Disparity in embrasure fill and papilla height between tooth- and implant-borne fixed restorations in the anterior maxilla: a cross-sectional study
|
|
|
- Reginald Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Clin Periodontol 2013; 40: doi: /jcpe Disparity in embrasure fill and papilla height between tooth- and implant-borne fixed restorations in the anterior maxilla: a cross-sectional study Jan Cosyn 1,2, Magalie Raes 1, Mathieu Packet 3, Roberto Cleymaet 2,3 and Hugo De Bruyn 1,4 1 Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School, University of Ghent, De Pintelaan 185, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium; 2 Dental Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Free University of Brussels (VUB), Laarbeeklaan 103, B-1090 Brussels, Belgium; 3 Private multidisciplinary practice, Ghent, Belgium; 4 Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Odontology, Malm o University, Malm o, Sweden Cosyn J, Raes M, Packet M, Cleymaet R, De Bruyn H. Disparity in embrasure fill and papilla height between tooth- and implant-borne fixed restorations in the anterior maxilla: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Periodontol 2013; 40: doi: /jcpe Abstract Purpose: The objective of the present study was to compare inter-proximal fill and papilla height between different embrasures. Material & Methods: One hundred and fifty non-smoking consecutive patients (mean age 54, range 32 73; 63 males and 87 females) without periodontal disease were selected in a multidisciplinary practice during regular supportive care. All had been treated for multiple tooth loss in the anterior maxilla at least 1 year earlier by means of a fixed restoration on teeth (n = 50) or implants (n = 100) using straightforward procedures (without hard and/or soft tissue augmentation). Embrasure fill was assessed by means of Jemt s papilla index and papilla height was registered following local anaesthesia by means of bone sounding by one clinician. Results: Tooth-pontic and tooth-implant embrasures demonstrated comparable inter-proximal fill and papilla height ( 58% Jemt s score 3; mean papilla height 4.1 mm). Between missing teeth, embrasure fill and papilla height were lower regardless of the embrasure type. The implant-implant and implant-pontic embrasure demonstrated comparable outcome ( 42% Jemt s score 3; mean papilla height 3.3 mm; p 0.416), which was significantly poorer when compared to the pontic-pontic embrasure (82% Jemt s score 3; mean papilla height 3.7 mm; p 0.019). Overall, papilla index and papilla height demonstrated a weak correlation (Spearman s correlation coefficient: 0.198; p = 0.002). Conclusions: The re-establishment of a papilla is difficult when there is no tooth involved. In that scenario a short papilla should be expected and implant-borne restorations demonstrate the poorest outcome. Moreover, an implant with a pontic may not perform better than adjacent implants. View the pubcast on this paper at Key words: dental implant; embrasure; fixed partial denture; papilla; tooth Accepted for publication 16 April 2013 Conflict of interest and source of funding The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests. The study was supported by the authors and their institutions. 728
2 Embrasure fill and papilla height 729 The aesthetic outcome of a prosthetic treatment is difficult to evaluate as it may be affected by many parameters. In a recent systematic review on the professional assessment of aesthetics in implant dentistry this complexity was highlighted and the need for a consensus on objective and well-defined aesthetic parameters was described (Benic et al. 2012). Albeit there is currently little agreement on such parameters, the presence of papillae may be considered an important characteristic of an aesthetic result. A number of studies have been published on papillae in the context of single implant treatment (Grunder 2000, Choquet et al. 2001, Kan et al. 2003, Henriksson & Jemt 2004, Cardaropoli et al. 2006, Juodzbalys & Wang 2007, den Hartog et al. 2008, 2011a,b, Lai et al. 2008, Chen et al. 2009, Buser et al. 2011, Cosyn et al. 2011, 2012a, Gallucci et al. 2011, Raes et al. 2011). Choquet et al. (2001) described complete papilla presence in 58% of the cases between a tooth and an implant with mean papilla height of nearly 4 mm as assessed by bone sounding. The latter may not differ substantially from papilla height between teeth (Tarnow et al. 1992), which has been explained by the preservation of bone and supracrestal fibres at the tooth facing the implant restoration. Hence, factors causing loss of these tissues such as periodontal disease, multiple surgeries with papilla openings and incorrect implant positioning in relation to the tooth, may in turn be responsible for partial or complete papilla loss (Cosyn et al. 2012c). A recent study has shown that a conventional bridge is still a common treatment concept for single tooth replacement in general practice (Cosyn et al. 2012b). In this concept, the embrasure is formed by a tooth and a pontic. The tissue preserving effect of a tooth may also apply here, which is in line with a predictable papilla length of about 5 mm for inter-proximal tooth surfaces as described by Salama and co-workers (1998). On the other hand, data on papilla index for a tooth-pontic (T-P) embrasure are lacking. Hence, the first objective was to compare papilla index and height between the tooth-implant (T-I) and the T-P embrasure. Complexity increases when two adjacent teeth need replacement in the anterior maxilla. Especially the re-establishment of a papilla between missing teeth is particularly challenging as the inter-dental bone peak will flatten following tooth loss. Essentially, such an embrasure can be formed by two pontics, two implants or an implant and a pontic. Salama and co-workers (1998) observed a predictable papilla length of about 5 mm for inter-proximal tooth surfaces, 4.5 mm between adjacent implants and 5.5 mm for interproximal implant surfaces not facing another implant. These data suggest that the most optimal papilla for an implant-pontic (I-P) and pontic-pontic (P-P) embrasure. However, the lack of clear selection criteria and the fact that papilla length was registered by sounding the first tooth- or implant-to-bone contact instead of the inter-proximal crestal