Lipodystrophies represent a heterogeneous group
|
|
|
- Adam Moody
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief Genetics Report Lamin A/C Gene Sex-Determined Expression of Mutations in Dunnigan-Type Familial Partial Lipodystrophy and Absence of Coding Mutations in Congenital and Acquired Generalized Lipoatrophy Corinne Vigouroux, Jocelyne Magré, Marie-Christine Vantyghem, Charlotte Bourut, Olivier Lascols, Sue Shackleton, David J. Lloyd, Bruno Guerci, Giuseppina Padova, Paul Valensi, André Grimaldi, Régis Piquemal, Philippe Touraine, Richard C. Trembath, and Jacqueline Capeau Missense mutations of the lamin A/C gene, LMNA, have been recently identified in Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD), which belongs to a heterogeneous group of rare disorders affecting adipose tissue distribution and metabolism. In this study, we sequenced the LMNA coding region from patients presenting with FPLD or other forms of lipodystrophy. We identified two heterozygous mutations in exon 8, R482W and R482Q, in FPLD patients (six families and one individual) with various clinical presentations. In addition, we found a novel heterozygous mutation (R584H) in exon 11, encoding specifically the lamin A isoform, in a patient with typical FPLD. Clinical and biochemical investigations in FPLD patients revealed that the expression and the severity of the phenotype were markedly dependent on sex, with female patients being more markedly affected. In subjects with generalized lipoatrophy, either congenital (13 case subjects) or acquired (14 case subjects), or Barraquer-Simon syndrome (2 case subjects), the entire LMNA coding sequence was normal. Although FPLD mutations are predominantly localized in exon 8 of LMNA, the finding of a novel mutation at codon 584, together with the R582H heterozygous substitution recently described, confirms that the C-terminal region specific to the From INSERM U.402, Faculté de Médecine Saint-Antoine (C.V., J.M., C.B., J.C.), and Laboratoire de Biologie Moléculaire (O.L.), Fédération de Biochimie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine; Service de Diabétologie (A.G.), Hôpital de la Pitié-Salpêtriere; Service d Endocrinologie (P.T.), Hôpital Necker, Paris; Service d Endocrinolgie (M.-C.V.), Clinique Marc Linquette, Lille; Service de Diabétologie (B.G.), Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Nancy; Service d Endocrinologie (P.V.), Hôpital Jean Verdier, Bondy; Service de Médicine Interne (R.P.), Centre Hospitalier, Blois, France; Division of Medical Genetics (S.S., D.J.L., R.C.T.), University of Leicester, Leicester, United Kingdom; and the Divisione di Endocrinologia (G.P.), Ospedale Garibaldi, Catania, Italy. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Jacqueline Capeau, INSERM U.402, Faculté de Médecine Saint-Antoine, 27 rue Chaligny, Paris Cedex 12, France. capeau@st-antoine.inserm.fr. Received for publication 30 March 2000 and accepted in revised form 17 July CMD1A, dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction-system disease; EDMD, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy; FPLD, familial partial lipodystrophy of the Dunnigan type; PCR, polymerase chain reaction. lamin A isoform is a second susceptibility region for mutations in FPLD. Diabetes 49: , 2000 Lipodystrophies represent a heterogeneous group of diseases characterized by alterations in body fat distribution and, in most cases, insulin resistance. The other cardinal signs are acanthosis nigricans, hyperandrogenism in females, muscular hypertrophy, hepatomegaly, altered glucose tolerance, and hypertriglyceridemia (1). Among them, the familial partial lipodystrophy of the Dunnigan type (FPLD), dominantly inherited, is characterized by a lack of adipose tissue in the limbs, buttocks, and trunk with fat accumulation in the neck and face, and results from heterozygous missense mutations of LMNA (2 5). Lamin A and C, encoded by this gene, are ubiquitous structural proteins that polymerize in the nuclear lamina, a meshwork underlying the inner nuclear membrane, in which they interact with integral proteins and chromatin (6). In the present study, we searched for mutations in LMNA in patients affected with FPLD or other lipodystrophies and analyzed the different clinical presentations. Concerning FPLD, we sequenced the coding region of LMNA in the probands from six families and two individuals. Previous haplotype analysis at the FPLD locus (chromosome 1q) confirmed that these Caucasian families were not related (data not shown). A heterozygous CGG TGG transition at codon 482 (exon 8), leading to an arginine to tryptophane substitution (R482W) was found in probands from families DE, DR, G, K, H, and P. At the same codon, patient J.M. displayed a heterozygous CGG CAG transition, which predicts an arginine to glutamine substitution (R482Q). These mutations have been previously reported in FPLD (2 5). In patient PI, we found a heterozygous CGC CAC transition at codon 584 (exon 11), leading to an arginine to histidine substitution (R584H). This DNA variation, which has not been previously reported, was absent in 100 unrelated control subjects screened using a Dra III restriction polymor DIABETES, VOL. 49, NOVEMBER 2000
2 C. VIGOUROUX AND ASSOCIATES phism (see RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS), therefore representing a new LMNA mutation. The dominant transmission of FPLD was evident in each of the families (Fig. 1) and was considered likely in individuals J.M. and P.I., because lipodystrophy was observed in their mothers, one of whom presented with acute pancreatitis. All the other LMNA nucleotide variations that we detected in these patients were silent polymorphisms either exonic (S17 [AGC AGT], A287 [GCT GCC], D446 [GAT GAC] and H566 [CAC CAT]), or intronic (intron 4: nt+13 [G T]; intron 8: nt-41 [C T] and intron 9: nt-5 [A G]). We also sequenced the 12 exons of LMNA in patients presenting with other forms of lipodystrophy as follows: 13 patients affected by a congenital and 14 by an acquired form of generalized lipoatrophy, and 2 patients by a Barraquer- Simon syndrome characterized by cephalothoracic lipoatro- FIG. 1. Dominant inheritance of an R482W heterozygous mutation in FPLD families. C T transition at codon 482 abolishes an MspI restriction site in the exon 8-PCR fragment of 229 bp. MspI digestion of the wild-type allele generates three fragments (of 114, 69, and 46 bp), whereas digestion of the R482W allele reveals a 183-bp band ( ). Phenotypes of patients are symbolized as follows: (, ) patients affected by FPLD, (, ) patients probably affected by FPLD, and (, ) nonclinically affected individuals. M, molecular-weight marker. DIABETES, VOL. 49, NOVEMBER
