Distribution and Significance of Heterotrophic Marine Bacteria with Antibacterial Activity
|
|
|
- Tabitha Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1987, p /87/ $02.00/0 Copyright C 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 53, No. 12 Distribution and Significance of Heterotrophic Marine Bacteria with Antibacterial Activity SHANTA NAIRt* AND USIO SIMIDU Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Nakanoku, Tokyo 164, Japan Received 22 June 1987/Accepted 18 September 1987 Bacteria with antibacterial activity were isolated from seawater, sediments, phytoplankton, and zooplankton of Suruga, Sagami, and Tokyo Bays and from soft corals and sponges collected from the Taiwan coast. Of the 726 strains isolated, 37 showed antibacterial activity against either Vibrio parahaemolyticus (ATCC 17802) or Staphylococcus aureus (P209). Sediment harbored the lowest number of these forms of bacteria, and those from Tokyo Bay did not show any activity. Attached isolates showed greater activity compared with freeliving forms. Relatively high numbers of strains with antibacterial activity were associated with phytoplankton. Among the zooplankton isolates, cladocerans harbored the maximum number of antibacterial strains. Isolates were more inhibitory to grampositive test cultures. Autoinhibition was observed only among 8% of the isolates. Marine nonproducers were more susceptible. Pseudomonas/Alteromonas species made up 81.0% of isolates, of which 30% were pigmented strains. The absence or reduction in number of bacteria with antibacterial activity in Tokyo Bay is attributed to its eutrophic nature, which may tend to moderate the production of antibacterial compounds. Many marine heterotrophic bacteria are known to produce antibacterial substances which inhibit or kill other bacteria. Recent studies have shown that these antibacterial compounds are not only inhibitory to terrestrial bacteria but also to indigenous bacterial strains, which is of considerable ecological significance (17, 18). Isolation and characterization of antibiotic components have been carried out by various researchers (2, 3). Few reports are available on the geographic distribution of these bacteria (2, 12, 16). The ecological amplifications of antibiotic interactions in marine waters remain obscure. In the present paper, the general distributions of antibacterial strains, obtained from various sources, such as water, sediment, plankton, sponges, and corals from three environments (Tokyo, Sagami, and Suruga Bays) located around Tokyo, are presented. MATERIALS AND METHODS Sea water samples from Tokyo, Sagami, and Suruga Bays (Fig. 1) were collected during the K.T. 847 cruise of R.V. Tanseimaru with Niskin bacteriological water samplers. Sediment samples from these stations were collected with a Phlegertype gravity corer. Zooplankton and phytoplankton were collected with G54 and XX13 nets (Rigosha & Co. Ltd., Japan), respectively. Sponges and soft corals were obtained from the southern coast of Taiwan. Bacterial strains from Tokyo Bay were isolated on spread plates, and colonies from Sagami and Suruga Bays were isolated on Nuclepore filters. Double filtration units with 5 and 0.2,umporesize filters were used, and those bacteria retained on 5,umporesize filters were referred to as attached bacteria, whereas those retained on 0.2p.mporesize filters were considered freeliving bacteria. For sediment samples, 5 ml of the slurry was suspended in 45 ml of prefiltered seawater. Enumeration and isolation were carried * Corresponding author. t Present address: National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa , India. out on ORI plates (20). Zooplankton samples were homogenized in 1 ml of seawater, and 0.1ml aliquots were spread on ORI medium. Phytoplankton samples were allowed to settle and then agitated with sterile seawater in a mortar. The plates were incubated at 20 C for 10 days. About 726 strains were isolated from various sources and locations and were purified and tested for antibacterial activity by the diffusion agar method used for antibiotic assays. The test strains used were Vibrio parahaemolyticus (ATCC 17802) and Staphylococcus aureus (P209). The positive strains were tested for their activities against 13 type cultures and a few nonantibioticproducing isolates to estimate their spectrum of activity. The isolates were identified on the basis of the Simidu scheme (21). RESULTS The percentages of strains from various sources which produced antibacterial substances are presented in Table 1. The highest percentage of strains showing antibacterial activity was observed in phytoplankton isolates, and the minimum was observed in those obtained from sponges. Among the total grampositive strains, however, the percentage was highest for antivibrio activity in the zooplankton isolates and antistaphylococcus activity in the phytoplankton isolates. In the water samples, isolates with more antibacterial activity were obtained from the attached as opposed to the freeliving forms. Sediment harbored the lowest percentage of antibacterial strains. Among the three bays, the isolates from Tokyo Bay did not show antibacterial activity, except for 5% antistaphylococcus activity in strains from phytoplankton (Table 2). No antivibrio activity was noted in freeliving strains isolated from the Suruga Bay water. However, antistaphylococcus activity was observed in 2.3% of the strains. The frequencies of isolates scoring positive from freeliving population of Sagami Bay were generally higher; however, it was less than the values obtained from attached bacterial population of Sagami and Suruga Bays. All bacterial strains isolated from Tokyo Bay sediments failed to show antibacterial activity. Similarly, those from Sagami Bay did not 2957
