CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar.
|
|
|
- Gyles Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
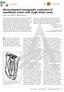
1 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (16): ISSN X CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar. Pablo Betancourt *, Pablo Navarro, Ramon Fuentes Research Center in Dental Sciences (CICO), Endodontic Laboratory, Dental School, Universidad de La Frontera, Temuco, Chile Abstract Introduction: One of the main causes of failure in endodontic treatment of maxillary molars is the inability to locate the secondary mesiobuccal canal, preventing proper debridement or obturation. The aim of this study was to describe in vivo the prevalence and location of the MB2 in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar through cone-beam computed tomography. Materials and methods: 60 maxillary first molars were analysed. To detect the MB2 canal, the observation and measurements were done 1 mm apically to the pulpal floor to standardize the methodology. The central point of the MB1, MB2 and P canals were located geometrically. Then straight lines were projected, connecting different points: line MB1-P and line MB1-MB2. A third line, MB2-T, corresponding to a perpendicular line between MB2 and MB1-P (T point) was drawn. The T point corresponding to a perpendicular line between the MB2 and MB1-P. The distance between the lines was measured in millimeters. The results were analysed using descriptive statistics, with a statistically significant value of p<0.05. Results: The MB2 canal was identified in 68.3% of cases. The average distance between MB1 and P was 6.91 ± 1.47 mm, between MB1 and MB ± 0.64 mm and MB2-T 1.26 ± 0.36 mm. There were no statistically significant differences in the presence and/or absence of the MB2 canal in terms of age or gender. Conclusions: The MB2 canal was found in a high percentage in the maxillary first molar. When present, it is advisable to take the main mesiobuccal canal as a parameter and explore some millimeters mesially and palatally to display it. CBCT is a good diagnostic tool for its detection and exploration. Keywords: First maxillary molar, Second mesiobuccal canal, MB2, Mesiobuccal root, Cone-beam computed tomography. Accepted on April 21, 2017 Introduction Variations in the anatomy of the root canal play an important role in the success of endodontic therapy, mainly in teeth with pulp necrosis. The morphology of the root canal system is complex and variable, especially in multi-rooted teeth [1]. Usually maxillary molar teeth are described as having three roots: Mesiobuccal (MB), Distobuccal (DB), and Palate (P); however, there have been variations in their root and canalicular anatomy, ranging from 1-5 and up to 7 different canals in a single root [2]. The permanent maxillary first molar is the tooth with the greatest complexity and variation [2,3], reflected in the higher rate of clinical failure [4], making it a constant challenge. One of the main causes of failure in the endodontic treatment of maxillary molars is the inability to locate the secondary Mesiobuccal canal (MB2), preventing proper debridement or obturation [5,6], which leads to poor long-term prognosis. Several studies have shown that the MB2 canal is present in more than 50% of first maxillary molars: Lee et al. (71.8%) [7], Rathi et al. (63.93%) [8], Abuabuara et al. (54%) [9] and Zheng et al. (50.40%) [3]; therefore, all possible methods must be used to locate and identify the canals of the root system. Different methods have been adopted to study the canalicular anatomy and location of the root canals, reporting differences in the results of their existence. An average detection rate of MB2 canals in in vivo studies of 40% has been considered compared with 80% described in in vitro studies [4]. Staining techniques [10], root cross-sections [11], X-ray examination [9,12], magnifying glass [11], clinical surgical microscope [13], ultrasound [5], scanning electron microscope [11], CBCT [1,7,8,14] and microcomputed tomography [15] have been used. The incorporation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) has enabled clinicians to visualize inaccessible anatomical structures, making it a valuable aid for providing additional information for diagnosis and treatment [16]. CBCT uses extraoral scanning to produce 3D orthogonal images of the maxillofacial skeleton and its structures, with a lower dose 6937
2 Betancourt/Navarro/Fuentes of radiation than conventional CT, has proven more accurate than digital x-rays in determining root canal systems. The significant increase in reports on the location of the MB2 canal in recent years can be attributed mainly to a better understanding of their location and prevalence due to advances in technology, in particular ultrasonic tips and magnification. However, the MB2 canal often goes undetected by the clinician in daily practice [12]. Clinically, the most common methods to evaluate the anatomy of root canals are the surgical microscope and conventional X-ray; however, access to microscope equipment, and the definition and detail that conventional X- ray provides limit detection of this canal. The aim of this study was to describe the prevalence and location of the MB2 canal in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary first molars using CBCT image analysis. Materials and Methods The investigation