3 LAMIN A/C MUTATIONS IN LIPODYSTROPHIES phy and accumulation of fat in the lower part of the body. We did not find any alteration in LMNA coding sequence in any of these patients. Furthermore, 5 of 10 congenital lipoatrophic patients born from consanguineous unions were heterozygous for several intragenic polymorphisms, suggesting that defects at the LMNA locus are not responsible for this rare autosomal recessive disease (7). The evaluation of the main clinical and biological characteristics of individuals bearing LMNA mutations revealed that the disease expressivity was variable, especially between men and women (Table 1). In women, limb and trunk lipoatrophy with muscular hypertrophy was generally present and associated with fat accumulation in face and neck, giving a cushingoid appearance. However, this classical phenotype was not universally evident, especially in lean patients, in whom lipoatrophic signs could be predominant. Signs of hyperandrogenism were generally present in affected women, albeit of varying severity. In men, the clinical diagnosis of FPLD was more problematic because of the absence of the characteristic lipodystrophy in most cases, as reported previously (8). Insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia were also generally more severe in women. Three individuals, all lean women (DE1, K3, JM), presented with severe diabetes poorly controlled despite high dose insulin therapy (>100 U per day), whereas their affected male relatives had either a normal glucose tolerance (K5) or milder forms of diabetes, easily controlled by oral hypoglycemic agents (DE2 and 3). In the same way, six patients (all women) had striking hypertriglyceridemia that led to acute pancreatitis in two of them (G3 and K3). In most cases, the lipodystrophy appeared progressively after puberty and was secondary to the first biological signs, either hyperinsulinemia or hypertriglyceridemia, when evaluated. Two prepubertal children, H13 and H15, were bearing the mutation without any phenotypic features of FPLD. At 22 years of age, subject DE4 still has a normal clinical and biological phenotype, suggesting either incomplete penetrance or a delayed form of the disease. Because mutations in LMNA are also responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) (9,10) and dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction-system disease (CMD1A) (11,12), we searched for clinical features of skele- TABLE 1 Clinical and biological characteristics of the patients with mutations in the lamin A/C gene Age at Diabetes (D) Plasma Antecedent of acute pancreatitis investigation BMI Clinical or severe insulin triglycerides or plasma triglycerides Patient (years) (kg/m 2 ) lipodystrophy resistance (IR)* >2.5 mmol/l >10 mmol/l Women DE FPLD D + + DE NO DR FPLD IR + DR LA IR + + DR LA IR + G FPLD D + + H FPLD IR + H FPLD IR + H10 42 NA IR K FPLD D K LA D + + P FPLD D NA P FPLD NA NA P FPLD D + P FPLD D P FPLD D + + JM LA D + + PI FPLD IR Men DE LA D + DE3 54 NO D G1 46 NO D + H1 45 NO IR H NO H11 38 NO H13 12 NO H15 7 NO K NO + P NO P FPLD NA NA All patients bear an R482W heterozygous mutation in LMNA, except JM and PI, who carry an R482Q and an R584H heterozygous mutation, respectively. *Severe insulin resistance is defined by severe hyperinsulinemia (>140 pmol/l in the fasting state and/or >700 pmol/l 2 h after a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test) in the absence of diabetes. FPLD, lipoatrophy of limbs and trunk with fat accumulation in neck and face; LA, predominant lipoatrophy; NO, not obvious; NA, not available; +, present;, absent DIABETES, VOL. 49, NOVEMBER 2000
4 C. VIGOUROUX AND ASSOCIATES tal or cardiac muscular dysfunction in our patients. With only one exception, FPLD patients had no history of muscular weakness and/or contractions. Most of them displayed a characteristic muscular hypertrophy with athletic appearance, whereas muscular atrophy is a typical feature of EDMD. In patient H10, a proximal myopathy that did not fit the diagnostic criteria for EDMD (13) was noted. The level of serum creatine-kinase was found within the normal range in all the patients tested. Electrocardiography performed in eight patients did not reveal any rhythm or conduction abnormality. No history of cardiac rhythm disturbance or cases of sudden death in patients relatives were reported. In FPLD, all of the previously reported mutations except one were clustered within exon 8, coding for a proximal C-terminal domain of lamin A/C, and concerned only three codons (465, 482, and 486) (2 5). In our patients, the LMNA mutation affected codon 482 in all of the cases but one, confirming that exon 8, and in particular codon 482, is indeed a mutational hot spot for FPLD. This is in contrast with what is seen in EDMD and CMD1A, in which most alterations reported to date are located either in the central rod dimerization or in the tail domain of lamin A/C, with only one reported mutation localized to exon 8 of the gene (I469T) (9 12). Interestingly, we found in a typical FPLD patient a novel mutation located at codon 584, in the distal part of the coding sequence, within a highly conserved region of the C-terminal domain specific for the lamin A isoform. Recently, a R582H heterozygous substitution has been reported in FPLD, although in a less clinically pronounced form (4). It has been observed in vitro that the lamin A specific C-terminal domain acts as a binding site for nuclear actin, with these two components being implicated in the organization of nuclear chromatin domains. Therefore, it is possible that these lamin A specific mutations, through alterations in the nuclear lamina-chromatin relations, could modify the expression of adipose tissue specific genes (5,14). Molecular screening for LMNA mutations in FPLD may not be limited to the exon 8 of the gene. It is important to distinguish FPLD from other forms of lipodystrophies, especially acquired generalized lipoatrophy, in which clinical presentation could be very similar and to ensure the diagnosis in men, in whom the clinical and biochemical features may be less marked. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS Patients. All patients and their families gave their informed consent for genetic studies, which were approved by an institutional review committee. The biological and clinical characteristics of patients DE1 and K3 have been previously reported (15,16). Patients DE1 and 2 were also affected by familial benign hypercalcemia caused by a heterozygous mutation in the calciumsensing receptor gene (17). Most patients with congenital and acquired generalized lipoatrophy have been previously presented (18,19). Genetic studies. Genomic DNA was obtained from peripheral white blood cells by standard procedures (20). LMNA exons 1 to 12 and the surrounding intronic sequences were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primers and conditions previously described (3,9). After purification on Qiagen columns, the PCR products were directly sequenced using the ABI Dye terminator mix. Reactions were run on an ABI 377 sequencer and analyzed with Sequence Analysis 3.2 software (Perkin Elmer). A rapid genotyping assay was used to screen for the mutations in exons 8 and 11 of LMNA. After amplification with specific primers (8F: 5 -CCAAGAG CCTGGGTGAGCCTC-3, 8R: 5 -GACACTTACCCCAGCGCTCC-3 or 11F: 5 -TG GTCAGTCCCAGACTCGCC-3, 11R: 5 -GCCTGCAGGATTTGGAAGA-3 ), PCR products (15 µl) were digested with 10 U of the specific restriction enzymes (New England BioLabs, Beverly, MA). After a 3-h incubation at 37 C, the fragments were separated on a 3% agarose gel and visualized after staining with ethidium bromide. The C to T transition at codon 482 abolishes an MspI restriction site in the exon 8-PCR fragment of 229 bp, leading to a 183 bp additional DNA fragment (Fig. 1). The G to A transition at codon 584 creates a unique Dra III restriction site in the exon 11-PCR product (360 bp), which generates two DNA fragments of 259 and 101 bp. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by grants from INSERM, Aide aux Jeunes Diabétiques, the British Diabetic Association (PhD studentship, D.J.L.), the British Heart Foundation (R.C.T.), and Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique and Direction de la Recherche Clinique-Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris at the Clinical Investigation Center of Saint-Antoine University Hospital. We thank the patients and their families for their collaboration; the physicians that have previously referred to us lipodystrophic patients; Drs. Pascale Benlian, Antoine Gancel, Caroline Lapouille, and Laurent Meyer for providing us with clinical and biological informations about their FPLD patients; Dr. Gisèle Bonne for the helpful advice about molecular analysis of LMNA; Drs Jon-Andoni Urtizberea and Henri- Marc Bécane for medical information about EDMD patients; Dr. Dominique Récan and her colleagues for immortalization of lymphocytes; the Molecular Biology Laboratory of St. Antoine Hospital, Paris (directed by Prof E. Clauser) for LMNA sequencing; and Muriel Meier for her technical expertise and Betty Jacquin for her expert secretarial assistance. REFERENCES 1. Moller DE, O Rahilly S: Syndromes of severe insulin resistance: clinical and patho-physiological features. In Insulin resistance. Moller DE, Ed. New York, Wiley and Sons, 1993, p Cao H, Hegele RA: Nuclear lamin A/C R482Q mutation in canadian kindreds with Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 9: , Shackleton S, Lloyd DJ, Jackson SNJ, Evans R, Niermeijer MF, Singh BM, Schmidt H, Brabant G, Kuma S, Durrington PN, Gregory S, O Rahilly S, Trembath RC: LMNA, encoding lamin A/C, is mutated in partial lipodystrophy. Nat Genet 24: , Speckman RA, Garg A, Du F, Bennett L, Veile R, Arioglu E, Taylor SI, Lovett M, Bowcock AM: Mutational and haplotype analyses of families with familial partial lipodystrophy (Dunnigan variety) reveal recurrent missense mutations in the globular C-terminal domain of lamin A/C. Am J Hum Genet 66: , Hegele RA, Anderson CM, Wang J, Jones DC, Cao H: Association between nuclear lamin A/C R482Q mutation and partial lipodystrophy with hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes. Genome Res 10: , Stuurman N, Heins S, Aebi U: Nuclear lamins: their structure, assembly, and interactions. J Struct Biol 122:42 66, Lander ES, Botstein D: Homozygosity mapping: a way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science 236: , Burn J, Baraitser M: Partial lipoatrophy with insulin resistant diabetes and hyperlipidaemia (Dunnigan syndrome). J Med Genet 23: , Bonne G, Raffaele Di Barletta M, Varnous S, Becane HM, Hammouda EH, Merlini L, Muntoni F, Greenberg CR, Gary F, Urtizberea JA, Duboc D, Fardeau M, Toniolo D, Schwartz K: Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet 21: , Raffaele Di Barletta M, Ricci E, Galluzzi G, Tonali P, Mora M, Morandi L, Romorini A, Voit T, Orstavik KH, Merlini L, Trevisan C, Biancalana V, Housmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Bione S, Ricotti R, Schwartz K, Bonne G, Toniolo D: Different mutations in the LMNA gene cause autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet 66: , Fatkin D, MacRae C, Sasaki T, Wolff MR, Porcu M, Frenneaux M, Atherton J, Vidaillet HJ Jr, Spudich S, De Girolami U, Seidmann JG, Seidman C, Muntoni F, Muehle G, Johnson W, McDonough B: Missense mutations in the rod DIABETES, VOL. 49, NOVEMBER
5 LAMIN A/C MUTATIONS IN LIPODYSTROPHIES domain of the lamin A/C gene as causes of dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction-system disease. N Engl J Med 341: , Brodsky GL, Muntoni F, Miocic S, Sinagra G, Sewry C, Mestroni L: Lamin A/C gene mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy with variable skeletal muscle involvement. Circulation 101: , Emery AE: Emery-Dreifuss syndrome. J Med Genet 26: , Sasseville AMJ, Langelier Y: In vitro interaction of the carboxy-terminal domain of lamin A with actin. FEBS Lett 425: , Meyer L, Hadjadj S, Guerci B, Delbachian I, Ziegler O, Drouin P: Lipoatrophic diabetes mellitus treated by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Metab 23: , Vantyghem MC, Vigouroux C, Magré J, Desbois-Mouthon C, Pattou F, Fontaine P, Lefebvre J, Capeau J: Late-onset lipoatrophic diabetes: phenotypic and genotypic familial studies and effect of treatment with metformin and lispro insulin analog. Diabetes Care 22: , Vigouroux C, Bourut C, Guerci B, Ziegler O, Magré J, Capeau J, Meyer L: A new missense mutation in the calcium-sensing receptor in familial benign hypercalcemia associated with partial lipoatrophy and insulin resistant diabetes. Clin Endocrinol, 53: , Desbois-Mouthon C, Magré J, Amselem S, Reynet C, Blivet MJ, Goossens M, Capeau J, Besmond C: Lipoatrophic diabetes: genetic exclusion of the insulinreceptor gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80: , Vigouroux C, Khallouf E, Bourut C, Robert JJ, De Kerdanet M, Tubiana-Rufi N, Fauré S, Weissenbach J, Capeau J, Magré J: Genetic exclusion of 14 candidate genes in lipoatropic diabetes using linkage analysis in 10 consanguineous families. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: , Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: In Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. New York, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989, p DIABETES, VOL. 49, NOVEMBER 2000
