First A Word About Sound
|
|
|
- Chloe Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 First A Word About Sound Sound is a mechanical disturbance propagated through elastic media Definition paraphrased from classroom discussion (10/22/02, Cornell University) In order to hear, our ears make use of two important features of sound: Frequency measured in Hertz Allows for differentiation of pitch Sound Pressure Level measured in decibels Allows for differentiation of intensity High pitches are represented as high frequencies and low pitches are represented as low frequencies. The following images show a graphical representation of a high and lowpitched sound. Note the difference in frequency.
2 Musical sound is just one of three different types of sounds The sound produced by vibration of a tuning fork is nearly a pure tone, as seen below. Note the sinusoidal representation. Musical instruments produce complex sounds that are a combination of the fundamental frequency (the lowest frequency) and the overtones. Each instrument produces a sound with a different combination of overtones; the difference between these sounds is called timbre. The following image shows a graph of a musical sound. Note the complex and periodic nature. The third type of sound is noise, in which there is no normal frequency.
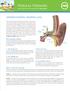
3 How We Hear The healthy ear processes sound frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. It detects sounds as soft as.0002 dynes/cm**2 (0 DB HL) and can tolerate sounds a million times more intense (200 dynes/cm**2 or 120 DB HL). Sound frequencies between 500 and 4000 Hz include the frequencies most important for speech. Normal hearing: sound waves are first collected in our outer ear (called the auricle or pinna), pass through our ear canal and cause our eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are in turn transmitted to our inner ear by the bones of our middle ear. Our inner ear plays a vital role in the transformation of these mechanical vibrations into electrical impulses, or signals, which can be recognized and decoded by our brain. When the vibrations reach the cochlea through movement of the bones in the middle ear, the fluid within it begins to move, resulting in back and forth motion of tiny hairs (sensory receptors) lining the cochlea. This motion results in the hair cells sending a signal along the auditory nerve to the brain. Our brain receives these impulses in its hearing centers and interprets them as a type of sound. Anatomy The most important structures involved in hearing are shown on the figure below. The outer ear (pinna or auricle) may provide a modest (10db) amplification of sounds at the upper range of speech processing frequencies. The middle ear, bounded by the eardrum (1) and the bony labyrinth, provides an additional Db of mechanical amplification by coupling the large eardrum (tympanic membrane) to the oval window into the fluid filled inner ear. The 20 to 30 db of amplification is approximately the difference in sound intensity between a whisper and normal conversation.
4 Figure: The outer ear consists of the auricle (unlabelled), the external auditory canal, and the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane (TM). The middle ear includes the medial surface of the eardrum, the ossicular chain, the eustachian tube, and the tympanic segment of the facial nerve. The inner ear includes the auditory-vestibular nerve, the cochlea and the vestibular system (semicircular canals). The auditory nerve, also called the cochlear nerve, transmits sound to the brain. Early Warnings of hearing loss Do people "mumble"? Do you frequently say "what?" or "Huh?" DO you misunderstand names and numbers? DO you like the TV/radio volume louder? Do you have trouble hearing in noisy rooms? Overview of causes of hearing loss There are three "pure" types of hearing loss encountered commonly in clinical practice: sensorineural, conductive, and central. A fourth type, denoted "mixed", is simply a combination of sensorineural and conductive.
