Management of Retraction Pockets of Pars Tensa and Pars Flaccida: A Systematic Review of Literature
|
|
|
- Earl Rudolph Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(2) INVITED ARTICLE Management of Retraction Pockets of Pars Tensa and Pars Flaccida: A Systematic Review of Literature Codruta Neumann, Matthew Yung Department of Otolaryngology, The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, Heath Road, Ipswich, Suffolk, United Kingdom Introduction: The treatment of retraction pockets and atelectatic tympanic membrane, both surgical and non-surgical, is highly variable amongst otologists and not always supported by good quality evidence. We undertook a systematic review of evidence to assess the quality of available evidence with the purpose of informing clinical practice. Materials and Methods: The following databases were systematically searched: PubMed, Embase, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (DARE, NHS EED, INAHTA), NICE, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane Economic Evaluations, Cochrane Technology Assessment and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. The date of the last search was 07/03/2012 and no language limitation was applied. The identified studies were screened independently by the two reviewers using pre-defined inclusion criteria and validated quality assessment instruments. Randomised controlled trials and comparative studies were considered for inclusion. Results: The scoping search identified 589 papers which were screened for relevance. A number of 66 papers were judged potentially eligible and were analysed independently by the authors. Two randomised controlled trials and one cohort study met the inclusion criteria. The quality of studies and standard of reporting were poor. Discussion: The literature published on the management of retraction pockets and tympanic atelectasis is of low level of evidence and suffers from poor reporting standard. The studies reviewed were small and suffered from many methodological flaws. In the absence of high level of evidence, the authors propose to undertake a consensus exercise amongst experts using the Delphi technique. Submitted : 18 September 2012 Introduction The European Academy of Otology and Neurotology wishes to produce guidelines on a number of otological and neurotological conditions, one of which is on Cholesteatoma. It was recognized that producing a guideline on any surgical condition based on high level of evidence is difficult if not impossible. There are many problems in designing a high quality randomized controlled study comparing different surgical techniques, as it is almost impossible to control the surgical skill of a surgeon, and it is difficult to eliminate observer bias. Some designs of RCTs in the past may not even pass the stage of the ethics committee [Thomsen et al., 1981]. The purpose of this systematic review on surgical and non-surgical interventions for retraction pockets and atelectasis is to identify if any high level of evidence exists that could be used for guideline development. Material and methods Data sources:, PubMed (1950 to 2012), Embase (1980 to 2012), Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (DARE, NHS EED, INAHTA), NICE, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane Economic Corresponding address: Matthew Yung Department of Otolaryngology, The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, Heath Road, Ipswich, Suffolk, United Kingdom Tel: Fax: matthewyung@btconnect.com Copyright 2005 The Mediterranean Society of Otology and Audiology 360
2 Management of Retraction Pockets of Pars Tensa and Pars Flaccida: A Systematic Review of Literature Evaluations, Cochrane Technology Assessment and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were systematically searched. The date of the last search was 07/03/2012. A search strategy was developed based on MESH terms identified in the scoping search: tympanic membrane, ear drum, epitympanic, retrotympanic, collaps*, atelectas*, atelectat* combined with tympanoplast*, myringotom*, tympanostom*, mastoidectom*, surg*, excis*, reconstruct*, ventilation or grommet* Bibliographies of identified studies were manually searched for relevant references. No language limitation was applied and papers in foreign languages were translated. Citations were exported to Reference Manager 12 and duplicates removed. Only published data was used as time and resource limitation did not allow for contacting authors for unpublished data. Study selection The inclusion/exclusion criteria were piloted on 10 papers and refined by discussion between reviewers. The following inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied: Study Design: randomised or non-randomised controlled trials. Non-comparative studies such as case series, cohorts and narrative reviews were excluded. Conference proceedings were also excluded as the limited information available would make the quality assessment impossible. Population: studies including patients of all ages with retraction pockets or atelectatic tympanic membrane. If a study reported on patients with other ear pathology (such as cholesteatoma or perforation), the study was included in the review only if the outcomes were reported separately on the disease of interest. Intervention: surgical intervention for retraction pockets/atelectasis. Comparator: surgical or non-surgical intervention, including watchful waiting. Outcome: Primary outcome was the clinical description of tympanic membrane such as resolution, cessation of progression, no effect or progression of disease. The secondary outcome of interest was audiological result. Only studies with a follow-up period of minimum a year were included. Data extraction and quality assessment The quality assessment and data extraction were undertaken by two independent reviewers in order to determine a minimum quality threshold for selection of studies; to explore quality differences as an explanation for heterogeneity of results; to guide interpretation for findings and aid in determining the strength of inferences and to guide recommendation for future. The forms used for data extraction and quality assessment were piloted on 10 studies and refined after discussion between reviewers. In assessing the RCT s we used the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias tool as described in the Handbook [2011]. The risk of bias was assesses in six main areas: sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants, personnel and outcome assessors, incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting. Other potential sources of bias were also considered. The criteria suggested by the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination[2009] were used for the quality assessment of non-randomised studies. 1. Is there sufficient description of groups and distribution of prognostic factors such as age, site and extent of retraction pocket/atelectasis, ossicular chain status, audiometric data, and infection status? 2. Are groups comparable on all confounding factors? 3. Is the intervention reliably ascertained? Is the surgical technique described in sufficient details? Is tympanoplasty performed and what materials are used? Any additional procedures such as Silastic insertion, ventilation tubes, etc given? 4. Is the comparator surgical technique/non-surgical treatment reliably described? 5. Is the follow-up periods long enough for residual/recurrent diseases to manifest itself? Are the results presented at similar post-operative intervals for the two groups compared? How is the outcome ascertained (i.e. otoscopy, audiometry, tympanometry, imaging)? 6. What proportion of cohort of followed up in each group? 7. Are there similar drop-out rates and reason for dropout rates between groups? 8. Is surgical expertise of operators similar between groups? 361
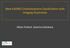
