The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important
|
|
|
- Coleen Claribel Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Antisense Inhibition of Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Decreased Blood Pressure in Chronic 2-Kidney, 1 Clip Hypertensive Rats Shuntaro Kagiyama, Adrian Varela, M. Ian Phillips, Sara M. Galli Abstract The systemic renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important role in blood pressure (BP) regulation during the development of 2-kidney, 1 clip (2K1C) hypertension. Its contributions decrease with time after constriction of the renal artery. During the chronic phase, the peripheral RAS returns to normal, but the hypertension is sustained for months. We hypothesized that in this phase the brain RAS contributes to the maintenance of high BP. To test the hypothesis, we studied the role of brain RAS by decreasing the synthesis of angiotensinogen (AGT) and the angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1a receptor (AT 1 R) with intracerebroventricular injections of antisense oligonucleotides (AS-ODNs). The response of systolic BP (SBP) to AS-ODNs to AGT mrna was studied in 2K1C rats at 6 months after clipping, and the response to AS-ODNs to AT 1 R mrna was studied at 10 months after clipping. Intracerebroventricular injection of AS-ODN-AGT (200 g/kg, n 5) significantly decreased SBP ( 22 6 mm Hg, P 0.05) compared with the sense ODN (n 5) and saline (n 3) groups. Intracerebroventricular injection of AS-ODN-AGT reduced the elevated hypothalamic Ang II level. The hypothalamic Ang II content in sense ODN and saline groups was significantly (P 0.05) higher than in the nonclipped group. Compared with inverted ODN, intracerebroventricular injection of AS-ODN-AT 1 R (250 g/kg, n 6) significantly decreased SBP ( 26 8 mm Hg, P 0.05) for 3 days after injection. This was a brain effect because intravenous AS-ODN-AT 1 R at a dose of 250 to 500 g/kg did not affect SBP. These results suggest that the brain RAS plays an important role in maintaining the elevated SBP in chronic 2K1C hypertension. (Hypertension. 2001;37[part 2]: ) Key Words: rats renin-angiotensin system brain hypertension, 2K1C antisense The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important role in blood pressure (BP) regulation during the development of renovascular hypertension. 1 In the rat model of unilateral renovascular hypertension (the 2-kidney, 1 clip Goldblatt [2K1C] hypertensive rat), renal stenosis elevates the RAS. The contributions of RAS in this model vary depending on the time after constriction of the renal artery. 2 In the acute phase of 2K1C hypertension, plasma renin activity rises, and the increase in BP is RAS dependent. Both plasma renin activity and plasma angiotensin II (Ang II) concentrations normalize in the chronic phase despite the continued high BP. To explain the antihypertensive effects of ACE inhibitors when the circulating RAS is not overtly activated, the concept of tissue RAS has been used. It is proposed that in 2K1C hypertension, the RAS in various tissues is activated, and the products act in a paracrine fashion and are not detectable in plasma. 3,4 An activation of tissue RAS in the acute phase of 2K1C hypertension has been extensively discussed. 3 9 By contrast, few studies have examined the mechanism of maintained hypertension in the chronic phase, 9,10 although clinically, this is much more relevant. Most renovascular hypertensive patients present with chronic high BP. We have shown that inhibiting the brain RAS in adult spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) significantly reduces hypertension. 11 Baltatu et al 12 have reported that the transgenic rat [TGR(ASrAoGEN)], which has permanent inhibition of brain-specific angiotensinogen (AGT) synthesis, shows a reduction of hypertension induced by a low-dose of Ang II. Therefore, we hypothesize that as the 2K1C hypertension progresses chronically, the brain RAS contributes to elevated BP in the absence of peripheral RAS elevation. To test this hypothesis, we used antisense (AS) oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs), which we previously designed to inhibit components of the brain RAS, including AGT mrna and Ang II type 1a receptor (AT 1 R) mrna AS-ODN has some advantages over drugs: the gene-based design is more specific than a pharmacological antagonist, and the AS-ODN can be delivered in vivo and can produce prolonged effects rather than the transient effects of currently used drugs. These AS-ODNs produce a significant decrease in BP for 3 to 7 days with a single injection Morishita et al 10 Received October 25, 2000; first decision December 11, 2000; revision accepted December 19, From the Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville. Correspondence to Dr Sara M. Galli, Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Florida, Box , 1600 SW Archer Rd, Gainesville, FL smgalli@phys.med.ufl.edu 2001 American Heart Association, Inc. Hypertension is available at 371
