Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct
|
|
|
- Frank Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPEN (2017) 9, ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin Woop 1, Brita Willershausen 1 and Benjamín Briseño-Marroquín 1 The aim of this study was to investigate the root canal configuration, accessory canals and number of main foramina of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-computed tomography. The teeth were scanned and reproduced with 3D software imaging. The root canal configuration and number of main foramina were evaluated by means of a four-digit system. The morphological complexity of human maxillary second molars is depicted by the number of accessory and connecting canals. The most frequently observed root canal configurations in the mesiobuccal root were 2-2-2/2 (19.5%), 2-2-1/1 (14.6%) and 2-1-1/1 (13.0%). A 1-1-1/1 configuration was observed in 93.5% and in 96.7% in the distobuccal and palatal roots, respectively. The MB1 root canal had one accessory canal (18.7%), and 8.9% of the MB2 root canal had one or two accessory canals. The distobuccal (11.3%) and palatal (14.6%) root canals had at least one accessory canal, and connecting canals were observed in 16.3% of mesiobuccal roots. The MB1, MB2, distobuccal and palatal root canals had one main foramen in 99.2%, 43.1%, 98.4% and 99.2% of samples, respectively. In the mesiobuccal root, one accessory foramen was detected in 14.6%, two were detected in 7.3%, and three were detected in 5.7%. The distobuccal root showed one or two accessory foramina in 9.1% of samples. The root canal configuration of maxillary second molars is quite heterogeneous; the mesiobuccal root has predominantly two root canal entrances (58.4%, 1 in 41.1%) with one main foramen (54.4%). Two main foramina were observed in 43.0%. Morphological variations, connecting and accessory canals were observed in all apical thirds. (2017) 9, 33 37; doi: /ijos ; published online 20 January 2017 Keywords: accessory and connecting canals; apical foramina; maxillary second molar; micro-ct; morphology; root canal configuration INTRODUCTION Expertise in the field of root canal morphology is crucial for successful endodontic treatment. 1 3 To avoid endodontic failure, especially during root canal preparation and/or obturation, the practitioner must have ample knowledge of the root morphology. 3 Due to each tooth s singularity, a large quantity of morphological variations is possible. 3 4 Such characteristics increase the difficulties in shaping, cleaning and filling the three-dimensional root canal system. Fulfilling such requirements is fundamental for a successful endodontic treatment and thus the long-term conservation of the tooth. 5 6 On the other hand, an inaccurate understanding of the complex internal root morphology invariably results in a deficient root canal preparation due to an inappropriate root canal shaping system and/or method. The most frequent anatomical root number described in the literature in maxillary second molars is three roots. 7 9 However, these studies exhibit a lack of methodological accuracy when detecting and locating morphological microstructures such as accessory and communicating canals. These studies have employed a two-dimensional method, such as the radiographic method, which lacks a minute morphological interpretation. Currently, technological advancements in tooth imaging in clinical and in vitro settings have allowed the acquisition of high-resolution images. Micro-computed tomography offers in vitro possibilities for a relatively recent imaging technique, which allows for a precise, extensive and comprehensive description tooth morphology; however, it is a relatively expensive ex vivo research method The root canal morphology of the maxillary second molar has not been extensively reported; however, it is still controversial. 7 9,12 To the best of our knowledge, no study has been performed to assess the maxillary second molar with a high sample number by means of microcomputed tomography, thus allowing the practitioner to gain a broad morphological minute overview of this tooth. Different root canal system configuration classification systems are currently employed in the literature; 1 2 however, they do not encompass all possible root canal configurations. Therefore, considering the lack of detailed morphological information, specifically the root canal configuration of maxillary second molars, the aim of the present study was to investigate the morphology of three-rooted maxillary second molars and to describe their root canal system configuration by means of a 1 Department of Operative Dentistry, Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center, Mainz, Germany and 2 Division of Endodontology, Department of Preventive Dentistry, Periodontology and Cariology, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland Correspondence: Dr TG Wolf, Department of Operative Dentistry, University Medical Center of the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Poliklinik für Zahnerhaltung, Augustusplatz 2, Mainz 55131, Germany thomaswolf@uni-mainz.de Accepted 8 October 2016
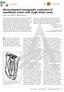
2 34 previously proposed four-digit code system suggested by Briseño Marroquín et al. 13 MATERIALS AND METHODS Tooth selection A total of 123 extracted human permanent maxillary second molars were obtained for reasons unrelated to the present study from dental clinics and dental practitioners. The teeth from an Egyptian population were stored in 5.25% sodium hypochlorite for 24 h for disinfection purposes. 14 According to their morphological appearance with three clear distinct roots and a mesiodistal crown diameter of 9.0 mm (±0.2 mm), 15 the selection criteria included complete development, no signs of root fracture or resorption, no radicular and coronal caries and no endodontic treatment. The teeth were cleaned, including any attached hard and soft tissues as well as calculus,with an ultrasonic scaler. The teeth were placed for one hour in a 3% hydrogen peroxide ultrasonic bath and then stored in 70% alcohol. For further investigation of the tooth s internal morphology not related to that reported in this paper, endodontic access cavities, taking care not to influence the root canal system morphology nor the pulp chamber floor, were prepared under a stereo microscope ( 7; OPMIPico, Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany) with a high-speed handpiece and a diamond round bur (Komet, Lemgo, Germany). When required, ultrasonic tips were used to remove pulp stones exclusively from the pulp chamber. The pulp chambers were rinsed with 1% sodium hypochlorite (60 s) and dried via