FirstRanker.com. [KT 541] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4062
|
|
|
- Ronald Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [KT 541] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and laboratory diagnosis of Echinococcus granulsosus. 2. Classify Herpes Viruses. Describe the morphology, pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of acute Herpes Simplex virus. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Morphology and laboratory diagnosis of kalaazar. 2. Laboratory diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection. 3. Differences between ortho myxo and Paramyxo viruses. 4. Sporotrichosis. 5. Cryptosporidium parvum. 6. Coxsachie Viruses. 7. Universal Precautions. 8. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. 9. Cryptococcus neoformans. 10. Microfilaria. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Vaccines against polimyelitis. 2. Four arbovirus infections prevalent in India. 3. Delta Hepatitis agent. 4. Draw the ovum of Enterobius vermicularis. 5. Two parasites infecting the eye. 6. Name two parasites causing (a) Anemia and (b) Visual larva migrans. 7. Chlamydospore. 8. Name two fungi causing occulomycosis. 9. Enumerate four dermatophytes. 10. Four organisms causing Mycetoma.
2 [KU 541] FEBRUARY 2009 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Classify Rhabdo virus. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and phophylaxis of rabies virus. 2. Classify nematodes. Describe the life cycle and laboratory diagnosis of ankylostoma duodenale. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Laboratory diagnosis of acute pyogenic meningitis. 2. Japanese B encephalitis. 3. Oppurtunistic fungi. 4. Nosocomial infection. 5. Pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of Hydatid disease. 6. Methods of HIV transmission. 7. Exo erythrocytic schizogony. 8. Laboratory diagnosis of fungal infections. 9. Viral Haemorrhagic fevers. 10. Varicella zoster. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Name four DNA viruses. 2. Draw and label a bacteriophage. 3. Define definitive host. Give two examples. 4. Otomycosis. 5. Trichomonas Vaginalis. 6. Mention four species of candida. 7. Complications of ascariasis (roundworm infestation). 8. Define an intermediate host. 9. Mention three antifungal agents. 10. Complication of dengue virus.
3 [KV 541] AUGUST 2009 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Name the viruses infecting the liver. Write the morphology, pathogenesis lab diagnosis and prophylaxis of hepatitis B virus. 2. Name the Haemoflagellates. Write the morphology, life cycle, clinical features and lab diagnosis of kala azar. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Viral multiplication. 2. Mycetoma. 3. Interferons. 4. Chikungunya virus. 5. Free living amoebae. 6. Life cycle of Balantidium coli. 7. Life cycle of taenia solium. 8. Stool examination of parasitic infections. 9. Candidiasis. 10. Dermatophytes. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Morphology of HIV virus. 2. Von magnus phenomenon. 3. Write four differences between salk and sabin vaccines. 4. Paul Bunnel test. 5. Draw the morphology of penicillium. 6. Name two pigment producing fungi. 7. Life cycle of taenia saginata. 8. Draw the diagram of ascaris egg. 9. N.N.N. Medium (Novy, Bicolle, Mcneal). 10. Name four oppurtunistic parasitic infections in AIDS. ******
4 [KW 541] FEBRUARY 2010 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the lifecycle, pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis Ascaris lumbricoides. 2. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and prophylaxis of poliomyelitis. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Extra intestinal amoebiasis. 2. Complications produced by plasmodium falciparum. 3. Larva migrans. 4. Casonis test. 5. Diagnosis and prophylaxis of H1N1 infection. 6. Rhinosporidiosis. 7. Prions. 8. Interferon. 9. Dimorphic fungi. 10. Antigenic drift. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Name four fungi causing opportunistic mycosis. 2. Fungi causing superficial mycosis. 3. Classify inclusion bodies. 4. Universal precautions. 5. Draw the diagram of microfilaria. 6. Name four parasites causing CNS infection. 7. Name the concentration methods of stool EXAMINATION 8. Kopliks spots. 9. Name the live viral vaccines. 10. Cryptosporidium.
5 [KX 541] AUGUST 2010 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Enumerate parasites causing Anemia. Describe in detail, morphology, life cycle and laboratory diagnosis of Anckylostoma duodenale. 2. Describe the morphology, pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of influenza virus. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Cytopathic effect. 2. Subcutaneous mycosis. 3. Dengue virus. 4. Life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica. 5. Dermatophytes. 6. Cryptococcus neoformans. 7. Toxoplasma gondii. 8. Cysticercus Cellulosae. 9. Life cycle of Ascaris Lumbricoidis. 10. Lab Diagnosis of Malaria. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Three methods of cultivation of viruses. 2. Viral interferons. 3. Hepatitis markers. 4. Complication of neural vaccine. 5. Bile-Stained eggs. 6. Germ Tube Technique. 7. Diagram of Trichomonas Vaginalis. 8. MMR. 9. Life cycle of Balantidium coli. 10. Visceral larva migrans.
6 [KY 541] FEBRUARY 2011 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Name the various haemoflagellates. Discuss the life cycle of Leishmania Donovani and describe the laboratory diagnosis of Kala-azar. 2. Discuss the various methods for isolation of viruses in the laboratory. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Bacteriophage. 2. Prophylaxis of rabies. 3. Oncogenes. 4. Laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infection. 5. Superficial mycoses. 6. Antibiogram. 7. Dimorphic fungi. 8. Cryptosporidium Parvum. 9. Examination of faeces for parasitic infection. 10. Classification of Nematodes according to the habitat of adult worms. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Bachman Intradermal test. 2. Oviparous nematodes. 3. Free living amoebae. 4. Deltavirus. 5. Orf. 6. Live viral vaccines. 7. Germ tube test. 8. Otomycosis. 9. RT-PCR. 10. Infection control policy.