5 Disorders of the middle ear are generally responsible for conductive losses. Disorders of the cochlea or cochlear nerve for sensorineural hearing loss, and disorders of the brainstem or brain account for central hearing loss. Sensorineural Hearing Loss Sensorineural hearing loss(snhl) accounts for about 90% of all hearing loss. This is sometimes also called "nerve deafness", although the term is not entirely accurate, leaving out disorders of the hair-cells of the inner ear. It is found in 23% of population older than 65 years of age. The term "sensorineural" is used to indicate that there is either a cochlear or an eighth nerve lesion. The diagnosis of a sensorineural pattern hearing loss is made through audiometry, which shows a significant hearing loss without the "air-bone gap" that is characteristic of conductive hearing disturbances. In other words, air conduction is equal to bone conduction. Common causes include old age, where the hearing pattern is often called presbycusis (see following section), Menieres disease, ototoxic medications (such as high-dose aspirin or certain strong diuretics), immune disorders, and noise exposure (see following section). Trauma (inner ear concussion) can cause both temporary and permanent hearing loss. Diabetes is associated with gradually progressive bilateral high-frequency SNHL. Pathological studies suggest that it is due to microangiopathic involvement of inner ear blood vessels and subsequent stria vascularis atrophy and hair cell loss (Fukushima et al, 2004) 13-20% of those with menigntis develop hearing loss (Dichgans et al, 1999; Wellman et al, 2003). Postmeningitic hearing loss can be due to lesions of the cochlea, brainstem and higher auditory pathways, but usually is related to suppurative labyrinthitis (cochlear). There are many causes of sensorineural hearing loss that are extremely rare. Tumors in general are a very rare cause of sensorineural hearing loss. Examples are acoustic neuroma and glomus tumor. Hyperviscosity syndromes such as Von Waldenstroms macroglobulinemia are another rare cause. Superficial siderosis, due to CNS bleeding, can cause a slowly progressive sensorineural hearing loss as well as cerebellar or vestibular disturbances. Kawasacki's disease is a rare cause of hearing loss in children. Radiation to the ear is often associated with a chronic, progressive hearing deterioration (Wang et al, 2004). References for sensorineural hearing loss: Fearnley J, Rudge P. Treatment of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Movement Disorders 10, 1995, Fukushima H and others. The effects of type I diabetes mellitus on the cochlear structure and vascularture in human temporal bones. The National Temporal Bone Registry, Summer 2004 issue, Volume 12, #1 Wang LF and others. A long-term study on hearing status in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy. Otol Neurotol 25: , 2004.
6 Wellman MB, Sommer DD, McKenna J. Sensorineural hearing loss in postmeningitic children. Otol Neurotol 2003; 24(6): Noise Noise is a common cause of hearing loss in the US. Twenty-five percent of the US work force is regularly exposed to potentially damaging noise (Suter and von Gierke, 1987). Because of occupational risk of noise induced hearing loss, there are government standards regulating allowable noise exposure. People working before the mid 1960's may have been exposed to higher levels of noise where there were no laws in the USA mandating use of devices to protect hearing. An example of an audiogram showing noise induced hearing loss is shown below. There is a clear "notch" at 3000 hz, with better hearing at both lower and higher frequencies. Noise can also cause a reversible hearing loss, called a temporary threshold shift. This typically occurs in individuals who are exposed to gunfire or firecrackers, and hear ringing in their ears after the event (tinnitus). Non-occupational noise are also regularly encountered during recreational activities and are a source of premature hearing reduction. Peak noise levels, in DB, are provided in the following table taken from Smith et al, 1999). NOISE Firecracker 180 Gunshot 167 Car Stereo 154 Children's toys 150 Sporting events 127 Rock Concert 120 Health Club 120 Motorboats 115 Video Arcade 110 Snowmobile 99 Movie 94 LEVEL Hearing loss and tinnitus (usually temporary), can also be associated with high doses of aspirin or other ototoxic drugs such as the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clark, W. W. and B. A. Bohne (1999). "Effects of noise on hearing." Jama 281(17): Suter, A. H. and H. E. von Gierke (1987). "Noise and public policy." Ear Hear 8(4):
