A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF
|
|
|
- Judith Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 597. A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF THE IRIS WITH PIGMENTATION OF THE SCLERA AND PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA* BY V. CAVKA Beograd, Yugoslavia THE significance of pigmentation of the anterior segment of the eye in the development of glaucoma, especially in the area of the trabecula of the chamber angle, has been studied by many authors. von Hippel (1901) considered that glaucoma was due to obstruction of the chamber angle with pigment (Hanssen, 1923). Levinsohn (1908) microscopically established infiltration of the chamber angle by pigmented granules. The corneal pigment spindle (Krukenberg, 1899a, b), as well as pigmentations of the anterior surface of the iris, anterior capsule of the lens, zonular fibres, vitreous body, and chamber fluid, were all included in the analysis of the symptomatology of pigmentary glaucoma. Among the older authors, Koeppe (1916a, b), in his clinical and microscopic findings, stressed the importance of pigmentation in the anterior sector of the eye in the development of glaucoma. In cases in which the intra-ocular pressure was not yet increased, he used the term preglaucomatous condition. Other authors who contributed to the study of this problem include Kraupa (1917), Hanssen (1923), Koby (1927), and Vogt (1930). Sugar (1940) mentioned finding pigment in the chamber angle in a case of chronic glaucoma. Sugar and Barbour (1949) described the clinical picture of pigmentary glaucoma. Later authors included Calhoun (1953), Bick (1957), Malbran (1957), Scheie and Fleischhauer (1958), and van Beuningen (1959). It is thought that the following cases of heterochromia of the iris represent a certain link with pigmentary glaucoma: Case Reports Case 1, a man aged 53 years, from Osijek, was examined in November, Right Eye.-There was slight pigmentation on the posterior surface and in the centre of the cornea. The iris was greyish-green and there were spots of pigment scattered over the surface of the iris and tiny pigmented naevi. At the same time there was a slight ectropion of the uvea and visible spots of pigment on the anterior capsule of the lens. Other findings in the eye were normal (Fig. 1). FiG. I.--Case 1, aged 53 years, heterochromia of the iris with pigmentary glaucoma in both A ; eyes. * Received for publication September 1,
2 598 V. CA VKA The visual acuity was 6/15, and with + 1 D sph. it was 6/6. The intra-ocular pressure was 30 mm. Hg., and 38 mm. Hg. after provocation. Gonioscopy showed that the corneal angle was unobstructed, and the pigmentation of the trabecula was medium. Translumination showed no changes. Left Eye.-Apart from diffuse pigmentation of the sclera in the lower portions, there was a definite Krukenberg spindle on the posterior surface of the cornea with small dots. The chamber fluid showed no cellular elements. The iris was dark brown in colour with marked pigmented layers which, in the pupillary zone for a width of 2 to 3 mm., gave the impression of continuous pigmented granules, while in the other portions they presented as layers of pigment of the naevoid sponge-like form. The iris was consequently thicker than normal so that the normal structure was not visible at all on the surface. Biomicroscopically this marked pigmentation presented the type of intensively-developed hypertrophy not only of the pigmented granules but also of the pigment cells. There were numerous tiny pigmented dots on the anterior capsule of the lens. The papilla showed a glaucomatous excavation and a pigmented conus temporally. The visual acuity was 6/30, and with Dsph. it was 6/10. The field of vision was concentrically narrowed by 400 to 50 for red and white. The intra-ocular pressure was 50 mm. Hg. Gonioscopy showed intensive pigmentation of the trabecula with pigrnentation of Schwalbe's line. Translumination of the iris and ciliary body showed no changes. All clinical and laboratory findings were normal. Case 2, a child aged 3 years from Kragujevac, was examined in November, eyes were seen to b- of different colours (Fig. 2). The FiG. 2.-Case 2, aged 3 years, the darker right eye shows mela- - ~~~~~~~~~~notic changes of the sclera with hyperpigmentation of the iris. Right Eye.-There was pigmentation of the sclera in the temporal and upper portion, and tiny pigmented dots on the cornea from the centre of the cornea downwards in the form of a triangle with the point turned upwards. The iris was dark brown with intensive pigmentation all over the anterior surface. The pigmentation was partly granulated, forming insular foci with intensive hypertrophy of the pigment, so that the iris presented a thickened structure throughout its surface with no visible normal structure. On the anterior capsule of the lens there were numerous tiny pigmented spots. The fundus along the papillary edge showed a circumferential pigmented conus, while ophthalmoscopically the pigmented layer of the retina was overdeveloped with intensively pigmented fundus. The visual acuity was impossible to determine.
