Radiological and Pathological Characteristics of Mandibular Cystic Lesion A Review
|
|
|
- Shanon Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
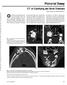
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. X (September). 2016), PP Radiological and Pathological Characteristics of Mandibular Cystic Lesion A Review Janardhanam Dineshshankar, M.D.S 1, Sahuthullah Yasmeenahamed, M.D.S 2, Nalliappan Ganapathy M.D.S 3, Shivakumar Sivaraman, M.D.S 4, 1 Reader, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Vivekanandha Dental College for Women 2 Reader, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Vivekanandha Dental College for Women 3 Professor & Head, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Vivekanandha Dental College for Women 4 Senior Lecturer, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Vivekanandha Dental College for Women Abstract: Many lesions that occur in the jaw have a similar radiological appearance and it is often difficult to differentiate among them. Cysts that are present in the mandible are commonly noted on head and neck imaging and present a diagnostic dilemma. These lesions are often identified as incidental lesions by the radiologist on imaging performed for different reasons. Collaborative interaction between the dentists, oral surgeon, radiologist and oral pathologist is essential for the appropriate evaluation, imaging, and treatment of cystic appearing lesions of the mandible. Keywords: Cyst of mandible, imaging, CT, MRI I. Introduction Even after development of many modern imaging modalities, still remains the most important mode of investigation for the evaluation of jaw lesions. A variety of cystic lesions occur within the mandible 1. Although the radiologic findings in some mandibular lesions may be nonspecific, there are often clues for histologic diagnosis within the anatomy surrounding each lesion. In many cases, correct diagnosis is achieved by the clinical history alone 2. Precise radiologic evaluation of a lesion can have a significant impact on diagnosis and subsequent patient treatment 1. In this article, we will review the process of odontogenesis, radiologic illustration and pathologic findings in various cystic lesions of mandible to aid in narrowing the differential diagnosis. II. Odontogenesis Odontogenesis is development of teeth: odont- tooth and genesis-origin. The first brachial arch forms the mandible during the fourth week of embryologic development by means of fusion of the bilateral mandibular prominences 3. These structures eventually give rise to the teeth through a process called odontogenesis. Each tooth develops from ectodermal cells that develop into ameloblasts and other outer tooth regions, and ectomesenchymal cells that form the odontoblasts and dental papillae. The process begins at the crown of the tooth and continues toward the root 4. Three stages of odontogenesis have been described, including the bud, cap, and bell 3. During the sixth week of intrauterine life, mesenchymal cells thicken and produce the primary dental lamina. These cells start to invaginate to form a tooth bud with an overlying cap. By the 20th week of intrauterine life, the tooth bud appears bell shaped with active odontoblastic and ameloblastic cells. Ameloblastic cells produce enamel, whereas odontoblastic cells produce the dentin. The production of enamel requires the complete formation of the dentin. These processes are completed during the crown stage, as the tooth enters the final stage of development 4. Before the completion of odontogenesis, both the primary and secondary dental lamina disappears. Any remnants of these embryonic cells may give rise to cystic lesions as well as benign and malignant lesions later in the life. The remaining ectomesenchymal cells surrounding a tooth create the dental sac, which form the periodontal ligament and cementum. A thin fibrous periodontal ligament attaches the cementum of each tooth to the surrounding alveolar bone (lamina dura) 3. This highly vascularised connective tissue allows limited motion of each tooth during mastication and also serves to provide sensation. Then the teeth migrate into the oral cavity, and the developmental process is complete 4. But few remnant cells may persist even after the degeneration of dental lamina. These remnants may be seen in the connective tissue of gingival or in the jaw bones and are named as cell rest of serres. These cell rests may proliferate under certain conditions giving rise to odontogenic cyst and odontogenic tumours. Odontogenic cyst occurring in the mandible is common so knowing the process of odontogenesis will give a clear cut idea of its cause 3, 4. DOI: / Page