2 2958 NAIR AND SIMIDU APPL. ENVIRON. MICROBIOL. N exhibit any antistaphylococcus properties, although 1 strain of the 19 strains tested did exhibit antivibrio activity (Table 2). Among the different groups of zooplankton, the maximum percentage of strains exhibiting antivibrio and antistaphylococcus activities was obtained from cladocerans, followed by chaetognaths, whereas the isolates from decapods did not show any antibacterial activity (Table 3). In general, the frequency of occurrence of isolates with antivibrio activity was higher among the various groups (35.3%; Table 3). The spectrum of antibacterial activity of the 37 producer strains (strains producing antibacterial compounds) tended to vary from strain to strain. Among the producer strains, two strains belonging to the Pseudomonas/Alteromonas genus inhibited all 13 type test cultures (Table 4). However, the activities were not uniform even among the species of the genus Pseudomonas, i.e., the activity differed even among the different strains of Pseudomonas. In general, grampositive bacteria were more susceptible against producer strains. Most of the pigmented strains showed narrow spec TABLE 1. Source (n) Percentage of bacterial strains exhibiting antibacterial activity isolated from different sources % (no.) of antibacterial Total % strains Antivi Antistaphylo Antivi Antistaphylobrio coccus brio coccus Free (126) Attached (116) Sediment (39) Phytoplankton (40) Zooplankton (262) Sponges (143) Total (726) 3.3 (24) 4.1 (30) FIG. 1. Location of sampling stations. tra of activity. Autoinhibition was observed in three strains (8.0%). Comparison of the spectra of producers against producers and against nonproducers (strains that did not produce antibacterial compounds) showed that the latter had higher susceptibility to inhibitory substances (Table 5 and Fig. 2). In contrast, strains isolated from phytoplankton of Sagami Bay had no activity against nonproducer strains. Interestingly, those strains which showed higher spectra of activity against nonproducers had narrow ranges of inhibition with other producers and relatively higher antagonism against type cultures tested. The most dominant group of antibacterial strains consisted of the Pseudomonas/Alteromonas isolates (81.0%) (Table 6). Vibrio isolates contributed 16.3%. Among the 37 producer strains obtained, 30% were pigmented and only one was a TABLE 2. Number and percentage of antibacterial strians obtained from different locations % of antibacterial strains Source (n) Antivibrio Antistaphylococcus Tokyo (35) Free Sagami (47) Suruga (44) Tokyo (28) Attached Sagami (45) Suruga (43) Tokyo (20) Sediment Sagami (19) Tokyo (20) Phytoplankton Sagami (20)
3 VOL. 53, 1987 MARINE BACTERIA WITH ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY 2959 TABLE 3. Antibacterial activity obtained from different groups of zooplankton at the Aburatsubo Inlet % of antibacterial strains Group (n) Antivibrio Antistaphylococcus Zooplankton (22) Copepod (19) Decapod (19) Cladoceran (19) Chaetognath (20) Total (99) Flavobacterium isolate; the rest were Alteromonas isolates. DISCUSSION Pseudomonas Producer or Of a total of 726 isolates tested, 24 strains inhibited Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and 30 strains inhibited Staphylococcus aureus. Krasilnokova (11) tested 326 isolates of marine bacteria from a worldwide study and found that 38% showed some degree of inhibition against laboratory strains. When the environments of Tokyo and Sagami Bays were compared, it was observed that 100% of antivibrio strains and 94.1% of antistaphylococcus strains were obtained from Sagami Bay. Okami (14) found that among the isolates from both Japan sea and Pacific Oceans, only a small percentage of bacteria had antibacterial property, whereas more than 20% of the actinomycetes showed antibiosis. Thus, the distribution of antibacterial strains varies from area to area. The actual reason for the suppression of antibiosis in Tokyo Bay remains unknown. However, it could be that in shallow areas such as Tokyo Bay, organic nutrients derived from metabolic processes or death and decay of a massive phytoplankton population and constant nutritional inputs from external sources assuage the necessity for bacterial populations to produce antibiotic compounds to survive competition. Among the various marine animals tested so far, it has been shown that sponges are a good source for antimicrobial compounds (4). Of the 16 isolates from Caribbean sponges, 7 inhibited growth of the assay bacteria (9). However, in the present study, only two strains having antibacterial activity were isolated from sponges. The isolates showed varied spectra of activity, inhibiting closely related and taxonomically distant microorganisms. This may be due to the fact that the same strain might TABLE 4. Spectra of activity of the 37 producers against type cultures Activity against type culture' Ti T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T, T8 T1TIO T1I T12 T _ _ _ T1, Lucibacterium harveyi NCMB 42; T2, Arthrobacter crystallopoietes ATCC 15481; T3, Pseudomonas putida ATCC 12633; T4, Vibrio anguillarum ATCC 18264; T5, Mycobacterium sp.; T6, Bacillus cereus var. mycoides; T7, Sarcina lutea; T8, Escherichia coli; T9, Pseudomonas fluorescens; TIO, Aeromonas hydrophila; T1l, Staphylococcus aureus P 209; T12, Micrococcus luteus TAM 1056; T13, Vibrio parahaemolyticus ATCC , Activity;, no activity.
4 2960 NAIR AND SIMIDU APPL. ENVIRON. MICROBIOL Producer TABLE 5. Spectrum of antibacterial activity of producers against producers Phytop 0 a. z 0 z Phytoplankton Animal/zooplankton Sediment ' 8 Fg F It VA VA..M WA produce different antibacterial compounds, depending on the culture medium (15). However, the production of antimicrobial compounds might be advantageous in competition for food and space, depending on the area and source of initial isolation. Gauthier and Flateau (8) observed that acidic polysaccharide antibiotics produced by marine violet bacteria played an advantageous role in the adhesion to the substrate (5). Autoinhibition was exhibited by three strains. This phenomenon had been observed in marine bacteria (1, 13). Autoinhibition could act as a sort of controlling factor in maintaining species diversity by perhaps allowing population to partially limit itself and coexist with competitors (6). Among the antibacterial substanceproducing isolates obtained, Pseudomonas isolates were the dominant strain. Rosenfeld and ZoBell (17) reported that the majority of species exhibiting inhibitory capabilities belonged to the Lt FIG. 2. Inhibition of marine nonproducers by producers. Inhibition ranged from none (Ol), poor (n), moderate (0), to strong (E).
