Mahesh Shinde s Dnyanadeep's IAS For UPSC - IAS / IPS / IFS. UPSC Pre Brain Teaser. Science (Diseases Caused by Mcroorganisms)
|
|
|
- August Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science (Diseases Caused by Mcroorganisms) Microbes or Microorganisms Microorganisms [microbes] include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, some algae, viruses, viroids and also prions that are proteinacious infectious agents. Viruses reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal. Microorganisms may be single-celled like bacteria, some algae and protozoa, or multicellular, such as algae and fungi. They can survive under all types of environment, ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands. Microorganisms like amoeba can live alone, while fungi and bacteria may live in colonies. Diseases Caused by Microorganisms Disease Causative Mode Of Type Of Details Agent Transmission Organism Affected Diseases Caused By Bacteria Acne vulgaris Propionibacterium Direct contact/ Humans/ Skin disease that occurs when hair (or simply acne acnes close contact Adolescents follicles become clogged with dead skin or pimples) cells and oil from the skin. Causes = = Genetics + Excessive growth of the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes. Anthrax Bacillus Contact with Most animals Causes skin infections and Gastrointestinal anthraces infected meat including (GI) infection that are fatal. humans French scientist Louis Pasteur developed the first effective vaccine in Cholera Vibrio cholerae Water/food Humans Effects small intestine. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and muscle cramps may also occur. Diarrhea can be so severe that it (1)
2 leads within hours to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Citrus Canker Xanthomonas Air Citrus fruit Infection causes lesions on the leaves, stems, axonopodis plants and fruit of citrus trees. Diptheria Corynebacterium Air/direct Humans Symptoms: sore throat and fever. diphtheriae contact The neck may swell in part due to large lymph nodes. Complications may include myocarditis, inflammation of nerves, kidney problems, and bleeding problems due to low blood platelets. Myocarditis may result in an abnormal heart rate and inflammation of the nerves mayresult in paralysis. Pneumonia Streptococcus Air borne Humans Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of [caused by pneumoniae and droplets of the lung affecting primarily the microscopic bacteria or Haemophilus sneeze air sacs known as alveoli. viruses] influenzae Peptic ulcers Helicobacter Humans Ulcers in the lining of stomach and pylori starting part of small intestine Plague Yersinia pestis Air/ direct Humans Unhygienic conditions is the main cause. [You contact know why Surat is one of the cleanest cities in India?] The symptoms of plague depend on the concentrated areas of infection in each person: bubonic plague in lymph nodes, septicemic plague in blood vessels, pneumonic plague in lungs. Tuberculosis Mycobacterium Air Humans Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but tuberculosis can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections do not have symptoms, known as latent tuberculosis. About 10% of latent infections eventually progresses to active dis- (2)
3 ease which, if left untreated, kills about half of those infected. The classic symptoms of active TB are a chronic cough with bloodtinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Typhoid Salmonella typhi Water Humans Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly Diseases Caused By Viruses AIDS Human Blood Humans and Severely weakens immunity and makes Immunodeficiency exchange primates way for a number of other pathogens. Virus (HIV) Chicken Pox varicella zoster Air/contact Humans Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a virus (VZV) highly contagious disease. The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters. Less severe than small pox. Almost eradicated after the invention of vaccination. Small Pox Variola major Air/contact/ Humans One of the highly dreaded diseases that is and Variola minor water highly contagious. Almost eradicated after the invention of vaccination. Chikungunya Chikungunya Aedes mosquitoes, Causes severe joint pains. Animal reservoirs virus such as A. aegypti of the virus include monkeys, birds, cattle, and A. albopictus and rodents. This is in contrast to dengue, for which primates are the only hosts Cold, influenza hino viruses Air borne Humans Summer are hostile for the virus. occur. (flu) and most droplets of sneeze Most common during winter months. coughs (3)