3 IRIS HETEROCHROMIA The intra-ocular pressure was 45 8 mm. Hg. Gonioscopy showed intensive pigmentation of the trabecula reaching Schwalbe's line. The chamber angle was uneven because of pigmented lumps. Translumination of the iris and ciliary body showed no changes. Left Eye.-The cornea showed no pigmentation. There were tiny pigmented dots in the iris, in some places scattered all over the surface. The anterior capsule of the lens showed dotted pigmentations but to a much lesser extent than in the right eye. There was no pigmented conus on the fundus. The visual acuity was impossible to determine. The intra-ocular pressure was 35-8 mm. Hg. As the child was very restless, it was not possible to perform a tonography. Gonioscopy showed less marked pigmentation of the trabecula, and the iris and ciliary body showed no changes. Iridencleisis of the right eye had already been performed; on this occasion a small section was taken for examination. Microscopically unusually intensive pigmentation of the iris tissue was established, individual cells showing intensive pigmentation (Fig. 3). FIG. 3.-Case 2, showing diffuse and granulated pigmentation of the iris with many pigmented cells in the stroma of the iris (haemalum x 300). Case 3, a man aged 50 years from Gospic, was examined in November, Right Eye.-There were melanotic changes of the sclera in the lower and temporal portion, and there was a Krukenberg corneal spindle. There were tiny dotted pigmentations on the anterior capsule of the lens. The iris showed dark pigmentation of the entire surface with slightly marked irregular pigmented granulations, and the structure as a whole was thickened. The normal structure of the iris surface had completely disappeared. There was a pigmented crescent on the temporal side of the disc. The visual acuity was 6/6. The intra-ocular pressure was 20 mm. Hg and 22 mm. Hg after provocation. Left Eye.-There was no Krukenberg spindle; the iris was light brown in colour. Other findings were normal. The visual acuity was 6/6. The intra-ocular pressure was 20 mm. Hg and 23 mm. Hg after provocation. Gonioscopy showed on the right marked dotted pigmentation of the trabecula up to Schwalbe's line. On the left side the pigmentation was poorly defined. 599
4 600 V. CA VKA Translumination of the iris and ciliary body showed nothing abnormal. Radiography of the head and spine was normal. Case 4, a man aged 49 years from Mitrovica, was examined in March, Right Eye.-There was a corneal Krukenberg spindle; the iris was greyish green, with a little fine pigment on the surface of the iris, and the iris structure was normal. Other findings were normal. The visual acuity was 6/6. The intra-ocular pressure was 18-5 mm. Hg and 23 mm. Hg after provocation. Gonioscopy showed slight trabecular pigmentation. Left Eye.-The Krukenberg spindle was more marked than in the right eye. The chamber fluid was normal. The iris showed intense pigmented hypertrophy in the form of sponge-like confluent pigmentation, and there was also hypertrophy of the pigment of the granular type so that the surface of the iris had lost its normal structure. There were numerous pigmented spots on the anterior capsule of the lens, and a glaucomatous excavation of the disc. The visual acuity was 4 5/60 and the field of vision was concentrically narrowed. The intra-ocular pressure was 54 2 mm. Hg. Gonioscopy showed strongly marked pigmentation with granular and dotted forms. Translumination of the iris and ciliary body was normal. Melanin and melanogen were normal. Radiography of the head and spine was normal. Case 5, a child aged 7 years from Sarajevo, was examined on April 13, Left Eye.-The lower portion of the sclera showed pigmentation in the form of spots. There was a Krukenberg's corneal spindle. The iris was darker brown than the other eye with hypertrophic pigmented changes and slight thickening. Examined under the biomicroscope this pigment hypertrophy was seen in the form of diffuse pigmented layers, and no granular structure could be discerned. On the anterior capsule of the lens, dotted pigment was more marked in the left eye. On the disc nasally and temporally a pigmented crescent was seen, while the fundus was more strongly pigmented as a whole. The visual acuity was 5/60, and with + 3 D cyl., axis 850, it was 6/24. The intra-ocular pressure was 20 mm. Hg and 23 mm. Hg after provocation. Gonioscopy showed strong pigmentation of the trabecula, more lightly marked in the area of Schwalbe's line. Right Eye.-There was superficial slight dotted pigmentation on the surface of the iris. The visual acuity was 5/60, and with + 2 D sph., D cyl., axis 900 it was 6/10. The intra-ocular pressure was 18 mm. Hg and 20 mm. Hg after provocation. Gonioscopy showed trabecular pigmentation. Translumination of the iris and ciliary body was normal in both eyes. Clinical and laboratory findings were normal. Melanin and melanogen were not found in the urine. Radiography of the head and spine was normal. Review of Findings The chief facts are assembled in Table I (opposite). The pigmentation of the trabecula was in all cases in keeping with the intensity of the pigmented hypertrophy of the iris, the latter being thickened to about one-fifth toone-quarter above its normal size. Only in Case 5 was the trabecular pigmentation less intense in the more pigmented eye.
5 IRIS HETEROCHROMIA TABLE I GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FIVE CASES OF HETEROCHROMIA OF THE IRIS Krukenberg Increased l KSpkendler Intra-ocular More Dotted More Intensive Case Age pide Pressure Pigmentation Pigmentation No. (yrs) - on Anterior in Chamber Capsule of Angle of Lighter Darker Lighter Darker Darker Eye Darker Eye Eye Eye Eye Eye No Yes No Yes No No No Yes No No ± ± Furthermore, translumination of the iris and ciliary body in both eyes showed normal findings and in no sector was it possible to establish even incipient atrophy of the tissue, by this method, with a diascleral lamp, or biomicroscopically. As already mentioned, in all these five cases with pigmentary glaucoma, there were no symptoms of heterochromia with cyclitis (Fuchs) nor any symptomatic heterochromia. All tests to elicit an altered sympathetic apparatus, either locally in the eye or in the cervical portion of the spine, remained negative. Considering that the history recorded heterochromia of the iris from birth, we consider this anomaly to be congenital and different from ordinary heterochromia of the iris in which there are no pathological symptoms of the eyes as were established in our cases. These five cases of a hypertrophic-pigmented form of pigmentary glaucoma with heterochromia of the iris present a new clinical picture of hyperpigmentary glaucoma, which is most probably due aetiologically to congenital hypertrophy of the pigmented layer of the iris leading to a considerable production of pigment on the anterior surface of the iris and in the chamber angle. It is possible that hypertrophic changes had occurred in the pigment cells close to the ciliary processes. It is especially significant that in these five cases, apart from pigmented hypertrophy on the darker eye together with intensive pigmented accumulations in the area of the whole trabecula up to the line of Schwalbe, the intraocular pressure was markedly higher in the darker and more pigmented eye. Only in Cases 3 and 5 was it not possible to establish an increased intra-ocular pressure even by provocation. 601