suction. Main and accessory foramina Main foramina were described as those whose diameters were 0.25 mm or more, and smaller foramina diameters were considered as accessory foramina. Morphological analysis with micro-computed tomography The teeth were scanned at an isotropic resolution of 20 μm in a desktop micro-computed tomography unit (μct 40; Scanco Medical, Brüttisellen, Switzerland) using a previously described method using settings of 70 kv and 114 μa, resulting in 800 to slices per tooth by rotation steps of 0.36 to 180. Different tooth structures were visualized through depiction in dummy colours in the 3D reconstructions of the micro-computed tomography scans using specific software (VGStudio Max 2.2; Volumegraphics, Heidelberg, Germany). The pulp chamber and root canal system were coloured red, the enamel and crown areas were coloured white to grey, and the root and dentin areas were coloured transparent grey (Figures 1 and 2). The root canal configuration was described by dividing the roots into thirds. The first, second and third configuration digits provide the root canal number at the respective coronal limit of the coronal, middle and apical thirds. The fourth digit is separated with a slash and indicates the number of main foramina. 13 The number of accessory and connecting root canals (the one that connects one root canal with the same one or another without merging into the periapical tissue) as well as the number of apical accessory foramina observed under micro-computed tomography were also investigated. The results are expressed as absolute and relative values according to the sample number. RESULTS The described root canal configurations of the mesiobuccal (MB), distobuccal (DB) and palatal (P) roots are shown in Table 1. The most frequently observed root canal configuration in the mesiobuccal root (MB1 and MB2 root canals together) was 2-2-2/2 (19.5%), followed Figure 1 Maxillary second molar depicting a 1-1-1/1 root canal configuration in the palatal and distobuccal roots. The configuration of the mesial root was considered to 2-2-2/2 with an accessory canal in the middle third and a connecting canal between MB1 and MB2 in the apical third. Figure 2 Maxillary second molar with a 1-1-1/1 root canal configuration in the palatal and distobuccal roots. Thisconfiguration type was found to be the most common (96.7% and 93.5%), respectively) in these roots. The configuration of the mesiobuccal root was 2-2-2/2 with a connecting canal in the middle third. This type of connecting canal could also be considered as an anastomosis; however, in this investigation, it was considered as a connecting canal for the sake of term consistency.
3 35 by 2-2-1/1 (14.6%), 2-1-1/1 (13.0%), 2-1-2/2 (8.1%) and /2 (7.3%). Nine additional different root canal configurations were observed with a frequency of o5% each. The distobuccal and palatal root canal configurations showed a 1-1-1/1 configuration as the highest incidence (93.5% and 96.7%, respectively). Five other root Table 1 Root canal configuration of the maxillary second molar observed under micro-computed tomography (n = 123) Root canal configuration of the maxillary second molar Frequency Root Configuration Absolute Mean MB (MB1 and MB2) 1-1-1/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / DB 1-1-1/ / / / / / P 1-1-1/ / / DB, distobuccal; MB, mesiobuccal; P, palatal. The MB root depicts the results of the MB1 and MB2 root canals together. The configuration numbers from left to right describe the root canal path from the coronal, middle and apical thirds, respectively (13). The last number, separated with a slash, shows the number of main foramina observed. canal configuration variations were observed in the distobuccal root, whereas in the palatal root, only two variations could be observed. The number and mean of accessory and connecting canals observed are shown in Table 2. Connecting canal I describes the communication between two root canals in the form of an isthmus, and connecting canal II resembles a handle like connecting canal that emerges from and returns to the same root canal. MB1, MB2, DB and P had no accessory canals in 74.8%, 91.1%, 79.7% and 85.4%, respectively. Connecting canals I and II were observed in only 20.3 and 6.5%, respectively. MB1 had one (18.7%), two (3.3%) or three (3.3%) accessory canals. MB2 showed one or two accessory canals in 8.9% of samples. The distobuccal (11.3%) and palatal (14.6%) roots had an incidence of at least one accessory canal. Connecting canal I was observed in 16.3% of teeth, and connecting canal II was observed in 6.5%. The number and mean of main and accessory (Acc) apical foramina observed are shown in Table 3. The MB1, distobuccal and palatal root canals had one main foramen in 99.2%, 98.4% and 99.2% of samples, respectively. A main foramen in MB2 was observed in only 43.1% of samples. An additional root canal was rarely observed in the mesiobuccal (MB3), distobuccal (DB2) and palatal (P2) roots. Accessory foramina in the mesiobuccal root (MB-Acc) were detected in one (14.6%), two (7.3%) and three (5.7%) instances. In the distobuccal root, one or two accessory foramina were observed in 9.1% of samples (DB-Acc). DISCUSSION A number of studies have investigated root canal morphology using various research methods. 2,4,11,19 For the analysis of the root canal system, the most accurate ex vivo method considered to be the gold standard 20 today is micro-computed tomography. 3 Fine internal morphological structures of the tooth can be observed with this noninvasive and reproducible technique after appropriate 3D reconstruction. 21 Although we cannot completely exclude the possibility of tooth dehydration caused by the 70% alcohol storing procedure, if it happened, it did not influence the results, as it was extremely rare to observe an artefact in the resulting images after software rendering with micro-computed tomography that could have suggested possible dehydration. In experimental endodontic research, this method renders detailed qualitative and quantitative information. 10,21 Knowledge of the three-dimensional root canal system is mandatory to avoid errors during all phases of root canal treatment; thus, it will enhance the success of endodontic therapy. Table 2 Numbers (n) and means (%) of accessory and connecting (Connecting I and II) canals observed under micro-computed tomography of the maxillary second molar (n = 123) MB1 MB2 Connecting I DB P Connecting II C n % n % n % n % n % n % C, canals; DB, distobuccal; MB, mesiobuccal; P, palatal. Connecting I describes a connecting canal between MB1 and MB2; Connecting II describes a connecting canal that emerges and returns to the same root canal.