5 VOL. 53, 1987 MARINE BACTERIA WITH ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY 2961 TABLE 5Continued lankton AnimalVzooplankton Sediment grampositive bacteria. Nonetheless, later studies showed that gramnegative producers also occur (7). Okami and Okazaki (16) studied these bacteria from different locations of the Sea of Japan and found that 35% of Pseudomonas showed antimicrobial activity. A high degree of antibacterial TABLE 6. Classification of antibacterial substanceproducing bacteria No. of antibacterial strains in genusa Source Pseudomonasl b F Alteromonas Vibrio Flavobacterium 12 1 Sediment 1 Phytoplankton 5 5 Zooplankton 10 1 Sponges 2 a In all, 81% were PseudomonaslAlteromonas isolates, 16.3% were Vibrio isolates, and 2.7% were Flavobacterium isolates. activity (81.0%) was obtained from PseudomonaslAlteromonas isolates in the present study, suggesting that this genus would be interesting in future studies of marine antibacterial compoundproducing strains. Pigments have been associated with antibacterial activity, as is the case for cyanobacteria (13). A high percentage of pigmented bacteria with antibacterial activity was reported by Shiba and Taga (19). However, in the present study, only 30% of the producers were pigmented and these did not show much variation in their spectra of activity compared with that of the nonpigmented. It was seen that gramnegative nonpigmented forms had antibacterial properties, with Pseudomonas/Alteromonas forming the dominant genus. The distribution of these bacteria varied with location and source. Their marked absence or presence in low numbers at Tokyo Bay suggest that high nutrient levels may not necessitate or inhibit synthesis of antibacterial compounds in bacteria. It is also possible that these microorganisms are not competing for the same nutrients or other resources. Among
6 2962 NAIR AND SIMIDU the three bays selected, Tokyo Bay was highly eutrophicated, with frequent outbreaks of red tide (10), compared with the less fertile Sagami and Suruga Bays. Further studies on the comparison of antagonistic properties in both copiotrophs and oligotrophs from their respective realms would help confirm the above hypothesis linking elaboration of antagonistic properties to oligotrophy. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS S.N. received a scholarship from MONBUSHO (Japanese Government). We thank R. R. Colwell, University of Maryland, for her valuable suggestions and constant encouragement. Thanks are also due to the captain and crew of R.V. Tanseimaru for helping with the sampling. LITERATURE CITED 1. Andersen, R. J., M. S. Wolfe, and N. J. Faulkner Autotoxic antibiotic production by a marine Chromobacterium. Mar. Biol. 27: Baam, B. R., N. M. Gandhi, and Y. M. Freitas Antibiotic activity of marine microorganisms. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters. 13: Buck, J. D., and S. P. Meyers Antiyeast activity in marine environment. 1. Ecological consideration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 10: Burkholder, P. R The ecology of marine antibiosis and coral reef. In 0. A. Edean (ed.), Biology and geology of coral reefs, vol. 2. Academic Press, Inc., New York. 5. Corpe, W. A Properties of polyanionic carbohydrates isolated from marine bacteria and the marine environment. Symp. Environ. Biogeochem. 22: Freitas, M. D., and A. G. Fredickson Inhibition as a factor in the maintenance of the diversit'y of microbial ecosystems. J. Gen. Microbiol. 106: Gauthier, M. J Substances antibacteriennes produites par les bacteries marines. 'I. Etude systematique de l'activite antagoniste de souches marines visavis de genres telluriques aerobies. Revue Int. Oceanogr. Med. 116, Gauthier, M. J., and G. N. Flateau Antibacterial activity of marine violetpigmented Alteromonas with special reference APPL. ENVIRON. MICROBIOL. to the production of brominated compounds. Can. J. Microbiol. 22: Gjessing, H. W., and R. Ruskin Antibiotic activity of bacteria isolated from some Caribbean sponges, p Proceedings of the 12th meeting of the' Association of Island Marine Laboratories of the Caribbean Curaivo (Netherlands Antilles) Sept Association of the Institute of Marine Laboratories of the Caribbean. 10. Izuhara, S The results of a survey of maximum densities in cell numbers of phytoplanktqn in coastal waters of Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jpn. 32: Krasilnokova, D. N On antibiotic properties of microorganism isolated from various depths of the world oceans. Microbiol. 30: Lebedeva, M. N., and E. M. Markianovic Antibiotic features of heterotrophic bacteria in southern seas, p Proceedings of the 5th International Colloquium of Medical Oceanography. 13. Lemos, M. L., A. Toranzo, and J. L. Barja Antibiotic activity of epiphytic bacteria isolated'from intertidal seaweeds. Microb. Ecol. 11: Okami, Y p In S. Motoda (ed.), Proceedings of the 5th JapanSoviet Joint Symposium on Aquaculture, Tokyo (Japan) Sept Tokai University, Tokyo. 15. Okami, Y Marine microorganisms as a source of bioactive substances, p In M. J. Klug and' C. A. Reddy (ed.), Current perspectives in microbial ecology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C. 16. Okami, Y., and T. Okazaki Studies on marine microorganisms. I.' Isolation from the Japan Sea. J. Antibiot. 25: Rosenfeld, W. D., and C. E. ZoBell Antibiotic production by marine organisms. J. Bacteriol. 54: Saz, A. V., S. Watson, S. R. Brown, and D. L. Lowery Antimicrobial activity of marine waters. 1. Macromolecular nature of antistaphylococcal factor. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8: Shiba, T., and N. Taga Heterotrophic bacteria attached to seaweeds. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 47: Simidu, U p In N. Taga (ed.), Marine microbiology. Tokyo University Press, Tokyo. (In Japanese) 21. Simidu, U p In H. Kadota and N. Taga (ed.), Methods in marine microbiology.
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences SCREENING FOR ANTIBIOTIC PRODUCING MARINE BACTERIA AGAINST FISH PATHOGENS ABSTRACT
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO TECHNOLOGY SCREENING FOR ANTIBIOTIC PRODUCING MARINE BACTERIA AGAINST FISH PATHOGENS *PREM ANAND, T., C. CHELLARAM 1., S. KUMARAN 1
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO TECHNOLOGY SCREENING FOR ANTIBIOTIC PRODUCING MARINE BACTERIA AGAINST FISH PATHOGENS *PREM ANAND, T., C. CHELLARAM 1., S. KUMARAN 1
SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO. Iyyanuchamy, S.K and A. Periyanayagasamy*
 Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
acteria in Sto Fis suratensis
 es acteria in Sto Fis suratensis K. R. SREEKUMARI, M. CHANDRASEKHARAN* and P. LAKSHMANAPERUMALSAMY** School of Marine Sciences, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin - 68 6 The distribution
es acteria in Sto Fis suratensis K. R. SREEKUMARI, M. CHANDRASEKHARAN* and P. LAKSHMANAPERUMALSAMY** School of Marine Sciences, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin - 68 6 The distribution
Seasonal Distribution of Vitamin B12 in Lake Kinneret'
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1977, p. 12-124 Copyright X) 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 34, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Seasonal Distribution of Vitamin B12 in Lake Kinneret'
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1977, p. 12-124 Copyright X) 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 34, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. Seasonal Distribution of Vitamin B12 in Lake Kinneret'
CLIMATE CHANGE, HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS AND HEALTH RISKS IN ONE HEALTH CONTEXT