2 372 Hypertension February 2001 Part II did not find an increase in the brain RAS at 16 weeks, but this may not have been long enough after clipping. In the present study, we investigate the role of brain RAS on BP regulation in chronic 2K1C rats at 6 and 10 months after clipping. To test the hypothesis, the rats received intracerebroventricular injections of AS-ODN to AGT or AT 1 R mrna. We also examined the activity of RAS by measuring Ang II levels in the brain tissue and plasma. Methods Animals and Surgery Experiments were performed in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (250 to 270 g, n 24). All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care Committee of the University of Florida. Surgical procedures were performed under anesthesia induced by subcutaneous injection of a mixture of ketamine, xylazine, and acepromazine (50, 5, 1 mg/kg, respectively). The left renal artery was exposed, and a silver clip (0.2-mm internal diameter) was applied over the left renal artery. One week after recovery from surgery, systolic BP (SBP) was measured by the tail-cuff method. Throughout the study, rats were given tap water to drink and standard rat chow to eat ad libitum and were kept on a 12-hour light and dark cycle. Two groups of chronic 2K1C rats were tested: the first group at 6 months and the second group at 10 months after clipping of the renal artery. One week before testing, the rats were again anesthetized and placed in a stereotaxic frame. A guide cannula (23 gauge) was implanted into the lateral cerebral ventricle by stereotaxic coordinates (1.5 mm posterior to the bregma, 1.7 mm lateral to the midline, and 5.0 mm below the skull surface). Rats were then allowed to recover for 3 to 5 days. Sham-operated age-matched control rats underwent a similar procedure with manipulation of the left renal artery and implantation of intracerebroventricular cannulas but without permanent application of a clip. At the end of the experiments, the position of the injection cannulas was verified by the injection of blue ink (5 L) and postmortem examination of the ventricular stain. Procedure for AS-ODNs to AGT mrna To investigate the effects of AS-ODNs to AGT mrna, thirteen 2K1C rats at 6 months after clipping were divided into 3 groups. An injection cannula (30 gauge), which was connected to a 10- L Hamilton syringe by a 20-cm piece of PE-10 tubing, was inserted into the lateral ventricle, and AS (50 g/5 L, n 5) or sense (50 g/5 L, n 5) ODNs to AGT mrna were injected for 1 minute. Three rats were injected with saline (5 L) by the same procedure. After 24 hours, we measured the SBP by the tail-cuff method. A blood sample was collected from the tail vein in 50 L of 0.5 mol/l EDTA and 2.5 L o-phenanthroline and centrifuged to collect plasma. Then the rats were deeply anesthetized, the brain was removed from the skull, and the hypothalamus and brain stem were separated. Ang II levels in plasma, hypothalamus, and brain stem were measured by radioimmunoassay. Plasma catecholamine concentrations were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Procedure for AS-ODNs to AT 1 R mrna We injected AS-ODNs to AT 1 R mrna (250 g/kg per 5 L, n 6) or inverted ODNs (250 g/kg per 5 L, n 5) into the cerebral ventricle of the 2K1C rats 10 months after clipping. SBPs were measured by the tail-cuff method after 14 days. Fourteen days after intracerebroventricular injection of ODN, when SBP returned to the baseline, we injected AS-ODN-AT 1 R (250 or 500 g/kg per 250 L, n 5) intravenously through the tongue vein. Antisense ODNs AS, sense, or inverted ODNs were synthesized as 18-mers targeted to bases 5 to 13 of AGT mrna and 15-mers to bases 63 to 77 of AT 1 R mrna. 13 All the ODNs were phosphorothioated. The ODNs were dissolved in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (mmol/l: NaCl Figure 1. Change in SBP (A) and heart rate (HR) (B) elicited by intracerebroventricular injection of saline (stippled bar, n 3), sense (hatched bar, n 5), or AS (closed bar, n 5) ODNs to AGT mrna on SBP in 2K1C rats 6 months after clipping of the renal artery. *P 0.05 vs saline or sense ODN treatment. 