7 [KZ 541] AUGUST 2011 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : Three hours I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the morphology, pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of Hepatitis B virus. 2. Enumerate the intestinal nematodes of medical importance. Describe the morphology, life cycle and laboratory diagnosis of Ascaris lumbricoides. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Viral cell cultures. 2. Measles virus. 3. Rota virus. 4. Rhinosporidiosis. 5. Cysticercosis. 6. Concentration methods for stool EXAMINATION 7. Primary anaerobic meningo encephalitis. 8. Laboratory diagnosis of HIV infection. 9. Opportunistic fungal infections. 10. Bacteriology of milk. III. Short Answer questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Name four dimorphic fungi. 2. Name the medically important trematodes. 3. Name the opportunistic viral infections in AIDS. 4. Name the killed viral vaccines. 5. Mention the diseases caused by Coxsackie virus. 6. Diagram of Balantidium coli. 7. Name four medically important candida. 8. Name the parasites causing anaemia. 9. Ectothrix and Endothrix infection of hair. 10. Name the virus causing conjunctivitis. ******
8 [LA 541] FEBRUARY 2012 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : 180 Minutes I. Elaborate on : Answer ALL questions in the same order. Maximum: 40 Marks 1. Classify nematodes. Describe the life cycle and laboratory diagnosis of hookworm. (10 x 1 = 10) 2. Describe the pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis and prophylaxis of poliomyelitis. (5 x 1 = 5) II. Write notes on : (10 x 1.5 = 15) 1. Dimorphic fungi 2. Varicella zoster 3. Laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infections 4. Dermatophytes 5. Free living amoebae 6. Extra intestinal amoebiasis 7. Prions 8. Universal precautions 9. Antigenic drift 10. Dengue virus. III. Short Answers on : (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Classify inclusion bodies 2. Mention three antifungal agents 3. Live viral vaccine 4. Name two pigment producing fungi 5. Name two parasites infecting the eye 6. Germ tube test 7. Hepatitis markers 8. Name three blood borne viruses 9. Name the concentration methods of stool examination 10. Name four bile stained ova.
9 [LB 541] AUGUST 2012 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : 180 Minutes Maximum: 40 Marks I. Elaborate on: Pages Time Marks (Max.) (Max.) (Max.) 1.Classify filarial worms. Write in detail about the life cycle, pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of Wuchereria bancrofti Name the hepatotrophic viruses. Write in detail about the pahogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of hepatitis B virus II. Write notes on: 1. Viral haemagglutinin Polio vaccine Cytomegalovirus Chromomycosis Mycotic keratitis Giardiasis Polymerase chain reaction Role of vectors in transmission of infectious agents Normal microbial flora Trichinellosis III. Short Answers: 1. Viral plaques Name four oncogenic viruses Name four viruses transmitted through mosquito Ectothrix Classify fungi based on morphology Name four dimorphic fungi Diagnosis of congenital HIV infection Fungal spores Name four parasites do not require intermediate host Name two viviparous nematode
10 [LC 541] FEBRUARY 2013 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : 180 Minutes I. Elaborate on: (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Classify Arbo viruses. Discuss briefly on pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of Dengue fever. 2. Discuss briefly on laboratory diagnosis of Leishmaniasis. II. Write notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Viral inclusion bodies. 2. Recent swine flu pandemic 3. Lab diagnosis of Hepatitis B infection 4. Viral gastroenteritis 5. Extra intestinal Amoebiasis 6. Visceral larva migrans 7. Bile stained eggs 8. Lab diagnosis of Filariasis. 9. Pneumocystis jirovecii 10. Superficial mycoses III. Short Answers on: (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Name two contraindications for MMR vaccine. 2. Name the transmitting agent of Yellow fever. 3. What is Dane particle? 4. Name two human slow viral infections. 5. Name a parasite transmitted by sexual contact. 6. Name the skin test used for the diagnosis of Hydatid cyst. 7. Name the definitive host of Wuchereria bancrofti. 8. Name the causative agent of cerebral malaria. 9. Name the mycotoxin produced by Aspergillus flavus. 10. Name two antifungal agents.
11 [LD 541] AUGUST 2013 Sub. Code : 4062 Time : 180 Minutes Maximum: 40 Marks I. Elaborate on: (2 x 7.5 = 15) 1. Discuss briefly on Immunoprophylaxis of viral diseases. 2. Describe the Life cycle of Drucunculus medinensis. II. Write notes on: (10 x 1.5 = 15) 1. Dermatophytes 2. Otomycosis 3. Viral haemorrhagic fevers. 4. Cytopathic effects 5. Lab diagnosis of Hepatitis C 6. Herpes zoster 7. Role of cyclops in parasitic diseases. 8. Viviparous parasites. 9. Free living amoeba. 10. Significant bacteriuria. III. Short Answers on: (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Name two opportunistic diseases associated with HIV. 2. What is the normal range of CD4 count? 3. Name the transmitting agent of Yellow fever. 4. What are Hypnozoites? 5. Name two hepatitis viruses associated with cirrhosis. 6. Name two media used for fungal culture. 7. Name the largest and the smallest tapeworms infecting humans. 8. Name the infective stage of Ancylostoma duodenale. 9. What is the ph of Sabourauds dextrose agar? 10. What is swimmers itch?