3 The Journal of International Advanced Otology Data synthesis The search resulted in 589 papers after de-duplication and the abstracts were screened for relevance independently by the two reviewers. Where sufficient information was available, for example if it was clear that they did not meet one of the inclusion criteria, papers were excluded at this stage. We analysed the full text of papers considered potentially eligible for inclusion, or if the information in the abstract was not enough to make a judgment. A number of 66 full text papers were independently assessed by two reviewers using clearly defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. Their references were screened for relevant studies but this search yielded no additional studies. Where disagreement existed it was resolved by discussion. A third reviewer was available for consultation if agreement could not be reached, but adjudication was not necessary. The selection process is illustrated using the PRISMA [2012] diagram (figure 1). One systematic review of surgery for tympanic membrane retraction pockets published by the Cochrane collaboration was identified [Nankivell and Pothier, 2010]. We also identified two RCTs[Barbara, 2008;Elsheikh et al., 2006] comparing surgical techniques for retraction pockets, both studies being included in the Cochrane review [Nankivell and Pothier, 2010]. One nonrandomised controlled study [Cassano and Cassano, 2010] published after the Cochrane review was included. After closer scrutiny for quality assessment, we decided to exclude this study as the many sources of bias and confounding factors made the interpretation of results impossible. Details of this study, along with its quality assessment and reasons for exclusion, are presented below Results Two randomised trials [Barbara, 2008;Elsheikh et al., 2006] satisfied the inclusion criteria and quality assessment. Figure 1. PRISMA diagram for studies selection 362
4 Management of Retraction Pockets of Pars Tensa and Pars Flaccida: A Systematic Review of Literature Barbara 2008 was a prospective randomised trial assigning adults with grade IICharachon retraction pocket(fixed and controllable retraction pocket) by sequential consecutive randomisation to either lateral attic reconstruction with tragal cartilage and perichondrum graft (15 patiens) or watchful waiting (15 patients). The follow up regime was similar for both groups at 15 days, 1, 2, 6 and 12 months. The outcomes of interest were otoscopic appearance of tympanic membrane, pure tone audiometry and tympanometry. Elsheikh 2006 was a prospective randomised study assigning adults with Sade grade 2 (tympanic membrane touching long process of incus) and 3 (tympanic membrane touching long process of incus and promontory) retraction pocket to either tragal cartilage and perichondrum tympanoplasty plus T tube insertion (23 patients) or tympanoplasty alone (23 patients). The outcomes assessed were clinical inspection at 3, 6 and 12 months and Eustachian tube function and audiometry at one year. The shortest follow-up period was 13 months. Risk of bias We assessed the risk of bias using the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias tool Handbook [2011]. Both studies had a high risk of bias. In Barbara 2008 the randomisation was sequential allocation on a consecutive cohort, with no allocation concealment or blinding (single investigator undertaking randomisation, surgery and outcome assessment). Although pure tone audiometry was undertaken no data is presented in the paper. The baseline tympanometry data is not presented for either group but the author report the tympanogram results for the intervention group. The clinical appearance of the tympanic membrane was assessed by one investigator alone introducing potential for bias. Five out of the initial 15 patients allocated to the control group were lost to follow up (high risk of attrition bias). Three patients from the control group demonstrated progression of disease (2 had widening of bony erosion and 1 had accumulation of keratin in the pocket) and required surgical intervention eventually. In Elsheikh 2006 the randomisation method was not specified but the two groups were comparable on all prognostic factors. No allocation concealment or blinding for assessors was reported either. Three patients from the initial 49 recruited were lost to follow up but it is not reported from which group. The primary outcome measure was the status of the tympanic membrane postoperatively. Although preoperatively the Sade grading for retraction was used there is no clinical staging reported postoperatively. Authors report only that the tympanic membrane has return to near normal in all patients and that is likely to introduce reporting bias, especially if the assessors were not blinded. In the group not receiving T tubes, 3 patients developed conductive hearing loss and two of them required myringotomy. Summary of effects of intervention a. Appearance of the tympanic membrane and Imaging Barbara 2008: No evidence of retraction of tympanic membrane at 12 months in the active treatment group (0/15). Five patients underwent CT scanning demonstrating hypodense area in the epitympanum and underwent revision with negative findings in all cases. In the control group 3/10 showed disease progression with widening of the bony erosion in two patients and keratin accumulation in one patient. They all underwent surgery subsequently. Elsheikh 2006: Sade grading used pre-operatively but not for post-operative results. Authors just stated that the tympanic membrane returned to near normal in all participants. b. Audiometry Barbara 2008 report that all participants had normal hearing at the beginning of the study and at 12 months follow up, irrespective of treatments received but no data is presented. Elsheikh 2006 report that pure tone average (0.5, 1, 2 and 3 KHz) and air-bone gap average improved in both groups postoperatively but there was no significant difference between the two groups (p>0.05). There was no significant difference between pre- and postoperative word discrimination scores in any group. The authors reported recurrent conductive hearing loss in 2 patients in group 1 (tympanoplasty and T tube %) and 3 patients in group 2 (tympanoplasty - 13%). c. Complications Barbara 2008: one patient in the active treatment group had an infection on day 15 that required topical and systemic antibiotics and resolved completely. 363
5 The Journal of International Advanced Otology Elsheikh 2006: no complications reported. One retrospective cohort [Cassano and Cassano, 2010] study satisfied the inclusion criteria but failed the quality assessment. Cassano 2010 treated 45 ears in 37 children in the intervention group. The pathology included otitis media with effusion, recurrent infections, polyps, perforations and major bilateral hearing loss. The pockets were described as 22 postero-superior, 8 postero-inferior, 2 antero-superior, 2 antero-inferior, 11 postero-superior and inferior. The severity of retraction was classified as follows: Sade grade 1 (annular retraction) and 2 (tympanic membrane touching long process of incus) 16 cases, grade 3(tympanic membrane touching long process of incus and promontory) 24 cases, grade 4(tympanic membrane adherent to promontory) 5 cases. Twenty eight children were younger than 8 years of age, while 17 ears were older than 8 years of age. No audiological data was presented. In the control group the authors included 40 ears but did not report how many patients were involved. The reasons for not treating these patients were very variable: treatment deemed unnecessary in 5 cases of Sade grade 1-2 and 3 cases of grade Sade 3 as condition mild, did not progress and/or no hearing loss was observed. Treatment was not performed in 25 cases grade 3 and 7cases grade 4 either because it was contra-indicated by co-morbidity (6 cases) or parental refusal of treatment in 26 cases. There was no information on the control group site of retraction or about infection, perforation and age distribution. There was no attempt by authors to perform statistical analysis for distribution of prognostic factors in the two groups. A number of surgical intervention were employed in the intervention group and they not uniformly applied, but chosen tailored to the severity of retraction and therefore biasing results. Patients with grade 1-2 Sade retraction (16 cases) underwent: toilet of nasal cavity, systemic or topical steroids, antibiotics, decongestants, tubotympanic insuflation and autoinsuflation and ventilation tubes in cases refractory to treatment. Patients with grade 3 retraction (24 cases) underwent: endaural incision, myringoplasty with composite tragal cartilage-perichodrum graft, some requiring scutum reconstruction, Silastic was used in 4 cases with adhesion to promontory and ossiculoplasty was performed in 7 cases, with cartilage (2 cases) and ceramic or titanium (5 cases).ventilation tube insertion alone was performed in 8 cases. In the control group the authors give no detail on what treatment, if any, was adopted, apart from regular follow-up with hearing tests. No details are given about follow-up intervals or audiological data. It is unclear when the results presented occurred and whether the same observer examined the child at all visits or whether another observer was available for verification. The authors give no details on how the results were documented (ie clinical pictures, drawings, clinical notes, etc). No information about losses to follow-up or surgical expertise of the operator is