6 602 V. eavka The symptoms are classified in Table II. TABLE II CLASSIFICATION OF SYMPTOMS IN HETEROCHROMIC EYES No. Lighter Eye Darker Eye 1 No melanotic changes on the sclera Melanotic changes on the sclera 2 Krukenberg spindle of the cornea non- Krukenberg spindle of the cornea more existent or slightly marked marked 3 Only dotted pigmentation on the iris Intensive hypertrophic granular and naevoid pigmentation of the iris 4 Slight or medium pigmentation of the Intensive pigmentation of the trabecula trabecula 5 Pigmented crescent of the disc non-existent Very marked pigmented crescent of the disc 6 Intra-ocular pressure normal or only Intra-ocular pressure more or less slightly increased intensively increased 7 Translumination of both eyes normal Discussion According to these symptoms we managed to establish a new clinical form of heterochromia of the iris linked with melanotic changes (i.e. intensive pigmentation in the sclera, cornea, iris, and chamber angle, and in the area of the optic disc and retina, always more marked in the darker eye). The pigmentary glaucoma established in three cases (1, 2, and 4) does not exclude the possibility that glaucoma may occur in due time in the other two patients as well, especially considering the intensive trabecular pigmentation seen in the darker eye in both of them. In Case 2, the microscopic findings in the excised part of the iris revealed, not only intensive diffusely scattered pigmented conglomerations and granules, but also large numbers of pigmented melanophoric cells. Accordingly the microscopic slide of the iris showed, not only pigmented cells, but also scattered, free, extracellular pigment. However, it was not possible to discover pathological mitoses or any other malignant changes in the cells. TIhe changes found in these cases, considered with the case history, indicate a congenital affliction of the eye, in which the pigment was most probably transported by the chamber fluid from the iris to the chamber angle, through the obstruction of the latter by pigment with the consequent occurrence of glaucoma. There was also slight pigmentation in the iris and chamber angle in the lighter eye, which might well be considered as a pathological finding. The establishment of glaucomatous hypertension in the lighter eye in two cases (1 and 2) confirms our opinion that there was pathological pigment in the chamber angle in the lighter eye also. The proliferation of pigment with obstruction of the chamber angle was most probably the only cause of the occurrence of the congenital pigmentary glaucoma in either eye.
7 IRIS HETEROCHROMIA 603 Summary In five patients whose ages ranged from 3 to 53 years, it was possible to establish a new ocular syndrome; melanotic changes in the sclera and retina, hyperpigmentation of the iris and chamber angle with heterochromia of the iris; and the clinical picture of pigmentary glaucoma. All the pigmentation in the eye is assumed to have occurred congenitally, and they may be described as cases of congenital pigmentary glaucoma. REFERENCES BEUNINGEN, E. G. A. VAN (1959). Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk., 135, 796. BICK, M. W. (1957). A.M.A. Arch. Ophthal., 58, 483. CALHOUN, F. P., (1953). Amer. J. Ophthal., 36, HANSSEN, R. (1923). Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk., 71, 399. HIPPEL, E. VON (1901). v. Graefes Arch. Ophthal., 52, 498. KOBY, F. E. (1927). Bull. Soc. Ophtal. Paris, 124. KOEPPE, L. (1916a). Ber. 40 Versammlung ophthal. Ges. Heidelberg, p (1916b). v. Graefes Arch. Ophthal., 91, 363. KRAUPA, E. (1917). Arch. Augenheilk., 82, 67. KRUKENBERG, F. (1899a, b). Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk., 37, 254, 478. LEVINSOHN, G. (1908). Arch. Augenheilk., 62, 131. MALBRAN, J. (1957). Mod. Probl. Ophthal., 1, 132. ScHEIE, H. G., and FLEIsCHHAUER, H. W. (1958). A.M.A. Arch. Ophthal., 59, 216. SUGAR, H. S. (1940). Amer. J. Ophthal., 23, 853. and BAnouR, T. A. (1949). Ibid., 32, 90. VOGT, A. (1930). "Lehrbuch und Atlas der Spaltlampenmikroskopie des lebenden Auges". Springer, Berlin. Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 September Downloaded from on 21 March 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
LEUKAEMIA*t INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC. pattemn * Received for pubiication November io, i967.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
NAEVUS OF OTA* naevus" occurring in the skin areas supplied by the ophthalmic and maxillary
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 364 NAEVUS OF OTA* BY G. P. GUPTA AND D. N. GANGWAR From the Muslim University Institute of Ophthalmology and Gandhi Fye Hospital, Aligarh, India THE naevus of Ota is characterized
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 364 NAEVUS OF OTA* BY G. P. GUPTA AND D. N. GANGWAR From the Muslim University Institute of Ophthalmology and Gandhi Fye Hospital, Aligarh, India THE naevus of Ota is characterized
HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Capsular exfoliation syndrome
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, I 20 G. C. SOOD, B. K. SOFAT, S. K. MEHROTRA, AND R. D. CHANDEL Department of Ophthalmology, H.P. Medical College, Simla- i, India The nature ofsenile capsular exfoliation
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, I 20 G. C. SOOD, B. K. SOFAT, S. K. MEHROTRA, AND R. D. CHANDEL Department of Ophthalmology, H.P. Medical College, Simla- i, India The nature ofsenile capsular exfoliation
DAMAGE TO CORNEA AND LENS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 460 PRIMARY ACUTE ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA DAMAGE TO CORNEA AND LENS* BY RONALD F. LOWE From the Glaucoma Unit, the Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, Melbourne, and the Ophthalmic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 460 PRIMARY ACUTE ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA DAMAGE TO CORNEA AND LENS* BY RONALD F. LOWE From the Glaucoma Unit, the Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, Melbourne, and the Ophthalmic
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Infra-red transillumination stereophotography of the iris in Fuchs's heterochromic cyclitis
