Manifestations of cyclical flank alopecia in a dog from Southern Brazil
|
|
|
- Bruce Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 59 Case Report Manifestations of cyclical flank alopecia in a dog from Southern Brazil Lucas A. Gomes 1, Márcia C. Sonoda 2, Lígia Bortolucci 3, Juliana Werner 4, Selwyn A. Headley 5 1 Departamentos de Clínica Médica de Pequenos Animais, 3 Clínicas Veterinárias e 5 Medicina Veterinária Preventiva, Centro de Ciências Agrárias, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Paraná, Brasil; 2 Clínica Autônoma Especializada em Dermatologia Veterinária, São Paulo, Brasil; 4 Werner & Werner Laboratório de Patologia Veterinária, Curitiba, Paraná, Brasil. Section of Veterinary Pathology, *Corresponding author: Selwyn A. Headley, Department of Basic Veterinary Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Helsinki. *Current address: Department of Basic Veterinary Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, St. Matthew s University, Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands, British West Indies. P.O. Box 30992, KY Tel: Ext. 4007, Fax: sheadley@smu.ky Submitted April 4 th 2008, Accepted August 11 th 2008 Abstract Canine cyclical flank alopecia is an uncommon dysplastic cutaneous disease described predominantly in the Northern Hemisphere. This condition is associated with recurrent hair-loss and subsequent hair regrowth at the lateral flank folds and other regions of the body. Diagnosis is based on characteristic histological findings with the exclusion of hormonal-related cutaneous diseases. This report describes a similar condition that occurred in a dog from Southern Brazil during three consecutive years. However, alopecia initiated during winter to spring with subsequent hair regrowth in summer. Histopathology of cutaneous biopsy revealed atrophy of hair follicles without an associated inflammatory reaction or the participation of infectious agents. The clinical manifestations associated with histopathological findings of this dog are suggestive of cyclical flank alopecia, but with an inverted occurrence of alopecia. Key Words: cyclical flank alopecia; skin; dog; histopathology. Introduction Canine cyclical flank alopecia (CFA), also referred to as seasonal flank alopecia, recurrent flank alopecia, and flank alopecia, is a rare dysplastic disease that occurs predominantly at the lateral flank folds (2, 3, 4). Affected dogs normally demonstrate, during consecutive years, loss of hair coat at the end of autumn, with spontaneous regrowth by spring (5). Clinically, CFA is characterized by bilateral symmetrical alopecia and altered quality of the hair coat, which may be darker or lighter than normal, and is normally dry, dull, and dishevelled (3). Manifestations of the disease are more frequently observed at the folds of the lateral flank (5), but the dorsal midline, the cranial ribcage, and auxiliary locations may also be affected (3). Characteristic histopathological findings of biopsy specimens from affected animals confirm the diagnosis (2,3,4), after the participation of hormonal-based diseases has been excluded (3). This report describes the clinical and histopathological findings associated with this condition in a dog from Southern Brazil, and confirms the seasonality of this disease irrespective of the geographical localization. In November 2006, a 12-year-old, male, Poodle breed of dog was taken to the Veterinary Hospital, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Paraná, Southern Brazil, for clinical examination. The owner related that the dog demonstrated recurrent hair loss and abnormal hair development, initially at the dorsum and the perianal regions, since the beginning of the transition period between winter to spring (August-September) of It
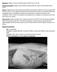
2 60 was also reported that hair regrowth, at the affected areas, was gradual and begun during early summer (January) of 2004; additionally, all treatment strategies realized at private veterinary clinics did not resolve the problem. In 2005, alopecia occurred during the previously described period with hair regrowth in early summer, but the alopecic area was extended to include the pelvic limbs; and treatment did not resolve the cutaneous problem. Due to previous frustrating therapeutic attempts at several veterinary clinics, the owner decided to consult at the Veterinary Teaching Hospital. There was bilateral symmetrical alopecia at the flank folds, the thoracic, lumbar, and dorsal regions, and at the pelvic members (Fig. 1, A-B). Further, the owner related that the problem had initiated one month earlier (October, i.e., spring). Clinical examination did not reveal any abnormality to vital parameters; the dog was in good nutritional condition without hypertrophy of regional lymph nodes. Polyuria, polydypsia, polyphagia, pendulated abdomen, and/or alterations to body weight were not observed. Therefore, the possible participation of an endocrine-related disease was discarded due to the absence of corresponding clinical signs; the owner also did not pursue this investigation due to financial constraints. Cyclic flank alopecia was suspected because of the recurrent and seasonal episodes of the hair loss followed by spontaneous regrowth during the three-yearperiod. Skin biopsy samples taken from various areas of abnormal skin coat were routinely prepared for histopathological evaluation; selected sections were stained by the Gomori Methenamine silver (GMS) and Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) methods to exclude infectious agents. Supportive therapy with melatonin (5 mg, PO, 12/12h) has since been initiated, and the animal is responding slowly. When, the dog was seen in March 2007, there was complete hair regrowth (Fig. 1, C-D). Histological evaluation revealed orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis and severe atrophy of hair follicles (Fig. 1, E-F). Most hair follicles demonstrated follicular atrophy and infundibular hyperkeratosis; some follicles were twisted, truncated, and dilated. In some areas, the enlarged infundibulum was observed above several affected follicles resulting in an inverted foot-like appearance to the structures; some hair follicles were inactive, the epithelial cells were filled with melanin granules; inflammatory reaction was not observed in any of the examined specimens. Special stains (GMS and PAS) did not reveal any infectious agents. In this case, a diagnosis of cyclical flank alopecia (CFA) was established based on the description of recurrent seasonal presentation of hair loss and subsequent regrowth associated with the histopathological findings that are consistent with this disease (3, 4). Further, the absence of inflammatory reaction associated with follicular atrophy (2), as observed in this case, is a hallmark of this condition. In this case, hyperpigmentation was not observed during hair regrowth; hyperpigmentation has been described in most cases of CFA (2,3), but is not the principal manifestation of this disease. The prime clinical features associated with this condition are bilateral symmetrical altered haircoat quality and alopecia (3). Although endocrine-related disease can manifest similar hair loss, this animal did not demonstrate clinical signs indicative of these diseases, and due to financial limitations associated with fact that hair regrowth occurred twice without effective treatment, the owner opted not to have these tests done. Therefore, the findings of this dog are highly suggestive of the manifestation of this unusual cutaneous disease in the Southern Hemisphere. Additionally, to the best of the authors knowledge, a similar case was not previously described in Brazil or in South America, so this adds to the geographical occurrence of this disease; there is also a recent description of this condition in Australia (1). The descriptions of CFA in Australia and in Brazil may also indicate that this cutaneous manifestation is not restricted to the Northern Hemisphere (4). Most reports of this disease have occurred