- Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion SPINE Volume 25, Number 1, pp 41 45 2000, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Jeffrey C. Wang, MD, Paul
Increased Fusion Rates With Cervical Plating for Two- Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion SPINE Volume 25, Number 1, pp 41 45 2000, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Jeffrey C. Wang, MD, Paul
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis Obaid-ur-Rahman, Saleem Ahmad and Tayyab Hussain ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate and compare the effectiveness of the modified Hong
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis Obaid-ur-Rahman, Saleem Ahmad and Tayyab Hussain ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate and compare the effectiveness of the modified Hong
Treatment Of Spondylodiscitis, Epidural Abscess And Spondylitis A Retrospective Study Of 20 Cases With Exclusion Of TB Cases
 BMH Med. J. 2019;6(1):4-12. Research Article Treatment Of Spondylodiscitis, Epidural Abscess And Spondylitis A Retrospective Study Of 20 Cases With Exclusion Of TB Cases Suresh S Pillai 1, Arunkumar C
BMH Med. J. 2019;6(1):4-12. Research Article Treatment Of Spondylodiscitis, Epidural Abscess And Spondylitis A Retrospective Study Of 20 Cases With Exclusion Of TB Cases Suresh S Pillai 1, Arunkumar C
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body lesions
 Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Anterior Versus Posterior Fixation for the Treatment of Lumbar Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis
 Anterior Versus Posterior Fixation for the Treatment of Lumbar Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis Meng Si, MD; Zhi-ping Yang, MD; Zhen-feng Li, MD; Qiang Yang, MD; Jian-min Li, MD abstract Full article available
Anterior Versus Posterior Fixation for the Treatment of Lumbar Pyogenic Vertebral Osteomyelitis Meng Si, MD; Zhi-ping Yang, MD; Zhen-feng Li, MD; Qiang Yang, MD; Jian-min Li, MD abstract Full article available
SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS
 STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
INTRODUCTION.
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
Interbody fusion is the most reliable fusion technique
 Original Article 170 Clinical Results of a Single Central Interbody Fusion Cage and Transpedicle Screws Fixation for Recurrent Herniated Lumbar Disc and Low-Grade Spondylolisthesis Kuo-Feng Huang, MD;
Original Article 170 Clinical Results of a Single Central Interbody Fusion Cage and Transpedicle Screws Fixation for Recurrent Herniated Lumbar Disc and Low-Grade Spondylolisthesis Kuo-Feng Huang, MD;
Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 1(Suppl 2): 79-85 Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis E. POLA, B. ROSSI, L.A. NASTO, D. COLANGELO, C.A. LOGROSCINO Division
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 1(Suppl 2): 79-85 Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis E. POLA, B. ROSSI, L.A. NASTO, D. COLANGELO, C.A. LOGROSCINO Division
Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach. Travios. Surgical Technique
 Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach Travios Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach Travios Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage posterior surgery: a case report
 Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
1105 two (2) vertebrae... 1, add on per additional vertebra
 SPINE STAGE OPERATIONS Staged operations shall be paid at 100% for the first stage and 85% for the second stage. Where the second stage pays a higher fee 100% shall be paid and the first stage shall be
SPINE STAGE OPERATIONS Staged operations shall be paid at 100% for the first stage and 85% for the second stage. Where the second stage pays a higher fee 100% shall be paid and the first stage shall be
Late Infection of Spinal Instrumentation
 Abstract Late Infection of Spinal Instrumentation Jae-Ik Shim, M.D., Taik-Seon Kim, M.D., Sung-Jong Lee, M.D., Suk-Ha Lee, M.D., Dong-Ki Lee, M.D., Yoen-Sik Yu, M.D., Yun-Yeup Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic
Abstract Late Infection of Spinal Instrumentation Jae-Ik Shim, M.D., Taik-Seon Kim, M.D., Sung-Jong Lee, M.D., Suk-Ha Lee, M.D., Dong-Ki Lee, M.D., Yoen-Sik Yu, M.D., Yun-Yeup Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic
A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint
 J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation With or Without Posterolateral Fusion. Ahmed Zaater, MD, Alaa Azzazi, MD, Sameh Sakr, MD, and Ahmed Elsayed, MD
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation With or Without Posterolateral Fusion Ahmed Zaater, MD, Alaa Azzazi, MD, Sameh Sakr, MD, and Ahmed Elsayed, MD Study Design: A prospective study assessing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation With or Without Posterolateral Fusion Ahmed Zaater, MD, Alaa Azzazi, MD, Sameh Sakr, MD, and Ahmed Elsayed, MD Study Design: A prospective study assessing
Transpedicular Curettage and Drainage of Infective Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Technique and Clinical Results
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:200-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.200 Transpedicular Curettage and Drainage of Infective Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Technique and Clinical
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:200-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.200 Transpedicular Curettage and Drainage of Infective Lumbar Spondylodiscitis: Technique and Clinical