12 [LE 541] FEBRUARY 2014 Sub. Code: 4062 SECOND YEAR MBBS DEGREE EXAMINATION Paper IV VIROLOGY, MYCOLOGY, PARASITOLOGY Q. P. Code: Time : 180 Minutes Maximum: 40 Marks I. Elaborate on: (2 x 7.5 = 15) 1. List out the malarial parasites infecting man. Describe the complications and Laboratory diagnosis of Malignant tertian Malaria. 2. Discuss briefly on viral vaccines. II. Write Notes on: (10 x 1.5 = 15) 1. Interferons types and importance. 2. Pathogenesis and complications of Measles. 3. Viral haemorrhagic fevers. 4. Suckling mice Definition & uses in virology. 5. Role of Cyclops in parasitic diseases. 6. Larval forms of Diphyllobothrium latum. 7. Cutaneous Larva migrans. 8. Viviparous parasites. 9. Dimorphic fungi. 10. Significant bacteriuria. III. Short Answers on: (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Name two Epstein-barr virus associated malignancies. 2. What is antigenic shift? 3. Name the transmitting agent of Chikungunya. 4. Name two hepatitis viruses producing chronic infection. 5. Name two parasitic diseases in which man is the intermediate host. 6. Name two opportunistic amoebae. 7. Name two bile stained parasitic eggs. 8. Name the infective stage of Ancylostoma duodenale. 9. What is the ph of Sabourauds dextrose agar? 10. What is the use of Casoni test?
13 [LF 541] AUGUST 2014 Sub. Code: 4062 Time: Three Hours SECOND YEAR M.B.B.S DEGREE EXAMINATION Paper IV VIROLOGY, MYCOLOGY, PARASITOLOGY Q. P. Code: Maximum: 40 Marks Answer ALL questions in the same order. I. Elaborate on: (2 x 7.5 = 15) 1. Classify Herpes viruses. Discuss the Laboratory diagnosis of chicken pox. 2. Discuss the pathogenesis and laboratory diagnosis of Kala Azar. II. Write Notes on: (10 x 1.5 = 15) 1. Tinea versicolor 2. Extraintestinal amoebiasis 3. Tissue culture in viruses 4. Ancylostoma duodenale 5. Prophylaxis of Influenza 6. Toxoplasma gondii 7. Mycetoma 8. Bacteriophage 9. Sporotrichosis 10. Laboratory diagnosis of poliomyelitis. III. Short Answers on: (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Name the parasites that cause anemia. Mention the type of anemia caused. 2. What are free living amoebae? Name them 3. What are the media used for fungal cultivation? 4. Name the most common bacteria causing nosocomial infections. 5. What is germ tube test? 6. What are calabar swellings? Which parasite causes this lesion? 7. What are the complications of Ascaris infection? 8. What is cysticercus cellulosae? 9. Name the parasites that produce operculated eggs. 10. What is benign tertian malaria? Name the parasite that causes it.
14 [LG 541] FEBRUARY 2015 Sub.Code :4062 SECOND YEAR M.B.B.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION PAPER IV VIROLOGY, MYCOLOGY, PARASITOLOGY Time: Three hours Q.P. Code: Answer All Questions Maximum : 40 Marks I. Elaborate on: (1 x 10 = 10) 1. Enumerate the viruses transmitted by blood transfusion. Write in detail about Hepatitis B virus and its Prophylaxis. II. Write notes on: (4 x 5 = 20) 1. Cutaneous and Genital warts 2. Rhinovirus Infection 3. Coccidioidomycosis 4. Microfilaria III. Short answers on: (5 x 2 = 10) 1. Define Bacteremia, Septicemia, Pyemia and Endotoxemia 2. How can the Virus be Isolated in the Laboratory? 3. Eijkman test 4. Superficial Mycoses 5. Balantidium Coli *
15 [LH 541] AUGUST 2015 Sub. Code: 4062 PAPER IV VIROLOGY, MYCOLOGY, PARASITOLOGY Q.P. Code: Time : Three Hours Maximum : 40 marks Answer ALL questions I. Elaborate: (1 x 10 = 10) 1. Write an essay on Emerging and Reemerging Infections and the factors responsible for this. II. Write notes on : (4 x 5 = 20) 1. Human Herpes Virus. 2. Prophylaxis against Poliomyelitis. 3. Japanese encephalitis. 4. Laboratory diagnosis of Malaria. III. Short answers on : (5 x 2 = 10) 1. Discuss various methods of detecting viral growth in cell culture. 2. Von Magnus Phenomenon. 3. Creeping eruption. 4. Malignancies associated with Epstein-Baar Virus. 5. Phage Typing.