4 Dengue fever Flavivirus Female Aedes Humans high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and mosquito joint pains, and a characteristic skin rash. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into the life-threatening dengue hemorrhagic fever, resulting in bleeding, low levels of blood platelets and blood plasma leakage, or into dengue shock syndrome, where dangerously low blood pressure occurs. Ebola Ebola virus Animal to man Humans and Ebola infection shows a sudden onset of the Some Animals disease resulting initially in flu-like symptoms: fever, chills and malaise. As the disease progresses, it results in multisystem involvements indicated by the person experiencing lethargy, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and headache. Foot and Picornavirus Close-contact Animals Serious problem to animal farming in India. Mouth Disease [genus animal-to-animal Aphthovirus] spread Hepatitis B hepatitis B Blood Exchange, HumansAffects the liver. Acute as well as virus (HBV) STD [Sexually chronic. transmitted disease] Measles measles virus Air Humans Complications occur in about 30% and may include diarrhea, blindness, inflammation of the brain, and pneumonia among others. Polio or Poliovirus Water/faecal- Humans Weak muscles leading to deformations. Poliomyelitis mouth Zika Zika virus Aedes mosquitoes, Humans such as A. aegypti and A. albopictus (4)
5 Diseases Caused By Protozoans Amoebiasis Entamoeba Contaminated Humans Symptoms may include abdominal pain, (amoebic histolytica Water/food mild diarrhoea, bloody diarrhea or severe dysentery) colitis with tissue death and perforation. This last complication may cause peritonitis. People affected may develop anemia due to Dysentery Leishmania loss of blood. Kala-Azar or Leishmania Sandflies Humans This disease is the second-largest parasitic Visceral genus killer in the world (after malaria). leishmaniasis The parasite migrates to the internal organs such as the liver, spleen (hence visceral ), and bone marrow, and, if left untreated, will almost always result in the death of the host. Signs and symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and substantial swelling of the liver and spleen. Malaria Different species Female Humans Malaria causes symptoms that typically of Plasmodium Anopheles include fever, fatigue, vomiting, and (P. vivax, P. malaria mosquito headaches. In severe cases it can cause and P. falciparum) yellow skin, seizures, coma, or death. Sleeping Trypanosoma Infected Humans Initially, in the first stage of the disease, there Sickness tsetse fly are fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains. This begins one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness and trouble sleeping. Yellow Vein Bhendi yellow Insect Okra plant Okra are dwarfed, malformed. Mosaic of Okra [Ladies finger] vein mosaic virus (5)
6 Diseases Caused By Fungi ingworms Fungi belonging Skin-skin Humans The fungi that cause parasitic infection, to the genera Micr contact collectively dermatophytes, feed on keratin, Trichophyton and the material found in the outer layer of skin, Epidermophyton hair, and nails. ust of wheat Puccinia rust Air/seeds Wheat and Wheat leaf rust is a fungal disease that fungus other crops affects wheat,barley and rye stems, leaves and grains. In temperate zones it is destructive on winter wheat because the pathogen. overwinters. Infections can lead up to 20% yield loss exacerbated by dying leaves which fertilize the fungus. (6)
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE
 NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial disease? (a) Cholera (b) Tuberculosis
Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial disease? (a) Cholera (b) Tuberculosis
CHAPTER AT A GLANCE. Science Class (SA-II)- IX
 13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
Nipah and Other Diseases Caused by Virus, Fungi & Bacteria - GK Notes
 Nipah and Other Diseases Caused by Virus, Fungi & Bacteria - GK Notes The recent outbreak of Nipah Virus is spreading very fast getting highlights in current scenario. There are many Diseases which have
Nipah and Other Diseases Caused by Virus, Fungi & Bacteria - GK Notes The recent outbreak of Nipah Virus is spreading very fast getting highlights in current scenario. There are many Diseases which have
Class 9 th Why do we fall ill?
