Breast reconstruction following mastectomy has
|
|
|
- Rachel Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Free full text on Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford, UK Address for correspondence: Dr. Venkat Ramakrishnan, St. Andrew`s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford, UK. vrven@aol.com ABSTRACT KEY WORDS Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction has become the standard of care in the western world. Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue can be performed in a safe, reliable and predictable fashion. The ultimate goal is to reconstruct a symmetrical autologous tissue mound comparable in shape, size and volume to the opposite breast without compromising the oncology clearance. Abdominal tissue remains the Þ rst choice for breast reconstruction though other alternatives are rapidly evolving. Breast reconstruction, DIEP ß ap, GAP ß ap, Latissimus dorsi ß ap, methods of breast reconstruction, TUG ß ap B Breast reconstruction following mastectomy has become the standard of care in most of the centers worldwide. The National Institute for Clinical Excellence in the United Kingdom stipulates that every woman contemplating a mastectomy must be offered the choice of reconstruction. The breast cancer management is done by a multi-disciplinary team, which includes surgical oncologist, reconstructive surgeon, medical and radiation oncologist, radiologist, pathologist, specialist breast care nurses, physiotherapists and support group members. The plastic surgeon in the team plays a vital role in psychological rehabilitation of the patient by performing the post-mastectomy breast reconstruction. The interaction between the breast oncosurgeon, the oncologist and the reconstructive surgeon must begin, soon after the decision to offer a mastectomy is made. THE MANAGEMENT OF SKIN ENVELOPE The concept of sparing the breast skin in mastectomy, without compromising the clearance is well established now. [1,2] In skin sparing mastectomy (SSM), the oncosurgeon removes the breast and nipple-areola complex through a circumareolar incision, along with the biopsy scar. When properly performed, it does not increase the risk of local or regional recurrence. [1] Even in cases of wide local excision, the skin is spared unless it is directly involved by the tumor. The preservation of skin envelope and the native inframammary fold plays a major role in achieving excellent esthetic results in immediate reconstruction [Figure 1]. It allows us to offer the option of prophylactic mastectomy to young women with a very high risk of developing breast cancer, without any stigma of mutilation. The better understanding of pathophysiology in breast cancer has led to a conservative surgical approach, which in turn has led to more favorable reconstructive results. The aim of surgery is optimum conservation and utilization of the local tissue for reconstruction. OPTIONS FOR RECONSTRUCTION The reconstructive options are broadly classified into i) implant-based reconstruction, ii) autologous reconstruction and iii) a combination of both. Implant- S82 82 CMYK
2 Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction based reconstruction can be either an implant-only reconstruction or an expander-implant reconstruction. Autologous reconstruction involves either a pedicle or free flap reconstruction with or without a skin paddle. In certain situations, an implant and the autologous flap together are used in combination for breast reconstruction. The choice of procedure depends on the availability of local skin, size of the opposite breast, patient s expectations and surgeon s experience. The commonly used autologous tissue flaps for breast reconstruction are Latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap with implant, extended Latissimus dorsi flap without implant, pedicled Transverse Rectus Abdominis Muscle flap (TRAM), free TRAM (muscle-sparing) flap, Deep Inferior Epigastric artery Perforator flap (DIEP), Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator flap (SGAP), Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator (IGAP) flap, Transverse Upper Gracilis (TUG) flap. The alternative flaps, e.g. Ruben s flap (DCIA), Anterolateral Thigh (ALT) flap, Transverse Fascia Lata flap (TFL), are occasionally used for breast reconstruction. This review will limit itself to the discussion of microsurgical free flaps since the non-microsurgical methods for breast