presented. This is a study of low quality and no meaningful comparison can be made although authors claim that there is a significant anatomical improvement in the treatment group when compared with controls. Discussion The treatment of retraction pockets is highly variable amongst otolaryngologist and there is no consensus as to the indication, timing and type of intervention used in its treatment. We set out to search for the highest level of evidence in an attempt to answer this important clinical dilemma. The scoping search identified a limited number of randomised controlled studies on this condition and also one systematic Cochrane review [Nankivell and Pothier, 2010]. Due to the paucity of data, we decided to widen the search and look for good quality comparative studies to ensure that good evidence that may be available is not overlooked due to over stringent inclusion criteria. The majority of studies identified were non-comparative and most of them were retrospective. The low level of evidence and poor reporting standards made this type of evidence not suitable for the purpose of this review. In the light of the finding of this review there is no high level of evidence to support any surgical intervention over watchful waiting in the management of mild to moderate degrees of retraction pockets (grade II Charachon and Grade 2 and 3 Sade) as there is also no good evidence to favour one particular treatment over the others. 364
6 Management of Retraction Pockets of Pars Tensa and Pars Flaccida: A Systematic Review of Literature Although a randomised controlled trial is the highest level of evidence for testing the efficacy of one form of treatment over another for retraction pocket or atelectasis, it may maybe not be the most suitable or practical way of answering this particular clinical dilemma. There is no universally accepted staging system for retraction pockets. All the currently used systems all suffer from a high degree of inter-observer and intra-observer variability[pothier DD, 2009]. This in turns raises the difficulty in recruiting patients with comparable staging and assessing the tympanic membrane postoperatively. Surgical interventions for atelectasis or retraction pockets are very variable and the surgical skills of the surgeons also vary, thus introducing a number of confounding factors. Also, recurrence of retraction pockets could take several years to manifest [Yung, 1997] and long-term follow up may be necessary for the comparative studies. In the light of the problems likely to be encountered in setting up a high quality comparative study we feel that the otological community may be better served by obtaining a consensus on the management of retraction pockets from experts in the field. We plan to use the Delphi method for obtaining census from the members of the European Academy of Otology and Neurotology and this will be presented in another paper. Conflicts of interest: none References 1. Systematic Reviews CRD s guidance for undertaking reviews in healthcare. p/sysrev3.htm. 2. Cochrane handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention cochrane-handbook. 3. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Barbara M: Lateral attic reconstruction technique: preventive surgery for epitympanic retraction pockets. Otol Neurotol 2008;29: Cassano M, Cassano P: Retraction pockets of pars tensa in pediatric patients: clinical evolution and treatment. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2010;74: Elsheikh MN, Elsherief HS, Elsherief SG: Cartilage tympanoplasty for management of tympanic membrane atelectasis: is ventilatory tube necessary? Otol Neurotol 2006;27: Nankivell PC, Pothier DD: Surgery for tympanic membrane retraction pockets. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;CD Pothier DD: The Sadé and Tos staging systems: not adequately reliable methods of staging retraction of the tympanic membrane? Clin Otolaryngol 2009;34: Thomsen J, Bretlau P, Tos M, Johnsen NJ: Meniere s disease: endolymphatic sac decompression compared with sham (placebo) decompression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1981;374: Yung MW: Retraction of the pars tensa long-term results of surgical treatment. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 1997;22:
The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment Line in Revision Myringoplasty
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 2, September: 53-57, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 2, September: 53-57, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment
AUDIOLOGY/ OTOLOGY CLINICAL ASSESSMENT FORM (Includes history, examination, audiological testing and outcome)
 (A) DEMOGRAPHICS AUDIOLOGY/ OTOLOGY CLINICAL ASSESSMENT FORM (Includes history, examination, audiological testing and outcome) A1 ID Number A2 Name A3 Date of Birth dd/mm/yy / / A4 Hospital Number A5 Today
(A) DEMOGRAPHICS AUDIOLOGY/ OTOLOGY CLINICAL ASSESSMENT FORM (Includes history, examination, audiological testing and outcome) A1 ID Number A2 Name A3 Date of Birth dd/mm/yy / / A4 Hospital Number A5 Today
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma. Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies (MOOSE): Checklist.
 Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies (MOOSE): Checklist. MOOSE Checklist Infliximab reduces hospitalizations and surgery interventions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease:
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies (MOOSE): Checklist. MOOSE Checklist Infliximab reduces hospitalizations and surgery interventions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease:
Original Research Article
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PALISADE CARTILAGE TYMPANOPLASTY WITH TEMPORALIS FASCIA TYMPANOPLASTY IN CSOM WITH SUBTOTAL PERFORATIONS Sathish Kumar K. N 1, M. K. Veenapani 2, Swathi V. M 3 1Assistant Professor,
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PALISADE CARTILAGE TYMPANOPLASTY WITH TEMPORALIS FASCIA TYMPANOPLASTY IN CSOM WITH SUBTOTAL PERFORATIONS Sathish Kumar K. N 1, M. K. Veenapani 2, Swathi V. M 3 1Assistant Professor,
A Working Classification of Retraction for the Whole Tympanic Membrane
 International Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 2013, 2, 143-147 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijohns.2013.24031 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijohns) A Working
International Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 2013, 2, 143-147 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijohns.2013.24031 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijohns) A Working
Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children (Review)
 Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children (Review) Browning GG, Rovers MM, Williamson I, Lous J, Burton MJ This is a reprint of a Cochrane review,
Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children (Review) Browning GG, Rovers MM, Williamson I, Lous J, Burton MJ This is a reprint of a Cochrane review,
The Natural History of Asymptomatic Deep Pars Tensa Retraction
 J Int Adv Otol 218; 14(1): -4 DOI:.12/iao.218.234 Original Article The Natural History of Asymptomatic Deep Pars Tensa Retraction John Cutajar, Maryam Nowghani, Bharti Tulsidas-Mahtani, John Hamilton Department
J Int Adv Otol 218; 14(1): -4 DOI:.12/iao.218.234 Original Article The Natural History of Asymptomatic Deep Pars Tensa Retraction John Cutajar, Maryam Nowghani, Bharti Tulsidas-Mahtani, John Hamilton Department
The palisade cartilage tympanoplasty technique: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Jeffery et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2017) 46:48 DOI 10.1186/s40463-017-0225-z REVIEW Open Access The palisade cartilage tympanoplasty technique: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jeffery et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2017) 46:48 DOI 10.1186/s40463-017-0225-z REVIEW Open Access The palisade cartilage tympanoplasty technique: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Cost-utility analysis of tympanomastoidectomy for adults with chronic suppurative otitis media Wang P C, Jang C H, Shu Y H, Tai C J, Chu K T
 Cost-utility analysis of tympanomastoidectomy for adults with chronic suppurative otitis media Wang P C, Jang C H, Shu Y H, Tai C J, Chu K T Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Cost-utility analysis of tympanomastoidectomy for adults with chronic suppurative otitis media Wang P C, Jang C H, Shu Y H, Tai C J, Chu K T Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Cholesteatoma-Pathogenesis and Surgical Management. Grand Rounds Presentation February 24, 1999 Kyle Kennedy, M.D. Jeffrey Vrabec,, M.D.