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Synex System TECHNIQUE GUIDE. An expandable vertebral body replacement device
 Synex System TECHNIQUE GUIDE An expandable vertebral body replacement device Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO ASIF Synex System Overview The Synex
Synex System TECHNIQUE GUIDE An expandable vertebral body replacement device Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO ASIF Synex System Overview The Synex
Study of functional outcomes of surgical treatment of tuberculosis of spine with debridement and spinal fixation
 2017; 3(1): 389-394 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 389-394 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 17-12-2016 Dr. Pallav Patel MS Ortho Poojan Orthopaedic Hospital Himmatnagar, Gujarat,
2017; 3(1): 389-394 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 389-394 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 17-12-2016 Dr. Pallav Patel MS Ortho Poojan Orthopaedic Hospital Himmatnagar, Gujarat,
Comparison of clinical, radiological and functional outcome of short segment V/S long segment posterior fixation of tuberculosis of spine
 2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING
 CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
Anterior cervical diskectomy icd 10 procedure code
 Home Anterior cervical diskectomy icd 10 procedure code Access to discounts at hundreds of restaurants, travel destinations, retail stores, and service providers. AAPC members also have opportunities to
Home Anterior cervical diskectomy icd 10 procedure code Access to discounts at hundreds of restaurants, travel destinations, retail stores, and service providers. AAPC members also have opportunities to
Preliminary Report of Instrumentation in Tuberculous Lumbosacral Spine
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1411.004 Preliminary Report of Instrumentation in Tuberculous Lumbosacral Spine, MRCS Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital, Yangon, Myanmar ABSTRACT
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1411.004 Preliminary Report of Instrumentation in Tuberculous Lumbosacral Spine, MRCS Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital, Yangon, Myanmar ABSTRACT
To study the outcomes of posterior decompression and fixation of tuberculosis of dorsolumbar spine
 2017; 3(3): 691-695 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 691-695 2017 IJOS wwworthopapercom Received: 15-05-2017 Accepted: 16-06-2017 Dr Manish Shah Assistant Professor, Department of Dr Kushal Suthar Dr Ravindra
2017; 3(3): 691-695 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 691-695 2017 IJOS wwworthopapercom Received: 15-05-2017 Accepted: 16-06-2017 Dr Manish Shah Assistant Professor, Department of Dr Kushal Suthar Dr Ravindra
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
PART III IN HOSPITAL ON CALL ANESTHESIA COVERAGE
 Anesthesia g) A consultation may not be claimed where the patient is referred to the anesthetist for the sole purpose of providing post-operative Patient Controlled Analgesia. h) Tariff 8406 may not be
Anesthesia g) A consultation may not be claimed where the patient is referred to the anesthetist for the sole purpose of providing post-operative Patient Controlled Analgesia. h) Tariff 8406 may not be
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:91-96 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.91 Perioperative Surgical Complications and Learning Curve Associated with Minimally Invasive Transforaminal
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:91-96 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.91 Perioperative Surgical Complications and Learning Curve Associated with Minimally Invasive Transforaminal
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Apache Cervical Interbody Fusion Device. Surgical Technique. Page of 13. LC-005 Rev F
 LC-005 Rev F Apache Cervical Interbody Fusion Device Page of 13 Surgical Technique INDICATIONS: When used as an intervertebral body fusion device, the Genesys Spine Interbody Fusion System is indicated
LC-005 Rev F Apache Cervical Interbody Fusion Device Page of 13 Surgical Technique INDICATIONS: When used as an intervertebral body fusion device, the Genesys Spine Interbody Fusion System is indicated
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberclous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis in Atypical Cases
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, pp 75~79, 2007 Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberclous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis in Atypical Cases Jae Sung Ahn, June Kyu Lee Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, pp 75~79, 2007 Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberclous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis in Atypical Cases Jae Sung Ahn, June Kyu Lee Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
ELY ASHKENAZI Israel Spine Center at Assuta Hospital Tel Aviv, Israel
 nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
 Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws
 Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Single stage posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal and lumbar spines
 Original Article interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal Pandey BK 1, Sangondimath GM 2, Chhabra HS 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu,
Original Article interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal Pandey BK 1, Sangondimath GM 2, Chhabra HS 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu,
Bone Cement-Augmented Percutaneous Short Segment Fixation : An Effective Treatment for Kummell s Disease?