reconstruction are dealt elsewhere in this issue. FREE FLAPS FROM ABDOMEN FOR BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Free TRAM flap Holstrom, [3] in 1979, described the modern free TRAM as `free abdominoplasty flap for breast reconstruction. The free variants of lower abdominal flaps [Figures 5 and 6] have superior vascularity as compared to the pedicled TRAM flap. The DIEA perforators supplying the skin and fat over the lower abdomen arise immediately after the main DIEA vessel enters the muscle. The free flap version also allows the necessary `freedom in insetting of the flap. The lower abdominal skin and fat can be raised as a free flap based on either the deep (DIEA) or superficial inferior epigastric (SIEA) vessels. There are four variants of deep inferior epigastric artery based flaps, viz, the conventional TRAM flap (with substantial ipsilateral rectus abdominis muscle); muscle-sparing (minimal muscle sacrificed) free TRAM flap; deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (no muscle is sacrificed, DIEP) flap. The superficial epigastric artery based SIEA flap is raised without involving the rectus muscle and sheath. Based on the amount of rectus abdominis muscle spared, Nahabedian et al., [4] have classified the free TRAM into four types: MS0: full width (partial length) of the rectus abdominis muscle is sacrificed; MS-1: lateral segment is preserved; MS-2 refers to preservation of lateral and medial segment and MS-3 refers to preservation of the entire muscle equivalent to DIEP flap. In muscle-sparing technique (MS-1), the innervated lateral rectus muscle is left intact. The middle/ medial rectus muscle just enough to support the perforators with a narrow strip of anterior sheath is harvested with the flap. The remaining anterior rectus sheath is closed by direct suturing. The abdominal complications are significantly reduced with this technique compared to the pedicled TRAM flap as both the lateral innervated muscle and rectus sheath are preserved. [5] Kroll S [6] compared 268 patients in four groups (free TRAM, free bilateral TRAM, pedicle TRAM, pedicle bilateral TRAM). He reported no difference in hernia and bulge rate in any group (2.6 and 3.8%). However, the ability to do sit-up from supine position was best retained in free TRAM (63%), followed by pedicled TRAM (57%), free bilateral TRAM (46.2%) and worse in pedicled bilateral TRAM. Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap (DIEP) Koshima [7] was the first to split the rectus abdominis muscle and raise a skin and fat only flap from lower abdomen for oral and groin reconstruction. The flap was based on the single paraumbilical perforator. The concept and popularity of perforator-based flaps led to the evolution of (DIEP) by Robert Allen [8-10] in The flap harvesting involves identification of at least one reliable perforator and the tedious intramuscular dissection of DIE vessels. The average pedicle length is 8-15 cm and diameter is mm. Technique: [8,9,11] The medial and lateral rows of perforators are marked preoperatively by hand-held Doppler (8 MHz) in lying-down position. Perforators with loud signal and central location are marked. The DIE vessels contralateral to the mastectomy side are preferred as it allows simultaneous operating by two teams. The flap is marked depending on the laxity, as in abdominoplasty procedure. The inferior incision is made at the level of suprapubic crease and extended up to the anterior superior iliac Spine (ASIS) on either side. The superior incision is marked skirting the umbilicus and joining the two ASIS. The umbilicus is first dissected free S83 CMYK83
3 Ramakrishnan, et al. on its pedicle. The flap dissection starts from lateral to medial side above the deep fascia. The superficial inferior epigastric vessels are preserved if significant in size. [11] The dissection continues till the first row of reliable lateral/ medial perforators is found. A central perforator with the visible pulsations is considered as a reliable perforator [Figure 2]. Rectus sheath is opened with a cuff of sheath left around the perforator to facilitate further dissection. Rectus muscle fibers are split longitudinally to identify and dissect the course of the deep inferior epigastric artery running under the muscle. The bipolar cautery and micro ligaclips are used carefully to avoid any inadvertent trauma to the perforators. We regularly sprinkle topical lignocaine on the rectus muscle to avoid