EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Norman Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor of Endodontics, Dental School, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran. 2 Assistant Professor of Endodontics, Dental School/Iranian Center for Endodontic Research, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran. 3 Assistant Professor of orofacial radiology, Dental School, Tehran University of Medical science, Tehran, Iran. * Post Graduated Student, EndodonticsDept, Islamic Azad University, Dental Branch, Tehran, Iran. ABSTRACT There are different methods for investigating anatomy and morphology of root canal. One useful clinical method is applying cone beam computed tomography which lessens the limitations of two dimensional radiography images and it has fewer rays with higher resolution. Considering the importance of anatomy and morphology of canal in cleaning and formation of root canal system, based on incompatible results from various studies, and due to insufficient researches in terms of planning and research methodology, this study aimed to investigate root anatomyand mandibular first and second canal by CBCT in Iranian population during This study was performed cross-sectional. Studied population included mandibular premolarteeth that were healthy and recognizable crown with healthy and evolved apex without central or internal desorption and root crack and without restoration from CBCT images. 300 CBCT images were studied statistically. What we examined was teeth of mandibular first and secondpremolarin terms of gender, root length, root number, numbers of each root canals, canal types, presence of isthmus, intervalscanal orifice, and finally anatomy symmetry. Statistical analysis was conducted by SPSS software. 95% of mandibular first premolar teeth in left side were single rooted and 5% were double rooted, 76/5% were single canal and 23/5% was double canal. In right side, 96/3% were single rooted and 2/7% were double rooted, 78% single canal and 2/9% were dc. 96/6% of second premolar teeth in left side were single rooted and % were double rooted, 85/5% were single rooted and /5% were double in right side 99/3% were single rooted and 0/7% were double rooted and 92/5% were single canal and 7/5% were double canal which all indicated that there was no significant difference between first and second premolars. Based on results it was illustrated that first and second premolar teeth were almost single rooted (95%, 99/6%) with one canal (type I) and secondlytype V had the most prevalence rate. Second premolars in nearly all cases were single rooted and there was no difference in tooth type. Direction of root curvature was direct in most cases (5%) and then distal direction was in second priority (37%) and there was no difference in tooth type. KEY WORDS: premolar canals, CBCT, root and canal anatomy, mandibularpremolarteeth INTRODUCTION Base tooth anatomy is main basis for science of root treatment. Today, root apex is not the only area in endodonticscience but the idea ofthree-dimensionalroot canal fillingimplies that although working length and maintaining it is more important, access to all complications of canal inside is also crucial in order to P- 33
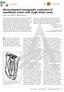
2 facilitate root canal filling().different methods are for investigating anatomy and morphology of root canal which all includes dental pulpcoloration with clearing, investigating it by electronic microscope (SEM) study of different sections by disc and providing dental models via clear resin which all are part of laboratory equipment's.(3,). One useful clinical method is cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) which decreases limitations of two dimensional radiography and it has less ray and more resolution (,). Studies indicated that for assessing dental sections, CBCT is more useful in anatomy investigations than other methods of radiography (, 2).In 205 HakanArslan conducted cone-beam computed tomographic study of root canal systems in mandibular premolars in a Turkish population. 287 CBCT images from mandibularpremolar teeth were provided from patients and then they studied in terms of different formations of orifice, age and gender of patient, dental type, its site, canal form, presence of C form canal, and radicular groove. Circle form of canal and condition of being circle were studied in terms of distance from orifice. A theoretical model has been defined for determining orifice form. Orifice form is almost planar (37%) and it is like key holes (23%).prevalence of T form canal was 3/8% and C form was 2/%. And also prevalence of circle form of canal in middle area and /3 epical was 95/% and prevalence of radicular groove was 2% in first premolarand.5% in second premolar. Average length of distance to circle formation of canal form had relation with patient age (5). In 205, Felsypremila et al studied Anatomic symmetry of root and root canal morphology of posterior teeth in Indian subpopulation using cone beam computed tomography. They selected 26 CBCTimages and they anterior