 Cholesteatoma-Pathogenesis and Surgical Management Grand Rounds Presentation February 24, 1999 Kyle Kennedy, M.D. Jeffrey Vrabec,, M.D. Introduction Cholesteatoma (keratoma)-essentially an accumulation
Cholesteatoma-Pathogenesis and Surgical Management Grand Rounds Presentation February 24, 1999 Kyle Kennedy, M.D. Jeffrey Vrabec,, M.D. Introduction Cholesteatoma (keratoma)-essentially an accumulation
Research Article Inferior Flap Tympanoplasty: A Novel Technique for Anterior Perforation Closure
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 758598, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/758598 Research Article Inferior Flap Tympanoplasty: A Novel Technique for Anterior Perforation Closure
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 758598, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/758598 Research Article Inferior Flap Tympanoplasty: A Novel Technique for Anterior Perforation Closure
Clinical analysis of secondary acquired cholesteatoma.
 Research Article Clinical analysis of secondary acquired cholesteatoma. http://www.alliedacademies.org/archives-of-general-internal-medicine/ ISSN : 2591-7951 Takashi Yamatodani 1 *, Kunihiro Mizuta 2,
Research Article Clinical analysis of secondary acquired cholesteatoma. http://www.alliedacademies.org/archives-of-general-internal-medicine/ ISSN : 2591-7951 Takashi Yamatodani 1 *, Kunihiro Mizuta 2,
Original Article. Hearing results after myringoplasty. Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 4, Issue 16,
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 4, Issue 16, 455-459 Hearing results after myringoplasty Original Article Shrestha S 1, Sinha K 2 1 Lecturer, Kathmandu Medical ollege Teaching
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 4, Issue 16, 455-459 Hearing results after myringoplasty Original Article Shrestha S 1, Sinha K 2 1 Lecturer, Kathmandu Medical ollege Teaching
ANTERIOR TUCKING VS CARTILAGE SUPPORT TYMPANOPLASTY
 ANTERIOR TUCKING VS CARTILAGE SUPPORT TYMPANOPLASTY K S Burse*, S. V. Kulkarni**, C. C. Bharadwaj***, S. Shaikh****, G. S. Roy***** ABSTRACT Objectives: To compare and analyze two methods of tympanoplasty
ANTERIOR TUCKING VS CARTILAGE SUPPORT TYMPANOPLASTY K S Burse*, S. V. Kulkarni**, C. C. Bharadwaj***, S. Shaikh****, G. S. Roy***** ABSTRACT Objectives: To compare and analyze two methods of tympanoplasty
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Yung Percutaneous Mastoid Vent. middleearcanleadtovariouspathologicconditions,
 The Yung Percutaneous Mastoid Vent A Medium-Term Follow-up Study Matthew Man-Wah Yung, PhD, FRCS, DLO ORIGINAL ARTICLE Background: I designed a percutaneous mastoid vent to provide permanent ventilation
The Yung Percutaneous Mastoid Vent A Medium-Term Follow-up Study Matthew Man-Wah Yung, PhD, FRCS, DLO ORIGINAL ARTICLE Background: I designed a percutaneous mastoid vent to provide permanent ventilation
CHOLESTEATOMA I DO IT?? TYMPANOPLASTY. Mohamed BADR-EL-DINE, M.D.
 CHOLESTEATOMA HOW AND I DO IT?? TYMPANOPLASTY Mohamed BADR-EL-DINE, M.D. Otologie et Neurotologie; Service d Otorhinolaryngologie Université d Alexandrie - EGYPTE. Panelists: Prof. Aziz Belal Prof. Douglas
CHOLESTEATOMA HOW AND I DO IT?? TYMPANOPLASTY Mohamed BADR-EL-DINE, M.D. Otologie et Neurotologie; Service d Otorhinolaryngologie Université d Alexandrie - EGYPTE. Panelists: Prof. Aziz Belal Prof. Douglas
Sliced Island Tragal Cartilage Perichondrial Composite Graft in Type I Tympanoplasty: Early Results and Experience
 Journal of Rhinolaryngo-Otologies, 2014, 2, 000-000 1 Sliced Island Tragal Cartilage Perichondrial Composite Graft in Type I Tympanoplasty: Early Results and Experience Mubarak M. Khan * and Sapna R. Parab
Journal of Rhinolaryngo-Otologies, 2014, 2, 000-000 1 Sliced Island Tragal Cartilage Perichondrial Composite Graft in Type I Tympanoplasty: Early Results and Experience Mubarak M. Khan * and Sapna R. Parab
GUIDANCE. Evidence for the use of grommets as a surgical intervention in otitis media with effusion.
 Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Priorities Forum Statement Number: 72 Subject: Grommet insertion in adults Date of decision: January 2017 Date of review: January 2020 GUIDANCE Criteria for the funding of
Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Priorities Forum Statement Number: 72 Subject: Grommet insertion in adults Date of decision: January 2017 Date of review: January 2020 GUIDANCE Criteria for the funding of
4 Cartilage Palisades in Underlay Tympanoplasty Techniques
 52 4 Cartilage Palisades in Underlay Tympanoplasty Techniques Definition Cartilage underlay palisade technique is the oldest and the most popular technique in cartilage tympanoplasty. As shown in Chapter
52 4 Cartilage Palisades in Underlay Tympanoplasty Techniques Definition Cartilage underlay palisade technique is the oldest and the most popular technique in cartilage tympanoplasty. As shown in Chapter
Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No.1, March 2013 Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion Ali Maeed S Al-Shehri, MD, Fach Arzt* Ahmad Neklawi, MD** Ayed A Shati, MD,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No.1, March 2013 Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion Ali Maeed S Al-Shehri, MD, Fach Arzt* Ahmad Neklawi, MD** Ayed A Shati, MD,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Closed reduction methods for acute anterior shoulder dislocation [Cochrane Protocol] Kanthan Theivendran, Raj Thakrar, Subodh Deshmukh,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Closed reduction methods for acute anterior shoulder dislocation [Cochrane Protocol] Kanthan Theivendran, Raj Thakrar, Subodh Deshmukh,
Cartilage Tympanoplasty for Management of TM Perforation: A Comparison with the Temporalis Fascia Graft Technique
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Cartilage Tympanoplasty for Management of TM Perforation: A Comparison with the Temporalis Fascia Graft Technique Authors: Dr Sudhakar
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Cartilage Tympanoplasty for Management of TM Perforation: A Comparison with the Temporalis Fascia Graft Technique Authors: Dr Sudhakar
Study of Eustachian Tube Function in Normal Adults And Those With Middle Ear Disease
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. V (May. 2017), PP 76-80 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Eustachian Tube Function in Normal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. V (May. 2017), PP 76-80 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Eustachian Tube Function in Normal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A 14-Year Prospective Follow-up Study of Children Treated Early in Life With Tympanostomy Tubes: Part 2: Hearing Outcomes
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 14-Year Prospective Follow-up Study of Children Treated Early in Life With Tympanostomy Tubes: Part 2: Hearing Outcomes Hannu Valtonen, MD, PhD; Henri Tuomilehto, MD, PhD; Yrjö Qvarnberg,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 14-Year Prospective Follow-up Study of Children Treated Early in Life With Tympanostomy Tubes: Part 2: Hearing Outcomes Hannu Valtonen, MD, PhD; Henri Tuomilehto, MD, PhD; Yrjö Qvarnberg,
Cartilage Tympanoplasty: A method for hearing reconstruction
 Original article: Cartilage Tympanoplasty: A method for hearing reconstruction 1. Dr. Sandeep B. Dabhekar, 2. Dr.Parag V. Doifode, 3 Dr. A.S. Deshpande 1. Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government
Original article: Cartilage Tympanoplasty: A method for hearing reconstruction 1. Dr. Sandeep B. Dabhekar, 2. Dr.Parag V. Doifode, 3 Dr. A.S. Deshpande 1. Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government
Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H
 Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H Authors' objectives To systematically review the incidence of deep vein
Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H Authors' objectives To systematically review the incidence of deep vein
Evaluation of hearing loss in relation to site & size of tympanic membrane perforation
 Original article: Evaluation of hearing loss in relation to site & size of tympanic membrane perforation 1 Dr. Anup Agrawal, 2 Dr. Beni Prasad*, 3 Dr. Sunil Sharma 1Resident, 2 Head of Department, 3 Senior
Original article: Evaluation of hearing loss in relation to site & size of tympanic membrane perforation 1 Dr. Anup Agrawal, 2 Dr. Beni Prasad*, 3 Dr. Sunil Sharma 1Resident, 2 Head of Department, 3 Senior
SD-DS. 34 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL JOURNAL ON DOWN SYNDROME 2003: vol. 7, núm. 3, pp
 34 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL JOURNAL ON DOWN SYNDROME 2003: vol. 7, núm. 3, pp. 34-38 Original Relationship between the size of the ear canal and Eustachian tube function in Down syndrome Joan Domènech 1-2,
34 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL JOURNAL ON DOWN SYNDROME 2003: vol. 7, núm. 3, pp. 34-38 Original Relationship between the size of the ear canal and Eustachian tube function in Down syndrome Joan Domènech 1-2,
Hearing is one of the most important special senses
 Comparative Study of Autologous Ossicular Graft versus Titanium Prosthesis (TORP & PORP) in Ossiculoplasty P Thamizharasan, 1 K Ravi 1 ABSTRACT Introduction This prospective cohort study aims to analyze
Comparative Study of Autologous Ossicular Graft versus Titanium Prosthesis (TORP & PORP) in Ossiculoplasty P Thamizharasan, 1 K Ravi 1 ABSTRACT Introduction This prospective cohort study aims to analyze
4 ENT. 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids. 4.2 Cochlear implants. (
 4 ENT 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids This commissioning responsibility has transferred to NHS England (http://www.england.nhs.uk/). Queries around treatment availability and eligibility, as well as referrals
4 ENT 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids This commissioning responsibility has transferred to NHS England (http://www.england.nhs.uk/). Queries around treatment availability and eligibility, as well as referrals
Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma
 Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2003 Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma Manabu Maeta Ryusuke Saito Fumio Nakagawa Takakazu Miyahara Okayama University
Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2003 Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma Manabu Maeta Ryusuke Saito Fumio Nakagawa Takakazu Miyahara Okayama University
A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Clinical Effectiveness of Group Analysis and Analytic/Dynamic Group Psychotherapy
 A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Clinical Effectiveness of Group Analysis and Analytic/Dynamic Group Psychotherapy Executive summary Aims of the review The main aim of the review was to assess the
A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Clinical Effectiveness of Group Analysis and Analytic/Dynamic Group Psychotherapy Executive summary Aims of the review The main aim of the review was to assess the
Original Article Factors affecting surgical outcome of myringoplasty
 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2011; 17(2): 82-87 Original Article Factors affecting surgical outcome of myringoplasty Md. Zakaria Sarker 1, Mesbauddin Ahmed 2, Khabiruddin Patwary 3, Rabiul Islam 4, Abul
Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2011; 17(2): 82-87 Original Article Factors affecting surgical outcome of myringoplasty Md. Zakaria Sarker 1, Mesbauddin Ahmed 2, Khabiruddin Patwary 3, Rabiul Islam 4, Abul
Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guideline version (Draft for Consultation) Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education NICE guideline: methods NICE guideline Methods
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Guideline version (Draft for Consultation) Alcohol interventions in secondary and further education NICE guideline: methods NICE guideline Methods
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy)
 Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy) Clinical Policy Number: 11.03.05 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: September 21, 2017 Next
Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy) Clinical Policy Number: 11.03.05 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: September 21, 2017 Next
Appendix 2 Quality assessment tools. Cochrane risk of bias tool for RCTs. Support for judgment
 Appendix 2 Quality assessment tools Cochrane risk of bias tool for RCTs Item Judgment (H/L/Unclear) Random sequence generation (selection bias) Allocation concealment (selection bias) Blinding of participants
Appendix 2 Quality assessment tools Cochrane risk of bias tool for RCTs Item Judgment (H/L/Unclear) Random sequence generation (selection bias) Allocation concealment (selection bias) Blinding of participants
GATE CAT Intervention RCT/Cohort Studies
 GATE: a Graphic Approach To Evidence based practice updates from previous version in red Critically Appraised Topic (CAT): Applying the 5 steps of Evidence Based Practice Using evidence about interventions
GATE: a Graphic Approach To Evidence based practice updates from previous version in red Critically Appraised Topic (CAT): Applying the 5 steps of Evidence Based Practice Using evidence about interventions
GROMMET INSERTION IN ADULTS WITH OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION (OME) SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY
 SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: Recommendation by: 1617.v3a Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 13 July 2016 Name of Originator/Author: Approved by Responsible
SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: Recommendation by: 1617.v3a Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning Policy Forum (CCPF) Date Ratified: 13 July 2016 Name of Originator/Author: Approved by Responsible
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) Produced by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination Copyright 2017 University of York.
 A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
GROMMET INSERTION 18 YEARS AND UNDER PERSISTENCE OF BILATERAL OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY
 SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: 1718.v3 Ratified by: Date Ratified: 05 April 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Name of Responsible Committee/Individual: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning
SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: 1718.v3 Ratified by: Date Ratified: 05 April 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Name of Responsible Committee/Individual: Somerset CCG Clinical Commissioning
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Efficacy of the 2-Staged Procedure in the Management of Cholesteatoma. paradigms have been published
 Efficacy of the 2-Staged Procedure in the Management of Cholesteatoma Steven Y. Ho, MD; John F. Kveton, MD ORIGAL ARTICLE Objective: To demonstrate the efficacy of intact canal wall procedure coupled with
Efficacy of the 2-Staged Procedure in the Management of Cholesteatoma Steven Y. Ho, MD; John F. Kveton, MD ORIGAL ARTICLE Objective: To demonstrate the efficacy of intact canal wall procedure coupled with
Surgical outcome in chronic otitis media with cholesteatoma
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20184260
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20184260
Erosion of the long process of the incus with incomplete ossicular discontinuity in simple chronic otitis media: Should we reconstruct or leave it be?
