Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled?
|
|
|
- Marlene Robinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL
2 Mycosis Fungoides Alibert in 1806 Patient whose skin lesions developed into mushroom like tumors Invariably fatal Bazin in 1862 Three classical stages: patch, plaque and tumor Brocq in 1902 Parapsoriasis (large and small plaque) Sézary syndrome 1938 Variants: Pagetoid reticulosis (1939) Folliculotropic (1957) Granulomatous MF (1970) Hypopigmented MF Pustular MF
3 Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma 1975 Cutaneous T cell lymphomas: the Sézary syndrome, mycosis fungoides, and related disorders. Lutzner M, Edelson R, Schein P, Green I, Kirkpatrick C, Ahmed A. Ann Intern Med Oct;83(4): Substantial evidence has accumulated to indicate not only that mycosis fungoides and the Sézary syndrome are closely related malignancies, but to suggest that they are part of a larger spectrum of cutaneous lymphomas. The neoplastic cells of these disorders have membrane features of thymus derived (T) lymphocytes, a characteristic tissue distribution (skin infiltration, marrow sparing, localization in T cell regions of lymphoid tissue), and distinctive morphology. For these reasons, we suggest that these lymphoproliferative disorders be grouped together as "cutaneous T cell lymphomas".
4 Historic overview on different concepts on the classification of cutaneous lymphomas EORTC Classification for Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas: The Best Guide to Good Clinical Management. Willemze, Rein; Meijer, Chris American Journal of Dermatopathology. 21(3): , June Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2
5 EORTC classification for Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas (1997) EORTC Classification for Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas: The Best Guide to Good Clinical Management. Willemze, Rein; Meijer, Chris American Journal of Dermatopathology. 21(3): , June Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2
6 Classification of disease entities of the EORTC in the proposed WHO classification EORTC Classification for Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas: The Best Guide to Good Clinical Management. Willemze, Rein; Meijer, Chris American Journal of Dermatopathology. 21(3): , June Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. 2
7 WHO EORTC and WHO 2008 Classification Cutaneous T Cell Lymphomas 78% Cutaneous B Cell Lymphomas 22% Mycosis fungoides Variants of MF Folliculotropic Granulomatous slack skin Pagetoid reticulosis Sezary syndrome CD30+ Lymphoproliferative disorders Cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (C ALCL) Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) Subcutaneous panniculitis like T Cell lymphoma ExtranodalNK/T cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous PTCL, NOS and variants Primary cutaneous marginal zone B cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma Primary cutaneous diffuse large B cell lymphoma, leg type Intravascular B cell lymphoma Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G et al. WHO EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005; 105 (10):
8 CTCL: Relative Frequency and Disease Specific Survival EORTC WHO Classification Frequency % 5 year survival % Indolent Mycosis fungoides Follicular mycosis fungoides Pagetoid reticulosis Granulomatous slack skin CD30 + lymphoproliferative diseases Anaplastic large cell lymphoma Lymphomatoid papulosis Subcutaneous panniculitis like T cell lymphoma CD4 + small/medium pleomorphic T cell lymphoma 44 4 <1 < Aggressive Sézary syndrome Cutaneous peripheral T cell lymphoma, unspecified Cutaneous aggressive CD8 + T cell lymphoma Cutaneous γ/δ T cell lymphoma Cutaneous NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type 3 2 <1 <1 < Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G et al. WHO EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005; 105 (10):
9 Mycosis Fungoides Most common type of CTCL Mostly adults (55 60 years of age) with male predominance ( :1) May affect children/adolescents Epidermotropic proliferation of small to medium sized T helper (CD4+) cells with cerebriform nuclei Indolent course spanning from years to decades with slow progression patch plaque tumors Systemic disease develops in minority of patients
10 Mycosis Fungoides Initial skin lesions tend to occur on the buttocks and other sun protected areas Patients in advanced stages show a combination of patches, plaques, and tumors Ulceration can occur Histopathology: Epidermotropism with Pautrier microabscesses, atypical lymphocytes with haloed appearance, minimal to absent spongiosis Phenotype: Most are CD4+ memory T cells, ~15% CD8+; loss of pan T cell markers (CD2, 3, 4, 5) not uncommon
11 CD3 CD5 CD4 CD8
12 Mycosis Fungoides: Diagnosis Dependent on a combination of clinical and histopathologic criteria which may be supplemented with Immunohistochemistry Molecular (gene rearrangement) studies
13 Mycosis Fungoides: Some Controversies and Advances Parapsoriasis en plaques, digitate dermatosis and patch stage MF Granulomatous slack skin and granulomatous MF Alopecial mucinosa and folliculotropic MF Transformed MF and CD30+ALCL Sezary syndrome and erythrodermic MF
14 Parapsoriasis of Brocq Large plaque parapsoriasis Parapsoriasis en plaques Parapsoriasis Lichenoides Parapsoriasis Variegata Xanthoerythroderma perstans Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans Small plaque parapsoriasis Digitate dermatosis Parapsoriasis guttata Both convert or transform rarely to mycosis fungoides
15 Large plaque parapsoriasis is mycosis fungoides!! that specific histologic diagnosis of mycosis fungoides cannot be made in the premycotic" or "eczematous" (patch) stage of the disease. that histologic features of the premycotic lesions were constantly said to be those of "chronic non specific dermatitis. 46 biopsy specimens of patch lesions from patients in whom mycosis fungoides was unequivocally established by clinical events (i.e., concurrence or later development of typical plaque and/or nodular lesions) and indubitable histologic findings Histologic diagnosis can be made with near certainty in patch lesions of the disease. increased number of mononuclear cells distributed singly or in small collections within an epidermis devoid of spongiotic microvesiculation. lacunae surrounding intraepidermal mononuclear cells which gives them the appearance of "haloed cells. Atypical mononuclear cells are not necessary for the diagnosis of early patch lesions of mycosis fungoides but are found in late patch lesions Sanchez JL, Ackerman AB. The patch stage of mycosis fungoides. Criteria for histologic diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol Spring;1(1):5 26.