February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705
![February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 February [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705](/thumbs/80/81975511.jpg) February 2009 [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks Answer All questions. I. Essays: (2x15=30) 1. Define hypersensitivity. Classify Hypersensitivity. Discuss in
February 2009 [KU 1014] Sub. Code: 4705 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks Answer All questions. I. Essays: (2x15=30) 1. Define hypersensitivity. Classify Hypersensitivity. Discuss in
1. Parasitology Protozoa 4
 Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
Contents 1. Parasitology 1 Host Parasite Relationship 2 Mode of Transmission 2 2. Protozoa 4 Classification 4 Reproduction 5 Immunity 5 Pathogenesis 6 Laboratory Diagnosis 6 Treatment 8 Entamoeba 8 Classification
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE. 1. Type of cell. 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE
 INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
INTRODUCTION TO PARASITOLOGY OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE Parasitology is the study of organisms that derive their nourishment from other living things and cause damage. The student will identify the morphology
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
namibia UniVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY
 namibia UniVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACUL TV OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBMES LEVEL: 7 COURSE
namibia UniVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACUL TV OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBMES LEVEL: 7 COURSE
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
स क ष मज व ववज ञ न ववभ ग DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY व.एम.एम.स ए व सफदरज ग अस पत ल VMMC & SAFDARJUNG HOSPITAL नई ददल ल ११००२९ NEW DELHI
 स क ष मज व ववज ञ न ववभ ग DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY व.एम.एम.स ए व सफदरज ग अस पत ल VMMC & SAFDARJUNG HOSPITAL नई ददल ल ११००२९ NEW DELHI 110029 Teaching Schedule for MBBS 4thSemester (January June 2017)
स क ष मज व ववज ञ न ववभ ग DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY व.एम.एम.स ए व सफदरज ग अस पत ल VMMC & SAFDARJUNG HOSPITAL नई ददल ल ११००२९ NEW DELHI 110029 Teaching Schedule for MBBS 4thSemester (January June 2017)
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases
 Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases Abdominal pain Entamoeba histolytica (amebic colitis, liver infection) Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium Intestinal helminths (Ascaris, Strongyloides) Anisakis (symptoms
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Diseases Abdominal pain Entamoeba histolytica (amebic colitis, liver infection) Giardia lamblia Cryptosporidium Intestinal helminths (Ascaris, Strongyloides) Anisakis (symptoms
Lectures. Experiments. General introduction 3. Introduction to Medical Protozoa 0.5. Lobosea (amoebae) 3 3. Flagellates 3 3.
 Teaching outline of Human Parasitology (Use for international students) Department of Human Parasitology Hainan Medical College Teaching Target Human Parasitology is the study of those species of the animal
Teaching outline of Human Parasitology (Use for international students) Department of Human Parasitology Hainan Medical College Teaching Target Human Parasitology is the study of those species of the animal
Bacteriology Virology Mycology Parasitology Immunology Pathology Epidemiology. Microbe alternate terms Germs, microorganisms, pathogens, agents, bugs
 1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM)
 HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory. 11 April 2013
 Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY. lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, hookworm. Human Parasitology (Code: ) Guideline
 HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
HUMAN PARASITOLOGY Human Parasitology (Code:1001021) Guideline I. Course Introduction 128 classes comprise 72 for lecturing, 54 for lab practice, and 2 for self-study. 6.0 credits; 5 th semester II. Lecturing
1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution. 2) know the mechanisms of host immune responses to viral infections
 VIROLOGY A The course aims to provide the student with the cognitive and methodological tools necessary to: 1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution 2) know the
VIROLOGY A The course aims to provide the student with the cognitive and methodological tools necessary to: 1) understand the structure and life cycle of viruses as well as viral evolution 2) know the
MUST KNOW QUESTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY
 MUST KNOW QUESTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY Systemic Bacteriology Chapter 1. Staphylococcus Name various virulence factors ( Enzymes & Toxins) of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA Catalase & Coagulase test Lesions caused
MUST KNOW QUESTIONS IN MICROBIOLOGY Systemic Bacteriology Chapter 1. Staphylococcus Name various virulence factors ( Enzymes & Toxins) of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA Catalase & Coagulase test Lesions caused
virology MCQs 2- A virus commonly transmitted by use of contaminated surgical tools & needles produces a disease called serum hepatitis.
 virology MCQs 1- A virus which causes AIDS is: a- Small pox virus. b- Coxsackie B virus. c- Mumps virus. d- Rubella virus. e- HIV-III virus. 2- A virus commonly transmitted by use of contaminated surgical
virology MCQs 1- A virus which causes AIDS is: a- Small pox virus. b- Coxsackie B virus. c- Mumps virus. d- Rubella virus. e- HIV-III virus. 2- A virus commonly transmitted by use of contaminated surgical
Overview IMPORTANCE CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS
 IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
IMPORTANCE Overview CLASSIFICATION SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROTOZOA WORMS BLOOD PARASITES ARTHROPODS DELUSIONAL PARASITOSIS QUIZZES GROSS - Of 6.6 billion people on Earth, 2.7 billion live on
Pathogens of the Digestive System
 Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN
 PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
Parasitology. Helminthology (Helminths)
 Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
GOYAL BROTHERS PRAKASHAN
 Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? IMPORTANT NOTES 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? IMPORTANT NOTES 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
Microbiology Final. 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea?
 Microbiology Final 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea? - EAEC* 2) Ab toxin A is stand for : - active* 3) Differentiate between staphylococcus and streptococcus : - catalase test* 4) Microsporum
Microbiology Final 1) E.coli that makes acute and chronic diarrhea? - EAEC* 2) Ab toxin A is stand for : - active* 3) Differentiate between staphylococcus and streptococcus : - catalase test* 4) Microsporum
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial disease? (a) Cholera (b) Tuberculosis
Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial disease? (a) Cholera (b) Tuberculosis
CHAPTER AT A GLANCE. Science Class (SA-II)- IX
 13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine)
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
Study Guide. Medical Parasitology. 3 rd. YEAR MEDICINE. Dr. Abdulkader M. D. Tonkal Head of Medical Parasitology department ACADEMIC YEAR
 Study Guide Medical Parasitology 3 rd. YEAR MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 2008 Dr. Abdulkader M. D. Tonkal Head of Medical Parasitology department 1428 ه 27/1 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Table of content I. FACULTY
Study Guide Medical Parasitology 3 rd. YEAR MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 2008 Dr. Abdulkader M. D. Tonkal Head of Medical Parasitology department 1428 ه 27/1 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Table of content I. FACULTY
What infections do returned travellers bring back to Australia?