2 III. Cystic Lesions Cysts commonly occur in the mandible and appear as unilocular or multilocular radiolucencies on dental radiographs. Cystic lesions within the mandible can cause bony remodeling that can weaken the bone, leading to functional changes and predisposing the patient to infection and pathologic fracture 5. The relationship of the cyst to adjacent structures is important, which includes features such as unerupted teeth, tooth displacement, root resorption, and canal displacement 5. A true mandibular cyst forms when developmental or inflammatory factors stimulate proliferation of epithelial cells surrounding a tooth. As the cells grow, their nutrient supply to the central cells is removed and vascular connective tissue become necrotic. Subsequently, a sac or an epithelium-lined cavity is formed 6. Mandibular cysts appear radiologically as well-defined lucent areas within the bone. Although sclerotic rim is present in most cysts, because of severe underlying inflammation there will be decrease in the degree of sclerosis 7. Classifications of cysts (TABLE: 1) done here is by its prevalence and with most of cysts in the mandibular jaw arising from odontogenic sources. However, cysts may also arise from prior trauma or surgery. The wide variation in the frequency with which various cystic lesions occurs often helps narrow the differential diagnosis 5. Here we will be discussing about the cyst that occurs commonly in the mandible and few other mandibular cysts are excluded because it s very less prevalence in the mandible. Table 1: According to the Prevalence, Cyst of Mandibular Lesions 6, 8 : Most common Fairly common Rare Radicular cyst Odontogenic keratocyst Calcifying odontogenic cyst Residual cyst Static bone cavity (Stafne cyst) Aneurysmal bone cyst Dentigerous cyst Solitary bone cyst Table 2: Radiographic investigations for cystic lesions 6, 7, 8 : Cystic Lesions Initial Radiographic Imaging Additional Radiologic Evaluation Radicular cyst/ Residual Cyst Dentigerous cyst Odontogenic Keratocyst Simple bone cyst (traumatic bone cyst) Static bone cavity (Stafne cyst) CT MRI PET/CT Extent of cyst, adjacent tooth involvement, preoperative planning Extent of cyst, adjacent NR; can tooth differentiate involvement, preoperative from planning ameloblastoma if lesions have overlapping Extent of disease, presence of daughter cysts None typically required If atypical features present, can aid in exclusion of other cystic lesions features Help differentiate from ameloblastoma; can suggest malignant transformation into SSC If atypical features present, can exclude simple bone cyst and ameloblastoma Staging of disease especially if SSC transformation Radicular Cyst It is also called as periapical cysts or apical periodontal cysts are the most common odontogenic cysts 7. Infection in the tooth leads to necrosis of the pulp cavity and it spreads to the tooth apex with ulterior development of a periapical granuloma or periapical abscess. These may later give rise to a radicular cyst 8. It is DOI: / Page
3 arise from epithelial cell rests of periodontal ligament, which are accelerated by the inflammatory mechanism. Most often, they are asymptomatic. It may be seen in all age groups, but, more frequently between 30 and 60 years of age which are often associated with a non-vital tooth. Radiographic features are straightforward and have a well-defined unilocular periapical lesion, with sclerotic borders in close proximity to the apical portion of the root in non-vital tooth (fig 1). No contrast material enhancement is seen on CT or MRI. With latero-dental location, CT or CBCT is very helpful for the correct diagnosis of atypical cases (fig: 2) 9. Almost all radicular cysts are lined totally or partially by stratified squamous epithelium. It may be discontinuous and range of about 6 20 cell layers thick. The epithelial lining may be proliferative and show arcading with an intense associated inflammatory process but as the cyst enlarges the lining becomes quiescent and fairly regular with a certain degree of differentiation to resemble a simple stratified squamous epithelium ( Fig: 3). 10 Fig 1: Arrow shows well defined radiolucency seen at the apex of 36 which is more than 3cm suggestive of radicular cyst Fig 2: CT axial section showing well defined radiolucency involving maxilla Fig 3: It shows proliferation of epithelium, arcading pattern with an intense associated inflammatory cells are seen Residual Cyst Residual cysts are periapical cysts retained in the jaw after surgical removal of a non-vital tooth. Residual cysts are common and have similar clinical and radiological features as that of radicular cyst. It is always associated with a missing tooth. Size of residual cysts is usually less than 1 cm. Sometimes, enlarging cysts may lead to displacement of the adjacent teeth, as well as bone expansion 9. The histopathological features DOI: / Page