16 Guttate parapsoriasis/digitate dermatosis (small plaque parapsoriasis) is mycosis fungoides..authors of most textbooks of dermatology and dermatopathology consider guttate parapsoriasis and digitate dermatosis to be variants of small plaque parapsoriasis which, they aver, is not related to mycosis fungoides. On the basis of a study of clinical and histopathologic findings in guttate parapsoriasis and digitate dermatosis, we conclude that those conditions actually represent two of the many clinical faces of mycosis fungoides. King Ismael D, Ackerman AB. Am J Dermatopathol Dec;14(6):518 30; discussion
17 Algorithm for the diagnosis of early MF+ Criteria Clinical Persistent and/or progressive patches and plaques plus (1) Non sun exposed location (2) Size/shape variation (3) Poikiloderma Histopathologic Superficial lymphoid infiltrate plus (1) Epidermotropism without spongiosis (2) Lymphoid atypia* Major (2 points) Any 2 Both Minor (1 point) Any1 Either Molecular/biologic: clonal TCR gene rearrangemen NA Present Immunopathologic (1) CD2, 3, 5, less than 50% of T cells (2) CD7 less than 10% of T cells (3) Epidermal discordance from expression of CD2, 3, 5 or CD7 on dermal T cells NA Any 1 *Lymphoid atypia is defined as cells with enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei and irregular or cerebriform nuclear contours. Not applicable since it cannot fulfill any major criteria. +Pimpinelli N, Olsen EA, Santucci M, et al for the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphoma. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol Dec; 53(6):
18 Folliculotropic MF and Alopecia Mucinosa Kreibech (1925); follicular mucin in a patient with wide spread plaques some of which were clinically similar to Brocq s large plaque parapsoriasis Pinkus (1957): 6 patients.. follicular papules and/or indurated plaques that demonstrate (mucin) in the hair follicles that lead to hair loss Kim and Winkelmann (1962); 10 patients one of whom had lesions of LPP and later developed MF Pinkus (1964): Follicular mucinosis: Idiopathic Lymphoblastoma seconday follicular mucinosis Alopecia mucinos transforming to lymphoblastoma Pinkus (1983): several patients >plaques/tumors of MF Pinkus H. Alopecia mucinosa. Inflammatory plaques with alopecia characterized by rootsheath mucinosis. Arch Dermatol Arch Dermatol. Aug 1983;119(8):690 7
19 Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic and follow up study of 51 patients. van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(2): Lesions from all 51 patients showed follicular mucinosis Not possible to distinguish follicular MF with follicular mucinosis from follicular MF without follicular mucinosis Follicular mucinosis: a critical reappraisal of clinicopathologic features and association with mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Cerroni L, Fink Puches R, Bäck B, Kerl H. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(2): Idiopathic follicular mucinosis may be a localized form of MF
20 Alopecia mucinosa is mycosis fungoides! Böer A, Guo Y, Ackerman AB. Am J Dermatopathol Feb;26(1): we propose a concept, and a terminology that derives from it, that synthesizes all that is known now about "alopecia mucinosa" and "follicular mucinosis," in particular the relationship of "alopecia mucinosa" to mycosis fungoides, including "follicular," "syringotropic," and erythrodermic manifestations of it. In short, we affirm that so called alopecia mucinosa is but one of many morphologic manifestations of mycosis fungoides. Epithelial mucinosis : deposits of mucin in infundibular, follicular and sebaceous epithelium; seen in host of conditions MF with epithelial mucinosis : fulfills criteria for MF clinically and histologically in addition to epithelial deposits of mucin
21 Folliculotropic MF Lacks characteristic patches/plaques Preferential involvement of head/neck region and presents as follicular papules, plaques and tumors Hair loss and secondary bacterial infections Severe pruritus Less amenable to local therapy More often large cell transformation and peripheral blood involvement Prognosis less favorable than classical MF (5 year survival 75% similar to tumor stage)
22 Folliculotropic MF Perivascular and periadnexal localization of dermal infiltrates of atypical lymphocytes T cell phenotype as in classical MF CD3+, CD4+, CD8, Admixed CD30+ cells Follicular mucinosis is present in most cases but not a prerequisite Folliculotropism and syringotropism (adnexotropism) instead of epidermotropism Keep in mind: 1/3 of cases of classic MF show eccrine gland involvement 1/2 of cases of classic MF show follicular involvement
23 Granulomatous MF and Granulomatous Slack Skin Ackerman AB, Flaxman BA. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides. Br J Dermatol 1970;82:397 An unusual form of mycosis fungoides was characterized clinically by the spontaneous resolution of ulcerated nodular lesions into poikiloderma and histologically by a granulomatous malignant lymphoma. a patient with widespread plaques and nodules of mycosis fungoides, and findings histopathologic of that lymphoma coupled with granulomas in the dermis of sections of tissue of several biopsy specimens. They termed the phenomenon granulomatous mycosis fungoides 1968 Bazex et al. described a clinical form similar to cutis laxa as 'Besnier Boeck Schaumann disease In 1978 Ackerman added the term 'granulomatous slack skin disease
24 Granulomatous MF versus GSS Granulomatous slack skin (GSS), however, does not appear to be merely mycosis fungoides (MF) associated with local elastic tissue destruction...a clinical presentation different from that of MF appears to be characteristic...a few patients with MF have shown granulomatous inflammation associated with the lymphomatous infiltrate, a process that has been termed granulomatous MF. LeBoit PE et al. Granulomatous slack skin: clonal rearrangement of the T cell receptor gene is evidence for the lymphoproliferative nature of a cutaneous elastolytic disorder. J Invest Dermatol 1987;89: GSS is a form of cutaneous lymphoma with an indolent but relentless course. It is characterized by circumscribed areas of pendulous lax skin that contain clonal infiltrates of helper T cells, which infiltrate the epidermis in a manner similar to that of mycosis fungoides and attract a granulomatous component that mediates massive dermal elastolysis. LeBoit PE Granulomatous slack skin. Dermatol Clin 1994; 12: Granulomatous inflammation in mycosis fungoides is a phenomenon that develops secondary to the lymphoma, and can be seen in such disparate representations of mycosis fungoides as parapsoriasis en plaques and granulomatous slack skin. Ackerman AB et al. Histologic Diagnosis of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. 2nd ed. 1997:842, 850.