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 110-115 Infra-red transillumination stereophotography of the iris in Fuchs's heterochromic cyclitis M. SAARI, I. VUORRE, AND H. NIEMINEN From the University
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 110-115 Infra-red transillumination stereophotography of the iris in Fuchs's heterochromic cyclitis M. SAARI, I. VUORRE, AND H. NIEMINEN From the University
COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS. photocoagulation of the rabbit's retina.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
non-perforating injury
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
HYALINE RIDGES ON THE POSTERIOR CORNEA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 257 HYALINE RIDGES ON THE POSTERIOR CORNEA*t BY J. C. McGRAND Royal Eye Hospital, London HYALINE or glassy ridge formation on the posterior corneal surface appears to be a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 257 HYALINE RIDGES ON THE POSTERIOR CORNEA*t BY J. C. McGRAND Royal Eye Hospital, London HYALINE or glassy ridge formation on the posterior corneal surface appears to be a
OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 242. OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS* BY J. R. HUDSON Institute of Ophthalmology, London HAEMOCHROMATOSIS is a rare condition, the chief clinical features of which are
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 242. OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS* BY J. R. HUDSON Institute of Ophthalmology, London HAEMOCHROMATOSIS is a rare condition, the chief clinical features of which are
RETINAL DETACHMENT AT THE POSTERIOR POLE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1958) 42, 749. RETINAL DETACHMENT AT THE POSTERIOR POLE* BY CALBERT I. PHILLIPSt Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE common feature of the cases to be described in this
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1958) 42, 749. RETINAL DETACHMENT AT THE POSTERIOR POLE* BY CALBERT I. PHILLIPSt Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE common feature of the cases to be described in this
Angle recession and secondary glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 6o8 Angle recession and secondary glaucoma D. MOONEY Kent County Ophthalmic and Aural Hospital, Maidstone In a previous article (Mooney, I972), the incidence and extent of
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 6o8 Angle recession and secondary glaucoma D. MOONEY Kent County Ophthalmic and Aural Hospital, Maidstone In a previous article (Mooney, I972), the incidence and extent of
THE DARK-ROOM TEST* patients with chronic simple glaucoma may have angles of any width and
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1954) 38, 242. THE DARK-ROOM TEST* BY A. C. HIGGITT From the Glaucoma Clinic, Institute of Ophthalmology, London. Director of Research: Sir Stewart Duke-Elder ONE of the provocative
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1954) 38, 242. THE DARK-ROOM TEST* BY A. C. HIGGITT From the Glaucoma Clinic, Institute of Ophthalmology, London. Director of Research: Sir Stewart Duke-Elder ONE of the provocative
_ Assessment of the anterior chamber. Review of anatomy of the angle
 Assessment of the anterior chamber Dr Simon Barnard PhD BSc FCOptom FAAO DCLP Department of Optometry & Visual Science City University London, UK Review of anatomy of the angle Figure 1. Anatomical section
Assessment of the anterior chamber Dr Simon Barnard PhD BSc FCOptom FAAO DCLP Department of Optometry & Visual Science City University London, UK Review of anatomy of the angle Figure 1. Anatomical section
CORNEO-SCLERAL TONOGRAPHY* t BY T. H. HODGSON AND R. K. MACDONALD From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto, Canada
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 301. CORNEO-SCLERAL TONOGRAPHY* t BY T. H. HODGSON AND R. K. MACDONALD From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto, Canada THAT pressure exerted on the eyeball
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 301. CORNEO-SCLERAL TONOGRAPHY* t BY T. H. HODGSON AND R. K. MACDONALD From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto, Canada THAT pressure exerted on the eyeball
Haemorrhagic glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 444 Haemorrhagic glaucoma Comparative study in diabetic and nondiabetic patients P. H. MADSEN From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Internal Medicine, the University Hospital,
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 444 Haemorrhagic glaucoma Comparative study in diabetic and nondiabetic patients P. H. MADSEN From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Internal Medicine, the University Hospital,
SCLERAL BUCKLING OPERATION WITH ROLLED SCLERAL FLAP*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 361. SCLERAL BUCKLING OPERATION WITH ROLLED SCLERAL FLAP* BY V. CAVKA Belgrade, Yugoslavia AMONG the various operative procedures carried out for detachment of the retina,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 361. SCLERAL BUCKLING OPERATION WITH ROLLED SCLERAL FLAP* BY V. CAVKA Belgrade, Yugoslavia AMONG the various operative procedures carried out for detachment of the retina,
CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME
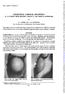 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
SYMPTOMS OF CONGESTIVE (CLOSED-ANGLE)*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 673. SYMPTOMS OF CONGESTIVE (CLOSED-ANGLE)* GLAUCOMA OCCURRING IN EYES WITH A WIDE CHAMBER ANGLEt BY P. L. BLAXTER Manchester THOUGH it has been acknowledged since the beginning
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 673. SYMPTOMS OF CONGESTIVE (CLOSED-ANGLE)* GLAUCOMA OCCURRING IN EYES WITH A WIDE CHAMBER ANGLEt BY P. L. BLAXTER Manchester THOUGH it has been acknowledged since the beginning
generalized neurofibromatosis
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I972) 56, 487 Glial hamartoma of the retina in generalized neurofibromatosis von Recklinghausen's disease L. J. MNIARTYN AND D. L. KNOX From the li'ilmer Institute, the Johns Hopkins
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I972) 56, 487 Glial hamartoma of the retina in generalized neurofibromatosis von Recklinghausen's disease L. J. MNIARTYN AND D. L. KNOX From the li'ilmer Institute, the Johns Hopkins
T O Normal male 0 Normal female II U* Affected male % t7 8 t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 536 Familial glaucoma In nine generations of a South Hampshire family J. P. MARTIN AND E. C. ZORAB Southampton Eye Hospital A. Zorab (1932) reported a family suffering from
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 536 Familial glaucoma In nine generations of a South Hampshire family J. P. MARTIN AND E. C. ZORAB Southampton Eye Hospital A. Zorab (1932) reported a family suffering from
