Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular first molars in a Chinese population: a clinical study
|
|
|
- Sherman Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 Evidence-Based Endodontics RESEARCH Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of root canal morphology in mandibular first molars in a Chinese population: a clinical study Na Ni 1,4*, Shen Cao 1, Lei Han 2, Linkun Zhang 3, Jing Ye 4 and Chengfei Zhang 5 Open Access Abstract Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the root canal morphology of mandibular first molars in a Chinese population by using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Methods: In this study, CBCT images of 900 mandibular first molars were evaluated for the following details: (1) number of roots, (2) number of apical foramina, (3) frequency distribution of root canal configurations defined in accordance with Vertucci s classification, and (4) frequency of occurrence of middle mesial (MM) canal. Results: Overall, 74.9% of the evaluated mandibular first molars possessed two roots, and 55.4% exhibited three apical foramina. The evaluated teeth exhibited a relatively high prevalence of type IV canals in mesial (M) roots (76.8%) and type I canals in the distal (D) (79.4%), distobuccal (DB) (98.7%), and distolingual (DL) (100%) roots. There were no significant differences in the number of roots, incidence of apical foramina, or distribution of different canal configurations of mandibular first molars between men and women (P > 0.05). 1.9% of mandibular first molars possessed three mesial canals, and the highest frequency of occurrence of MM canals (4.1%) was among Chinese people below the age of 30 years. Conclusions: CBCT scanning facilitates identification of the root canal system. In order to increase the success rate of treatment, it is important to obtain information about the variable morphology of root canals before endodontic treatment. Trial registration: TJSKE Registered 12 April Keywords: Mandibular first molar, Anatomic variation, Cone-beam computed tomography Background Permanent mandibular first molars exhibit a wide variation in root canal anatomy. They appear to be the tooth type that most often requires root canal treatment (Silva et al. 2013). Long-term success of endodontic treatment depends on complete cleaning, shaping, and filling of all existing canals (Tian et al. 2016; Zheng et al. 2010). The highly variable morphology of the root canal system * Correspondence: nina_tjskq@163.com 1 Department of Endodontics, Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, No.75 Dagu Road, Heping District, Tianjin , China 4 Department of Stomatology, Tianjin Hospital, 406 Jiefangnan road, Hexi District, Tianjin , China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article presents clinical challenges that mainly affect the results of chemomechanical preparation (Versiani et al. 2011). In order to increase the success rate of root canal treatment, it is essential that clinicians have thorough knowledge of anatomic variations of the root canal system. According to previous studies, a common root and canal configuration of mandibular first molars involves two roots with one or two canals in the distal (D) root and two canals in the mesial (M) root, characterized by a widened buccolingual surface and flattened mesiodistal surface (Tian et al. 2016). A systematic review has reported the incidences of three, four, and five root canals in mandibular first molars to be 61.3, 35.7, and about 1%, respectively (de Pablo et al. 2010). In 1974, Vertucci The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
2 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 Page 2 of 6 and Williams identified the presence of the middle mesial (MM) canal in mandibular first molars (Vertucci and Williams 1974). An MM canal is occasionally observed in the developmental groove between the mesiobuccal (MB) and mesiolingual (ML) canals, with an incidence of % (Aminsobhani et al. 2010; Navarro et al. 2007). Sundaresh et al. reported five canal orifices (three M and two D) in the pulp chamber of a mandibular first molar in their case report (Sundaresh et al. 2013). Sharma et al. reported a case about endodontic management of a mandibular first molar with six canals (three canals in the M root and three in the D root) (Sharma et al. 2016). These studies serve to demonstrate the anatomic variation of root canals in mandibular first molars. Several techniques, including intraoral periapical radiography, use of transparent samples and polyester resin impressions, and sectioning, have been used for in vivo and in vitro evaluation of root canal morphology (Chen et al. 2009; Martos et al. 2010; Navarro et al. 2007; Yew and Chan 1993). However, because of superimposition of dental structures or irreversible changes to tooth samples, the results obtained by these methods are not completely reliable (Song et al. 2010). Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) allows accurate and immediate three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction imaging of axial, sagittal, and coronal planes and minimizes the superimposition of dental structures (Zhang et al. 2011; Zhang et al. 2011). Matherne et al. demonstrated that CBCT image analysis provides more accurate data about root canal systems than digital radiograph analysis (Matherne et al. 2008). For this reason, CBCT is used as a noninvasive tool in endodontic treatment for effective evaluation of root and canal morphologies (Cotton et al. 2007; Nair and Nair 2007; Patel et al. 2007; Tyndall and Rathore 2008). To date, few studies have evaluated the root canal morphology of mandibular first molars according to sex or the incidence of MM canals according to age in a Chinese population. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the variation of root canal morphology in permanent mandibular first molars in a Chinese population by using CBCT. Methods CBCT images of 900 mandibular first molars were acquired from 646 patients (female, 344; male, 302; age, years) who visited the hospital, between May and September These images had been acquired as a part of preoperative assessment for root canal treatment, implant surgery, or orthodontic treatment. Mandibular first molars were selected in accordance with the following criteria: (1) mature teeth with completely formed roots and (2) mandibular first molars without carious cavities, root resorption, root canal treatment, or restoration. The procedure for collection of imaging data was explained to the patients or legal guardians, and appropriate informed consent was obtained. Image acquisition and analysis Images were acquired using a CBCT device (J. Morita Mfg. Corp., Kyoto, Japan) operated at 80 kvp and 5 ma, with field of view of 8 cm 8 cm, a scanning time of 9.4 s, and slice thickness of mm. Image acquisition was performed by an experienced oral radiologist in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. The images were then adjusted and analyzed using the Volume Viewer software. Serial sagittal, coronal, and axial images were analyzed independently by two endodontists and an oral radiologist. Disagreements were settled by discussion for reaching a consensus. Additionally, 20% of the images were randomly selected and reevaluated by the three examiners after 2 months. The kappa value for repeatability was 0.9, which indicated that the data were reliable. CBCT images of mandibular first molars were evaluated for the following details: (1) number of roots according to sex, (2) number of apical foramina according to sex, (3) frequency distribution of root canal configurations defined in accordance with Vertucci s classification, and (4) frequency of occurrence of MM canals according to age. The MM images of each layer were imported into the Mimics software (Mimics, V 10.01, Materialise, Belgium) and edited to create closed contours according to the gray scale of enamel, dentine, and pulp, respectively. This contour on different layers was matched to reconstruct the 3D surface model of the root canals. Statistical analysis Data were recorded, tabulated, and analyzed for descriptive statistics using the SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA). The chi-square test was used for the comparison of number of roots and apical foramina between the sexes. The distribution frequency of root canal morphologies was analyzed with the Fisher exact and chi-square tests. Differences in frequency of occurrence of MM canals according to age were analyzed with the chi-square test. Significant differences were considered at P < Results Number of roots in mandibular first molars according to sex A total of 900 CBCT images were selected in accordance with the inclusion criteria. As shown in Table 1, the percentages of two- and three-rooted mandibular first molars were 74.9% (674/900) and 25.0% (225/900), respectively. A mandibular first molar with fused roots was detected, where it was difficult to distinguish the M
3 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 Page 3 of 6 Table 1 Number and frequency of roots in mandibular first molars according to sex Sex 1 root (%) 2 roots (%) 3 roots (%) Additional (%) Kappa value P value Female (469) 344 (73.3%) 125 (26.7%) Male (431) 330 (76.6%) 100 (23.2%) 1 (0.2%) Total (900) 674 (74.9%) 225 (25.0%) 1 (0.1%) and D roots. The numbers of mandibular first molars with two roots (M and D roots) among the female and male patients were 344 (73.3%) and 330 (76.6%), respectively; the corresponding numbers of teeth with three roots (M, distobuccal (DB), and distolingual (DL) roots) were 125 (26.7%) and 100 (23.2%), respectively. There was no significant difference in the distribution frequency of number of roots in mandibular first molars between the sexes (P > 0.05). Number of apical foramina in mandibular first molars according to sex The frequency of number of apical foramina was evaluated by CBCT images of axial plane and following the coronal to apical direction. Table 2 presents the number and distribution of apical foramina among the 900 eligible mandibular first molars. While 134 teeth (14.9%) possessed two apical foramina (M and D), 499 (55.4%) and 267 (29.7%) mandibular first molars exhibited three (MB, ML, and D) and four apical foramina (MB, ML, DB, and DL), respectively. The frequencies of occurrence of two, three, and four apical foramina among the female patients were 13.6% (64/469), 55.4% (260/469), and 30.9% (145/469), respectively; the corresponding frequencies among the male patients were 16.2% (70/431), 55.5% (239/431), and 28.3% (122/431). There were no significant differences in the frequencies of occurrence of apical foramina in mandibular first molars between the sexes (P > 0.05). Distribution of root canal configurations in mandibular first molars according to sex Table 3 and Fig. 1 present the variations in root canal configurations of mandibular first molars. Among the 899 evaluated two- and three-rooted mandibular first molars, the most common root canal configuration in M roots was type IV (690/899; 76.8%), followed by types II (149/899; 16.6%), I (27/899; 3.0%), V (12/899; 1.3%), III (3/899; 0.3%), and VI (1/899; 0.1%); in addition, 17 teeth (1.9%) exhibited three mesial canals (type VIII+). All MM canals merged with ML canals at the apical or middle third level. In D roots, type I root canal configuration (535/674; 79.4%) was the most prevalent, followed by type II (43/674; 6.4%). Among DB roots, 98.7% (222/ 225) exhibited type IV canal configuration, while 1.3% (3/225) exhibited type II configuration. All DL roots possessed type I root canals. There were no significant differences in the distribution frequencies of different canal configurations among M, D, DB, or DL roots of mandibular first molars between the sexes (P > 0.05). Frequency of occurrence of MM canals according to age The overall frequency of occurrence of MM canals was 1.9% (17/899). Table 4 presents the distribution frequency of MM root canals in three age groups (groups A C: < 30, 30 50, and > 50 years). Among these age groups, group A exhibited a greater occurrence of MM canals (10/241; 4.1%) than group B (6/431; 1.4%) or C (1/227; 0.4%; P = 0.003). All MM canals merged with ML canals in the apical or middle third level by observing the 3D surface models of the root canals (Fig. 2). Discussion In root canal treatment, overlooked canals may hinder the effectiveness of the shaping, cleaning, and filling procedures and lead to microbial colonization, thus affecting the prognosis of endodontic treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to always evaluate the root canal system at the start of the treatment. Clinical and radiographic examinations are essential methods used for evaluating root canals and detecting most anatomic variations (Mukhaimer 2014). In this study, we evaluated the anatomic variations of the root canal system in vivo by using CBCT. Several studies have demonstrated that serial sagittal, coronal, and axial views allow excellent visualization of root canal anatomy, and the number of roots and canals can be visually evaluated in serial axial images acquired by CBCT at a low radiation dosage. Blattner et al. and Zheng et al. demonstrated the reliability of CBCT in detecting the second mesiobuccal (MB2) Table 2 Number and frequency of apical foramina in mandibular first molars according to sex Sex 1 (%) 2 (%) 3 (%) 4 (%) 5 (%) Kappa value P value Female (469) 64 (13.6%) 260 (55.4%) 145 (30.9%) Male (431) 70 (16.2%) 239 (55.5%) 122 (28.3%) Total (900) 134 (14.9%) 499 (55.4%) 267 (29.7%)
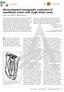
4 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 Page 4 of 6 Table 3 Frequency of distribution of root canal configurations in mandibular first molars according to sex Type I Type II Type III Type IV Type V Type VI Type VII Type VIII + Root Sex Mesial F (469) 23 (4.9%) 69 (14.7%) 2 (0.4%) 357 (76.1%) 9 (1.9%) 1 (0.2%) 8 (1.7%) M (430) 4 (0.9%) 80 (18.6%) 1 (0.2%) 333 (77.4%) 3 (0.7%) 9 (2.1%) T (899) 27 (3.0%) 149 (16.6%) 3 (0.3%) 690 (76.8%) 12 (1.3%) 1 (0.1%) 17 (1.9%) Distal F (344) 260 (75.6%) 26 (7.6%) 4 (1.2%) 30 (8.7%) 24 (7.0%) M (330) 275 (83.3%) 17 (5.2%) 1 (0.3%) 23 (7.0%) 12 (3.6%) 2 (0.6%) T (674) 535 (79.4%) 43 (6.4%) 5 (0.7%) 53 (7.9%) 36 (5.3%) 2 (0.3%) Distobuccal F (125) 123 (98.4%) 2 (1.6%) M (100) 99 (99%) 1 (1%) T (225) 222 (98.7%) 3 (1.3%) Distolingual F (125) 125 (100%) M (100) 100 (100%) T (225) 225 (100%) canal in maxillary first molars (Blattner et al. 2010; Zheng et al. 2010). Wang et al., too, evaluated the root canal morphology of mandibular first molars by CBCT and indicated that CBCT is a useful tool for the study of anatomic variations (Wang et al. 2010). In general, mandibular first molars have two roots, located mesially and distally (de Pablo et al. 2010). In the present study, two-rooted mandibular first molars (74.9%) were greater in proportion than three-rooted ones (25.0%); this proportion of two-rooted mandibular first molars is lower than that reported in a Brazilian population (87%) but higher than that reported in Korean children (66.9%) (Silva et al. 2013; Song et al. 2009). However, the present results are in general agreement with those of a previous study in a western Chinese population, in which 73.5 and 25.8% of mandibular first molars possessed two and three roots, respectively (Wang et al. 2010). The incidence of four roots in mandibular first molars is rare and has only been reported in three cases to date (Friedman et al. 1986; Ghoddusi et al. 2007; Lee et al. 2006). Four-rooted mandibular first molars were not detected among the present 900 CBCT images. As shown in Table 2, mandibular first molars with three apical foramina (55.4%) were greater in proportion than those with four (29.7%) or two (14.9%) apical foramina. This anatomic variation Fig. 1 Examples of root canal anatomy: (a) CBCT images of coronal plane in mandibular first molars, (b) CBCT images of sagittal plane in M roots, (c) CBCT images of sagittal plane in D roots, and (d f) CBCT images of axial plane in mandibular first molars Table 4 Frequency of occurrence of middle mesial (MM) canals in mandibular first molars in three age groups Age groups A (< 30 years) B (30 50 years) C (> 50 years) Teeth with MM, n (%) 10 (4.1%) 6 (1.4%) 1 (0.4%) Teeth without MM, n (%) 231 (95.9%) 425 (98.6%) 226 (99.6%) Total
5 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 Page 5 of 6 Fig. 2 The 3D surface model of the root canal. a, b MM canal merged with ML canal could be evaluated by 3D image analysis, which allows accurate observation in the sagittal, coronal, and axial directions, ultimately leading to accurate conclusions about the number of roots and apical foramina. In the present study, the most frequent canal configuration among M roots was type IV (76.8%), followed by type II (16.6%); among D roots, the most frequent canal configuration was type I (79.4%), followed by type II (6.4%). In a Palestinian population, Mukhaimer et al. found that the most common canal configurations among M and D roots were types IV (53.8%) and I (57.5%), respectively, followed by type II (both; 38.8 and 22.5%, respectively) (Mukhaimer 2014). Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi et al. also found types IV (55.3%) and I (61.3%) to be the most common canal configurations among M and D roots in an Iranian population (Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi et al. 2017). The differences in distribution frequencies of root canal configurations between the present and previous studies might be because of differences in analysis methods or ethnicity of study populations. In most studies, M roots have most frequently been described as possessing two canals. However, three canals are occasionally observed in M roots in cases where the isthmus between the MB and ML canals is clinically evident. The isthmus is one of the more difficult clinical challenges because the area is complex and not easy to clean thoroughly by mechanical preparation. As shown in Tables 3 and 4, 1.9% of mandibular first molars in the present study possessed three mesial canals, and the highest frequency of occurrence of MM canals was among patients in the age group A (< 30 years) (4.1%). In most case reports to date, the MM canal has been shown to join the MB or ML canal at the apical third level (Aminsobhani et al. 2010; Reyhani et al. 2007; Sharma et al. 2016). In the present study, all MM canals merged with ML canals in the apical or middle third level, and we found no instances of three independent canals in the M root. These findings suggest that endodontists should pay greater attention to the occurrence of MM canals among Chinese people below the age of 30 years. The limitation of our study protocol was the small sample size of different ethnic groups. Further research is warranted to evaluate the variation of root canal morphology in permanent mandibular first molars among different ethnic groups with larger sample sizes. Conclusions Mandibular first molars most commonly possess two roots. The most common canal configurations were types IV, I, and II. The highest frequency of MM canals occurs in the population below the age of 30 years. No statistically significant differences were found between the sexes in terms of number of roots, incidence of apical foramina, or distribution of different canal configurations of mandibular first molars. Abbreviations 3D: Three-dimensional; CBCT: Cone-beam computed tomography; D: Distal; DB: Distobuccal; DL: Distolingual; M: Mesial; MB: Mesiobuccal; MB2: The second mesiobuccal; ML: Mesiolingual; MM: Middle mesial Acknowledgements We thank the patients for their support during this study. Funding This work was supported by the Key Scientific and Technological Project of Tianjin Health Industry (grant no. 14KG132). Availability of data and materials A CBCT device (J. Morita Mfg. Corp., Kyoto, Japan) The Volume Viewer software The Mimics software (Mimics, V 10.01, Materialise, Belgium) The SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
6 Ni et al. Evidence-Based Endodontics (2018) 3:1 Page 6 of 6 Authors contributions NN designed the experiment. NN, SC, LH, and LKZ collected and analyzed the data. NN, SC, and JY wrote the manuscript. CFZ and NN edited and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate The Institutional Review Board of Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, Tianjin, China (TJSKE ), has approved this research, registered 12 April Consent for publication The procedure for the collection of imaging data (CBCT images) was explained to the patients or legal guardians, and appropriate informed consent was obtained. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Department of Endodontics, Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, No.75 Dagu Road, Heping District, Tianjin , China. 2 Department of Radiology, Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, No.75 Dagu Road, Heping District, Tianjin , China. 3 Department of Orthodontics, Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, No.75 Dagu Road, Heping District, Tianjin , China. 4 Department of Stomatology, Tianjin Hospital, 406 Jiefangnan road, Hexi District, Tianjin , China. 5 Endodontology, Faculty of Dentistry, The University of Hong Kong, 34 Hospital Road, Sai Ying Pun, Hong Kong, Special Administrative Region of China. Received: 24 December 2017 Accepted: 19 February 2018 References Aminsobhani M, Bolhari B, Shokouhinejad N, Ghorbanzadeh A, Ghabraei S, Rahmani MB. Mandibular first and second molars with three mesial canals: a case series. Iran Endod J. 2010;5:36 9. Blattner TC, George N, Lee CC, Kumar V, Yelton CD. Efficacy of cone-beam computed tomography as a modality to accurately identify the presence of second mesiobuccal canals in maxillary first and second molars: a pilot study. J Endod. 2010;36: Chen G, Yao H, Tong C. Investigation of the root canal configuration of mandibular first molars in a Taiwan Chinese population. Int Endod J. 2009;42: Cotton TP, Geisler TM, Holden DT, Schwartz SA, Schindler WG. Endodontic applications of cone-beam volumetric tomography. J Endod. 2007;33: de Pablo OV, Estevez R, Peix Sanchez M, Heilborn C, Cohenca N. Root anatomy and canal configuration of the permanent mandibular first molar: a systematic review. J Endod. 2010;36: Friedman S, Moshonov J, Stabholz A. Five root canals in a mandibular first molar. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1986;2: Ghoddusi J, Naghavi N, Zarei M, Rohani E. Mandibular first molar with four distal canals. J Endod. 2007;33: Lee SJ, Jang KH, Spangberg LS, Kim E, Jung IY, Lee CY, Kum KY. Threedimensional visualization of a mandibular first molar with three distal roots using computer-aided rapid prototyping. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101: Martos J, Lubian C, Silveira LF, Suita de Castro LA, Ferrer Luque CM. Morphologic analysis of the root apex in human teeth. J Endod. 2010;36: Matherne RP, Angelopoulos C, Kulild JC, Tira D. Use of cone-beam computed tomography to identify root canal systems in vitro. J Endod. 2008;34:87 9. Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi N, Khalilak Z, Vatanpour M, Mohammadi S, Pirmoradi S, Fazlyab M, Safavi K. Root canal anatomy and morphology of mandibular first molars in a selected Iranian population: an in vitro study. Iran Endod J. 2017;12: Mukhaimer RH. Evaluation of root canal configuration of mandibular first molars in a Palestinian population by using cone-beam computed tomography: an ex vivo study. Int Sch Res Notices. 2014;2014: Nair MK, Nair UP. Digital and advanced imaging in endodontics: a review. J Endod. 2007;33:1 6. Navarro LF, Luzi A, Garcia AA, Garcia AH. Third canal in the mesial root of permanent mandibular first molars: review of the literature and presentation of 3 clinical reports and 2 in vitro studies. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007;12:E Patel S, Dawood A, Ford TP, Whaites E. The potential applications of cone beam computed tomography in the management of endodontic problems. Int Endod J. 2007;40: Reyhani MF, Rahimi S, Shahi S. Root canal therapy of a mandibular first molar with five root canals: a case report. Iran Endod J. 2007;2: Sharma P, Shekhar R, Sharma A. Endodontic management of mandibular first molar with six canals using CBCT report of a case. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016; 10:ZJ12 3. Silva EJ, Nejaim Y, Silva AV, Haiter-Neto F, Cohenca N. Evaluation of root canal configuration of mandibular molars in a Brazilian population by using conebeam computed tomography: an in vivo study. J Endod. 2013;39: Song JS, Choi HJ, Jung IY, Jung HS, Kim SO. The prevalence and morphologic classification of distolingual roots in the mandibular molars in a Korean population. J Endod. 2010;36: Song JS, Kim SO, Choi BJ, Choi HJ, Son HK, Lee JH. Incidence and relationship of an additional root in the mandibular first permanent molar and primary molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;107:e Sundaresh KJ, Srinivasan R, Mallikarjuna R, Rajalbandi S. Endodontic management of middle mesial canal of the mandibular molar. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; Tian XM, Yang XW, Qian L, Wei B, Gong Y. Analysis of the root and canal morphologies in maxillary first and second molars in a Chinese population using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2016;42: Tyndall DA, Rathore S. Cone-beam CT diagnostic applications: caries, periodontal bone assessment, and endodontic applications. Dent Clin N Am. 2008;52: vii Versiani MA, Pecora JD, de Sousa-Neto MD. Flat-oval root canal preparation with self-adjusting file instrument: a micro-computed tomography study. J Endod. 2011;37: Vertucci FJ, Williams RG. Root canal anatomy of the mandibular first molar. J N J Dent Assoc. 1974;45:27 28 passim. Wang Y, Zheng QH, Zhou XD, Tang L, Wang Q, Zheng GN, Huang DM. Evaluation of the root and canal morphology of mandibular first permanent molars in a western Chinese population by cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2010;36: Yew SC, Chan K. A retrospective study of endodontically treated mandibular first molars in a Chinese population. J Endod. 1993;19: Zhang R, Wang H, Tian YY, Yu X, Hu T, Dummer PM. Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate root and canal morphology of mandibular molars in Chinese individuals. Int Endod J. 2011;44: Zhang R, Yang H, Yu X, Wang H, Hu T, Dummer PM. Use of CBCT to identify the morphology of maxillary permanent molar teeth in a Chinese subpopulation. Int Endod J. 2011;44: Zheng QH, Wang Y, Zhou XD, Wang Q, Zheng GN, Huang DM. A cone-beam computed tomography study of maxillary first permanent molar root and canal morphology in a Chinese population. J Endod. 2010;36:
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
Correspondence should be addressed to Raed Hakam Mukhaimer;
 International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 583621, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/583621 Research Article Evaluation of Root Canal Configuration of Mandibular First Molars in a Palestinian
Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 237302, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/237302 Case Report Four-Rooted Mandibular First Molar with an Unusual Developmental Root Fusion Line: A Case Report Jojo
Failure of root canal therapy often
 Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Anatomy Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of mandibular molars with single distal canals Arthur F. Lamia, DDS, MS n N.J. McDonald, BDS, MS The aim of this study was to evaluate, using microcomputed
Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
Original Article Evaluation of the Root and Canal Morphology of Mandibular Permanent Anterior Teeth in an Iranian Population by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Mohsen Aminsobhani 1,2, Mona Sadegh 3, Naghmeh
Usage of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) to Evaluate Root and Canal Morphology of maxillary First Molar
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 2 (9) August 2013: 19-23 2013 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar
 Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2017;29(3):143-148. Accuracy of CBCT as modality to identify the presence of secondary mesiobuccal root canal in the maxillary first molar Haikal Halil*, Mazlifa Mahidin*,
Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 389387, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/389387 Case Report Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with Two Palatal Canals and a Single Buccal Canal:
Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate root and canal morphology of mandibular first and second molars in Turkish individuals
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013 Jul 1;18 (4):e73744. Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 Use of conebeam computed