 CLIMATE CHANGE, HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS AND HEALTH RISKS IN ONE HEALTH CONTEXT Iddya Karunasagar Nitte University Mangalore-575018, India Iddya.Karunasagar@nitte.edu.in Climate change and human health During
CLIMATE CHANGE, HARMFUL ALGAL BLOOMS AND HEALTH RISKS IN ONE HEALTH CONTEXT Iddya Karunasagar Nitte University Mangalore-575018, India Iddya.Karunasagar@nitte.edu.in Climate change and human health During
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences IMPACT OF PLANT EXTRACT, COCCINIA GRANDIS ON DIGESTIVE TRACT MICROFLORA ABSTRACT
 Research Article Biotechnology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 IMPACT OF PLANT EXTRACT, COCCINIA GRANDIS ON DIGESTIVE TRACT MICROFLORA HEMALATHA.J*, KALEENA.P.K AND K. VALIVITTAN
Research Article Biotechnology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 IMPACT OF PLANT EXTRACT, COCCINIA GRANDIS ON DIGESTIVE TRACT MICROFLORA HEMALATHA.J*, KALEENA.P.K AND K. VALIVITTAN
Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic. nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the
 1 2 3 Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the southern Yellow Sea, China 4 5 Hongmei Li a, Yongyu Zhang a *, Xiurong Han b, Xiaoyong
1 2 3 Growth responses of Ulva prolifera to inorganic and organic nutrients: Implications for macroalgal blooms in the southern Yellow Sea, China 4 5 Hongmei Li a, Yongyu Zhang a *, Xiurong Han b, Xiaoyong
SCREENING OF METHICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA)
 Chapter 4 Results 4. RESULTS SCREENING OF METHICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) Totally 92 wound samples were collected from the major sites of coastal area such as Cuddalore, Pondicherry,
Chapter 4 Results 4. RESULTS SCREENING OF METHICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) Totally 92 wound samples were collected from the major sites of coastal area such as Cuddalore, Pondicherry,
SPECIAL ASPECTS OF ASSESSING THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND SESTON USING NEUTRON ACTIVATION ANALYSIS
 SPECIAL ASPECTS OF ASSESSING THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND SESTON USING NEUTRON ACTIVATION ANALYSIS Nekhoroshkov P. S., Frontasyeva M. V. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, FLNP, SNAAAR
SPECIAL ASPECTS OF ASSESSING THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND SESTON USING NEUTRON ACTIVATION ANALYSIS Nekhoroshkov P. S., Frontasyeva M. V. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, FLNP, SNAAAR
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER OF PLASMID DNA BETWEEN DIFFERENT BACTERIA SPECIES UNDER MICROBIAL INTERACTIONS
 Special Issue on Science, Engineering & Environment, ISSN:2186-2990, Japan DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21660/2017.30.2525 HORIZONTAL TRANSFER OF PLASMID DNA BETWEEN DIFFERENT BACTERIA SPECIES UNDER MICROBIAL
Special Issue on Science, Engineering & Environment, ISSN:2186-2990, Japan DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21660/2017.30.2525 HORIZONTAL TRANSFER OF PLASMID DNA BETWEEN DIFFERENT BACTERIA SPECIES UNDER MICROBIAL
Evaluation of Low Temperature Depuration for Reducing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Oysters
 Evaluation of Low Temperature Depuration for Reducing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Oysters Yi-Cheng Su 1, Daniel Cheney 2, and Andy Suhrbier 2 1 Oregon State University Seafood Laboratory, Astoria, OR 97103
Evaluation of Low Temperature Depuration for Reducing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Oysters Yi-Cheng Su 1, Daniel Cheney 2, and Andy Suhrbier 2 1 Oregon State University Seafood Laboratory, Astoria, OR 97103
Akira Ishikawa, Yumi Takeichi. Setsuko Sakamoto, Mineo Yamaguchi
 Akira Ishikawa, Yumi Takeichi (Mie University) Setsuko Sakamoto, Mineo Yamaguchi (National Researchi Institute of Fisheries and Environment of Inland Sea) Background Gambierdiscus spp. is the benthic and
Akira Ishikawa, Yumi Takeichi (Mie University) Setsuko Sakamoto, Mineo Yamaguchi (National Researchi Institute of Fisheries and Environment of Inland Sea) Background Gambierdiscus spp. is the benthic and
In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa carandas leaf extracts
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Jigna Parekh, Nehal Karathia and Sumitra Chanda*
 African Journal of Biomedical Research, Vol. 9 (); 53-5 ISSN 1119 59 Ibadan Biomedical Communications Group Full Length Research Article Evaluation of antibacterial activity and phytochemical analysis
African Journal of Biomedical Research, Vol. 9 (); 53-5 ISSN 1119 59 Ibadan Biomedical Communications Group Full Length Research Article Evaluation of antibacterial activity and phytochemical analysis
Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Disulfiram.
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.5, pp 1476-1481, Sept-Oct 2014 Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Disulfiram., Muthukumar.V Janakiraman.K
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.6, No.5, pp 1476-1481, Sept-Oct 2014 Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Disulfiram., Muthukumar.V Janakiraman.K
Higher plants produced hundreds to thousands of diverse chemical compounds with different biological activities (Hamburger and Hostettmann, 1991).
 4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page:
 Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes R. Prasanna PRIST University, Tamilnadu
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes R. Prasanna PRIST University, Tamilnadu
Reduction of Population Levels of Some Indigenous Bacteria by Lactobacilli in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Gnotobiotic Rats
 Microbiol. Immunol. Vol. 21 (9), 495-503, 1977 Reduction of Population Levels of Some Indigenous Bacteria by Lactobacilli in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Gnotobiotic Rats Tsugio WATANABE, Masami MOROTOMI,
Microbiol. Immunol. Vol. 21 (9), 495-503, 1977 Reduction of Population Levels of Some Indigenous Bacteria by Lactobacilli in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Gnotobiotic Rats Tsugio WATANABE, Masami MOROTOMI,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
Grazing Indices of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton in the San Juan Channel in Jordan Omoto. University of Washington and Friday Harbor Labs
 Grazing Indices of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton in the San Juan Channel in 216 Jordan Omoto University of Washington and Friday Harbor Labs PEF Ocean 492 Email: jdomoto@uw.edu Keywords: phytoplankton,
Grazing Indices of Zooplankton on Phytoplankton in the San Juan Channel in 216 Jordan Omoto University of Washington and Friday Harbor Labs PEF Ocean 492 Email: jdomoto@uw.edu Keywords: phytoplankton,
An Automated Membrane Filtration System for Direct Gram Staining
 1507 An Automated Membrane Filtration System for Direct Gram Staining G. Tsabary 1, D. Gohman 1, D. Shimonov 1, Y. Gluckman-Yavo 1, A. Shinderman 1, G. Ingber 1 and M. Pezzlo 2 1 POCARED Diagnostics, Ltd.,
1507 An Automated Membrane Filtration System for Direct Gram Staining G. Tsabary 1, D. Gohman 1, D. Shimonov 1, Y. Gluckman-Yavo 1, A. Shinderman 1, G. Ingber 1 and M. Pezzlo 2 1 POCARED Diagnostics, Ltd.,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
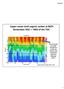 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Relation of the Heat Resistance of Salmonellae to