teeth without dentalresorption were examined in each quadrant.form 305 examined teeth (8 maxilla premolar, 85 mandibular premolar, 738 maxillary molars, 62 mandibular molar), There was no significant difference in root number and symmetry of maxillary first and second premolar (8/5%). mandibular second premolar had more symmetry than second molar. The most prevalence rate of anatomy was observed in maxilla first premolar (double rooted, double canal), maxilla second premolar (single rooted and four canal), mandibular first and second premolar (single rooted and single canal), maxillary first and second molar (three root and fourth canal), mandibular first and second molar (double rooted and three canal). In contrast, there was the most asymmetry between maxillary second molars (8).Considering the importance of anatomy and morphology of canal in cleaning and shaping of root canal system, based on incompatible results from various studies, and due to insufficient researches in terms of planning and research methodology, this study aimed to research effect of gender in root with mandibular first and second premolar morphology and teeth canals of CBCT in Iranian population. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY This study was performed cross-sectional. Studied population included mandibularpremolar teeth that were healthy and recognizable crown with healthy and developedapex without external or internal resorption and root crack and without restoration from CBCT images. 300 CBCT images were studied statistically. What we examined was teeth of mandibular first and secondpremolarin terms of gender, root length, root number, numbers of each root canals, canal types, presence of isthmusand finally anatomy symmetry. Root numbers, canal numbers in each root, canal type in each three dimension of axial, coronal and sagittal were studied. Canal types were reported based on categorization of Vertucci. Root length were measured in two view of coronal and sagittal. Root curvature and root curvatureangle were examined in both view of coronal and sagittal through Schnieder method and curvature angle were recorded by degree. Axial slice were in 0.2mm sections. It should be mentioned that all noted cases were studied by endodontic and radiologist's professional assistance twice. And also complicated anatomic cases including c form canal, fusion, and dense invagination.statistical analysis was conducted by SPSS software. P- 3
3 * Cross sectional CBCT images of the mandibular premolar a) axial plan, b) sagittal plan c) coronal plan RESULTS In this study, 300 CBCT images of 33 teeth including 593 firstpremolarteeth and 50 mandibular secondpremolarwere examined among which images belonged to men and 59 women with average age of 2 (20-62 year old). First and secondpremolarteeth were single rooted in most cases (95% and 99/6%) and single canal (type I) and then the most prevalence designed to type V and respectively to type III, II, IV. 3 cases did not belong to Vertucci s categorization (table,2). Prevalence of more than two canal was greater in women than men while this difference was not statistically significant (p>0/) (diagram ). Diagram Distribution33 teeth in respect of double canals and more by tooth type consideration P- 35
4 Table Distribution of canal type in respect of tooth under study Total Other issues V IV III II I type Canal type Tooth 296 (0/3%) (5/7%)7 6(5/%) 5(/7%) 226(75/6%) 297-8(6%) 3(/3%) 3(%) 232(7/3%) 272 3(0/3%) (/3%) 3(%) 232(77/3%) 268 (/7%) 3(%) 28(82/%) Table 2 Distribution of canal number in respect of tooth under study total bigger than 2 (0/3%) - (0/%) (0/%) 2 69 (23/3%) 65(2/9) 39 (/3%) 9 (7/%) 226 (76/%) 232 (78/%) 232 (78/%) 28 (92/5%) number Canal In almost all double canal cases, isthmus was observed in /3 epical. Orifice site in nearly all cases was located in CEJ area. Orifice form was also observed in CEJ area ellipticalforms in most cases and in a few cases was circle form. Mandibular first premolarteeth in left side were 95% single rooted, 5% double rooted, 76/5% single canal and 23/5% double canal. In right side they were 96/3% single rooted and 2/7% double rooted, 78% single canal, and 2/9% double canal. second premolarteeth in left side were 99/6% single rooted and 0/% double rooted, 85/5% single canal and /5% double canal and in right side they were 99/3% single rooted and 0/7% double rooted, 92/5% single canal and 7/5% double canal while there was no significant difference between first and second premolar in both side. (Table 2 and 3). P- 36
5 Table 3 Distribution of root number in respect of tooth under study Total 2 Root number (/%) 28 (95/9%) 297 8(2/7%) 289(97/3% (99/6%) 268 2(0/7%) 266(99/3%) Other cases such as distribution of root curvature, separation location of canals, root length and angel of root curvature of premolarteeth are stated in table -7. Table Distribution of root curvature regarding tooth under study total distolingual distobuccal buccal lingula masial distal direct root of Direction curvature Tooth type 296 (0/3%) 7 (2/%) 6 (2%) 7 (2/%) 5 (5/%) 29 (3/6%) 3 (/3%) mandibular first premolar 297 (0/3%) 2(0/7%) (/3%) (/3%) 5 (5/%) 27 (2/8%) (8/5%) mandibular first premolar (0/8%) (/5%) 6 (2/2%) (%) 72 (26/5%) 77 (65/%) mandibular second premolar (/5%) 5 (/9%) (0/%) 7 (2/6%) 8 (3/3%) 67 (62/3%) mandibular second premolar P- 37