CORNEAL VASCULARIZATION AFTER CATARACT EXTRACTION BY ZONULYSIS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal (1959) 43, 325. CORNEAL VASCULARIZATION AFTER CATARACT EXTRACTION BY ZONULYSIS* BY D. W. HILL St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London CATARACT extraction, after the zonule has been dissolved
Brit. J. Ophthal (1959) 43, 325. CORNEAL VASCULARIZATION AFTER CATARACT EXTRACTION BY ZONULYSIS* BY D. W. HILL St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London CATARACT extraction, after the zonule has been dissolved
Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma
 Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
ANTERIOR SEGMENT EXAMINATION TECHNIQUES
 ANTERIOR SEGMENT EXAMINATION TECHNIQUES GERS October 2017 Amanda Harding - Principal Optometrist, MREH MSc., MCOptom, Dip Glauc., Dip TP (IP). Anterior Segment Examination Depth of anterior chamber Central
ANTERIOR SEGMENT EXAMINATION TECHNIQUES GERS October 2017 Amanda Harding - Principal Optometrist, MREH MSc., MCOptom, Dip Glauc., Dip TP (IP). Anterior Segment Examination Depth of anterior chamber Central
High incidence of corneal epithelium antibodies in
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1988, 72, 921-925 High incidence of corneal epithelium antibodies in Fuchs' heterochromic cyclitis E LA HEY, G S BAARSMA, A ROTHOVA, L BROERSMA, R VAN DER GAAG, AND A
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1988, 72, 921-925 High incidence of corneal epithelium antibodies in Fuchs' heterochromic cyclitis E LA HEY, G S BAARSMA, A ROTHOVA, L BROERSMA, R VAN DER GAAG, AND A
Family studies in glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 529 Family studies in glaucoma E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is now strong evidence for a genetic basis to glaucoma. Numerous family
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 529 Family studies in glaucoma E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is now strong evidence for a genetic basis to glaucoma. Numerous family
MIXED GLAUCOMA* glaucoma may be the first episode. DURING the past 20 years it has become widely accepted that primary
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 503. MIXED GLAUCOMA* BY J. D. ABRAMS London DURING the past 20 years it has become widely accepted that primary glaucoma consists of two distinct conditions: chronic simple
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 503. MIXED GLAUCOMA* BY J. D. ABRAMS London DURING the past 20 years it has become widely accepted that primary glaucoma consists of two distinct conditions: chronic simple
JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY AND RELATED SCIENCES
 JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY AND RELATED SCIENCES BILATERAL ACUTE TRANSILLUMINATION OF THE IRIS Kavitha Avadhani 1, MD, MS, Jay Kalliath 1, MS, FRCS 1 Department of Ophthalmology, NMC Speciality Hospital,
JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY AND RELATED SCIENCES BILATERAL ACUTE TRANSILLUMINATION OF THE IRIS Kavitha Avadhani 1, MD, MS, Jay Kalliath 1, MS, FRCS 1 Department of Ophthalmology, NMC Speciality Hospital,
_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... I~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~...x'..'.i ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA*
 '..,S''''. t ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. g.# lgl,~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.%. : Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 164. ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA* BY ALY MORTADA Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
'..,S''''. t ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. g.# lgl,~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.%. : Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 164. ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA* BY ALY MORTADA Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
Lymphangiectasia haemorrhagica
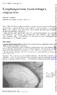 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (i 969) 53, 274 Lymphangiectasia haemorrhagica conjunctivae PHILIP AWDRY Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London, E.C. I Leber (i 88o) described a condition in which a connexion between
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (i 969) 53, 274 Lymphangiectasia haemorrhagica conjunctivae PHILIP AWDRY Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London, E.C. I Leber (i 88o) described a condition in which a connexion between
OCULAR DISORDERS REPORT BOSTON TERRIER
 OCULAR DISORDERS REPORT BOSTON TERRIER 1991-1999 2000-2009 2010-2012 TOTAL DOGS EXAMINED 2723 6803 2004 Diagnostic Name # % # % # % GLOBE 0.110 microphthalmia 1 0.0% 1 0.0% 0 EYELIDS 20.140 ectopic cilia
OCULAR DISORDERS REPORT BOSTON TERRIER 1991-1999 2000-2009 2010-2012 TOTAL DOGS EXAMINED 2723 6803 2004 Diagnostic Name # % # % # % GLOBE 0.110 microphthalmia 1 0.0% 1 0.0% 0 EYELIDS 20.140 ectopic cilia
Ross. *March, 1927, an attempt was made to classify congenital defects
 608 'HE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY A CASE OF ATYPICAL COLOBOMA ASSOCIATED WITH ABNORMAL RETINAL VESSELS BY IDA MANN AND JAMES A. LONDON CARLISLE Ross IN a paper on" Certain abnormal conditions of
608 'HE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY A CASE OF ATYPICAL COLOBOMA ASSOCIATED WITH ABNORMAL RETINAL VESSELS BY IDA MANN AND JAMES A. LONDON CARLISLE Ross IN a paper on" Certain abnormal conditions of
UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
KERATECTOMY* CORNEAL OPACITY AFTER PARTIAL LAMELLAR. depends upon that of the opacity, usually from one-third to a half of the
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 45. CORNEAL OPACITY AFTER PARTIAL LAMELLAR KERATECTOMY* BY Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt CASTROVEJO (1955) stated that opacities
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 45. CORNEAL OPACITY AFTER PARTIAL LAMELLAR KERATECTOMY* BY Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt CASTROVEJO (1955) stated that opacities
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
Corneal blood staining after hyphaema
 Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
3/16/2018. Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim. Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University
 Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
Relationship between limbal incisions. angle. and the structures of the anterior chamber
 Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Brit. _7. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 722 Relationship between limbal incisions and the structures of the anterior chamber angle MOHAMED I. AYOUB AND AHMED H. SAID Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine,