 APPLED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1970, p. 9- Copyright 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 19, No. Printed in U.S.A. Relation of the Heat Resistance of Salmonellae to the Water Activity of the Environment1
APPLED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1970, p. 9- Copyright 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 19, No. Printed in U.S.A. Relation of the Heat Resistance of Salmonellae to the Water Activity of the Environment1
Microflora in the Digestive Tract of
 Mem. Fac. Fish., Kagoshima Univ. Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 65-71 (1978) Microflora in the Digestive Tract of Marine Fish-I General Characterization of the Isolates from Yellow Tail Taizo Sakata*1, Makoto Nakaji*2
Mem. Fac. Fish., Kagoshima Univ. Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 65-71 (1978) Microflora in the Digestive Tract of Marine Fish-I General Characterization of the Isolates from Yellow Tail Taizo Sakata*1, Makoto Nakaji*2
New genomic typing method MLST
 New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds
 Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS
 CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
Influence of Different Prebiotics and Probiotics on Selective Intestinal Pathogens
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 657-663 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Influence of Different Prebiotics and Probiotics on Selective Intestinal Pathogens Anayata Sharma 1*
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 657-663 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Influence of Different Prebiotics and Probiotics on Selective Intestinal Pathogens Anayata Sharma 1*
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college
 A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
Analysis of Rifampin Disk Diffusion and Stability in 7H10 Agar
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 1975, p. 187-193 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 8, No. 2 Printed in U.SA. Analysis of Rifampin Disk Diffusion and Stability in 7H1 Agar
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 1975, p. 187-193 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 8, No. 2 Printed in U.SA. Analysis of Rifampin Disk Diffusion and Stability in 7H1 Agar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantity of phosphorus spared via phospholipid substitutions by picocyanobacteria. (1 6 P atoms cell -1 )* (% of P in DNA) Synechococcus WH812.7 ±.1 15 ± 2 Synechococcus WH783 2.7
Supplementary Table 1. Quantity of phosphorus spared via phospholipid substitutions by picocyanobacteria. (1 6 P atoms cell -1 )* (% of P in DNA) Synechococcus WH812.7 ±.1 15 ± 2 Synechococcus WH783 2.7
THE "REVERSAL," NEUTRALIZATION, AND SELECTIVITY
 THE "REVERSAL," NEUTRALIZATION, AND SELECTIVITY OF GERMICIDAL CATIONIC DETERGENTS' MORTON KLEIN AND ZELMA G. KARDON Department of Bacteriology, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
THE "REVERSAL," NEUTRALIZATION, AND SELECTIVITY OF GERMICIDAL CATIONIC DETERGENTS' MORTON KLEIN AND ZELMA G. KARDON Department of Bacteriology, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
東南アジア 中部太平洋海域と港湾における Vibrio parahaemolyticus の分布
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) 東南アジア 中部太平洋海域と港湾における Vibrio parahaemolyticus の分布 青木, 義勇 ; 許, 書刀 ; 全, 燾基 Citation 長崎大学風土病紀要 8(4), p.191-202, 1967 Issue Date 1967-01-15 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/3988
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) 東南アジア 中部太平洋海域と港湾における Vibrio parahaemolyticus の分布 青木, 義勇 ; 許, 書刀 ; 全, 燾基 Citation 長崎大学風土病紀要 8(4), p.191-202, 1967 Issue Date 1967-01-15 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/3988
Survival of Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria in
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1968, p. 445-449 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Survival of Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria in Chicken Meat During Freeze-Dehydration,
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1968, p. 445-449 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Survival of Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria in Chicken Meat During Freeze-Dehydration,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 ISSN: 09758585 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Detection of Antimicrobial Activity of Oscimum sanctum (Tulsi) & Trigonella foenum graecum (Methi) against some selected
ISSN: 09758585 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Detection of Antimicrobial Activity of Oscimum sanctum (Tulsi) & Trigonella foenum graecum (Methi) against some selected
In-Use Evaluation Report
 In-Use Evaluation Report 160127.3WIN Pall QPoint TM Shower Water Filter Assembly Reusable Docking Station - Shower Assembly (QDS) and Disposable Filter Capsule for up to 62 Day Use - Shower (QR212 and
In-Use Evaluation Report 160127.3WIN Pall QPoint TM Shower Water Filter Assembly Reusable Docking Station - Shower Assembly (QDS) and Disposable Filter Capsule for up to 62 Day Use - Shower (QR212 and
Survival of antibiotic resistant Pseudomonas strains in different types of water
 Bangladesh}. Fish. Res., 1 (2) : 39-45 Bangladesh Fisheries Research Institute July 1997 Survival of antibiotic resistant Pseudomonas strains in different types of water M. S. Islam and M. B. R. Chowdhury
Bangladesh}. Fish. Res., 1 (2) : 39-45 Bangladesh Fisheries Research Institute July 1997 Survival of antibiotic resistant Pseudomonas strains in different types of water M. S. Islam and M. B. R. Chowdhury
Feeding Measurements
 Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Seasonal and vertical difference in negative and positive effects of grazers on heterotrophic bacteria in Lake Biwa
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1689 1696 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Seasonal and vertical difference in negative and positive effects of grazers on heterotrophic
Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(8), 2000, 1689 1696 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Seasonal and vertical difference in negative and positive effects of grazers on heterotrophic
The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of. Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli
 The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli George Kendros Bio 2290 Section 001 TM Gray 2013 04 10 Abstract The use of mouthwash
The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli George Kendros Bio 2290 Section 001 TM Gray 2013 04 10 Abstract The use of mouthwash
Prophylactic effect of yogurt on Fusobacterium nucleatum in the mouth. Brigham Yang
 Prophylactic effect of yogurt on Fusobacterium nucleatum in the mouth Brigham Yang BIOL 494 Mentor: Dr. R. Shane Gold 8 th April 2014 Abstract Periodontal diseases are closely related to the activity of
Prophylactic effect of yogurt on Fusobacterium nucleatum in the mouth Brigham Yang BIOL 494 Mentor: Dr. R. Shane Gold 8 th April 2014 Abstract Periodontal diseases are closely related to the activity of
Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products
 Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products Presented by Akram Najafi Marine actinobacteria Actinobacteria are a group of Gram positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial (soil)
Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products Presented by Akram Najafi Marine actinobacteria Actinobacteria are a group of Gram positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial (soil)
Inter-island comparison of phytoplankton growth rates and herbivory rates. Wendy Guo. University of Washington. School of Oceanography.