 Accepted: 30 August 2017 DOI: 10.1111/coa.12974 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Erosion of the long process of the incus with incomplete ossicular discontinuity in simple chronic otitis media: Should we reconstruct or
Accepted: 30 August 2017 DOI: 10.1111/coa.12974 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Erosion of the long process of the incus with incomplete ossicular discontinuity in simple chronic otitis media: Should we reconstruct or
2016 European Phoniatrics Hearing EUHA Award
 2016 European Phoniatrics Hearing EUHA Award Efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure on middle ear atelectasis: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial Corresponding author: Sevtap Akbulut,
2016 European Phoniatrics Hearing EUHA Award Efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure on middle ear atelectasis: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial Corresponding author: Sevtap Akbulut,
Pediatric Tympanoplasty Type I (Cartilage Vs Temporalis Fascia Graft)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. V (Feb. 2016), PP 61-65 www.iosrjournals.org Pediatric Tympanoplasty Type I (Cartilage
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. V (Feb. 2016), PP 61-65 www.iosrjournals.org Pediatric Tympanoplasty Type I (Cartilage
ENT approach to middle ear disease in children: the evidence. Dr Trish MacFarlane MBBS, FRACS.
 ENT approach to middle ear disease in children: the evidence. Dr Trish MacFarlane MBBS, FRACS. Outline: Extent of the problem. Defining the problem. Tips to improving diagnostic accuracy. Review of current
ENT approach to middle ear disease in children: the evidence. Dr Trish MacFarlane MBBS, FRACS. Outline: Extent of the problem. Defining the problem. Tips to improving diagnostic accuracy. Review of current
Outcomes assessed in the review
 The effectiveness of mechanical compression devices in attaining hemostasis after removal of a femoral sheath following femoral artery cannulation for cardiac interventional procedures Jones T Authors'
The effectiveness of mechanical compression devices in attaining hemostasis after removal of a femoral sheath following femoral artery cannulation for cardiac interventional procedures Jones T Authors'
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews High-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous haematopoietic cell transplantation for children, adolescents and young adults with first
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews High-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous haematopoietic cell transplantation for children, adolescents and young adults with first
New EAONO Cholesteatoma Classification with imaging illustration. Milan Profant, Katarina Sláviková
 New EAONO Cholesteatoma Classification with imaging illustration Milan Profant, Katarina Sláviková EAONO/JOS Joint Consensus Statements on the Definitions, Classification and Staging of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma
New EAONO Cholesteatoma Classification with imaging illustration Milan Profant, Katarina Sláviková EAONO/JOS Joint Consensus Statements on the Definitions, Classification and Staging of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma
Meta-analyses: analyses:
 Meta-analyses: analyses: how do they help, and when can they not? Lee Hooper Senior Lecturer in research synthesis & nutrition l.hooper@uea.ac.uk 01603 591268 Aims Systematic Reviews Discuss the scientific
Meta-analyses: analyses: how do they help, and when can they not? Lee Hooper Senior Lecturer in research synthesis & nutrition l.hooper@uea.ac.uk 01603 591268 Aims Systematic Reviews Discuss the scientific
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 4, Issue 28,
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 4, Issue 28, 397-401 Original Article Observation of hearing loss in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media tubotympanic type Maharjan M
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2009), Vol. 7, No. 4, Issue 28, 397-401 Original Article Observation of hearing loss in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media tubotympanic type Maharjan M
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled
Congenital Middle Ear Cholesteatoma in Children; Retrospective Review of 35 Cases
 J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 126-31 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.126 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Congenital Middle Ear Cholesteatoma in Children; Retrospective Review of
J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24: 126-31 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.126 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Congenital Middle Ear Cholesteatoma in Children; Retrospective Review of
Nonsurgical home treatment of middle ear effusion and associated hearing loss in children. Part II: Validation study
 ORIGINAL SILMAN, ARICK, ARTICLE EMMER Nonsurgical home treatment of middle ear effusion and associated hearing loss in children. Part II: Validation study Shlomo Silman, PhD; Daniel S. Arick, MD, FACS;
ORIGINAL SILMAN, ARICK, ARTICLE EMMER Nonsurgical home treatment of middle ear effusion and associated hearing loss in children. Part II: Validation study Shlomo Silman, PhD; Daniel S. Arick, MD, FACS;
Mastoid cavities CAUSES OF FAILURE?
 Management of troublesome mastoid cavities J. Magnan, Université de la Mediterranée Marseille, France ALEXANDRIA 2009 Mastoid cavities CAUSES OF FAILURE? Facial bridge Pneumatisation Skin Mucosa Meatoplasty
Management of troublesome mastoid cavities J. Magnan, Université de la Mediterranée Marseille, France ALEXANDRIA 2009 Mastoid cavities CAUSES OF FAILURE? Facial bridge Pneumatisation Skin Mucosa Meatoplasty
2. The effectiveness of combined androgen blockade versus monotherapy.
 Relative effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methods of androgen suppression in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, Aronson N, Seidenfeld J Authors' objectives
Relative effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of methods of androgen suppression in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, Aronson N, Seidenfeld J Authors' objectives
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library)
 A systematic review of smoking cessation and relapse prevention interventions in parents of babies admitted to a neonatal unit (after delivery) Divya Nelson, Sarah Gentry, Caitlin Notley, Henry White,
A systematic review of smoking cessation and relapse prevention interventions in parents of babies admitted to a neonatal unit (after delivery) Divya Nelson, Sarah Gentry, Caitlin Notley, Henry White,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews A systematic review of behaviour change interventions targeting physical activity, exercise and HbA1c in adults with type 2 diabetes Leah
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews A systematic review of behaviour change interventions targeting physical activity, exercise and HbA1c in adults with type 2 diabetes Leah
Cochrane Breast Cancer Group
 Cochrane Breast Cancer Group Version and date: V3.2, September 2013 Intervention Cochrane Protocol checklist for authors This checklist is designed to help you (the authors) complete your Cochrane Protocol.
Cochrane Breast Cancer Group Version and date: V3.2, September 2013 Intervention Cochrane Protocol checklist for authors This checklist is designed to help you (the authors) complete your Cochrane Protocol.