4 36 Table 3 Numbers (n) and means (%) of the main (mesiobuccal root and distobuccal root) and accessory apical foramina of the maxillary second molar observed under micro-computed tomography (n = 123) MB1 MB2 MB3 MB-Acc DB DB2 DB-Acc P P2 F n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % Acc, accesory; DB, distobuccal; F, apical foramina; MB, mesiobuccal; P, palatal. No accessory foramina were observed in the palatal root. To keep the number of samples high, only three-rooted maxillary second molars were included in the present study because two- 7 and four-rooted maxillary second molars are rare. 8 The most common root canal configuration systems employed are those of Vertucci 2 and Weine et al. 1 However, with different computer-supported imaging techniques such as micro-computed tomography, it has been possible to depict further root canal configurations that cannot be properly classified with these classification systems. 4,22 25 The present study offers a comprehensive four-digit classification system based on dividing the root into thirds and using the fourth digit to describe the number of main apical foramina. 13 The successive introduction of actual treatment modalities (microscopes) and different investigation methodologies 9,26,27 showed that the prevalence of the MB2 root canal in maxillary molars is higher in comparison to radiographic studies. 4 Therefore, only reports of highresolution imaging systems were taken into consideration in the discussion. In this study, 15 different root canal configurations were observed in the mesiobuccal root in maxillary second molars compared with 10 observed in the conventional microscopic investigation. 28 The most frequently observed root canal configuration in the mesiobuccal root canal in this study was 1-1-1/1 (26.0%). With the same methodology, similar values of 26.0% were reported by Sert and Bayirli 23 using teeth of male origin. Other authors 4,20,29 report a relatively higher frequency of this configuration ranging from 38.1% to 45.09%. Versiani et al. 12 reported a higher frequency of this configuration (76%) with the same investigative methodology; however, they used a smaller research sample (n = 25) in four-rooted maxillary second molars. The frequency contrast with other investigations 2,23,24 ranging from 56.0% to 71.0% and employing different methodologies also contrasted with these results. In the present study, a 2-2-2/2 configuration was observed in 19.5% of samples. Different authors using different methods 2,4,12,23,26,29 reported similar results to ours, whereas the results of other investigations with different methodologies or sample numbers that reported frequencies of 3.9% 24 or 57.0%, 11 and 60.3% 22 deviated noticeably from ours. The 2-2-1/1 and 2-1-1/1 root canal configurations were observed in 14.6% and 13.0% of the distobuccal and palatal roots, respectively. Indeed, when using different classification systems, these root canal configurations showed a similar outcome when compared with the results of other authors. 2,23 The findings of Sert and Bayirli 23 (31.0% male and 22.0% female derived teeth) and Alavi et al. 19 (7.7%) differed from ours; however, these authors used the type II (2-1) classification of Vertucci. 2 A 1-1-1/1 root canal configuration in the distobuccal (93.5%) and palatal (96.7%) roots was observed in the present study. Similar results were obtained by Alavi et al. 19 (98.1% 100% and 100%, respectively), Kim et al. 24 (97.58% and 97.58%, respectively) and Sert and Bayirli 23 (98% and 100%, respectively). Although a MB2 root canal entrance was quite often present in the pulp chamber floor in this study (57.6%), our results and those of Vertucci 2 show that the subsequent root canal configuration in the apical direction does not always reveal two separate root canals. A second mesiobuccal canal in the mesiobuccal roots was reported in 57%, % 29 and 70.3%; 23 however, Versiani et al. 12 and Kim et al. 24 observed it in only 24.0% and 34.39%, respectively. Different investigations 11,23,30 report that 450% of maxillary second molars have a second root canal (MB2) in the mesiobuccal root; therefore, if it is not properly anticipated, instrumented and filled, success in endodontic treatment is endangered. Vertucci 2 reported to have frequently found one main foramen in the mesiobuccal (88.0%), distobuccal (100.0%) and palatal (100.0%) roots. These results are similar when compared to those obtained in the present study (99.2%, 98.4% and 99.2%, respectively). One, two and three lateral canals were observed in mesiobuccal roots in 14.6%, 7.3% and 5.7% of these roots, respectively. In the present study, the distobuccal root showed one or two lateral canals in 9.1% of samples. Contrastingly, Vertucci 2 reported higher values in the mesiobuccal (50%), distobuccal (29%) and palatal (42%) roots. Alavi et al. 19 reported lateral canals in 11.0% of the middle (0.5%) and apical thirds (10.5%), a result thatwas similar to our results. Furthermore, Alavi et al. 19 reported a frequency of connecting canals between the mesiobuccal root canals of 16.2%, which was also in accordance with our results (16.3%). Vertucci 2 reported a 21.0% frequency; however, he describes such connecting canals as anastomosis. We could also describe many of these connecting canals as anastomosis; however, we decided to compromise, using the term connecting canal for the sake of terminus unification to remain consistent throughout any reporting in this and other investigations. In the present study, one to six accessory canals were observed in 27.6% of molars when considering the entire mesiobuccal and distobuccal root canal length. Similar findings were reported by De Deus 31 in a study of three-rooted molars (23.3%). A higher prevalence in four-rooted maxillary second molars (38.0%) was reported by Versiani et al. 12 These results are also in contrast with those of Cleghorn et al. 3 in which they reported observing only one accessory canal in 10.8% of the mesiobuccal roots. Differences between this and other studies can be explained by sample size, study methodology and design, ethnic origin of samples, and differences in age 26 and sex. 24,32 However, to the best of our knowledge, only one micro-computed tomography study has