7 Musicians and the prevention of hearing loss: Musical instruments can generate considerable sound and thus can also cause hearing loss. The most damaging type of sounds is in the high-frequencies. Violins and violas can be sufficiently loud to cause permanent hearing loss. This is typically worse in the left ear which is nearer the instrument. Unlike other instruments, the ability to hear the highfrequency harmonics is crucial to these musicians. Mutes can be used while practicing to reduce long term exposure. (Karlsson, Lundquist et al. 1983; Ostri, Eller et al. 1989; Royster, Royster et al. 1991; Sataloff 1991; Palin 1994; Teie 1998; Obeling and Poulsen 1999; Hoppmann 2001; Kahari, Axelsson et al. 2001). In a study of rock/jazz musicions, almost 3/4 had a hearing disorder, with hearing loss, hyperacusis and tinnitus being the most common maladies. (Kaharit, Zachau et al. 2003) There are a number of strategies that can be used to reduce the chance of noise injury from other instrumentalists. Musicians ear plugs are generally "flat" so that bass and treble notes are not relatively favored, thus distorting perception. Nevertheless, a"vented" ear plug can be used to tune the ear cavity to low frequencies, which are less damaging. Drummers should use musicians ear plugs, such as the ER-25. Guitarists and vocalists can use the less attenuating ER-15. Too much ear protection can result in overplaying and not enough protection can result in hearing loss. Plexiglass baffles can be used to reduce the noise from other instruments.these are particularly relevent for drummer's high-hat cymbals. Drums and brass can be particularly a problem. Ear monitors are small in-the-ear devices that look like hearing aids, that can be used to electronically protect hearing, while allowing the musicians to hear themselves. Acoustic monitors are stethescope like devices that block sound from other in the group, but allow the instrumentalist to hear their own instrument. Loudspeakers produce both high and low frequency sounds. High frequencies tend to emanate in almost a straight line, while low frequencies are present in nearly all directions. Thus, standing besides a high-frequency source may provide some protection. Humming just prior to, and through a loud noise such as a cymbal crash or rim shot may provide some protection. Small protective muscles in the ear contract naturally when we sing or hum, and thus humming may protect from other noises. Chasin M. Music appreciation 101. Woodwinds, large stringed instruments, violins and violas. The Hearing REview, Jan 2000, 46. Chasin M. Music Appreciation 101. Bass players and drummers and guitar and rock/blues vocalists. Hoppmann, R. A. (2001). "Instrumental musicians' hazards." Occup Med 16(4): , iv-v. Kahari, K. R., A. Axelsson, et al. (2001). "Hearing assessment of classical orchestral musicians." Scand Audiol 30(1): Kaharit, K., G. Zachau, et al. (2003). "Assessment of hearing and hearing disorders in rock/jazz musicians." Int J Audiol 42(5):
8 Karlsson, K., P. G. Lundquist, et al. (1983). "The hearing of symphony orchestra musicians." Scand Audiol 12(4): Obeling, L. and T. Poulsen (1999). "Hearing ability in Danish symphony orchestra musicians." Noise Health 1(2): Ostri, B., N. Eller, et al. (1989). "Hearing impairment in orchestral musicians." Scand Audiol 18(4): Palin, S. L. (1994). "Does classical music damage the hearing of musicians? A review of the literature." Occup Med (Lond) 44(3): Royster, J. D., L. H. Royster, et al. (1991). "Sound exposures and hearing thresholds of symphony orchestra musicians." J Acoust Soc Am 89(6): Sataloff, R. T. (1991). "Hearing loss in musicians." Am J Otol 12(2): Teie, P. U. (1998). "Noise-induced hearing loss and symphony orchestra musicians: risk factors, effects, and management." Md Med J 47(1): Presbycusis Presbycusis is defined as hearing loss associated with degenerative changes of aging. Presbyacusis is the most common type of hearing loss in the United States. This type of hearing loss is typically gradual, bilateral, and characterized by difficulty hearing high frequencies. There are four types: sensory presbycusis is caused by loss of sensory elements in the basal end (high-frequency end) of the cochlea with preservation of neurons. These patients have symmetrical, high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss (as shown below). Pathology shows loss of hair cells. Neural presbycusis is caused by loss of cochlear neurons. These patients have poorer discrimination than patients with sensory presbycusis. Striatal presbycusis is caused by loss of the stria vascularis with aging. Patients have a flat or slightly sloping hearing loss with good speech discrimination. Mixed presbycusis is also possible. A final type is cochlear conductive presbycusis. This is a sensorineural hearing loss caused by thickening of the basilar membrane caused by deposition of basophilic substance. This diagnosis is made on postmortem. (Harris, 1998). An example of presbycusis is shown below. Presbycusis can be inherited -- a recent study suggested that heritability of medium and low frequencies was.38 and.31 (DeStefano et al, 2003). More information about presbycusis is found here. Statistical data from the US vital statistics can be found here. References for Presbycusis Destefano AL and others. Genomewide linkage analysis to presbycusis in the Framingham heart study. Arch Otolaryngol HNS :
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
Chapter x. Causes of Hearing Damage. 1. Introduction.