 Class 9 th Why do we fall ill? Health: health is a state of physical, mental and social well being. The health of all individuals is dependent on their physical environment, social environment, and their
Class 9 th Why do we fall ill? Health: health is a state of physical, mental and social well being. The health of all individuals is dependent on their physical environment, social environment, and their
Downloaded from
 Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
GOYAL BROTHERS PRAKASHAN
 Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? IMPORTANT NOTES 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
Assignments in Science Class IX (Term II) 13 Why Do We Fall Ill? IMPORTANT NOTES 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine)
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
Bacteriology Virology Mycology Parasitology Immunology Pathology Epidemiology. Microbe alternate terms Germs, microorganisms, pathogens, agents, bugs
 1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
Cholera. Ebola. Symptoms of Ebola include. Fever. Severe headache. Muscle pain. Weakness. Fatigue. Diarrhea. Vomiting. Abdominal (stomach) pain
 Cholera Cholera is caused by a bacterial infection of the intestine. In many cases the infection is mild sometimes producing no symptoms at all. But approximately one in 20 people infected with cholera
Cholera Cholera is caused by a bacterial infection of the intestine. In many cases the infection is mild sometimes producing no symptoms at all. But approximately one in 20 people infected with cholera
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
CE Unit. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Chapter 17. Infectious Diseases
 Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE
 2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms. Mutualism both organisms benefit. Commensalism one organisms and the other is not harmed
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora Many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms. Mutualism both organisms benefit. Commensalism one organisms and the other is not harmed
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease
 The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
Human Health and Infectious Diseases
 Human Health and Infectious Diseases Shwetha M Avila Convent Matriculation HSS, Coimbatore, 641022 India Abstract Human body has a defence mechanism to act against various agents which disturb the well
Human Health and Infectious Diseases Shwetha M Avila Convent Matriculation HSS, Coimbatore, 641022 India Abstract Human body has a defence mechanism to act against various agents which disturb the well
LEC 2, Medical biology, Theory, prepared by Dr. AYAT ALI
 General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
CE Unit 7. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Infectious Disease. Unit 6 Lesson 1
 Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
Why do we Fall ill IX Science C.B.S.E. Practice Paper Page 81
 13. Why do we Fall ill Q 1 Write the name of the organism that causes kala-azar. Q 2 What is a disease? Q 3 Write one example of both infectious and non-infectious disease? Q 4 Which type of disease is
13. Why do we Fall ill Q 1 Write the name of the organism that causes kala-azar. Q 2 What is a disease? Q 3 Write one example of both infectious and non-infectious disease? Q 4 Which type of disease is
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1
 Influenza influenza Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis stomach flu gastroenteritides gastroenterities food poisoning campylobacter colitis gastroenterocolitis gastrointestinal
Influenza influenza Flu adenovirus h1n1 h3n2 h5n1 ah1n1 Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis stomach flu gastroenteritides gastroenterities food poisoning campylobacter colitis gastroenterocolitis gastrointestinal
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Pathogens!! What are Pathogens? 12/7/14. Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens
 Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Vectors and Virulence
 Vectors and Virulence UNM Evolutionary Medicine 2009 Joe Alcock MD Goals Understand disease severity in relation to modes of transmission Appreciate clinical applications of virulence evolution Answer
Vectors and Virulence UNM Evolutionary Medicine 2009 Joe Alcock MD Goals Understand disease severity in relation to modes of transmission Appreciate clinical applications of virulence evolution Answer
Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Captive Carnivores
 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Captive Carnivores 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Journal Articles References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Captive Carnivores 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Infectious And Parasitic Diseases Of Journal Articles References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
Thank you for not chewing gum!
 March 25 th, 2015 What do I need today? 1. Pencil 2. Science Notebook 3. Epidemiology note sheet Learning Target: Today we will continue to learn about the fascinating world of disease and epidemiology
March 25 th, 2015 What do I need today? 1. Pencil 2. Science Notebook 3. Epidemiology note sheet Learning Target: Today we will continue to learn about the fascinating world of disease and epidemiology
Blood Borne Pathogens. November 2010
 Blood Borne Pathogens November 2010 Objectives Meet requirements of OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 OSHA Blood Borne Pathogens Post Test Routes of Transmission Types of Pathogens BSI / PPE Common Diseases
Blood Borne Pathogens November 2010 Objectives Meet requirements of OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 OSHA Blood Borne Pathogens Post Test Routes of Transmission Types of Pathogens BSI / PPE Common Diseases
Communicable Diseases. Detection and Prevention
 Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Invest in the future, defeat malaria
 Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Chapter 8 Review. 4. Scientists do not consider viruses as true living organisms because they
 Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Many of you asked about this topic
 Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
Many of you asked about this topic Water borne disease: The largest water quality problem in developing countries. CEE 3510 Environmental Quality Engineering According to: Chemical and Engineering News
How Do You Catch An Infection?
 How Do You Catch An Infection? Animals Insects Water People Food Infectious Diseases Considerations for the 21 st Century Viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminths Infectious diseases are the second
How Do You Catch An Infection? Animals Insects Water People Food Infectious Diseases Considerations for the 21 st Century Viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminths Infectious diseases are the second
Zimbabwe Weekly Epidemiological Bulletin
 Number 182 Epidemiological week 38(week ending 23 September 2012) Highlights: Week 38: -17-23 September 2012) 4 new suspected typhoid cases from Chitungwiza City 5 diarrhoea deaths reported Contents A.