25 Granulomatous MF/GSS In 1997 and 2005 'granulomatous slack skin' was included in the EORTC and then the WHO EORTC classification as a provisional entity. GSS Rare subtype with a striking clinical picture Granulomatous T cell infiltrates and loss of elastic fibers lead to asymptomatic skin wrinkles and slow development of lax skin, mainly in the flexures (axillae and groin) May be preceded by erythematous scaling patches or macules, and may coexist with classical MF lesions. In 33 50% of cases coexistence with Hodgkin lymphoma or nodal non Hodgkin lymphoma The pathogenesis of granuloma formation in lymphoma is unknown but its occurrence is not specific for MF
26 MF Large cell transformation Large cells >25% of total infiltrate or microscopic nodules of large cells with or without expression of CD % incidence Associated with poor prognosis Median survival months 5 year 11 32% Prognostic factors % of large cells CD30 expression Folliculotropism Stage Extent of skin involvement
27 Fig 2 MF LCT vs CD30+ALCL US Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium algorithm for the classification of skin tumors in patients with CTCL Source Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2014; 70: (DOI: /j.jaad ) Copyright 2014 American Academy of Dermatology, Inc. Terms and Conditions
28 Sézary Syndrome Erythroderma Hyperkeratosis of palms and soles Generalized lymphadenopathy Clonal T cells (Sézary cells) in skin, lymph nodes, and peripheral blood (No history of MF) Similar phenotype as MF 5 year survival 20 30% Skin biopsy: +/ Similar histology as MF
29 Erythrodermic CTCL International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma Concensus definitions and terminology Sezary syndrome (leukemic phase E CTCL) Erythrodermic mycosis fungoides in patients with MF (Secondary E CTCL) E CTCL, NOS
30 Update on Erythrodermic Cutaneous T cell Lymphoma: report of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphoma The hematologic criteria recommended for Sézary syndrome are intended to identify patients with a worse prognosis compared with the other E CTCL subsets and consist of one or more of the following: (1) an absolute Sézary cell count of 1000 cells/mm3 or more; (2) a CD4/CD8 ratio of 10 or higher caused by an increase in circulating T cells and/or an aberrant loss or expression of pan T cell markers by flow cytometry; (3) increased lymphocyte counts with evidence of a T cell clone in the blood by the Southern blot or polymerase chain reaction technique; or (4) a chromosomally abnormal T cell clone Vonderheid EC, Bernengo MG, Burg G. J Am Acad Dermatol Jan;46(1):
31 MF versus SS Both MF and SS: Monoclonal population of CD4+/CD45RO+ helper T cells Loss of mature T cell antigens Involve skin (and other organs) Erythrodermic MF: Preceded by typical patch/plaque lesions Skin biopsy shows classical features of MF Absent or low circulating neoplastic cells SS Distinctive erythrodermic CTCL with hematologic evidence of leukemic involvement Skin biopsy may be non specific (in >30%); cells monomorphous, epidermotropism may be absent Not preceded by clinically typical MF
32 SS is a distinct entity and not merely a leukemic phase or variant of MF Differential Expression of Programmed Death 1 (PD 1) in Sézary Syndrome and Mycosis Fungoides Çetinözman F, Jansen PM, Maarten H, Vermeer, MH, Willemze, R. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(12): Sezary syndrome and mycosis fungoides arise from distinct T cell subsets: a biologic rationale for their distinct clinical behaviors. Campbell JJ, Clark RA, Watanabe R et al. Blood. 2010; 116(5):
33 ISCL/EORTC Clinical Staging System for Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome* Stage I Disease confined to the skin with patches/papules/plaques <10% (1A) or >10% (1B) of skin surface, N0 II Skin involvement with patches /papules/plaques associated with early (N1 N2) lymph node involvement (IIA) or skin involvement with tumors (>1cm) (IIB) III Erythroderma, +/ lymph node involvement (N0, N1, N2) and absent or low blood tumor burden (<1000/μl circulating Sézary cells) IV High blood tumor burden (>1000/μl circulating Sézary cells) and/or extensive lymph node involvement (N3) or visceral involvement (M1) * Olsen E, Vonderheid E, Pimpinelli N, et al. Revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the cutaneous lymphoma task force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood. 2007;110(6):
34 Mycosis Fungoides References 1. Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G et al. WHO EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005; 105 (10): Song SX, Willemze R, Swerdlow SH et al. Mycosis fungoides. Am J Clin Pathol 2013;139: Lutzner M, Edelson R, Schein P et al. Cutaneous T cell lymphomas: The Sezary syndrome, mycosis fungoides and related disorders. Ann Intern Med. 1975; Sanchez JL, Ackerman AB. The patch stage of mycosis fungoides. Criteria for histologic diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1979; 1(1): Pimpinelli N, Olsen EA, Santucci M, et al for the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphoma. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol Dec; 53(6): Review 6. King Ismael D, Ackerman AB. Guttate parapsoriasis/digitate dermatosis (small plaque parapsoriasis) is mycosis fungoides. Am J Dermatopathol. 1992; 14(6):518 30; discussion Howard MS, Smoller BR. Mycosis fungoides: classic disease and variant presentations. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2000;19(2): Ackerman AB, Flaxman BA. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides. Br J Dermatol 1970;82: LeBoit PE, Zackheim HS, White CR Jr. Granulomatous variants of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. The histopathology of granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988; 12(2): van Doorn R, Scheffer E, Willemze R. Follicular mycosis fungoides, a distinct disease entity with or without associated follicular mucinosis: a clinicopathologic and follow up study of 51 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(2): Cerroni L, Fink Puches R, Bäck B, Kerl H. Follicular mucinosis: a critical reappraisal of clinicopathologic features and association with mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(2): Böer A, Guo Y, Ackerman AB. Alopecia mucinosa is mycosis fungoides. Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26(1):33 52.