 Inter-island comparison of phytoplankton growth rates and herbivory rates Wendy Guo University of Washington School of Oceanography 04 March 2006 [Running title: Phytoplankton growth and grazing dynamics]
Inter-island comparison of phytoplankton growth rates and herbivory rates Wendy Guo University of Washington School of Oceanography 04 March 2006 [Running title: Phytoplankton growth and grazing dynamics]
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean
 Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Killing of Cells in Bacterial Colonies
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar., 1967, p. 334-339 Vol. 15, No. 2 Copyright @ 1967 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Killing of Cells in Bacterial Colonies DALE E. HUNT AmN ROBERT F. PIlTILLO
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar., 1967, p. 334-339 Vol. 15, No. 2 Copyright @ 1967 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Killing of Cells in Bacterial Colonies DALE E. HUNT AmN ROBERT F. PIlTILLO
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus Frequently Asked Questions What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus? What type of illness is caused by V. parahaemolyticus? How does infection with V. parahaemolyticus occur? How common
Vibrio parahaemolyticus Frequently Asked Questions What is Vibrio parahaemolyticus? What type of illness is caused by V. parahaemolyticus? How does infection with V. parahaemolyticus occur? How common
Nonculturable State of Vibrio vulnificus
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1989, p. 2837-2842 0099-2240/89/112837-06$02.00/0 Copyright D 1989, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 55, No. 11 Membrane Fatty Acid and Virulence Changes
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1989, p. 2837-2842 0099-2240/89/112837-06$02.00/0 Copyright D 1989, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 55, No. 11 Membrane Fatty Acid and Virulence Changes
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos
 Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Effect of Acartia grazing on the size distribution of phytoplankton in Academy Bay, Galapagos Jonathan Herzog University of Washington School of Oceanography 1 NON-TECHNICAL SUMMARY The goal of this experiment
Chandan Prasad.et.al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Application ISSN : , Vol. 7, Issue 9, ( Part -6) September 2017, pp.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Antibacterial properties of Unripened Fruits of Trapa natans, Annona squamosa, Ficus carica and Anthocephalus cadamba against Pathogenic Gram Positive and Negative Bacteria.
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Antibacterial properties of Unripened Fruits of Trapa natans, Annona squamosa, Ficus carica and Anthocephalus cadamba against Pathogenic Gram Positive and Negative Bacteria.
The Effect of the Methods of Farming on the Environment and Growth of Cultured Red Sea Bream, Pagrus major
 29 The Effect of the Methods of Farming on the Environment and Growth of Cultured Red Sea Bream, Pagrus major Takashi UEDE * Abstract The environment of fish farming areas and aquaculture production are
29 The Effect of the Methods of Farming on the Environment and Growth of Cultured Red Sea Bream, Pagrus major Takashi UEDE * Abstract The environment of fish farming areas and aquaculture production are
Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event
 Vol. 16: 121-126, 1984 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published February 29 Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event R. G. Barlow Sea Fisheries
Vol. 16: 121-126, 1984 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Published February 29 Dynamics of the decline of a phytoplankton bloom after an upwelling event R. G. Barlow Sea Fisheries
Comparison of Anti- Vibrio Activities of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, and Glycerol and Sucrose Esters of Fatty
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1980, p. 1178-1182 0099-2240/80/06-1178/05$02.00/0 Vol. 39, No. 6 Comparison of Anti- Vibrio Activities of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, and Glycerol
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1980, p. 1178-1182 0099-2240/80/06-1178/05$02.00/0 Vol. 39, No. 6 Comparison of Anti- Vibrio Activities of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, and Glycerol
Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus reveals distinct differences in strains from the Pacific Northwest of the U.S.
 Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle) May 2nd, 8:30 AM - 10:00 AM Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle) May 2nd, 8:30 AM - 10:00 AM Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater
 Vol. 36: 171-175, 1987 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1 Published March I Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater Knut
Vol. 36: 171-175, 1987 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1 Published March I Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater Knut
Antibacterial activities of extracts and their fractions of leaves of Tridax procumbens Linn
 Antibacterial activities of extracts and their fractions of leaves of Tridax procumbens Linn Dhasarathan. P 1, Hemalatha. N 2, Theriappan. P 1 and Ranjitsingh, A.J.A 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, Prathyusha
Antibacterial activities of extracts and their fractions of leaves of Tridax procumbens Linn Dhasarathan. P 1, Hemalatha. N 2, Theriappan. P 1 and Ranjitsingh, A.J.A 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, Prathyusha
Bacterial Screening of Platelet Concentrates
 Bacterial Screening of Platelet Concentrates Enda Cadden Platelet Donations Very Short shelf-life
Bacterial Screening of Platelet Concentrates Enda Cadden Platelet Donations Very Short shelf-life
PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY
 18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
LECTURE OUTLINE. The genus Vibrio Vibrio cholerae Epidemiology of cholera Pathogenesis. Vaccine development Ecology of V. cholerae
 LECTURE OUTLINE The genus Vibrio Vibrio cholerae Epidemiology of cholera Pathogenesis Disease Virulence factors Vaccine development Ecology of V. cholerae Environmental survival and persistence Phase variation
LECTURE OUTLINE The genus Vibrio Vibrio cholerae Epidemiology of cholera Pathogenesis Disease Virulence factors Vaccine development Ecology of V. cholerae Environmental survival and persistence Phase variation
Available online at Scholars research library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2011, 3 (5):581-586 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Isolation
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2011, 3 (5):581-586 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Isolation
Jl. Perintis Kemerdekaan KM.5 Makassar 90231, South Sulawesi Indonesia.
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com ANTIMICROBIAL POTENCY OF PASSIFLORA FOETIDA LINN FROM SOUTH SULAWESI INDONESIA AGAINST BACTERIA IN VITRO Andi
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com ANTIMICROBIAL POTENCY OF PASSIFLORA FOETIDA LINN FROM SOUTH SULAWESI INDONESIA AGAINST BACTERIA IN VITRO Andi
Patchiness of the Plankton
 Patchiness of the Plankton Within the geographical boundaries inhabited by any species, the individuals of that species are not distributed uniformly or randomly, but are usually aggregated into discrete
Patchiness of the Plankton Within the geographical boundaries inhabited by any species, the individuals of that species are not distributed uniformly or randomly, but are usually aggregated into discrete
Coliforms Isolated from Water Samples
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1983, p. 79-83 0099-2240/83/010079-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 45, No. 1 Antibiotic Resistance Among Different Species
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1983, p. 79-83 0099-2240/83/010079-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 45, No. 1 Antibiotic Resistance Among Different Species
Biological Consulting Services
 Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
PHOSPHORUS FRACTIONS IN GULF OF MANNAR AND THEIR RELATION TO ORGANIC PRODUCTION
 J. mar. biot. Ass. India, 1912, 14(2): 752-757 PHOSPHORUS FRACTIONS IN GULF OF MANNAR AND THEIR RELATION TO ORGANIC PRODUCTION P. V. RAMACHANDRAN NAIR Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Cochin
J. mar. biot. Ass. India, 1912, 14(2): 752-757 PHOSPHORUS FRACTIONS IN GULF OF MANNAR AND THEIR RELATION TO ORGANIC PRODUCTION P. V. RAMACHANDRAN NAIR Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Cochin
Dehydration, Rehydration, and Storagel
 APPLIED MIROBIOLOGY, May, 1965 opyright 1965 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Fate of Bacteria in hicken Meat During Freeze- Dehydration, Rehydration, and Storagel K.