 Chapter x Causes of Hearing Damage 1. Introduction. 2. Noise induced hearing damage. 3. Other causes of hearing loss. 4. Tests and Exercises. 5. References. 1. Introduction. This chapter explains the main
Chapter x Causes of Hearing Damage 1. Introduction. 2. Noise induced hearing damage. 3. Other causes of hearing loss. 4. Tests and Exercises. 5. References. 1. Introduction. This chapter explains the main
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist
 WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Hearing Evaluation: Diagnostic Approach
 Hearing Evaluation: Diagnostic Approach Hearing Assessment Purpose - to quantify and qualify in terms of the degree of hearing loss, the type of hearing loss and configuration of the hearing loss - carried
Hearing Evaluation: Diagnostic Approach Hearing Assessment Purpose - to quantify and qualify in terms of the degree of hearing loss, the type of hearing loss and configuration of the hearing loss - carried
Acquired Deafness Loss of hearing that occurs or develops sometime in the course of a lifetime, but is not present at birth.
 Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Sound and Hearing. Decibels. Frequency Coding & Localization 1. Everything is vibration. The universe is made of waves.
 Frequency Coding & Localization 1 Sound and Hearing Everything is vibration The universe is made of waves db = 2log(P1/Po) P1 = amplitude of the sound wave Po = reference pressure =.2 dynes/cm 2 Decibels
Frequency Coding & Localization 1 Sound and Hearing Everything is vibration The universe is made of waves db = 2log(P1/Po) P1 = amplitude of the sound wave Po = reference pressure =.2 dynes/cm 2 Decibels
Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss
 Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss Diana Callesano, Au.D., CCC-A Eric Nelson, Au.D., CCC-A Clinical Audiologists Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hearing and Speech Services
Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss Diana Callesano, Au.D., CCC-A Eric Nelson, Au.D., CCC-A Clinical Audiologists Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hearing and Speech Services
Hearing Loss: From Audiogram to RFC Learn How to Effectively Represent Deaf and Hard of Hearing Claimants
 V Hearing Loss: From Audiogram to RFC Learn How to Effectively Represent Deaf and Hard of Hearing Claimants Michael Liner, Esq. Mark Mehle, MD Andrew November, Esq. Hearing Loss: From Audiogram to RFC
V Hearing Loss: From Audiogram to RFC Learn How to Effectively Represent Deaf and Hard of Hearing Claimants Michael Liner, Esq. Mark Mehle, MD Andrew November, Esq. Hearing Loss: From Audiogram to RFC
HEARING IMPAIRMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Divisions of the Ear. Inner Ear. The inner ear consists of: Cochlea Vestibular
 HEARING IMPAIRMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Recognize the clinical manifestation and to be able to request appropriate investigations Interpret lab investigations for basic management.
HEARING IMPAIRMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Recognize the clinical manifestation and to be able to request appropriate investigations Interpret lab investigations for basic management.
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective
 Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What the Regulations say about noise Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection What is Sound? Hertz
Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What the Regulations say about noise Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection What is Sound? Hertz
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE. 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1
 HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1 Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What does OSHA says about noise? Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1 Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What does OSHA says about noise? Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection
Audiology (Clinical Applications)
 (Clinical Applications) Sasan Dabiri, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Last Updated in February 2015
(Clinical Applications) Sasan Dabiri, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Last Updated in February 2015
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg
 Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_HealthProvider-Flip_FINAL02.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS HCE_HealthProvider-Flip_FINAL02.indb 1 In both on- and off-duty settings, hearing is an important element of life. ON DUTY Situational awareness
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS HCE_HealthProvider-Flip_FINAL02.indb 1 In both on- and off-duty settings, hearing is an important element of life. ON DUTY Situational awareness
2 Background. 2.1 The Hearing Sense