 + What infections do returned travellers bring back to Australia? Sarah McGuinness (sarah.mcguinness@monash.edu) MBBS, DTMH, MPH&TM, FRACP Infectious Diseases Physician, Alfred Hospital PhD candidate,
+ What infections do returned travellers bring back to Australia? Sarah McGuinness (sarah.mcguinness@monash.edu) MBBS, DTMH, MPH&TM, FRACP Infectious Diseases Physician, Alfred Hospital PhD candidate,
Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan
 Parasitoses Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan Epidemiology for clinicians JMAJ 48(3): 148 154, 2005 Yoshiya SATO Professor, University of the Ryukyus Abstract: The recent profile of parasitic diseases
Parasitoses Recent State of Parasitoses in Japan Epidemiology for clinicians JMAJ 48(3): 148 154, 2005 Yoshiya SATO Professor, University of the Ryukyus Abstract: The recent profile of parasitic diseases
Parasitology lab. ü interdiction
 Parasitology lab ü interdiction "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derived from our primate ancestors and some acquired from the animals we
Parasitology lab ü interdiction "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derived from our primate ancestors and some acquired from the animals we
Protozoans and Helminthes
 Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Protozoans and Helminthes 1 Protozoans 2 3 4 5 6 Worm: Leishmania donovani General Family: Trypanosomes (Blood/tissue flagellates) Larvae or Adult Sketch of dermal, post-visceral kala-azar Life Cycle:
Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia.
 Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Infectious Disease SHORT AND CRISP CRAMMER POINTS
 Infectious Disease SHORT AND CRISP CRAMMER POINTS 1 Reservoir of Important Infectious Disease Reservoir Human Rodents Non Living Disease Epidemic typhus, Dracunculiasis, Ancylostomiasis, Trench fever,
Infectious Disease SHORT AND CRISP CRAMMER POINTS 1 Reservoir of Important Infectious Disease Reservoir Human Rodents Non Living Disease Epidemic typhus, Dracunculiasis, Ancylostomiasis, Trench fever,
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE
 NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
Overview of Microbiology. James D. Dick, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens
 Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
INFECTIOUS DISEASES CONTAGIOUS DISEASES COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites TYPICAL
 APPENDIX 9.1 Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites COMMON FOODBORNE S CAUSED BY BACTERIA Bacillus cereus food poisoning diarrheal Bacillus
APPENDIX 9.1 Enteric infections and common food borne diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, protozoa and parasites COMMON FOODBORNE S CAUSED BY BACTERIA Bacillus cereus food poisoning diarrheal Bacillus
Chapter 38 Viral Infections
 Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester FRIDAY. MICROBIOLOGY Lecture (Head Building) 11:00-12:30
 SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester Lectures -Head Building, Friday 11:00-12:30 Seminars/Practical Lessons-Lab.Room Instutute of Microbiology and Immunology, Friday 13:00-15:30
SUMMER SEMESTER/ II nd ACADEMIC YEAR BACTERIOLOGY 4th semester Lectures -Head Building, Friday 11:00-12:30 Seminars/Practical Lessons-Lab.Room Instutute of Microbiology and Immunology, Friday 13:00-15:30
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MD (MEDICAL PARASITOLOGY) EXAMINATION JANUARY, 2001 PAPER 1
 JANUARY, 2001 Date: 15 th January 2001 Time: 2.00 p.m. -500 p.m. PAPER 1 Answer all five (5) questions Answer each question in a separate book 1. Discuss the underlying principles relating to the use of
JANUARY, 2001 Date: 15 th January 2001 Time: 2.00 p.m. -500 p.m. PAPER 1 Answer all five (5) questions Answer each question in a separate book 1. Discuss the underlying principles relating to the use of
Intestinal Parasites. James Gaensbauer MD, MScPH Fellow, Pediatric Infectious Diseases University of Colorado School of Medicine November 12, 2012
 Intestinal Parasites James Gaensbauer MD, MScPH Fellow, Pediatric Infectious Diseases University of Colorado School of Medicine November 12, 2012 Outline Parasites 101 Global Burden of Disease An Evolutionary
Intestinal Parasites James Gaensbauer MD, MScPH Fellow, Pediatric Infectious Diseases University of Colorado School of Medicine November 12, 2012 Outline Parasites 101 Global Burden of Disease An Evolutionary
-, ~~I. 1. Classify Mycobacteria? Discuss the Laboratory diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis? Add a note on concentration methods = 10
 q A }lajaga:n:~f~vyj]i::;.:t}~~jep! ~AL J-;OI,J,,~iJj:..IXHOSl'ITAL 7 BANGMOEE. DLyARTMENT OF I\UCROBIOLOGY Tn Internal Assessment Examination -,.-----. ~~I 04106/08 Time: ~:1hrs M~x h'i.arks: 100 LO:fH.~
q A }lajaga:n:~f~vyj]i::;.:t}~~jep! ~AL J-;OI,J,,~iJj:..IXHOSl'ITAL 7 BANGMOEE. DLyARTMENT OF I\UCROBIOLOGY Tn Internal Assessment Examination -,.-----. ~~I 04106/08 Time: ~:1hrs M~x h'i.arks: 100 LO:fH.~
General Properties of Viruses
 1 I. Viruses as Agents of Disease. V. F. Righthand, Ph.D. August 15, 2001 General Properties of Viruses Viruses can infect every form of life. There are hundreds of different viruses that can produce diseases
1 I. Viruses as Agents of Disease. V. F. Righthand, Ph.D. August 15, 2001 General Properties of Viruses Viruses can infect every form of life. There are hundreds of different viruses that can produce diseases
Reading material: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY
 1 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY Pathology Residents rotate for at least three months in Medical Microbiology. These rotations are designed to introduce the resident to Medical Microbiology and allow them to become
1 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY Pathology Residents rotate for at least three months in Medical Microbiology. These rotations are designed to introduce the resident to Medical Microbiology and allow them to become
Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1
 Influenza influenza Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis stomach flu gastroenteritides gastroenterities food poisoning campylobacter colitis gastroenterocolitis gastrointestinal
Influenza influenza Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis stomach flu gastroenteritides gastroenterities food poisoning campylobacter colitis gastroenterocolitis gastrointestinal
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Nematodes (Round worms)
 The Nematodes (Round worms) - Small, round, elongated, Non-segmented worms with body cavity. They have separate sexes, usually don t need an I.H and do not multiply in human host because eggs don t hatch
The Nematodes (Round worms) - Small, round, elongated, Non-segmented worms with body cavity. They have separate sexes, usually don t need an I.H and do not multiply in human host because eggs don t hatch