The Outcome of Shield Graft Tympanoplasty: A Single Center Descriptive Study at KAMC
 ISSN: 2250-0359 VOLUME 4 ISSUE 2 2014 The Outcome of Shield Graft Tympanoplasty: A Single Center Descriptive Study at KAMC Mohamed Sa ad Eldin Aly, MD 1, Malak Jamal Gazzaz, MBBS 2, Doaa Abdelmoety, MD
ISSN: 2250-0359 VOLUME 4 ISSUE 2 2014 The Outcome of Shield Graft Tympanoplasty: A Single Center Descriptive Study at KAMC Mohamed Sa ad Eldin Aly, MD 1, Malak Jamal Gazzaz, MBBS 2, Doaa Abdelmoety, MD
Systematic Reviews and Meta- Analysis in Kidney Transplantation
 Systematic Reviews and Meta- Analysis in Kidney Transplantation Greg Knoll MD MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Kidney Transplantation University of Ottawa and The Ottawa Hospital KRESCENT
Systematic Reviews and Meta- Analysis in Kidney Transplantation Greg Knoll MD MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Kidney Transplantation University of Ottawa and The Ottawa Hospital KRESCENT
Outcome of intact canal wall mastoidectomy for limited attic cholesteatoma
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Reddy R. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):596-600 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Reddy R. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):596-600 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
GRADE. Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation. British Association of Dermatologists April 2018
 GRADE Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation British Association of Dermatologists April 2018 Previous grading system Level of evidence Strength of recommendation Level of evidence
GRADE Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation British Association of Dermatologists April 2018 Previous grading system Level of evidence Strength of recommendation Level of evidence
Results of single stage ossicular reconstruction by incus transposition in patients with chronic otitis media
 Original Article Results of single stage ossicular reconstruction by incus transposition in patients with chronic otitis media Masoud Naderpour, 1 Yalda Jabbari-Moghaddam, 1 Reza Radfar, 2 Sina Zarrintan,
Original Article Results of single stage ossicular reconstruction by incus transposition in patients with chronic otitis media Masoud Naderpour, 1 Yalda Jabbari-Moghaddam, 1 Reza Radfar, 2 Sina Zarrintan,
T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S
 Short-term psychodynamic psychotherapies for anxiety, depression and somatoform disorders (Unknown) Abbass AA, Hancock JT, Henderson J, Kisely S This is a reprint of a Cochrane unknown, prepared and maintained
Short-term psychodynamic psychotherapies for anxiety, depression and somatoform disorders (Unknown) Abbass AA, Hancock JT, Henderson J, Kisely S This is a reprint of a Cochrane unknown, prepared and maintained
Page: 1 of 6. Transtympanic Micropressure Applications as a Treatment of Meniere's Disease
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: December 2013 as a Treatment of Meniere's Disease Description Transtympanic micropressure treatment for Meniere s disease involves use of a hand-held air pressure
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: December 2013 as a Treatment of Meniere's Disease Description Transtympanic micropressure treatment for Meniere s disease involves use of a hand-held air pressure
Data extraction. Specific interventions included in the review Dressings and topical agents in relation to wound healing.
 Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson E A, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D Authors' objectives
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (2) dressings and topical agents used in the healing of chronic wounds Bradley M, Cullum N, Nelson E A, Petticrew M, Sheldon T, Torgerson D Authors' objectives
Selective Epitympanic Dysventilation Syndrome
 The Laryngoscope VC 2010 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Selective Epitympanic Dysventilation Syndrome Daniele Marchioni, MD; Matteo Alicandri-Ciufelli, MD; Gabriele
The Laryngoscope VC 2010 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Selective Epitympanic Dysventilation Syndrome Daniele Marchioni, MD; Matteo Alicandri-Ciufelli, MD; Gabriele
Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy)
 Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy) Clinical Policy Number: 1135 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 1, 2018 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy) Clinical Policy Number: 1135 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 1, 2018 Next Review
A Clinical Study of Hearing Outcome after Type I Tympanoplasty
 Original Research Article A Clinical Study of Hearing Outcome after Type I Tympanoplasty Khushboo Jain 1, Anil Pandey 2, Shubhankur Gupta 2*, Rahul 3 1 Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College, Jabalpur,
Original Research Article A Clinical Study of Hearing Outcome after Type I Tympanoplasty Khushboo Jain 1, Anil Pandey 2, Shubhankur Gupta 2*, Rahul 3 1 Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College, Jabalpur,
Myringoplasty in Simple Chronic Otitis Media: Critical Analysis of Long-Term Results in a 1,000-Adult Patient Series
 Otology & Neurotology 33:48Y53 Ó 2011, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Myringoplasty in Simple Chronic Otitis Media: Critical Analysis of Long-Term Results in a 1,000-Adult Patient Series *Massimiliano Nardone,
Otology & Neurotology 33:48Y53 Ó 2011, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Myringoplasty in Simple Chronic Otitis Media: Critical Analysis of Long-Term Results in a 1,000-Adult Patient Series *Massimiliano Nardone,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews The effect of probiotics on functional constipation: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials EIRINI DIMIDI, STEPHANOS CHRISTODOULIDES,
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews The effect of probiotics on functional constipation: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials EIRINI DIMIDI, STEPHANOS CHRISTODOULIDES,
Nasal septal perichondrium versus temporalis fascia in transmeatal myringoplasty
 Egyptian Journal of Ear, Nose, Throat and Allied Sciences (2011) 12, 1 6 Egyptian Society of Ear, Nose, Throat and Allied Sciences Egyptian Journal of Ear, Nose, Throat and Allied Sciences www.esentas.org
Egyptian Journal of Ear, Nose, Throat and Allied Sciences (2011) 12, 1 6 Egyptian Society of Ear, Nose, Throat and Allied Sciences Egyptian Journal of Ear, Nose, Throat and Allied Sciences www.esentas.org
Cartilage Palisades in Type 3 Tympanoplasty: Functional and Hearing Results
 DOI 10.1007/s12070-014-0717-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cartilage Palisades in Type 3 Tympanoplasty: Functional and Hearing Results Ashish Vashishth Neeraj Narayan Mathur Deepak Verma Received: 30 January 2014
DOI 10.1007/s12070-014-0717-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cartilage Palisades in Type 3 Tympanoplasty: Functional and Hearing Results Ashish Vashishth Neeraj Narayan Mathur Deepak Verma Received: 30 January 2014
Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy
 Case report Videosurgery Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy Emilia B. Karchier, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Adam Orłowski Department
Case report Videosurgery Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy Emilia B. Karchier, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Adam Orłowski Department
Assessment of otological and audiological status in patients of allergic rhinitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kumar S et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul;4(4):956-960 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kumar S et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul;4(4):956-960 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Type 1 tympanoplasty in pediatric patients: a review of 102 cases
 Baklaci et al. BMC Pediatrics (2018) 18:345 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1326-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Type 1 tympanoplasty in pediatric patients: a review of 102 cases Deniz Baklaci *, Ismail
Baklaci et al. BMC Pediatrics (2018) 18:345 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1326-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Type 1 tympanoplasty in pediatric patients: a review of 102 cases Deniz Baklaci *, Ismail
School of Dentistry. What is a systematic review?