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study.
 ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
SURGICAL INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CAPENER TECHNIQUE (COSTO-TRANSVERSECTOMY).
 SURGICAL INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CAPENER TECHNIQUE (COSTO-TRANSVERSECTOMY). TRANSVERSECTOMY). Patricia Álvarez González, Javier Pizones Arce, Felisa SánchezS nchez-mariscal, Lorenzo ZúñZ úñiga
SURGICAL INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CAPENER TECHNIQUE (COSTO-TRANSVERSECTOMY). TRANSVERSECTOMY). Patricia Álvarez González, Javier Pizones Arce, Felisa SánchezS nchez-mariscal, Lorenzo ZúñZ úñiga
PATIENT: DOB: TODAY S DATE:
 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand this material. I also understand that if certain sections are not
1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand this material. I also understand that if certain sections are not
Case Report Two-year follow-up results of C2/3 Prestige-LP cervical disc replacement: first report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(4):7349-7353 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0018962 Case Report Two-year follow-up results of C2/3 Prestige-LP cervical disc replacement: first report Yi Yang 1, Mengying
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(4):7349-7353 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0018962 Case Report Two-year follow-up results of C2/3 Prestige-LP cervical disc replacement: first report Yi Yang 1, Mengying
Single-stage debridement and instrumentation for pyogenic spinal infections
 Neurosurg Focus 17 (6):E5, 2004 Single-stage debridement and instrumentation for pyogenic spinal infections ALFRED T. OGDEN, M.D., AND MICHAEL G. KAISER, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, Columbia
Neurosurg Focus 17 (6):E5, 2004 Single-stage debridement and instrumentation for pyogenic spinal infections ALFRED T. OGDEN, M.D., AND MICHAEL G. KAISER, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, Columbia
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Surgical Technique INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE
 R INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE NEOCIF IMPLANTS NEOCIF is an implant designed to make anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) easier and to remove the need for structural autologous graft. The cage is made
R INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE NEOCIF IMPLANTS NEOCIF is an implant designed to make anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) easier and to remove the need for structural autologous graft. The cage is made
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2014 Jun;21(2): Originally published online June 30, 2014;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Spinal Epidural Abscess and Psoas Abscess Combined with Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Following Vertebroplasty - A Case Report - Jin Sung Park, M.D., Dong Hee Kim,
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Spinal Epidural Abscess and Psoas Abscess Combined with Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Following Vertebroplasty - A Case Report - Jin Sung Park, M.D., Dong Hee Kim,
REFERENCE DOCTOR Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture
 779 Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture T. M. H. Chakera 1 George Bedbrook C. M. Bradley3 We reviewed the records of 8 patients with 30 burst-dispersion spinal
779 Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture T. M. H. Chakera 1 George Bedbrook C. M. Bradley3 We reviewed the records of 8 patients with 30 burst-dispersion spinal
Extended indications of percutaneous endoscopic lavage and drainage for the treatment of lumbar infectious spondylitis
 Eur Spine J (2014) 23:846 853 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3157-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extended indications of percutaneous endoscopic lavage and drainage for the treatment of lumbar infectious spondylitis Shih-Chieh
Eur Spine J (2014) 23:846 853 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3157-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extended indications of percutaneous endoscopic lavage and drainage for the treatment of lumbar infectious spondylitis Shih-Chieh
Surgical Technique. Apache Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
 Surgical Technique Apache Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion 2 Table of Contents Page Preoperative Planning 4 Patient Positioning 4 Disc and Endplate Preparation 4 Distraction/Size Selection 5 Implantation
Surgical Technique Apache Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion 2 Table of Contents Page Preoperative Planning 4 Patient Positioning 4 Disc and Endplate Preparation 4 Distraction/Size Selection 5 Implantation
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Anterior cervical interbody fusion with radiolucent carbon fiber cages : clinical and radiological results