4 of the residual cyst are similar to those described above for conventional radicular cyst. Nevertheless the cause of the cyst has been removed; it may gradually become less inflamed so that eventually the cyst wall is composed of uninflamed collagenous fibrous tissue. The epithelial lining may be thin and regular and indistinguishable from a developmental cyst such as a dentigerous cyst or lateral periodontal cyst. 10 Dentigerous Cyst It is the second most common odontogenic mandibular cysts and the most common odontogenic developmental cysts. They are mainly seen in patients with years of age. The fluid accumulates between remnants of enamel organ and the tooth crown of the unerupted tooth (most commonly in the lower third molar) 1. Imaging features are characteristic which include a well-defined unilocular radiolucent lesion with sclerotic borders around an unerupted tooth crown. Small follicular cysts may be tough to differentiate from a normal dental follicle (fig 3). It has been suggested that if the distance between the dental sac and the crown is more than 3 mm, the diagnosis of a follicular cyst should be made. It is mostly attached to the neck of the displaced and the unerupted tooth, and the crown commonly protrudes into the cyst while the roots remain outside the lesion (fig 4). It may become very large and may remodel the mandible, predisposing the patient to the infections and even pathological fracture 11, 12. They may thin the cortical layer of the mandible and may be seen around the mandibular canal, which makes surgical excision delicate 13. CT and CBCT are used to determine the relationship of the unerupted tooth with the cyst to the mandibular canal and maxillary sinus prior to surgery and to assess cyst contents and the integrity of the cortical rim 14, 15 (fig: 5). MRI is indicated only in atypical cases to differentiate follicular cysts from other cystic mandibular lesions 12. It will often be found accidentally in patients undergoing head and neck MRI for other reason. MRI findings include variable signal intensity on T1 due to variable protein content seen within the cyst, high signal on T2 and sometimes slight enhancement of the thin cyst wall. In spite most cysts show no significant FDG uptake on PET/CT and mild tracer uptake may be present during the infection or inflammation 16. On histological examination it usually shows a thin fibrous cyst wall which is derived from the dental follicle and consists of young fibroblasts widely separated by stroma and ground substance. Characteristically epithelial lining is of reduced enamel epithelium and it is non-keratinised in nature. It consists of 2 4 cell layers of flat or cuboidal cells (Fig: 6). 10 Fig 4: Yellow arrow indicates tooth follicle which is less than 3mm. Red arrow indicates well defined radiolucency arising from neck of impacted premolar which is more than 1.5 cm suggestive of dentigerous cyst Fig: 5. CT coronal section showing cystic lesion extending into maxillary sinus Fig 6: shows epithelial lining of 2 4 cell layers of flat or cuboidal cells with a fibrous cyst wall and young fibroblasts DOI: / Page
5 Odontogenic Keratocyst It is also called keratocystic odontogenic tumours (KCOTs) as per WHO 2005, but still there is controversies going on regarding its name so here we are using the name as Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC). OKC are most commonly seen in the body or ramus of the mandible. Mainly, OKCs possess destructive potential, and have a high recurrence rate after resection 7. It develops from the dental lamina, which is found in the jaw and overlying alveolar mucosa and lined by stratified keratinizing squamous epithelium. Thus, the cysts can be found throughout periapical or primordial regions 17. Unlike follicular cysts, OKCs can expand cortical bone and erode the cortex with scalloping borders (fig 7). The malignant transformation of these lesions is rare. The lesion is multiloculated, usually with daughter cysts that extend to the surrounding bone. The adjacent teeth resorption is very rare; nevertheless, when this is the case, differentiation from ameloblastoma may be very difficult on CT, OPT or CBCT 18, 19. It contain a cheese-like material and typically show soft tissue density (up to 50 HU) on CT (Fig: 8), while on MRI, because of the variable protein content, a low to high signal intensity can be seen on T1, a heterogeneous signal on T2. T2 relaxation times in OKC have been reported to be shorter than in ameloblastoma 19, 20. Weak enhancement of the uniformly thin and the regular cyst walls is noted after injection of gadolinium chelates, it is helpful from differentiating from ameloblastoma 21, 22. Young patient with Multiple OKCs should raise the possibility of basal cell nevus syndrome. Associated findings with this autosomal dominant disorder include frontal bossing, prognathism, midface hypoplasia, mental retardation, and calcification of the falx cerebri 20, 23, 24. Histologically it shows the cysts which are lined by a regular, narrow, keratinised, and stratified squamous epithelium. Thickness of the epithelium is about 5 8 cell layers thick and there will be absence of rete ridges. Mostly parakeratinisation is present in (80 90%) of cases, but sometimes orthokeratinisation (8-13%) and even combination para and orthokeratinisation (1%) is also seen. Usually it is a well-defined, often palisaded basal layer consisting of columnar or cuboidal cells or a mixture of both (Fig: 9). 