6 Table 5. Distribution of detachment location of canals regarding under study tooth type Total Third epical Middle third Location of canal detachment (8%) 7 (%) 2 (3/8%) (22%) 57 (82%) 58 (89%) 27 (69/2%) 5 (78%) Table 6. Distribution of root length by consideration of under study tooth C.V Mean±S.D Maximum Minimum Root length 8/37 8/99 8/03 8/77 2/6±/8 2/6±/9 /7±2/9 /9± /6 27/2 27/7 7 7/3 8 6/5 Table 7. Distribution of angel of root curvature by teeth considering under study C.V mean±s.d Maximum Minimum Angle of root curvature 96/7 /309 / 7 /960 6/22±6/36 5/6±3/95 3/7±9/37 3/53±9/9 6/3 62/28 52/5 6/ Left mandibular first premolar DISCUSSION Based on results of this study generally in Iranian race mandibular first premolar teeth in left side were 95% single rooted, 5% double rooted, 76/% single canal and 23/3% double canal. In right side 96/3% they were single rooted and 2/7% double rooted, 78% single canal and 2/9% double canal. Second premolarteeth in left side were 99/6% single rooted, % double rooted, 85/3% single canal and /3% double canal. In right side they were 99/3% single rooted, and 7% double rooted, 92/5 single canal, and 7/ were double canal which proved there was no significant difference between first and second premolarin both side. First results of Hess et al studies in 925 about complication of root canal anatomy it is illustrated that one root with one P- 38
7 canal is an exception not a law(9). In a successfulendodontic treatment, canal availability is a crucial point. It should be emphasized that lack of knowledge about canal anatomy is main reason of treatment failure.many researches has been conducted on anatomy and formation of pulp. With many limitations in this context, internal anatomies of teeth are not clear enough. In similar studies of Kazemi pour et al conducted a research aimed comparing root morphology and teeth canals ofmandibularpremolarbetween male and females in Iranian population. Mandibular first premolar teeth in left side were 86% single rooted and % double rooted, 69% single canal and 30% double canal. In right side they were 87% single root and 2/7% double rooted, 66/5% single canal and 30% double canal which indicated that there was no significant difference between first premolars in both side. In right side they were 78% single root, 66/5% single canal and 33/5% double canal which there was no significant difference first premolars in both side. In right side they were 95/% single rooted, /% double rooted, 83/% single canal and 6/6% double canal while there was not significant difference in canal numbers between secondpremolars of both side (7).In our study mandibular first premolar teeth in left side were 95% single rooted and 5% double rooted, 76% single canal and 23/3% double canal. In right side they were 96/3% single rooted and 2/7% double rooted, 78% single canal and 2/9% double canal. Second premolarteeth in left side were 9/6% single rooted and 0/% double rooted, 85/3% were single canal and /3% double canal. In right side they were 99/3% single rooted and 0/7% double rooted, 92/5% single canal and 7/% double canal which there is no significant difference between first and second premolars in both sides. First double rooted premolars numbers in left side was higher and second premolars were almost single rooted in all cases. Prevalence rate of double canal teeth in our study was less especially second premolar teeth.in other study performed by Felsypremila et al studied Anatomic symmetry of root and root canal morphology of posterior teeth in Indian subpopulation using cone beam computed tomography. They selected 26 CBCT images and investigated about posterior teeth without dental restoration and restoration in each quadrant. Mandibular second premolar had more symmetry in root and canal number (98/3%) than first premolars (96/%). Most prevalence of anatomy was observed in mandibular first and second premolar with single rooted and single canal. In our study firstpremolars showed more symmetry (95%) that secondpremolar s (90%) in root number. But in canal numbers of both first and second premolar it was illustrated that there is similar symmetry equals to 83% may be due to racial difference and sample volume (8).Bulult et al studied about evaluation of root morphology and root canal configuration of premolars in the Turkish individuals using cone beam computed tomography. Mostmandibular premolars were single rooted. Prevalent anatomy in mandibular first premolar was single canal and type I (9%) and type V (3/2%) which mandibular second premolars with single canal and type I (98%) were most prevalent. There was no difference between types and numbers of canal among men and women (9). However, in our research prevalence of a canal and type I in mandibular first premolars was (77/7%) and type V (5/6%). And it was (90%) of canal type I