Workshop report. 1. Introduction
 Neuromuscular Disorders 12 (2002) 187 194 Workshop report www.elsevier.com/locate/nmd 82nd ENMC international workshop, 5th international Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) workshop, 1st Workshop
Neuromuscular Disorders 12 (2002) 187 194 Workshop report www.elsevier.com/locate/nmd 82nd ENMC international workshop, 5th international Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) workshop, 1st Workshop
Mandibuloacral Dysplasia Is Caused by a Mutation in LMNA-Encoding Lamin A/C
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71:426 431, 2002 Report Mandibuloacral Dysplasia Is Caused by a Mutation in LMNA-Encoding Lamin A/C Giuseppe Novelli, 1 Antoine Muchir, 6 Federica Sangiuolo, 1 Anne Helbling-Leclerc,
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71:426 431, 2002 Report Mandibuloacral Dysplasia Is Caused by a Mutation in LMNA-Encoding Lamin A/C Giuseppe Novelli, 1 Antoine Muchir, 6 Federica Sangiuolo, 1 Anne Helbling-Leclerc,
Diabetes Care 26: , 2003
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Köbberling Type of Familial Partial Lipodystrophy An underrecognized syndrome KAREN L. HERBST, MD, PHD 1 LISA R. TANNOCK,
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Köbberling Type of Familial Partial Lipodystrophy An underrecognized syndrome KAREN L. HERBST, MD, PHD 1 LISA R. TANNOCK,
L aminopathies represent a heterogeneous group of genetic
 1of5 ONLINE MUTATION REPORT Mutation analysis of the lamin A/C gene (LMNA) among patients with different cardiomuscular phenotypes M Vytopil, S Benedetti, E Ricci, G Galluzzi, A Dello Russo, L Merlini,
1of5 ONLINE MUTATION REPORT Mutation analysis of the lamin A/C gene (LMNA) among patients with different cardiomuscular phenotypes M Vytopil, S Benedetti, E Ricci, G Galluzzi, A Dello Russo, L Merlini,
Risk Factors for Diabetes in Familial Partial Lipodystrophy, Dunnigan Variety
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Risk Factors for Diabetes in Familial Partial Lipodystrophy, Dunnigan Variety WASIM A. HAQUE, MD 1 ELIF ARIOGLU ORAL, MD 2 KELLY DIETZ, MS
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Risk Factors for Diabetes in Familial Partial Lipodystrophy, Dunnigan Variety WASIM A. HAQUE, MD 1 ELIF ARIOGLU ORAL, MD 2 KELLY DIETZ, MS
Hypoglycaemia revealing heterozygous insulin receptor mutations.
 Hypoglycaemia revealing heterozygous insulin receptor mutations. Vanessa Preumont, Christine Feincoeur, Olivier Lascols, Carine Courtillot, Philippe Touraine, Dominique Maiter, Corinne Vigouroux To cite
Hypoglycaemia revealing heterozygous insulin receptor mutations. Vanessa Preumont, Christine Feincoeur, Olivier Lascols, Carine Courtillot, Philippe Touraine, Dominique Maiter, Corinne Vigouroux To cite
T he LMNA gene encodes two nuclear envelope proteins,
 1of5 ELECTRONIC LETTER A new mutation of the lamin A/C gene leading to autosomal dominant axonal neuropathy, muscular dystrophy, cardiac disease, and leuconychia C Goizet, R Ben aou, L Demay, P Richard,
1of5 ELECTRONIC LETTER A new mutation of the lamin A/C gene leading to autosomal dominant axonal neuropathy, muscular dystrophy, cardiac disease, and leuconychia C Goizet, R Ben aou, L Demay, P Richard,
Lipoatrophic Diabetes: What can zebras teach us about horses? Ranganath Muniyappa, MD, PhD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Obesity Branch NIDDK, NIH
 Lipoatrophic Diabetes: What can zebras teach us about horses? Ranganath Muniyappa, MD, PhD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Obesity Branch NIDDK, NIH Objectives 1. Describe the clinical manifestations of abnormal
Lipoatrophic Diabetes: What can zebras teach us about horses? Ranganath Muniyappa, MD, PhD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Obesity Branch NIDDK, NIH Objectives 1. Describe the clinical manifestations of abnormal
THURSDAY, JANUARY
 THURSDAY, JANUARY 15 2015 08.30-09.00 WELCOME COFFEE 09.00-09.15 Welcome and opening comments. A. De Sandre-Giovannoli, N. Lévy Presentation of the French Network on EDMD and other nucleopathies. G. Bonne,
THURSDAY, JANUARY 15 2015 08.30-09.00 WELCOME COFFEE 09.00-09.15 Welcome and opening comments. A. De Sandre-Giovannoli, N. Lévy Presentation of the French Network on EDMD and other nucleopathies. G. Bonne,
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene Goals Explore how mutations can lead to disease using the myosin gene as a model system. Explore how changes in the
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene Goals Explore how mutations can lead to disease using the myosin gene as a model system. Explore how changes in the
Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy
 Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy Pr Philippe Charron Centre de Référence pour les maladies cardiaques héréditaires (1) Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne
Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy Pr Philippe Charron Centre de Référence pour les maladies cardiaques héréditaires (1) Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne
Heterozygous mutation in the pore of potassium channel gene KvLQT1 causes an apparently normal phenotype in long QT syndrome
 European Journal of Human Genetics (1998) 6, 129 133 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1018 4813/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejhg ORIGINAL PAPER Heterozygous mutation in the pore of
European Journal of Human Genetics (1998) 6, 129 133 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1018 4813/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejhg ORIGINAL PAPER Heterozygous mutation in the pore of
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most
 Brief Genetics Report Type A Insulin Resistance Syndrome Revealing a Novel Lamin A Mutation Jacques Young, 1 Louise Morbois-Trabut, 2 Béatrice Couzinet, 1 Olivier Lascols, 2,3 Elisabeth Dion, 4 Véronique
Brief Genetics Report Type A Insulin Resistance Syndrome Revealing a Novel Lamin A Mutation Jacques Young, 1 Louise Morbois-Trabut, 2 Béatrice Couzinet, 1 Olivier Lascols, 2,3 Elisabeth Dion, 4 Véronique
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY
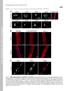 Supplemental Material Mejat et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200811035/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. SUN1, SUN2, and Nesprin-1 localization in muscle fibers. (A) SUN1 and SUN2
Supplemental Material Mejat et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200811035/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. SUN1, SUN2, and Nesprin-1 localization in muscle fibers. (A) SUN1 and SUN2
Non-Mendelian inheritance
 Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Progeria. Premature human aging: t he progerias. Progerias as models for aging. Hutchinson-Gilford syndrome. Definition:
 Premature human aging: t he progerias Reading: Genetic alterations in accelerated ageing syndromes Do they play a role in natural ageing? Monika Puzianowska- Kuznicka. Jacek Kuznicki. 2005. IJBCB, 37;
Premature human aging: t he progerias Reading: Genetic alterations in accelerated ageing syndromes Do they play a role in natural ageing? Monika Puzianowska- Kuznicka. Jacek Kuznicki. 2005. IJBCB, 37;
Cardiac effects of the c.1583 C G LMNA mutation in two families with Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 5065-5071, 2015 Cardiac effects of the c.1583 C G LMNA mutation in two families with Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy LI ZHANG 1, HONGRUI SHEN 2, ZHE ZHAO 2, QI BING 2 and
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 5065-5071, 2015 Cardiac effects of the c.1583 C G LMNA mutation in two families with Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy LI ZHANG 1, HONGRUI SHEN 2, ZHE ZHAO 2, QI BING 2 and
Brief Genetics Report PPARG F388L, a Transactivation-Deficient Mutant, in Familial Partial Lipodystrophy
 Brief Genetics Report PPARG F388L, a Transactivation-Deficient Mutant, in Familial Partial Lipodystrophy Robert A. Hegele, 1 Henian Cao, 1 Christy Frankowski, 2 Suresh T. Mathews, 3 and Todd Leff 3 Autosomal
Brief Genetics Report PPARG F388L, a Transactivation-Deficient Mutant, in Familial Partial Lipodystrophy Robert A. Hegele, 1 Henian Cao, 1 Christy Frankowski, 2 Suresh T. Mathews, 3 and Todd Leff 3 Autosomal
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients
 Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Accepted Preprint first posted on 14 June 2012 as Manuscript EJE
 Page 1 of 27 Accepted Preprint first posted on 14 June 2012 as Manuscript EJE-12-0268 1 Phenotypic diversity in patients with lipodystrophy associated with LMNA mutations Patricia B. Mory 1, Felipe Crispim
Page 1 of 27 Accepted Preprint first posted on 14 June 2012 as Manuscript EJE-12-0268 1 Phenotypic diversity in patients with lipodystrophy associated with LMNA mutations Patricia B. Mory 1, Felipe Crispim
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
Novel LMNA Mutation in a Taiwanese Family with Autosomal Dominant Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
 ASE REPORT Novel LMNA Mutation in a Taiwanese Family with Autosomal Dominant Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Wen-hen Liang, 1 hung-yee Yuo, 2 hun-ya Liu, 3 hee-siong Lee, 4 Kanako Goto, 5 Yukiko K. Hayashi,
ASE REPORT Novel LMNA Mutation in a Taiwanese Family with Autosomal Dominant Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Wen-hen Liang, 1 hung-yee Yuo, 2 hun-ya Liu, 3 hee-siong Lee, 4 Kanako Goto, 5 Yukiko K. Hayashi,
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by the presence of 3
 Variation in the Lamin A/C Gene Associations With Metabolic Syndrome Nanette I. Steinle, Rasa Kazlauskaite, Ikhide G. Imumorin, Wen-Chi Hsueh, Toni I. Pollin, Jeffrey R. O Connell, Braxton D. Mitchell,
Variation in the Lamin A/C Gene Associations With Metabolic Syndrome Nanette I. Steinle, Rasa Kazlauskaite, Ikhide G. Imumorin, Wen-Chi Hsueh, Toni I. Pollin, Jeffrey R. O Connell, Braxton D. Mitchell,
Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling
 4th International Melorheostosis Association Conference Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling Howard J. Worman Columbia University New York, NY The Nuclear Envelope By
4th International Melorheostosis Association Conference Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling Howard J. Worman Columbia University New York, NY The Nuclear Envelope By
HYBRID GENE THERAPY FOR AD-EDMD
 HYBRID GENE THERAPY FOR AD-EDMD Gene Therapy Prof. Isabella Saggio 2017/2018 Bertani Camilla Dezi Clara Difeo Giorgia di Palma Carmen AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT EMERY-DREIFUSS MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Fig.1 Adapted
HYBRID GENE THERAPY FOR AD-EDMD Gene Therapy Prof. Isabella Saggio 2017/2018 Bertani Camilla Dezi Clara Difeo Giorgia di Palma Carmen AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT EMERY-DREIFUSS MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Fig.1 Adapted
Early-Onset LMNA-Associated Muscular Dystrophy with Later Involvement of Contracture
 JCN Open Access pissn 1738-6586 / eissn 2005-5013 / J Clin Neurol 2017;13(4):405-410 / https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.405 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early-Onset LMNA-Associated Muscular Dystrophy with Later
JCN Open Access pissn 1738-6586 / eissn 2005-5013 / J Clin Neurol 2017;13(4):405-410 / https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.405 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early-Onset LMNA-Associated Muscular Dystrophy with Later
Natural History of Dilated Cardiomyopathy Due to Lamin A/C Gene Mutations
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 5, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02954-6
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 5, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02954-6
Human Genetics Notes:
 Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Human Genetics Notes: Human Chromosomes Cell biologists analyze chromosomes by looking at. Cells are during mitosis. Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the and group them together in pairs. A
Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS
 Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS Chapter Summary In order to study the transmission of human genetic traits to the next generation, a different method of operation had to be adopted. Instead
Chapter 4 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS IN HUMAN GENETICS Chapter Summary In order to study the transmission of human genetic traits to the next generation, a different method of operation had to be adopted. Instead
Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD
 Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated LV/RV, reduced EF, in the absence of CAD valvulopathy pericardial disease Prevalence:40/100.000 persons Natural
Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated LV/RV, reduced EF, in the absence of CAD valvulopathy pericardial disease Prevalence:40/100.000 persons Natural
variant led to a premature stop codon p.k316* which resulted in nonsense-mediated mrna decay. Although the exact function of the C19L1 is still
 157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
The laminopathies: a clinical review
 Clin Genet 2006: 70: 261 274 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Review # 2006 The Authors Journal compilation # 2006 Blackwell Munksgaard CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00677.x
Clin Genet 2006: 70: 261 274 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Review # 2006 The Authors Journal compilation # 2006 Blackwell Munksgaard CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00677.x
Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy. Disclosures. Cardiovascular Health and Risk Prevention Program. Neither presenter has any financial disclosures
 Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy A Case Presentation Lisa Guerra, BSN, RN, CPN Aimee Vinson, BSN, RN Endocrine and Diabetes Clinic Fort Worth, TX Disclosures Neither presenter has any financial disclosures
Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy A Case Presentation Lisa Guerra, BSN, RN, CPN Aimee Vinson, BSN, RN Endocrine and Diabetes Clinic Fort Worth, TX Disclosures Neither presenter has any financial disclosures
Basic Definitions. Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi MBChB MSc DCH (UK) MRCPCH
 Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Advances in genetic diagnosis of neurological disorders
 Acta Neurol Scand 2014: 129 (Suppl. 198): 20 25 DOI: 10.1111/ane.12232 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Review Article Advances in genetic diagnosis
Acta Neurol Scand 2014: 129 (Suppl. 198): 20 25 DOI: 10.1111/ane.12232 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Review Article Advances in genetic diagnosis
LAMIN MUTATIONS AND DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY
 LAMIN MUTATIONS AND DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY MISSENSE MUTATIONS IN THE ROD DOMAIN OF THE LAMIN A/C GENE AS CAUSES OF DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY AND CONDUCTION-SYSTEM DISEASE DIANE FATKIN, M.D., CALUM MACRAE,
LAMIN MUTATIONS AND DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY MISSENSE MUTATIONS IN THE ROD DOMAIN OF THE LAMIN A/C GENE AS CAUSES OF DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY AND CONDUCTION-SYSTEM DISEASE DIANE FATKIN, M.D., CALUM MACRAE,
The phenotype of Arg555Trp mutation in a large Turkish family with corneal granular dystrophy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 11 no. 4, 2001 / pp. 333-337 The phenotype of Arg555Trp mutation in a large Turkish family with corneal granular dystrophy H. KIRATLI 1, M. İRKEÇ 1, K. ÖZGÜL 2,
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 11 no. 4, 2001 / pp. 333-337 The phenotype of Arg555Trp mutation in a large Turkish family with corneal granular dystrophy H. KIRATLI 1, M. İRKEÇ 1, K. ÖZGÜL 2,
Nuclear Envelope and Muscular Dystrophy
 Nationwide Children s Hospital August 25, 2015 Nuclear Envelope and Muscular Dystrophy Howard J. Worman, M.D. Columbia University Columbia University Medical Center The Nuclear Envelope By D. W. Fawcett
Nationwide Children s Hospital August 25, 2015 Nuclear Envelope and Muscular Dystrophy Howard J. Worman, M.D. Columbia University Columbia University Medical Center The Nuclear Envelope By D. W. Fawcett
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES (LGMD) Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a heterogeneous group of genetically determined disorders with a
READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES (LGMD) Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a heterogeneous group of genetically determined disorders with a
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 5, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 5, 2017, 2792 2796 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) POLYMORPHISM IN EXON 9 OF HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR 4 (HSF4) GENE IN EXOTIC
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 5, 2017, 2792 2796 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) POLYMORPHISM IN EXON 9 OF HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR 4 (HSF4) GENE IN EXOTIC
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
LIPOATROPIC diabetes (LD) designates a group of syndromes
 0021-972X/98/$03.00/0 Vol. 83, No. 2 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 1998 by The Endocrine Society Leptin Levels, -Cell Function, and Insulin Sensitivity in
0021-972X/98/$03.00/0 Vol. 83, No. 2 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 1998 by The Endocrine Society Leptin Levels, -Cell Function, and Insulin Sensitivity in
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
 Challenging Cases in Obesity Management Jonathan Q. Purnell, MD Knight Cardiovascular Institute Division of Endocrinology Oregon Health & Science University DISCLOSURE STATEMENT Speaker: Jonathan Q. Purnell,
Challenging Cases in Obesity Management Jonathan Q. Purnell, MD Knight Cardiovascular Institute Division of Endocrinology Oregon Health & Science University DISCLOSURE STATEMENT Speaker: Jonathan Q. Purnell,
D ilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), the most frequent form
 560 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Expanding the phenotype of LMNA mutations in dilated cardiomyopathy and functional consequences of these mutations P Sébillon, C Bouchier, L D Bidot, G Bonne, K Ahamed, P Charron,
560 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Expanding the phenotype of LMNA mutations in dilated cardiomyopathy and functional consequences of these mutations P Sébillon, C Bouchier, L D Bidot, G Bonne, K Ahamed, P Charron,
C ongenital lipodystrophy of the Berardinelli-Seip type
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Genotype-phenotype relationships in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy L Van Maldergem, J Magré, T E Khallouf, T Gedde-Dahl Jr, M Delépine, O Trygstad, E Seemanova, T Stephenson,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Genotype-phenotype relationships in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy L Van Maldergem, J Magré, T E Khallouf, T Gedde-Dahl Jr, M Delépine, O Trygstad, E Seemanova, T Stephenson,