was approved by the science ethics committee of the Universidad de La Frontera, Temuco, Chile (protocol nº 048/13). A cross-sectional observational descriptive study was designed. Sixty-three maxillary first molar images obtained through CBCT from the Department of Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, Universidad de La Frontera (Temuco, Chile), in patients of both genders between November 2011 and August 2012 were examined. Imaging was taken as part of the diagnosis and treatment planning, using Pax Zenith CBCT equipment (Vatech, Korea, 2011), using 90 kv and 120 ma; 8 6 cm FOV and 0.12 mm voxel size. Images were selected that met the following inclusion criteria: subjects aged between 10 and 75 y, with the presence of the maxillary first molar with complete root formation. The molar root canals with endodontic filling or posts, rehabilitated using fixed prosthesis, calcified canals, evidence of periapical radectomy or surgery were excluded. Three patients were excluded, two due to endodontic treatment and one due to dental implant. Observation methodology The CBCT of 60 permanent first molar teeth (30 right and 30 left) were processed with the Ez 3D 2009 software, projected onto a LG 42LE4300-SA LED display. An apical crown scan was performed to identify the MB2 canal; to do this; the transverse plane was corrected, guiding the mesiodistal axis direction and the axial plane along the long axis of each tooth. The CBCT sections were calibrated with a range of 0.5 mm and 1 mm thickness. In teeth where the MB2 canal was present, the following protocol was performed: the furcation was located on the axial plane, and progress to the apex was made in 1 mm sections (two sections of 0.5 mm), where all root canals were observed. On this image, achieved in all teeth, the MB1 and palatal canals were located geometrically. The center point of each root canal was located: MB1 (center mesiobuccal canal), MB2 (center of second mesiobuccal canal) and P (center palatal canal). Then straight lines were projected, connecting different points: the MB1-P line and the MB1-MB2 line. A third line, MB2-T, corresponding to a perpendicular line between the MB2 and MB1-P (T point) line was drawn according to the parameters described by Gorduysus et al. [12] and Tuncer et al. [17] (Figure 1). Finally, the distance between the lines was measured in millimeters. All images were analysed by two examiners after training and consensus was reached. The data obtained in relation to gender, age, side and distances between different points (line length) were entered into an Excel crosstab. Figure 1. Morphometric measurements applied to characterize the location of the MB2 canal in the mesiobuccal root of left maxillary first molar (axial view). Location of the central points of the MB1 (Mesiovestibular canal), MB2 (secondary Mesiovestibular canal) and P (Palatal canal). The red lines represent the join between the established points. The T point is the intersection of the perpendicular line drawn between point MB2 and line MB1-P. The distance between the lines was measured in millimeters. Statistical analysis The results were analysed using the SPSS software through descriptive statistics and a chi-squared test, establishing the relationship between the presence of MB2 canal by gender and jaw position (right or left). To establish the relationship with age, an ANOVA was used. Finally, to calculate the average distances between the MB2, MB1, P and T points, confidence intervals were calculated with a reliability of 95%. Results The MB2 canal was identified in 68.3% of cases (41/60). In all cases, presence or absence, there were no differences in the observation. Of the maxillary first molars analysed by gender (29 in females and 31 in males), the MB2 canal was identified in the molars of women in 23 cases (56.1% of total identified) and in 18 cases in men (43.9%). According to the chi-squared test, there were no significant differences between gender and the absence or presence of the MB2 canal (p=0.313) (Table 1). Depending on the position, the MB2 canal was present in 21 cases on the right side with a total frequency of 51.2%, and in 6938
3 CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar 20 cases on the left side with a frequency of 48.8%. According to the chi-squared test, there were no significant differences between the absence or presence of the MB2 and position (p=0.781) (Table 2). Regarding age, in cases where the MB2 canal was present (n=41), the mean was 24.9 ± 10.5 y, and in the absence (n=19) 28.1 ± y. There were no significant differences between the presence and/or absence of MB2 by age (p=0.280) (Table 3). According to the average distances between the points discussed, among MB2-P the average distance was 6.91 ± 1.47 mm with an average range between and mm. For points MB2-MB1 the average distance was 2.61±0.64 mm, with a range between and mm, and for MB2-T the average distance was 1.26 ± 0.36 mm, with a range between and mm (Table 4). Figure 2 illustrates the variability of the analysed distance dispersion. Left side 10 (52.64%) 20 (48.8%) 30 (50%) Total 19 (100%) 41 (100%) 60 (100%) MB2: Secondary Mesiobuccal Canal Table 3. Average age associated with the presence of the MB2 canal in the population-specific sample of Temuco, Chile. MB2 n Age SD p Absent Present MB2: Secondary Mesiobuccal Canal; SD: Standard Deviation. Table 