bone peak, make a correct interpretation difficult. Tarnow and co-workers (2003) described mean papilla height of 3.4 mm between implants as assessed by sounding the inter-proximal crestal bone peak on the basis of a quite heterogeneous sample in terms of implant position (anterior as well as posterior), implant type (one- as well as two-piece implants) and bone conditions (native as well as regenerated bone). To overcome aesthetic failures as a result of a deficient papilla, Tarnow et al. (2003) and Barreto et al. (2008) suggested to place only one implant instead of two and to splint it to a cantilevered ovate pontic. Interestingly, however, Tymstra et al. (2011) demonstrated identical embrasure fill for the implant-implant (I-I) and I-P embrasure. Limitations include a very small study sample (5 patients per embrasure type) and lack of data on papilla height. This information clearly shows that the available literature falls short when it comes to data on papillae formed by two pontics, two implants or an implant and a pontic. Hence, another objective was to compare papilla index and height between these embrasures. This information is important from an aesthetic point of view (Tarnow et al. 1992, Jemt 1997) and may become one of the reasons to select or refute a prosthetic treatment option in clinical practice. Material and Methods Patient selection This cross-sectional study was based on a convenience sample of 150 consecutive patients consulting for regular supportive care in a multidisciplinary practice in Ghent between September 2009 and January Patients were selected on the basis of specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria were as follows: Fixed restoration on teeth (FRT) or implants (FRI) replacing 2 or more adjacent teeth in the anterior maxilla (15 25) and at least 1 year in function. Prosthetic procedures performed by 1 of 2 restorative dentists (RC/MP). With respect to FRI, surgical procedures performed by 1 of 2 implant surgeons only using twopiece implant systems (JC/MP). Informed consent. Exclusion criteria were as follows: Systemic diseases. Intake of medication that could induce gingival overgrowth. Smoking or history of smoking. Prostheses without ovate pontic design. History of periodontal treatment. Periodontal disease at the time of examination. Hard and/or soft tissue augmentation procedures. With respect to FRI, suboptimal implant position (T-I distance < 2 mm, I-I distance < 3 mm) as clinically and/or radiographically assessed. With respect to FRI, periimplant probing depth >4 mm and/or bone loss 2 mm. Measurements between an abutment tooth and adjacent pontic (T-P) and between pontics (P-P) were performed in 50 patients with a FRT. Measurements between a tooth and an implant (T- I) and between adjacent implants (I- I) were performed in 50 patients with a FRI. In another
3 730 Cosyn et al. 50 patients with a FRI, papillae were studied between an implant and a pontic (I-P) (Group III). All embrasures were evaluated in the anterior maxilla and if the embrasure type of interest was present at multiple locations in a patient, the most central location was selected. The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University Hospital in Ghent. Outcome variables The following outcome variables were registered for 250 embrasures with different embrasures in 150 patients by the same experienced and calibrated clinician (JC): Embrasure fill was assessed by means of Jemt s papilla index (Jemt 1997). Papilla height was registered following local anaesthesia by means of bone sounding using a periodontal probe (PCPUNC 15, Hu-Friedy â, Leimen, Germany) as described by Tarnow et al. (1992). All recordings were rounded off to the nearest 0.5 mm. (gender, papilla index). Disparities between patient groups in terms of age and years in function were evaluated using the Kruskal Wallis test. For gender, the Fisher s exact test was adopted. The Wilcoxon signed ranks test was used to study disparities in papilla index and papilla height between paired data (T-P and P-P within the same patient; T-I and I-I within the same patient). The Fisher s exact test was adopted to compare unpaired data in terms of papilla index (T-P and T-I in different patients; P-P, I-I and I-P in different patients). Disparities in papilla height between unpaired data were evaluated using the Mann Whitney test (T-P and T-I in different patients) or Kruskal Wallis test (P-P, I-I and I-P in different patients). The level of significance was set at 0.05 with no correction for multiple testing. Results The total sample included 150 patients with a mean age of 54 (range 32 73). Sixty-three were males and 87 were females. Restorations had been on average 4 years in function (range 1 10). Table 1 gives an overview of patient s age, gender and years in function of the restoration per patient group. Patient groups did not differ in any of these aspects (p 0.091). Sixty-seven patients were re-habilitated using parallel-walled Biomet 3i â (Palm Beach, FL, USA) implants with an external connection, 22 using tapered Biomet 3i â implants with an internal connection and 11 using Replace Select tapered TiUnite â (Nobel Biocare, G oteborg, Sweden) implants. Embrasure fill Duplicate registration of papilla index resulted in high intra-examiner agreement (Spearman s correlation coefficient: 0.915; p 0.001). Table 2 shows frequency distributions on papilla index sorted per embrasure type. T-P and P-P embrasures assessed in the FRT group, did not differ significantly in papilla index (p = 0.439). In the FRI group with adjacent implants, however, significantly less inter-proximal fill was observed for I-I when compared to T-I embrasures (p < 0.001). Comparison of unpaired data in different patient groups revealed comparable Calibration for papilla index was based on 20 duplicate recordings in 4 patients with a time interval of 1 week. Calibration for papilla height was based on a comparison of clinical height to radiographic height of 10 central maxillary papillae in 10 patients. Radiographic papilla height was determined on the basis of digital radiographs taken with the long-cone paralleling technique. Designated software (DBSWIN, D urr Dental AG, Bietigheim-Bissingen, Germany) was used to calculate radiographic papilla height. Cases used for calibration included all