twitching during vessel dissection. The superior end of deep inferior epigastric vessels is divided above the perforator. The anterior rectus sheath is opened laterally to facilitate pedicle dissection till its origin from the external iliac vessels. Once the pedicle is dissected, flap from the opposite side is raised above the fascia. The outer contralateral flap (zone IV) is discarded and the area under the mastectomy skin flaps is de-epithelialized. The bulky medial flap is used for inferior and medial breast reconstruction, while the lateral part of the flap is placed high up towards the axilla. Superiorly, the flap is sutured to pectoral fascia. The flap can be folded onto itself to increase the projection inferiorly. A circular skin paddle is left to simulate the areola and for nipple reconstruction in future [Figure 3]. The thoracodorsal or internal mammary vessels are used as recipient vessels for anastomosis, depending on the surgeon s preference. [12,13] After the flap inset, anterior rectus sheath is repaired in two layers to minimize donor site complications and morbidity [Figure 4]. Umbilicus is relocated at a level above anterior superior iliac spine. The scarpa`s layer is sutured separately, while the abdominal skin is sutured in two layers. Abdominal wall is supported by a binder and the patient is nursed in `hip flexed position in the immediate postoperative period. The advantages of DIEP flap are as follows: The rectus muscle with its anterior sheath is left intact to maintain the strength and integrity of the abdominal wall. It significantly minimizes the abdominal wall complications [4,14] and donor site pain. [15] Blondeel [14] has compared the donor site morbidity in free TRAM (20 patients) and DIEP flap (18 patients). All his patients were subjected to clinical examination, physical exercises and isokinetic dynamometry preoperatively, 2 months and 1 year after the operation. Only 02/18 patients with DIEP presented with abdominal asymmetry, while 10/20 free TRAM patients had abdominal bulge and significant reduction in strength of flexion and rotation of trunk movements. [14] The reported hernia rates following the DIEP flap (0-4%) are significantly less than free TRAM flap (3-10%) and the pedicled TRAM flap (1-15.6%). [4] The disadvantages of DIEP flap include 1) a steep learning curve, 2) tedious intramuscular dissection, 3) flap elevation is time consuming with consequent morbidity and 4) unreliable position and size of the perforators. [16] Choice of recipient vessels: It depends on the surgeon s preference and timing of reconstruction. We prefer the thoracodorsal vessels as a recipient pedicle. Majority of our cases involve immediate reconstruction where the thoracodorsal vessels are already exposed during axillary dissection. Vascular anastomosis, re-exploration and revision are technically easier in axilla. The hematoma can be identified and managed easily in the axilla. The choice of thoracodorsal vessels may shift the flap inset laterally, causing lateral fullness and leading to an inferior esthetic outcome. This can be avoided by harvesting a longer pedicle. The internal mammary vessels are also used as recipient vessels. The internal mammary pedicle allows easier medial inset of the flap, leading to superior esthetic outcome in terms of shape and cleavage. [12] The arm and shoulder movements are free. The disadvantages include i) delicate thin-walled internal mammary vein, ii) difficult anastomosis due to respiratory movements, iii) risk of pneumothorax and iv) contour deformity due to rib cartilage excision. The perforators arising from the internal mammary vessels have also been used as recipient vessels. [13] Blondeel found the internal mammary artery (IMA) perforator (1-1.7 mm diameter) in the second intercostal space (30%) or in the third intercostal space in 70% of his cases. [13] The IMA perforator spares the main IMA for coronary bypass, saves time and tedious dissection and avoids contour deformity due to cartilage excision. In rare situations, sub-scapular vessels, circumflex scapular vessels, transverse cervical vessels and lateral thoracic vessels have been used as recipient vessels. Superficial inferior epigastric artery flap (SIEA) The lower abdominal wall is also supplied by the superficial inferior epigastric vessels. The SIEA flap for breast S84 84 CMYK