Number 182 Epidemiological week 38(week ending 23 September 2012) Highlights: Week 38: -17-23 September 2012) 4 new suspected typhoid cases from Chitungwiza City 5 diarrhoea deaths reported Contents A.
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES. Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs
 OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens
 Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
AOHS Global Health. Unit 1, Lesson 3. Communicable Disease
 AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
WHY DO WE FALL ILL? Q1: Define Health? What do you interpret when we say a person is in good health? Answer:
 WHY DO WE FALL ILL? By : Arvind Q1: Define Health? What do you interpret when we say a person is in good health? Answer: Health is a state of physical, mental and social well being of an individual not
WHY DO WE FALL ILL? By : Arvind Q1: Define Health? What do you interpret when we say a person is in good health? Answer: Health is a state of physical, mental and social well being of an individual not
301 W. Alder, Missoula, MT or
 301 W. Alder, Missoula, MT 59802 406-258-4745 or 406-258-3363 Routine Immunizations are available on a walk-in basis: Mondays, Tuesdays, Thursdays, and Fridays from 9:00am to 4:30pm Wednesdays, 10:00am-4:30pm
301 W. Alder, Missoula, MT 59802 406-258-4745 or 406-258-3363 Routine Immunizations are available on a walk-in basis: Mondays, Tuesdays, Thursdays, and Fridays from 9:00am to 4:30pm Wednesdays, 10:00am-4:30pm
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Create the Following Chart in your notebook. Fill in as you go through each one.
 Diseases of Africa Create the Following Chart in your notebook. Fill in as you go through each one. History of disease? Affected Population? How do you catch the disease? Symptoms? Prevention / Treatment?
Diseases of Africa Create the Following Chart in your notebook. Fill in as you go through each one. History of disease? Affected Population? How do you catch the disease? Symptoms? Prevention / Treatment?
Chapter 13. Preventing Infectious Diseases. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Lesson 3: Immunizations
 K-W-L Graphic Organizer K (Know) What do you know about W (Want) What do you want to know about L (Learned) What did you learn about Glossary 1. antibodies: proteins created by the immune system to fight
K-W-L Graphic Organizer K (Know) What do you know about W (Want) What do you want to know about L (Learned) What did you learn about Glossary 1. antibodies: proteins created by the immune system to fight
INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES
 FEBRUARY 2018 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES MULTI-COUNTRY OUTBREAK CONTACT + VECTOR NIGERIA, BRAZIL YELLOW FEVER The previously reported outbreak of Yellow Fever in Nigeria has now infected 358 people
FEBRUARY 2018 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES MULTI-COUNTRY OUTBREAK CONTACT + VECTOR NIGERIA, BRAZIL YELLOW FEVER The previously reported outbreak of Yellow Fever in Nigeria has now infected 358 people
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 03
 Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
The Immune System and Pathology
 The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
WHY DO WE FALL ILL. Question Bank in Science Class-IX (Term-II) CONCEPTS
 Question Bank in Science Class-IX (Term-II) 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CONCEPTS 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
Question Bank in Science Class-IX (Term-II) 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CONCEPTS 1. A disease is the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or the other. 2. The term disease literally means without
A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include:
 BSL-1 A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include: Work should be performed on an open lab bench or table Spills must be decontaminated immediately Infectious
BSL-1 A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include: Work should be performed on an open lab bench or table Spills must be decontaminated immediately Infectious
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines.
 Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines.
 Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have been eliminated. But
Fever virus going around 2017
 Fever virus going around 2017 Bad cough that won't quit part of winter virus going around. by LIZ BONIS, WKRC. Monday, December 25th 2017. June 9, 2017. Every time May and June roll around these viruses
Fever virus going around 2017 Bad cough that won't quit part of winter virus going around. by LIZ BONIS, WKRC. Monday, December 25th 2017. June 9, 2017. Every time May and June roll around these viruses
The Struggle with Infectious Disease. Lecture 5
 The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
Diseases Acute, Chronic, Communicable Diseases
 Diseases Acute, Chronic, Communicable Diseases Based on GROUP-IV Examination syllabus -prepared by G.SRIRAM NOTE: Dear kalam achievers kindly read at lest 4 to 5 times you can easily understand.. Acute
Diseases Acute, Chronic, Communicable Diseases Based on GROUP-IV Examination syllabus -prepared by G.SRIRAM NOTE: Dear kalam achievers kindly read at lest 4 to 5 times you can easily understand.. Acute
46825 (260) $UPONT
 Be wise. Immunize. Keeping track of the shots your children receive can be confusing. This is an important responsibility that is shared by you and your immunization providers. This booklet contains the
Be wise. Immunize. Keeping track of the shots your children receive can be confusing. This is an important responsibility that is shared by you and your immunization providers. This booklet contains the
Where is Yellow Fever found?