in 3-4 yr-old-dogs (2,5), but in this case the dog was 10-yr-old when the initial lesions were observed; this might suggest that there is no specific age limit for the manifestation of CFA. The etiology of this disease is currently unknown. CFA is most frequently described in the Airedale terriers, English bulldogs, Schnauzer, and Boxers breeds of dogs (4,7). However, other breeds at increased risk include the Miniature Poodle, Scottish terrier, Rottweiler, and Doberman Pinscher (2). In this case, the dog was of the Poodle breed, while the case from Australia occurred in a Tibetan terrier (1). The alopecia and abnormal hair growth associated with CFA in the northern hemisphere is know to occur between autumn and spring with hair regrowth by the end of spring (3, 6). However, during the three consecutive years of this disease, the occurrence was inverted; alopecia began during winter to spring and hair regrowth with effect from summer. The case described in Australia also initiated during the winter (1). Further, cases of CFA in North America have also occurred with this inverted appearance of alopecia (3,5). In Southern Brazil, the four seasons are well defined, so this difference in the occurrence of CFA in this case relative to previously described cases from North America, might be directly associated with the alterations in the photoperiod between the northern and southern hemispheres. This inverted appearance of alopecia observed in this case might be the pattern associated with this disorder in the southern hemisphere. Photoperiod and variations in seasonal climatic conditions have been related to the occurrence of this disorder in North America (3), while the participation of melatonin cannot be discarded (4) from the pathogenesis of CFA. Canine diseases with alopecia that might be confused with recurrent flank alopecia are endocrinerelated cutaneous diseases and alopecia X (5). However,
3 Gomes et al; Manifestations of cyclical flank alopecia in a dog from Southern Brazil. Braz J Vet Pathol; 2008, 1(2): Figure 1. Cyclical flank alopecia, 12-yr-old Poodle. Bilateral lost of hair coat at the flank folds, at the pelvic members, the thoracic, lumbar, and dorsal regions (A, B). Complete regrowth occurred during the summer of 2007 (C,D). There is hyperkeratosis and atrophy of hair follicles (E, F; HE, E, Obj. 10 x; F Obj. 20x).
4 62 the histological patterns and the associated clinical manifestations of these diseases are distinct (3), and are useful to obtain a definite histopathological diagnosis. Common hormonal-associated cutaneous manifestations of dogs are hyperadrenocorticism, hypothyroidism, and Sertoli cell tumors (3,5). Additionally, these alterations are not of cyclic manifestations and normally disappear when the underlying cause is removed. The salient features of these cutaneous alterations of dogs are briefly described, and compared with this case, so that clinicians and pathologist can effectively obtain a differential diagnosis. Canine hyperadrenocorticism (commonly known as Cushing s disease) is frequently induced by bilateral adrenocortical hyperplasia due to a pituitary neoplasm, a tumor of the adrenal cortex, or due to iatrogenic hyperglucocorticism (2). Clinically, this disease demonstrates bilateral symmetric alopecia, pendulous abdomen, thin skin, telangiectasia, scaling, comedones, calcinosis cutis (2), polydypsia, polyuria, lethargy (3,5), and hyperpigmentation (2,5). Microscopically, canine hyperadrenocorticism is characterized by thin epidermal and follicular epithelium (2), with orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis, follicular hyperkeratosis, severe accumulation of keratin within thin-walled follicular infundibula (comedone), and calcinosis cutis (3). Additionally, calcinosis cutis is pathognomonic for canine hyperadrenocorticism (2). In this case, there was no neoplastic adrenal or pituitary growth or iatrogenic hyperglucocorticism, and the clinical manifestations associated with canine hyperadrenocorticism were not present. Further, the characteristic cutaneous histological manifestation of this dysfunction, dermal calcinosis, was not observed microscopically. Therefore, these findings excluded the necessity to evaluate imbalances of the adenocorticotropic hormone that is associated with canine hyperadrenocorticism. Hypothyroidism in dogs is associated with direct lesions to the thyroid gland due to lymphocytic thyroiditis and idiopathic thyroid atrophy (2,5); there is a definite breed predisposition (2). Clinically, cutaneous manifestations associated with canine hypothyroidism include secondary seborrhea, dry, coarse, brittle hair without hair regrowth (2), hyperpigmentation, bilateral symmetric truncal alopecia (3), secondary bacterial or mycotic infections, and comedones (5). Systemic manifestation of canine hypothyroidism might result in bradycardia, anemia, lethargy, obesity, disorientation, and seizures (5). The histological cutaneous pattern is nonspecific (2) and consequently not diagnostic (3) for canine hypothyroidism. However, thyroid biopsy is diagnostic but not frequently done at most clinics (5). Microscopic cutaneous alterations include follicular infundibular hyperplasia, hyperpigmentation (3), orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis, follicular keratosis, and epidermal hyperplasia (2). Diagnosis is based on alterations of the serum concentrations of basal total of the thyroid hormone (T 4 ), free T 4, and the thyroid-stimulating hormone (5). The clinical manifestations of this dog were not indicative of thyroid dysfunctions. Further, there was cyclic hair regrowth and the histological features of this dog were not consistent with that described in canine hypothyroidism; therefore, the evaluation of thyroid hormones were not considered as necessary and essential in this case. Testicular Sertoli cell tumor (also known as the male femininizing syndrome) occurs in male cryptorchidic dogs (3,5). This syndrome might result in bilateral symmetrical alopecia, enlarged nipples, gynecomastia, and pendulous prepuce (3,5). Additionally, diffuse hyperpigmentation of the lateral thighs, secondary superficial pyoderma, pruritis, attraction to male dogs, urination in female position, and prostatitis might occur (3). This was an intact male dog and these clinical manifestations were not observed. Alopecia X is a cutaneous canine disease that is characterized by progressive bilaterally symmetric noninflammatory alopecia with hyperpigmentation (3). The exact pathogenesis associated with this disorder has not been elucidated (2), but there is a definite breed predisposition (3). Nordic canine breeds are more frequently affected (2); the dog described in this report is a Poodle. In most cases, the thyroid and adrenal functions are normal, but there might be an imbalance or deficiency of sex and/or growth hormones (2). Further, most cases have been diagnosed in dogs that are between 9 months and 2 years of age (2,3); this dog was 12-years-old. In conclusion, the clinical manifestations during three consecutive years associated with the histological findings seen in this case are highly suggestive of canine flank alopecia. References 1. BASSETT, R. T., BURTON, G.G., ROBSON, D. C. Recurrent flank alopecia in a Tibetan terrier. Australian Veterinary Journal. 83, GINN, P, MANSELL EKL, RAKICH PM. Skin an appendages. In: Jubb, Kennedy, and Palmer s Pathology of domestic animals. Maxie MG. (Ed). Vol ed. Saunders/Elsevier, Philadelphia. pp , GROSS, T. L., IHRKE, P. J., WALDER, E. J. AFFOLTER, V. K. (2005) Skin diseases of the dog and cat: clinical and histopathological diagnosis. 2nd ed. Ames: Blackwell Publishing. 932 p. 4. HARGIS, A. M. & GINN, P. E. (2007) The integument. In: McGavin, M. D. & Zachary, J. F. Eds. Pathological basis of veterinary disease. 4th ed. Cap. 17, pp MUELLER, R. S. (2003) Noninflammatory alopecia in dogs. Veterinary Medicine. 98, SCOTT, D. W., MILLER, W. H. JR., GRIFFIN, G. E. (1996) Miller e Kirk - Dermatologia de Pequenos Animais. 5ª. Ed., Interlivros, Rio de Janeiro p.