Diabetes in children and youth
 Nonobese, Nonketotic Childhood-Onset Diabetes: Look for Lipodystrophies Partha P. Chakraborty, 1 Sayantan Ray, 2 Subhodip Pramanik, 2 Rana Bhattacharjee, 2 Sujoy Ghosh, 2 and Subhankar Chowdhury 2 1 Department
Nonobese, Nonketotic Childhood-Onset Diabetes: Look for Lipodystrophies Partha P. Chakraborty, 1 Sayantan Ray, 2 Subhodip Pramanik, 2 Rana Bhattacharjee, 2 Sujoy Ghosh, 2 and Subhankar Chowdhury 2 1 Department
The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex
 The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex 1 Location and Organization of the HLA Complex on Chromosome 6 NEJM 343(10):702-9 2 Inheritance of the HLA Complex Haplotype Inheritance (Family Study) 3 Structure
The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex 1 Location and Organization of the HLA Complex on Chromosome 6 NEJM 343(10):702-9 2 Inheritance of the HLA Complex Haplotype Inheritance (Family Study) 3 Structure
Familial partial lipodystrophy: two types of an. hemizygous state. X linked dominant syndrome, lethal in the
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 120-127 Familial partial lipodystrophy: two types of an X linked dominant syndrome, lethal in the hemizygous state J KOBBERLING* AND M G DUNNIGANt From *the Department
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 120-127 Familial partial lipodystrophy: two types of an X linked dominant syndrome, lethal in the hemizygous state J KOBBERLING* AND M G DUNNIGANt From *the Department
H utchinson-gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS; MIM
 609 LETTER TO JMG Homozygous missense mutation in the lamin A/C gene causes autosomal recessive Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome M Plasilova*, C Chattopadhyay*, P Pal, N A Schaub, S A Buechner, Hj
609 LETTER TO JMG Homozygous missense mutation in the lamin A/C gene causes autosomal recessive Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome M Plasilova*, C Chattopadhyay*, P Pal, N A Schaub, S A Buechner, Hj
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Disruption of spermatogenesis in mice lacking A-type lamins
 Research Article 1173 Disruption of spermatogenesis in mice lacking A-type lamins Manfred Alsheimer 1, *, Bodo Liebe 2, *, Lori Sewell 3, Colin L. Stewart 3, Harry Scherthan 2, and Ricardo Benavente 1,
Research Article 1173 Disruption of spermatogenesis in mice lacking A-type lamins Manfred Alsheimer 1, *, Bodo Liebe 2, *, Lori Sewell 3, Colin L. Stewart 3, Harry Scherthan 2, and Ricardo Benavente 1,
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
SALSA MLPA KIT P060-B2 SMA
 SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
Reply to The question of heterogeneity in Marfan syndrome
 Reply to The question of heterogeneity in Marfan syndrome Catherine Boileau, Claudine Junien, Gwenaëlle Collod, Guillaume Jondeau, Olivier Dubourg, Jean-Pierre Bourdarias, Catherine Bonaïti-Pellié, Jean
Reply to The question of heterogeneity in Marfan syndrome Catherine Boileau, Claudine Junien, Gwenaëlle Collod, Guillaume Jondeau, Olivier Dubourg, Jean-Pierre Bourdarias, Catherine Bonaïti-Pellié, Jean
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase
 6866 Med Genet 1991; 28: 686-690 Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene as an aid to the diagnosis of phenylketonuria L Kalaydjieva, B Dworniczak, C Aulehla-Scholz,M Devoto, G Romeo, M
6866 Med Genet 1991; 28: 686-690 Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene as an aid to the diagnosis of phenylketonuria L Kalaydjieva, B Dworniczak, C Aulehla-Scholz,M Devoto, G Romeo, M
Myoglobin A79G polymorphism association with exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage
 Myoglobin A79G polymorphism association with exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage T. Cui and M.S. Jiang College of Physical Education, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Ji nan, Shandong,
Myoglobin A79G polymorphism association with exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage T. Cui and M.S. Jiang College of Physical Education, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Ji nan, Shandong,
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
J. Environ. Res. Develop. Journal of Environmental Research And Development Vol. 8 No. 3A, January-March 2014
 ASSOCIATION OF THE 45 T/G AND 276 G/T POLYMOR- PHISMS IN THE ADIPONECTIN GENE WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOUTH INDIAN POPULATION Thirunavukkarasu A.,* Nithya R., 1 Muthukumaran K. and Sivasankari C. 2 1.
ASSOCIATION OF THE 45 T/G AND 276 G/T POLYMOR- PHISMS IN THE ADIPONECTIN GENE WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES IN SOUTH INDIAN POPULATION Thirunavukkarasu A.,* Nithya R., 1 Muthukumaran K. and Sivasankari C. 2 1.
Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE. Dr Rasime Kalkan
 SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Association of the LMNA gene single nucleotide polymorphism rs4641 with dilated cardiomyopathy
 Association of the LMNA gene single nucleotide polymorphism rs4641 with dilated cardiomyopathy J. Yin 1,2, J. Yang 3, F.X. Ren 3, C.M. Sun 4, L.D. Li 3, L.Y. Han 5, S.L. Cai 1, C.H. Zhang 3, Z.Q. Zhang
Association of the LMNA gene single nucleotide polymorphism rs4641 with dilated cardiomyopathy J. Yin 1,2, J. Yang 3, F.X. Ren 3, C.M. Sun 4, L.D. Li 3, L.Y. Han 5, S.L. Cai 1, C.H. Zhang 3, Z.Q. Zhang
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome accompanied by severe skeletal abnormalities in two Chinese siblings: two case reports
 Xiong et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:63 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome accompanied by severe skeletal abnormalities in two
Xiong et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:63 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome accompanied by severe skeletal abnormalities in two
UNIT IV. Chapter 14 The Human Genome
 UNIT IV Chapter 14 The Human Genome UNIT 2: GENETICS Chapter 7: Extending Medelian Genetics I. Chromosomes and Phenotype (7.1) A. Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype 1. Most human traits
UNIT IV Chapter 14 The Human Genome UNIT 2: GENETICS Chapter 7: Extending Medelian Genetics I. Chromosomes and Phenotype (7.1) A. Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype 1. Most human traits
Chapter 11 Gene Expression
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
TP53 mutational profile in CLL : A retrospective study of the FILO group.