35 13. Lehman JS, Cook Norris RH, Weed BR, et al. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: single center study and systematic review. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146(6): Pileri A, Facchetti F, Rütten A, et al. Syringotropic mycosis fungoides: a rare variant of the disease with peculiar clinicopathologic features. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35(1): Haghighi B, Smoller BR, LeBoit PE, et al. Pagetoid reticulosis (Woringer Kolopp disease): an immunophenotypic, molecular, and clinicopathologic study. Mod Pathol. 2000; 13(5): Werner B, Brown S, Ackerman AB. "Hypopigmented mycosis fungoides" is not always mycosis fungoides! Am J Dermatopathol. 2005; 27(1): Review. 17. Castano E, Glick S, Wolgast L, et al. Hypopigmented mycosis fungoides in childhood and adolescence: a long term retrospective study. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40(11): Benner MF, Jansen PM, Vermeer MH, Willemze R. Prognostic factors in transformed mycosis fungoides: a retrospective analysis of 100 cases. Blood Feb 16;119(7): Kadin ME, Hughey LC, Wood GS. Large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides differential diagnosis with implications for clinical management: A consensus statement of the US Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium. J Am Acad Dermatol Feb;70(2): Campbell JJ, Clark RA, Watanabe R et al. Sezary syndrome and mycosis fungoides arise from distinct T cell subsets: a biologic rationale for their distinct clinical behaviors. Blood. 2010; 116(5): Çetinözman F, Jansen PM, Maarten H, Vermeer, MH, Willemze, R Differential Expression of Programmed Death 1 (PD 1) in Sézary Syndrome and Mycosis Fungoides. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(12): Whittaker S, Knobler R Ortiz P et al. Major achievements of the EORTC Cutaneous Lymphoma Task Force (CLTF). European Journal of Cancer Supplements. March 2012; 10(1): Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): Part I. Diagnosis: Clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers. J Am Acad Dermatol Feb;70(2):205.e1 205.e16. doi: /j.jaad
36 24. Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): Part II. Prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol Feb;70(2):223.e1 223.e Willemze R. Thirty years of progress in cutaneous lymphoma research. G Ital Dermatol Venereol Dec;147(6): Review. 26. Olsen E, Vonderheid E, Pimpinelli N, et al. Revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the cutaneous lymphoma task force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Blood Sep 15;110(6):
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology
 Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD
 Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Disclosures. Advisory Board. Consultant. Investigator. MiRagen, Actelion, Celgene, Therakos. Mindera
 Cutaneous Lymphomas Christiane Querfeld, MD, PhD Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Program City of Hope ~ How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Symposium March 10 13, 2017 Disclosures Advisory Board
Cutaneous Lymphomas Christiane Querfeld, MD, PhD Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Program City of Hope ~ How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Symposium March 10 13, 2017 Disclosures Advisory Board
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants
 Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma
 Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
SH/EAHP Workshop 2011 Los Angeles, California, USA
 SH/EAHP Workshop 2011 Los Angeles, California, USA October 27-29, 2011 Session 3 Non-Mycosis Fungoides CTCL Patty Jansen & Rein Willemze Introduction Submitted: 101 cases + 7 cases group 1: 108 Deactivated
SH/EAHP Workshop 2011 Los Angeles, California, USA October 27-29, 2011 Session 3 Non-Mycosis Fungoides CTCL Patty Jansen & Rein Willemze Introduction Submitted: 101 cases + 7 cases group 1: 108 Deactivated
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin
 Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Review Article. Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders. NJ Trendell-Smith
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2010) 18, 190-201 Review Article Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders NJ Trendell-Smith Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders (CLD) include reactive lymphoid hyperplasias,
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2010) 18, 190-201 Review Article Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders NJ Trendell-Smith Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders (CLD) include reactive lymphoid hyperplasias,
ISPUB.COM. M Duvic, E Olsen PURPOSE OF REVISION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies. Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab
 Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end
Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end
Interhospital Dermatology Conference 2013
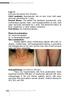 Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Fig. 3.1 Fig Past history: She was previously healthy and not taking any medication.