5 63 7. WALDMAN, I. (1995) Seasonal flank alopecia in Affenpinschers. Journal of Small Animal Practice. 36,
Symmetric alopecia in the dog: not always an endocrine disorder. Lluis Ferrer Department of Clinical Sciences
 Symmetric alopecia in the dog: not always an endocrine disorder Lluis Ferrer Department of Clinical Sciences Alaskan Malamute Club of America Sturbridge Massachusetts, Nov. 2015 Alopecia: clinical presentations
Symmetric alopecia in the dog: not always an endocrine disorder Lluis Ferrer Department of Clinical Sciences Alaskan Malamute Club of America Sturbridge Massachusetts, Nov. 2015 Alopecia: clinical presentations
Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics OVERVIEW Clinical condition that results from inadequate production and release of thyroid
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics OVERVIEW Clinical condition that results from inadequate production and release of thyroid
Cushing's disease, Cushing's syndrome
 Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Canine hyperadrenocorticism Cushing's disease, Cushing's syndrome AffectedAnimals: Although dogs of almost every
Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Canine hyperadrenocorticism Cushing's disease, Cushing's syndrome AffectedAnimals: Although dogs of almost every
Hyperadrenocorticism or Cushing's Syndrome in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Hyperadrenocorticism or Cushing's Syndrome in Dogs (Excessive Levels of Steroids
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Hyperadrenocorticism or Cushing's Syndrome in Dogs (Excessive Levels of Steroids
Spontaneously occurring canine hyperadrenocorticism
 Peer reviewed Canine Hyperadrenocorticism Challenges Establishing the Diagnosis TABLE 1. Clinical Signs & Examination Findings Indicative of HAC Polyuria and polydipsia Polyphagia endocrine alopecia (thin
Peer reviewed Canine Hyperadrenocorticism Challenges Establishing the Diagnosis TABLE 1. Clinical Signs & Examination Findings Indicative of HAC Polyuria and polydipsia Polyphagia endocrine alopecia (thin
A LOOK AT CANINE HYPOTHYROIDISM
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A LOOK AT CANINE HYPOTHYROIDISM Author : Isabelle Cattin, Jordi Puig Categories : Vets Date : June 25, 2012 Isabelle Cattin,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A LOOK AT CANINE HYPOTHYROIDISM Author : Isabelle Cattin, Jordi Puig Categories : Vets Date : June 25, 2012 Isabelle Cattin,
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism)
 Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism) Although Cushing's disease is a severe disease the changes it causes can be quite subtle in the early stages. Many owners do not recognise the signs of Cushing's
Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism) Although Cushing's disease is a severe disease the changes it causes can be quite subtle in the early stages. Many owners do not recognise the signs of Cushing's
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg
 Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Histiocytic Neoplasms of the Dog and Cat
 Histiocytic Neoplasms of the Dog and Cat V.E. Valli DVM Histiocytic and Dendritic Cell Populations Both lineages are bone marrow derived. Macrophages are part of the innate immune system that are phagocytic
Histiocytic Neoplasms of the Dog and Cat V.E. Valli DVM Histiocytic and Dendritic Cell Populations Both lineages are bone marrow derived. Macrophages are part of the innate immune system that are phagocytic
HYPOTHYROID DOGS Is Your Dog Overweight and Lazy with Thinning Hair? Your Dog May Need a Thyroid Screening.