21, 25 Fig 7: Multiple multilocular radiolucencies seen in relation to impacted teeth with scalloped borders Fig: 8. CT coronal section reveals at the level of the symphysis region, the lesion is approximately 7 x 3 cm in size, roughly oval in shape, well defined periphery with thinning of cortex. Fig 9: Shows stratified, squamous epithelium of 5 8 cell layers and palisaded, basal layer is seen DOI: / Page
6 Simple bone cyst It is also known as traumatic bone cyst, solitary bone cyst; haemorrhagic cyst or idiopathic bone cavity is filled with serous or haemorrhagic fluid and which is characterised by the absence of an epithelial lining 26, 27. Simple bone cyst (SBC) is not a true cyst but preferably a pseudocyst. SBC of the mandible usually occur secondary to trauma, mainly after tooth extraction with subsequent intramedullary haemorrhage 27, 28, 29. It is commonly present before the age of 20, and usually occurs in female. Of about 75 % of cases, they are seen in the marrow of the posterior mandible. Most lesions are found incidentally on dental radiographs and they are asymptomatic in nature 30. It occurs in close proximity to a vital tooth and bone swelling is usually very rare unless there is any associated infection 18. Surgical exploration may be needed in selected cases to exclude from other unilocular radiolucent lesions like keratocysts 29, 31. Imaging features suggest that it will appear as welldefined unilocular radiolucent lesions that may vary in size. Sometimes rarely, poorly defined borders can be seen 32. Extension to the cortical bone is usually rare and there is no tooth displacement. The superior margins are irregular and scalloped around roots. CT and MRI can give information on the haemorrhagic content but the density or signal intensity may vary depending on the age of the haemorrhage 29, 31. On MRI, SBC displays a T1 have a homogeneous intermediate signal, whereas T2 have a homogeneous high signal and no enhancement after injection of intravenous contrast media 15, 30. Histologically it shows loose vascular fibrous connective tissue membrane of variable thickness with the absence of epithelial lining, although fragments of fibrin with enmeshed red cells may be present. There will a presence of haemorrhage and haemosiderin pigments which are scattered, small multinucleate cells are often found. Few cyst walls, possibly a long standing case, are more 8, 32 densely fibrous. If adjacent bone is included it shows osteoclastic resorption on its inner surface. Stafne cyst It is also called static bone cavity or salivary gland inclusion defect. Stafne cyst is a pseudocyst arising from bone remodelling caused by the adjacent submandibular gland. Therefore, it does not have an epithelial lining 1, 33, 34. They are often incidental findings, as the patients are asymptomatic. It is more common in men than in women. The radiological features include ovoid, well-defined radiolucent cortical defects on the lingual surface of the posterior mandible measuring less than 2 cm 34, 35. Location is typical and the lesion contains fat or salivary gland tissue. An OPT is sufficient for diagnosis but sometimes CT or MRI can be performed in cases of 8, 36 atypical presentation to exclude it from an ameloblastoma or a traumatic bone cyst. IV. Conclusions Cystic Lesions of the mandible arise from both odontogenic and nonodontogenic sources with a variety of both cystic and solid appearances. Given the extensive range of pathologic features but similar imaging findings, familiarity with the embryologic characteristics and secondary imaging findings is crucial. Moreover, the prevalence and location in the mandible of a particular lesion of will helpful in differentiating it from other pathologic conditions. Imaging is not always expected to provide a specific diagnosis but should help narrow the differential diagnosis, thereby helping to guide patient treatment. References [1]. Dunfee BL, Sakai O, Pistey R, Gohel A. Radiologic and pathologic characteristics of benign and malignant lesions of the mandible. Radiographics 2006; 26: [2]. Preece JW. Dental radiographic techniques and normal roentgen anatomy. Semin Roentgenol 1971; 6: [3]. Avery JK, Steele PF. Essentials of oral histology and embryology: a clinical approach. St. Louis, MO: Mosby, 2000:53 70 [4]. Abrahams JJ, Rock R, Hayt MW. Embryology and anatomy of the jaw and dentition. In: Som PM, Curtin HD, eds. Head and neck imaging, 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby, 2003: [5]. Weber AL, Kaneda T, Scrivani SJ, Aziz S. Jaw: cysts, tumors and nontumorous lesions. In: Som PM, Curtin HD, eds. Head and neck imaging, 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby, 2003: [6]. Yoshiura K, Weber AL, Scrivani SJ. Cystic lesions of the mandible and maxilla. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 2003; 13(3): [7]. Neyaz Z, Gadodia A, Gamanagatti S, Mukhopadhyay S. Radiographical approach to jaw lesions. Singapore Med J, 2008; 49(2): [8]. Scholl RJ, Kellett HM, Neumann DP, Lurie AG. Cysts and cystic lesions of the mandible: clinical and radiologic-histopathologic review. Radiographics, 1999; 19: [9]. Eversole LR, Rovin S. Differential radiographic diagnosis of lesions of the jawbones. Radiology 1972; 105: [10]. Shear M. Developmental odontogenic cysts. An update. J Oral Pathol Med 1994; 23: [11]. Freitas DQ, Tempest LM, Sicoli E, Lopes-Neto FC. Bilateral dentigerous cysts: review of the literature and report of an unusual case. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2006; 35: [12]. Edamatsu M, Kumamoto H, Ooya K, Echigo S: Apoptosis related factors in the epithelial components of dental follicles and dentigerous cysts associated with impacted third molars of the mandible. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontics, 2005; 99: [13]. Stathopoulos P, Mezitis M, Kappatos C, Titsinides S, Stylogianni E. Cysts and tumors associated with impacted third molars: is prophylactic removal justified? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69: [14]. Zhang LL, Yang R, Zhang L, Li W, MacDonald-Jankowski D, Poh CF. Dentigerous cyst: a retrospective clinicopathological analysis of 2082 dentigerous cysts in British Columbia, Canada. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2010; 39: DOI: / Page
7 [15]. Khambete N, Kumar R, Risbud M, Kale L, Sodhi S. Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases. Imaging Science in Dentistry. 2012; 42: [16]. MinamiM, Kaneda T, Ozawa K, Yamamoto H, Itai Y, OzawaM et al. Cystic lesions of the maxillomandibular region: MR imaging distinction of odontogenic keratocysts and ameloblastomas from other cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996; 166: [17]. Nohl FSA, Gulabivala K. Odontogenic keratocyst as periradicular radiolucency in the anterior mandible. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1996; 81: [18]. Theodorou SJ, Theodorou DJ, Sartoris DJ. Imaging characteristics of neoplasms and other lesions of the jawbones. Part 1. Odontogenic tumors and tumor like lesions. Clin Imaging 2007; 31: [19]. Boffano P, Ruga E, Gallesio C. Keratocystic odontogenic tumor (odontogenic keratocyst): preliminary retrospective review of epidemiologic, clinical, and radiologic features of 261 lesions from University of Turin. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010;68(12): [20]. Lindeboom JA, Kroon FH, de Vires J, van den Akker HP. Multiple recurrent and de novo odontogenic keratocysts associated with oral-facial-digital syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2003; 95: [21]. Ali M, Baughman RA. Maxillary odontogenic keratocyst. J Am Dent Assoc : [22]. Giuliani M, Grossi GB, Lajolo C, Biscegila M, Herb KE: Conservative management of a large odontogenic keratocyst: Report of a case and review of literature. Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, 2006; 64(2): [23]. Gonzalez-Alva P, Tanaka A, Oku Y, Yoshizawa D, Itoh S, Sakashita H, Idle F, Tajima Y, Kusama K: Keratocystic odontogenic Tumor: A retrospective study of 183 cases. Journal Of Oral Science, 2008; 50 (2): [24]. Shear M: Odontogenic keratocysts: Clinical Features: Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America, 2003; 15(3): [25]. Tolstunov L, Treasure T: Surgical treatment algorithm for Odontogenic Keratocyst: Combined treatment of Odontogenic Keratocyst and mandibular defect with marsupialization, enucleation, iliac crest bone grafts and dental implants. Journal of Oral and maxillofacial Surgery, 2008;66: [26]. Donkor P, Punnia-Moorthy A. Biochemical analysis of simple bone cyst fluid: report of a case. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1994; 23: [27]. Suei Y, Taguchi A, Kurabayashi T, Kobayashi F, Nojiri M, Tanimoto K. Simple bone cyst: investigation on the presence of gas in the cavity using computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1998; 86: [28]. Suei Y, Taguchi A, Tanimoto K. Simple bone cyst of the jaws: evaluation of treatment outcome by review of 132 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65: [29]. Narang R, Jarrett JH. Large traumatic bone cyst of the mandible. J Oral Surg 1980; 38: [30]. Ferreira Júnior FO, Damante JH, Lauris JR. Simple bone cyst versus odontogenic keratocyst: differential diagnosis by digitized panoramic. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2004; 33: [31]. Matsumura S, Murakami S, Kakimoto N, Furukawa S, Kishino M, Takeshi I et al. Histologic and radiographic findings of the simple bone cyst. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998; 85: [32]. Lokiec F, Wientroub S. Simple bone cyst: etiology, classification, pathology, and treatment modalities. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1998; 7: [33]. Segev Y, Puterman M, Bodner L. Stafne bone cavity - Magnetic resonance imaging Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2006;11: [34]. Katz J, Chaushu G, Rotstein I. Stafne s Bone Cavity in the Anterior Mandible: A Possible Diagnostic Challenge Journal Of Endodontics 2001;27: [35]. Ariji E, Fujiwara N, Tabata O, et al. Stafne s bone cavity: Classification based on outline and content determined by computer tomography Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1993;76: [36]. Shields ED. Technical note: Stafne static mandibular bone defect further expression on the buccal aspect of the ramus. Am J Phys Anthropol 2000; 111: DOI: / Page
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report
 Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
06 Tooth Development and Eruption
 + 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
+ 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
Oral Embryology and Histology
 Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview
 Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Chapter 5. Developmental Disorders. Copyright 2014, 2009, 2004, 2000, 1996, 1992 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc 1
 Chapter 5 Developmental Disorders Copyright 2014, 2009, 2004, 2000, 1996, 1992 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc 1 Outline Ø Embryonic Development of the Face, Oral Cavity, and Teeth Ø Developmental
Chapter 5 Developmental Disorders Copyright 2014, 2009, 2004, 2000, 1996, 1992 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc 1 Outline Ø Embryonic Development of the Face, Oral Cavity, and Teeth Ø Developmental
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst
 A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst Onuki, M; Saito, A; Hosokawa, S; Oh Author(s) Hayakawa, H; Seta, S; Muramatsu, T; Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst Onuki, M; Saito, A; Hosokawa, S; Oh Author(s) Hayakawa, H; Seta, S; Muramatsu, T; Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Bilocular Stafne Bone Defect above And Below the Inferior Alveolar Canal Assessed by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report
 Original Research Bilocular Stafne Bone Defect above And Below the Inferior Alveolar Canal Assessed by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report Mahrokh Imanimoghaddam 1, Mansoore Darijani 2, Maryam
Original Research Bilocular Stafne Bone Defect above And Below the Inferior Alveolar Canal Assessed by Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report Mahrokh Imanimoghaddam 1, Mansoore Darijani 2, Maryam
Cystic and Cystic-Appearing Lesions of the Mandible: Review
 AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Cystic and Cystic-Appearing Lesions of the Mandible: Review Brooke Devenney-Cakir 1, Rathan M. Subramaniam 1,2, Susmitha M. Reddy 1, Heather Imsande
AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Cystic and Cystic-Appearing Lesions of the Mandible: Review Brooke Devenney-Cakir 1, Rathan M. Subramaniam 1,2, Susmitha M. Reddy 1, Heather Imsande
Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Radicular cyst associated with a primary first molar: A case report
 Case Report Radicular cyst associated with a primary first molar: A case report L. Toomarian 1, M. Moshref 2, M. Mirkarimi 3, A. Lotfi 4, M. Beheshti 5 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
Case Report Radicular cyst associated with a primary first molar: A case report L. Toomarian 1, M. Moshref 2, M. Mirkarimi 3, A. Lotfi 4, M. Beheshti 5 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Only 40% of the Story
 X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report
 Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report Aydin Ozkan 1, Gurkan Rasit Bayar 2, Hasan Ayberk Altug 2, Metin Sencimen
Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report Aydin Ozkan 1, Gurkan Rasit Bayar 2, Hasan Ayberk Altug 2, Metin Sencimen
Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.04.40.5.5 pissn 34-550 eissn 34-5930 Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.04.40.5.5 pissn 34-550 eissn 34-5930 Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic tumours: a study over a decade
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51408 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51408 Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51408 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51408 Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic
Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation
 European Journal of Therapeutics DOI: 10.5152/EurJTher.2018.496 Case Report Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation Arvind Karikal
European Journal of Therapeutics DOI: 10.5152/EurJTher.2018.496 Case Report Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation Arvind Karikal
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions
 Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted Canines: Report of Five Cases Sulabha AN, Sachin Deshpande, Sameer C
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Developmental Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect
 Developmental Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect The Importance of Clinical Evaluation Authored by Sako Ohanesian, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity 1 CE credit hour may be awarded A Peer-Reviewed
Developmental Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect The Importance of Clinical Evaluation Authored by Sako Ohanesian, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity 1 CE credit hour may be awarded A Peer-Reviewed
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
EXTENSIVE PERIAPICAL CYST IN THE MAXILLARY SINUS A CASE REPORT
 May, 2012 INTERNATIONAL DENTAL JOURNAL OF STUDENT S RESEARCH: CASE REPORT Article Code: IDJSR 0002 EXTENSIVE PERIAPICAL CYST IN THE MAXILLARY SINUS A CASE REPORT Authors Bouguezzi Adel, DDS, Resident 1
May, 2012 INTERNATIONAL DENTAL JOURNAL OF STUDENT S RESEARCH: CASE REPORT Article Code: IDJSR 0002 EXTENSIVE PERIAPICAL CYST IN THE MAXILLARY SINUS A CASE REPORT Authors Bouguezzi Adel, DDS, Resident 1
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM. Dr. Fatin Awartani
 ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Dentigerous Cyst in Children: A Case Report and Outline of Clinical Management for Pediatric and General Dentists
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1051 M Zakirulla et al CASE REPORT Dentigerous Cyst in Children: A Case Report and Outline of Clinical Management for Pediatric and General Dentists M Zakirulla, CM Yavagal, DN
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1051 M Zakirulla et al CASE REPORT Dentigerous Cyst in Children: A Case Report and Outline of Clinical Management for Pediatric and General Dentists M Zakirulla, CM Yavagal, DN
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Arun V Subramaniam et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2014; 5(3): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION
 A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
Tooth eruption and movement
 Tooth eruption and movement Dr. Krisztián Nagy Diphydont dentition Deciduous dentition primary dentition Diphydont dentition Permanent dentition secondary dentition Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions
Tooth eruption and movement Dr. Krisztián Nagy Diphydont dentition Deciduous dentition primary dentition Diphydont dentition Permanent dentition secondary dentition Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions
Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma
 Volume 2012, Article ID 729467, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/729467 Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Kellen Cristine Tjioe, 1 José Humberto Damante, 1 anddenisetostesoliveira 2, 3 1 Department
Volume 2012, Article ID 729467, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/729467 Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Kellen Cristine Tjioe, 1 José Humberto Damante, 1 anddenisetostesoliveira 2, 3 1 Department
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 18/May 05, 2014 Page 4859
 CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Imaging findings in a case of Gorlin-Goltz syndrome: a survey using advanced modalities
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2011; 41 : 171-5 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2011.41.4.171 Pegah ronoosh, Ali Reza Shakibafar*, Maneli Houshyar, Shima Nafarzade** Oral Radiology Department, Dental School,
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2011; 41 : 171-5 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2011.41.4.171 Pegah ronoosh, Ali Reza Shakibafar*, Maneli Houshyar, Shima Nafarzade** Oral Radiology Department, Dental School,
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