4 Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Figure 1: Right envelope mastectomy with immediate DIEP reconstruction Figure 2: DIEP perforator dissection Figure 4: Abdominal closure after bilateral DIEP ß ap Figure 5: Unilateral DIEP ßap for breast reconstruction - post op result Figure 3: DIEP ready for transfer; circular skin paddle simulates prospective areola Figure 6: Bilateral DIEP ßap for reconstruction post op result S85 CMYK85
5 Ramakrishnan, et al. reconstruction was first described by Grotting in [17] The SIEA artery arises from the femoral artery as a common trunk with superficial circumflex iliac artery (SCIA) in 48% and independently in 17% of the cases. The vessel arises below the inguinal ligament but ascends up, pierces the cribriform fascia and supplies the subcutaneous tissue and skin of the lower abdomen. Though the artery has accompanying vena comitantes, an additional prominent vein runs 3-4 cm medial to the artery. Advantages: There is no risk of abdominal hernia or bulge following the flap harvest as the vessels run above the rectus sheath. It also saves significant operating time as it does not involve any tedious intramuscular vessel dissection. Disadvantages: The disadvantages include small vessel caliber (1.4 mm), short pedicle length (7 cm (6-15 cm) and limited flap territory. The flap reliably supplies the zones I and II (ipsilateral hemiabdomen), but zones III and IV (contra lateral hemi abdomen) are not reliable. Also the skin territory is lower than DIE vessels; therefore, the flap has to be marked well below the umbilicus extending up to the pubic hairline. Blondeel [11] has emphasized the inverse relationship between superficial and deep inferior epigastric veins. The superficial inferior epigastric vessels are always dissected and preserved if more than 1.5 mm in diameter, irrespective of DIEP, SIEA or MS-1 TRAM. The SIE vein can be used for turbocharging in case of insufficient deep inferior epigastric vein (DIEV) drainage. In a series of 1,095 cases of breast reconstruction by Allen, [19] 79% (867) cases had DIEP flaps, while 21% (228) had prominent SIEA vessels leading to SIEA flaps. Abdominal free flaps in patients that have had prior abdominal surgery Scars directly increase the chance of skin and fat necrosis. Free TRAM/ DIEP flaps can be raised safely by tailoring the flaps in appendicectomy, hysterectomy, low cesarean section, laparoscopy, cholecystectomy and other laparoscopic scars [Figure 7]. The blood supply is significantly compromised with paramedian, colostomy, ileostomy and midline vertical scars. [16] In a case of midline vertical scar, we have raised one hemi-diep flap from each side and stacked the flaps by joining the vessels of one flap to the side branch of DIEP vessels of the other flap [Figure 8]. In doubtful cases, a CT angiogram should be arranged preoperatively to assess the status of perforators and the main vessels. It also allows the surgeon to straightway head for the reliable perforator, instead of exploring for a suitable perforator. We find color Doppler assessment more useful as it differentiates between artery and vein and also comments on the velocity of blood flow. We consider esthetic abdominoplasty as a contraindication for harvesting any lower abdominal flaps, although Hamdi et al [20] have recently published their successful experience of harvesting DIEP flaps on patients with previous abdominoplasty. FREE FLAPS FROM OTHER SITES In cases where abdominal tissue is not available for reconstruction, focus shifts on the gluteal or upper thigh region as donor sites. The superior gluteal artery perforator (SGAP, Robert Allen, 1994), inferior gluteal artery perforator (IGAP, Robert Allen, 1995) and transverse upper gracilis myocutaneous flap (TUG, Schoeller, Arnez ) [21] are the flaps of choice where abdominal tissue is not available. In a review of consecutive 31 GAP cases by Allen et al, [19] 20 (65%) were due to inadequate abdominal tissue, 6 (19%) were due to patients donor site choice, 2 (8%) were due to failed DIEP flap. Superior gluteal artery perforator (SGAP) flap [10] Superior gluteal artery emerges from the greater sciatic foramen. The perforator is marked at the junction of upper one-third and lower two-thirds on a line joining the posterior superior iliac spine to greater trochanter. The skin paddle is designed as an oblique ellipse of cm, keeping the marked perforator in center. The whole flap can be raised on single perforator and the donor site is closed primarily. The average pedicle length is 6-8 cm and diameter is mm. The SGAP flap donor site often needs revision in the form of surrounding liposuction or fat injection to conceal the contour deformity. Inferior gluteal artery perforator (IGAP) flap [19] Inferior gluteal artery is the terminal branch of internal iliac artery and emerges through greater sciatic foramen below the piriformis muscle, with sciatic nerve and posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh. The vessel runs a more oblique course and therefore provides a longer pedicle than the SGAP flap. The skin paddle is marked parallel to the gluteal fold. The postoperative contour deformity is less obvious than the SGAP flap. S86 86 CMYK