 HYPOTHYROID DOGS Is Your Dog Overweight and Lazy with Thinning Hair? Your Dog May Need a Thyroid Screening. The thyroid glands located in the neck produce hormones that affect the function of many parts
HYPOTHYROID DOGS Is Your Dog Overweight and Lazy with Thinning Hair? Your Dog May Need a Thyroid Screening. The thyroid glands located in the neck produce hormones that affect the function of many parts
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
CLINICAL, ULTRASOUND AND LABORATORY CHANGES IN CUSHING SYNDROME IN DOGS
 CLINICAL, ULTRASOUND AND LABORATORY CHANGES IN CUSHING SYNDROME IN DOGS Gabriela Marin (Ivaşcu), M.D. Codreanu, V. Nicorescu, Iuliana Codreanu, Maria Crivineanu Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Bucharest,
CLINICAL, ULTRASOUND AND LABORATORY CHANGES IN CUSHING SYNDROME IN DOGS Gabriela Marin (Ivaşcu), M.D. Codreanu, V. Nicorescu, Iuliana Codreanu, Maria Crivineanu Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Bucharest,
POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY. PgC & GPCert (DERM) SYLLABUS
 POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (DERM) 2018 SYLLABUS POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE IN DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (Derm) 2018 SYLLABUS This syllabus is designed as a guideline to the key areas
POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (DERM) 2018 SYLLABUS POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE IN DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (Derm) 2018 SYLLABUS This syllabus is designed as a guideline to the key areas
Ultrasonographic and Clinical Studies on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Dogs
 Theriogenology Insight: 6(1): 67-72, April, 2016 DOI Number: 10.5958/2277-3371.2016.00009.7 Ultrasonographic and Clinical Studies on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Dogs K. Rajkumar* and C. Ansarkamran
Theriogenology Insight: 6(1): 67-72, April, 2016 DOI Number: 10.5958/2277-3371.2016.00009.7 Ultrasonographic and Clinical Studies on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Dogs K. Rajkumar* and C. Ansarkamran
Urine Dipstick Analysis
 ASAP LABORATORY NEWS APRIL 2015 Hi everyone Please find below the latest ASAP news. Urine Dipstick Analysis Urine dipstick analysis is an important component of the urinalysis and can be easily performed
ASAP LABORATORY NEWS APRIL 2015 Hi everyone Please find below the latest ASAP news. Urine Dipstick Analysis Urine dipstick analysis is an important component of the urinalysis and can be easily performed
DIAGNOSIS OF CANINE HYPERADRENOCORTICISM: A CASE-BASED APPROACH Ellen N. Behrend, VMD, PhD, DACVIM
 DIAGNOSIS OF CANINE HYPERADRENOCORTICISM: A CASE-BASED APPROACH Ellen N. Behrend, VMD, PhD, DACVIM Case 1: Signalment: 10 yr old, CM, Miniature poodle; History: Presented for teeth cleaning; PE: Severe
DIAGNOSIS OF CANINE HYPERADRENOCORTICISM: A CASE-BASED APPROACH Ellen N. Behrend, VMD, PhD, DACVIM Case 1: Signalment: 10 yr old, CM, Miniature poodle; History: Presented for teeth cleaning; PE: Severe
Canine Cutaneous Melanoma
 Canine Cutaneous Melanoma By Elizabeth Downing Clinical Advisor: Dr. Angharad Waite, VMD Basic Science Advisor: Dr. Cheryl Balkman, DVM, DACVIM Senior Seminar Paper Cornell University College of Veterinary
Canine Cutaneous Melanoma By Elizabeth Downing Clinical Advisor: Dr. Angharad Waite, VMD Basic Science Advisor: Dr. Cheryl Balkman, DVM, DACVIM Senior Seminar Paper Cornell University College of Veterinary
Metastasis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Pelvis of a Dog
 Acta Scientiae Veterinariae, 2013. 41 (Suppl 1): 31. CASE REPORT Pub. 31 ISSN 1679-9216 Metastasis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Pelvis of a Dog Tiago Barbalho Lima 1, Leonardo Martins Leal 1, Gláucia
Acta Scientiae Veterinariae, 2013. 41 (Suppl 1): 31. CASE REPORT Pub. 31 ISSN 1679-9216 Metastasis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Pelvis of a Dog Tiago Barbalho Lima 1, Leonardo Martins Leal 1, Gláucia
Basic endocrinology. Pituitary Gland. Endocrine disorders. Endocrine disorders. Endocrine disorders Tech CE for the Upstate 2/10/2013
 Basic endocrinology Hyperadrenocorticism Rob Presley, DVM, MS, DACVIM Upstate Veterinary Specialists TCTC Veterinary Technician Program February 10, 2013 Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Functional organ Thyroid
Basic endocrinology Hyperadrenocorticism Rob Presley, DVM, MS, DACVIM Upstate Veterinary Specialists TCTC Veterinary Technician Program February 10, 2013 Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Functional organ Thyroid
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
Cushing s Disease. Avondale Veterinary Group. Avondale House Strathaven Rural Centre Strathaven Lanarkshire ML10 6SY.
 Avondale Veterinary Group Avondale House Strathaven Rural Centre Strathaven Lanarkshire ML10 6SY Tel: 01357 520251 Cushing s Disease Equine Cushing s Disease (ECD), also known as Pars Pituitary Intermedia
Avondale Veterinary Group Avondale House Strathaven Rural Centre Strathaven Lanarkshire ML10 6SY Tel: 01357 520251 Cushing s Disease Equine Cushing s Disease (ECD), also known as Pars Pituitary Intermedia
Pilosebaceous Dysplasia (Abnormal Orientation of Pilosebaceous Units): A Histopathological Finding Indicative of Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs
 22 (2): 97 103, 2016 Original Pilosebaceous Dysplasia (Abnormal Orientation of Pilosebaceous Units): A Histopathological Finding Indicative of Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs 毛嚢脂腺の異形成 ( 毛嚢脂腺の異常な適応 ): 犬の酵母による皮膚炎を暗示させる病理組織学的所見
22 (2): 97 103, 2016 Original Pilosebaceous Dysplasia (Abnormal Orientation of Pilosebaceous Units): A Histopathological Finding Indicative of Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs 毛嚢脂腺の異形成 ( 毛嚢脂腺の異常な適応 ): 犬の酵母による皮膚炎を暗示させる病理組織学的所見
Exfoliative Dermatoses (Skin Disorders Characterized by the Presence of Scales) Basics
 Exfoliative Dermatoses (Skin Disorders Characterized by the Presence of Scales) Basics OVERVIEW Excessive or abnormal shedding of skin cells, resulting in the clinical presentation of accumulations of
Exfoliative Dermatoses (Skin Disorders Characterized by the Presence of Scales) Basics OVERVIEW Excessive or abnormal shedding of skin cells, resulting in the clinical presentation of accumulations of
Steroid induced hyperadrenocorticism in dogs- A Short study
 Journal of Animal Research: v.5 n.1, p. 203-207. April. 2015 DOI Number: 10.5958/2277-940X.2015.00033.9 SHORT COMMUNICATION Steroid induced hyperadrenocorticism in dogs- A Short study M. Sandhya Bhavani
Journal of Animal Research: v.5 n.1, p. 203-207. April. 2015 DOI Number: 10.5958/2277-940X.2015.00033.9 SHORT COMMUNICATION Steroid induced hyperadrenocorticism in dogs- A Short study M. Sandhya Bhavani
Paraneoplastic diseases in cats and dogs in veterinary dermatology
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Paraneoplastic diseases in cats and dogs in veterinary dermatology Wilhelm,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Paraneoplastic diseases in cats and dogs in veterinary dermatology Wilhelm,
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2).