5 37 investigated the root canal morphology and configuration of maxillary second molars. 12 The results of our study also suggest that reported differences might be associated with the total root number of maxillary second molars. The results of this study show that 49.5% of the mesiobuccal roots of maxillary second molars have two root canal entrances and that only 27.6% of them have only one physiological foramen. These conditions suggest that 55.7% of these teeth with two root canal entrances merge at some level of the root to ultimately end in only one physiological foramen. The meaning of these results could be erroneously interpreted as comforting for the operator. They could clinically explain why success has been achieved in many cases where only three root canals have been treated. However, the operator will practically never be aware of this clinical situation. Furthermore, the analysis of this information is beyond the scope of this investigation and will be extensively addressed in a future report. A precise understanding of endodontic morphology of the maxillary second molar by means of imaging of a large sample number through micro-computed tomography is provided in the present study. This information will enable practitioners to understand and anticipate the challenge of three-dimensional endodontic treatment, especially during the cleaning and shaping of the root canal system. The results of this study showed that the maxillary second molar has a high incidence of morphological endodontic variables, indicating that it is even more complex than the maxillary first molar. 13 CONCLUSIONS 1. The most frequently observed root canal configurations in the mesiobuccal root were 1-1-1/1 (26.0%), 2-2-2/2 (19.5%), 2-2-1/1 (14.6%) and 2-1-1/1 (13.0%). 2. The 1-1-1/1 root canal configuration was observed in the distobuccal root in 93.5% of samples and in the palatal root in 96.7% of samples. 3. The MB1 had one accessory canal in 18.7% of samples and the MB2 had one or two accessory canals in 8.9% of samples. The distobuccal and palatal root canals had at least one accessory canal in 11.3 and 14.6% of samples, respectively. Connecting canals were observed in 16.3% of the mesiobuccal roots. 4. Only one main foramen at the apex was observed in the MB1, distobuccal and palatal root canals in 99.2%, 98.4% of samples, respectively. A main foramen of MB2 was observed in 43.1% of samples. In 56.1% of samples, it did not exist due to the one (/1) final configuration in the mesiobuccal root. 5. One accessory foramen in mesiobuccal roots was detected in 14.6% of samples, two in 7.3% and three in 5.7%. The distobuccal root showed one or two accessory foramina in 9.1% of samples. 6 Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am 1974; 18(2): Eskoz N, Weine FS. Canal configuration of the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary second molar. JEndod1995; 21(1): Libfeld H, Rotstein I. Incidence of four-rooted maxillary second molars: literature review and radiographic survey of 1200 teeth. JEndod1989; 15(3): Peikoff MD, Christie WH, Fogel HM. The maxillary second molar: variations in the number of roots and canals. Int Endod J 1996; 29(6): Rhodes JS, Ford TR, Lynch JA et al. Micro-computed tomography: a new tool for experimental endodontology. Int Endod J 1999; 32(3): Domark JD, Hatton JF, Benison RP et al. An ex vivo comparison of digital radiography and cone-beam and micro computed tomography in the detection of the number of canals in the mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars. J Endod 2013; 39(7): Versiani MA, Pécora JD, de Sousa-Neto MD. Root and root canal morphology of fourrooted maxillary second molars: a micro-computed tomography study. J Endod 2012; 38(7): Briseño-Marroquín B, Paqué F, Maier K et al. Root canal morphology and configuration of 179 maxillary first molars by means of micro-computed tomography. An ex vivostudy. JEndod2015; 41(12): Marroquín BB, El-Sayed MA, Willershausen-Zönnchen B. Morphology of the physiological foramen: I. Maxillary and mandibular molars. JEndod2004; 30(5): Jordan RE, Abrams L, Kraus BS. Kraus Dental Anatomy and Occlusion. St Louis: Mosby Year Book, Paqué F, Ganahl D, Peters OA. Effects of root canal preparation on apical geometry assessed by micro-computed tomography. J Endod 2009; 35(7): Peters OA, Boessler C, Paqué F. Root canal preparation with a novel nickel-titanium instrument evaluated with micro-computed tomography: canal surface preparation over time. J Endod 2010; 36(6): Peters OA, Paqué F. Root canal preparation of maxillary molars with the self-adjusting file: a micro-computed tomography study. J Endod 2011; 37(1): Alavi AM, Opasanon A, Ng YL et al. Root and canal morphology of Thai maxillary molars. Int Endod J 2002; 35(5): Park JW, Lee JK, Ha BH et al. Three-dimensional analysis of maxillary first molar mesiobuccal root canal configuration and curvature using micro-computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009; 108(3): Plotino G, Grande NM, Pecci R et al. Three-dimensional imaging using microcomputed tomography for studying tooth macromorphology. JAmDentAssoc2006; 137(11): Kim Y, Perinpanayagam H, Lee JK et al. Comparison of mandibular first molar mesial root canal morphology using micro-computed tomography and clearing technique. Acta Odontol Scand 2015; 73(6): Sert S, Bayirli GS. Evaluation of the root canal configurations of the mandibular and maxillary permanent teeth by gender in the Turkish population. JEndod2004; 30(6): Kim Y, Lee SJ, Woo J. Morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a korean population: variations in the number of roots and canals and the incidence of fusion. JEndod2012; 38(8): Lee KW, Kim Y, Perinpanayagam H et al. Comparison of alternative image reformatting techniques in micro-computed tomography and tooth clearing for detailed canal morphology. JEndod2014; 40(3): Pineda F, Kuttler Y. Mesiodistal and buccolingual roentgenographic investigation of 7275 root canals. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1972; 33(1): Weine FS, Hayami S, Hata G et al. Canal configuration of the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar of a Japanese sub-population. Int Endod J 1999; 32(2): Kulild JC, Peters DD. Incidence and configuration of canal systems in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first and second molars. JEndod1990; 16(7): Silva EJ, Nejaim Y, Silva AI et al. Evaluation of root canal configuration of maxillary molars in a Brazilian population using cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: an in vivo study. J Endod 2014; 40(2): Imura N, Hata GI, Toda T et al. Two canals in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars. Int Endod J 1998; 31(6): De Deus QD. Frequency, location, and direction of the lateral, secondary, and accessory canals. JEndod1975; 1(11): Thomas RP, Moule AJ, Bryant R. Root canal morphology of maxillary permanent first molar teeth at various ages. Int Endod J 1993; 26(5): Weine FS, Healey HJ, Gerstein H et al. Canal configuration in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar and its endodontic significance. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1969; 28(3): Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984; 58(5): Cleghorn BM, Christie WH, Dong CC. Root and root canal morphology of the human permanent maxillary first molar: a literature review. JEndod2006; 32(9): Degerness RA, Bowles WR. Dimension, anatomy and morphology of the mesiobuccal root canal system in maxillary molars. JEndod2010; 36(6): Schilder H. Filling root canals in three dimensions. Dent Clin North Am 1967, This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ r The Author(s) 2017
Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars by means of micro-computed tomography: an ex vivo study
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars
Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct
 (2017) 9, 151 157 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank
(2017) 9, 151 157 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank
Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 5, MAY 2004 Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 5, MAY 2004 Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
Failure of root canal therapy often
 Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT
 Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo
 The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
Usage of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) to Evaluate Root and Canal Morphology of maxillary First Molar
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
CANAL CONFIGURATION AND THE PREVALENCE OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR OF A SAUDI SUB-POPULATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CANAL CONFIGURATION AND THE PREVALENCE OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR OF A SAUDI SUB-POPULATION Atif Saleem Agwan 1 Zeeshan Sheikh 2 Haroon Rashid 3 BDS, FCPS Dip.Dh,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CANAL CONFIGURATION AND THE PREVALENCE OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR OF A SAUDI SUB-POPULATION Atif Saleem Agwan 1 Zeeshan Sheikh 2 Haroon Rashid 3 BDS, FCPS Dip.Dh,
Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01472.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis F. Somma 1, D. Leoni 1, G. Plotino 1,
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01472.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis F. Somma 1, D. Leoni 1, G. Plotino 1,
e74 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College a Reader.
 Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Research Article. Key Words: First premolar, Mandibular, Maxillary, Vertucci s classification, Spiral computed tomography.
 Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with unusual mesiobuccal root anatomy
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST
 CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
Success in root canal treatment (RCT) is dependent. Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study
 Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study Marcelo Santos Coelho, DDS, MSc; Jeffrey M. Parker, DMD; Peter Z. Tawil, DMD, MS, FRCD(C), Dip ABE Abstract:
Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study Marcelo Santos Coelho, DDS, MSc; Jeffrey M. Parker, DMD; Peter Z. Tawil, DMD, MS, FRCD(C), Dip ABE Abstract:
Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
The variation of root canal morphology, especially in multirooted teeth, is a
 Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with a Single Root and a Single Canal Diagnosed with the Aid of Spiral CT: A Case Report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, Narayanan Bhargavi, BDS, and Deivanayagam
Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with a Single Root and a Single Canal Diagnosed with the Aid of Spiral CT: A Case Report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, Narayanan Bhargavi, BDS, and Deivanayagam
Gorduysus MO et al. Operating Microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.J.C.M.R Operating microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal in mandibular ıncisors Mehmet Omer Gorduysus, Melahat Gorduysus, Zeliha Yilmaz * Department of Endodontics,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.J.C.M.R Operating microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal in mandibular ıncisors Mehmet Omer Gorduysus, Melahat Gorduysus, Zeliha Yilmaz * Department of Endodontics,
Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series
 Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/35023.11615 Dentistry Section Review Article Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration Rashmi Bansal
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/35023.11615 Dentistry Section Review Article Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration Rashmi Bansal
Lodha Ena* M. Kala** INTRODUCTION
 Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
An unusual maxillary canine with two separated root canals
 pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
endodontics Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth T he main objective of endodontic therapy is the
 endodontics Editor: MILTON SISKIN, D.D.S. College of Dentistry The University of Tennessee 847 Monroe Avenue Memphis, Tennessee 38163 Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth Frank J. Vertucci,
endodontics Editor: MILTON SISKIN, D.D.S. College of Dentistry The University of Tennessee 847 Monroe Avenue Memphis, Tennessee 38163 Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth Frank J. Vertucci,
Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar
 Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Root Canal Space Using Micro-CT
 3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Canal Space Using Micro-CT M.A. Versiani 1, G. De-Deus 2, J. Vera 3, E. Souza 4, L. Steier 5, J.D. Pécora 1, M.D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry,
3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Canal Space Using Micro-CT M.A. Versiani 1, G. De-Deus 2, J. Vera 3, E. Souza 4, L. Steier 5, J.D. Pécora 1, M.D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry,
Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography
 Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a polish population
 Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Correspondence should be addressed to Raed Hakam Mukhaimer;
 International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
The main objective of root canal treatment is thorough cleaning and shaping of all
 Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Eight Root Canal Systems Evaluated Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography Scanning: A Case Report Jojo Kottoor, MDS, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, MDS,
Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Eight Root Canal Systems Evaluated Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography Scanning: A Case Report Jojo Kottoor, MDS, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, MDS,
CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (16): 6937-6941 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar. Pablo Betancourt *, Pablo Navarro, Ramon Fuentes Research
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (16): 6937-6941 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar. Pablo Betancourt *, Pablo Navarro, Ramon Fuentes Research
Introduction. Abstract
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01991.x Hard-tissue debris accumulation created by conventional rotary versus self-adjusting file instrumentation in mesial root canal systems of mandibular molars F. Paqué
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01991.x Hard-tissue debris accumulation created by conventional rotary versus self-adjusting file instrumentation in mesial root canal systems of mandibular molars F. Paqué
Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Canals
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 320196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/320196 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Canals Sirisha Gundam, 1 Radhika
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 320196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/320196 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Canals Sirisha Gundam, 1 Radhika
Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population
 International Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 745152, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/745152 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population Hemant Ramesh
International Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 745152, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/745152 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population Hemant Ramesh
Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral Computed Tomographic
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars Hacer Deniz Arisu a Tayfun Alacam b Abstract Anatomical variations must be considered in clinical and radiographical evaluations during endodontic
Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars Hacer Deniz Arisu a Tayfun Alacam b Abstract Anatomical variations must be considered in clinical and radiographical evaluations during endodontic
Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS
 ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ABSTRACT
 EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor
EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor
P. Variant Anatomy of Mandibular First Permanent Molar:
 Case Report Variant Anatomy of Mandibular 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1119 First Permanent Molar: A Case Series Variant Anatomy of Mandibular First Permanent Molar: A Case Series 1 Pratima R Shenoi, 2 Rajesh
Case Report Variant Anatomy of Mandibular 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1119 First Permanent Molar: A Case Series Variant Anatomy of Mandibular First Permanent Molar: A Case Series 1 Pratima R Shenoi, 2 Rajesh
The morphology of the apical foramen in posterior teeth in a North Indian population
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01597.x The morphology of the apical foramen in posterior teeth in a North Indian population S. Arora & S. Tewari Department of Operative Dentistry and Endodontics, Government
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01597.x The morphology of the apical foramen in posterior teeth in a North Indian population S. Arora & S. Tewari Department of Operative Dentistry and Endodontics, Government
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 14, 238-242 Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report Pai ARV 1, Kamath MP 2, Basnet P 3 1 Associate
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 14, 238-242 Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report Pai ARV 1, Kamath MP 2, Basnet P 3 1 Associate
Journal of American Science 2014;10(12)
 Morphological variations in the root canal system of mandibular Premolars : A case series Youssef A. Algarni, BDS Specialist of Endodontics, Jeddah, KSA dr_yousseef@hotmail.com Abstract: The mandibular
Morphological variations in the root canal system of mandibular Premolars : A case series Youssef A. Algarni, BDS Specialist of Endodontics, Jeddah, KSA dr_yousseef@hotmail.com Abstract: The mandibular
Endodontic Management of Four Rooted Maxillary Second Molar Using CBCT as A Diagnostic Aid -A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. II (June. 2017), PP 125-129 www.iosrjournals.org Endodontic Management of Four Rooted
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. II (June. 2017), PP 125-129 www.iosrjournals.org Endodontic Management of Four Rooted
Science & Technologies ROOT CANAL MORPHOLOGY OF MAXILLAR AND MANDIBULAR MOLARS
 ROOT CANAL MORPHOLOGY OF MAXILLAR AND MANDIBULAR MOLARS Cena Dimova*, Gordana Panova*, Zlanovska Kerina*, Lidija Popovska** *- Faculty of Medical Science, University Goce Delcev, Stip, Republic of Macedonia
ROOT CANAL MORPHOLOGY OF MAXILLAR AND MANDIBULAR MOLARS Cena Dimova*, Gordana Panova*, Zlanovska Kerina*, Lidija Popovska** *- Faculty of Medical Science, University Goce Delcev, Stip, Republic of Macedonia
Maxillary First Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Root Canals: A Case Report
 JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 19 No. 2, pp: 99-108 (2012 A.D. / 1433 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 19-2.8 Maxillary First Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Root Canals: A Case Report Laila A. Bahammam, BDS, MSC, CERT ENDOD
JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 19 No. 2, pp: 99-108 (2012 A.D. / 1433 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 19-2.8 Maxillary First Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Root Canals: A Case Report Laila A. Bahammam, BDS, MSC, CERT ENDOD
Cleaning and shaping of root canals successfully require the presence of irrigation
 Root Canal Preparation of Maxillary Molars With the Self-adjusting File: A Micro-computed Tomography Study Ove A. Peters, DMD, MS, PhD,* and Frank Paqué, Dr med dent Abstract Introduction: The aim of this
Root Canal Preparation of Maxillary Molars With the Self-adjusting File: A Micro-computed Tomography Study Ove A. Peters, DMD, MS, PhD,* and Frank Paqué, Dr med dent Abstract Introduction: The aim of this
FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS
 Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report.
 Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report. Author(s) Kato, H. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3722
Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report. Author(s) Kato, H. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3722
Root canal morphology of mandibular permanent molars at different ages
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01428.x Root canal morphology of mandibular permanent molars at different ages H. R. D. Peiris 1, T. N. Pitakotuwage 2, M. Takahashi 1, K. Sasaki 3 & E. Kanazawa 3 1 Department
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01428.x Root canal morphology of mandibular permanent molars at different ages H. R. D. Peiris 1, T. N. Pitakotuwage 2, M. Takahashi 1, K. Sasaki 3 & E. Kanazawa 3 1 Department
Index. shapes, sizes, and locations, 282 small bone defects, through-and-through bone defect, treatment techniques, 285, 287
 Index A Accessory canal, 18 20 Accidental pulp exposure, 100, 103 104 Adhesive dentistry, 174 175 Ankylosis, 69 70 Anterior superior alveolar (ASA), 81 Anxiety, 36 Apical periodontitis asymptomatic, 214
Index A Accessory canal, 18 20 Accidental pulp exposure, 100, 103 104 Adhesive dentistry, 174 175 Ankylosis, 69 70 Anterior superior alveolar (ASA), 81 Anxiety, 36 Apical periodontitis asymptomatic, 214
Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case report
 495 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 3, 495-499, 2010 Case Report Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case
495 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 3, 495-499, 2010 Case Report Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case
Effects of Simulated Lateral Canals on the Accuracy of Measurements by an Electronic Apex Locator
 ca Applied Research Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2010;76:aXXX 2012;78:c65 Effects of Simulated Lateral Canals on the Accuracy of Measurements by an Electronic Apex Locator Özgür Uzun, DDS, PhD;
ca Applied Research Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2010;76:aXXX 2012;78:c65 Effects of Simulated Lateral Canals on the Accuracy of Measurements by an Electronic Apex Locator Özgür Uzun, DDS, PhD;
Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
The aim of the present work is to study the External and Internal Root anatomy of
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 29:36 January, 2008 A study on the External and Internal Root Anatomy of Egyptian Maxillary First Permanent Molar Reham Magdy Ameen 1 and Rania Mossad Hassan 2 1.
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 29:36 January, 2008 A study on the External and Internal Root Anatomy of Egyptian Maxillary First Permanent Molar Reham Magdy Ameen 1 and Rania Mossad Hassan 2 1.
An In Vivo Evaluation of Two Types of Files used to Accurately Determine the Diameter of the Apical Constriction of a Root Canal: An In Vivo Study
 An In Vivo Evaluation of Two Types of Files used to Accurately Determine the Diameter of the Apical Constriction of a Root Canal: An In Vivo Study Sumeet Darda, BDS, MDS; Narendra Manwar, BDS, MDS; Manoj
An In Vivo Evaluation of Two Types of Files used to Accurately Determine the Diameter of the Apical Constriction of a Root Canal: An In Vivo Study Sumeet Darda, BDS, MDS; Narendra Manwar, BDS, MDS; Manoj
Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study
 ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
Root canal preparation of maxillary molars with the self-adjusting file: a micro-computed tomography study.
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Root canal preparation of maxillary molars with the self-adjusting file:
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Root canal preparation of maxillary molars with the self-adjusting file:
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Anatomic Variations And Anomalies in Mandibular Central Incisors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. IX January. (2018), PP 71-77 www.iosrjournals.org Anatomic Variations And Anomalies
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. IX January. (2018), PP 71-77 www.iosrjournals.org Anatomic Variations And Anomalies
Working length changes following straight-line access and different coronal flaring methods
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Working length changes following straight-line access and different coronal flaring methods Shiva Sadeghi 1 * DDS, MS and Zeinab Doago 2, DDS 1. Assistant Professor of Endodontics, Dental
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Working length changes following straight-line access and different coronal flaring methods Shiva Sadeghi 1 * DDS, MS and Zeinab Doago 2, DDS 1. Assistant Professor of Endodontics, Dental
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry. Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
Shah. Management of a maxillary second premolar with an S-shaped root canal - An endodontic. Management of a maxillary second premolar
 Case Report Management of a maxillary second premolar with an S-shaped root canal - An endodontic challenge Nabi Shahnaz 1, Amin Khalid 2, Hussain Aijaz 3, Baba Irfan Ashraf 4*, Aasim Farooq Shah 5 1 PG
Case Report Management of a maxillary second premolar with an S-shaped root canal - An endodontic challenge Nabi Shahnaz 1, Amin Khalid 2, Hussain Aijaz 3, Baba Irfan Ashraf 4*, Aasim Farooq Shah 5 1 PG
Evaluation of canal preparation with Ni-Ti rotary files by micro computed tomography
 대한치과보존학회지 :Vol. 29, No. 4, 2004 Evaluation of canal preparation with Ni-Ti rotary files by micro computed tomography Jeong-Ho Lee, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Woo-Cheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek* Department of
대한치과보존학회지 :Vol. 29, No. 4, 2004 Evaluation of canal preparation with Ni-Ti rotary files by micro computed tomography Jeong-Ho Lee, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Woo-Cheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek* Department of
In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study
 Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC
 Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
IJCMR 214. REVIEW ARTICLE Root Canal Curvatures: A Literature Review. Smita Agrawal 1, Swapna.D.V 2, Roopa. R Nadig 3, Bijo Kurian 1
 IJCMR 214 REVIEW ARTICLE Root Canal Curvatures: A Literature Review Smita Agrawal 1, Swapna.D.V 2, Roopa. R Nadig 3, Bijo Kurian 1 ABSTRACT Preparation of curved root canals during endodontic treatment
IJCMR 214 REVIEW ARTICLE Root Canal Curvatures: A Literature Review Smita Agrawal 1, Swapna.D.V 2, Roopa. R Nadig 3, Bijo Kurian 1 ABSTRACT Preparation of curved root canals during endodontic treatment
5 Days Comprehensive Endodontic Course Topics
 5 Days Comprehensive Endodontic Course Topics 1. Pulp Dentin Complex/Retrogressive Changes: The significance of structural elements and its physiological, pathological and age related changes on the diagnosis
5 Days Comprehensive Endodontic Course Topics 1. Pulp Dentin Complex/Retrogressive Changes: The significance of structural elements and its physiological, pathological and age related changes on the diagnosis
Corresponding Author:Dr.Sneha Vaidya 3
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 07/05/2016
 Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 1 Compromised structural or mechanical integrity of teeth results in different types of tooth fractures,
Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 1 Compromised structural or mechanical integrity of teeth results in different types of tooth fractures,
ENDODONTIC TREATMENT OF PREMOLAR WITH UNUSUAL ANATOMY AND HYPERCEMENTOSIS CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC TREATMENT OF PREMOLAR WITH UNUSUAL ANATOMY AND HYPERCEMENTOSIS CASE REPORT ABSTRACT NOUMAN NOOR 2 MANZOOR AHMED 3 NUSRAT JABEEN 4 SADAF HUMAYOUN The purpose of this article was to report the
ENDODONTIC TREATMENT OF PREMOLAR WITH UNUSUAL ANATOMY AND HYPERCEMENTOSIS CASE REPORT ABSTRACT NOUMAN NOOR 2 MANZOOR AHMED 3 NUSRAT JABEEN 4 SADAF HUMAYOUN The purpose of this article was to report the
Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study
 Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study SHUE-FEN YANG 1,2 JENN-RONG HSU 1 CHIA-LIN TSAI 1 SHENG-FANG PAI 2 1 Department of Dentistry,
Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study SHUE-FEN YANG 1,2 JENN-RONG HSU 1 CHIA-LIN TSAI 1 SHENG-FANG PAI 2 1 Department of Dentistry,
Comparison of Curved Root Canals Prepared with Various Chelating Agents
 Comparison of Curved Root Canals Prepared with Various Chelating Agents by Kelli Swenson, LT, DC, USN A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Endodontics Graduate Program Naval Postgraduate Dental School
Comparison of Curved Root Canals Prepared with Various Chelating Agents by Kelli Swenson, LT, DC, USN A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Endodontics Graduate Program Naval Postgraduate Dental School
Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional Analysis with Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images
 Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images A. Garay 1, J.H. Legarreta 1, I. Macía 1, R. C. Aza 2 1 Vicomtech-ik4, Mikeletegi Pasealekua, 57 Teknologi Parkea 20009 Donostia, Spain
Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images A. Garay 1, J.H. Legarreta 1, I. Macía 1, R. C. Aza 2 1 Vicomtech-ik4, Mikeletegi Pasealekua, 57 Teknologi Parkea 20009 Donostia, Spain
Successful endodontic therapy stems from thorough canal debridement and effective
 Comparative Evaluation of Modified Canal Staining and Clearing Technique, Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography, Spiral Computed Tomography, and Plain and Contrast
Comparative Evaluation of Modified Canal Staining and Clearing Technique, Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography, Spiral Computed Tomography, and Plain and Contrast
Pulpal Morphology. Raney J. Deschenes, DMD, MS Pauline Hayes-Garrett, DDS. Contributing Efforts by:
 Pulpal Morphology Contributing Efforts by: Raney J. Deschenes, DMD, MS Pauline Hayes-Garrett, DDS Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This
Pulpal Morphology Contributing Efforts by: Raney J. Deschenes, DMD, MS Pauline Hayes-Garrett, DDS Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This
Influence of cervical preflaring on apical file size determination - An in vitro study
 Original Research Influence of cervical preflaring on apical file size determination - An in vitro study VASUNDHARA SHIVANNA * DEEPALI AGARWAL ** ABSTRACT Aim: To investigate the influence of cervical
Original Research Influence of cervical preflaring on apical file size determination - An in vitro study VASUNDHARA SHIVANNA * DEEPALI AGARWAL ** ABSTRACT Aim: To investigate the influence of cervical
Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 893980, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893980 Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient Vandana B. Kokane, Swapnil
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 893980, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893980 Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient Vandana B. Kokane, Swapnil
Evaluation of The Root Morphology of Maxillary Permanent First And Second Molars in An Indian Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer
 Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Micro-CT study of the root canal anatomy of maxillary canines
 Maxillary canine Journal section: Operative Dentistry and Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54235 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54235 Micro-CT study of the root canal of maxillary
Maxillary canine Journal section: Operative Dentistry and Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54235 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54235 Micro-CT study of the root canal of maxillary
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular first molars in a Chinese population: a clinical study
 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41121-018-0015-8 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular
Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41121-018-0015-8 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular
Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Study
 10.2478/bjdm-2018-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography () Study SUMMARY Background/Aim:
10.2478/bjdm-2018-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography () Study SUMMARY Background/Aim:
Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars
 Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars BY TIMOTHY ROGERS B.S. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign D.D.S., University of Illinois, Chicago, College
Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars BY TIMOTHY ROGERS B.S. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign D.D.S., University of Illinois, Chicago, College
Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars of Bangladeshi Population
 Original Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars of Bangladeshi Population Mohammad Aminul Islam 1, Tasnim Wakia 2, Md. Shamsul Alam 3 1. FCPS trainee Dept. of Conservative Dentistry
Original Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars of Bangladeshi Population Mohammad Aminul Islam 1, Tasnim Wakia 2, Md. Shamsul Alam 3 1. FCPS trainee Dept. of Conservative Dentistry
Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 216491, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216491 Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar Haridoss Selvakumar, 1 Swaminathan
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 216491, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216491 Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar Haridoss Selvakumar, 1 Swaminathan
Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Root and canal configuration of the maxillary first molar in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study
 Original Article Root and canal configuration of the maxillary first molar in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study Sultan Al Shehri, Saad Al Nazhan 1, Shreen Shoukry 2, Emad Al
Original Article Root and canal configuration of the maxillary first molar in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study Sultan Al Shehri, Saad Al Nazhan 1, Shreen Shoukry 2, Emad Al