6 Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction The advantages of gluteal artery perforator flaps for breast reconstruction are 1) adequate autologous tissue to reconstruct a moderate- to large-sized breast, 2) adequatelength vascular pedicle through intramuscular dissection and 3) concealed donor site scar. The disadvantages includes steep learning curve, difficult haemostasis, postoperative contour deformity with unilateral flap, frequent donor site seroma, smaller skin paddle and the risk of sciatic nerve injury. [16] The flap is harvested in prone/ lateral position and inset is done in supine position, which increases the operating time. Patients with IGAP flap may complain about the painful donor site scar, particularly Figure 8: Stack ß aps; DIEV of second DIEP ß ap anastamosed to a branch of the DIE Vessels of main DIEP ß ap Figure 9: Bilateral TUG ß ap for small volume breast reconstruction. Figure 7: Diagram showing relationship of previous scars to abdominal ß aps F1; both TRAM flaps can be harvested, f2; only Left TRAM flap can be harvested, f3 ; if low then both ß aps can be harvested but if high then needs careful assessment Figure 10: Donor site scars for TUG ß ap S87 CMYK87
7 Ramakrishnan, et al. in sitting position. The absolute contraindications for gluteal artery flaps are active smoking and previous liposuction. [19] Transverse upper gracilis (TUG) flap Recently Arnez and Wechselberger, in 2004, [21] have simultaneously described the TUG flap for breast reconstruction [Figure 9]. The skin paddle (up to 12 cm width) is oriented transversely on the upper part of gracilis muscle just below the groin crease. Flap derives its blood supply through the ascending branch of medial circumflex femoral artery. The average pedicle length is 5-6 cm, with the vessel diameter around 1.6 mm. The donor site is closed primarily, resulting in a concomitant thigh lift. The advantages are 1) concealed scars [Figure 10], 2) negligible donor site functional morbidity; 3) the skin paddle can be refashioned to reconstruct the nipple at first stage. The disadvantages are 1) shorter pedicle length, 2) inadequate tissue bulk to reconstruct a large-sized breast [TUG flap is more suitable for a small- to medium-sized breast reconstruction, though we have used bilateral TUG flaps to reconstruct a single large-sized breast], 3) wound dehiscence, 4) lymphorrhea and 5) risk of lymphedema. Ruben flap Peter Paul Ruben, a 16 th century painter, depicted the fat folds over iliac crest prominently in all his female forms. A cutaneous perforator from the ascending branch of deep circumflex iliac artery (DCIA) supplies this redundant fat fold. Ruben flap is described for breast reconstruction by Hartrampf [22] in The flap pedicle is 5-6 cm in length and 2.5 mm in diameter. The disadvantages of Ruben flap are steep learning curve, difficult dissection and nerve paresthesias. The improper reinsertion of donor site muscles on the iliac crest can cause postoperative hernia. Postoperative care and monitoring is similar to any other free flap. Patients are managed in a special microsurgery bay under the care of specialist nurses. Every breast reconstruction patient needs two to three procedures over the next couple of months for procedures to get symmetry, viz, liposuction of flap, breast reduction/ mastopexy of the contra lateral breast and excision of dog-ears at the donor site. The final stage involves nipple reconstruction by local flaps in 3 months time. Tattooing for areola is done by our breast care specialist nurse in her outpatient clinic following the nipple reconstruction. REFERENCES 1. Singletary SE, Kroll SS. Skin sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction. Adv Surg 1996;30: Mosahebi A, Ramakrishnan V, Gittos M, Collier J. Aesthetic outcome of different techniques of reconstruction following nipple-areola preserving envelope mastectomy with immediate reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2007;119: Holstrom H. The free abdominoplasty ß ap and its use in breast reconstruction: An experimental study and clinical case report. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 1979;13: Nahabedian MY, Momen B, Galdino G, Manson PN. Breast reconstruction with the free TRAM or DIEP: Patient selection, choice of ß ap and outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110: Kroll SS, Evans GR, Reece GP, Miller MJ, Robb GL, Baldwin BJ, et al. Comparison of resource costs of free and conventional TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1996;98: Kroll SS, Schusterman MA, Reece GP, Miller MJ, Robb G, Evans G. Abdominal wall strength, bulging and hernia after TRAM ß ap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1995;96: Koshima I, Moriguchi T, Tanaka H, Umeda N. Free thin paraumblical perforator based ß ap. Ann Plast Surg 1992;29: Granzow JW, Levine JL, Chiu ES, Allen RJ. Breast reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric perforator ßap, history and an update on current technique. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2006;59: Allen RJ, Treece P. Deep inferior epigastric perforator ßap for breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 1994;32: Allen RJ, Tucker C Jr. Superior gluteal artery perforator free ßap for breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1995;95: Blondeel PN. One hundred free DIEP ßap breast reconstructions: A personal experience. Br J Plast Surg 1999;52: Ninkovic M, Anderl H, Hefel L, Schwabegger A, Wechselberger G. Internal mammary vessels: A reliable recipient system for free ß aps in breast reconstruction. Br J Plast Surg 1995;48: Hamdi M, Blondeel P, Van Landuyt K, Monstrey S. Algorithm in choosing recipient vessels for perforator free ß ap in breast reconstruction: The role of the internal mammary perforators. Br J Plast Surg 2004;57: Blondeel PN, Vanderstraeten CG, Monstrey SJ, Van Landuyt K, Tonnard P, Lysens R, et al. The donor site morbidity for free DIEP ßap and free TRAM ßaps for breast reconstruction. Br J Plast Surg 1997;50: Kroll S, Sharma S, Koutz C, Langstein HN, Evans GR, Robb GL, et al. Postoperative morphine requirements of free TRAM and DIEP ß aps. Plast Reconstr Surg 2001;107: Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Board Review - McGraw Hill Medical Publications: ISBN Grotting JC. The free abdominoplasty ß ap for immediate breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 1991;27: Allen RJ, Levine JL, Granzow JW. The in-the-crease inferior gluteal artery perforator ß ap for breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006;118: S88 88 CMYK
8 Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction 19. Granzow JW, Levine JL, Chiu ES, Allen RJ. Breast Reconstruction with gluteal artery perforator ß aps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2006;59: De Ferne B, van Landuyt K, Hamdi M, Blondeel P, Roche N, Voet D, et al. Free DIEAP and SGAP falp breast reconstruction after abdominal / gluteal liposuction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2006;59: Wechselberger G, Schoeller T. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis free ß ap: A valuable tissue source in autologous breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004;114: Hartrampf CR Jr, Noel RT, Drazan L, Elliot FL, Bennett GK, Beegle PH. Rubens fat pad for breast reconstruction: A peri iliac soft tissue free ß ap. Plast Reconstr Surg 1994;93: Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None declared. S89 CMYK89
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
The most common type of breast reconstruction
 BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
Few would deny that lower abdominal tissue BREAST. An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction.
 BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps
 Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps
 Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction
 The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
INTRODUCTION. Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2, Kazunori Yasumura 1, Taro Mikami 2, Shinji Kobayashi 3, Jiro Maegawa 2. Idea and Innovation
 Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014). Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health?