Viral Diseases. T Bamdad, PhD, Tarbiat Modares University
 Viral Diseases 1 Categorizing viral infections by the organ system most commonly affected (eg, lungs, GI tract, skin, liver, CNS, mucous membranes) can be clinically useful, although certain viral disorders
Viral Diseases 1 Categorizing viral infections by the organ system most commonly affected (eg, lungs, GI tract, skin, liver, CNS, mucous membranes) can be clinically useful, although certain viral disorders
Size nm m m
 1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
Multiple Choice Questions - Paper 1
 Multiple Choice Questions - Paper 1 Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could
Multiple Choice Questions - Paper 1 Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS
 Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
CMV. Inclusions predominantly in endothelial cells. Immunostaining greater sensitivity than H&E alone.
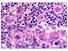 CMV Inclusions predominantly in endothelial cells. Immunostaining greater sensitivity than H&E alone. CMV inclusions are often present in a very patchy distribution Carefully examine all levels CMV CMV
CMV Inclusions predominantly in endothelial cells. Immunostaining greater sensitivity than H&E alone. CMV inclusions are often present in a very patchy distribution Carefully examine all levels CMV CMV
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE
 2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms. Mutualism both organisms benefit. Commensalism one organisms and the other is not harmed
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms. Mutualism both organisms benefit. Commensalism one organisms and the other is not harmed
Montgomery County Community College BIO 241 Clinical Microbiology II 4-3-3
 Montgomery County Community College BIO 241 Clinical Microbiology II 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course that introduces Immunology, Virology, Mycology, and Parasitology as well as the immunological
Montgomery County Community College BIO 241 Clinical Microbiology II 4-3-3 AY16-17 COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course that introduces Immunology, Virology, Mycology, and Parasitology as well as the immunological
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
 The Microbial Size The Viruses Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Electron Micrograph Images of Viruses Influenza virus (RNA virus) Rotavirus (RNA virus) Adenovirus, showing
The Microbial Size The Viruses Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Electron Micrograph Images of Viruses Influenza virus (RNA virus) Rotavirus (RNA virus) Adenovirus, showing
a 13. Describe the biology, pathogenesis and methods of diagnosis of Family
 Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Assiut University Department of Faculty of Pharmacy Parasitology (MD 406) Programme(s) on which the course is given: BSc. of Clinical Pharmacy Major or Minor
Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Assiut University Department of Faculty of Pharmacy Parasitology (MD 406) Programme(s) on which the course is given: BSc. of Clinical Pharmacy Major or Minor
Lecture 1: Overview of Medical Parasitology #AsturiaNOTES Parasitology: Introduction to Parasitology
 Human Parasitology The study of organisms which are parasitic to humans. In the broadest sense of parasitology which is anything parasitic to humans therefore, it includes study of: o Viruses o Bacteria
Human Parasitology The study of organisms which are parasitic to humans. In the broadest sense of parasitology which is anything parasitic to humans therefore, it includes study of: o Viruses o Bacteria
Chapter 12. Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes. Part 2
 Chapter 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Part 2 Chapter 12 includes the fungal pathogens section from chapter 22 and Helminths from chapter 23 Fungi Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
Chapter 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Part 2 Chapter 12 includes the fungal pathogens section from chapter 22 and Helminths from chapter 23 Fungi Chemoheterotrophic Have cell walls typically
DRUGS TO FIGHT AGAINST MICROORGANISMS. Fungi, Viruses, Protozoa, & Helminths Chapter s 42 & 43
 DRUGS TO FIGHT AGAINST MICROORGANISMS Fungi, Viruses, Protozoa, & Helminths Chapter s 42 & 43 FUNGI Simple, plant like, lack green pigment, like dark, damp environments Molds- fuzzy, filamentous (mushrooms,
DRUGS TO FIGHT AGAINST MICROORGANISMS Fungi, Viruses, Protozoa, & Helminths Chapter s 42 & 43 FUNGI Simple, plant like, lack green pigment, like dark, damp environments Molds- fuzzy, filamentous (mushrooms,
GI Micro Lab. B- After that the stool sample should be cultured on different types of media
 GI Micro Lab A- Stool sample is taken and added to Selenite broth to: - 1- Inhibit growth of normal flora bacteria 2- Enhance growth of pathogenic bacteria B- After that the stool sample should be cultured
GI Micro Lab A- Stool sample is taken and added to Selenite broth to: - 1- Inhibit growth of normal flora bacteria 2- Enhance growth of pathogenic bacteria B- After that the stool sample should be cultured
Gut parasites in general practice
 Gut parasites in general practice A biased account Dr. Samson Wong Department of Microbiology The University of Hong Kong Classification of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes (roundworms)
Gut parasites in general practice A biased account Dr. Samson Wong Department of Microbiology The University of Hong Kong Classification of parasites Protozoa Helminths Arthropods Nematodes (roundworms)
Exam Prep? Infectious Diseases. A Balancing Act. Ehrlichia
 Exam Prep? Infectious Diseases A Balancing Act Ehrlichia 1 SARS SARS Infiltrate Bioterrorism Category A Category A Cholera Cot Hantavirus 2 Viral Diseases By far the most common Direct killing Autoimmune
Exam Prep? Infectious Diseases A Balancing Act Ehrlichia 1 SARS SARS Infiltrate Bioterrorism Category A Category A Cholera Cot Hantavirus 2 Viral Diseases By far the most common Direct killing Autoimmune
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM IN BULGARIA
 COMMUNICABLE DISEASES SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM IN BULGARIA Episouth First Training module Madrid, 10-14 September, 2007 Dr. Kremena Parmakova Dr. Teodora Georgieva Bulgaria BULGARIA MAIN CITIES AND NEIGHBORING
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM IN BULGARIA Episouth First Training module Madrid, 10-14 September, 2007 Dr. Kremena Parmakova Dr. Teodora Georgieva Bulgaria BULGARIA MAIN CITIES AND NEIGHBORING
Introduction to Medical Parasitology
 Introduction to Medical Parasitology Lecture I Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Suggested Textbooks 1. Cheesbrough (2009), District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries.