106, KCl 3, MgCl 2 1.3, NaHCO , CaCl 2 2, and glucose 10, ph 7.4) or saline for intracerebroventricular or intravenous injection, respectively, and stored at 20 C until use. Ang II Assay Plasma was frozen at 70 C until extraction with methanol on reversed-phase phenylsilylsilica extraction cartridges (Alpco; approximate recovery, 90%). Samples were analyzed by doubleantibody Ang II radioimmunoassay (RK-A22, Alpco). The assay is sensitive to 0.7 pg/ml (0.7 pmol/l). Ang II levels were determined by a -counter (Beckman DP 550). Statistical Analysis Data are expressed as mean SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by 1-way ANOVA, followed by the Fisher least significant difference method, with the use of Statview SE. A value of P 0.05 was viewed as statistically significant. Results Effects of AS-ODNs to AGT mrna The baseline SBP was similar between the saline-treated, AS-ODN treated, and sense ODN treated groups (179 7, , and mm Hg, respectively). Twenty-four hours after injection, SBP was significantly (P 0.05) decreased in the AS-ODN-AGT treated group compared with the control sense ODN treated or saline-treated group (Figure 1A). Heart rate did not change in any group (Figure 1B). No significant differences in plasma Ang II were observed in 3 treatment groups, and plasma Ang II was significantly higher in aged-matched nonclipped rats (P 0.05). However, the hypothalamic and brain stem Ang II levels in sense ODN treated and saline-treated groups were significantly higher than those in age-matched nonclipped rats (P 0.05),
3 Kagiyama et al Central RAS Inhibition in Chronic 2K1C 373 Figure 2. Effects of intracerebroventricular injection of saline (stippled bar, n 3), sense (hatched bar, n 5), or AS (closed bar, n 5) ODNs to AGT mrna on plasma (A), hypothalamic (B), and brain stem (C) Ang II levels in 2K1C rats 6 months after clipping of the renal artery are compared with the intracerebroventricular injection of saline in age-matched Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (open bar, n 3). *P 0.05 vs saline, AS, or sense ODN treatment of 2K1C rats. P 0.05 vs saline or sense ODN treatment of 2K1C rats. and AS-ODN-AGT treatment significantly reduced the elevated hypothalamic Ang II levels to nonclipped concentrations (P 0.05), but no change in Ang II was found in the brain stem (Figure 2). Plasma levels of epinephrine were significantly lower in the AS-ODN treated group than in the sense-treated group ( compared with pg/ml, respectively; P 0.05). Effects of AS-ODNs to AT 1 R mrna The baseline SBP was similar between the AS-treated and inverted ODN treated groups (168 7 and mm Hg, respectively). The time course of SBP after intracerebroventricular injection of ODN is shown Figure 3A. From 1 to 3 days after injection, SBP in the AS-ODN treated group was significantly (P 0.05) lower than the baseline value. The decrease in SBP was also significant compared with the inverted ODN treated group. Inverted ODN did not change SBP in the observation period. In contrast to the intracerebroventricular route, intravenous injection of AS-ODN-AT 1 R Figure 3. A, Effects of intracerebroventricular injection of AS (closed circle, n 7) or inverted (open triangle, n 6) ODNs to AT 1 R mrna on SBP in 2K1C rats 10 months after clipping of the renal artery. B, Effects of intravenous injection of low dose (250 g/kg, closed triangle, n 5) and high dose (500 g/kg, closed square, n 5) of AS-ODNs to AT 1 R mrna on SBP in 2K1C rats 10 months after clipping of the renal artery. *P 0.05 and **P 0.01 vs inverted ODN treatment; P 0.05 and P 0.01 vs day 0. did not affect SBP even at the higher dose (500 g/kg) (Figure 3B). Discussion Chronic renovascular hypertension, lasting many months, is more clinically relevant than is acute renovascular hypertension, but few studies have investigated 2K1C hypertension many months after clipping. In the present study, we show that at 6 to 10 months after clipping of the renal artery, high BP persists even though plasma Ang II levels are no longer elevated. Indeed, the plasma Ang II levels were reduced in the chronic 2K1C rats. We hypothesized that the brain RAS is contributing to the maintenance of hypertension in chronic renovascular hypertension. The results show that brain RAS inhibition by AS-ODN-AGT and AS-ODN-AT 1 R decreased SBP in the chronic phase of 2K1C rats. This inhibition was
4 374 Hypertension February 2001 Part II not due to leakage of AS-ODN out of the brain into the peripheral circulation, because intravenous injection of AS- ODN-AT 1 R at the same intracerebroventricular dose or at an even higher dose did not produce a change in BP. Therefore, we conclude that the lowering of BP in these rats by AS-ODNs reflected the role of brain RAS on the maintenance of BP in chronic renovascular hypertension. Previously, it has been reported that in 2K1C rats, brain AGT mrna is not different from that in normotensive rats. 3,10 However, that was up to 4 months after clipping the renal artery. The present study shows significantly higher Ang II levels in the hypothalamus at 6 to 10 months after clipping. The hypothalamic Ang II level was significantly increased in 2K1C hypertensive rats compared with agematched control rats, and this result is consistent with 1 other report. 