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction BREAST
 BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography
 BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
Michael A. Howard a, Babak Mehrara b, * REVIEW. Introduction
 International Journal of Surgery (2005) 3, 53e60 www.int-journal-surgery.com REVIEW Emerging trends in microsurgical breast reconstruction: Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) and the superior
International Journal of Surgery (2005) 3, 53e60 www.int-journal-surgery.com REVIEW Emerging trends in microsurgical breast reconstruction: Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) and the superior
A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction
 Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
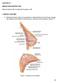 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Achieving ideal donor site aesthetics with autologous breast reconstruction
 Review Article Achieving ideal donor site aesthetics with autologous breast reconstruction Maurice Y. Nahabedian Department of Plastic Surgery, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20007, USA Correspondence
Review Article Achieving ideal donor site aesthetics with autologous breast reconstruction Maurice Y. Nahabedian Department of Plastic Surgery, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20007, USA Correspondence
Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan. Introduction
 Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction
 Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
Anterolateral Thigh Flap for Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction
 Anterolateral Thigh Flap for Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Fu-chan Wei, M.D., Sinikka Suominen, M.D., Ph.D., Ming-huei Cheng, M.D., Naci Celik, M.D., and Yung-lung Lai, M.D. Taipei, Taiwan Most
Anterolateral Thigh Flap for Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Fu-chan Wei, M.D., Sinikka Suominen, M.D., Ph.D., Ming-huei Cheng, M.D., Naci Celik, M.D., and Yung-lung Lai, M.D. Taipei, Taiwan Most
How many procedures to make a breast?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap and its Relevant Vascular Anatomy in Korean Women
 The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap and its Relevant Vascular Anatomy in Korean Women Original Article Byung Jun Kim, Jun Ho Choi, Tae Hoon Kim, Ung Sik Jin, Kyung Won Minn, Hak Chang Department
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap and its Relevant Vascular Anatomy in Korean Women Original Article Byung Jun Kim, Jun Ho Choi, Tae Hoon Kim, Ung Sik Jin, Kyung Won Minn, Hak Chang Department
Soft tissue reconstruction with the superior gluteal artery perforator f lap
 Clin Plastic Surg 30 (2003) 371 382 Soft tissue reconstruction with the superior gluteal artery perforator f lap Phillip N. Blondeel, MD, PhD*, Koenraad Van Landuyt, MD, Moustapha Hamdi, MD, Stan J. Monstrey,
Clin Plastic Surg 30 (2003) 371 382 Soft tissue reconstruction with the superior gluteal artery perforator f lap Phillip N. Blondeel, MD, PhD*, Koenraad Van Landuyt, MD, Moustapha Hamdi, MD, Stan J. Monstrey,
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Flaps vs Grafts. Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC
 Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
4/30/2010. Options for abdominal wall reconstruction. Scott L. Hansen, MD
 Components Separation Scott L. Hansen, MD University of California, San Francisco Chief, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Overview Options for abdominal wall reconstruction
Components Separation Scott L. Hansen, MD University of California, San Francisco Chief, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Overview Options for abdominal wall reconstruction
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY RECTUS ABDOMINIS FLAP FOR HEAD & NECK RECONSTRUCTION Patrik Pipkorn, Brian Nussenbaum The rectus abdominis flap is based on the deep inferior
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY RECTUS ABDOMINIS FLAP FOR HEAD & NECK RECONSTRUCTION Patrik Pipkorn, Brian Nussenbaum The rectus abdominis flap is based on the deep inferior
Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient
 CASE REPORT Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient Han-Tsung Liao, MD, Ming-Huei Cheng, MD, Betul Gozel Ulusal,
CASE REPORT Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient Han-Tsung Liao, MD, Ming-Huei Cheng, MD, Betul Gozel Ulusal,
Breast cancer has become so
 The three stages of breast reconstruction BY FORTUNE C IWUAGWU Breast cancer has become so common that most people reading this article will know someone (either professionally or personally) who has been
The three stages of breast reconstruction BY FORTUNE C IWUAGWU Breast cancer has become so common that most people reading this article will know someone (either professionally or personally) who has been
Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast reconstruction: an analysis of perioperative factors and complications
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY ANATOMY. is normally accompanied by two venae comitantes.
 Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY This is a composite flap that is situated over the scapula with various incisional arrangements. It can be harvested as a skin and subcutaneous tissue flap,
Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY This is a composite flap that is situated over the scapula with various incisional arrangements. It can be harvested as a skin and subcutaneous tissue flap,
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni
 SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
Skin sparing mastectomy: Technique and suggested methods of reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document
 breastreconstructioncanada.ca Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document By Dr. Nicolas Guay Dr. Haemi Lee STANDARDIZED BREAST RECONSTRUCTION PATIENT INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary...
breastreconstructioncanada.ca Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document By Dr. Nicolas Guay Dr. Haemi Lee STANDARDIZED BREAST RECONSTRUCTION PATIENT INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary...