embrasure types. Statistical analysis Data analysis was performed with the patient as the experimental unit. The majority of the data were non-normally distributed and therefore nonparametric tests were applied. For all continuous variables (age, years in function, papilla height) mean values and standard deviations were calculated, whereas frequency distributions were made for categorical variables Table 1. Demographic data and years in function of the restoration sorted per patient group Patient group Age* Gender Years in function of the restoration* Group I 54 (10) [33 73] 21 males, 29 females 5 (3) [1 10] Group II 53 (10) [32 71] 18 males, 32 females 4 (2) [1 8] Group III 54 (10) [33 73] 24 males, 26 females 4 (2) [1 9] p-value *Mean (standard deviation) [range]. Group I: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on teeth (tooth-pontic and pontic-pontic measurements). Group II: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on implants (tooth-implant and implant-implant measurements). Group III: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on implants (implant-pontic measurements). Table 2. Frequency distributions (%) on papilla index sorted per embrasure type (n = 250) Jemt s papilla index Tooth-pontic Tooth-implant Pontic-pontic Implant-implant Implant-pontic (Group III) Score Score Score Score Score Group I: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on teeth (tooth-pontic and pontic-pontic measurements). Group II: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on implants (tooth-implant and implant-implant measurements). Group III: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on implants (implant-pontic measurements).
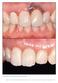
4 Embrasure fill and papilla height 731 papilla index for T-P and T-I embrasures (p = 0.185). Particularly interesting from an aesthetic point of view was the evaluation of papilla index between missing teeth with P-P, I-I or I-P embrasures as possible solutions. Significantly more inter-proximal fill was observed for the P-P embrasure when compared to I-I (p < 0.001) and I-P (p < 0.001). I-I and I-P embrasures demonstrated comparable papilla index (p = 0.416). As also shown in Table 2, complete interproximal fill was only accomplished in less than half of the cases when one or two implants formed the embrasure. A clinical example of an I-P embrasure is shown in Fig. 1. Papilla height Clinical and radiographic papilla height demonstrated high agreement (Spearman s correlation coefficient: 0.994; p 0.001). Based on the total patient sample papilla height and years in function demonstrated a significant, yet weak correlation (Spearman s correlation coefficient: 0.178; p = 0.029). Table 3 shows the results on papilla height sorted per embrasure type. T-P and P-P embrasures as assessed in the FRT group, differed significantly in papilla height with papillae being on average 0.5 mm shorter between pontics (p = 0.001). In the FRI group with adjacent implants, papillae were on average 0.8 mm shorter for I-I when compared to T-I embrasures (p < 0.001). Comparison of unpaired data in different patient groups revealed comparable papilla height for T-P and T-I embrasures (p = 0.383). When scrutinizing possible solutions for recreating papillae between missing teeth, papillae were on average mm higher for the P-P embrasure when compared to I-I (p = 0.019) and I-P (p = 0.004). I-I and I-P embrasures demonstrated comparable papilla height (p = 0.486). As also shown in Table 3, the probability of ending up with an ideal papilla ( 4 mm) between missing teeth was reduced by half when one or two implants formed the embrasure. Correlation of papilla index with papilla height On the basis of the total sample (n = 250) papilla index and papilla height demonstrated a weak, yet significant correlation (Spearman s correlation coefficient: 0.198; p = 0.002). Fig. 1. Clinical example of an embrasure formed by an implant (tooth 23) and pontic (tooth 22). Papilla index = 2; papilla height = 3 mm. Discussion The amount of soft tissues filling the embrasure may be affected by ample factors. These have been identified in a study on single implant treatment using multivariate analyses and include periodontal disease, multiple surgeries with papilla openings and factors relating to the implant and contact point position (Cosyn et al. 2012c). In the present study patient selection was very strict taking into account most of these factors. Albeit this stringent intake took many years, it ensured a quite homogeneous study sample allowing for comparisons of multiple embrasures in different patient groups. Salama and co-workers (1998) were the first to document predictable papilla length for different embrasures. However, their findings are difficult to interpret given the lack of clear selection criteria and the fact that papilla length was registered by sounding the first tooth- or implantto-bone contact instead of the interproximal crestal bone peak. Clearly, accurate data on papillae for different embrasures are needed as these may be important from an aesthetic point of view. A key finding was that the T-I and T-P embrasure demonstrated similar papilla index ( 58% with complete fill) and papilla height ( 4.1 mm on average). These data do not differ substantially from those between teeth (Tarnow et al. 1992), suggesting a tissue preserving effect of the tooth. On the other hand, when the embrasure was not formed by a tooth significantly less embrasure fill and/or papilla height were found. This situation occurs when adjacent teeth are missing and need replacement. The most favourable outcome was found when such an embrasure was formed by two pontics (82% with complete fill and 3.7 mm mean papilla height). When- Table 3. Papilla height (mm) sorted per embrasure type (n = 250) Papilla height Tooth-pontic Tooth-implant Pontic-pontic Implant-implant Implant-pontic (Group III) Mean (SD) [range] 4.2 (0.8) [ ] 4.1 (0.8)[ ] 3.7 (0.9) [ ] 3.3 (0.7) [ ] 3.2 (0.8) [ ] % 4 mm Group I: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on teeth (tooth-pontic and pontic-pontic measurements). Group II: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on implants (tooth-implant and implant-implant measurements). Group III: 50 patients with a fixed restoration on implants (implant-pontic measurements).