 22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
Use of Histopathology and Microbiology in Veterinary Dermatology
 Use of Histopathology and Microbiology in Veterinary Dermatology Dr R D Last BVSc; M.Med.Vet (Pathology) Specialist Veterinary Pathologist Introduction The skin is the largest of the organ systems and
Use of Histopathology and Microbiology in Veterinary Dermatology Dr R D Last BVSc; M.Med.Vet (Pathology) Specialist Veterinary Pathologist Introduction The skin is the largest of the organ systems and
Hypoadrenocorticism or Addison's Disease (Inadequate Production of Hormones by the Adrenal Glands) Basics
 Hypoadrenocorticism or Addison's Disease (Inadequate Production of Hormones by the Adrenal Glands) Basics OVERVIEW A hormonal disorder resulting from decreased production of hormones (glucocorticoids and/or
Hypoadrenocorticism or Addison's Disease (Inadequate Production of Hormones by the Adrenal Glands) Basics OVERVIEW A hormonal disorder resulting from decreased production of hormones (glucocorticoids and/or
In the past few years, a new disease has been identified called Sudden Acquired Retinal Degeneration Syndrome (SARDS).
 SARDS CLINCAL CASE STUDIES In the past few years, a new disease has been identified called Sudden Acquired Retinal Degeneration Syndrome (SARDS). The disease manifests itself as a loss of vision which
SARDS CLINCAL CASE STUDIES In the past few years, a new disease has been identified called Sudden Acquired Retinal Degeneration Syndrome (SARDS). The disease manifests itself as a loss of vision which
Submission of samples. Cytology of Lumps and Bumps. Evaluation of samples. Use caution interpreting. Criteria of malignancy.
 Submission of samples Cytology of Lumps and Bumps Paul Avery VMD, PhD, DACVP paul.avery@colostate.edu Air dry only No wet fixation using formalin or ethanol Stain 1-2 on-site to evaluate quality Send all
Submission of samples Cytology of Lumps and Bumps Paul Avery VMD, PhD, DACVP paul.avery@colostate.edu Air dry only No wet fixation using formalin or ethanol Stain 1-2 on-site to evaluate quality Send all
FOLLICULAR DYSPLASIAS AND OTHER ALOPECIAS
 FOLLICULAR DYSPLASIAS AND OTHER ALOPECIAS 4th Latin American Congress of Veterinary Dermatology, Mérida, México 13-16 de junio, 2018 Manon Paradis, DMV, MScV, Dipl. ACVD, Department of clinical sciences,
FOLLICULAR DYSPLASIAS AND OTHER ALOPECIAS 4th Latin American Congress of Veterinary Dermatology, Mérida, México 13-16 de junio, 2018 Manon Paradis, DMV, MScV, Dipl. ACVD, Department of clinical sciences,
Name the condition: Canine sterile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet s syndrome)
 5-year-old male miniature Schnauzer dog with acute onset of severe macular erythema and multiple tender violaceus plaques all over the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Canine
5-year-old male miniature Schnauzer dog with acute onset of severe macular erythema and multiple tender violaceus plaques all over the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Canine
Signalment: 2-year-old male castrated Chihuahua beagle mix. Presenting complaint: Areas of alopecia and ulcers/erosions. Figure 1. Figure 2.
 Signalment: 2-year-old male castrated Chihuahua beagle mix. Presenting complaint: Areas of alopecia and ulcers/erosions Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Figure 4. Figure 5. Figure 6. Figure 7. Clinical history:
Signalment: 2-year-old male castrated Chihuahua beagle mix. Presenting complaint: Areas of alopecia and ulcers/erosions Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Figure 4. Figure 5. Figure 6. Figure 7. Clinical history:
IDIOPATHIC EPILEPSY (SEIZURE DISORDER OF UNKNOWN CAUSE)
 IDIOPATHIC EPILEPSY (SEIZURE DISORDER OF UNKNOWN CAUSE) BASICS OVERVIEW Idiopathic is the medical term for a disease or disorder of unknown cause; epilepsy is a brain disorder, in which the animal has
IDIOPATHIC EPILEPSY (SEIZURE DISORDER OF UNKNOWN CAUSE) BASICS OVERVIEW Idiopathic is the medical term for a disease or disorder of unknown cause; epilepsy is a brain disorder, in which the animal has
Endocrine Diseases Of The Dog
 Peterson ME, Wheeler SH: Endocrine diseases of the dog. American Kennel Gazette 99:42-49, 1982 Endocrine Diseases Of The Dog Cushing's Syndrome, Hypothyroidism and Diabetes Mellitus are the three most
Peterson ME, Wheeler SH: Endocrine diseases of the dog. American Kennel Gazette 99:42-49, 1982 Endocrine Diseases Of The Dog Cushing's Syndrome, Hypothyroidism and Diabetes Mellitus are the three most
Title. Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): Issue Date
 Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
CUSHING'S DISEASE. What is Cushing's Disease?
 CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's Disease? Cushing's Disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's Disease? Cushing's Disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021)
 BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021) The thymus is of a pinkish-gray colour, soft, and lobulated
BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021) The thymus is of a pinkish-gray colour, soft, and lobulated
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Small Animal Medicine Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
REGULATION OF THYROID HORMONES
 HORMONAL SYSTEMS THYROID DISEASE Michael E. Herrtage Department of Veterinary Medicine Negative feedback REGULATION OF THYROID HORMONES Total T4 Free T4 TRH Total T3 Free T3 Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary
HORMONAL SYSTEMS THYROID DISEASE Michael E. Herrtage Department of Veterinary Medicine Negative feedback REGULATION OF THYROID HORMONES Total T4 Free T4 TRH Total T3 Free T3 Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
SCHEDULE OF EVENTS. Saturday September 30, Sunday October 1, Dr. Dennis Chew. Dr. Ed Feldman. Drs. Elliott, Reusch, Nelson
 SCHEDULE OF EVENTS Saturday September 30, 2006 7:30 am Registration/Continental Breakfast 8:00 am Welcome Dr. Dennis Chew 8:05 am Approach to Polyuria and Polydipsia - Diabetes Insipidus, Psychogenic Polydipsia
SCHEDULE OF EVENTS Saturday September 30, 2006 7:30 am Registration/Continental Breakfast 8:00 am Welcome Dr. Dennis Chew 8:05 am Approach to Polyuria and Polydipsia - Diabetes Insipidus, Psychogenic Polydipsia
Developmental Kidney Diseases
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Developmental Kidney Diseases (Diseases That Are Inherited or Occur during Development
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Developmental Kidney Diseases (Diseases That Are Inherited or Occur during Development
BALD ISN T ALWAYS BEAUTIFUL THINKING OUTSIDE THE BOX PART TWO NON-INFLAMMATORY ALOPECIA - WHAT S NEW
 BALD ISN T ALWAYS BEAUTIFUL THINKING OUTSIDE THE BOX PART TWO NON-INFLAMMATORY ALOPECIA - WHAT S NEW Anthony Yu DVM, MS, ACVD Yu of Guelph Veterinary Dermatology, Guelph Ontario Tel: 519-821-7546 email:
BALD ISN T ALWAYS BEAUTIFUL THINKING OUTSIDE THE BOX PART TWO NON-INFLAMMATORY ALOPECIA - WHAT S NEW Anthony Yu DVM, MS, ACVD Yu of Guelph Veterinary Dermatology, Guelph Ontario Tel: 519-821-7546 email:
TREATING MALASSEZIA DERMATITIS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATING MALASSEZIA DERMATITIS Author : Katerina Varjonen, Ross Bond Categories : Vets Date : May 25, 2009 Katerina Varjonen
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATING MALASSEZIA DERMATITIS Author : Katerina Varjonen, Ross Bond Categories : Vets Date : May 25, 2009 Katerina Varjonen
1. Mucocutaneous Pyoderma
 Top 5 Lip Depigmentation Causes in Dogs Alexander Werner, VMD, DACVD Animal Dermatology Center Studio City, California Skin pigmentation in mammals is primarily produced by the transfer of eumelanin (ie,
Top 5 Lip Depigmentation Causes in Dogs Alexander Werner, VMD, DACVD Animal Dermatology Center Studio City, California Skin pigmentation in mammals is primarily produced by the transfer of eumelanin (ie,
Pathology of the Integumentary System. Lecture 5 Endocrine / Miscellaneous / Neoplasia (web) Paul Hanna Fall 2017
 Pathology of the Integumentary System Lecture 5 Endocrine / Miscellaneous / Neoplasia (web) Paul Hanna Fall 2017 ENDOCRINE SKIN DISEASE hormones act on skin & other organs by modifying existing physiological
Pathology of the Integumentary System Lecture 5 Endocrine / Miscellaneous / Neoplasia (web) Paul Hanna Fall 2017 ENDOCRINE SKIN DISEASE hormones act on skin & other organs by modifying existing physiological
NUCLEAR MORPHOMETRY IN RELATION TO METASTASES IN CANINE SPONTANEOUS CUTANEOUS SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp 74-78, 2010 Copyright 2009 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp 74-78, 2010 Copyright 2009 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
information/submit- your-dog-points/.
 June 01, 2017 Volume 4, Issue 6 NEFHRC Coming Events 06/03-06/04/2017 North Alabama HRC Hunt Test The Hunter s Blind About NEFHRC Newsletter T his monthly newsletter is to help members keep updated on
June 01, 2017 Volume 4, Issue 6 NEFHRC Coming Events 06/03-06/04/2017 North Alabama HRC Hunt Test The Hunter s Blind About NEFHRC Newsletter T his monthly newsletter is to help members keep updated on
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
 S023 Hair and Scalp Dermoscopy Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Bruna Duque Estrada, M.D. Instituto de Dermatologia Prof. Rubem David Azulay Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Disclosure of Relationship with Industry
S023 Hair and Scalp Dermoscopy Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Bruna Duque Estrada, M.D. Instituto de Dermatologia Prof. Rubem David Azulay Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Disclosure of Relationship with Industry
Corticosteroids. Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System. University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year
 Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System Corticosteroids University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year 2008-9 Goudarz Sadeghi, DVM, PhD, DSc Associate Professor of Pharmacology Introduction
Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System Corticosteroids University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year 2008-9 Goudarz Sadeghi, DVM, PhD, DSc Associate Professor of Pharmacology Introduction
Hypothyroidism part two diagnosis, treatment and nursing
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Hypothyroidism part two diagnosis, treatment and nursing Author : Gemma Reid Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2008 Gemma Reid
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Hypothyroidism part two diagnosis, treatment and nursing Author : Gemma Reid Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2008 Gemma Reid
Histopathologic patterns of pancreatic lesions induced by Eurytrema coelomaticum in cattle from the
 3 Original full paper Histopathologic patterns of pancreatic lesions induced by Eurytrema coelomaticum in cattle from the central-west region of the State of Paraná, Southern Brazil Selwyn A. Headley 1,
3 Original full paper Histopathologic patterns of pancreatic lesions induced by Eurytrema coelomaticum in cattle from the central-west region of the State of Paraná, Southern Brazil Selwyn A. Headley 1,
Animal Disease States
 Animal Disease States Keri Chandley, CPhT, MBA Behavioral Problems Often human psychotropic drugs Require modification Opportunity for compounding Improved compliance Dose modification Types of behavior
Animal Disease States Keri Chandley, CPhT, MBA Behavioral Problems Often human psychotropic drugs Require modification Opportunity for compounding Improved compliance Dose modification Types of behavior
CUSHING'S DISEASE. Sent from the Diagnostic Imaging Atlas Page 1 of 5
 CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's disease? Cushing's disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's disease? Cushing's disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol
 Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol Cells derived from the bone marrow that mature and take part in cellular immune reactions are called lymphocytes. When lymphocytes undergo transformation and
Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol Cells derived from the bone marrow that mature and take part in cellular immune reactions are called lymphocytes. When lymphocytes undergo transformation and
GLANDULAR DISEASES. Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2
 GLANDULAR DISEASES Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology,
GLANDULAR DISEASES Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology,
Saluki Studies supported by Saluki Health Research, Inc.
 Saluki Studies supported by Saluki Health Research, Inc. prepared by MaryDee Sist, DVM for the Saluki World Congress in Helsinki, Finland, June 2008 MaryDee Sist, DVM is the President and Director of Saluki
Saluki Studies supported by Saluki Health Research, Inc. prepared by MaryDee Sist, DVM for the Saluki World Congress in Helsinki, Finland, June 2008 MaryDee Sist, DVM is the President and Director of Saluki
Pododermatitis. (Inflammation of Skin of the Paws) Basics OVERVIEW SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET SIGNS/OBSERVED CHANGES IN THE PET
 Pododermatitis (Inflammation of Skin of the Paws) Basics OVERVIEW Podo- refers to the feet or paws; dermatitis is the medical term for inflammation of the skin Pododermatitis is an inflammatory, multifaceted
Pododermatitis (Inflammation of Skin of the Paws) Basics OVERVIEW Podo- refers to the feet or paws; dermatitis is the medical term for inflammation of the skin Pododermatitis is an inflammatory, multifaceted
Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Increased levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood (known as hyperglycemia ) when the dog has
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Increased levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood (known as hyperglycemia ) when the dog has
Endocrine system pathology
 Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs
 Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Thyroid Disorders. Hypothyroidism. Low Total T4 Antiseizure meds Glucocorticoids. Free T4. Howard J. Sachs, MD.
 Thyroid Disorders Free T4 Low Total T4 Antiseizure meds Glucocorticoids Hypothyroidism Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Primary Hypothyroidism High TSH Low free T4 Primary = End organ failure
Thyroid Disorders Free T4 Low Total T4 Antiseizure meds Glucocorticoids Hypothyroidism Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Primary Hypothyroidism High TSH Low free T4 Primary = End organ failure
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Glomerulonephritis (Kidney Inflammation Involving the Glomerulus, the Blood Filter ) Basics
 Glomerulonephritis (Kidney Inflammation Involving the Glomerulus, the Blood Filter ) Basics OVERVIEW The kidney filters the blood and removes various waste products from the body as it produces urine;
Glomerulonephritis (Kidney Inflammation Involving the Glomerulus, the Blood Filter ) Basics OVERVIEW The kidney filters the blood and removes various waste products from the body as it produces urine;
ANHIDROSIS. The last several weeks at Brazos Valley Equine Hospital Navasota have seen an
 ANHIDROSIS Ben Buchanan, DVM Diplomate American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diplomate American College of Emergency and Critical Care Brazos Valley Equine Hospital Navasota, Texas The last
ANHIDROSIS Ben Buchanan, DVM Diplomate American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diplomate American College of Emergency and Critical Care Brazos Valley Equine Hospital Navasota, Texas The last
Diagnosis of canine atopic dermatitis (including food allergy)
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Diagnosis of canine atopic dermatitis (including food allergy) Favrot,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Diagnosis of canine atopic dermatitis (including food allergy) Favrot,
Hyperthyroidism in Cats
 Hyperthyroidism in Cats The thyroid gland is located in the neck and plays a very important role in regulating the body's rate of metabolism. Hyperthyroidism is a disorder characterized by the overproduction
Hyperthyroidism in Cats The thyroid gland is located in the neck and plays a very important role in regulating the body's rate of metabolism. Hyperthyroidism is a disorder characterized by the overproduction
The Adrenal Glands. I. Normal adrenal gland A. Gross & microscopic B. Hormone synthesis, regulation & measurement. II.
 The Adrenal Glands Thomas Jacobs, M.D. Diane Hamele-Bena, M.D. I. Normal adrenal gland A. Gross & microscopic B. Hormone synthesis, regulation & measurement II. Hypoadrenalism III. Hyperadrenalism; Adrenal
The Adrenal Glands Thomas Jacobs, M.D. Diane Hamele-Bena, M.D. I. Normal adrenal gland A. Gross & microscopic B. Hormone synthesis, regulation & measurement II. Hypoadrenalism III. Hyperadrenalism; Adrenal
WHEN IS PYODERMA NOT PYODERMA?
 WHEN IS PYODERMA NOT PYODERMA? Alison Diesel, DVM, Diplomate American College of Veterinary Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University Introduction Staphylococcal
WHEN IS PYODERMA NOT PYODERMA? Alison Diesel, DVM, Diplomate American College of Veterinary Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University Introduction Staphylococcal
Demodectic Mange. The initial increase in number of demodectic mites in the hair follicles may be the result of a genetic disorder
 Demodectic Mange (Demodicosis) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory parasitic skin disease of dogs and rarely cats, caused by a species of the mite genus, Demodex Skin disease is characterized by an increased
Demodectic Mange (Demodicosis) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory parasitic skin disease of dogs and rarely cats, caused by a species of the mite genus, Demodex Skin disease is characterized by an increased
Diagnosing neuromuscular disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosing neuromuscular disease Author : Victoria Doyle Categories : Vets Date : June 13, 2011 Victoria Doyle discusses the
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Diagnosing neuromuscular disease Author : Victoria Doyle Categories : Vets Date : June 13, 2011 Victoria Doyle discusses the
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
11/11/2015. Inflammatory. Non-inflammatory. Requires good health and nutrition Genetically influenced Influenced by photoperiod
 Inflammatory Exposed skin is clinically inflamed Primary lesions usually present Typically focal or asymmetrical Non-inflammatory Exposed skin appears normal No primary lesions initially Focal, asymmetrical,
Inflammatory Exposed skin is clinically inflamed Primary lesions usually present Typically focal or asymmetrical Non-inflammatory Exposed skin appears normal No primary lesions initially Focal, asymmetrical,
Epidemiological Aspects and Differential Diagnosis of the Cutaneous Round Cell Tumors in Dogs
 Epidemiological Aspects and Differential Diagnosis of the Cutaneous Round Cell Tumors in Dogs Roxana CORA, Adrian Florin GAL*, Marian TAULESCU, Flaviu TᾸBᾸRAN, Andras NAGY, Mihai NEGRU, Cornel CǍTOI Faculty
Epidemiological Aspects and Differential Diagnosis of the Cutaneous Round Cell Tumors in Dogs Roxana CORA, Adrian Florin GAL*, Marian TAULESCU, Flaviu TᾸBᾸRAN, Andras NAGY, Mihai NEGRU, Cornel CǍTOI Faculty
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
OVERVIEW OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL TUMORS IN DOG
 OVERVIEW OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL TUMORS IN DOG Georgeta Dinescu, Elvira Condruţ, Virginia Şerbănică, A. Feghiu Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,
OVERVIEW OF THE EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL TUMORS IN DOG Georgeta Dinescu, Elvira Condruţ, Virginia Şerbănică, A. Feghiu Faculty of Veterinary Medicine,
FROM ANNUAL WELLNESS VISIT TO ADRENALECTOMY!