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 604-609 ORIGINAL STUDY Anterior cervical interbody fusion with radiolucent carbon fiber cages : clinical and radiological results Ibo VAN DER HAVEN, Piet J. M. VAN LOON, Ronald
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 604-609 ORIGINAL STUDY Anterior cervical interbody fusion with radiolucent carbon fiber cages : clinical and radiological results Ibo VAN DER HAVEN, Piet J. M. VAN LOON, Ronald
vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in
 e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): 1448-1452 Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis. Jiawen Wu 1, Juanjuan Wang 2, Ming
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): 1448-1452 Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis. Jiawen Wu 1, Juanjuan Wang 2, Ming
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Topic: Percutaneous Axial Anterior Lumbar Fusion Date of Origin: June Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: June 2013
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Percutaneous Axial Anterior Lumbar Fusion Date of Origin: June 2007 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: June 2013 Policy No: 157 Effective Date: August 1, 2013 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Percutaneous Axial Anterior Lumbar Fusion Date of Origin: June 2007 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: June 2013 Policy No: 157 Effective Date: August 1, 2013 IMPORTANT REMINDER
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia with Anterior Spinal Decompression & Stabilisation with Rib Graft Alone
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2016), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2016), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia
ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc disease: Is there a difference at 12 months?
 Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
ASJ. Percutaneous Drainage Combined with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Pyogenic Spondylitis with Iliopsoas Abscess. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):253-259 Pyogenic spondylitis http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.253 with iliopsoas abscess 253 Percutaneous Drainage Combined
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):253-259 Pyogenic spondylitis http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.253 with iliopsoas abscess 253 Percutaneous Drainage Combined
Back Pain Policies Summary
 Back Pain Policies Summary These policies are part of the wider project, Reviewing local health policies, which is reviewing and updating more than 100 policies, of which back pain are part of. This review
Back Pain Policies Summary These policies are part of the wider project, Reviewing local health policies, which is reviewing and updating more than 100 policies, of which back pain are part of. This review
Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis
 29 29 33 Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis Author Institution Sreedharan Namboothiri Kovai Medical Center and Hospitals, Coimbatore,
29 29 33 Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis Author Institution Sreedharan Namboothiri Kovai Medical Center and Hospitals, Coimbatore,
Although unstable thoracolumbar injuries are a common
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior-Only Stabilization of Three-Column Thoracolumbar Injuries Rick C. Sasso, MD, Natalie M. Best, BS, Thomas M. Reilly, MD, and Robert A. McGuire, Jr., MD Objective: The optimal treatment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior-Only Stabilization of Three-Column Thoracolumbar Injuries Rick C. Sasso, MD, Natalie M. Best, BS, Thomas M. Reilly, MD, and Robert A. McGuire, Jr., MD Objective: The optimal treatment
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
Posterior. Lumbar Fusion. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Yongchun Zhou 1, Weiwei Li 1*, Jun Liu 1, Liqun Gong 1 and Jing Luo 2*
 Zhou et al. BMC Surgery (2018) 18:71 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0405-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of single posterior debridement, bone grafting and instrumentation with single-stage
Zhou et al. BMC Surgery (2018) 18:71 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0405-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of single posterior debridement, bone grafting and instrumentation with single-stage
Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with and without Instrumentation
 Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.18 Research Article Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with without Instrumentation ABSTRACT Sanjay
Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.18 Research Article Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with without Instrumentation ABSTRACT Sanjay