17 The levels of Ang II in the brain stem were also elevated in the chronic 2K1C rats, but only in the hypothalamus was the AS-ODN effective in reducing Ang II. Thus, the site of hypotensive action of AS-ODN appears to be the hypothalamus. Microinjection of AS-ODN-AT 1 R into the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus (PVN) decreased the BP in Ren-2d gene transgenic rats. 18 Injection of AS-ODN- AGT into the PVN of SHR attenuates vasopressin and catecholamine release. 19 We have previously shown that the fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled AS-ODN was taken up into the tissue around the third or lateral ventricle by intracerebroventricular injection 15 and that AS-ODN-AT 1 R decreased brain angiotensin receptors by use of membrane binding and autoradiographic analysis. 20 Other nuclei of the brain such as the lateral parabrachial nucleus 21 and the area postrema 22 have been reported to be important in Ang II induced hypertensive rats. Therefore, the brain stem as a site of action cannot be ruled out because the AS-ODN injected in the cerebral ventricle may not have reached brain stem sites in sufficient amounts. Martin and Haywood 23 have reported that stimulation of the PVN increases BP concomitant with an increase in plasma catecholamines, indicating activation of the sympathetic nervous system. The hypertension induced by a low dose of Ang II, which does not affect the plasma Ang II, is analogous to the chronic phase of renovascular hypertension. The centrally acting sympatholytic drug clonidine reverses the development of low-dose Ang II induced hypertension. 24 In the present study, AS-ODN-AGT decreased plasma epinephrine. Therefore, we propose that the mechanism of maintenance of high BP in chronic 2K1C hypertension involves high Ang II in the hypothalamus activating the PVN to increase sympathetic outflow, as shown by an elevation of circulating catecholamines. The brain RAS may also be involved in the early stages of 2K1C hypertension, inasmuch as intracerebroventricular injection of Ang II antagonists such as saralasin can reduce BP However, Sweet el al 28 have reported that intracerebroventricular injection of a renin inhibitor or ACE inhibitor in 2K1C rats does not result in any change in SBP. This may indicate that an alternate pathway of Ang II synthesis was in action. AS-ODN-AGT decreased the elevated hypothalamic Ang II level in the present study. We speculate that the Ang II in the brain might be produced from AGT directly. 29 The AS-ODN approach provides a specific and long-acting reduction in the brain RAS synthesis. A single injection of AS-ODN-AT 1 R reduced SBP for 3 days in the present study. The time course of the reduction of SBP seems to be characteristic of AS-ODN action and is similar to that which we previously reported in SHR. 15 The largest reduction of BP was observed on the second day after injection in chronic 2K1C hypertensive rats and in SHR. 15 From these and other studies, the inhibitory effects of AS-ODN take 24 hours to show a reduction of BP by inhibition of AT 1 R or AGT protein synthesis. Compared with a single dose of current pharmacological agents, the onset of the action of AS-ODN is slower, but the effect lasts much longer. We showed that an intravenous injection of AS-ODN- AT 1 R in the same dose that was given intracerebroventricularly did not decrease SBP. We previously reported that the peripheral injection of liposome-encapsulated AS-ODN-AGT reduced BP in SHR. 30 A liposome encapsulation increases uptake and decreases degradation of ODN. 31 However, we did not use liposomes in the brain, because we have found that they are toxic in the central nervous system. Therefore, because the intracerebroventricular injection of AS-ODN was without liposomes, we did not use AS-ODN with liposomes for the control intravenous injection. This did not preclude the AS-ODN from having an effect, inasmuch as peripheral injection of AS-ODN-AT 1 R decreased SBP in cold-induced hypertension without liposome encapsulation. 32 Thus, when the peripheral RAS is activated, as in cold-induced hypertension, AS-ODN inhibition of RAS can reduce BP. The dose of injection in a previous study 32 was similar to that of the lower dose in the present study. Because we could not observe a reduction of BP in the chronic 2K1C rat with an intravenous injection of AS-ODN even at the higher dose, we conclude that peripheral RAS does not have an important role in the maintenance of BP in the chronic phase of renovascular hypertension. We studied the chronic phase in 2K1C hypertensive rats because human patients presenting with renovascular hypertension have generally had the disease for a long time. Although there is no direct evidence that the brain RAS contributes to the maintenance of high BP in human renovascular hypertension, an overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system is observed, 33 and centrally acting drugs such as clonidine have been shown to reduce BP in chronic unilateral renal artery stenosis. 34 Therefore, the results are relevant to understanding the mechanisms of chronic renovascular hypertension, and we conclude that the brain RAS plays a significant role by elevating sympathetic outflow from the brain. The results also point to a therapy strategy that could be developed to treat this form of hypertension. Acknowledgments This work was supported by National Institutes of Health MERIT award HL Dr Kagiyama is supported by the Japan Heart Foundation and a Bayer Yakuhin Research Grant Abroad. References 1. DeForrest JM, Knappenberger RC, Antonaccio MJ, Ferrone RA, Creekmore JS. Angiotensin II is a necessary component for the devel-