4. Distance between the reference points chosen for the geometric location of the MB2 canal in the maxillary first molar. Distance (mm) Range (mm) MB2-P 6.91 ± 1.47 mm MB1-MB ± 0.64 mm MB2-T 1.26 ± 0.36 mm Figure 2. Axial view of the left maxillary first molar. Dispersion of location between points MB1 and MB2 (red dots), MB-P (green dots) and MB2-T (blue dots) in the entire analysed sample. Table 1. Number and frequency of the MB2 canal in the mesiobuccal roots of the maxillary first molars by gender. MB2 Total p Absent Present Female 6 (31.6%) 23 (56.1%) 29 (48.3%) Male 13 (68.4%) 18 (43.9%) 31 (51.7%) Total 19 (100%) 41 (100%) 60 (100%) MB2: Secondary Mesiobuccal Canal. Table 2. Number and frequency of the MB2 canal in the mesiobuccal roots of the maxillary first molars by tooth position. MB2 Absent Present Total Right side 9 (47.36%) 21 (51.2%) 30 (50%) p Figure 3. Graph of correlations between the different variables. Discussion The location of the MB2 canal in the maxillary first molar is complex due to its variable position and narrow foramen. The presence of the MB2 canal was observed in vivo using CBCT in 68.3% of cases, similar to those reported by Abarca et al. (73.44%) [1], Lee et al. (71.8%) [7], Betancourt et al. (68.75%) [14] and Rathi et al. (63.93%) [8]. Although frequencies below 54% [9], 50.40% [3] and 37.05% [18] have also been identified using CBCT. On the other hand, computed microtomography frequencies of 80% [15] and 90% [19] have been reported in 6939
4 Betancourt/Navarro/Fuentes extracted teeth, probably due to factors such as a high sensitivity exam, sample size or the population studied. The use of CBCT to explore the anatomy of root canals has been compared to histological studies with a high correlation (Figure 3) [20]. The in vitro methods used to study the MB2 show a frequency similar to this study; Alavi et al. [10] reported 65% by clarification; Baratto et al. [18] and Alacam et al. [5], 67.14% by microscopy and 67% respectively, and by combining microscopy and ultrasound achieved a detection of 74%. By using these methods in vivo, frequencies of 53.26% and 62% are achieved while using periapical radiographs, where they were observed in only 8% [9], demonstrating the effectiveness of CBCT. The findings of our specific population are close to those observed in Korea (71.8%) [7], Thailand (68.5%) [6], the UK 65% [10] and India (63.93%) [8] and are superior to those observed in Brazil (54%) [9] and China (52%) [4], whereas it is low compared to the populations of Italy (80%) [15] and Turkey (78.18%) [21]. The frequency of the MB2 canal was greater in 24.9 ± 10.5 y of age, similar to what was reported by Betancourt et al. (25.31 ± y) [14]. The limited literature exploring the use of CBCT is variable, observed between years [3], y [7], and y [8]. This may be due to the sample size used and studies on the age concentration of the study subjects, although all the studies showed ranges from 14 ± 4 to 75 ± 3 y. There are no studies that categorize age ranges to establish a basis for comparison. No differences were found for gender or location in the maxilla, similar to that reported by Zheng et al. [3]. Other research has shown some non-significant trends [7], which may be related to a population-specific factor. The MB2 canal was located 2.61 mm palatally to the MB1 canal, the highest reported in the literature, and comparable with the results of Gilles and Reader [22], that placed the MB2 canal with respect to the MB1 canal at a distance of 2.31 mm by scanning electron microscopy and Zhang et al. [4] at 2 mm using light microscopy. Shorter distances have been reported by Kulid and Peters [23] with 1.82 mm. Gorduysus et al. [12], who located the MB2 canal in 45 extracted maxillary molars with a distance between MB1-MB2 of 1.81 ± 0.38 mm, and Vasudev and Goel [24] with 1.8 mm. Tuncer et al. [17] located the MB2 canal in 65 molars at 1.73 mm palatally to the MB1 canal, and 21 molars at a distance of 1.86 mm palatally. Even smaller distances have been reported by Peeters et al. (1.55 mm) [6], and Degerness et al. (1.3 mm) [25]. This could be explained by the higher sensitivity of the in vitro studies or the use of microscopes, having a magnification of 6.4X, which distorts image scales. The location of the MB2 is also variable with respect to the palatal canal [4,12]. In our observations, it was located mesially to the MB1 and palatine canals, consistent with that described by Vasudev and Goel [24]. The total distance between MB1-P was 6.91 mm and MB2-T was 1.26 mm. Gorduysus et al. [12] located the mesial MB2 canal at a distance of 0.69 ± 0.42 mm (MB2-T), while Zhang et al. [4] less than 1 mm mesially to the MB-P line, and Tuncer et al. [17] 0.87 mm distally to the MB1 canal (65 molars) and 0.72 mm mesially (21 molars). We believe that the variation in the location distally or mesially, depends on the type of study, as in vitro experiences show the anatomical relationship but the proportion in the arc is lost; by contrast, in vivo studies, particularly with CBCT, can view the axes and planes with a better orientation. These observations suggest modifying the design in the cavity chamber access due to the MB2 canal position, an initial access more rhomboid or quadrilateral in shape would be better than the classic triangular access [17,24] and would allow a shortcut in the presence of the MB2 canal, or increase the