 TP53 mutational profile in CLL : A retrospective study of the FILO group. Fanny Baran-Marszak Hopital Avicenne Bobigny France 2nd ERIC workshop on TP53 analysis in CLL, Stresa 2017 TP53 abnormalities :
TP53 mutational profile in CLL : A retrospective study of the FILO group. Fanny Baran-Marszak Hopital Avicenne Bobigny France 2nd ERIC workshop on TP53 analysis in CLL, Stresa 2017 TP53 abnormalities :
Disturbances in tooth development lead to various dental anomalies,
 RESEARCH REPORTS Clinical S.A. Frazier-Bowers 1, D.C. Guo 2, A. Cavender 1, L. Xue 2, B. Evans 3, T. King 2, D. Milewicz 2, and R.N. D'Souza 1* 1 Department of Orthodontics, Dental Branch, Suite 371, and
RESEARCH REPORTS Clinical S.A. Frazier-Bowers 1, D.C. Guo 2, A. Cavender 1, L. Xue 2, B. Evans 3, T. King 2, D. Milewicz 2, and R.N. D'Souza 1* 1 Department of Orthodontics, Dental Branch, Suite 371, and
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome. Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France
 A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France Disclosures I am an employee of decode genetics, Reykjavik, Iceland. Sick sinus syndrome SSS is
A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France Disclosures I am an employee of decode genetics, Reykjavik, Iceland. Sick sinus syndrome SSS is
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Goals of Pedigree Analysis Basic Symbols More Symbols Y-Linked Inheritance
 Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Mitochondrial DNA (T/C) Polymorphism, Variants and Heteroplasmy among Filipinos with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Mitochondrial DNA (T/C) 16189 Polymorphism, Variants and Heteroplasmy among Filipinos with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Elizabeth Paz-Pacheco 1, Eva Maria Cutiongco-Dela Paz 2, Cynthia Halili-Manabat 3, Mary
Mitochondrial DNA (T/C) 16189 Polymorphism, Variants and Heteroplasmy among Filipinos with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Elizabeth Paz-Pacheco 1, Eva Maria Cutiongco-Dela Paz 2, Cynthia Halili-Manabat 3, Mary
Human Genetic Diseases (Ch. 15)
 Human Genetic Diseases (Ch. 15) 1 2 2006-2007 3 4 5 6 Genetic counseling Pedigrees can help us understand the past & predict the future Thousands of genetic disorders are inherited as simple recessive
Human Genetic Diseases (Ch. 15) 1 2 2006-2007 3 4 5 6 Genetic counseling Pedigrees can help us understand the past & predict the future Thousands of genetic disorders are inherited as simple recessive
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Skeletal myopathy in a family with lamin A/C cardiac disease
 Original Article Skeletal myopathy in a family with lamin A/C cardiac disease Subha Ghosh 1, Rahul Renapurkar 1, Subha V. Raman 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH, USA; 2 The Ohio State University
Original Article Skeletal myopathy in a family with lamin A/C cardiac disease Subha Ghosh 1, Rahul Renapurkar 1, Subha V. Raman 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH, USA; 2 The Ohio State University
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 19;
 SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders. Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital
 Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Obesity: Physiology, Health and Diseases 5 July Genetic of Obesity
 Obesity: Physiology, Health and Diseases 5 July 2017 Genetic of Obesity Voraluck Phatarakijnirund, MD. Division of Endocrinology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital Phramongkutklao Colleague
Obesity: Physiology, Health and Diseases 5 July 2017 Genetic of Obesity Voraluck Phatarakijnirund, MD. Division of Endocrinology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital Phramongkutklao Colleague
Hutterite brothers both affected with two forms of limb girdle muscular dystrophy: LGMD2H and LGMD2I
 (2005) 13, 978 982 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1018-4813/05 $30.00 ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg Hutterite brothers both with two forms of limb girdle muscular dystrophy: LGMD2H and
(2005) 13, 978 982 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1018-4813/05 $30.00 ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg Hutterite brothers both with two forms of limb girdle muscular dystrophy: LGMD2H and
ABSENCE OF APO B R3500Q MUTATION AMONG KELANTANESE MALAYS WITH HYPERLIPIDAEMIA
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2000 (16-21) ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSENCE OF APO B R3500Q MUTATION AMONG KELANTANESE MALAYS WITH HYPERLIPIDAEMIA Win Mar Kyi, Mohd. Nizam Isa*,
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2000 (16-21) ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSENCE OF APO B R3500Q MUTATION AMONG KELANTANESE MALAYS WITH HYPERLIPIDAEMIA Win Mar Kyi, Mohd. Nizam Isa*,
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
IVF Michigan, Rochester Hills, Michigan, and Reproductive Genetics Institute, Chicago, Illinois
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
What do you think of when you here the word genome?
 What do you think of when you here the word genome? What do you think of when you here the word genome? Personal Genomics Outline Review of pre-lab work Genomics and Medicine Case Overview & Assignment
What do you think of when you here the word genome? What do you think of when you here the word genome? Personal Genomics Outline Review of pre-lab work Genomics and Medicine Case Overview & Assignment
Background 11/8/2011. Disclosure. Hereditary Periodic Fever Syndromes Mutations in Idiopathic Acute Recurrent Pericarditis.
 Mutations in Idiopathic Acute Recurrent Pericarditis Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose Guillaume Geri, Pierre Hausfater, Catherine Dodé, Zahir Amoura, Jean-Charles Piette,
Mutations in Idiopathic Acute Recurrent Pericarditis Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose Guillaume Geri, Pierre Hausfater, Catherine Dodé, Zahir Amoura, Jean-Charles Piette,
Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies
 Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies Γεώργιος Κ Ευθυμιάδης Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας ΑΠΘ No conflict of interest Genetic terms Proband: The first individual diagnosed in a family Mutation: A
Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies Γεώργιος Κ Ευθυμιάδης Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας ΑΠΘ No conflict of interest Genetic terms Proband: The first individual diagnosed in a family Mutation: A
HLA Complex Genetics & Biology
 HLA Complex Genetics & Biology M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info Mount Sinai Medical Center
HLA Complex Genetics & Biology M. Tevfik DORAK Environmental & Occupational Health College of Public Health Florida International University Miami, USA http://www.dorak.info Mount Sinai Medical Center
5/2/18. After this class students should be able to: Stephanie Moon, Ph.D. - GWAS. How do we distinguish Mendelian from non-mendelian traits?
 corebio II - genetics: WED 25 April 2018. 2018 Stephanie Moon, Ph.D. - GWAS After this class students should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast methods used to discover the genetic basis of traits or
corebio II - genetics: WED 25 April 2018. 2018 Stephanie Moon, Ph.D. - GWAS After this class students should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast methods used to discover the genetic basis of traits or
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Distribution of Disease Genes, Spectrum of Mutations, and Implications for a Molecular Diagnosis Strategy
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Distribution of Disease Genes, Spectrum of Mutations, and Implications for a Molecular Diagnosis Strategy Pascale Richard, PhD; Philippe Charron, MD, PhD; Lucie Carrier, PhD;
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Distribution of Disease Genes, Spectrum of Mutations, and Implications for a Molecular Diagnosis Strategy Pascale Richard, PhD; Philippe Charron, MD, PhD; Lucie Carrier, PhD;
Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3. Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented in our
 1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