in second premolars and (7/7%) of canal type V. In Iranian population double canal premolars was more prevalent maybe due to racial difference or sample volume. AditiaShetty performed similar research in Indian population by CBCT. They studied 86 mandibular first and second premolar teeth investigated by CBCT and indicated that most 83/8% first premolar teeth and second premolar 93/% were type I and then type V had more prevalence rate (0).Junbeam park performed similar research in Korean population by CBCT. Most first premolar s 99/3% and second premolars 99/9% were single rooted (). Our research had similar results. Xuan Yu et al conducted Cone-beam computed tomography study of root and canal morphology of mandibular premolars in a western Chinese population. 9 CBCT images including 78 mandibular first premolar and 78 mandibular second premolar were studied. Results indicated that 98% of mandibular first premolar were single rooted and 2 percent were double rooted. 87% were single canal and /2% double canal and 0/% were with three canal. Prevalence of Cshape canal was / percent. All second premolars were single rooted and 97/2 percent were single canal and 2/2 % were double canal. And also prevalence of C-shape canal was 0/6%. First premolar type V had the most prevalence of canal while second premolar had low anatomic variation in Chine's population (). About root curvature, Vertucci stated the most prevalence for first and second premolar teeth as buccal<distal<direct. As Sobhani et al stated the most prevalence of root is respectively as mesial<buccal<lingual<mesiolingual<mesiobuccal<distal<distolingual<distobuccal<direct. Inthis study most prevalence of root curvature was respectively related to distoligual<distobuccal<lingual=buccal< (CurveS) bayonet<mesial<distal< direct (2). The most brilliant achievement of this study is utilizing CBCT for investigation canal anatomy which is in vivo method and it is not like other methods as pulling tooth and P- 39
8 it doesn t have problems related to two dimensional images with common radiographies.premolarteeth studies which is the most difficult teeth problems in root therapy regarding to different anatomic aspects and high sample volume by CBCT is brilliant accomplishment of this research. CONCLUSION First and second premolarteeth were mostly single rooted (95%, 99/6%) and single canal (type I). Secondly, type V was mostly prevalent. Orifice site was in tooth center in CEJ area almost in all cases. Orifice formation in CEJ area and almost in all sites was elliptical and rarely was it circle form.second premolars were single rooted in nearly all cases and there was no difference in tooth type. Direction of root curvature was direct in most cases (5%) and in other cases was distal (37%) and there was no difference in tooth type.prevalence of S-curve curvature had been observed in 2% of cases (22cases) which had more prevalence in first premolar (9%). Limitations and problems Study of more than 000 CBCT in order to obtain appropriate samples. Considering all CBCT samples took a lot time and it was so elaborating. Recommendation Study of other teeth by CBCT and compiling data as general reference in Iranian population. REFERENCES. Amin Sobhani M, Razmi H, Sadegh M. Evaluation of anatomy and morphology of human mandibular premolar teeth by cone-beam computed tomography in airanian population.journal of Dental Medicine- Tehran University of medical science.203:26(3): Sert S, Bayiril GS. Evaluation of root canal configuration of the mandibular and maxillary permanent teeth by gender in the Turkish population. J Endod 200;30(6): Pope O, Sathorn C, Parashos P. A comparative investigation of cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiography in the diagnosis of a healthy periapex. J Endod. 20 Mar; 0(3): Yu X, Guo B, Li KZ, Zhang R, Tian YY, Wang H, Hu T. Cone-beam computed tomography study of root and canal morphology of mandibular premolars in a western Chinese population. BMC medical imaging. 202 Jul 20;2():. 5. Arslan H, Davut Capar I. A cone-beam computed tomographic study of root canal systems in mandibular premolars in a Turkish population: Theoretical model for determining orifice shape. European Journal of Dentistry. 205 Jan-Mar;9 () :-9 6. Hess W, Zürcher E, Dolamore WH. The anatomy of the root-canals of the teeth of the permanent dentition. J. Bale, sons & Danielsson, ltd.; Kazemipoor M, Poorkheradmand M, Rezaeian M, Safi Y. Evaluation by CBCT of root and kanal Morphology in Mandibulars Premolars in an Iranian population. Chin J Dent Res. 205 Sep; 8(3): FelsypremilaG, Vinothkuma T, Kandaswamy D. Anatomic symmetry of root and root canal morphology of posterior teeth in Indian subpopulation using cone beam computed tomography: A retrospective study. Eur J Dent.205 October-December;9(): Bulut D, Kose D, Ozcan G, Sekerci A.E, Canger E, Sisman Y. Evaluation of root morphology and root canal configuration of premolars in the Turkish individuals using cone beam computed tomography. Eur J Dent.205 October-December;9(): Shetty A, Hegde M, Shetty S.A three dimensional study of variation in root canal morphology using cone-beam computed tomography of mandibular premolars in south Indian population.jcdr.20 Aug; 8(8):ZC22-ZC2. Park J, Kim N, Ko Y. Evaluation ofroot anatomy and morphology of mandibular premolars & molars with conebeam computed tomography in a koreanpopulation. Eur J Dent.203;7(): Amin Sobhani M, Razmi H, Sadegh M. Evaluation ofanatomy and morphology of human mandibular premolar teethby cone-beam computed tomography in a Iranian population.journal of Dental Medicine- Tehran University of medical science. 203 autumn; 26(3): P- 0