probability of finding it. CBCT provides better results than other methods such as intraoral radiography, microscopy and visual observation. It is an effective and non-destructive tool to study the presence and location of the MB2 canal in vivo, preoperative planning of its access, unlike ultrasound microscopy, where locating the MB2 is random after gaining access. Preoperatively, intraoral X- rays, even when different angles are taken, can only study the morphology of the two-dimensional canals with distortion and overlapping structures. By contrast, CBCT allows threedimensional reconstructions and multiplanar measurements canalicular morphology, with a low dose of radiation being limited to the anatomical area investigated, with a high resolution spiral CT. This is used increasingly for resolving endodontic problems [16]. However, drawbacks like dispersion due to high density structures such as enamel, metal posts or restoration imaging affect quality and diagnostic accuracy. In addition, the patient must lie still during the exposure time, and it is still expensive in terms of a cost-benefit ratio, however, this is insignificant. In conclusion, the clinician must be satisfied that the MB2 canal is present in a high percentage of maxillary first molars. When present, it is advisable to take the main mesiobuccal canal as a parameter and explore some millimeters mesially and palatally to display it. The average distance between MB1 and P was 6.91 ± 1.47 mm, between MB1 and MB ± 0.64 mm and MB2-T 1.26 ± 0.36 mm. The inability to locate and treat it can lead to bacterial colonization, infection and endodontic failure; even partial treatment will increase the likelihood of success [12]. The location of the MB2 canal is essential, and the use of clinical tools like the microscope or ultrasound with a diamond or square access and performing further examination by CBCT may be important factors for successful endodontic treatment or re-treatment. Acknowledgements This study was supported by DIUFRO project # DI , Universidad de La Frontera, Temuco, Chile. Radiology Unit for providing CBCT exams and the Master of Dentistry Program at the Universidad de La Frontera, Temuco, Chile. 6940
5 CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar References 1. Abarca J, Gomez B, Zaror C, Monardes H, Bustos L, Cantin, M. Assessment of mesial root morphology and frequency of mb2 canals in maxillary molars using cone beam computed tomography. Int J Morphol 2015; 33: Kottoor J, Albuquerque D, Velmurugan NA. New anatomically based nomenclature for the roots and root canals-part 1: maxillary molars. Int J Dent 2012; 2012: Zheng Q, Wang Y, Zhou X, Wang Q, Zheng G, Huang D. A cone-beam computed tomography study of maxillary first permanent molar root and canal morphology in a Chinese population. J Endod 2010; 36: Zhang R, Yang H, Yu X, Wang H, Hu T, Dummer PMH. Use of CBCT to identify the morphology of maxillary permanent molar teeth in a Chinese subpopulation. Int Endod J 2011; 44: Alacam T, Cemal AC, Genc O, Kayaoglu G. Second mesiobuccal canal detection in maxillary first molars using microscopy and ultrasonics. Aust Endod J 2008; 34: Peeters H, Suardita K, Setijanto D. Prevalence of a second canal in the mesiobuccal root of permanent maxillary first molars from an Indonesian population. J Oral Sci 2011; 53: Lee J, Kim K, Lee J, Park W, Jeong J, Lee Y, Gu Y, Chang S, Son W, Lee W, Baek S, Bae K, Kum K. Mesiobuccal root canal anatomy of Korean maxillary first and second molars by cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2011; 111: Rathi S, Patil J, Jaju PP. Clinical study detection of mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars and dis-tolingual canal in mandibular molars by dental CT: A retrospective study of 100 Cases. Int J Dent 2010; 2010: Abuabara A, Baratto-Filho F, Aguiar Anele J, Leonardi DP, Sousa-Neto MD. Efficacy of clinical and radiological methods to identify second mesiobuccal canals in maxillary first molars. Acta Odontol Scand 2013; 71: Alavi A, Opasanon A, Ng YL, Gulavibala K. Root and canal morphology of thai maxillary molars. Int Endod J 2002; 35: Schwarze T, Baethge C, Stecher T, Geurtsen W. Identification of second canals in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first and second molars using magnifying loupes or an operating microscope. Aust Endod J 2002; 28: Gorduysus OM, Gorduysus M, Friedman S. Operating microscope improves negotiation of second mesiobuccal canals in maxillary molars. J Endod 2001; 27: Das S, Warhadpande MM, Redij SA, Jibhkate NG, Sabir H. Frequency of second mesiobuccal canal in permanent maxillary first molars using the operating microscope and selective dentin removal: A clinical study. Contemp Clin Dent 2015; 6: Betancourt P, Fuentes R, Aracena Rojas S, Cantin M, Navarro Caceres P. Prevalence of a second canal in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars by cone-beam computed tomography. Av Odontoestomatol 2013; 29: Somma F, Leoni D, Plotino D, Grande NM, Plasschaert A. Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis. Int Endod J 2009; 42: Patel S, Dawood A, Whaites E, Pitt Ford T. New dimensions in endodontic imaging: Part 1. Conventional and alterna- tive radiographic systems. Int Endod J 2009; 42: Tuncer AK, Haznedaroglu F, Sert S. The location and accessibility of the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary first molar. Eur J Dent 2010; 4: Baratto F, Zaitter S, Aihara G, Alves E, Abuabara A, Maria G. Analysis of the internal anatomy of maxillary first molars by using different methods. J Endod 2009; 35: Verma P, Love RM. A Micro CT study of the mesio- buccal root canal morphology of the maxillary first molar tooth. Int Endod J 2011; 44: Michetti J, Maret D, Mallet JP, Diemer F. Validation of cone beam computed tomography as a tool to explore root canal anatomy. J Endod 2010; 36: Sert S, Bayirli GS. Evaluation of the root canal configurations of the mandibular and maxillary permanent teeth by gender in the Turkish population. J Endod 2004; 30: Gilles J, Reader A. An SEM investigation of the mesiolingual canal in human maxillary first and second molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1990; 70: Kulild J, Peters D. Incidence and configuration of canal systems in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first and second molars. J Endod 1990; 16: Vasudev SK, Goel BR. Endodontic miscellany: Negotiation and Management of canal in max- illary molar. Endodon 2003; 15: Degerness R, Bowles W. Anatomic determination of the mesiobuccal root resection level in maxillary molars. J Endod 2008; 34: * Correspondence to Pablo Betancourt Research Center in Dental Sciences (CICO) Endodontic Laboratory Dental School Universidad de La Frontera Chile 6941
Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar
 Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Usage of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) to Evaluate Root and Canal Morphology of maxillary First Molar
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a polish population
 Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Evaluation of The Root Morphology of Maxillary Permanent First And Second Molars in An Indian Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with unusual mesiobuccal root anatomy
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June Volume 4
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June 1 2011 Volume 4 Endodontic Treatment Utilizing 3D Imaging Recent advances in technology, such as rotary
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June 1 2011 Volume 4 Endodontic Treatment Utilizing 3D Imaging Recent advances in technology, such as rotary
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo
 The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST
 CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT
 Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography
 Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL. Mesiobuccal Root Canal Morphology of the Permanent Maxillary First Molar in A Sri Lankan Population
 MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Mesiobuccal Root Canal Morphology of the Permanent Maxillary First Molar in A Sri Lankan Population Peiris R 1 and Royal Oman Air Force 2 1 Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Mesiobuccal Root Canal Morphology of the Permanent Maxillary First Molar in A Sri Lankan Population Peiris R 1 and Royal Oman Air Force 2 1 Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty
Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct
 OPEN (2017) 9, 33 37 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin
OPEN (2017) 9, 33 37 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin
IDENTIFICATION OF THE SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN FIRST MAXILLARY MOLAR USING ULTRASONICS AND VISUALS AIDS
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 05 IDENTIFICATION OF THE SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN FIRST MAXILLARY MOLAR USING ULTRASONICS AND VISUALS AIDS Soumaya
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 05 IDENTIFICATION OF THE SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN FIRST MAXILLARY MOLAR USING ULTRASONICS AND VISUALS AIDS Soumaya
Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Canals
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 320196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/320196 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Canals Sirisha Gundam, 1 Radhika
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 320196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/320196 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Canals Sirisha Gundam, 1 Radhika
Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
Success in root canal treatment (RCT) is dependent. Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study
 Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study Marcelo Santos Coelho, DDS, MSc; Jeffrey M. Parker, DMD; Peter Z. Tawil, DMD, MS, FRCD(C), Dip ABE Abstract:
Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study Marcelo Santos Coelho, DDS, MSc; Jeffrey M. Parker, DMD; Peter Z. Tawil, DMD, MS, FRCD(C), Dip ABE Abstract:
Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Evaluation of Complex Mesiobuccal Root Anatomy in Maxillary First Molar Teeth
 Int. J. Morphol., 36(2):460-464, 2018. Evaluation of Complex Mesiobuccal Root Anatomy in Maxillary First Molar Teeth Evaluación de la Anatomía de la Raíz Mesiobucal Compleja en los Primeros Dientes Molares
Int. J. Morphol., 36(2):460-464, 2018. Evaluation of Complex Mesiobuccal Root Anatomy in Maxillary First Molar Teeth Evaluación de la Anatomía de la Raíz Mesiobucal Compleja en los Primeros Dientes Molares
Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral Computed Tomographic