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty?
 Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
National Mastectomy & Breast Reconstruction Audit Datasheet - Mastectomy +/- Immediate Reconstruction
 Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis
 Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2012) 65, 1474e1480 REVIEW Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis
Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2012) 65, 1474e1480 REVIEW Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
Reconstruction with autologous tissue remains a
 Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Lipoabdominoplasty: Liposuction with Reduced Undermining and Traditional Abdominal Skin Flap Resection
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 30:1 8, 2006 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-004-0084-7 Original Articles Lipoabdominoplasty: Liposuction with Reduced Undermining and Traditional Abdominal Skin Flap Resection Ruth Graf, M.D.,
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 30:1 8, 2006 DOI: 10.1007/s00266-004-0084-7 Original Articles Lipoabdominoplasty: Liposuction with Reduced Undermining and Traditional Abdominal Skin Flap Resection Ruth Graf, M.D.,
Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction
 893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
FREE DIEP-FLAP RECONSTRUCTION OF TUMOUR RELATED DEFECTS IN HEAD AND NECK
 JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2008, 59, Suppl 5, 59 67 www.jpp.krakow.pl H. LEONHARDT 1, R. MAI 1, W. PRADEL 1, J. MARKWARDT 1, T. PINZER 2, A. SPASSOV 3, G. LAUER 1 FREE DIEP-FLAP RECONSTRUCTION
JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2008, 59, Suppl 5, 59 67 www.jpp.krakow.pl H. LEONHARDT 1, R. MAI 1, W. PRADEL 1, J. MARKWARDT 1, T. PINZER 2, A. SPASSOV 3, G. LAUER 1 FREE DIEP-FLAP RECONSTRUCTION
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION/REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF IMPLANTS
 Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon
Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
Novel Interpositional Vein Grafting for Pedicle Extension of Island Pedicle Flaps
 e50 Case Report THIEME Novel Interpositional Vein Grafting for Pedicle Extension of Island Pedicle Flaps Shuhei Yoshida, MD 1 Isao Koshima, MD 1 Shogo Nagamatsu, MD 2 Kazunori Yokota, MD 2 Shuji Yamashita,
e50 Case Report THIEME Novel Interpositional Vein Grafting for Pedicle Extension of Island Pedicle Flaps Shuhei Yoshida, MD 1 Isao Koshima, MD 1 Shogo Nagamatsu, MD 2 Kazunori Yokota, MD 2 Shuji Yamashita,
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices
 20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY. Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services. Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow
 Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
SET - SNOMED Plastic Surgery (Aus.)
 NAME: Trainee Logbooks RACS ID: 18214 NOMINATED SUPERVISOR(S): Supervisor Logbooks ALTERNATE SUPERVISOR(S): Fellow Logbooks HOSPITAL(S): Flinders Medical Centre ROTATION PERIOD: T2 216 SET LEVEL: Year
NAME: Trainee Logbooks RACS ID: 18214 NOMINATED SUPERVISOR(S): Supervisor Logbooks ALTERNATE SUPERVISOR(S): Fellow Logbooks HOSPITAL(S): Flinders Medical Centre ROTATION PERIOD: T2 216 SET LEVEL: Year
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
Aesthetic Subunits of the Breast
 Aesthetic Subunits of the Breast Scott L. Spear, M.D., and Steven P. Davison, D.D.S., M.D. Washington, D.C. Surgery for breast cancer has traditionally addressed the breast as if it were a geometric circle
Aesthetic Subunits of the Breast Scott L. Spear, M.D., and Steven P. Davison, D.D.S., M.D. Washington, D.C. Surgery for breast cancer has traditionally addressed the breast as if it were a geometric circle
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