Table of Contents 1 Orbit 3 2 Eyelids 7
 Table of Contents Preface, x List of abbreviations xi Glossary xii Section I Atlas 1 1 Orbit 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital neoplasia 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital cellulitis 3 Enophthalmos
Table of Contents Preface, x List of abbreviations xi Glossary xii Section I Atlas 1 1 Orbit 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital neoplasia 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital cellulitis 3 Enophthalmos
STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 343. STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY* OBSERVATIONS BY MEANS OF THE PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE BY ANTONIO A. ROSSI From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London (Director of Research,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 343. STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY* OBSERVATIONS BY MEANS OF THE PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE BY ANTONIO A. ROSSI From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London (Director of Research,
Vascular changes in the iris in chronic
 Vascular changes in the iris in chronic anterior uveitis LEILA LAATIKAINEN From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Helsinki, Finland British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 145-149 SUMMARY
Vascular changes in the iris in chronic anterior uveitis LEILA LAATIKAINEN From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Helsinki, Finland British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 145-149 SUMMARY
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
PERIPHERAL IRI]DECTOMY IN CLOSED-ANGLE GLAUCOMA*
![PERIPHERAL IRI]DECTOMY IN CLOSED-ANGLE GLAUCOMA* PERIPHERAL IRI]DECTOMY IN CLOSED-ANGLE GLAUCOMA*](/thumbs/92/109283083.jpg) Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 114. PERIPHERAL IRI]DECTOMY IN CLOSED-ANGLE GLAUCOMA* BY Manchester Royal Eye Hospital PERIPHERAL iridectomy has become an accepted method of treating closedangle glaucoma.
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 114. PERIPHERAL IRI]DECTOMY IN CLOSED-ANGLE GLAUCOMA* BY Manchester Royal Eye Hospital PERIPHERAL iridectomy has become an accepted method of treating closedangle glaucoma.
arthritis "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid (opposite). Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 Peterborough District Hospital
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid arthritis A. J. LYNE Peterborough District Hospital It has been noted that patients suffering from long-standing rheumatoid arthritis
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid arthritis A. J. LYNE Peterborough District Hospital It has been noted that patients suffering from long-standing rheumatoid arthritis
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.155 Posner Schlossman Syndrome Authors Lt
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.155 Posner Schlossman Syndrome Authors Lt
chamber pigment in the anterior L beration of iris phenylephrine hydrochloride solution. After instillation of io per cent.
 Brit.. Ophthal. (I 97 I) 55, 544 L beration of iris chamber After instillation of io per cent. hydrochloride solution J. L. AGGARWAL AND B. BEVERIDGE Wolverhampton and Midland Counties Eye Infirmary pigment
Brit.. Ophthal. (I 97 I) 55, 544 L beration of iris chamber After instillation of io per cent. hydrochloride solution J. L. AGGARWAL AND B. BEVERIDGE Wolverhampton and Midland Counties Eye Infirmary pigment
Leiomyoma of the ciliary body
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1970) 54, 383 Leiomyoma of the ciliary body A clinico-pathological case report RONALD F. LOWE AND C. H. GREER Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, East Melbourne, Australia Although
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1970) 54, 383 Leiomyoma of the ciliary body A clinico-pathological case report RONALD F. LOWE AND C. H. GREER Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, East Melbourne, Australia Although
Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 823 Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma F. H. STEFANI AND ELISABETH ROTHEMUND From the University Eye Clinic and the Max Planck Institute ofpsychiatry, Munich, Federal Republic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 823 Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma F. H. STEFANI AND ELISABETH ROTHEMUND From the University Eye Clinic and the Max Planck Institute ofpsychiatry, Munich, Federal Republic
MELANOMA OF THE CHOROID EXAMINED WITH AN ACOUSTIC BIOMICROSCOPE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 218. MELANOMA OF THE CHOROID EXAMINED WITH AN ACOUSTIC BIOMICROSCOPE* BY ARVO OKSALA From the Ophthalmic Department of the Central-Finland Regional Hospital, Jyvdskyld, Finland
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 218. MELANOMA OF THE CHOROID EXAMINED WITH AN ACOUSTIC BIOMICROSCOPE* BY ARVO OKSALA From the Ophthalmic Department of the Central-Finland Regional Hospital, Jyvdskyld, Finland
PRIMARY ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA*t A REVIEW OF PROVOCATIVE TESTS
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 727 PRIMARY ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA*t A REVIEW OF PROVOCATIVE TESTS BY RONALD F. LOWE From The Glaucoma Unit of The Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, Melbourne, and The
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 727 PRIMARY ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA*t A REVIEW OF PROVOCATIVE TESTS BY RONALD F. LOWE From The Glaucoma Unit of The Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, Melbourne, and The
HYPERTENSION IN MARFAN'S SYNDROME*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 123. BILATERAL SECONDARY GLAUCOMA AND SYSTEMIC HYPERTENSION IN MARFAN'S SYNDROME* BY The Benn Hospital, Belfast SINCE Marfan (1896) first described the condition of "dolichostenomalie",
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 123. BILATERAL SECONDARY GLAUCOMA AND SYSTEMIC HYPERTENSION IN MARFAN'S SYNDROME* BY The Benn Hospital, Belfast SINCE Marfan (1896) first described the condition of "dolichostenomalie",
Trabeculectomy combined with cataract extraction: a follow-up study
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 720-724 Trabeculectomy combined with cataract extraction: a follow-up study R. S. EDWARDS From the Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital, Church Street, Birmingham
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 720-724 Trabeculectomy combined with cataract extraction: a follow-up study R. S. EDWARDS From the Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital, Church Street, Birmingham
Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D.
 Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D., FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others
Gonioscopy and 3-Mirror Retinal Evaluation Workshop Edeline Lu, O.D., FAAO Benedicte Gonzalez, O.D., MPH, FAAO Tina Zheng, O.D., FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others
CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID*
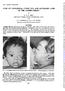 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
ANGLE VESSELS IN NORMAL EYES
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 551. ANGLE VESSELS IN NORMAL EYES A GONIOSCOPIC EVALUATION AND ANATOMIC. CORRELATION*t BY PAUL HENKIND From the Department of Ophthalmology, New York University College of
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 551. ANGLE VESSELS IN NORMAL EYES A GONIOSCOPIC EVALUATION AND ANATOMIC. CORRELATION*t BY PAUL HENKIND From the Department of Ophthalmology, New York University College of
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE
 SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
SAFE, PERMANENT EYE-COLOR CHANGE Prepared by Gregg Homer JSD (PhD) February 1, 2012 THE PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA ISSUE Glaucoma Defined Glaucoma is currently defined as a disturbance of the structural or functional
Sinus trabeculectomy. Preliminary results of IOO operations
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 833 Sinus trabeculectomy Preliminary results of IOO operations A. P. NESTEROV, N. V. FEDEROVA, AND Y. E. BATMANOV Department of Ophthalmology, Kazan Medical Institute, Kazan,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 833 Sinus trabeculectomy Preliminary results of IOO operations A. P. NESTEROV, N. V. FEDEROVA, AND Y. E. BATMANOV Department of Ophthalmology, Kazan Medical Institute, Kazan,
PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
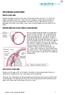 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Conservative management of retinal
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 482 Conservative management of retinal breaks A follow-up study of subsequent retinal detachment E. NEUMANN AND S. HYAMS From the Eye Department of the Rothschild Municipal-Government
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 482 Conservative management of retinal breaks A follow-up study of subsequent retinal detachment E. NEUMANN AND S. HYAMS From the Eye Department of the Rothschild Municipal-Government
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes
 Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
SEGMENTAL LESIONS OF THE RETINAL ARTERIES*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 562. SEGMENTAL LESIONS OF THE RETINAL ARTERIES* BY R. K. BLACH London FEW cases with segmental lesions of the retinal arteries have been described. Suganuma (1927) reported
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 562. SEGMENTAL LESIONS OF THE RETINAL ARTERIES* BY R. K. BLACH London FEW cases with segmental lesions of the retinal arteries have been described. Suganuma (1927) reported
COMMUNICATIONS INTRAVENOUS UREA THERAPY IN GLAUCOMA* given into the vein of a dog. This resulted in "an excessive secretion of
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 769. COMMUNICATIONS INTRAVENOUS UREA THERAPY IN GLAUCOMA* BY S. J. CREWS AND S. I. DAVIDSON Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital THE use of intravenous urea as a therapeutic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 769. COMMUNICATIONS INTRAVENOUS UREA THERAPY IN GLAUCOMA* BY S. J. CREWS AND S. I. DAVIDSON Birmingham and Midland Eye Hospital THE use of intravenous urea as a therapeutic
CHOLESTEROL CRYSTALS IN THE ANTERIOR CHAMBER*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 295. CHOLESTEROL CRYSTALS IN THE ANTERIOR CHAMBER* BY Muslim University Institute of Ophthalmology. Aligarh, India THE occurrence of crystals in the anterior chamber of the
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 295. CHOLESTEROL CRYSTALS IN THE ANTERIOR CHAMBER* BY Muslim University Institute of Ophthalmology. Aligarh, India THE occurrence of crystals in the anterior chamber of the
ADENOMA OF THE LIMBAL CONJUNCTIVA*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 237. ADENOMA OF THE LIMBAL CONJUNCTIVA* BY J. FRAN(OIS AND M. RABAEY From the Ophthalmological Clinic of the University of Ghent Director: Prof. J. Franpois, M.D. ADENOMATA of the
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 237. ADENOMA OF THE LIMBAL CONJUNCTIVA* BY J. FRAN(OIS AND M. RABAEY From the Ophthalmological Clinic of the University of Ghent Director: Prof. J. Franpois, M.D. ADENOMATA of the
Are traditional assessments a waste of time? NZAO 2015
 Are traditional assessments a waste of time? NZAO 2015 Disclosures No financial interests other than Optometry Practice owner Full time optometrist Not a glaucoma prescriber ODOB Board Chair Previously
Are traditional assessments a waste of time? NZAO 2015 Disclosures No financial interests other than Optometry Practice owner Full time optometrist Not a glaucoma prescriber ODOB Board Chair Previously
GLAUCOMA SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES
 SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
(ALBERS-SCHONBERG DISEASE)*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 218. NEURO-HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN OSTEOPETROSIS (ALBERS-SCHONBERG DISEASE)* BY F. VRABEC AND J. SEDLA(KOVA From the Eye Clinic of the Medical Faculty of Hygiene of the Charles
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 218. NEURO-HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN OSTEOPETROSIS (ALBERS-SCHONBERG DISEASE)* BY F. VRABEC AND J. SEDLA(KOVA From the Eye Clinic of the Medical Faculty of Hygiene of the Charles
Familial iris melanosis -a misnomer?