 Case 3 A 41-year-old Thai female from Bangkok Chief compliant: Erythematous patch at left thigh for 2 months Present illness: The patient presented with a 10- year history of erythematous patch on her
Case 3 A 41-year-old Thai female from Bangkok Chief compliant: Erythematous patch at left thigh for 2 months Present illness: The patient presented with a 10- year history of erythematous patch on her
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous
 Mycosis fungoides variants clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and treatment Rein Willemze, MD, PhD Abstract Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Mycosis fungoides variants clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and treatment Rein Willemze, MD, PhD Abstract Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides
 Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides
 Case Report DOI: 10.6003/jtad.16102c5 CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides Esra Adışen, 1 MD, Özlem Erdem, 2 MD, Mehmet Ali Gürer, 1 MD Address: 1 Gazi University
Case Report DOI: 10.6003/jtad.16102c5 CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides Esra Adışen, 1 MD, Özlem Erdem, 2 MD, Mehmet Ali Gürer, 1 MD Address: 1 Gazi University
A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides
 Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: (Istodax) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.314 Effective Date: 01.01.17 Last Review Date: 11.18 Line of Business: Medicaid, HIM-Medical Benefit Coding Implications Revision Log See Important
Clinical Policy: (Istodax) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.314 Effective Date: 01.01.17 Last Review Date: 11.18 Line of Business: Medicaid, HIM-Medical Benefit Coding Implications Revision Log See Important
Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study
 Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
STUDY. fungoides (FMF) is an uncommon
 STUDY Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides Single-Center Study and Systematic Review Julia S. Lehman, MD; Robert H. Cook-Norris, MD; Brent R. Weed, MD; Roger H. Weenig, MD; Lawrence E. Gibson, MD; Amy L.
STUDY Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides Single-Center Study and Systematic Review Julia S. Lehman, MD; Robert H. Cook-Norris, MD; Brent R. Weed, MD; Roger H. Weenig, MD; Lawrence E. Gibson, MD; Amy L.
U006 Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis, Staging and When to Refer M. Yadira Hurley, MD
 U006 Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis, Staging and When to Refer M. Yadira Hurley, MD hurleyy@slu.edu DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Actelion: Speaker Honoraria, Investigator Grants, Consultant
U006 Primary Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis, Staging and When to Refer M. Yadira Hurley, MD hurleyy@slu.edu DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Actelion: Speaker Honoraria, Investigator Grants, Consultant
Malignant Lymphomas Decision Making and Problem Solving
 Malignant Lymphomas Decision Making and Problem Solving Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (including rare subtypes). Current concepts. II. [haematologica] 2004;89:1372-1388 MARCO PAULLI EMILIO BERTI A B S T R
Malignant Lymphomas Decision Making and Problem Solving Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (including rare subtypes). Current concepts. II. [haematologica] 2004;89:1372-1388 MARCO PAULLI EMILIO BERTI A B S T R
Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560
 285..288 Australasian Journal of Dermatology (2009) 50, 285 288 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00560.x CASE REPORT Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560 Shano Nassem, 1 Rajesh Kashyap,
285..288 Australasian Journal of Dermatology (2009) 50, 285 288 doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00560.x CASE REPORT Sézary syndrome presenting with leonine facies ajd_560 Shano Nassem, 1 Rajesh Kashyap,
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week
 CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
A rare clinical presentation of non Hodgkin Lymphoma as multiple neurofibromas with review of literature
 Original article A rare clinical presentation of non Hodgkin Lymphoma as multiple neurofibromas with review of literature Dr.C.R.Sirajunnisa Begum, Professor 1, Dr. Ira Bharadhwaj, Professor 1, Dr. Lavanya,
Original article A rare clinical presentation of non Hodgkin Lymphoma as multiple neurofibromas with review of literature Dr.C.R.Sirajunnisa Begum, Professor 1, Dr. Ira Bharadhwaj, Professor 1, Dr. Lavanya,
New Haven, Connecticut
 New Haven, Connecticut Yale University Main Campus Yale mascot: Handsome Dan Cutaneous Lymphomas Tony Subtil, MD, MBA Associate Professor Yale University Cutaneous Lymphomas: 1. Intro 2. CTCL/NK 3. CBCL
New Haven, Connecticut Yale University Main Campus Yale mascot: Handsome Dan Cutaneous Lymphomas Tony Subtil, MD, MBA Associate Professor Yale University Cutaneous Lymphomas: 1. Intro 2. CTCL/NK 3. CBCL
ISPUB.COM. Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose Methotrexate. S Parker INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10/11
 Clinical Policy: (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10/11 Last Review Date: 12/16 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
Clinical Policy: (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10/11 Last Review Date: 12/16 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
2. Sézary syndrome (SS)
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Clinical images are available in hardcopy only. Clinical images are available in Clinical images are available in d e f g h i j Fig..36-2
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Clinical images are available in hardcopy only. Clinical images are available in Clinical images are available in d e f g h i j Fig..36-2
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype. Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital
 Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Primary Cutaneous Acral CD8 þ T-Cell Lymphoma
 Primary Cutaneous Acral CD8 þ T-Cell Lymphoma Vivian M. Hathuc, DO; Alexandra C. Hristov, MD; Lauren B. Smith, MD Primary cutaneous acral CD8 þ T-cell lymphoma is a new provisional entity in the 2016 revision
Primary Cutaneous Acral CD8 þ T-Cell Lymphoma Vivian M. Hathuc, DO; Alexandra C. Hristov, MD; Lauren B. Smith, MD Primary cutaneous acral CD8 þ T-cell lymphoma is a new provisional entity in the 2016 revision
Unusual cutaneous presentation of a T-cell lymphoproliferation
 Department of Pathology and Cytology University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia Unusual cutaneous presentation of a T-cell lymphoproliferation Snjezana Dotlic, Stefan Dojcinov, Leticia Quintanilla-Fend