APPLIED MIROBIOLOGY, May, 1965 opyright 1965 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Fate of Bacteria in hicken Meat During Freeze- Dehydration, Rehydration, and Storagel K.
PLANKTON LAB SEATTLE AQUARIUM OVERVIEW:
 PLANKTON LAB SEATTLE AQUARIUM GRADES: 9 12 DURATION: 30 60 minutes MATERIALS: - Plankton sample - Dissecting microscopes - Petri dishes - Droppers - Plankton ID cards - Student lab worksheets STANDARDS:
PLANKTON LAB SEATTLE AQUARIUM GRADES: 9 12 DURATION: 30 60 minutes MATERIALS: - Plankton sample - Dissecting microscopes - Petri dishes - Droppers - Plankton ID cards - Student lab worksheets STANDARDS:
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Parameters of Foods That Affect Microbial Growth
 Lec.3 Food microbiology Dr.Jehan Abdul Sattar Intrinsic and Extrinsic Parameters of Foods That Affect Microbial Growth The ability of microorganisms to grow or multiply in a food is determined by the food
Lec.3 Food microbiology Dr.Jehan Abdul Sattar Intrinsic and Extrinsic Parameters of Foods That Affect Microbial Growth The ability of microorganisms to grow or multiply in a food is determined by the food
STUDIES ON THE ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF SOME PLANTS
 Cairo University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Department of Microbiology STUDIES ON THE ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF SOME PLANTS A Thesis Presented By Ahmed Hany Mohamed Fathy (B. V.Sc., Faculty of Veterinary
Cairo University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Department of Microbiology STUDIES ON THE ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF SOME PLANTS A Thesis Presented By Ahmed Hany Mohamed Fathy (B. V.Sc., Faculty of Veterinary
The medicinal use of honey has been known since ancient
 THE JOURNAL OF ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE Volume 13, Number 4, 2007, pp. 439 441 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/acm.2007.6366 Bactericidal Activity of Different Types of Honey Against
THE JOURNAL OF ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE Volume 13, Number 4, 2007, pp. 439 441 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/acm.2007.6366 Bactericidal Activity of Different Types of Honey Against
DIVERSITY AND ABUNDANCE OF ZOOPLANKTON IN CORAL COMMUNITIES AT KO SAK, CHONBURI PROVINCE FOLLOWING THE 2010 CORAL BLEACHING EVENT
 I_I0030 1 DIVERSITY AND ABUNDANCE OF ZOOPLANKTON IN CORAL COMMUNITIES AT KO SAK, CHONBURI PROVINCE FOLLOWING THE 2010 CORAL BLEACHING EVENT Arporn Sompaonoi,* Sittiporn Pengsakun, Wanlaya Klinthong, Makamas
I_I0030 1 DIVERSITY AND ABUNDANCE OF ZOOPLANKTON IN CORAL COMMUNITIES AT KO SAK, CHONBURI PROVINCE FOLLOWING THE 2010 CORAL BLEACHING EVENT Arporn Sompaonoi,* Sittiporn Pengsakun, Wanlaya Klinthong, Makamas
Study On Marine Pigmented Bacteria I
 Mem. Fac. Fish., Kagoshima Univ. Vol. 29 pp. 339347 (1980) Study On Marine Pigmented BacteriaI Distribution and Characteristics of Pigmented Bacteria Daiichi Kakimoto*, Hiroto Maeda**, Taizo Sakata*, William
Mem. Fac. Fish., Kagoshima Univ. Vol. 29 pp. 339347 (1980) Study On Marine Pigmented BacteriaI Distribution and Characteristics of Pigmented Bacteria Daiichi Kakimoto*, Hiroto Maeda**, Taizo Sakata*, William
Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases
 Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases HOST DISEASE TRIAD PATHOGEN ENVIRONMENT OTHER MICROBES Microbial Interactions KOCH'S POSTULATES Four criteria that were established
Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases HOST DISEASE TRIAD PATHOGEN ENVIRONMENT OTHER MICROBES Microbial Interactions KOCH'S POSTULATES Four criteria that were established
BIOTECHNOLOGY Vol. IX - Molecular Tools for Improving Seafood Safety - Karunasagar, Iddya MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY
 MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY Karunasagar, Iddya University of Agricultural Sciences, College of Fisheries, Mangalore, India Keywords: Seafood, aquaculture, pathogens, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio
MOLECULAR TOOLS FOR IMPROVING SEAFOOD SAFETY Karunasagar, Iddya University of Agricultural Sciences, College of Fisheries, Mangalore, India Keywords: Seafood, aquaculture, pathogens, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
Deep-Sea Benthic Macrofauna Collected at Various Depths in
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1980, p. 746-755 0099-2240/80/10-0746/10$02.00/0 Vol. 40, No. 4 Species Composition and Barotolerance of Gut Microflora of Deep-Sea Benthic Macrofauna Collected
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1980, p. 746-755 0099-2240/80/10-0746/10$02.00/0 Vol. 40, No. 4 Species Composition and Barotolerance of Gut Microflora of Deep-Sea Benthic Macrofauna Collected
Journal of Student Research on Puget Sound The collected reports of the student scientific explorations aboard the SV Carlyn
 Journal of Student Research on Puget Sound The collected reports of the student scientific explorations aboard the SV Carlyn Salish Sea Expeditions is a catalyst for students in their inquiry of Puget
Journal of Student Research on Puget Sound The collected reports of the student scientific explorations aboard the SV Carlyn Salish Sea Expeditions is a catalyst for students in their inquiry of Puget
CHAPTER 7 PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOCIN PRODUCED BY LACTOBACILLUS PLANTARUM AS1
 CHAPTER 7 PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOCIN PRODUCED BY LACTOBACILLUS PLANTARUM AS1 7.1. Introduction Bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have received special attention
CHAPTER 7 PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOCIN PRODUCED BY LACTOBACILLUS PLANTARUM AS1 7.1. Introduction Bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have received special attention
Lab #9. Introduction. Class samples:
 Lab #9 Introduction Food-borne illness is largely caused by the presence of bacteria in red meat. However, much of these harmful bacteria can be destroyed and prevented by sanitation and safe cooking practices.
Lab #9 Introduction Food-borne illness is largely caused by the presence of bacteria in red meat. However, much of these harmful bacteria can be destroyed and prevented by sanitation and safe cooking practices.
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT.