5 Kagiyama et al Central RAS Inhibition in Chronic 2K1C 375 opment of hypertension in the two kidney, one clip rat. Am J Cardiol. 1982;49: Martinez-Maldonado M. Pathophysiology of renovascular hypertension. Hypertension. 1991;17: Nishimura M, Milsted A, Block CH, Brosnihan KB, Ferrario CM. Tissue renin-angiotensin systems in renal hypertension. Hypertension. 1992;20: Okamura T, Miyazaki M, Inagami T, Toda N. Vascular renin-angiotensin system in two-kidney, one clip hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1986;8: Samani NJ, Godfrey NP, Major JS, Brammar WJ, Swales JD. Kidney renin mrna levels in the early and chronic phases of two-kidney, one clip hypertension in the rat. J Hypertens. 1989;7: Morishita R, Higaki J, Okunishi H, Tanaka T, Ishii K, Nagano M, Mikami H, Ogihara T, Murakami K, Miyazaki M. Changes in gene expression of the renin-angiotensin system in two-kidney, one clip hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1991;9: el-dahr SS, Dipp S, Guan S, Navar LG. Renin, angiotensinogen, and kallikrein gene expression in two-kidney Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 1993;6: Mai M, Hilgers KF, Wagner J, Mann JF, Geiger H. Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme in renovascular hypertensive rat kidney. Hypertension. 1995;25: Sen S, Smeby RR, Bumpus FM, Turcotte JG. Role of renin-angiotensin system in chronic renal hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1979;1: Morishita R, Higaki J, Okunishi H, Nakamura F, Nagano M, Mikami H, Ishii K, Miyazaki M, Ogihara T. Role of tissue renin angiotensin system in two-kidney, one-clip hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1993;264: F510 F Phillips MI, Mann JF, Haebara H, Hoffman WE, Dietz R, Schelling P, Ganten D. Lowering of hypertension by central saralasin in the absence of plasma renin. Nature. 1977;270: Baltatu O, Silva JA Jr, Ganten D, Bader M. The brain renin-angiotensin system modulates angiotensin II induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension. 2000;35: Phillips MI, Wielbo D, Gyurko R. Antisense inhibition of hypertension: a new strategy for renin-angiotensin candidate genes. Kidney Int. 1994; 46: Wielbo D, Sernia C, Gyurko R, Phillips MI. Antisense inhibition of hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1995; 25: Gyurko R, Tran D, Phillips MI. Time course of inhibition of hypertension by antisense oligonucleotides targeted to AT 1 angiotensin receptor mrna in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 1997;10:56S 62S. 16. Makino N, Sugano M, Ohtsuka S, Sawada S. Intravenous injection with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides against angiotensinogen decreases blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1998;31: Morishita R, Higaki J, Nakamura Y, Aoki M, Yamada K, Moriguchi A, Rakugi H, Tomita N, Tomita S, Yu H, et al. Effect of an antihypertensive drug on brain angiotensin II levels in renal and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1995;22: Li P, Morris M, Diz DI, Ferrario CM, Ganten D, Callahan MF. Role of paraventricular angiotensin AT 1 receptors in salt-sensitive hypertension in mren-2 transgenic rats. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:R1178 R Kagiyama S, Tsuchihashi T, Abe I, Matsumura K, Fujishima M. Antisense inhibition of angiotensinogen attenuates vasopressin release in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 1999;829: Ambühl P, Gyurko R, Phillips MI. A decrease in angiotensin receptor binding in rat brain nuclei by antisense oligonucleotides to the angiotensin AT 1 receptor. Regul Pept. 1995;59: Fink GD, Pawloski CM, Ohman LE, Haywood JR. Lateral parabrachial nucleus and angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 1991;17: Fink GD, Bruner CA, Mangiapane ML. Area postrema is critical for angiotensin-induced hypertension in rats. Hypertension. 1987;9: Martin DS, Haywood JR. Sympathetic nervous system activation by glutamate injections into the paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res. 1992; 577: Gorbea-Oppliger VJ, Fink GD. Clonidine reverses the slowly developing hypertension produced by low doses of angiotensin II. Hypertension. 