Department of Pathology and Cytology University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia Unusual cutaneous presentation of a T-cell lymphoproliferation Snjezana Dotlic, Stefan Dojcinov, Leticia Quintanilla-Fend
A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides
 A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides Robin T. Vollmer, MD From the VA and Duke University Medical Centers, Durham, NC. Key Words: Mycosis fungoides; Survival; Hazard function; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides Robin T. Vollmer, MD From the VA and Duke University Medical Centers, Durham, NC. Key Words: Mycosis fungoides; Survival; Hazard function; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Primer of Immunohistochemistry (Leukocytic)
 Primer of Immunohistochemistry (Leukocytic) Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Torrance, CA BENIGN LYMPHOID SKIN LESIONS CAPABLE OF SIMULATING LYMPHOMA -Jessner s lymphoid infiltrate -Dermal-subcutaneous
Primer of Immunohistochemistry (Leukocytic) Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Torrance, CA BENIGN LYMPHOID SKIN LESIONS CAPABLE OF SIMULATING LYMPHOMA -Jessner s lymphoid infiltrate -Dermal-subcutaneous
Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides
 Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
clinical recommendations
 19 (Supplement 2): ii72 ii76, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn095 Primary cutaneous lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up R. Dummer 1 & M. Dreyling 2 On behalf of the
19 (Supplement 2): ii72 ii76, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn095 Primary cutaneous lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up R. Dummer 1 & M. Dreyling 2 On behalf of the
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4): /ISSN: /IJCEP Tadashi Terada
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4):749-756 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1301060 Case Report Mycosis fungoides in plaque stage with pronounced eosinophilic infiltration, folliculotropism, and concomitant
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4):749-756 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1301060 Case Report Mycosis fungoides in plaque stage with pronounced eosinophilic infiltration, folliculotropism, and concomitant
Lymphocytoma Cutis. Cynthia M. Magro MD. Director of Dermatopathology Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, New York
 Lymphocytoma Cutis Cynthia M. Magro MD Professor of Pathology Director of Dermatopathology Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, New York Lymphocytoma Cutis Falls under other designations
Lymphocytoma Cutis Cynthia M. Magro MD Professor of Pathology Director of Dermatopathology Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, New York Lymphocytoma Cutis Falls under other designations
Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated with Interferon-Alfa 2a
 Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms
 J Hematopathol (2009) 2:65 73 DOI 10.1007/s12308-009-0034-z COMMENT Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms Megan S. Lim & Laurence de Leval & Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
J Hematopathol (2009) 2:65 73 DOI 10.1007/s12308-009-0034-z COMMENT Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms Megan S. Lim & Laurence de Leval & Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas
 Review Article DOI: 10.1159/000470845 Received: February 06, 2017 Accepted: March 13, 2017 Published online: April 6, 2017 Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas Bouthaina
Review Article DOI: 10.1159/000470845 Received: February 06, 2017 Accepted: March 13, 2017 Published online: April 6, 2017 Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas Bouthaina
Follicular lymphomatoid papulosis revisited: a study of 11 cases, with new histopathological findings
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Follicular lymphomatoid papulosis revisited: a study of 11 cases, with
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2013 Follicular lymphomatoid papulosis revisited: a study of 11 cases, with
Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review
 Case-based review Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review Anna Campanati 1 Katia Giuliodori 1 Emanuela Martina 1 Luca Conocchiari 1 Giulia Ganzetti 1 Gaia Goteri 2 Annamaria Offidani
Case-based review Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review Anna Campanati 1 Katia Giuliodori 1 Emanuela Martina 1 Luca Conocchiari 1 Giulia Ganzetti 1 Gaia Goteri 2 Annamaria Offidani
The clinical recognition of a folliculotropic pattern in
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Spectrum of Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Findings in Pedram Gerami, MD and Joan Guitart, MD Background: Since the original designation of folliculotropic mycosis fungoides
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Spectrum of Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Findings in Pedram Gerami, MD and Joan Guitart, MD Background: Since the original designation of folliculotropic mycosis fungoides
Given that mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common
 Histopathologic approach to epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrates Shyam S Raghavan, MD 1 and Jinah Kim, MD, PhD 2 Abstract Mycosis fungoides is the most common and therefore quintessential cutaneous lymphoma
Histopathologic approach to epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrates Shyam S Raghavan, MD 1 and Jinah Kim, MD, PhD 2 Abstract Mycosis fungoides is the most common and therefore quintessential cutaneous lymphoma
Case 1 A 61 year-old Thai woman from Bangkok Chief complaint: Multiple nodules and ulcerative masses on both arms, forearms and legs for 2 weeks
 Case 1 A 61 year-old Thai woman from Bangkok Chief complaint: Multiple nodules and ulcerative masses on both arms, forearms and legs for 2 weeks Fig. 1.1 Present illness: Five years ago, the patient presented
Case 1 A 61 year-old Thai woman from Bangkok Chief complaint: Multiple nodules and ulcerative masses on both arms, forearms and legs for 2 weeks Fig. 1.1 Present illness: Five years ago, the patient presented
Mycosis fungoides beyond the classical Alibert- Bazin disease: report of seventeen atypical variants
 Research Article Mycosis fungoides beyond the classical Alibert- Bazin disease: report of seventeen atypical variants Aarón Kaminsky Award 2007 Alejandra Abeldaño 1, Mariana Arias 2, Karina Ochoa 3, Adriana
Research Article Mycosis fungoides beyond the classical Alibert- Bazin disease: report of seventeen atypical variants Aarón Kaminsky Award 2007 Alejandra Abeldaño 1, Mariana Arias 2, Karina Ochoa 3, Adriana