5 732 Cosyn et al. ever one or two implants formed such an embrasure, significantly less embrasure fill ( 42% with complete fill) and papilla height ( 3.3 mm on average) were demonstrated. Tarnow et al. (2003) described mean papilla height of 3.4 mm between implants, which is very similar to our observation (3.3 mm on average). Interestingly, the I-P embrasure did not perform better than the I-I embrasure in contrast to previous beliefs (Tarnow et al. 2003, Barreto et al. 2008), which is in agreement with a recent pilot study (Tymstra et al. 2011). This information is clinically relevant when it comes to replacing two missing adjacent teeth in the anterior maxilla. The installation of only one implant with a cantilevered pontic is less expensive than two implants, but may not result in superior aesthetics as shown in this study. Moreover, clinicians should be aware of the fact that there are only limited data on implant success and complications for a cantilever bridge on only one implant (Aglietta et al. 2009, 2012, Tymstra et al. 2011). By and large, about 1 mm shorter papillae were demonstrated between implants or between an implant and a pontic when compared to embrasures formed by one or two teeth. Possibly this is related to a lack of inserting supracrestal fibres around implants (Berglundh et al. 1991). In addition, one may also expect significant loss in the vertical dimension in such embrasures as the bone peak will flatten following tooth extraction. The papillary asymmetry may therefore even become 2 mm as described by Kourkouta et al. (2009), which is detrimental from an aesthetic point of view when a central and lateral incisor or a lateral incisor and a cuspid on one side need replacement. Ridge preservation, orthodontic extrusion, bone augmentation, distraction osteogenesis and root submergence have been proposed as treatment options (Zetu & Wang 2005, Salama et al. 2007). Given the technical complexity of these concepts and their single focus on bone foundation, it is clear that implant dentistry has no straightforward solution for this problem and a FRT with a P-P embrasure may be considered the best option from an aesthetic point of view to treat this. On the other hand, the range on papilla height for a P-P embrasure was very high in this study and one could question whether it is ethical to remove sound tooth structure in order to install a FRT. Future studies should therefore focus on papilla reconstruction between implants or between an implant and a pontic using connective tissue grafting. As it is also unclear whether further improvement in the papilla formed by two pontics is possible using connective tissue grafting, prospective studies should also focus on FRT. In this study the papilla index by Jemt (1997) was used to study embrasure fill. As this index was initially designed for single tooth implants with adjacent teeth, it may not really hold up when there is no tooth forming the embrasure, i.e. between pontics, beween adjacent implants or between an implant and a pontic. In these situations, the two adjacent crowns can be made to any shape to close down the embrasure space resulting in a high papilla index score whereas papilla height may remain low. This phenomenon may explain why the P-P embrasure demonstrated complete fill in 82% of the cases, whereas mean papilla height was only 3.7 mm. Hence, it is not surprising that papilla index and papilla height only demonstrated a weak correlation. Clearly, the results on papilla height may be considered crucial in this study and papilla index data should be interpreted with caution as these may be prone to bias. A second limitation of this study relates to the fact that T-T embrasures were not included. On the other hand, it was our objective to study embrasures in the context of different treatment options for tooth loss and these do not include T-T embrasures. Another concern of this study relates to the bone sounding technique and the associated risk of soft tissue damage. Because of this, imaging techniques may be preferred in future studies. However, an important limitation of these methods is a lack of visibility of the tip of the papilla due to overlap of teeth. This is especially the case in the canine and premolar region and was the very reason why we only included digital radiographs of the central papilla to evaluate accuracy of clinical registrations. A final concern of this study relates to the external validity of the results. An attempt was made to select a homogeneous sample in terms of clinicians, periodontal and peri-implant conditions, implant types and positions, and pontic design. However, more factors may affect the presence of a papilla (Chang 2007, Chow et al. 2010), and the impact of socioeconomic and geographic aspects remains to be investigated. In conclusion, this clinical study showed that the re-establishment of a papilla is difficult when there is no tooth involved. In that scenario a short papilla should be expected and implant-borne restorations demonstrate the poorest outcome. Moreover, an implant with a pontic may not perform better than adjacent implants. Acknowledgements The authors wish to thank all participants for their contribution. References Aglietta, M., Iorio Siciliano, V., Blasi, A., Sculean, A., Br agger, U., Lang, N. P. & Salvi, G. E. (2012) Clinical and radiographic changes at implants supporting single-unit crowns (SCs) and fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) with one cantilever extension. A retrospective study. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23, Aglietta, M., Siciliano, V. I., Zwahlen, M., Br agger, U., Pjetursson, B. E., Lang, N. P. & Salvi, G. E. (2009) A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant supported fixed dental prostheses with cantilever extensions after an observation period of at least 5 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research 20, Barreto, M., Francischone, C. E. & Filho, H. N. (2008) Two prosthetic crowns supported by a single implant: an esthetic alternative for restoring the anterior maxilla. Quintessence International 39, Benic, G. I., Wolleb, K., Sancho-Puchades, M. & H ammerle, C. H. F. (2012) Systematic review of parameters and methods for the professional assessment of esthetics in dental implant research. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 39 (Suppl. 12), Berglundh, T., Lindhe, J., Ericsson, I., Marinello, C. P., Liljenberg, B. & Thomsen, P. (1991) The soft tissue barrier at implants and teeth. Clinical Oral Implants Research 2, Buser, D., Wittneben, J., Bornstein, M. M., Gr utter, L., Chappuis, V. & Belser, U. C. (2011) Stability of contour augmentation and esthetic outcomes of implant-supported single crowns in the esthetic zone: 3-year results of a prospective study with early implant placement postextraction. Journal of Periodontology 82,
6 Embrasure fill and papilla height 733 Cardaropoli, G., Lekholm, U. & Wennstr om, J. L. (2006) Tissue alterations at implantsupported single-tooth replacements: a 1-year prospective clinical study. Clinical Oral Implants Research 17, Chang, L. C. (2007) The association between embrasure morphology and central papilla recession. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 34, Chen, S. T., Darby, I. B., Reynolds, E. C. & Clement, J. G. (2009) Immediate implant placement postextraction without flap elevation. Journal of Periodontology 80, Choquet, V., Hermans, M., Adriaenssens, P., Daelemans, P., Tarnow, D. P. & Malevez, C. (2001) Clinical and radiographic evaluation of the papilla level adjacent to single-tooth dental implants. A retrospective study in the maxillary anterior region. Journal of Periodontology 72, Chow, Y. C., Eber, R. M., Tsao, Y. P., Shotwell, J. L. & Wang, H. L. (2010) Factors associated with the appearance of gingival papillae. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 37, Cosyn, J., De Bruyn, H. & Cleymaet, R. (2012a). Soft tissue preservation and pink aesthetics around single immediate implant restorations: a 1-year prospective study. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research doi: /j x. Cosyn, J., Eghbali, A., De Bruyn, H., Collys, K., Cleymaet, R. & De Rouck, T. (2011) Immediate single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla: a 3-year case cohort study on hard and soft tissue response and aesthetics. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38, Cosyn, J., Raes, S., De Meyer, S., Raes, F., Buyl, R., Coomans, D. & De Bruyn, H. (2012b) An analysis of the decision-making process for single implant treatment in general practice. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 39, Cosyn, J., Sabzevar, M. M. & De Bruyn, H. (2012c) Predictors of inter-proximal and midfacial recession following single implant treatment in the anterior maxilla: a multivariate analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 39, Gallucci, G. O., Gr utter, L., Chuang, S. K. & Belser, U. C. (2011) Dimensional changes of peri-implant soft tissue over 2 years with single-implant crowns in the anterior maxilla. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38, Grunder, U. (2000) Stability of the mucosal topography around single-tooth implants and adjacent teeth: 1-year results. International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry 20, den Hartog, L., Raghoebar, G.M., Slater, J.J., Stellingsma, K., Vissink, A. & Meijer, H.J. (2011a) Single-tooth implants with different neck designs: a randomized clinical trial evaluating the aesthetic outcome. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research doi: /j x. den Hartog, L., Raghoebar, G. M., Stellingsma, K., Vissink, A. & Meijer, H. J. (2011b) Immediate non-occlusal loading of single implants in the aesthetic zone: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38, den Hartog, L., Slater, J. J., Vissink, A., Meijer, H. J. & Raghoebar, G. M. (2008) Treatment outcome of immediate, early and conventional single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone: a systematic review to survival, bone level, soft-tissue, aesthetics and patient satisfaction. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 35, Henriksson, K. & Jemt, T. (2004) Measurements of soft tissue volume in association with singleimplant restorations: a 1-year comparative study after abutment connection surgery. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 6, Jemt, T. (1997) Regeneration of gingival papillae after single-implant treatment. International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry 17, Juodzbalys, G. & Wang, H. L. (2007) Soft and hard tissue assessment of immediate implant placement: a case series. Clinical Oral Implants Research 18, Kan, J. Y., Rungcharassaeng, K., Umezu, K. & Kois, J. C. (2003) Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans. Journal of Periodontology 74, Kourkouta, S., Dedi, K. D., Paquette, D. W. & Mol, A. (2009) Interproximal tissue dimensions in relation to adjacent implants in the anterior maxilla: clinical observations and patient aesthetic evaluation. Clinical Oral Implants Research 20, Lai, H. C., Zhang, Z. Y., Wang, F., Zhuang, L. F., Liu, X. & Pu, Y. P. (2008) Evaluation of soft-tissue alteration around implant-supported single-tooth restoration in the anterior maxilla: the pink esthetic score. Clinical Oral Implants Research 19, Raes, F., Cosyn, J., Crommelinck, E., Coessens, P. & De Bruyn, H. (2011) Immediate and conventional single implant treatment in het anterior maxilla: one-year results of a case series on hard and soft tissue response and aesthetics. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38, Salama, H., Salama, M. A., Garber, D. & Adar, P. (1998) The interproximal height of bone: a guidepost to predictable aesthetic strategies and soft tissue contours in anterior tooth replacement. Practical Periodontics and Aesthetic Dentistry 10, Salama, M., Ishikawa, T., Salama, H., Funato, A. & Garber, D. (2007) Advantages of the root submergence technique for pontic site development in esthetic implant therapy. International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry 27, Tarnow, D., Elian, N., Fletcher, P., Froum, S., Magner, A., Cho, S. C., Salama, M., Salama, H. & Garber, D. A. (2003) Vertical distance from the crest of bone to the height of the interproximal papilla between adjacent implants. Journal of Periodontology 74, Tarnow, D. P., Magner, A. W. & Fletcher, P. (1992) The effect of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence or absence of the interproximal dental papilla. Journal of Periodontology 63, Tymstra, N., Raghoebar, G. M., Vissink, A. & Meijer, H. J. (2011) Dental implant treatment for two adjacent missing teeth in the maxillary aesthetic zone: a comparative pilot study and test of principle. Clinical Oral Implants Research 22, Zetu, L. & Wang, H. L. (2005) Management of inter-dental/inter-implant papilla. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 32, Address: Jan Cosyn Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School University of Ghent De Pintelaan 185 B-9000 Ghent Belgium jan.cosyn@ugent.be Clinical Relevance Scientific rationale for the study: The objective of the present study was to compare inter-proximal fill and papilla height between different embrasures in 150 consecutive patients with fixed restorations on teeth or implants. Principal findings: The re-establishment of a papilla was most difficult between missing teeth. The implantimplant and implant-pontic embrasure demonstrated comparable outcome, which was significantly poorer when compared to the pontic-pontic embrasure. Practical implications: An implant with a pontic may not perform better than adjacent implants in terms of papilla presence.
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported
 PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version)
 Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version) Title A prospective cohort study on the impact of smoking on soft tissue alterations around single implants Running title Soft tissue alterations
Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version) Title A prospective cohort study on the impact of smoking on soft tissue alterations around single implants Running title Soft tissue alterations
Dimension of Gingival Papillae between External Hexagon Dental Implants in Superior Anterior Sites
 Wagner A Calado et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1554 Dimension of Gingival Papillae between External Hexagon Dental Implants in Superior Anterior Sites 1 Wagner A Calado, 2 Geraldo AP
Wagner A Calado et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1554 Dimension of Gingival Papillae between External Hexagon Dental Implants in Superior Anterior Sites 1 Wagner A Calado, 2 Geraldo AP
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone.
 Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone. Introduction Francisco Teixeira Barbosa. Private practice. Barcelona. Spain. Nowadays, implantology
Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone. Introduction Francisco Teixeira Barbosa. Private practice. Barcelona. Spain. Nowadays, implantology
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Dental treatment for two adjacent missing teeth in the maxillary aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; Meijer, Hendrikus Published in: CLINICAL ORAL IMPLANTS
University of Groningen Dental treatment for two adjacent missing teeth in the maxillary aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; Meijer, Hendrikus Published in: CLINICAL ORAL IMPLANTS
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of a Case Series
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
Dental Implants and Esthetics
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Review Article. r 2008 The Authors Journal compilation r 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard
 J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35: 1073 1086 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01330.x Treatment outcome of immediate, early and conventional single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone: a systematic review to survival,
J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35: 1073 1086 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01330.x Treatment outcome of immediate, early and conventional single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone: a systematic review to survival,
PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR. MED. DENT. GÜNTER DHOM, DR. MED. DENT.
 Reproducibility of the Pink Esthetic Score Rating Soft Tissue Esthetics Around Single-Implant Restorations with Regard to Dental Observer Specialization PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR.
Reproducibility of the Pink Esthetic Score Rating Soft Tissue Esthetics Around Single-Implant Restorations with Regard to Dental Observer Specialization PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR.
Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography of the interdental papilla
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:273-278 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.6.273 Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:273-278 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.6.273 Analysis of the embrasure dimensions between maxillary central incisors in relation to the topography
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Treatment outcome of two adjacent implant crowns with different implant platform designs in the aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; den Hartog, Laurens;
University of Groningen Treatment outcome of two adjacent implant crowns with different implant platform designs in the aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; den Hartog, Laurens;
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla
 Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
To obtain optimal esthetics with single implants, the
 LITERATURE REVIEW Soft Tissues Changes After Immediate and Delayed Single Implant Placement in Esthetic Area: A Systematic Review André Barbisan, DDS 1 Cintia Santana Dias, DDS 1 Paula Furlan Bavia, DDS
LITERATURE REVIEW Soft Tissues Changes After Immediate and Delayed Single Implant Placement in Esthetic Area: A Systematic Review André Barbisan, DDS 1 Cintia Santana Dias, DDS 1 Paula Furlan Bavia, DDS
Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Immediate implant placement, with or without simultaneous implant provisionalization,
 Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
The refinement of adhesive technology and contemporary
 CONTINUING EDUCATION 3 4 THE INTERPROXIMAL HEIGHT OF BONE: A GUIDEPOST TO PREDICTABLE AESTHETIC STRATEGIES AND SOFT TISSUE CONTOURS IN ANTERIOR TOOTH REPLACEMENT Henry Salama, DMD* Maurice A. Salama, DMD
CONTINUING EDUCATION 3 4 THE INTERPROXIMAL HEIGHT OF BONE: A GUIDEPOST TO PREDICTABLE AESTHETIC STRATEGIES AND SOFT TISSUE CONTOURS IN ANTERIOR TOOTH REPLACEMENT Henry Salama, DMD* Maurice A. Salama, DMD
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites Santing, Hendrik J.; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink,
University of Groningen Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites Santing, Hendrik J.; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink,
S oft tissue problems (ie, gingival
 406 ASSOCIATION OF ILBT AND CLSTT LE AND BORZABADI-FARAHANI Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Maxillary Implants Associated with Crestal Labial Soft Tissue Thickness Bach T. Le, DDS, MD,* and Ali
406 ASSOCIATION OF ILBT AND CLSTT LE AND BORZABADI-FARAHANI Labial Bone Thickness in Area of Anterior Maxillary Implants Associated with Crestal Labial Soft Tissue Thickness Bach T. Le, DDS, MD,* and Ali
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE ABSTRACT
 SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE Dr. Arshiya Goswamy., Dr. H.S. Grover.,Dr. Shalini Kapoor *Department of Periodontology, SGT Dental College & Research Institute, Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR (Received on Date: 7 th
SMALL TISSUE WITH BIG ISSUE Dr. Arshiya Goswamy., Dr. H.S. Grover.,Dr. Shalini Kapoor *Department of Periodontology, SGT Dental College & Research Institute, Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR (Received on Date: 7 th
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Esthetic evaluation of single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla following autologous bone augmentation
 M. Hof B. Pommer G. D. Strbac D. Sütö G. Watzek W. Zechner Esthetic evaluation of single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla following autologous bone augmentation Authors affiliations: M. Hof, B. Pommer,
M. Hof B. Pommer G. D. Strbac D. Sütö G. Watzek W. Zechner Esthetic evaluation of single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla following autologous bone augmentation Authors affiliations: M. Hof, B. Pommer,
The Bulletin Spring 2000
 The Bulletin Spring 2000 Spring Meeting - Friday March 31, 2000 Joint Symposium: Northeastern Society of Periodontists and Northeastern Gnathological Society New York Marriott Marquis Hotel 1535 Broadway
The Bulletin Spring 2000 Spring Meeting - Friday March 31, 2000 Joint Symposium: Northeastern Society of Periodontists and Northeastern Gnathological Society New York Marriott Marquis Hotel 1535 Broadway
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
Biology of periodontal and periimplant. The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants
 The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants Biology of periodontal and periimplant tissues Individualized abutment Péter Windisch Prof. Dr. Med. Dent. Head Of The Department Of Periodontology
The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants Biology of periodontal and periimplant tissues Individualized abutment Péter Windisch Prof. Dr. Med. Dent. Head Of The Department Of Periodontology
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Alterations of papilla dimensions after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study
 J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016 Jun;46(3):197-206 pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Research Article after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study Jin-Seok
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016 Jun;46(3):197-206 pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Research Article after orthodontic closure of the maxillary midline diastema: a retrospective longitudinal study Jin-Seok
Implants are a part of IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY CLINICAL
 CLINICAL IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Clifford B. Starr, DMD Mohamed A. Maksoud, DMD KEY WORDS Dental implants General dentistry Resident
CLINICAL IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Clifford B. Starr, DMD Mohamed A. Maksoud, DMD KEY WORDS Dental implants General dentistry Resident