 2 Background 2.1 The Hearing Sense People hear by detecting sounds vibration. Hearing is one of the five senses (sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch) that humans possess. The human ear consists of
2 Background 2.1 The Hearing Sense People hear by detecting sounds vibration. Hearing is one of the five senses (sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch) that humans possess. The human ear consists of
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
ﺎﻨﺘﻤﻠﻋ ﺎﻣ ﻻا ﺎﻨﻟ ﻢﻠﻋ ﻻ ﻚﻧﺎﺤﺒﺳ اﻮﻟﺎﻗ ﻢﻴﻜﺤﻟا ﻢﻴﻠﻌﻟا ﺖﻧأ ﻚﻧا ﻢﻴﻈﻌﻟا ﷲا قﺪﺻ HEARING LOSS
 قالوا سبحانك لا علم لنا الا ما علمتنا انك أنت العليم الحكيم صدق االله العظيم HEARING LOSS 1 Hearing loss: Deviation from normal hearing in one or both ears. Hearing handicap: This term refers to total
قالوا سبحانك لا علم لنا الا ما علمتنا انك أنت العليم الحكيم صدق االله العظيم HEARING LOSS 1 Hearing loss: Deviation from normal hearing in one or both ears. Hearing handicap: This term refers to total
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Chapter 6: Hearing Loss
 The American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF) Presents... Chapter 6: Hearing Loss Daiichi Pharmaceutical Corporation, marketers and distributors of FLOXIN Otic (ofloxacin
The American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF) Presents... Chapter 6: Hearing Loss Daiichi Pharmaceutical Corporation, marketers and distributors of FLOXIN Otic (ofloxacin
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Sound Waves. Sensation and Perception. Sound Waves. Sound Waves. Sound Waves
 Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss
 DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss VI. How Do We Hear? Sound waves enter our ears and are amplified by the ear drum and middle ear bones (ossicles), allowing
DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss VI. How Do We Hear? Sound waves enter our ears and are amplified by the ear drum and middle ear bones (ossicles), allowing
PRESBYACUSIS A REVIEW
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 24, 2014 PRESBYACUSIS A REVIEW Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/82/ Presbyacusis A Review Balasubramanian
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 24, 2014 PRESBYACUSIS A REVIEW Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/82/ Presbyacusis A Review Balasubramanian
THE MECHANICS OF HEARING
 CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
Anatomy of the ear: Lymphatics
 Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary
 photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com American Sign Language (ASL): a manual language with its own word order and grammar, used primarily by people who are Deaf. Atresia (aural):
photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com American Sign Language (ASL): a manual language with its own word order and grammar, used primarily by people who are Deaf. Atresia (aural):
managing safely Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23
 Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23 Course Content 1. What is noise? 2. Sound - Sound Waves 3. How do we hear? - The
Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23 Course Content 1. What is noise? 2. Sound - Sound Waves 3. How do we hear? - The
Outline. The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
 The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing. Figure 1. The human ear (from Kessel and Kardon, 1979)
 Hearing The nervous system s cognitive response to sound stimuli is known as psychoacoustics: it is partly acoustics and partly psychology. Hearing is a feature resulting from our physiology that we tend
Hearing The nervous system s cognitive response to sound stimuli is known as psychoacoustics: it is partly acoustics and partly psychology. Hearing is a feature resulting from our physiology that we tend
Protect Your Hearing!
 Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Occupational Noise Exposure 29 CFR
 Occupational Noise Exposure 29 CFR 1910.95 Is There a Problem? More than 30 million Americans are exposed to hazardous sound levels on a regular basis 10 million have suffered irreversible noise induced
Occupational Noise Exposure 29 CFR 1910.95 Is There a Problem? More than 30 million Americans are exposed to hazardous sound levels on a regular basis 10 million have suffered irreversible noise induced
Hearing Aids. Bernycia Askew
 Hearing Aids Bernycia Askew Who they re for Hearing Aids are usually best for people who have a mildmoderate hearing loss. They are often benefit those who have contracted noise induced hearing loss with
Hearing Aids Bernycia Askew Who they re for Hearing Aids are usually best for people who have a mildmoderate hearing loss. They are often benefit those who have contracted noise induced hearing loss with
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Glossary For Parents. Atresia: closure of the ear canal or absence of an ear opening.
 Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
Hearing. By Jack & Tori
 Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Educational Module Tympanometry. Germany D Germering
 Educational Module anometry PATH medical Germany D-82110 Germering Our educational modules 1 are made for providing information on how the hearing organ works and which test procedures are used to test
Educational Module anometry PATH medical Germany D-82110 Germering Our educational modules 1 are made for providing information on how the hearing organ works and which test procedures are used to test
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
Hearing for life Facts about hearing. How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing
 Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY
 Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Chapter 17 Sound Sound and Hearing. Properties of Sound Waves 1/20/2017. Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action
 Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING
 COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
Chapter 3. Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics
 Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
Hearing ConservationTraining
 Hearing ConservationTraining Introduction Employees who are exposed to hazardous levels of noise in the workplace are at risk for developing noise-induced hearing loss. Noise-induced hearing loss is 100
Hearing ConservationTraining Introduction Employees who are exposed to hazardous levels of noise in the workplace are at risk for developing noise-induced hearing loss. Noise-induced hearing loss is 100
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Hearing Lectures. Acoustics of Speech and Hearing. Auditory Lighthouse. Facts about Timbre. Analysis of Complex Sounds
 Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Guide to Your Hearing Health
 Guide to Your Hearing Health Hearing loss is the 3rd most common chronic physical condition in the U.S. X Don t suffer in silence we ve got solutions to help keep you connected! Table of Contents Hearing
Guide to Your Hearing Health Hearing loss is the 3rd most common chronic physical condition in the U.S. X Don t suffer in silence we ve got solutions to help keep you connected! Table of Contents Hearing
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Hearing Screening, Diagnostics and Intervention
 JCIH Newborn Hearing Screening Guidelines 1-3-6 Model By 1 month Screenhearing Hearing Screening, Diagnostics and Intervention By 3 months: Evaluate hearing and complete diagnosticaudiology and otolaryngology
JCIH Newborn Hearing Screening Guidelines 1-3-6 Model By 1 month Screenhearing Hearing Screening, Diagnostics and Intervention By 3 months: Evaluate hearing and complete diagnosticaudiology and otolaryngology
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA. Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002
 Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests
 Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
whether or not the fundamental is actually present.
 1) Which of the following uses a computer CPU to combine various pure tones to generate interesting sounds or music? 1) _ A) MIDI standard. B) colored-noise generator, C) white-noise generator, D) digital
1) Which of the following uses a computer CPU to combine various pure tones to generate interesting sounds or music? 1) _ A) MIDI standard. B) colored-noise generator, C) white-noise generator, D) digital
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
Guide to Your Hearing Health
 X Guide to Your Hearing Health Hearing loss is the 3rd most common chronic physical condition in the U.S. Don t suffer in silence we ve got solutions to help keep you connected! Are you having difficulty
X Guide to Your Hearing Health Hearing loss is the 3rd most common chronic physical condition in the U.S. Don t suffer in silence we ve got solutions to help keep you connected! Are you having difficulty
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment
 INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
Almost 9 million people in the UK, 1 in 7 of the population, suffer from deafness or experience significant hearing difficulty i
 Deafness the facts HOW MANY PEOPLE ARE AFFECTED? Almost 9 million people in the UK, 1 in 7 of the population, suffer from deafness or experience significant hearing difficulty i CHILDHOOD DEAFNESS It is
Deafness the facts HOW MANY PEOPLE ARE AFFECTED? Almost 9 million people in the UK, 1 in 7 of the population, suffer from deafness or experience significant hearing difficulty i CHILDHOOD DEAFNESS It is
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics
 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals Gelatinous mass. Cilia. Hair cells. Vestibular nerve. Vestibular ganglion
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
Audiology Curriculum Foundation Course Linkages
 Audiology Curriculum Foundation Course Linkages Phonetics (HUCD 5020) a. Vowels b. Consonants c. Suprasegmentals d. Clinical transcription e. Dialectal variation HUCD 5140 HUCD 6360 HUCD 6560 HUCD 6640
Audiology Curriculum Foundation Course Linkages Phonetics (HUCD 5020) a. Vowels b. Consonants c. Suprasegmentals d. Clinical transcription e. Dialectal variation HUCD 5140 HUCD 6360 HUCD 6560 HUCD 6640
It a graph that represents the hearing thresholds across frequencies.
 It a graph that represents the hearing thresholds across frequencies. The audiometric worksheet might represent all or some of the following information; Patient s name. Patient s age (date of birth).
It a graph that represents the hearing thresholds across frequencies. The audiometric worksheet might represent all or some of the following information; Patient s name. Patient s age (date of birth).
Hearing Lectures. Acoustics of Speech and Hearing. Subjective/Objective (recap) Loudness Overview. Sinusoids through ear. Facts about Loudness
 Hearing Lectures coustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-8 Hearing 1: Perception of Intensity 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for
Hearing Lectures coustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-8 Hearing 1: Perception of Intensity 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