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ABSTRACT
 EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor
EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor
The variation of root canal morphology, especially in multirooted teeth, is a
 Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with a Single Root and a Single Canal Diagnosed with the Aid of Spiral CT: A Case Report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, Narayanan Bhargavi, BDS, and Deivanayagam
Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with a Single Root and a Single Canal Diagnosed with the Aid of Spiral CT: A Case Report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, Narayanan Bhargavi, BDS, and Deivanayagam
MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS
 ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
e74 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College a Reader.
 Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study
 Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study SHUE-FEN YANG 1,2 JENN-RONG HSU 1 CHIA-LIN TSAI 1 SHENG-FANG PAI 2 1 Department of Dentistry,
Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study SHUE-FEN YANG 1,2 JENN-RONG HSU 1 CHIA-LIN TSAI 1 SHENG-FANG PAI 2 1 Department of Dentistry,
Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 5, MAY 2004 Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 5, MAY 2004 Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS
 Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography Gurudutt
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography Gurudutt
Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars Hacer Deniz Arisu a Tayfun Alacam b Abstract Anatomical variations must be considered in clinical and radiographical evaluations during endodontic
Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars Hacer Deniz Arisu a Tayfun Alacam b Abstract Anatomical variations must be considered in clinical and radiographical evaluations during endodontic
CANAL CONFIGURATION AND THE PREVALENCE OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR OF A SAUDI SUB-POPULATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CANAL CONFIGURATION AND THE PREVALENCE OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR OF A SAUDI SUB-POPULATION Atif Saleem Agwan 1 Zeeshan Sheikh 2 Haroon Rashid 3 BDS, FCPS Dip.Dh,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CANAL CONFIGURATION AND THE PREVALENCE OF SECOND MESIOBUCCAL CANAL IN MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR OF A SAUDI SUB-POPULATION Atif Saleem Agwan 1 Zeeshan Sheikh 2 Haroon Rashid 3 BDS, FCPS Dip.Dh,
Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars
 Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars BY TIMOTHY ROGERS B.S. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign D.D.S., University of Illinois, Chicago, College
Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars BY TIMOTHY ROGERS B.S. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign D.D.S., University of Illinois, Chicago, College
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
The main objective of root canal treatment is thorough cleaning and shaping of all
 Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Eight Root Canal Systems Evaluated Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography Scanning: A Case Report Jojo Kottoor, MDS, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, MDS,
Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Eight Root Canal Systems Evaluated Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography Scanning: A Case Report Jojo Kottoor, MDS, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, MDS,
Assessment of Mesial Root Morphology and Frequency of MB2 Canals in Maxillary Molars using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Int. J. Morphol., 33(4):1333-1337, 2015. Assessment of Mesial Root Morphology and Frequency of MB2 Canals in Maxillary Molars using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Determinación de la Morfología de la Raíz
Int. J. Morphol., 33(4):1333-1337, 2015. Assessment of Mesial Root Morphology and Frequency of MB2 Canals in Maxillary Molars using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Determinación de la Morfología de la Raíz
Gorduysus MO et al. Operating Microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.J.C.M.R Operating microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal in mandibular ıncisors Mehmet Omer Gorduysus, Melahat Gorduysus, Zeliha Yilmaz * Department of Endodontics,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.J.C.M.R Operating microscope improves ability to locate and negotiate second canal in mandibular ıncisors Mehmet Omer Gorduysus, Melahat Gorduysus, Zeliha Yilmaz * Department of Endodontics,
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars
 Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography
 Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct
 (2017) 9, 151 157 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank
(2017) 9, 151 157 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank
Correspondence should be addressed to Raed Hakam Mukhaimer;
 International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
Knowledge of tooth and root canal anatomy is important for dental practice and for