Morphologic assessment of mandibular anterior teeth root canal using CBCT
 Original article Acta Medica Academica 2017;46(2):85-93 DOI: 10.5644/ama2006-124.193 Morphologic assessment of mandibular anterior teeth root canal using CBCT Sina Haghanifar 1, Ehsan Moudi 1, Ali Bijani
Original article Acta Medica Academica 2017;46(2):85-93 DOI: 10.5644/ama2006-124.193 Morphologic assessment of mandibular anterior teeth root canal using CBCT Sina Haghanifar 1, Ehsan Moudi 1, Ali Bijani
Usage of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) to Evaluate Root and Canal Morphology of maxillary First Molar
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
The. Cone Beam. Conversation. A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT
 The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar
 Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study
 ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Study
 10.2478/bjdm-2018-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography () Study SUMMARY Background/Aim:
10.2478/bjdm-2018-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography () Study SUMMARY Background/Aim:
Lodha Ena* M. Kala** INTRODUCTION
 Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Evaluation of The Root Morphology of Maxillary Permanent First And Second Molars in An Indian Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Investigating the Sizes of Anatomical Landmarks of Coronal Pulp in the First Permanent Human Molars on Bite Wing Radiography
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Volume 5, Issue 5, Page No: 102-107 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Investigating
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Volume 5, Issue 5, Page No: 102-107 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Investigating
FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS
 Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June Volume 4
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June 1 2011 Volume 4 Endodontic Treatment Utilizing 3D Imaging Recent advances in technology, such as rotary
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June 1 2011 Volume 4 Endodontic Treatment Utilizing 3D Imaging Recent advances in technology, such as rotary
Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography L Demiriz, E Hazar Bodrumlu, M İçen 1 Departments of Pediatric Dentistry
Original Article Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography L Demiriz, E Hazar Bodrumlu, M İçen 1 Departments of Pediatric Dentistry
Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE
 Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular First Premolar With Three Root Canals: A Case Report
 J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci http://www.jrdms.dentaiau.ac.ir e(issn): 2383-2754 p(issn):2588-4166 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular First Premolar
J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci http://www.jrdms.dentaiau.ac.ir e(issn): 2383-2754 p(issn):2588-4166 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular First Premolar
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo
 The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 216491, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216491 Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar Haridoss Selvakumar, 1 Swaminathan
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 216491, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216491 Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar Haridoss Selvakumar, 1 Swaminathan
Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/35023.11615 Dentistry Section Review Article Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration Rashmi Bansal
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/35023.11615 Dentistry Section Review Article Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration Rashmi Bansal
Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
PREVALENCE OF ROOT ANGULATION IN VIDARBH POPULATION: A PANORAMIC RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 05 PREVALENCE OF ROOT ANGULATION IN VIDARBH POPULATION: A PANORAMIC RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY Aarti Dubey 1,Suwarna Dangore
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 05 PREVALENCE OF ROOT ANGULATION IN VIDARBH POPULATION: A PANORAMIC RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY Aarti Dubey 1,Suwarna Dangore
e74 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College a Reader.
 Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST
 CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography
 Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
Correspondence should be addressed to Raed Hakam Mukhaimer;
 International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a polish population
 Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Failure of root canal therapy often
 Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral Computed Tomographic
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
A Rare Case of Radicular Dens in Dente diagnosed by Clinical, Radiographic, Tomographic, and Histopathological Examinations
 A Rare Case of Radicular Dens in Dente diagnosed by Clinical, Radiographic, 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1152 Tomographic and Examinations CASE REPORT A Rare Case of Radicular Dens in Dente diagnosed by Clinical,
A Rare Case of Radicular Dens in Dente diagnosed by Clinical, Radiographic, 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1152 Tomographic and Examinations CASE REPORT A Rare Case of Radicular Dens in Dente diagnosed by Clinical,
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC
 Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional Analysis with Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars: An in vitro Study
 Original research Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root 10.5005/jp-journals-10060-0004 Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary
Original research Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root 10.5005/jp-journals-10060-0004 Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary
Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars of Bangladeshi Population
 Original Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars of Bangladeshi Population Mohammad Aminul Islam 1, Tasnim Wakia 2, Md. Shamsul Alam 3 1. FCPS trainee Dept. of Conservative Dentistry
Original Article Root Canal Morphology of Mandibular First Premolars of Bangladeshi Population Mohammad Aminul Islam 1, Tasnim Wakia 2, Md. Shamsul Alam 3 1. FCPS trainee Dept. of Conservative Dentistry
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry. Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate root and canal morphology of mandibular first and second molars in Turkish individuals
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013 Jul 1;18 (4):e73744. Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 Use of conebeam computed
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013 Jul 1;18 (4):e73744. Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 Use of conebeam computed
PORTFOLIO 01. Assigning a Level of Difficulty to Your Endodontic Cases
 PORTFOLIO 01 Assigning a Level of Difficulty to Your Endodontic Cases Root Canal Specialty Associates provides care in all phases of surgical and nonsurgical endodontics. With decades of combined experience,
PORTFOLIO 01 Assigning a Level of Difficulty to Your Endodontic Cases Root Canal Specialty Associates provides care in all phases of surgical and nonsurgical endodontics. With decades of combined experience,
An unusual maxillary canine with two separated root canals
 pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct
 OPEN (2017) 9, 33 37 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin
OPEN (2017) 9, 33 37 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin
Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular first molars in a Chinese population: a clinical study
 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41121-018-0015-8 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular
Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41121-018-0015-8 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular
Evaluation of Morphology and Anatomical Measurement of Nasopalatine Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of Morphology and Anatomical Measurement of Nasopalatine Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Mehrdad Panjnoush 1, Hamideh Norouzi 2, Yasaman Kheirandish 3, Ahmad Reza
Original Article Evaluation of Morphology and Anatomical Measurement of Nasopalatine Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Mehrdad Panjnoush 1, Hamideh Norouzi 2, Yasaman Kheirandish 3, Ahmad Reza
Research Article. ISSN (Print)
 Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 2015; 2(7):401-408 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 2015; 2(7):401-408 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
Effect of extraction of permanent first molars on the development and eruption of third molars
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22122/johoe.v7i3.417 Published by Vesnu Publications Received: 19 Aug. 2017 Accepted: 01 Nov. 2017 Effect of extraction of permanent first molars on the development and eruption
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22122/johoe.v7i3.417 Published by Vesnu Publications Received: 19 Aug. 2017 Accepted: 01 Nov. 2017 Effect of extraction of permanent first molars on the development and eruption
Human, Child (7 years +/- 2 years)
 Human, Child (7 years +/- 2 years) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-276 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations:
Human, Child (7 years +/- 2 years) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-276 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations:
Paper submission. Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case
 Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Case Report The unusual anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular molars diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1393-1398 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0039297 Case Report The unusual anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular molars diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography Fengqin
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1393-1398 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0039297 Case Report The unusual anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular molars diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography Fengqin
Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 07/05/2016
 Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 1 Compromised structural or mechanical integrity of teeth results in different types of tooth fractures,
Minimal invasive access for endodontic treatment. PAV succesvolle endodontie Wortelkanaalpreparatie 1 Compromised structural or mechanical integrity of teeth results in different types of tooth fractures,