Dermatologica Sinica
 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal
DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal
Cutaneous T-Cell and NK-Cell Lymphomas The WHO-EORTC Classification and the Increasing Recognition of Specialized Tumor Types
 AJCP / SHP/EAHP WORKSHOP Cutaneous T-Cell and NK-Cell Lymphomas The WHO-EORTC Classification and the Increasing Recognition of Specialized Tumor Types Marsha C. Kinney, MD, 1 and Dan Jones, MD, PhD 2 Key
AJCP / SHP/EAHP WORKSHOP Cutaneous T-Cell and NK-Cell Lymphomas The WHO-EORTC Classification and the Increasing Recognition of Specialized Tumor Types Marsha C. Kinney, MD, 1 and Dan Jones, MD, PhD 2 Key
Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency
 The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 17-21 17 Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency Asaad Shujaa*,1 and M. Owais Suriya 2 Open Access Department of Emergency Medicine College of Medicine,
The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 17-21 17 Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency Asaad Shujaa*,1 and M. Owais Suriya 2 Open Access Department of Emergency Medicine College of Medicine,
Research Article Characteristics of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in Iran: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
 International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 820921, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/820921 Research Article Characteristics of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in Iran: A 10-Year Retrospective
International Scholarly Research Notices, Article ID 820921, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/820921 Research Article Characteristics of Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma in Iran: A 10-Year Retrospective
STUDY. a group of 6 patients with. with localized alopecia characterized histopathologically
 Follicular Mucinosis STUDY A Critical Reappraisal of Clinicopathologic Features and Association With Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome Lorenzo Cerroni, MD; Regina Fink-Puches, MD; Barbara Bäck; Helmut
Follicular Mucinosis STUDY A Critical Reappraisal of Clinicopathologic Features and Association With Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome Lorenzo Cerroni, MD; Regina Fink-Puches, MD; Barbara Bäck; Helmut
CHAPTER 22 Brocq s alopecia (pseudopelade of Brocq) and burnt out scarring alopecia
 CHAPTER 22 Brocq s alopecia (pseudopelade of Brocq) and burnt out scarring alopecia BROCQ S ALOPECIA The term pseudopelade of Brocq is a source of much confusion and fruitless debate, and should be abandoned.
CHAPTER 22 Brocq s alopecia (pseudopelade of Brocq) and burnt out scarring alopecia BROCQ S ALOPECIA The term pseudopelade of Brocq is a source of much confusion and fruitless debate, and should be abandoned.
CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA PROFORMA
 STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital]
![Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital] Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital]](/thumbs/80/80529096.jpg) Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital] By Michelle, M.S., J.D. Johnson;Rebecca, PhD Frey READ ONLINE If searched for a ebook Cutaneous
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: An Entry From Thomson Gale's Gale Encyclopedia Of Cancer, 2nd Ed. [HTML] [Digital] By Michelle, M.S., J.D. Johnson;Rebecca, PhD Frey READ ONLINE If searched for a ebook Cutaneous
CUTIS. Do Not Copy. Pityriasis lichenoides is a T cell mediated papular. Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients. Pediatric Dermatology
 Series Editor: Camila K. Janniger, MD Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients Tanda N. Lane, MD; Sareeta S. Parker, MD Pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC) is a cutaneous disease of unknown
Series Editor: Camila K. Janniger, MD Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients Tanda N. Lane, MD; Sareeta S. Parker, MD Pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC) is a cutaneous disease of unknown
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy. Faizi Ali, MD
 88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
ISPUB.COM. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis. E Kim PHYSICAL FINDINGS INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants
 Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
184 Cutaneous Lymphomas: Morphology, Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Testing. David Cassarino MD, PhD Aaron Auerbach MD
 184 Cutaneous Lymphomas: Morphology, Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Testing David Cassarino MD, PhD Aaron Auerbach MD 2011 Annual Meeting Las Vegas, NV AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 33 W.
184 Cutaneous Lymphomas: Morphology, Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Testing David Cassarino MD, PhD Aaron Auerbach MD 2011 Annual Meeting Las Vegas, NV AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 33 W.
STUDY. with a benign clinical course but a malignant appearance
 Lymphomatoid Papulosis STUDY Reappraisal of Clinicopathologic Presentation and Classification Into Subtypes A,, and C Laila El Shabrawi-Caelen, MD; Helmut Kerl, MD; Lorenzo Cerroni, MD Objectives: To analyze
Lymphomatoid Papulosis STUDY Reappraisal of Clinicopathologic Presentation and Classification Into Subtypes A,, and C Laila El Shabrawi-Caelen, MD; Helmut Kerl, MD; Lorenzo Cerroni, MD Objectives: To analyze
Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides (MF), the subtype of cutaneous
 DOI 10. 5001/omj.2012.28 The Histological Spectrum of Early Mycosis Fungoides: A Study of 58 Saudi Arab patients Maha Arafah, Shaesta Naseem Zaidi, Hala Kassouf Kfoury, Ammar Al Rikabi, Khalid Al Ghamdi
DOI 10. 5001/omj.2012.28 The Histological Spectrum of Early Mycosis Fungoides: A Study of 58 Saudi Arab patients Maha Arafah, Shaesta Naseem Zaidi, Hala Kassouf Kfoury, Ammar Al Rikabi, Khalid Al Ghamdi
CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY
 Female, 24 Painful ulcerated lesion Left buttock Developed over a few weeks?abscess Excision CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY Two months later developed a similar lesion on right buttock CD30 CD3 CD4
Female, 24 Painful ulcerated lesion Left buttock Developed over a few weeks?abscess Excision CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY Two months later developed a similar lesion on right buttock CD30 CD3 CD4
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Protocol applies to non-hodgkin lymphoma involving any organ system except the gastrointestinal tract.