 Detection of Permanent Three-rooted Mandibular First Molars by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Imaging in Taiwanese Individuals Ming-Gene Tu, DDS, MS, PhD,* Heng-Li Huang, PhD,* Shui-Sang Hsue, DDS, MS,
Detection of Permanent Three-rooted Mandibular First Molars by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Imaging in Taiwanese Individuals Ming-Gene Tu, DDS, MS, PhD,* Heng-Li Huang, PhD,* Shui-Sang Hsue, DDS, MS,
Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series
 Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01472.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis F. Somma 1, D. Leoni 1, G. Plotino 1,
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01472.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis F. Somma 1, D. Leoni 1, G. Plotino 1,
Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular first molars in a Chinese population: a clinical study
 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41121-018-0015-8 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular
Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41121-018-0015-8 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular
An unusual maxillary canine with two separated root canals
 pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study
 ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC
 Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Root and canal configuration of the maxillary first molar in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study
 Original Article Root and canal configuration of the maxillary first molar in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study Sultan Al Shehri, Saad Al Nazhan 1, Shreen Shoukry 2, Emad Al
Original Article Root and canal configuration of the maxillary first molar in a Saudi subpopulation: A cone-beam computed tomography study Sultan Al Shehri, Saad Al Nazhan 1, Shreen Shoukry 2, Emad Al
Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE
 Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case report
 495 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 3, 495-499, 2010 Case Report Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case
495 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 3, 495-499, 2010 Case Report Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography L Demiriz, E Hazar Bodrumlu, M İçen 1 Departments of Pediatric Dentistry
Original Article Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography L Demiriz, E Hazar Bodrumlu, M İçen 1 Departments of Pediatric Dentistry
Periapical Radiography
 Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Failure of root canal therapy often
 Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars by means of micro-computed tomography: an ex vivo study
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars
Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report.
 Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report. Author(s) Kato, H. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3722
Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report. Author(s) Kato, H. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3722
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision
 Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Maxillary and mandibular first molar with five root canals diagnosed with cone-beam computed tomography: A review and two case reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 10, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 06-11 Maxillary and mandibular first molar with five root canals diagnosed
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 10, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 06-11 Maxillary and mandibular first molar with five root canals diagnosed
Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Awareness and Attitude among Dental Professional towards CBCT
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 10, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 55-59 Awareness and Attitude among Dental Professional towards CBCT
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 10, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 55-59 Awareness and Attitude among Dental Professional towards CBCT
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Journal of American Science 2014;10(12)
 Morphological variations in the root canal system of mandibular Premolars : A case series Youssef A. Algarni, BDS Specialist of Endodontics, Jeddah, KSA dr_yousseef@hotmail.com Abstract: The mandibular
Morphological variations in the root canal system of mandibular Premolars : A case series Youssef A. Algarni, BDS Specialist of Endodontics, Jeddah, KSA dr_yousseef@hotmail.com Abstract: The mandibular
Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography Evaldo Rodrigues 1, Antônio Henrique Braitt 2, Bruno
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography Evaldo Rodrigues 1, Antônio Henrique Braitt 2, Bruno
Analysis of Root Resorption in Dentistry using Collaborative Tools & Strategies
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 2, Issue 12 (August 2012), PP. 37-42 Analysis of Root Resorption in Dentistry using
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 2, Issue 12 (August 2012), PP. 37-42 Analysis of Root Resorption in Dentistry using
Research Article. Key Words: First premolar, Mandibular, Maxillary, Vertucci s classification, Spiral computed tomography.
 Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Investigating the Sizes of Anatomical Landmarks of Coronal Pulp in the First Permanent Human Molars on Bite Wing Radiography
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Volume 5, Issue 5, Page No: 102-107 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Investigating
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Volume 5, Issue 5, Page No: 102-107 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Investigating
Maxillary First Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Root Canals: A Case Report
 JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 19 No. 2, pp: 99-108 (2012 A.D. / 1433 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 19-2.8 Maxillary First Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Root Canals: A Case Report Laila A. Bahammam, BDS, MSC, CERT ENDOD
JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 19 No. 2, pp: 99-108 (2012 A.D. / 1433 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 19-2.8 Maxillary First Molar with Three Mesiobuccal Root Canals: A Case Report Laila A. Bahammam, BDS, MSC, CERT ENDOD
A comparative study of cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiography in detecting mandibular molars root perforations
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 115-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.2.115 A comparative study of cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiography in detecting mandibular
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 115-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.2.115 A comparative study of cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiography in detecting mandibular
Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate root and canal morphology of mandibular first and second molars in Turkish individuals
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013 Jul 1;18 (4):e73744. Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 Use of conebeam computed
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013 Jul 1;18 (4):e73744. Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 Use of conebeam computed
Lodha Ena* M. Kala** INTRODUCTION
 Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional Analysis with Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
IJCMR 214. REVIEW ARTICLE Root Canal Curvatures: A Literature Review. Smita Agrawal 1, Swapna.D.V 2, Roopa. R Nadig 3, Bijo Kurian 1
 IJCMR 214 REVIEW ARTICLE Root Canal Curvatures: A Literature Review Smita Agrawal 1, Swapna.D.V 2, Roopa. R Nadig 3, Bijo Kurian 1 ABSTRACT Preparation of curved root canals during endodontic treatment
IJCMR 214 REVIEW ARTICLE Root Canal Curvatures: A Literature Review Smita Agrawal 1, Swapna.D.V 2, Roopa. R Nadig 3, Bijo Kurian 1 ABSTRACT Preparation of curved root canals during endodontic treatment
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars: An in vitro Study
 Original research Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root 10.5005/jp-journals-10060-0004 Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary
Original research Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root 10.5005/jp-journals-10060-0004 Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary
P. Variant Anatomy of Mandibular First Permanent Molar:
 Case Report Variant Anatomy of Mandibular 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1119 First Permanent Molar: A Case Series Variant Anatomy of Mandibular First Permanent Molar: A Case Series 1 Pratima R Shenoi, 2 Rajesh
Case Report Variant Anatomy of Mandibular 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1119 First Permanent Molar: A Case Series Variant Anatomy of Mandibular First Permanent Molar: A Case Series 1 Pratima R Shenoi, 2 Rajesh
Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 893980, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893980 Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient Vandana B. Kokane, Swapnil
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 893980, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893980 Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient Vandana B. Kokane, Swapnil
Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 07/05/2016
 Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 1 Compromised structural or mechanical integrity of teeth results in different types of tooth fractures,
Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 1 Compromised structural or mechanical integrity of teeth results in different types of tooth fractures,
The. Cone Beam. Conversation. A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT
 The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
Case Report Independent and Confluent Middle Mesial Root Canals in Mandibular First Molars: A Report of Four Cases
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 103125, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/103125 Case Report Independent and Confluent Middle Mesial Root Canals in Mandibular First Molars: A Report of Four Cases
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 103125, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/103125 Case Report Independent and Confluent Middle Mesial Root Canals in Mandibular First Molars: A Report of Four Cases
Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population
 International Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 745152, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/745152 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population Hemant Ramesh
International Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 745152, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/745152 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Permanent Molars in an Indian Population Hemant Ramesh
Mandibular first molar with four canals in the mesial root
 C L I N I C A L Mandibular first molar with four canals in the mesial root Hamed Karkehabadi 1, Ricardo Machado 2 and Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia 3 Abstract A 35-year-old female patient with intermittent
C L I N I C A L Mandibular first molar with four canals in the mesial root Hamed Karkehabadi 1, Ricardo Machado 2 and Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia 3 Abstract A 35-year-old female patient with intermittent
Effect of extraction of permanent first molars on the development and eruption of third molars
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22122/johoe.v7i3.417 Published by Vesnu Publications Received: 19 Aug. 2017 Accepted: 01 Nov. 2017 Effect of extraction of permanent first molars on the development and eruption
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22122/johoe.v7i3.417 Published by Vesnu Publications Received: 19 Aug. 2017 Accepted: 01 Nov. 2017 Effect of extraction of permanent first molars on the development and eruption
Andres Torres 1, *, Reinhilde Jacobs 1, Paul Lambrechts 2, Claudia Brizuela 3, Carolina Cabrera 3, Guillermo Concha 4, María Eugenia Pedemonte 3
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 95-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.2.95 Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 95-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.2.95 Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability
Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week and 12 months after root-end resection
 (2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
(2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