 Yellow Fever Introduction Yellow Fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease transmitted by a female mosquito of the Aedes family (Aedes aegypti). Man and monkeys are the only reservoir for this virus.
Yellow Fever Introduction Yellow Fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease transmitted by a female mosquito of the Aedes family (Aedes aegypti). Man and monkeys are the only reservoir for this virus.
Chapter 38 Viral Infections
 Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Pathogens. How Do They Cause Disease?
 Pathogens How Do They Cause Disease? A. Pathogens I. Overview 1. definition: a disease-causing agent a. disease: a disturbance in the state of health such that the affected organism experiences some loss
Pathogens How Do They Cause Disease? A. Pathogens I. Overview 1. definition: a disease-causing agent a. disease: a disturbance in the state of health such that the affected organism experiences some loss
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines.
 Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. 40976_CDCupdate.indd 1 Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have
Help protect your child. At-a-glance guide to childhood vaccines. 40976_CDCupdate.indd 1 Why vaccines matter. Thanks to widespread vaccination programs, several diseases that can infect our children have
Microbiology. Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites
 Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Vaccines for Children
 Vaccines for Children 12 24 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
Vaccines for Children 12 24 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
2) Sanitation is. 3) List six practices of sanitation. a. d. b. e. c. f. 4) List four poor hygiene habits that teens must stop. a. c. b. d.
 This is a guided packet for the PowerPoint, Food Safety Unit. Please fill out all information. If you are absent, a copy of this presentation is available on my webpage under the name of the unit. Consumer
This is a guided packet for the PowerPoint, Food Safety Unit. Please fill out all information. If you are absent, a copy of this presentation is available on my webpage under the name of the unit. Consumer
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 01a
 ! What Does It Test For? Very Low Low Glucose Electrolytes Ferritin Blood ph The glucose test measures the amount of sugar, or glucose, in the blood or urine. A very high or very low glucose test can indicate
! What Does It Test For? Very Low Low Glucose Electrolytes Ferritin Blood ph The glucose test measures the amount of sugar, or glucose, in the blood or urine. A very high or very low glucose test can indicate
BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES PURPOSE: To prevent the spread of communicable diseases to client and staff of Brainz Home care Agency from staff with contagious illnesses. POLICY:
BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES PURPOSE: To prevent the spread of communicable diseases to client and staff of Brainz Home care Agency from staff with contagious illnesses. POLICY:
Epidemiology. Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Human Reservoir :
 Lecture ( 3 ) Dr. Ismail I. Daood Epidemiology Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Infectious disease is disease that is caused the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host's
Lecture ( 3 ) Dr. Ismail I. Daood Epidemiology Reservoir & Resources of Infectious Agent : Infectious disease is disease that is caused the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host's
Glucose Electrolytes Ferritin Blood ph. Possible Results White Bright pink Clear White. Bright pink; fades to light pink. Light Pink fades to clear
 What Does It Test For? Very Low Low Glucose Electrolytes Ferritin Blood ph The glucose test An electrolyte Ferritin is a protein The blood ph test The liver is an White blood cells measures the test measures
What Does It Test For? Very Low Low Glucose Electrolytes Ferritin Blood ph The glucose test An electrolyte Ferritin is a protein The blood ph test The liver is an White blood cells measures the test measures
COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS
 www.calcuttakids.org info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS For Community Health Workers Created by Calcutta Kids, May 2012 COUNSELING POINTS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS Sheet 1 Tuberculosis Sheet
www.calcuttakids.org info@calcuttakids.org COUNSELING CARDS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS For Community Health Workers Created by Calcutta Kids, May 2012 COUNSELING POINTS FOR IMMUNIZATIONS Sheet 1 Tuberculosis Sheet
INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES
 CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
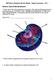 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
Cleaning for Additional Precautions Table symptom based
 for Additional Precautions Table symptom based The need to wear personal protective equipment () for Routine Practices is dependent on the risk of contact or contamination with blood or body fluids. should
for Additional Precautions Table symptom based The need to wear personal protective equipment () for Routine Practices is dependent on the risk of contact or contamination with blood or body fluids. should
8.L.1 Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Infectious Disease Learning Packet 3. Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention
 Name Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention Objective #3: The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways
Name Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention Objective #3: The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways
MICROORGANISM NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS
 MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
Class XII Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Biology
 Question 1: What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases? Public health measures are preventive measures which are taken to check the spread
Question 1: What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases? Public health measures are preventive measures which are taken to check the spread
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Section 6. Communicable Diseases
 Section 6 Communicable Diseases 89 Learning objectives Section 6 Communicable Diseases After completing this section, you will be able to: Describe how communicable diseases spread. Identify some specific
Section 6 Communicable Diseases 89 Learning objectives Section 6 Communicable Diseases After completing this section, you will be able to: Describe how communicable diseases spread. Identify some specific
Immune System and Disease. Chapter 31
 Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Khaled Ali Abu Ali. BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. -Nursing. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer
 Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
LECTURE topics: 1. Immunology. 2. Emerging Pathogens
 LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
Introduction to Microbes and Infectious Disease
 Name: Date: Introduction to Microbes and Infectious Disease Station 1) Pathogens Pathogens are capable of causing. Examples: Station 3) Discovery My name is Anton von Leeuwenhoek, and in I documented my
Name: Date: Introduction to Microbes and Infectious Disease Station 1) Pathogens Pathogens are capable of causing. Examples: Station 3) Discovery My name is Anton von Leeuwenhoek, and in I documented my
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Describe the process or chain of infection. Ø Discuss the body s defenses for fighting infection and disease
 Infectious Diseases LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Describe the process or chain of infection Ø Discuss the body s defenses for fighting infection and disease Ø Discuss the spread of infectious disease Ø Explain
Infectious Diseases LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Describe the process or chain of infection Ø Discuss the body s defenses for fighting infection and disease Ø Discuss the spread of infectious disease Ø Explain
Immune System Review. 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes.
 Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
Communicable and Noncommunicable. Diseases
 Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Communicable Diseases
 Chapter 23 Communicable Diseases Disease that s spread from one living organism to another or through the environment Infection occurs when pathogens in the body multiply and damage body cells Main Pathogens
Chapter 23 Communicable Diseases Disease that s spread from one living organism to another or through the environment Infection occurs when pathogens in the body multiply and damage body cells Main Pathogens
Baby Friendly Vaccines
 Baby Friendly Vaccines What exactly are Baby Friendly Vaccines? Background on Immunity Immunity is the ability of the body to resist and fight germs (disease causing organisms) that can cause infectious
Baby Friendly Vaccines What exactly are Baby Friendly Vaccines? Background on Immunity Immunity is the ability of the body to resist and fight germs (disease causing organisms) that can cause infectious
TABLE OF CONTENTS. In what way can this educational material help me? Why are vaccinations important? Who needs vaccinations?
 www.promovax.eu TABLE OF CONTENTS A B C D E F G H In what way can this educational material help me? Why are vaccinations important? Who needs vaccinations? Which diseases do vaccines prevent? Are vaccinations
www.promovax.eu TABLE OF CONTENTS A B C D E F G H In what way can this educational material help me? Why are vaccinations important? Who needs vaccinations? Which diseases do vaccines prevent? Are vaccinations
OPERATION IRAQI FREEDOM
 Notes/Changes Briefer if service members are completing the health assessment through AKO you may hide/omit/modify slides 25 though 31. They are for use if the service member is filling out the hard copy
Notes/Changes Briefer if service members are completing the health assessment through AKO you may hide/omit/modify slides 25 though 31. They are for use if the service member is filling out the hard copy
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L AA
 OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
Immunizations Offered
 Immunizations Offered Most vaccines commercially available in the United States are available at the health clinic. A partial list of available vaccines follows. For more information about specific vaccines
Immunizations Offered Most vaccines commercially available in the United States are available at the health clinic. A partial list of available vaccines follows. For more information about specific vaccines