 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Protocol applies to non-hodgkin lymphoma involving any organ system except the gastrointestinal tract. Protocol revision date: January 2005 No AJCC/UICC staging system Procedures Cytology
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Protocol applies to non-hodgkin lymphoma involving any organ system except the gastrointestinal tract. Protocol revision date: January 2005 No AJCC/UICC staging system Procedures Cytology
How I treat patients whose biopsies are reported descriptively Youn H Kim, MD
 How I treat patients whose biopsies are reported descriptively Youn H Kim, MD Director, Multidisciplinary Cutaneous Lymphoma Group Stanford Cancer institute & School of Medicine NCCN NHL Panel Member Disclosure
How I treat patients whose biopsies are reported descriptively Youn H Kim, MD Director, Multidisciplinary Cutaneous Lymphoma Group Stanford Cancer institute & School of Medicine NCCN NHL Panel Member Disclosure
A review of the solitary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas
 J Cutan Pathol 2014: 41: 703 714 doi: 10.1111/cup.12353 John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Review A review
J Cutan Pathol 2014: 41: 703 714 doi: 10.1111/cup.12353 John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Review A review
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA
 FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
Granulomatous mycosis fungoides (GMF) is
 CASE REPORT Granulomatous mycosis fungoides, a rare subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma Marta Kogut, MD, a Eva Hadaschik, MD, a Stephan Grabbe, MD, b Mindaugas Andrulis, MD, c Alexander Enk, MD, a and
CASE REPORT Granulomatous mycosis fungoides, a rare subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma Marta Kogut, MD, a Eva Hadaschik, MD, a Stephan Grabbe, MD, b Mindaugas Andrulis, MD, c Alexander Enk, MD, a and
The World of Dermatology
 The World of Dermatology, F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates, LTD Objectives Cite the advances in management
The World of Dermatology, F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates, LTD Objectives Cite the advances in management
Burkitt lymphoma. Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8
 Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP)
 Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
 Annals of Oncology 24 (Supplement 6): vi149 vi154, 2013 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt242 Published online 17 July 2013 Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
Annals of Oncology 24 (Supplement 6): vi149 vi154, 2013 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt242 Published online 17 July 2013 Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
Forum 115 Management Issues in Cutaneous Lymphomas. Management of Transformed Mycosis Fungoides
 Forum 115 Management Issues in Cutaneous Lymphomas Management of Transformed Mycosis Fungoides Madeleine Duvic, MD Deputy Chairman -Department of Dermatology Blanche Bender Professor of Cancer Research
Forum 115 Management Issues in Cutaneous Lymphomas Management of Transformed Mycosis Fungoides Madeleine Duvic, MD Deputy Chairman -Department of Dermatology Blanche Bender Professor of Cancer Research
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center
 Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma)
 Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Lymphoma: The Basics. Dr. Douglas Stewart
 Lymphoma: The Basics Dr. Douglas Stewart Objectives What is lymphoma? How common is it? Why does it occur? How do you diagnose it? How do you manage it? How do you follow patients after treatment? What
Lymphoma: The Basics Dr. Douglas Stewart Objectives What is lymphoma? How common is it? Why does it occur? How do you diagnose it? How do you manage it? How do you follow patients after treatment? What
Key words: diagnosis, mycosis fungoides. British Journal of Dermatology 2003; 149:
 British Journal of Dermatology 2003; 149: 513 522. Clinical and Laboratory Investigations A simple clinical scoring system to improve the sensitivity and standardization of the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides
British Journal of Dermatology 2003; 149: 513 522. Clinical and Laboratory Investigations A simple clinical scoring system to improve the sensitivity and standardization of the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides
ISPUB.COM. Alopecia Areata preceding Mycosis Fungoides. R Creed, J Vu, R Singh, D Jones, M Duvic CASE 1
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 5 Number 2 Alopecia Areata preceding Mycosis Fungoides R Creed, J Vu, R Singh, D Jones, M Duvic Citation R Creed, J Vu, R Singh, D Jones, M Duvic. Alopecia
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 5 Number 2 Alopecia Areata preceding Mycosis Fungoides R Creed, J Vu, R Singh, D Jones, M Duvic Citation R Creed, J Vu, R Singh, D Jones, M Duvic. Alopecia
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months
 A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
ECP meeting, Lisbon, september 2012 Slide seminar New and old challenges in the diagnosis of peripheral T-cell lymphomas
 ECP meeting, Lisbon, september 2012 Slide seminar New and old challenges in the diagnosis of peripheral T-cell lymphomas Philippe Gaulard, Dept of Pathology, INSERM U955, Hôpital Henri Mondor, 94010 -
ECP meeting, Lisbon, september 2012 Slide seminar New and old challenges in the diagnosis of peripheral T-cell lymphomas Philippe Gaulard, Dept of Pathology, INSERM U955, Hôpital Henri Mondor, 94010 -
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/39089 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Cetinozman, F. Title: PD-1 Expression in primary cutaneous lymphoma Issue Date:
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/39089 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Cetinozman, F. Title: PD-1 Expression in primary cutaneous lymphoma Issue Date:
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
TOX expression in cutaneous B-cell lymphomas
 Arch Dermatol Res (2016) 308:423 427 DOI 10.1007/s00403-016-1654-7 ORIGINAL PAPER TOX expression in cutaneous B-cell lymphomas Anne M. R. Schrader 1 Patty M. Jansen 1 Rein Willemze 2 Received: 20 January
Arch Dermatol Res (2016) 308:423 427 DOI 10.1007/s00403-016-1654-7 ORIGINAL PAPER TOX expression in cutaneous B-cell lymphomas Anne M. R. Schrader 1 Patty M. Jansen 1 Rein Willemze 2 Received: 20 January
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach
 Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