 Volume 9 Issue 3 March 2017 Clinical Consults What s Your Diagnosis? PATIENT HISTORY SIGNALMENT: Mia Sophia is a 10 year old FS Shih Tzu. Weight 18.3 pounds/8.3 kg. PERTINENT PAST HISTORY: Mia Sophia has
Volume 9 Issue 3 March 2017 Clinical Consults What s Your Diagnosis? PATIENT HISTORY SIGNALMENT: Mia Sophia is a 10 year old FS Shih Tzu. Weight 18.3 pounds/8.3 kg. PERTINENT PAST HISTORY: Mia Sophia has
Ettinger & Feldman Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine
 Ettinger & Feldman Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Client Information Sheet Hyperthyroidism in Cats Edward C. Feldman What is hyperthyroidism? The thyroid is a two-lobed gland located in the neck
Ettinger & Feldman Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Client Information Sheet Hyperthyroidism in Cats Edward C. Feldman What is hyperthyroidism? The thyroid is a two-lobed gland located in the neck
Cutaneous adverse food reactions in the canine patient
 Cutaneous adverse food reactions in the canine patient D R. M I C H A E L A. R O S S I, D V M, M N S D I P. A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F V E T E R I N A R Y D E R M A T O L O G Y C O A S T A L V E
Cutaneous adverse food reactions in the canine patient D R. M I C H A E L A. R O S S I, D V M, M N S D I P. A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F V E T E R I N A R Y D E R M A T O L O G Y C O A S T A L V E
Hyperthyroidism in Cats
 Hyperthyroidism in Cats What is hyperthyroidism? The thyroid is a two-lobed gland located at the front of the neck in people, dogs, cats, and other animals. Each lobe sits on either side of the trachea
Hyperthyroidism in Cats What is hyperthyroidism? The thyroid is a two-lobed gland located at the front of the neck in people, dogs, cats, and other animals. Each lobe sits on either side of the trachea
Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics
![Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics](/thumbs/75/72552398.jpg) Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics OVERVIEW A group of conditions of differing cause in which insoluble proteins (amyloid) are deposited outside
Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics OVERVIEW A group of conditions of differing cause in which insoluble proteins (amyloid) are deposited outside
Canine Mast Cell Tumors
 Canine Mast Cell Tumors By: Dr. Custead WVRC Introduction Mast cells Resident inflammatory cell of the skin, lungs, gastro- intestinal tract Reactions secondary to IgE binding Allergic reactions Granules
Canine Mast Cell Tumors By: Dr. Custead WVRC Introduction Mast cells Resident inflammatory cell of the skin, lungs, gastro- intestinal tract Reactions secondary to IgE binding Allergic reactions Granules
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics
 Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Diabetes, sugar. Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA (724)
 Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Feline diabetes mellitus Diabetes, sugar AffectedAnimals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when
Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Feline diabetes mellitus Diabetes, sugar AffectedAnimals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when
Updates on Feline Atopic Dermatitis (or should we say CATopy?)
 Updates on Feline Atopic Dermatitis (or should we say CATopy?) Sandra N. Koch, DVM, MS, DACVD Associate Professor, Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota INTRODUCTION Despite
Updates on Feline Atopic Dermatitis (or should we say CATopy?) Sandra N. Koch, DVM, MS, DACVD Associate Professor, Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota INTRODUCTION Despite
AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND COLLEGE OF VETERINARY SCIENTISTS. FELLOWSHIP GUIDELINES Animal Reproduction (Dog and Cat)
 Approved 1999 AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND COLLEGE OF VETERINARY SCIENTISTS FELLOWSHIP GUIDELINES Animal Reproduction (Dog and Cat) ELIGIBILITY 1. The candidate shall meet the eligibility prerequisites for
Approved 1999 AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND COLLEGE OF VETERINARY SCIENTISTS FELLOWSHIP GUIDELINES Animal Reproduction (Dog and Cat) ELIGIBILITY 1. The candidate shall meet the eligibility prerequisites for
The endocrine system is complex and sometimes poorly understood.
 1 CE Credit Testing the Endocrine System for Adrenal Disorders and Diabetes Mellitus: It Is All About Signaling Hormones! David Liss, BA, RVT, VTS (ECC) Platt College Alhambra, California For more information,
1 CE Credit Testing the Endocrine System for Adrenal Disorders and Diabetes Mellitus: It Is All About Signaling Hormones! David Liss, BA, RVT, VTS (ECC) Platt College Alhambra, California For more information,
Acta Scientiae Veterinariae ISSN: Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul. Brasil
 Acta Scientiae Veterinariae ISSN: 1678-0345 actascivet-submission@ufrgs.br Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul Brasil da Silva Meirelles, Luana; Bianchini Moresco, Maurício; de Jesus, Luciana; Carvalho
Acta Scientiae Veterinariae ISSN: 1678-0345 actascivet-submission@ufrgs.br Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul Brasil da Silva Meirelles, Luana; Bianchini Moresco, Maurício; de Jesus, Luciana; Carvalho
Tumors of the Spleen
 Tumors of the Spleen 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Tumors of the Spleen 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Tips on getting the most from your alopecia pathology reports. D irector, H a ir C linic, Boston Medical C e n ter
 Tips on getting the most from your alopecia pathology reports Lynne J. Goldberg, MD J a g Bhawan Professor o f Dermatology a n d Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Boston U n iversity School of Medicine D
Tips on getting the most from your alopecia pathology reports Lynne J. Goldberg, MD J a g Bhawan Professor o f Dermatology a n d Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Boston U n iversity School of Medicine D
Originally trained to find live game, their temperament makes them an ideal family dog
 Originally trained to find live game, their temperament makes them an ideal family dog Labrador Retriever Lifetime costs: 20,648 Annual costs: 2,332.85 Purchase price: 681 Feeding costs: 537.37 Insurance:
Originally trained to find live game, their temperament makes them an ideal family dog Labrador Retriever Lifetime costs: 20,648 Annual costs: 2,332.85 Purchase price: 681 Feeding costs: 537.37 Insurance:
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics
 Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
Atopy. What are the signs of atopy?
 Atopy Atopy is a fairly common condition in dogs. Animals with atopy are allergic to substances in the environment that are inhaled or absorbed through the skin. The resulting allergic reaction is seen
Atopy Atopy is a fairly common condition in dogs. Animals with atopy are allergic to substances in the environment that are inhaled or absorbed through the skin. The resulting allergic reaction is seen