 International Journal of Advanced Research and Review www.ijarr.in ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT. Dr.Mayuri Thanwar 1, Dr.Dhananjay Dwivedi 2 1. Scientific Officer,
International Journal of Advanced Research and Review www.ijarr.in ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT. Dr.Mayuri Thanwar 1, Dr.Dhananjay Dwivedi 2 1. Scientific Officer,
In-vitro analysis of the microbial-load in raw meat and finished products
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 12 (2014) pp. 643-648 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro analysis of the microbial-load in raw meat and finished products M. P.Prasad* Department of
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 12 (2014) pp. 643-648 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro analysis of the microbial-load in raw meat and finished products M. P.Prasad* Department of
Acoustic measurements of zooplankton using a dual frequency echo sounder
 Vol. 180: 105-109, 1999 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar Ecol Prog Ser I Published May 3 Acoustic measurements of zooplankton using a dual frequency echo sounder K. Miyashita*, I. Aoki** Ocean Research
Vol. 180: 105-109, 1999 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar Ecol Prog Ser I Published May 3 Acoustic measurements of zooplankton using a dual frequency echo sounder K. Miyashita*, I. Aoki** Ocean Research
Proficiency Testing. Food Microbiology. April 2015
 Proficiency Testing Food Microbiology April 215 Edition Version 1 (215-5-28) Editor in chief Hans Lindmark, head of Biology department, National Food Agency Responsible for the scheme Laurence Nachin,
Proficiency Testing Food Microbiology April 215 Edition Version 1 (215-5-28) Editor in chief Hans Lindmark, head of Biology department, National Food Agency Responsible for the scheme Laurence Nachin,
Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Microbiology Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials T Wadhwani, K Desai, D Patel, D Lawani,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Microbiology Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials T Wadhwani, K Desai, D Patel, D Lawani,
Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific
 PICES 2014 Annual Meeting Yeosu, Korea Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific T. Fujiki 1, K. Matsumoto 1, Y.
PICES 2014 Annual Meeting Yeosu, Korea Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton community structure and photophysiological state in the western subarctic gyre of the North Pacific T. Fujiki 1, K. Matsumoto 1, Y.
Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula
 , ISSN 2249 4340 Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 175-179, September 2011 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula M. Golam MOSTAFA, Mahdia RAHMAN, M. Manjurul KARIM* Department of Microbiology,
, ISSN 2249 4340 Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 175-179, September 2011 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula M. Golam MOSTAFA, Mahdia RAHMAN, M. Manjurul KARIM* Department of Microbiology,
Isolation and Identification of pigment producing marine isolate and testing of Antioxidant activity and Cytotoxicity effect of pigment
 [VOLUME 5 I ISSUE 4 I OCT. DEC. 2018] e ISSN 2348 1269, Print ISSN 2349-5138 http://ijrar.com/ Cosmos Impact Factor 4.236 Isolation and Identification of pigment producing marine isolate and testing of
[VOLUME 5 I ISSUE 4 I OCT. DEC. 2018] e ISSN 2348 1269, Print ISSN 2349-5138 http://ijrar.com/ Cosmos Impact Factor 4.236 Isolation and Identification of pigment producing marine isolate and testing of
EFFICIENT UTILIZATION OF DISSOLVED FREE AMINO ACIDS BY SUSPENDED MARINE BACTERIA
 EFFICIENT UTILIZATION OF DISSOLVED FREE AMINO ACIDS BY SUSPENDED MARINE BACTERIA By: Anthony V. Palumbo, Randolph L. Ferguson, and Parke A. Rublee Palumbo, A.V., R.L. Ferguson, and P.A. Rublee. 1983. Efficient
EFFICIENT UTILIZATION OF DISSOLVED FREE AMINO ACIDS BY SUSPENDED MARINE BACTERIA By: Anthony V. Palumbo, Randolph L. Ferguson, and Parke A. Rublee Palumbo, A.V., R.L. Ferguson, and P.A. Rublee. 1983. Efficient
Effect of Lactic Acid Concentration on Growth on Meat of Gram-Negative Psychrotrophs from a Meatworks
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p. 284-288 0099-2240/82/020284-05$02.00/0 Vol. 43, No. 2 Effect of Lactic Acid Concentration on Growth on Meat of Gram-Negative Psychrotrophs from a Meatworks
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1982, p. 284-288 0099-2240/82/020284-05$02.00/0 Vol. 43, No. 2 Effect of Lactic Acid Concentration on Growth on Meat of Gram-Negative Psychrotrophs from a Meatworks
Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials
 The Internet Journal of Microbiology 2009 : Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials Teena Wadhwani M.Sc.(semester IV) Nirma
The Internet Journal of Microbiology 2009 : Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials Teena Wadhwani M.Sc.(semester IV) Nirma
Journal of Research in Biology
 Journal of Research in Biology Original Research paper An International Online Open Access Publication group Assessment of the in vitro antibacterial activity of honey on some common human pathogens Journal
Journal of Research in Biology Original Research paper An International Online Open Access Publication group Assessment of the in vitro antibacterial activity of honey on some common human pathogens Journal
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling
 Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Duong Minh Lam ( ) and Nguyen Thanh Dat Hanoi National University of Education ( )
 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE OF HNUE Natural Sci., 2011, Vol. 56, No. 7, pp. 109-116 STUDY ON SOME ACTINOMYCETES ISOLATED FROM MANGROVE SOIL IN GIAO THUY, NAM DINH PROVINCE Duong Minh Lam ( ) and Nguyen Thanh Dat
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE OF HNUE Natural Sci., 2011, Vol. 56, No. 7, pp. 109-116 STUDY ON SOME ACTINOMYCETES ISOLATED FROM MANGROVE SOIL IN GIAO THUY, NAM DINH PROVINCE Duong Minh Lam ( ) and Nguyen Thanh Dat
Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea
 The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
Antimicrobial Effects of Vinegar. Daniel Crawford Grade 9 Central Catholic High School
 Antimicrobial Effects of Vinegar Daniel Crawford Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Antibacterial Agents Humans interest in microbial growth/survivorship for over 100 years Many products/technologies
Antimicrobial Effects of Vinegar Daniel Crawford Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Antibacterial Agents Humans interest in microbial growth/survivorship for over 100 years Many products/technologies
In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.)
 INDIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL & BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH (IJPBR). Vol. 1 (1), March., 13 In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.) G.Ramakrishnaiah * 1, T. Hariprasad
INDIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL & BIOLOGICAL RESEARCH (IJPBR). Vol. 1 (1), March., 13 In vitro antimicrobial activity of leaves and bark extracts of Ficus religiosa (Linn.) G.Ramakrishnaiah * 1, T. Hariprasad
Research Article. The effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphological physiological differentiation of Lactobacillus
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):368-372 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphological
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):368-372 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphological