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2013 Jul 1;18 (4):e73744. Journal section: Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18473 Use of conebeam computed
Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography
 Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
Research article ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using conebeam computed tomography Hyoung-Hoon
EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ABSTRACT
 EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor
EVALUATION OF ROOT ANATOMY AND MORPHOLOGY OF MANDIBULAR PREMOLARS WITH CBCT IN IRANIAN POPULATION ROGHANIZAD NASRIN, KHALILAKZOHREH 2, PANJNOUSH MEHRDAD 3 AND GHOLAMSHAHI MAHBOUBEH * Assistant Professor
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo
 The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
Andres Torres 1, *, Reinhilde Jacobs 1, Paul Lambrechts 2, Claudia Brizuela 3, Carolina Cabrera 3, Guillermo Concha 4, María Eugenia Pedemonte 3
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 95-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.2.95 Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 95-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.2.95 Characterization of mandibular molar root and canal morphology using cone beam computed tomography and its variability
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
Knowledge of tooth and root canal anatomy is important for dental practice and for
 Detection of Permanent Three-rooted Mandibular First Molars by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Imaging in Taiwanese Individuals Ming-Gene Tu, DDS, MS, PhD,* Heng-Li Huang, PhD,* Shui-Sang Hsue, DDS, MS,
Detection of Permanent Three-rooted Mandibular First Molars by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Imaging in Taiwanese Individuals Ming-Gene Tu, DDS, MS, PhD,* Heng-Li Huang, PhD,* Shui-Sang Hsue, DDS, MS,
Evaluation of The Root Morphology of Maxillary Permanent First And Second Molars in An Indian Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VIII (October. 2016), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of The Root Morphology
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional Analysis with Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 697323, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/697323 Case Report Management of Complex Root Canal Curvature of Bilateral Radix Entomolaris: Three-Dimensional
Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology. c Professor, Department of Cariology, Endodontology, and Operative
 The ability of cone-beam computerized tomography to detect vertical root fractures in endodontically treated and nonendodontically treated teeth: a report of 3 cases Xiaoying Zou, DDS, MD, a Denggao Liu,
The ability of cone-beam computerized tomography to detect vertical root fractures in endodontically treated and nonendodontically treated teeth: a report of 3 cases Xiaoying Zou, DDS, MD, a Denggao Liu,
FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS
 Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Original Article FREQUENCY OF FOURTH CANAL IN PERMANENT MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLARS 1 Fozia Rajput, BDS, MSc, FCPS 2 Muhammad Arif Shaikh, BDS, MSc 3 Mohammad Ilyas Shaikh, BDS, FCPS 4 Khawar Karim, BDS ABSTRACT
Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct
 OPEN (2017) 9, 33 37 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin
OPEN (2017) 9, 33 37 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology and configuration of 123 maxillary second molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank Paqué 2, Anja-Christin
Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography L Demiriz, E Hazar Bodrumlu, M İçen 1 Departments of Pediatric Dentistry
Original Article Evaluation of Root Canal Morphology of Human Primary Mandibular Second Molars by Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography L Demiriz, E Hazar Bodrumlu, M İçen 1 Departments of Pediatric Dentistry
Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/35023.11615 Dentistry Section Review Article Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration Rashmi Bansal
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/35023.11615 Dentistry Section Review Article Classification of Root Canal Configurations: A Review and a New Proposal of Nomenclature System for Root Canal Configuration Rashmi Bansal
Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 216491, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216491 Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar Haridoss Selvakumar, 1 Swaminathan
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 216491, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216491 Case Report Five Canalled and Three-Rooted Primary Second Mandibular Molar Haridoss Selvakumar, 1 Swaminathan
Lodha Ena* M. Kala** INTRODUCTION
 Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Indian Journal of Dental Education 23 Volume 2 Number 4 October-December 2010 A clinical study on the incidence of C shaped root canals in mandibular second molars in patients visiting the department of
Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars by means of micro-computed tomography: an ex vivo study
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Root canal morphology and configuration of 118 mandibular first molars
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Anatomy Research International, Article ID 731859, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/731859 Research Article Root Canal Morphology of Permanent Maxillary and Mandibular Canines in Indian Population
Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE
 Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 891849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891849 Case Report Three Independent Mesial Canals in a Mandibular Molar: Four-Year Followup of a Case Using
Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral Computed Tomographic
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 816576, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/816576 Case Report Root Canal Treatment of Mandibular Second Premolar with Three Separate Roots and Canals Using Spiral
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Morphologic assessment of mandibular anterior teeth root canal using CBCT
 Original article Acta Medica Academica 2017;46(2):85-93 DOI: 10.5644/ama2006-124.193 Morphologic assessment of mandibular anterior teeth root canal using CBCT Sina Haghanifar 1, Ehsan Moudi 1, Ali Bijani
Original article Acta Medica Academica 2017;46(2):85-93 DOI: 10.5644/ama2006-124.193 Morphologic assessment of mandibular anterior teeth root canal using CBCT Sina Haghanifar 1, Ehsan Moudi 1, Ali Bijani
Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series
 Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
Case Series Primary molars with extra root canals - a case series Sagar Chawla, 1 Mousami Goswami, 2 Priyanka Sachdeva, 3 Vidhi Walia. 4 1,3,4 Postgraduate student, 2 Professor and Head, Department of
e74 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College a Reader.
 Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with two palatal roots and a single fused buccal root diagnosed with spiral computed tomography - a case report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, a Joseph Reuben,
An unusual maxillary canine with two separated root canals
 pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
pissn 225-0864 / eissn 2093-879 http://dx.doi.org/0.5395/jkacd.20.36.5.43 Case report A maxillary canine with two separated root canals: a case report Dong-Ryul Shin, Jin-Man Kim 2, Duck-Su Kim 3, Sun-Young
The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography in a polish population
 Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Olczak and Pawlicka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:68 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0243-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The morphology of maxillary first and second molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/138 Internal Root Morphology of Maxillary First and Second Molars of South Indian Population by Canal Staining and Clearing Technique Kishore Gopalakrishna Naik
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT
 Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report Rosaline Hannah 1 *, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy 1, Nachimuthu
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic management of a mandibular second molar with radix entomolaris: a case report Rosaline Hannah 1 *, Deivanayagam Kandaswamy 1, Nachimuthu
Case Report Mandibular First Molar with a Single Root and Single Canal
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2014, Article ID 159846, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/159846 Case Report Mandibular First Molar with a Single Root and Single Canal Chandrasekaran Sooriaprakas,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2014, Article ID 159846, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/159846 Case Report Mandibular First Molar with a Single Root and Single Canal Chandrasekaran Sooriaprakas,
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Study
 10.2478/bjdm-2018-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography () Study SUMMARY Background/Aim:
10.2478/bjdm-2018-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Second Root Canal in Mandibular Incisors: an Ex Vivo Cone-Beam Computed Tomography () Study SUMMARY Background/Aim:
Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 5, MAY 2004 Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 5, MAY 2004 Morphology of the Physiological Foramen: I. Maxillary and Mandibular Molars
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Cone Beam in the Modern Dental Office Better Imaging, Better Outcomes Incorporation of CBCT Data into Treatment Planning
 1 Cone Beam in the Modern Dental Office Better Imaging, Better Outcomes Incorporation of CBCT Data into Treatment Planning Rick Ferguson DMD Clinical Assistant Professor University of Florida Diplomate
1 Cone Beam in the Modern Dental Office Better Imaging, Better Outcomes Incorporation of CBCT Data into Treatment Planning Rick Ferguson DMD Clinical Assistant Professor University of Florida Diplomate
Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography in detecting external root resorption
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 153-8 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.3.153 Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography in detecting external root resorption
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 153-8 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.3.153 Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography in detecting external root resorption
Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: A technical note
 Technical Note pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):129-134 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.129 Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block
Technical Note pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):129-134 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.129 Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC
 Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Douglas D. Lancaster, COL, DC 3 August 2016 Army Post Graduate Dental School Prevalence of the middle mesial canal in non-surgical root canal treated mandibular first and second molars in a local military
Review Article Fusion of a supernumerary tooth to right mandibular second molar: a case report and literature review
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):11890-11895 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010163 Review Article Fusion of a supernumerary tooth to right mandibular second molar: a case report and literature review
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):11890-11895 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010163 Review Article Fusion of a supernumerary tooth to right mandibular second molar: a case report and literature review
Endodontic management of radix entomolaris: Case reports
 2015; 2(1): 15-19 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2015; 2(1): 15-19 2015 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 24-02-2015 Accepted: 08-04-2015 Dr. Uday Kamath Dentistry and Endodontics,
2015; 2(1): 15-19 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2015; 2(1): 15-19 2015 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 24-02-2015 Accepted: 08-04-2015 Dr. Uday Kamath Dentistry and Endodontics,
Mandibular first molar with four canals in the mesial root
 C L I N I C A L Mandibular first molar with four canals in the mesial root Hamed Karkehabadi 1, Ricardo Machado 2 and Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia 3 Abstract A 35-year-old female patient with intermittent
C L I N I C A L Mandibular first molar with four canals in the mesial root Hamed Karkehabadi 1, Ricardo Machado 2 and Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia 3 Abstract A 35-year-old female patient with intermittent
Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular First Premolar With Three Root Canals: A Case Report
 J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci http://www.jrdms.dentaiau.ac.ir e(issn): 2383-2754 p(issn):2588-4166 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular First Premolar
J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci http://www.jrdms.dentaiau.ac.ir e(issn): 2383-2754 p(issn):2588-4166 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Endodontic Treatment of a Mandibular First Premolar
Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study
 Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study SHUE-FEN YANG 1,2 JENN-RONG HSU 1 CHIA-LIN TSAI 1 SHENG-FANG PAI 2 1 Department of Dentistry,
Efficacy of microscopy and dye for determining the presence of root canals in root end resections-an in vitro study SHUE-FEN YANG 1,2 JENN-RONG HSU 1 CHIA-LIN TSAI 1 SHENG-FANG PAI 2 1 Department of Dentistry,
CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (16): 6937-6941 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar. Pablo Betancourt *, Pablo Navarro, Ramon Fuentes Research
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (16): 6937-6941 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info CBCT technique for location of the MB2 canal of maxillary first molar. Pablo Betancourt *, Pablo Navarro, Ramon Fuentes Research
Case Report The unusual anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular molars diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1393-1398 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0039297 Case Report The unusual anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular molars diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography Fengqin