 Familial iris melanosis -a misnomer? BRIAN C JOONDEPH AND MORTON F British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 289-293 GOLDBERG From the Department of Ophthalmology, Eye and Ear Infirmary, University of
Familial iris melanosis -a misnomer? BRIAN C JOONDEPH AND MORTON F British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 289-293 GOLDBERG From the Department of Ophthalmology, Eye and Ear Infirmary, University of
Meet Libby. Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies Definitions. Dr. Victor Malinovsky
 Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
is not uncommon but may pass unrecognized unless the pupil is very wide,
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 348. SOEMMERRING'S RING* A REVIEW AND THREE ILLUSTRATIVE CASES BY N. L. STOKOE General Infirmary, Leeds A PERUSAL of the literature suggests that the ring-shaped tumour (cristallwulst)
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 348. SOEMMERRING'S RING* A REVIEW AND THREE ILLUSTRATIVE CASES BY N. L. STOKOE General Infirmary, Leeds A PERUSAL of the literature suggests that the ring-shaped tumour (cristallwulst)
2/26/2017. Sameh Galal. M.D, FRCS Glasgow. Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology
 Sameh Galal M.D, FRCS Glasgow Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology No financial interest in the subject presented 1 Managing cataracts in children remains a challenge. Treatment
Sameh Galal M.D, FRCS Glasgow Lecturer of Ophthalmology Research Institute of Ophthalmology No financial interest in the subject presented 1 Managing cataracts in children remains a challenge. Treatment
Metastatic tapioca iris melanoma
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 744-749 Metastatic tapioca iris melanoma KAMAL A. ZAKKA, ROBERT Y. FOOS, AND HECTOR SULIT From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology, Jules Stein Eye
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 744-749 Metastatic tapioca iris melanoma KAMAL A. ZAKKA, ROBERT Y. FOOS, AND HECTOR SULIT From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology, Jules Stein Eye
dystrophy, and angle closure glaucoma-a new syndrome?
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 69, 624-628 Bilateral nanophthalmos, pigmentary retinal dystrophy, and angle closure glaucoma-a new syndrome? SUPRIYO GHOSE, MAHIPAL S SACHDEV, AND HARSH KUMAR From the
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 69, 624-628 Bilateral nanophthalmos, pigmentary retinal dystrophy, and angle closure glaucoma-a new syndrome? SUPRIYO GHOSE, MAHIPAL S SACHDEV, AND HARSH KUMAR From the
Inadequate diagnostic value of the
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 55 Inadequate diagnostic value of the water-drinking test J. A. ROTH Department of Experimental Ophthalmology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is a large
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 55 Inadequate diagnostic value of the water-drinking test J. A. ROTH Department of Experimental Ophthalmology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is a large
Downloaded from:
 Philippin, H; Shah, P; Burton, M (2012) The next step: Detailed assessment of an adult glaucoma patient. Community eye health / International Centre for Eye Health, 25 (79-80). pp. 50-53. ISSN 0953-6833
Philippin, H; Shah, P; Burton, M (2012) The next step: Detailed assessment of an adult glaucoma patient. Community eye health / International Centre for Eye Health, 25 (79-80). pp. 50-53. ISSN 0953-6833
PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation
 C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
INTRA-CORNEAL LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 629. INTRA-CORNEAL LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY* BY TADEUSZ KRWAWICZ Ophthalmological Clinic, Medical Academy, Lublin, Poland THE operative technique of lamellar keratoplasty is still
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 629. INTRA-CORNEAL LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY* BY TADEUSZ KRWAWICZ Ophthalmological Clinic, Medical Academy, Lublin, Poland THE operative technique of lamellar keratoplasty is still
The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs
 The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman BSc MCOptom FBDO CET Accreditation C19095 2 CET Points (General)
The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman BSc MCOptom FBDO CET Accreditation C19095 2 CET Points (General)
Secondary open-angle glaucoma
 Secondary open-angle glaucoma Kathy Hondeghem ZNA Middelheim MaNaMa 12/10/13 Definition Open anterior chamber angle (at least 270 ) Trabecular meshwork (and thus aqueous humor outflow) is occluded by a
Secondary open-angle glaucoma Kathy Hondeghem ZNA Middelheim MaNaMa 12/10/13 Definition Open anterior chamber angle (at least 270 ) Trabecular meshwork (and thus aqueous humor outflow) is occluded by a
WAARDENBURG'S SYNDROME*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 755 WAARDENBURG'S SYNDROME*t REPORT OF A FAMILY BY From the Tennent Institute of Ophthalmology, University of Glasgow WAARDENBURG'S syndrome, or more fully the van der Hoeve-Halbertsma-Waardenburg-Klein
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 755 WAARDENBURG'S SYNDROME*t REPORT OF A FAMILY BY From the Tennent Institute of Ophthalmology, University of Glasgow WAARDENBURG'S syndrome, or more fully the van der Hoeve-Halbertsma-Waardenburg-Klein
Preliminary report on effect of retinal panphotocoagulation on rubeosis iridis and
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1977, 61, 278-284 Preliminary report on effect of retinal panphotocoagulation on rubeosis iridis and neovascular glaucoma LEILA LAATIKAINEN From Moorfields Eye Hospital,
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1977, 61, 278-284 Preliminary report on effect of retinal panphotocoagulation on rubeosis iridis and neovascular glaucoma LEILA LAATIKAINEN From Moorfields Eye Hospital,
4/22/16. Eye. External Anatomy of Eye. Accessory Structures. Bio 40B Dr. Kandula
 Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
EXUDATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* SPONTANEOUS CHANGES AND EFFECTS OF A CORN OIL DIET
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 666. EXUDATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* SPONTANEOUS CHANGES AND EFFECTS OF A CORN OIL DIET BY R. C. KING, J. H. DOBREE, D'A. KOK, W. S. FOULDS, AND W. G. DANGERFIELD St. Bartholomew's
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 666. EXUDATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* SPONTANEOUS CHANGES AND EFFECTS OF A CORN OIL DIET BY R. C. KING, J. H. DOBREE, D'A. KOK, W. S. FOULDS, AND W. G. DANGERFIELD St. Bartholomew's
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy. Reviewed & ratified by: Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:101-105 Graefe's Archive for CliniCal and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma* J. Reimer Wolter
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:101-105 Graefe's Archive for CliniCal and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma* J. Reimer Wolter