Andres Torres 1, *, Reinhilde Jacobs 1, Paul Lambrechts 2, Claudia Brizuela 3, Carolina Cabrera 3, Guillermo Concha 4, María Eugenia Pedemonte 3
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 95-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.2.95 Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 95-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.2.95 Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability
Root surface areas of maxillary permanent teeth in anterior normal overbite and anterior open bite assessed using cone-beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2017; 47: 241-6 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.4.241 Root surface areas of maxillary permanent teeth in anterior normal overbite and anterior open bite assessed using
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2017; 47: 241-6 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.4.241 Root surface areas of maxillary permanent teeth in anterior normal overbite and anterior open bite assessed using
Periapical Radiography
 Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars
 Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars
 Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with unusual mesiobuccal root anatomy
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant Planning: A Clinical Study
 JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
Index. shapes, sizes, and locations, 282 small bone defects, through-and-through bone defect, treatment techniques, 285, 287
 Index A Accessory canal, 18 20 Accidental pulp exposure, 100, 103 104 Adhesive dentistry, 174 175 Ankylosis, 69 70 Anterior superior alveolar (ASA), 81 Anxiety, 36 Apical periodontitis asymptomatic, 214
Index A Accessory canal, 18 20 Accidental pulp exposure, 100, 103 104 Adhesive dentistry, 174 175 Ankylosis, 69 70 Anterior superior alveolar (ASA), 81 Anxiety, 36 Apical periodontitis asymptomatic, 214
Diagnosis and endodontic management of two rooted mandibular second premolar: A case report
 International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Diagnosis and endodontic management of two rooted mandibular second premolar: A case report Saima Jamal*, Swathi, Rajaram Naik Department
International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Diagnosis and endodontic management of two rooted mandibular second premolar: A case report Saima Jamal*, Swathi, Rajaram Naik Department
Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
The Premolars. Chapter 17 Permanent Posterior Teeth (p )
 The Premolars Chapter 17 Permanent Posterior Teeth (p. 230-244) General Information Function: u Hold and grind food u Work with molars in mastication. u Even without molars one may be able to chew well
The Premolars Chapter 17 Permanent Posterior Teeth (p. 230-244) General Information Function: u Hold and grind food u Work with molars in mastication. u Even without molars one may be able to chew well
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Multiple Idiopathic Apical Root Resorption: a Case Report
 Case Report Multiple Idiopathic Apical Root Resorption: a Case Report L. Khojastepour 1, P. Bronoosh 2, M. Azar 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, School of Dentistry, Shiraz University
Case Report Multiple Idiopathic Apical Root Resorption: a Case Report L. Khojastepour 1, P. Bronoosh 2, M. Azar 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, School of Dentistry, Shiraz University
Case Report: Maxillary second molar with two palatal canals diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: a case report
 Case Report: Maxillary second molar with two palatal canals diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: a case report Dr Dhara Shukla 1,Dr Girish Parmar 2, Dr Abhishek Parmar 3 1 PG Part II Student,
Case Report: Maxillary second molar with two palatal canals diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: a case report Dr Dhara Shukla 1,Dr Girish Parmar 2, Dr Abhishek Parmar 3 1 PG Part II Student,
J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci. e(issn): Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences
 J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci http://www.jrdms.dentaliau.ac.ir e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Radiographic Evaluation of the Developmental Stages of Second and
J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci http://www.jrdms.dentaliau.ac.ir e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Radiographic Evaluation of the Developmental Stages of Second and
Technical quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate dental students
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Technical quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate dental students Bahareh Dadresanfar 1 * DDS, MS, Nahid Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi 1 DDS, MS, Mehdi Vatanpour 1 DDS, MS,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Technical quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate dental students Bahareh Dadresanfar 1 * DDS, MS, Nahid Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi 1 DDS, MS, Mehdi Vatanpour 1 DDS, MS,
Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series
 Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS
 ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
Survey on Knowledge about Access Cavity Preparation
 Survey on Knowledge about Access Cavity Preparation 1 Sanjay Madhavan, 2 Dr.Chandana 1 II BDS student, Saveetha Dental College and Hospital, Chennai 2 Department of Conservative Endodontics, Saveetha Dental
Survey on Knowledge about Access Cavity Preparation 1 Sanjay Madhavan, 2 Dr.Chandana 1 II BDS student, Saveetha Dental College and Hospital, Chennai 2 Department of Conservative Endodontics, Saveetha Dental
Evaluation of technical quality and periapical
 www.scielo.br/jaos http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720140110 Evaluation of technical quality and periapical Bilge Gülsüm NUR 1, Evren OK 2, Mustafa ALTUNSOY 1 3, Mehmet ÇOLAK 4, Enes GÜNGÖR 4 4- Department
www.scielo.br/jaos http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720140110 Evaluation of technical quality and periapical Bilge Gülsüm NUR 1, Evren OK 2, Mustafa ALTUNSOY 1 3, Mehmet ÇOLAK 4, Enes GÜNGÖR 4 4- Department
Lecture. Permanent maxillary premolars
 Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Research Article. Key Words: First premolar, Mandibular, Maxillary, Vertucci s classification, Spiral computed tomography.
 Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
MORPHOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHICAL DENTAL ANATOMY OF ADULT BUFFALOES
 Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (April-June 2017) Vol.36 No.2 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHICAL DENTAL ANATOMY OF ADULT BUFFALOES R.K. Singh 1, R.P. Pandey 1, S. Purohit 1, S.P. Singh 2, *, A.K.
Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (April-June 2017) Vol.36 No.2 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHICAL DENTAL ANATOMY OF ADULT BUFFALOES R.K. Singh 1, R.P. Pandey 1, S. Purohit 1, S.P. Singh 2, *, A.K.
The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography
 Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
LOCATING CANALS. Strategies, Armamentarium and Techniques. by Clifford J. Ruddle, DDS. Advanced Endodontics DENTISTRY TODAY February 2017
 Advanced Endodontics DENTISTRY TODAY February 2017 LOCATING CANALS Strategies, Armamentarium and Techniques by Clifford J. Ruddle, DDS Over the past decades, many technologies have come to market to help
Advanced Endodontics DENTISTRY TODAY February 2017 LOCATING CANALS Strategies, Armamentarium and Techniques by Clifford J. Ruddle, DDS Over the past decades, many technologies have come to market to help
Evaluation of cortical bone thickness of mandible with cone beam computed tomography for orthodontic mini implant installation
 ISSN: 2203-1413 Vol.02 No.02 Evaluation of cortical bone thickness of mandible with cone beam computed tomography for orthodontic mini implant installation Seyed Hossein Moslemzade 1, Yusef Kananizadeh
ISSN: 2203-1413 Vol.02 No.02 Evaluation of cortical bone thickness of mandible with cone beam computed tomography for orthodontic mini implant installation Seyed Hossein Moslemzade 1, Yusef Kananizadeh
Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report Rosaline Hannah 1 *, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy 1, Nachimuthu
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report Rosaline Hannah 1 *, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy 1, Nachimuthu
Advanced ESX Instrumentation:! Segmental Crown Down & Hybridization of Tapers!
 Advanced ESX Instrumentation: Segmental Crown Down & Hybridization of Tapers Introduction: All human root canals are not created equal. The variety of root canal shapes we face on daily basis are as unique
Advanced ESX Instrumentation: Segmental Crown Down & Hybridization of Tapers Introduction: All human root canals are not created equal. The variety of root canal shapes we face on daily basis are as unique
Radix paraentomolaris- A rarest of rare structural entity
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2014), PP 45-50 Radix paraentomolaris- A rarest of rare structural entity Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2014), PP 45-50 Radix paraentomolaris- A rarest of rare structural entity Dr.
Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 14, 238-242 Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report Pai ARV 1, Kamath MP 2, Basnet P 3 1 Associate
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 14, 238-242 Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report Pai ARV 1, Kamath MP 2, Basnet P 3 1 Associate
Treatment of a Rare Bilateral Severe Ectopic Eruption of the Maxillary First Permanent Molar: A Case Report
 Case Report Treatment of a Rare Bilateral Severe Ectopic Eruption of the Maxillary First Permanent Molar: A Case Report MS. Ahmad Akhoundi 1, 2, AH. Sadrhaghighi 3 1 Associate Professor, Dental Research
Case Report Treatment of a Rare Bilateral Severe Ectopic Eruption of the Maxillary First Permanent Molar: A Case Report MS. Ahmad Akhoundi 1, 2, AH. Sadrhaghighi 3 1 Associate Professor, Dental Research
Comparison of conventional radiography with cone beam computed tomography for detection of vertical root fractures: an in vitro study
 593 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 4, 593-597, 2010 Original Comparison of conventional radiography with cone beam computed tomography for detection of vertical root fractures: an in vitro study
593 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 4, 593-597, 2010 Original Comparison of conventional radiography with cone beam computed tomography for detection of vertical root fractures: an in vitro study
The aim of the present work is to study the External and Internal Root anatomy of
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 29:36 January, 2008 A study on the External and Internal Root Anatomy of Egyptian Maxillary First Permanent Molar Reham Magdy Ameen 1 and Rania Mossad Hassan 2 1.
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 29:36 January, 2008 A study on the External and Internal Root Anatomy of Egyptian Maxillary First Permanent Molar Reham Magdy Ameen 1 and Rania Mossad Hassan 2 1.