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1393-1398 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0039297 Case Report The unusual anatomy of the maxillary and mandibular molars diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography Fengqin
Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with unusual mesiobuccal root anatomy
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Arch Orofac Sci (2012), 7(2): 101-106. Case Report Management of a maxillary first molar tooth with
Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case report
 495 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 3, 495-499, 2010 Case Report Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case
495 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 3, 495-499, 2010 Case Report Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar having three mesiobuccal canals with the aid of spiral computed tomography: a case
Case Report: Maxillary second molar with two palatal canals diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: a case report
 Case Report: Maxillary second molar with two palatal canals diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: a case report Dr Dhara Shukla 1,Dr Girish Parmar 2, Dr Abhishek Parmar 3 1 PG Part II Student,
Case Report: Maxillary second molar with two palatal canals diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography: a case report Dr Dhara Shukla 1,Dr Girish Parmar 2, Dr Abhishek Parmar 3 1 PG Part II Student,
Research Article. ISSN (Print)
 Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 2015; 2(7):401-408 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 2015; 2(7):401-408 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study
 ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
ORIGINA L RESEAR CH Correlation of the Bucco-lingual Width and the Incidence of Two Canals in Mandibular Incisors An Observational Study Mintu E B, 1 Usha C, 2 Saranya R, 3,Sathyanarayanan R 4 ABSTRACT
MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS
 ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
ISSN: 0976-3104 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR : AN ENIGMA FOR ENDODONTISTS Sowmya B*, Sarika Chandra, Abha Telang, Sylvia Mathew, John V George Department of Conservative Dentistry and
The variation of root canal morphology, especially in multirooted teeth, is a
 Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with a Single Root and a Single Canal Diagnosed with the Aid of Spiral CT: A Case Report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, Narayanan Bhargavi, BDS, and Deivanayagam
Endodontic Management of a Maxillary First Molar with a Single Root and a Single Canal Diagnosed with the Aid of Spiral CT: A Case Report Velayutham Gopikrishna, MDS, Narayanan Bhargavi, BDS, and Deivanayagam
Success in root canal treatment (RCT) is dependent. Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study
 Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study Marcelo Santos Coelho, DDS, MSc; Jeffrey M. Parker, DMD; Peter Z. Tawil, DMD, MS, FRCD(C), Dip ABE Abstract:
Second Mesiobuccal Canal Treatment in a Predoctoral Dental Clinic: A Retrospective Clinical Study Marcelo Santos Coelho, DDS, MSc; Jeffrey M. Parker, DMD; Peter Z. Tawil, DMD, MS, FRCD(C), Dip ABE Abstract:
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report
 Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Comparison of conventional radiography with cone beam computed tomography for detection of vertical root fractures: an in vitro study
 593 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 4, 593-597, 2010 Original Comparison of conventional radiography with cone beam computed tomography for detection of vertical root fractures: an in vitro study
593 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 4, 593-597, 2010 Original Comparison of conventional radiography with cone beam computed tomography for detection of vertical root fractures: an in vitro study
Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01472.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis F. Somma 1, D. Leoni 1, G. Plotino 1,
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01472.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Root canal morphology of the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molars: a micro-computed tomographic analysis F. Somma 1, D. Leoni 1, G. Plotino 1,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars Hacer Deniz Arisu a Tayfun Alacam b Abstract Anatomical variations must be considered in clinical and radiographical evaluations during endodontic
Diagnosis and Treatment of Three-Rooted Maxillary Premolars Hacer Deniz Arisu a Tayfun Alacam b Abstract Anatomical variations must be considered in clinical and radiographical evaluations during endodontic
ROOT CANAL MORPHOLOGY; CONCEPT IN MANDIBULAR 3RD MOLAR BY CONVENTIONALLY ENDODONTIC TREATMENT
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.599 ORIGINAL PROF-599 ROOT CANAL MORPHOLOGY; CONCEPT IN MANDIBULAR RD MOLAR BY CONVENTIONALLY ENDODONTIC TREATMENT 1. BDS, MSc Senior Lecturer Department
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.599 ORIGINAL PROF-599 ROOT CANAL MORPHOLOGY; CONCEPT IN MANDIBULAR RD MOLAR BY CONVENTIONALLY ENDODONTIC TREATMENT 1. BDS, MSc Senior Lecturer Department
Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography Evaldo Rodrigues 1, Antônio Henrique Braitt 2, Bruno
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography Evaldo Rodrigues 1, Antônio Henrique Braitt 2, Bruno
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars: An in vitro Study
 Original research Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root 10.5005/jp-journals-10060-0004 Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary
Original research Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root 10.5005/jp-journals-10060-0004 Canal Anatomy in Primary Molars Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Root Canal Anatomy in Primary
International Journal of Basic and Clinical Studies (IJBCS) 2014;3(1): Uysal I and Oztekin F
 Endodontic Treatment of Mandibular Incisors with Periapical Lesion by Using Single Instrument: Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging Ibrahim Uysal 1 Faruk Oztekin 2 1 PhD, Dicle University, Faculty of
Endodontic Treatment of Mandibular Incisors with Periapical Lesion by Using Single Instrument: Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging Ibrahim Uysal 1 Faruk Oztekin 2 1 PhD, Dicle University, Faculty of
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report.
 Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report. Author(s) Kato, H. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3722
Non-surgical endodontic treatment f invaginatus type III using cone bea Title tomography and dental operating mic report. Author(s) Kato, H. Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3722
Could cone-beam computed tomography demonstrate the lateral accessory canals?
 Ji et al. BMC Oral Health (2017) 17:142 DOI 10.1186/s12903-017-0430-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Could cone-beam computed tomography demonstrate the lateral accessory canals? Yan Ji 1, Shanhui Wen 2,
Ji et al. BMC Oral Health (2017) 17:142 DOI 10.1186/s12903-017-0430-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Could cone-beam computed tomography demonstrate the lateral accessory canals? Yan Ji 1, Shanhui Wen 2,
Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontics: An Overview.
 e-issn:2320-7949 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontics: An Overview. Mithra N Hegde, Priyadarshini Hegde, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, and Litty
e-issn:2320-7949 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontics: An Overview. Mithra N Hegde, Priyadarshini Hegde, Aditya Shetty, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, and Litty
Research Article. Key Words: First premolar, Mandibular, Maxillary, Vertucci s classification, Spiral computed tomography.
 Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Research Article A Computed Tomographic Study of Canal Variations in Maxillary & Mandibular first Premolar Teeth in Jaipur Population An in vitro Study. Deepak Sharma, Meetu Mathur Department of Conservative
Comparison of Periapical Radiography and Limited Cone-Beam Tomography in Posterior Maxillary Teeth Referred for Apical Surgery
 Comparison of Periapical Radiography and Limited Cone-Beam Tomography in Posterior Maxillary Teeth Referred for Apical Surgery Kenneth M.T. Low, BDS,*, Karl Dula, PD DMD,* Walter Bürgin, MS, BE,* and Thomas
Comparison of Periapical Radiography and Limited Cone-Beam Tomography in Posterior Maxillary Teeth Referred for Apical Surgery Kenneth M.T. Low, BDS,*, Karl Dula, PD DMD,* Walter Bürgin, MS, BE,* and Thomas
Accuracy of Conventional and Digital Radiography in Detecting External Root Resorption
 Accuracy of Conventional and Digital Radiography in Detecting External Root Resorption Abbas Mesgarani a, Sina Haghanifar b, Maryam Ehsani c*, Samereh Dokhte Yaghub d, Ali Bijani e a Department of Endodontics,
Accuracy of Conventional and Digital Radiography in Detecting External Root Resorption Abbas Mesgarani a, Sina Haghanifar b, Maryam Ehsani c*, Samereh Dokhte Yaghub d, Ali Bijani e a Department of Endodontics,
The. Cone Beam. Conversation. A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT
 The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
Diagnosis and endodontic management of two rooted mandibular second premolar: A case report
 International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Diagnosis and endodontic management of two rooted mandibular second premolar: A case report Saima Jamal*, Swathi, Rajaram Naik Department
International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Diagnosis and endodontic management of two rooted mandibular second premolar: A case report Saima Jamal*, Swathi, Rajaram Naik Department
Cone-Beam Computed Tomography as a Tool in Endodontic Detection and Diagnosis
 REVIEW ARTICLE Cone-Beam Computed Tomography as a Tool in Endodontic Detection and Diagnosis Krishnan Hari, G Anuradha ABSTRACT Radiographic imaging is essential in diagnosis, treatment planning and follow-up
REVIEW ARTICLE Cone-Beam Computed Tomography as a Tool in Endodontic Detection and Diagnosis Krishnan Hari, G Anuradha ABSTRACT Radiographic imaging is essential in diagnosis, treatment planning and follow-up
Radix paraentomolaris- A rarest of rare structural entity
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2014), PP 45-50 Radix paraentomolaris- A rarest of rare structural entity Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2014), PP 45-50 Radix paraentomolaris- A rarest of rare structural entity Dr.
THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST
 CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June Volume 4
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June 1 2011 Volume 4 Endodontic Treatment Utilizing 3D Imaging Recent advances in technology, such as rotary
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists June 1 2011 Volume 4 Endodontic Treatment Utilizing 3D Imaging Recent advances in technology, such as rotary
PORTFOLIO 01. Assigning a Level of Difficulty to Your Endodontic Cases
 PORTFOLIO 01 Assigning a Level of Difficulty to Your Endodontic Cases Root Canal Specialty Associates provides care in all phases of surgical and nonsurgical endodontics. With decades of combined experience,
PORTFOLIO 01 Assigning a Level of Difficulty to Your Endodontic Cases Root Canal Specialty Associates provides care in all phases of surgical and nonsurgical endodontics. With decades of combined experience,
3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Root Canal Space Using Micro-CT
 3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Canal Space Using Micro-CT M.A. Versiani 1, G. De-Deus 2, J. Vera 3, E. Souza 4, L. Steier 5, J.D. Pécora 1, M.D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry,
3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Canal Space Using Micro-CT M.A. Versiani 1, G. De-Deus 2, J. Vera 3, E. Souza 4, L. Steier 5, J.D. Pécora 1, M.D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry,
Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars
 Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars BY TIMOTHY ROGERS B.S. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign D.D.S., University of Illinois, Chicago, College
Clinical and radiographic methods to find the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars BY TIMOTHY ROGERS B.S. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign D.D.S., University of Illinois, Chicago, College
Endodontic Management of Mandibular Second Molars with C Shaped Root Canal Configuration Reports of Three Cases
 Endodontic Management of Mandibular Second Molars with C Shaped Root Canal Configuration Reports of Three Cases *Pradeep Jain, Yogesh Pant, Ruchi Jain, Pragati Phaphariya, Deepak Singh Kirar *Department
Endodontic Management of Mandibular Second Molars with C Shaped Root Canal Configuration Reports of Three Cases *Pradeep Jain, Yogesh Pant, Ruchi Jain, Pragati Phaphariya, Deepak Singh Kirar *Department
Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct
 (2017) 9, 151 157 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank
(2017) 9, 151 157 www.nature.com/ijos ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-dimensional analysis of the physiological foramen geometry of maxillary and mandibular molars by means of micro-ct Thomas Gerhard Wolf 1, Frank
endodontics Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth T he main objective of endodontic therapy is the
 endodontics Editor: MILTON SISKIN, D.D.S. College of Dentistry The University of Tennessee 847 Monroe Avenue Memphis, Tennessee 38163 Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth Frank J. Vertucci,
endodontics Editor: MILTON SISKIN, D.D.S. College of Dentistry The University of Tennessee 847 Monroe Avenue Memphis, Tennessee 38163 Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth Frank J. Vertucci,
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung- Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim,
The detection of periapical pathosis using periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography Part 1: pre-operative status
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01989.x The detection of periapical pathosis using periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography Part 1: pre-operative status S. Patel 1,2, R. Wilson 3, A. Dawood
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01989.x The detection of periapical pathosis using periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography Part 1: pre-operative status S. Patel 1,2, R. Wilson 3, A. Dawood
Case Report Independent and Confluent Middle Mesial Root Canals in Mandibular First Molars: A Report of Four Cases
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 103125, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/103125 Case Report Independent and Confluent Middle Mesial Root Canals in Mandibular First Molars: A Report of Four Cases
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 103125, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/103125 Case Report Independent and Confluent Middle Mesial Root Canals in Mandibular First Molars: A Report of Four Cases
AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015
 AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015 Title: Clinical and iomechanical Considerations of TADs in Challenging Cases: Sagittal Correction beyond Orthodontic oundaries
AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015 Title: Clinical and iomechanical Considerations of TADs in Challenging Cases: Sagittal Correction beyond Orthodontic oundaries