 School of Dentistry What is a systematic review? Screen Shot 2012-12-12 at 09.38.42 Where do I find the best evidence? The Literature Information overload 2 million articles published a year 20,000 biomedical
School of Dentistry What is a systematic review? Screen Shot 2012-12-12 at 09.38.42 Where do I find the best evidence? The Literature Information overload 2 million articles published a year 20,000 biomedical
Water precautions for prevention of infection in children with ventilation tubes(grommets)(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Water precautions for prevention of infection in children with ventilation tubes(grommets)(review) Moualed D, Masterson L, Kumar S, Donnelly N Moualed D, Masterson
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Water precautions for prevention of infection in children with ventilation tubes(grommets)(review) Moualed D, Masterson L, Kumar S, Donnelly N Moualed D, Masterson
GROMMET INSERTION RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (WITHOUT EFFUSION) SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY
 Version: 1718.v1 Ratified by: SCCG COG Date Ratified: 05 April 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Name of Responsible Committee/Individual: IFR SCCG CCPF/ IFR Date issued: 18 April 2017 Review date: Target
Version: 1718.v1 Ratified by: SCCG COG Date Ratified: 05 April 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Name of Responsible Committee/Individual: IFR SCCG CCPF/ IFR Date issued: 18 April 2017 Review date: Target
USDA Nutrition Evidence Library: Systematic Review Methodology
 USDA Nutrition Evidence Library: Systematic Review Methodology Julie E. Obbagy, PhD, RD USDA Center for Nutrition Policy & Promotion Meeting #2 October 17, 2016 The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering,
USDA Nutrition Evidence Library: Systematic Review Methodology Julie E. Obbagy, PhD, RD USDA Center for Nutrition Policy & Promotion Meeting #2 October 17, 2016 The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering,
Instrument for the assessment of systematic reviews and meta-analysis
 Appendix II Annex II Instruments for the assessment of evidence As detailed in the main body of the methodological appendix (Appendix II, "Description of the methodology utilised for the collection, assessment
Appendix II Annex II Instruments for the assessment of evidence As detailed in the main body of the methodological appendix (Appendix II, "Description of the methodology utilised for the collection, assessment
Status of Ossicles in Cholesteatoma
 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(2): 97-101 Original Article Status of Ossicles in Cholesteatoma Lt Col Mohammad Delwar Hossain 1, Brig Gen Md Nasir Uddin Ahamed 2, Major Mohammad Misbah Al Kabir
Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(2): 97-101 Original Article Status of Ossicles in Cholesteatoma Lt Col Mohammad Delwar Hossain 1, Brig Gen Md Nasir Uddin Ahamed 2, Major Mohammad Misbah Al Kabir
The diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis
 The diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis 1. Background The diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis (CP) is challenging. Chronic pancreatitis is a disease process consisting of: fibrosis of the pancreas (potentially
The diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis 1. Background The diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis (CP) is challenging. Chronic pancreatitis is a disease process consisting of: fibrosis of the pancreas (potentially
Tympanoplasty with and without cortical mastoidectomy in CSOM: A comparative study
 Original article: Tympanoplasty with and without cortical in CSOM: A comparative study 1 Dr. Parag V. Doifode, 2 Dr. Sandeep Dabhekar, 3 Dr. S. H. Gawarle 1Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government
Original article: Tympanoplasty with and without cortical in CSOM: A comparative study 1 Dr. Parag V. Doifode, 2 Dr. Sandeep Dabhekar, 3 Dr. S. H. Gawarle 1Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government
Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy)
 Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy) Clinical Policy Number: 11.03.05 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: September 21, 2016 Next
Clinical Policy Title: Ear tubes (tympanostomy) Clinical Policy Number: 11.03.05 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: September 21, 2016 Next
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews
 PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Drug-eluting balloon angioplasty versus non-stenting balloon angioplasty for peripheral arterial disease of the lower limbs [Cochrane Protocol]
PROSPERO International prospective register of systematic reviews Drug-eluting balloon angioplasty versus non-stenting balloon angioplasty for peripheral arterial disease of the lower limbs [Cochrane Protocol]
Medialization of Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis in Mastoid Obliteration
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2013; 9:(1) 110-114 CLINICAL STUDY Medialization of Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis in Mastoid Obliteration Ali Sanei-Moghaddam, Sanjiv Kumar, Neil Donnelly, Patrick Axon ENT, Medway
Int. Adv. Otol. 2013; 9:(1) 110-114 CLINICAL STUDY Medialization of Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis in Mastoid Obliteration Ali Sanei-Moghaddam, Sanjiv Kumar, Neil Donnelly, Patrick Axon ENT, Medway
Cholesteatoma in children
 Cholesteatoma in children British Association of Paediatricians in Audiology London Conference, Jan.2012 Matthew Clark FRCS (ORL-HNS) Consultant Otologist Gloucestershire Royal Hospital Overview: Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma in children British Association of Paediatricians in Audiology London Conference, Jan.2012 Matthew Clark FRCS (ORL-HNS) Consultant Otologist Gloucestershire Royal Hospital Overview: Cholesteatoma
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
Study selection Study designs of evaluations included in the review Diagnosis.
 Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Diagnosis and treatment of worker-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity: epicondylitis Chapell R, Bruening W, Mitchell M D, Reston J T, Treadwell J R Authors' objectives The objectives
Evidence-based Practice Center Systematic Review Protocol. Project Title: Otitis Media With Effusion: Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments
 Evidence-based Practice Center Systematic Review Protocol Project Title: Otitis Media With Effusion: Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments Amendment Date(s) if applicable: July 30, 2012 (Amendments Details
Evidence-based Practice Center Systematic Review Protocol Project Title: Otitis Media With Effusion: Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments Amendment Date(s) if applicable: July 30, 2012 (Amendments Details
Lateral Tympanoplasty for Total or Near-Total Perforation: Prognostic Factors
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2006 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Lateral Tympanoplasty for Total or Near-Total Perforation: Prognostic Factors
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2006 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Lateral Tympanoplasty for Total or Near-Total Perforation: Prognostic Factors
Surgical management of otitis media with effusion in children
 Issue date: February 2008 Surgical management of otitis media with effusion in children Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health About this booklet This is a quick
Issue date: February 2008 Surgical management of otitis media with effusion in children Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health About this booklet This is a quick
Introduction. Types of Cholesteatoma
 TITLE: Cholesteatoma SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: January 25, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Garrett Hauptman, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Tomoko Makishima, MD, PhD SERIES
TITLE: Cholesteatoma SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: January 25, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Garrett Hauptman, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Tomoko Makishima, MD, PhD SERIES
A pilot randomized controlled trial comparing bismuth iodine paraffin paste external ear pack and no ear pack after middle ear surgery
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2015) 272:543 550 DOI 10.1007/s00405-013-2812-6 OTOLOGY A pilot randomized controlled trial comparing bismuth iodine paraffin paste external ear pack and no ear pack after middle
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2015) 272:543 550 DOI 10.1007/s00405-013-2812-6 OTOLOGY A pilot randomized controlled trial comparing bismuth iodine paraffin paste external ear pack and no ear pack after middle