Introduction to Medical Parasitology Lecture I Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Suggested Textbooks 1. Cheesbrough (2009), District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries.
Non-reproductive tissues and cells
 Colour key Minimum requirements as set out in Directive 2004/23/EC More stringent - legy binding on national level More stringent - recommended on national level Not legy binding and not recommended on
Colour key Minimum requirements as set out in Directive 2004/23/EC More stringent - legy binding on national level More stringent - recommended on national level Not legy binding and not recommended on
Microbiology and Pathogens. Teacher - Peter Mitchell
 Microbiology and Pathogens Teacher - Peter Mitchell BSc (Anatomy & Histology). Dip Health Science (Massage Therapy) Microbiology is the study of organisms not visible to the naked eye. Thus requiring the
Microbiology and Pathogens Teacher - Peter Mitchell BSc (Anatomy & Histology). Dip Health Science (Massage Therapy) Microbiology is the study of organisms not visible to the naked eye. Thus requiring the
Downloaded from
 Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
EVALUATION OF PROTOZOAN PARASITES CAUSING DIARRHOEA IN HIV POSITIVE PATIENTS
 EVALUATION OF PROTOZOAN PARASITES CAUSING DIARRHOEA IN HIV POSITIVE PATIENTS Uday Shankar 1, Saral J. Ghosh 2 1Post Graduate Student, Department of Microbiology, D. Y. Patil Medical College, Kolhapur,
EVALUATION OF PROTOZOAN PARASITES CAUSING DIARRHOEA IN HIV POSITIVE PATIENTS Uday Shankar 1, Saral J. Ghosh 2 1Post Graduate Student, Department of Microbiology, D. Y. Patil Medical College, Kolhapur,
Introduction Parasitology. Parasitology Department Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera Utara
 Introduction Parasitology Parasitology Department Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera Utara Parasite Definition: Dependence of one living organism on another 2 CLASSIFICATION (based on habitat) t)
Introduction Parasitology Parasitology Department Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera Utara Parasite Definition: Dependence of one living organism on another 2 CLASSIFICATION (based on habitat) t)
Class 9 th Why do we fall ill?
 Class 9 th Why do we fall ill? Health: health is a state of physical, mental and social well being. The health of all individuals is dependent on their physical environment, social environment, and their
Class 9 th Why do we fall ill? Health: health is a state of physical, mental and social well being. The health of all individuals is dependent on their physical environment, social environment, and their
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; September 2014: Vol.-3, Issue- 4, P
 Original article: Comparison of stool concentration methods for detection of prevalence of enteroparasitic infection in rural tertiary care teaching hospital of Maharashtra 1 Dr. Jaishree Puri, 2 Dr. S.
Original article: Comparison of stool concentration methods for detection of prevalence of enteroparasitic infection in rural tertiary care teaching hospital of Maharashtra 1 Dr. Jaishree Puri, 2 Dr. S.
Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Captive Carnivores
 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Captive Carnivores 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Journal Articles References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Captive Carnivores 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Journal Articles References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES. 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES I. CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES A. General Characteristics 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells 2. Contain a single
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE CHAPTER 13: VIRUSES I. CHARACTERISTICS OF VIRUSES A. General Characteristics 1. Obligate intracellular parasites that multiply in living host cells 2. Contain a single
BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES
 BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES Topic 3 This topic links in with MICROBES (from unit 1) 1. What are the 3 types of microbes? 2. Which microbe do antibiotics destroy? 3. What microbe
BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES Topic 3 This topic links in with MICROBES (from unit 1) 1. What are the 3 types of microbes? 2. Which microbe do antibiotics destroy? 3. What microbe
Chapter 13. Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology
 Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Diseases Acute, Chronic, Communicable Diseases
 Diseases Acute, Chronic, Communicable Diseases Based on GROUP-IV Examination syllabus -prepared by G.SRIRAM NOTE: Dear kalam achievers kindly read at lest 4 to 5 times you can easily understand.. Acute
Diseases Acute, Chronic, Communicable Diseases Based on GROUP-IV Examination syllabus -prepared by G.SRIRAM NOTE: Dear kalam achievers kindly read at lest 4 to 5 times you can easily understand.. Acute
Viruses. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 3.5 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.4 Viruses 1. Explain the problem of defining what a virus is - living or non-living? 2. show you
Name: 3.5 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.4 Viruses 1. Explain the problem of defining what a virus is - living or non-living? 2. show you
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS
 COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
Parasitology third year
 Quality Assurance Unit Tanta University Faculty of Medicine Department of Parasitology Course Specifications Parasitology third year 011-01 Course Specifications: parasitology third Year, 011-01 Parasitology
Quality Assurance Unit Tanta University Faculty of Medicine Department of Parasitology Course Specifications Parasitology third year 011-01 Course Specifications: parasitology third Year, 011-01 Parasitology
Medical Parasitology (EEB 3895) Lecture Exam #3
 1 Name December 2016 Medical Parasitology (EEB 3895) Lecture Exam #3 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. The
1 Name December 2016 Medical Parasitology (EEB 3895) Lecture Exam #3 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. The
Virus. Landmarks in Virology. Introduction to Virology. Landmarks in Virology. Definitions. Definitions. Latin for slimy liquid or poison
 Landmarks in Virology Introduction to Virology Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Introduction of concept of filterable agents for plant pathogens (Mayer, Ivanofsky, Beijerinck in late 1880 s) First filterable agent
Landmarks in Virology Introduction to Virology Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Introduction of concept of filterable agents for plant pathogens (Mayer, Ivanofsky, Beijerinck in late 1880 s) First filterable agent
Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens
 Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Aspergillus species Pneumocystis carinii 1 Dermatophytes Named for derma skin Cause
Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Aspergillus species Pneumocystis carinii 1 Dermatophytes Named for derma skin Cause
Chapter 8 Review. 4. Scientists do not consider viruses as true living organisms because they
 Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
الحترمونا من خري الدعاء
 الحترمونا من خري الدعاء Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could be true or
الحترمونا من خري الدعاء Instructions for candidates The examination consists of 30 multiple choice questions, each divided into 5 different parts. Each part contains a statement which could be true or
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Infectious Disease
 Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Infectious Disease Faculty representative: Eva Piessens, MD, MPH Resident representative: Karen Ganz, MD Revision date: February 1, 2006
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Infectious Disease Faculty representative: Eva Piessens, MD, MPH Resident representative: Karen Ganz, MD Revision date: February 1, 2006
Parasite Life Cycles. Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou. Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo
 Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
Parasite Life Cycles Dickson D. Despommier John W Karapelou Parasite Life Cycles With 49 Life Cycle Drawings Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Dickson D. Despommier, Ph.D. Professor
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
Nucleic acid: singled stranded, double stranded, RNA, or DNA, linear or circular. Capsid: protein coat that is most of the mass of the virus.
 Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses 1. Depending on view may be regarded as exceptionally complex aggregates of nonliving chemicals or as exceptionally simple living microbes. 2. Contain a single
Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses 1. Depending on view may be regarded as exceptionally complex aggregates of nonliving chemicals or as exceptionally simple living microbes. 2. Contain a single
MICROORGANISM NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS
 MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
Mahesh Shinde s Dnyanadeep's IAS For UPSC - IAS / IPS / IFS. UPSC Pre Brain Teaser. Science (Diseases Caused by Mcroorganisms)
 Science (Diseases Caused by Mcroorganisms) Microbes or Microorganisms Microorganisms [microbes] include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, some algae, viruses, viroids and also prions that are proteinacious infectious
Science (Diseases Caused by Mcroorganisms) Microbes or Microorganisms Microorganisms [microbes] include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, some algae, viruses, viroids and also prions that are proteinacious infectious
PRINCIPLES OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY MODULE II THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE PROCESS
 PRINCIPLES OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY MODULE II THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE PROCESS This outline is provided as an aid to the student. It contains only the basic content of the module. To view the supporting
PRINCIPLES OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY MODULE II THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE PROCESS This outline is provided as an aid to the student. It contains only the basic content of the module. To view the supporting
The Immune System and Pathology
 The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
Exclusion Periods for Infectious Diseases
 Exclusion Periods for Infectious Diseases Amoebiasis (Entamoeba Histolytica) Campylobacter Candidiasis Chickenpox (Varicella) CMV (Cytomegalovirus Infection) Conjunctivitis Cryptosporidium Infection Diarrhoea
Exclusion Periods for Infectious Diseases Amoebiasis (Entamoeba Histolytica) Campylobacter Candidiasis Chickenpox (Varicella) CMV (Cytomegalovirus Infection) Conjunctivitis Cryptosporidium Infection Diarrhoea
Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
 Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Unofficial translation No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Unofficial translation No. 786/1986 Communicable Diseases Decree Issued on 31 October 1986 Section 1 has been repealed by Decree of 30 December 2003/1383.
Class XII Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Biology
 Question 1: What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases? Public health measures are preventive measures which are taken to check the spread
Question 1: What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases? Public health measures are preventive measures which are taken to check the spread
Medical Parasitology: It is the science which deals with the parasites that infect man. Parasite: Is an organism, which lives on or within another
 By: Nader Alaridah Medical Parasitology: It is the science which deals with the parasites that infect man. Parasite: Is an organism, which lives on or within another organism (host) for survival. Host:
By: Nader Alaridah Medical Parasitology: It is the science which deals with the parasites that infect man. Parasite: Is an organism, which lives on or within another organism (host) for survival. Host:
