T he implant mechanical stability at
|
|
|
- Imogen Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
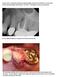
1 24 NEW OSSEODENSIFICATION IMPLANT SITE PREPARATION TRISI ET AL New Osseodensification Implant Site Preparation Method to Increase Bone Density in Low-Density Bone: In Vivo Evaluation in Sheep Paolo Trisi, PhD, DDS,* Marco Berardini, DDS, Antonello Falco, PhD, DDS, and Michele Podaliri Vulpiani, VMD T he implant mechanical stability at the time of surgery, known as primary stability, is a crucial factor to achieve implant osseointegration. 1 High primary implant stability is even more necessary in immediate loading protocols, and it was reported that an implant micromotion above 50 to 100 mm could induce periimplant bone resorption or implant failures. 2 4 The factors that mainly involved in enhancing implant primary stability are bone density, 5,6 surgical protocol, 7 and implant thread type, and geometry. 8 The insertion torque peak was demonstrated to be directly related to implant primary stability and host bone density 9 ;high insertion torque could significantly increase the initial bone-to-implant contact percentage (%BIC) with respect to implant inserted with low insertion torque values. 10 Ottoni et al 11 demonstrated a failure reduction rate of 20% in single tooth implant restoration for every 9.8 N cm of torque added. Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate a new surgical technique for implant site preparation that could allow to enhance bone density, ridge width, and implant secondary stability. Materials and Methods: The edges of the iliac crests of 2 sheep were exposed and ten mm Dynamix implants (Cortex) were inserted in the left sides using the conventional drilling method (control group). Ten mm Dynamix implants (Cortex) were inserted in the right sides (test group) using the osseodensification procedure (Versah). After 2 months of healing, the sheep were killed, and biomechanical and histological examinations were performed. Results: No implant failures were observed after 2 months of healing. A significant increase of ridge width and bone volume percentage (%BV) (approximately 30% higher) was detected in the test group. Significantly better removal torque values and micromotion under lateral forces (value of actual micromotion) were recorded for the test group in respect with the control group. Conclusion: Osseodensification technique used in the present in vivo study was demonstrated to be able to increase the %BV around dental implants inserted in low-density bone in respect to conventional implant drilling techniques, which may play a role in enhancing implant stability and reduce micromotion. (Implant Dent 2016;25:24 31) Key Words: bone volume, osseodensification, osseointegration, bone expansion, poor bone density *Scientific Director, Biomaterial Clinical Research Association, Pescara, Italy; Private Practice, Pescara, Italy. Biomaterial Clinical Research Association, Pescara, Italy; Private Practice, Pescara, Italy. Veterinary Surgeon, G. Caporale Institute, Teramo, Italy. Reprint requests and correspondence to: Marco Berardini, DDS, Via Galilei 8, Pescara, Italy, Phone: , Fax: , dottmarcoberardini@gmail.com ISSN /16/ Implant Dentistry Volume 25 Number 1 Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives License 4.0 (CC BY-NC-ND), which permits downloading and sharing the work provided it is properly cited. The work cannot be changed in any way or used commercially. DOI: /ID The mechanical friction between implant surface and bone walls of the osteotomic site gives primary implant stability. The osseointegration process leads to new bone apposition on the implant surface and allows reaching the implant secondary stability that is the functional contact between alive bone and titanium dental implant. In case of poor bone density, such as upper human jaw, the insufficient bone amount around the implants could negatively influence the histomorphometric parameters (such as %BIC and bone volume percentage [%BV]) and, consequently, both primary and secondary implant stabilities. Undersized implant site preparation 12,13 and the use of osteotomes to condense bone 14,15 are surgical techniques proposed to increase primary implant stability and %BIC in poor density bone. Different healing patterns and periimplant bone remodeling models were also observed 16,17 between standard site
2 TRISI ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 25, NUMBER preparation and undersized implant site preparation. Specifically designed implants for low-density bone were also developed 18 testifying the hardness of the challenge to reach a sufficient implant stability in poor bone density. The use of the osteotomes in poor density bone allows fracturing and condensing of bone trabeculae, 19,20 but this technique does not improve periimplant bone density (%BV) or implant stability. It is demonstrated that fractured trabeculae in periimplant bone, caused using the osteotome technique, induce a delayed secondary stability with respect to conventional drilling procedures during healing. 21 Besides, tooth loss, old age, and removable or unsuitable removable dentures inevitably lead to alveolar bone resorption both in height and width. 22 It was reported that bone reduction in a width of approximately 25% after 1 year of tooth extraction and the mandible showed a bone loss rate 4 times higher than the upper maxilla. 23 Narrow alveolar bone ridges are common in edentulous patients needing dental implant restoration, and many surgical techniques have been developed, over the years, to perform bone expansion or augmentation. The alveolar ridge splitting/ expansion technique in 1 stage was proposed as a valid alternative to the 2-stage Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR). 24 The predictability of horizontal and vertical augmentation techniques by bone regeneration, using bone substitutes or autogenous bone, is still not clear, and surgical complications are common. 25 However, osteodistraction osteogenesis and ridge splitting technique 26 are considered efficient to increase bone width 27 with lesser complication incidence. Osseodensification (OD), a nonextraction technique, was developed by Huwais in and made possible with specially designed burs to increase bone density as they expand an osteotomy. 29 These burs combine advantages of osteotomes with the speed and tactile control of the drilling procedures. Standard drills remove and excavate bone during implant site preparation; while osteotomes preserve bone, they tend to induce fractures of the trabeculae that require long remodeling time and delayed secondary implant stability. The new burs allow bone preservation and condensation through compaction autografting during osteotomy preparation, increasing the periimplant bone density (%BV), and the implant mechanical stability was reported by in vitro testing. 30 According to the manufacturer, these special burs demonstrated the ability to expand narrow bone ridges similarly to split crest techniques. The bur geometry, rotating in reverse mode at a rotating speed of 800 to 1500 rpm with profuse saline solution irrigation to prevent bone overheating, allows to compact the bone along the inner surface of the implant osteotomic site without cutting. The bouncing motion (in and out movement) is helpful to create a rate-dependent stress to produce a ratedependent strain, and allows saline solution pumping to gently pressurize the bone walls. This combination facilitates an increased bone plasticity and bone expansion. The aim of the present in vivo study is to evaluate the efficacy of this new OD technique of implant site preparation to enhance implant secondary stability, periimplant bone density (%BV) and to increase ridge width in poor density bone. MATERIALS AND METHODS Surgery The Ethics Committee for Animal Research of the Veterinary School of the University of Teramo (Teramo, Italy) approved the study protocol, which followed guidelines established by the European Union Council Directive of February 2013 (R.D.53/2013). Two female sheep, 4 to 5 years old, were included in the study. Clinical examination determined that all animals were in good general health. Exclusion criteria included general contraindications (pregnancy, systemic disease) to implant surgery and active infection, or severe inflammation in the area intended for implant placement. The animals were given thiopental (Thiopental, Höchst, Austria) for induction of anesthesia as needed. After orotracheal intubation and ventilation, anesthesia was sustained with nitrous oxide oxygen with 0.5% halothane. Physiologic saline solution was administered during surgery for fluid replacement. The edges of the iliac crests were exposed through a skin incision of 15 cm in length. The skin and fascial layers were opened and closed separately. After dissection of the soft tissues, the bone was exposed and 5 osteotomic sites were prepared in each (left and right) side of the iliac crest for a total of 20 osteotomic implant sites. On the left side of both animals, the implant conventional drilling procedure was performed after the drill sequence recommended by the manufacturer under profuse saline irrigation (1000 rpm). Ten mm Fig. 1. Left side: Clinical photograph of osteotomic site preparation in test group. The bone ridge width was 4 to 6 mm but no dehiscence or fenestration occurred after the 5-mm diameter site preparation. The blue arrows indicate the areas in which the bone ridge expansion is more evident. Right side: A particular osteotomic site in test group. This typical bone hole margins testified that OD burs did not cut the bone but expand it.
3 26 NEW OSSEODENSIFICATION IMPLANT SITE PREPARATION TRISI ET AL Each animal underwent systemic antibiotic therapy for 5 days with 8-mL long acting Clamoxil (Pfizer Limited, Sandwich,MA).Afterthesurgery,animals received appropriate veterinary care and were allowed free access to water and standard laboratory nutritional support throughout the trial period. The sheep were killed 2 months after implantation by an overdose of sodium thiopental (Thiopental, Höchst, Austria). Fig. 2. Left side: Clinical photograph of OD burs in action under profuse saline solution irrigation. No bone dehiscence occurred despite the great bur diameter. Right side: Implant positioning in test group. The blue arrows indicate the areas in which bone ridge expansion is more evident. Dynamix implants (Cortex, Shlomi, Israel) were inserted in the left iliac crest side of each sheep (control group) because the bone ridge width did not allow inserting wider diameter implants. The initial bone ridge width measured between 4 and 6 mm and did not allow to insert implants with a diameter wider than 3.8 mm using conventional drilling procedures. At first, we tried to have an osteotomic site of 5 mm with conventional burs but it inevitably involved a bone defect generation (dehiscence). We decided to use 3.8-mm diameter implants in the control group to compare between them implants surrounded by bone and not implants with bone dehiscence to others with healthy bone. On the right side of both animals, the implant site was prepared using Densah Burs (Versah, LLC, Jackson, MI) ( following the OD protocol for implants used: 2-mm pilot drill (1200 rpm), Densah Bur VT1828 in reverse rotation at 1200 rpm, Densah Bur VT2838 in reverse rotation at 1200 rpm, and Densah Bur VT3848 in reverse rotation at 1200 rpm. Ten mm Dynamix implants (Cortex) were inserted in the right iliac crest side of each sheep (test group). The burs were used in a bouncing motion under profuse saline sterile solution irrigation. In the right iliac crest, the 5.0-mm diameter implant was used to test whether the ridge expansion could be obtained with this new technique (Figs. 1 2). Cover screws were secured and the surgical wounds were closed by a resorbable periosteal muscular inner suture, followed by an external cutaneous 2-0 silk suture. Fig. 3. Sample after animal sacrifice in test group. Implants appear osteointegrated and showed no bone resorption. Value of Actual Micromotion Analysis Bone blocks containing the implants were retrieved from each side of the iliac crest. Each implant was fitted with a 1-piece 11-mm straight abutment. The bone blocks were, then, fixed on a customized loading device to measure implant secondary stability according to a previously described technique. Briefly, a digital force gauge (AccuForce Cadet; Ametek, Largo, FL) and, on the opposite side, a digital micrometer (Mitutoyo Digimatic Micrometer, Kawasaki, Japan) was used to measure implant micromotion during load application. Horizontal forces of 25 N/mm were applied onto the abutment of each implant perpendicularly to the major axis, and the lateral displacement was measured by the digital micrometer 10 mm above the crest. This parameter represents the value of the actual micromotion (VAM) and it was previously published. 31 RTV Testing Removal torque value (RTV) was measured at the time of animal sacrifice (2 months after implantation). The RTV was evaluated and recorded for each implant and in every group. It was measured with a digital hand-operated torque wrench (Tonichi STC400CN) by unscrewing the implants until interfacial failure occurred. The digital torque wrench automatically registered the peak removal torque value on the digital display. After the initial interface detachment, the implants were screwed back into their initial position as accurately as possible and retrieved for histological analysis. Although the interfacial detachment created an artifact at the interface, its analysis would still be reliable accordingtosennerbyetal, 32 who useda similar procedure to study the morphology of the bone-metal rupture.
4 TRISI ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 25, NUMBER a JVC TK-C1380 Color Video Camera (JVC Victor Company, Yokohama, Japan) and a frame grabber. The images were acquired with a 310 objective over the entire implant surface. Subsequently, the digitized images were analyzed by the image analysis software IAS 2000 (Delta Sistemi, Roma, Italy). For each section, the 2 most central sections were analyzed and morphometrically measured. The histomorphometric parameters calculated were %BIC and %BV. Fig. 4. Implants in the control group. It is evident that bone ridge width did not allow inserting the wider diameter implant without creating bone defects. Newly formed bone connected bone trabeculae to titanium implant surface. Bone resorption of approximately 0.3 to 0.5 mm in implant neck area is visible in both samples (toluidine blue, 310 magnification). Histological Analysis After biomechanical measurements, the specimen were immediately fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin and processed for histological analysis. After dehydration, the specimens were infiltrated with a methyl-methacrylate resin from a starting solution 50% ethanol/resin and subsequently 100% resin, with each step lasting 24 hours. After polymerization, the blocks were sectioned and then ground down to approximately 40 microns. Toluidine blue staining was used to analyze the different ages and remodeling pattern of the bone. The histomorphometric analysis was performed by digitizing the images from the microscope through Fig. 5. Left side: Test group. The most peculiar feature of the healing pattern was the unusual granular aspect. The granules observed in the trabeculae, seemed like mineralization nuclei (highlighted by blue arrows). These granules were surrounded by active osteoblasts, osteoid tissue, and osteons (toluidine blue, 330 magnification) Right side: Implant coronal area in test group. No bone resorption was observed. Many mineralization nuclei were present in the most coronal implant area (toluidine blue, 325 magnification). Statistical Analysis Statistical differences of %BIC, %BV, RTV, and VAM between the 2 groups were checked using the statistical software GraphPad Prism 5 (www. graphpad.com). An unpaired t test with Welch correction was used to verify the statistical significance (P, 0.05) of the differences between the average values of each parameter evaluated. RESULTS No implant failure was observed after 2 months of healing. The clinical examination, performed immediately after the bone block retrieval, showed no crestal bone resorption and no implants had bone fenestration or dehiscence (Fig. 3). A considerable bone expansion (ridge width) was clinically observed in the test group; 5-mm diameter implants were easily inserted in the narrow ridge (about 4- to 6-mm width) using the OD method without any bone dehiscence around implants. Histological Results Control group. A thin layer of newly formed bone covered implant threads. Some bone fractured trabeculae were observed. Newly formed bone connected the fractured bone trabeculae to bone fragments and/or to the implant surface (Fig. 4). The newly woven bone contained fractured bone trabeculae and some bone chips or bone powder. Some bone chips were present at the bone-implant interface. A bone remodeling process, involving bands of osteoid tissue and bone resorption areas, was evident, in a lesser quantity with respect to the test side. Test group. The thickening of the bone ridge at the coronal zone was observed.
5 28 NEW OSSEODENSIFICATION IMPLANT SITE PREPARATION TRISI ET AL model and in the control group. The increase of bone density was particularly evident in the most coronal implant region. Bone chips and resorption of newly formed trabeculae were also observed. Active bone remodeling was found to be directed more toward bone apposition and bone density increase than toward bone resorption. Fig. 6. Implants in the test group. The granular aspect was more visible in the coronal portion of the implants. The bone density increase is also evident in this area. The cortical wall changed its direction denoting a bone ridge expansion (red arrows) (toluidine blue, 310 magnification). The bone, in this area, presented many small circular or ellipsoidal medullary cavities lined by osteoid tissue layers with active osteoblasts (Fig. 5). In the central implant region, bone trabeculae repaired by composite bone in direct contact with the titanium implant surface were observed and ridge expansion was evident (Fig. 6). Some bone chips were involved in the bone remodeling process, mostly in the apical implant zone. The most peculiar feature of the healing pattern was at the level of the more coronal cortical walls where the bone presented an unusual granular aspect. In these areas, osteoid tissue bands, osteons, and newly formed bone were also visible (Fig. 5). In these zones, the bone trabeculae showed the specific granular aspect also in the inner part, whereas the outer side showed lamellar bone layers. These bone trabeculae were thickened because of incorporation of autogenous bone fragments during the healing process. The granules observed in the trabeculae seemed like mineralization nuclei. Close to these granules, woven bone areas mixed with lamellar bone were also observed. The percentage of bone surface lined by osteoid bands in the coronal area was much higher than that found in other areas of the implants and higher than that usually observed after 2 months of healing in this animal Table 1. Mean Value of %BIC, %BV, RTV, and VAM of Each Group Test Group: OD Preparation Site Control Group: Conventional Preparation Site %BIC %BV * * RTV (N/cm) * * VAM (mm) * * The %BV analysis revealed a bone density increase of approximately 30% higher, a statistically significant value (P, 0.05), in test group in respect to the control group. Data expressing secondary implant stability, such as VAM and RTV, demonstrated a significantly stronger osseointegration in implants inserted using OD procedures (test group) than those implants inserted with conventional drilling procedures. *Significantly (P, 0.05) different between test and control group. Histomorphometric Results The mean values of %BIC, %BV, RTV, and secondary stability (VAM) for conventional site preparation (control group) and in implants inserted in sites prepared using OD burs (test group) are summarized in the Table 1. No significant difference in %BIC was detected between the 2 groups. The %BV analysis revealed a bone density increase of approximately 30% higher, a statistically significant value (P, 0.05), in test group in respect to control group. Biomechanical Results The test group showed statistically significant (P, 0.05) better biomechanical performances (approximately 30% 40% higher) than control group in the parameters evaluated as the RTV and the VAM. Mean values of each parameter evaluated are expressed in Table 1. DISCUSSION Poor bone density is common in human upper jaw, especially in elderly patients needing a fixed implant supported rehabilitation. In D3 or D4 bone type, it is difficult to achieve a good implant primary stability because of the poor %BV around the titanium implant surface. 5 Bone density classification according to Lekholm and Zarb (1985), 33 based on the morphology and distribution of cortical and trabecular bones, individuated 4 bone quality types. Poor bone density (D3-D4) is common in the upper jaw region, 34 and in this bone type, it is difficult to achieve a high implant primary stability. If the primary implant stability is inadequate, the early implant failure rate could rise beyond critical levels. 35 Immediate loading protocols are also discouraged in case of poor bone quality or low primary implant stability and longer
6 TRISI ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 25, NUMBER healing time is needed in these cases, with some disadvantages for the patient. In case of poor bone density, such as in the human upper jaw, the insufficient bone amount around the implants could negatively influence the histomorphometric parameters (such as %BIC and %BV) and, consequently, both primary and secondary implant stabilities. Several surgical techniques 36 have been proposed to avoid or reduce bone sacrifice during implant placement procedures in low-density bone and to enhance primary implant stability and bone quality. Some authors suggested to undersize the osteotomic implant site in respect to the implant diameter of approximately 10% to reduce bone cutting and enhance primary implant stability. 7,13 An undersized osteotomic site greater than 10% did not add mechanical benefit and, however, this expedient allows to increase implant initial stability but it is not able to modify the %BV around the implant as compared with nonundersized sites. 37 The alternative to implant drilling procedures is the osteotome technique 14 that aimed to compact the bone with the mechanical action of cylindrical steel instruments along the osteotomic walls. This procedure created trabecular fractures with debris, which caused an obstruction of the osseointegration process. 21,38 The healing process, in case of osteotome preparation method, involve 2 phases: fractured trabeculae and bone chips resorption followed by new bone formation onto the implant surface. The OD technique, using special burs in noncutting rotation, tested in this study demonstrated the ability to increase in a significant way (approximately 30% higher) the %BV around the implants and to improve secondary implant stability (expressed as removal torque values and micromotion under lateral forces). The histological analysis showed that the healing process is not obstructed by this bone condensation and, moreover, that bone density increase is evident around implant surface (especially in the upper portion of the implant). Besides, the high presence of mineralization nuclei lined by osteoid tissue and osteoblast observed in test group strongly suggests that, in the long run, the bone could still increase its density. The special geometry design of the burs tested allows pulverizing the bone, creating higher mineralization nuclei number than that of the control group. Implants inserted using this new OD method showed statistically higher biomechanical values of 30% to 40% than implants inserted with conventional drills. This osseodensification technique allows enhancing the primary implant stability, as it was demonstrated by lower VAM recorded in test group in this study. The VAM of the implant is a parameter already published 39 to successfully evaluate implant stability that is directly correlated to stability parameters as %BIC, RTV, and ISQ. The removal torque values (RTVs), which is a parameter directly correlated with the periimplant %BV and %BIC, was positively influenced by 30% of BV rise in test group and reached values of approximately 40% more in OD sites than in the conventional sites. The differences in RTVs and micromotion under lateral forces (VAM) are very remarkable between the 2 groups (high statistical meaning) and only a little amount of these differences could be attributed to greater implant surfaces in the test group (in the control group, implant diameters are 1 mm smaller than those of the test group). In fact, the surface area of the mm implant is only 26% more extended than the mm implant (official data from the manufacturer). In the test group, wider diameter implants were used with respect to the control group (5 vs 3.8 mm), whereas the bone ridge width was 4 to 6 mm: a high risk of bone dehiscence existed with conventional drilling procedures. It was decided to place smaller diameter implants in the control group because implants associated to bone dehiscence should not be compared with implant surrounded by healthy bone. No bone resorption, dehiscence, or fenestration were demonstrated during the clinical and histological examinations; after 2 months of healing, using the OD technique, testifying that this surgical method is able to expand the bone taking advantage of viscoelastic bone properties and compacting bone chips (autografting) along the osteotomy without useless bone sacrifice. The ridge expansion obtained with OD tecnique is particularly evident in samples showed in Figure 6, in which the cortical wall changes its original direction testifying the bone width increase. Moreover, the great increase of the biomechanical strength in the test group did not negatively affect %BIC or %BV (was not related to a similar increase of the %BIC or %BV), but nevertheless enhanced healing. This could be explained by the change in the bone strength observed under the microscope induced by the OD procedure. This new implant site preparation technique significantly improved the secondary implant stability and the histological analysis revealed new a healing pattern of the surgical bone with a fast and big amount of newly formed bone along osteotomy walls. CONCLUSION The OD technique, used in the present in vivo study, was demonstrated to be able to increase implant primary stability and maintained implant secondary stability, and to increase the %BV around dental implants inserted in low-density bone in respect with conventional implant drilling procedures. OD allowed to avoid bone sacrifice, that appears unavoidable with conventional drilling procedures, and to prevent fractured trabeculae causing a delayed bone growth, as happened with the osteotome technique. Additionally, this study validated the bone expansion attitude of this OD technique showing that wider implant diameter could be inserted in narrow ridge without creating bone dehiscence or fenestration. Future in vivo human studies are needed to confirm the results showed in the present article. DISCLOSURE P. Trisi is a consultant for Cortex Dental Implants. The other authors claim to have no financial interest, either directly or indirectly, in the products or information listed in the article. APPROVAL The Ethics Committee for Animal Research of the Veterinary School of the University of Teramo (Teramo,
7 30 NEW OSSEODENSIFICATION IMPLANT SITE PREPARATION TRISI ET AL Italy) approved the study protocol with the protocol number ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors wish to thank Cortex Dental Implants and Versah, LLC for providing the burs and implants used in this study. REFERENCES 1. Albrektsson T, Brånemark PI, Hansson HA, et al. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop Scand. 1981;52: Søballe K, Brockstedt-Rasmussen H, Hansen ES, et al. Hydroxyapatite coating modifies implant membrane formation. Controlled micromotion in dogs. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63: Søballe K, Hansen ES, Brocksted- Rasmussen H, et al. Hydroxyapatite coating converts fibrous tissue to bone around loaded implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75: Szmukler-Moncler S, Salama H, Reingewirtz J, et al. Timing of loading and effect of micromotion on bone-dental implant interface: Review of experimental literature. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998;43: Marquezan M, Osório A, Sant Anna E, et al. Does bone mineral density influence the primary stability of dental implants? A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23: Trisi P, De Benedittis S, Perfetti G, et al. Primary stability, insertion torque and bone density of cylindric implant ad modum Brånemark: Is there a relationship? An in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22: Turkyilmaz I, Aksoy U, McGlumphy EA. Two alternative surgical techniques for enhancing primary implant stability in the posterior maxilla: A clinical study including bone density, insertion torque, and resonance frequency analysis data. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2008;10: Dos Santos MV, Elias CN, Cavalcanti Lima JH. The effects of superficial roughness and design on the primary stability of dental implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2011;13: Trisi P, Perfetti G, Baldoni E, et al. Implant micromotion is related to peak insertion torque and bone density. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20: Capparé P, Vinci R, Di Stefano DA, et al. Correlation between initial BIC and the Insertion Torque/Depth Integral Recorded with an Instantaneous Torque- Measuring Implant Motor: An in vivo Study. Clin implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17 (suppl 2):e613 e Ottoni JM, Oliveira ZF, Mansini R, et al. Correlation between placement torque and survival of single-tooth implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005;20: Alghamdi H, Anand PS, Anil S. Undersized implant site preparation to enhance primary implant stability in poor bone density: A prospective clinical study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69: Degidi M, Daprile G, Piattelli A. Influence of underpreparation on primary stability of implants inserted in poor quality bone sites: An in vitro study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73: Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: The osteotome technique. Compendium. 1994;15:152, , 158 passim; quiz Boustany CM, Reed H, Cunningham G, et al. Effect of a modified stepped osteotomy on the primary stability of dental implants in low-density bone: A cadaver study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2015;30: Campos FE, Gomes JB, Marin C, et al. Effect of drilling dimension on implant placement torque and early osseointegration stages: An experimental study in dogs. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70: e43 e Coelho PG, Marin C, Teixeira HS, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of undersized drilling on implant biomechanical stability at early implantation times. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71:e69 e Munjal S, Munjal S, Hazari P, et al. Evaluation of specifically designed implants placed in the low-density jaw bones: A clinico-radiographical study. Contemp Clin Dent. 2015;6: Shalabi MM, Wolke JG, de Ruijter AJ, et al. A mechanical evaluation of implants placed with different surgical techniques into trabecular bone of goats. J Oral Implantol. 2007;33: Shalabi MM, Wolke JG, de Ruijter AJ, et al. Histological evaluation of oral implants inserted with different surgical techniques into trabecular bone of goats. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18: Büchter A, Kleinheinz J, Wiesmann HP, et al. Biological and biomechanical evaluation of bone remodelling and implant stability after using an osteotome technique. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005;16: Hansson S, Halldin A. Alveolar ridge resorption after tooth extraction: A consequence of a fundamental principle of bone physiology. J Dent Biomech. 2012;3: Carlsson G, Persson G. Morphologic changes of the mandible after extraction and wearing dentures: A longitudinal clinical and x-ray cephalometric study covering5years.odontol Revy. 1967;18: Bassetti MA, Bassetti RG, Bosshardt DD. The alveolar ridge splitting/ expansion technique: A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res Jan 14. [Epub ahead of print]. 25. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Felice P, et al. The efficacy of horizontal and vertical bone augmentation procedures for dental implants: A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2009;2: Stricker A, Fleiner J, Stübinger S, et al. Bone loss after ridge expansion with or without reflection of the periosteum. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26: Tang YL, Yuan J, Song YL, et al. Ridge expansion alone or in combination with guided bone regeneration to facilitate implant placement in narrow alveolar ridges: A retrospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26: Huwais S, inventor; Fluted osteotome and surgical method for use. US Patent Application US2013/ January 3, Huwais S. Autografting Osteotome. Geneva, Switzerland: World Intellectual Property Organization Publication; WO2014/ Huwais S, Meyer E. Osseodensification: A novel approach in implant o preparation to increase primary stability, bone mineral density and bone to implant contact. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants Trisi P, Berardini M, Falco A, et al. Effect of implant thread geometry on secondary stability, bone density, and boneto-implant contact: A biomechanical and histological analysis. Implant Dent. 2015; 24: Sennerby L, Thomsen P, Ericson LE. A morphometric and biomechanic comparison of titanium implants inserted in rabbit cortical and cancellous bone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992;7: Lekholm U, Zarb GA. Patient selection and preparation. In: Brånemark PI, Zarb GA, Alberktsson T, eds. Tissue Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Chicago, IL: Quintessence; 1985: Hao Y, Zhao W, Wang Y, et al. Assessments of jaw bone density at implant sites using 3D cone-beam computed tomography. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18: Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11: Tabassum A, Walboomers XF, Wolke JG, et al. Bone particles and the undersized surgical technique. J Dent Res. 2010;89: Tabassum A, Meijer GJ, Walboomers XF, et al. Evaluation of primary
8 TRISI ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 25, NUMBER and secondary stability of titanium implants using different surgical techniques. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25: Stavropoulos A, Nyengaard JR, Lang NP, et al. Immediate loading of single SLA implants: Drilling vs. osteotomes for the preparation of the implant site. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19: Trisi P, Berardini M, Falco A, et al. Validation of Value of Actual Micromotion (VAM) as a direct measure of implant micromobility after healing (secondary implant stability): An in vivo histologic and biomechanical study. Clin Oral Implants Res
In 1981, Dr. Albrektsson, a member of
 Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
OSSEODENSIFICATION: A Paradigm Shift In Implant Osteotomy Preparation. Introducing Densah Bur Technology
 OSSEODENSIFICATION: A Paradigm Shift In Implant Osteotomy Preparation Introducing Densah Bur Technology Densah Bur Technology * The Innovation That Makes Osseodensification Possible A New Paradigm In Dental
OSSEODENSIFICATION: A Paradigm Shift In Implant Osteotomy Preparation Introducing Densah Bur Technology Densah Bur Technology * The Innovation That Makes Osseodensification Possible A New Paradigm In Dental
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The nternational Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2009 BY QUNTESSENCE PUBLSHNG CO, NC. PRNTNG OF THS DOCUMENT S RESTRCTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY. NO PART OF THS ARTCLE 549 Time Sequence of
The nternational Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2009 BY QUNTESSENCE PUBLSHNG CO, NC. PRNTNG OF THS DOCUMENT S RESTRCTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY. NO PART OF THS ARTCLE 549 Time Sequence of
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper*
 Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper* Alan Meltzer, DMD, MScD; Harold Baumgarten, DMD; Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS; Paolo Trisi, DDS, PhD Published by Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration:
Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper* Alan Meltzer, DMD, MScD; Harold Baumgarten, DMD; Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS; Paolo Trisi, DDS, PhD Published by Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration:
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
 A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Osseointegration of dental implants without primary stability: an experimental study in sheep
 Osseointegration of dental implants without primary stability: an experimental study in sheep Received: 3/4/2016 Accepted: 2/5/2016 Omed Ikram Shihab * Abduljaleel Azad Samad * Hozak Zahir Ali * Othman
Osseointegration of dental implants without primary stability: an experimental study in sheep Received: 3/4/2016 Accepted: 2/5/2016 Omed Ikram Shihab * Abduljaleel Azad Samad * Hozak Zahir Ali * Othman
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
GMI FRONTIER implant system. Surgical procedures guide
 GMI implant system Surgical procedures guide ABOUT THIS MANUAL This surgical procedures guide or surgical manual for the GMI implant system is designed solely to provide instructions for using GMI products,
GMI implant system Surgical procedures guide ABOUT THIS MANUAL This surgical procedures guide or surgical manual for the GMI implant system is designed solely to provide instructions for using GMI products,
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Densah Bur Surgical Technique Manual
 Densah Bur Surgical Technique Manual 2 SECTIONS 1. Osteotomy Preparation...p04 2. Unique Characteristics and Clinical Advantages...p08 3. Densah Burs Versatile Utilization...p11 4. The Densah Bur Kit...p17
Densah Bur Surgical Technique Manual 2 SECTIONS 1. Osteotomy Preparation...p04 2. Unique Characteristics and Clinical Advantages...p08 3. Densah Burs Versatile Utilization...p11 4. The Densah Bur Kit...p17
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited
 10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Implant System MAKE IT SIMPLE
 Implant System MAKE IT SIMPLE P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P. 10-13 P. 14 P. 15-17 P. 18-19 P. 20-21 MIS Warranty: MIS exercises great care and effort in maintaining the superior quality of its products. All MIS
Implant System MAKE IT SIMPLE P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P. 10-13 P. 14 P. 15-17 P. 18-19 P. 20-21 MIS Warranty: MIS exercises great care and effort in maintaining the superior quality of its products. All MIS
The surgical placement of dental implants has
 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
 227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
It is of interest to develop and evaluate
 RESEARCH Validation of Resonance Frequency Analysis by Comparing Implant Stability Quotient Values With Histomorphometric Data Ashish Thomas Kunnekel, MDS 1 * K. Chandrasekharan Nair, MDS 2 E. Munirathnam
RESEARCH Validation of Resonance Frequency Analysis by Comparing Implant Stability Quotient Values With Histomorphometric Data Ashish Thomas Kunnekel, MDS 1 * K. Chandrasekharan Nair, MDS 2 E. Munirathnam
THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS. Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel GTO I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E
 GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
4766 Research Dr. San Antonio, TX insightdentalsystems.com
 OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Bicortically Stabilized Implant Load Transfer
 Bicortically Stabilized Implant Load Transfer Chang Mo Jeong, DDS, PhD 1 /Angelo A. Caputo, PhD 2 /Robert S. Wylie, DDS 3 / Seung C. Son, DDS, MS 3 /Young Chan Jeon, DDS, PhD 4 Purpose: Questions exist
Bicortically Stabilized Implant Load Transfer Chang Mo Jeong, DDS, PhD 1 /Angelo A. Caputo, PhD 2 /Robert S. Wylie, DDS 3 / Seung C. Son, DDS, MS 3 /Young Chan Jeon, DDS, PhD 4 Purpose: Questions exist
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
The effect of undersizing and tapping on bone to implant contact and implant primary stability: A histomorphometric study on bovine ribs
 https://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2018;10:227-35 https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2018.10.3.227 The effect of undersizing and tapping on bone to implant contact and implant primary stability: A histomorphometric
https://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2018;10:227-35 https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2018.10.3.227 The effect of undersizing and tapping on bone to implant contact and implant primary stability: A histomorphometric
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
scientific compendium
 scientific compendium Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Success Stories in Stability and Survival Rates Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Scientific Compendium table of contents CLINICAL & PRE-CLINICAL
scientific compendium Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Success Stories in Stability and Survival Rates Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Scientific Compendium table of contents CLINICAL & PRE-CLINICAL
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI:10.4047/jkap.2008.46.6.628 DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT Seong-Kyun Kim 1, DDS, PhD, Seong-Joo Heo 2, DDS, PhD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI:10.4047/jkap.2008.46.6.628 DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT Seong-Kyun Kim 1, DDS, PhD, Seong-Joo Heo 2, DDS, PhD,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution.
 More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT. simultaneous implant placement and is an alternative Summer s osteotome both clinical use as well as the
 BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
Hiron Andreaza da Cunha, MS 1 /Carlos Eduardo Francischone, DMD 2 /Hugo Nary Filho, DDS 3 / Rubelisa Cândido Gomes de Oliveira, BDS 4
 A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Bone augmentation with biomaterials
 Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY
 NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY MANUAL Grand Morse Connection Helix Implant GRAND POSSIBILITIES WITH A LIMITLESS SOLUTION. GRAND MORSE NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY. 4 5 6 CONTENTS 1. CLINICAL STEP BY STEP OF GRAND
NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY MANUAL Grand Morse Connection Helix Implant GRAND POSSIBILITIES WITH A LIMITLESS SOLUTION. GRAND MORSE NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY. 4 5 6 CONTENTS 1. CLINICAL STEP BY STEP OF GRAND
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences 2018; 4(1): Dr. Renu gupta, Dr. RP Luthra, Suhani Kukreja
 2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
Sinus elevation with short implant
 Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
High-end solution STEP-BY-STEP USER GUIDE
 High-end solution STEP-BY-STEP USER GUIDE System Contents REAL TIME Restoration Guided Conical drill Multi-Unit abutment, Conical connection Guided kit for conical connection implant procedure C1 & V3
High-end solution STEP-BY-STEP USER GUIDE System Contents REAL TIME Restoration Guided Conical drill Multi-Unit abutment, Conical connection Guided kit for conical connection implant procedure C1 & V3
Astra Tech Implant System. Manual and product catalog OsseoSpeed TX Profile
 Astra Tech Implant System Manual and product catalog OsseoSpeed TX Profile Adapting with nature OsseoSpeed TX Profile anatomically designed implants for sloped ridges Imagine being able to achieve 360
Astra Tech Implant System Manual and product catalog OsseoSpeed TX Profile Adapting with nature OsseoSpeed TX Profile anatomically designed implants for sloped ridges Imagine being able to achieve 360
B&B DENTAL. implant company
 B&B DENTAL implant company Histological analysis of a Novocor Plus implant inserted in sheep bone FACULTY OF NORMAL HUMAN ANATOMY of the UNIVERSITY OF MODENA and PARMA (1990) Micro x-ray of a thick section
B&B DENTAL implant company Histological analysis of a Novocor Plus implant inserted in sheep bone FACULTY OF NORMAL HUMAN ANATOMY of the UNIVERSITY OF MODENA and PARMA (1990) Micro x-ray of a thick section
During the last 30 years, endosseous oral
 Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
- RESTORATIVE PRODUCT CATALOG
 - RESTORATIVE PRODUCT CATALOG MADE IN USA Others make Implants to sell... Tatum Surgical makes Implants to treat your Patients. Your Source for Implants To Meet Every Clinical Need Tatum... 4 Angled Post
- RESTORATIVE PRODUCT CATALOG MADE IN USA Others make Implants to sell... Tatum Surgical makes Implants to treat your Patients. Your Source for Implants To Meet Every Clinical Need Tatum... 4 Angled Post
NobelActive. The NobelActive technical story
 NobelActive The NobelActive technical story The NobelActive technical story NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years of research and development on a self-drilling and bone-condensing
NobelActive The NobelActive technical story The NobelActive technical story NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years of research and development on a self-drilling and bone-condensing
Biomechanical Evaluation of Undersized Drilling on Implant Biomechanical Stability at Early Implantation Times
 Biomechanical Evaluation of Undersized Drilling on Implant Biomechanical Stability at Early Implantation Times Paulo G. Coelho, DDS, PhD,* Charles Marin, DDS, PhD,y Hellen S. Teixeira, DDS, MS,z Felipe
Biomechanical Evaluation of Undersized Drilling on Implant Biomechanical Stability at Early Implantation Times Paulo G. Coelho, DDS, PhD,* Charles Marin, DDS, PhD,y Hellen S. Teixeira, DDS, MS,z Felipe
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus.
 Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Case study 25. Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla Using Short Implants. Dr. Ariel Labanca Mitre
 Case study 25 Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla Using Short Implants Dr. Ariel Labanca Mitre Oral Implantology Specialist Prosthodontics Specialist Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla
Case study 25 Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla Using Short Implants Dr. Ariel Labanca Mitre Oral Implantology Specialist Prosthodontics Specialist Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla
In Vivo Evaluation of BioSphere Bioactive Bone Graft Putty: Improved Bone Formation
 In Vivo Evaluation of BioSphere Bioactive Bone Graft : Improved Bone Formation ABSTRACT BioSphere is a novel bone graft product that was developed using spherical particles of bioactive glass with a narrow,
In Vivo Evaluation of BioSphere Bioactive Bone Graft : Improved Bone Formation ABSTRACT BioSphere is a novel bone graft product that was developed using spherical particles of bioactive glass with a narrow,
Rigid Fixation by Means of Titanium Mesh in Edentulous Ridge Expansion for Horizontal Ridge Augmentation in the Maxilla
 Rigid Fixation by Means of Titanium Mesh in Edentulous Ridge Expansion for Horizontal Ridge Augmentation in the Maxilla Luciano Malchiodi, MD, DDS*/Antonio Scarano, DDS**/Manlio Quaranta, MD, DDS***/ Adriano
Rigid Fixation by Means of Titanium Mesh in Edentulous Ridge Expansion for Horizontal Ridge Augmentation in the Maxilla Luciano Malchiodi, MD, DDS*/Antonio Scarano, DDS**/Manlio Quaranta, MD, DDS***/ Adriano
Derma S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N. Acellular dermal matrix
 Derma A XENOGENIC GRAFT FOR S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N Acellular dermal matrix A xenogenic graft for soft tissue augmentation CHARACTERISTICS Obtained from derma of porcine origin, using
Derma A XENOGENIC GRAFT FOR S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N Acellular dermal matrix A xenogenic graft for soft tissue augmentation CHARACTERISTICS Obtained from derma of porcine origin, using
Smarter Thinking. Simpler Design. Prima Plus. Surgical Manual
 Smarter Thinking. Simpler Design. Prima Plus Surgical Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS PRIMA PLUS IMPLANT SURGICAL MANUAL SURGERY Prima Plus Characteristics 4 Surgical Considerations 5 Prima Plus Surgical Sequence
Smarter Thinking. Simpler Design. Prima Plus Surgical Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS PRIMA PLUS IMPLANT SURGICAL MANUAL SURGERY Prima Plus Characteristics 4 Surgical Considerations 5 Prima Plus Surgical Sequence
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
03 Best combination for thin ridge
 MILAkit TM BonEx kit TM 03 Best combination for thin ridge Joel A. Gonzales RDA Product Specialist Email: Cell: joelg@megagenus.com (480) 440-3927 Thor MEGAGEN Implant 28 29 Why Thor? 1. Simple & Strong
MILAkit TM BonEx kit TM 03 Best combination for thin ridge Joel A. Gonzales RDA Product Specialist Email: Cell: joelg@megagenus.com (480) 440-3927 Thor MEGAGEN Implant 28 29 Why Thor? 1. Simple & Strong
INTRODUCTION. General Information. Important Warning
 S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
REASONS TO USE R.T.R.
 3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
Tapered Screw-Vent Implant System
 Tapered Screw-Vent Implant System The implant of choice brings flexibility to your practice. 1 clinical results and secondary stability Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Celebrates 11 Years of Quality Celebrating
Tapered Screw-Vent Implant System The implant of choice brings flexibility to your practice. 1 clinical results and secondary stability Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Celebrates 11 Years of Quality Celebrating
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