Clinical Research by the UofT Prosthodontics Graduate Residents of Importance for the Practicing Dentist
 Toronto Academy of Dentistry Winter Clinic. Nov 4, 2011 Clinical Research by the UofT Prosthodontics Graduate Residents of Importance for the Practicing Dentist ASBJORN JOKSTAD, DDS, PhD Prosthodontics,
Toronto Academy of Dentistry Winter Clinic. Nov 4, 2011 Clinical Research by the UofT Prosthodontics Graduate Residents of Importance for the Practicing Dentist ASBJORN JOKSTAD, DDS, PhD Prosthodontics,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of an impacted maxillary canine: two case reports
 Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Available online at International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp , December, 2015
 z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
EFFECT OF DISTANCE BETWEEN ONE PIECE IMPLANTS ON CRESTAL BONE RESORPTION
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF INFLAMMATION Vol. 9, no. 2 (S), 0-0 (2011) EFFECT OF DISTANCE BETWEEN ONE PIECE IMPLANTS ON CRESTAL BONE RESORPTION S. FANALI 1, F. CARINCI 2, I. ZOLLINO 2, G. BRUNELLI 3, R. MONGUZZI
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF INFLAMMATION Vol. 9, no. 2 (S), 0-0 (2011) EFFECT OF DISTANCE BETWEEN ONE PIECE IMPLANTS ON CRESTAL BONE RESORPTION S. FANALI 1, F. CARINCI 2, I. ZOLLINO 2, G. BRUNELLI 3, R. MONGUZZI
Vertical and Horizontal Dimensions of Implant Dentistry: Numbers Every Dentist Should Know
 INSIDE DENTISTRY JULY/AUGUST 9 CONTINUING THIS CE LESSON WAS UNDERWRITTEN BY: Vertical and Horizontal Dimensions of Implant Dentistry: Numbers Every Dentist Should Know Steven Kendrick, DDS; and David
INSIDE DENTISTRY JULY/AUGUST 9 CONTINUING THIS CE LESSON WAS UNDERWRITTEN BY: Vertical and Horizontal Dimensions of Implant Dentistry: Numbers Every Dentist Should Know Steven Kendrick, DDS; and David
The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method. Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS
 Original Article 445 The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS Background: The distance from bone crest to contact
Original Article 445 The Association between Embrasure Morphology and Central Papilla Recession: A Noninvasive Assessment Method Li-Ching Chang, DDS, MS Background: The distance from bone crest to contact
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental implants with cone beam computed tomography in the esthetic region
 Slagter et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:8 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental
Slagter et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:8 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 69 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 69 Analysis of the Shapes of Maxillary Central Incisors in a Caucasian Population Luca Gobbato, DDS*/Teppei Tsukiyama, DDS*/Paul A. Levi,
Recently, the success of osseointegration
 RESEARCH Esthetics in Implant-Supported Prostheses: A Literature Review Juliana Aparecida Délben, DDS, DMD, PhD Marcelo Coelho Goiato, DDS, DMD, PhD* Humberto Gennari-Filho, DDS, DMD, PhD Wirley Gonçalves
RESEARCH Esthetics in Implant-Supported Prostheses: A Literature Review Juliana Aparecida Délben, DDS, DMD, PhD Marcelo Coelho Goiato, DDS, DMD, PhD* Humberto Gennari-Filho, DDS, DMD, PhD Wirley Gonçalves
Abstract. A Case Of External Resorption
 SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
Daniel Buser,* Vivianne Chappuis,* Michael M. Bornstein,* Julia-Gabriela Wittneben, Marc Frei,* and Urs C. Belser
 Long-Term Stability of Contour Augmentation With Early Implant Placement Following Single Tooth Extraction in the Esthetic Zone: A Prospective, Cross-Sectional Study in 41 Patients With a 5- to 9-Year
Long-Term Stability of Contour Augmentation With Early Implant Placement Following Single Tooth Extraction in the Esthetic Zone: A Prospective, Cross-Sectional Study in 41 Patients With a 5- to 9-Year
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal papilla in healthy subjects
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:160-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.4.160 An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:160-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.4.160 An analysis on the factors responsible for relative position of interproximal
Esthetic evaluation of implant-supported single crowns: a comparison of objective and patient-reported outcomes
 Altay et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2019) 5:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0153-3 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Open Access Esthetic evaluation of implant-supported
Altay et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2019) 5:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0153-3 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Open Access Esthetic evaluation of implant-supported
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 61 Incision Design and Soft Tissue Management to Maintain or Establish an Interproximal Papilla Around Integrated Implants: A Case Series
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 61 Incision Design and Soft Tissue Management to Maintain or Establish an Interproximal Papilla Around Integrated Implants: A Case Series
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations
 case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures
 Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
SMILE DESIGN SEVEN KEY AREAS
 SMILE DESIGN SEVEN KEY AREAS I SHADING SYSTEM Computerized Shading 1. Unknown Base Shade 2. Additional Dimensions 3. Practice Builder Cervical Shade Incisal Shade Basic Shade Mix Colors Bleached Shades
SMILE DESIGN SEVEN KEY AREAS I SHADING SYSTEM Computerized Shading 1. Unknown Base Shade 2. Additional Dimensions 3. Practice Builder Cervical Shade Incisal Shade Basic Shade Mix Colors Bleached Shades