1994;23: Schoelkens BA, Jung W, Steinback R. Blood pressure response to central and peripheral injection of angiotensin II and 8-C-phenylglycine analogue of angiotensin II in rats with experimental hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976;3:403s 406s. 26. Mann JFE, Phillips MI, Dietz R, Haebara H, Ganten D. Effects of central and peripheral angiotensin blockade in hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1978;234:H629 H Suzuki H, Kondo K, Handa M, Saruta T. Role of the brain iso-renin-angiotensin system in experimental hypertension in rats. Clin Sci. 1981;61: Sweet CS, Columbo JM, Gaul SL. Central antihypertensive effects of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system in rats. Am J Physiol. 1976; 231: Phillips MI, Sumners C. Angiotensin II in central nervous system physiology. Regul Pept. 1998;78: Wielbo D, Simon A, Phillips MI, Toffolo S. Inhibition of hypertension by peripheral administration of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Hypertension. 1996;28: Phillips MI. Antisense inhibition and adeno-associated viral vector delivery for reducing hypertension. Hypertension. 1997;29: Peng JF, Kimura B, Fregly MJ, Phillips MI. Reduction of cold-induced hypertension by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to angiotensinogen mrna and AT 1 -receptor mrna in brain and blood. Hypertension. 1998; 31: Johansson M, Elam M, Rundqvist B, Eisenhofer G, Herlitz H, Lambert G, Friberg P. Increased sympathetic nerve activity in renovascular hypertension. Circulation. 1999;99: Mathias CJ, Wilkinson A, Lewis PS, Peart WS, Sever PS, Snell ME. Clonidine lowers blood pressure independently of renin suppression in patients with unilateral renal artery stenosis. Chest. 1983;83:
Antisense inhibition for gene therapy of hypertension is a
 Attenuation of Hypertension and Heart Hypertrophy by Adeno-Associated Virus Delivering Angiotensinogen Antisense Birgitta Kimura, Dagmara Mohuczy, Xiaoping Tang, M. Ian Phillips Abstract Angiotensinogen
Attenuation of Hypertension and Heart Hypertrophy by Adeno-Associated Virus Delivering Angiotensinogen Antisense Birgitta Kimura, Dagmara Mohuczy, Xiaoping Tang, M. Ian Phillips Abstract Angiotensinogen
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
IT has been suggested that the central nervous system
 Effect of Lesions of the Anteroventral Third Ventricle (AV3V) on the Development of Hypertension in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats FRANK J. GORDON, PH.D., JOSEPH R. HAYWOOD, PH.D., MICHAEL J. BRODY, PH.D.,
Effect of Lesions of the Anteroventral Third Ventricle (AV3V) on the Development of Hypertension in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats FRANK J. GORDON, PH.D., JOSEPH R. HAYWOOD, PH.D., MICHAEL J. BRODY, PH.D.,
Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
AT 1 receptor in rostral ventrolateral medulla mediating blunted baroreceptor reflex in spontaneously hypertensive rats 1
 Gao XY et al / Acta Pharmacol Sin 2004 Nov; 25 (11): 1433-1438 1433 2004, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com
Gao XY et al / Acta Pharmacol Sin 2004 Nov; 25 (11): 1433-1438 1433 2004, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com
Mechanisms responsible for postmenopausal hypertension in a rat model: Roles of the renal sympathetic nervous system and the renin angiotensin system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Mechanisms responsible for postmenopausal hypertension in a rat model: Roles of the renal sympathetic nervous system and the renin angiotensin system
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Mechanisms responsible for postmenopausal hypertension in a rat model: Roles of the renal sympathetic nervous system and the renin angiotensin system
CNS Effects of Aldosterone :
 CNS Effects of Aldosterone : Critical Roles in salt-sensitive sensitive hypertension and CHF. Frans HH Leenen MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAHA 2 Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Circulatory RAAS Tissue RAAS: -
CNS Effects of Aldosterone : Critical Roles in salt-sensitive sensitive hypertension and CHF. Frans HH Leenen MD, PhD, FRCPC, FAHA 2 Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System Circulatory RAAS Tissue RAAS: -
Interrelationship between Angiotensin Catecholamines. Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D.
 Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
The Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Contributes to the Hypertension in Mice Containing Both the Human Renin and Human Angiotensinogen Transgenes
 The Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Contributes to the Hypertension in Mice Containing Both the Human Renin and Human Angiotensinogen Transgenes Robin L. Davisson, Gongyu Yang, Terry G. Beltz, Martin D.
The Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Contributes to the Hypertension in Mice Containing Both the Human Renin and Human Angiotensinogen Transgenes Robin L. Davisson, Gongyu Yang, Terry G. Beltz, Martin D.
Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS
 Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS Phenomenon: shipwrecked sailor on raft in ocean ("water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink") Why are the sailors thirsty? (What stimulated thirst?) Why
Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS Phenomenon: shipwrecked sailor on raft in ocean ("water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink") Why are the sailors thirsty? (What stimulated thirst?) Why
Catheter-Based Renal Denervation Reduces Total Body and Renal Noradrenaline Spillover and Blood Pressure in Resistant Hypertension
 Catheter-Based Renal Denervation Reduces Total Body and Renal Noradrenaline Spillover and Blood Pressure in Resistant Hypertension Murray Esler, Markus Schlaich, Paul Sobotka, Rob Whitbourn, Jerzy Sadowski,
Catheter-Based Renal Denervation Reduces Total Body and Renal Noradrenaline Spillover and Blood Pressure in Resistant Hypertension Murray Esler, Markus Schlaich, Paul Sobotka, Rob Whitbourn, Jerzy Sadowski,
Central Pressor Response by Olmesartan in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
 Clinical Medicine Reviews in Cardiology Original Research Central Pressor Response by Olmesartan in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Zhu Jie 1, Wang Shaojiu 1, Zhang
Clinical Medicine Reviews in Cardiology Original Research Central Pressor Response by Olmesartan in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Zhu Jie 1, Wang Shaojiu 1, Zhang
Oral Calcium Treatment Lowers Blood Pressure in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System
 Hypertension Laboratory Studies Oral Calcium Treatment Lowers Blood Pressure in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System Yo KAGEYAMA, HIROMICHI SUZUKI, KOICHIRO ARIMA,
Hypertension Laboratory Studies Oral Calcium Treatment Lowers Blood Pressure in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System Yo KAGEYAMA, HIROMICHI SUZUKI, KOICHIRO ARIMA,
Special Lecture 11/08/2013. Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz
 Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Cardiac Output in Conscious One-clip, Two-kidney Renovascular Hypertensive Rats*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 32, No. 1, March, 1983 HIJM 32-9 59 Cardiac Output in Conscious One-clip, Two-kidney Renovascular Hypertensive Rats*) Yasuhiro TERANISHI and Juro IRIUCHIJIMA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 32, No. 1, March, 1983 HIJM 32-9 59 Cardiac Output in Conscious One-clip, Two-kidney Renovascular Hypertensive Rats*) Yasuhiro TERANISHI and Juro IRIUCHIJIMA
Central gain of the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in dogs with heart failure
 Central gain of the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in dogs with heart failure RONG MA, IRVING H. ZUCKER, AND WEI WANG Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Nebraska College of Medicine,
Central gain of the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in dogs with heart failure RONG MA, IRVING H. ZUCKER, AND WEI WANG Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Nebraska College of Medicine,
Veins. VENOUS RETURN = PRELOAD = End Diastolic Volume= Blood returning to heart per cardiac cycle (EDV) or per minute (Venous Return)
 Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Central Progesterone Involvement in Estrogen- Induced Prolactin and Luteinizing Hormone Secretion Surges in Female Rats
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Honors Theses University Honors Program 5-10-2014 Central Progesterone Involvement in Estrogen- Induced Prolactin and Luteinizing Hormone Secretion Surges
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Honors Theses University Honors Program 5-10-2014 Central Progesterone Involvement in Estrogen- Induced Prolactin and Luteinizing Hormone Secretion Surges
Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Angiotensinogen: Insights from Animal Studies. Saha Cardiovascular Research Center 2
 Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Adrenocorticotropin Responses to Corticotropin Releasing Factor and Vasopressin in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
 Laboratory Studies Adrenocorticotropin Responses to Corticotropin Releasing Factor and Vasopressin in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats TERUHIKO HATTORI, KOZO HASHIMOTO, AND ZENSUKE OTA SUMMARY The effects
Laboratory Studies Adrenocorticotropin Responses to Corticotropin Releasing Factor and Vasopressin in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats TERUHIKO HATTORI, KOZO HASHIMOTO, AND ZENSUKE OTA SUMMARY The effects
Renal Denervation. Henry Krum MBBS PhD FRACP. Centre of Cardiovascular Research & Monash University/Alfred Hospital;
 Renal Denervation Henry Krum MBBS PhD FRACP Centre of Cardiovascular Research & Education in Therapeutics, Monash University/Alfred Hospital; Alfred Heart Centre, The Alfred Hospital, Melbourne Australia
Renal Denervation Henry Krum MBBS PhD FRACP Centre of Cardiovascular Research & Education in Therapeutics, Monash University/Alfred Hospital; Alfred Heart Centre, The Alfred Hospital, Melbourne Australia
Erythrocytosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
 Erythrocytosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats SUBHA SEN, GEORGE C. HOFFMAN, NICHOLAS T. STOWE, ROBERT R. SMEBY, and F. MERLIN BUMPUS From the Research Division and Department of Laboratory Hematology,
Erythrocytosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats SUBHA SEN, GEORGE C. HOFFMAN, NICHOLAS T. STOWE, ROBERT R. SMEBY, and F. MERLIN BUMPUS From the Research Division and Department of Laboratory Hematology,
Hypertension represents one of the most
 AJH 1998;11:1376 1380 Changes in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Variability During Dental Surgery Kiyoshi Matsumura, Keiko Miura, Yutaka Takata, Hideo Kurokawa, Minoru Kajiyama, Isao Abe, and Masatoshi
AJH 1998;11:1376 1380 Changes in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Variability During Dental Surgery Kiyoshi Matsumura, Keiko Miura, Yutaka Takata, Hideo Kurokawa, Minoru Kajiyama, Isao Abe, and Masatoshi
Differential effects of isoproterenol on the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the rat heart and aorta
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 355-360 Isoproterenol and angiotensin-converting enzyme activity ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 355 Differential effects of isoproterenol
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 355-360 Isoproterenol and angiotensin-converting enzyme activity ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 355 Differential effects of isoproterenol
The role of angiotensin II (AngII) in maintaining
 AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
AJH 1999;12:705 715 Chronic Captopril Administration Decreases Vasodilator Responses in Skeletal Muscle Arterioles Jefferson C. Frisbee, David S. Weber, and Julian H. Lombard Changes in arteriolar reactivity
Responsiveness vs. basal activity of plasma ANG II as a determinant of arterial pressure salt sensitivity
 Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285: H2142 H2149, 2003. First published July 24, 2003; 10.1152/ajpheart.00200.2003. Responsiveness vs. basal activity of plasma ANG II as a determinant of arterial pressure
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285: H2142 H2149, 2003. First published July 24, 2003; 10.1152/ajpheart.00200.2003. Responsiveness vs. basal activity of plasma ANG II as a determinant of arterial pressure
Cardiovascular System. Heart
 Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice. Akito Tanoue
 Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products
 Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
Bulletin of saka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2007) Brief Reviews *,a b c The Antihypertensive Effect of Sesame Seed-derived Products Daisuke NAKAN, *, a Yoshinobu KIS, b Yasuo MATSUMURA c
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Cholecystokinin antagonist, proglumide, stimulates growth hormone release in the rat
 J. Biosci., Vol. 15, Number 1, March 1990, pp. 17 21. Printed in India. Cholecystokinin antagonist, proglumide, stimulates growth hormone release in the rat E. VIJAYAN* and S. M. McCANN Department of Physiology,
J. Biosci., Vol. 15, Number 1, March 1990, pp. 17 21. Printed in India. Cholecystokinin antagonist, proglumide, stimulates growth hormone release in the rat E. VIJAYAN* and S. M. McCANN Department of Physiology,
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats
 Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
Peptides-Derived from Thai Rice Bran Improve Hemodynamics and Induce Vasorelaxation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Orachorn Boonla 1, Phattharaphon Tuangpolkrung 1, Poungrat Pakdeechote 1, Upa Kukongviriyapan
It has been shown that hereditary and environmental factors
 Kidney Renal Arteriolar Injury by Salt Intake Contributes to Salt Memory for the Development of Hypertension Hideyo Oguchi, Hiroyuki Sasamura, Kazunobu Shinoda, Shinya Morita, Hidaka Kono, Ken Nakagawa,
Kidney Renal Arteriolar Injury by Salt Intake Contributes to Salt Memory for the Development of Hypertension Hideyo Oguchi, Hiroyuki Sasamura, Kazunobu Shinoda, Shinya Morita, Hidaka Kono, Ken Nakagawa,
Elevated sympathetic activity has long been associated
 Sympathetic Nervous System Levels of Renal and Extrarenal Sympathetic Drive in Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension Sandra L. Burke, Roger G. Evans, John-Luis Moretti, Geoffrey A. Head Abstract We examined
Sympathetic Nervous System Levels of Renal and Extrarenal Sympathetic Drive in Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension Sandra L. Burke, Roger G. Evans, John-Luis Moretti, Geoffrey A. Head Abstract We examined
Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
Pregnanolone effects on the blood pressure of stress-induced hypertension in rats
 Acta Physiologica Sinica August June 25 25 2004 2004 56 56 (3) (4) 269-274 471-475 http//www.actaps.com.cn 471 * 130021 (pregnanolone ) (stress-induced hypertension SIH) (0.24 mg/kg) (angiotensin Ang )
Acta Physiologica Sinica August June 25 25 2004 2004 56 56 (3) (4) 269-274 471-475 http//www.actaps.com.cn 471 * 130021 (pregnanolone ) (stress-induced hypertension SIH) (0.24 mg/kg) (angiotensin Ang )
Blood Pressure. a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
 Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Reciprocal Hunger-Regulating Circuits Involving Alphaand
 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2, pp. 1063-1070, October 1970 Reciprocal Hunger-Regulating Circuits Involving Alphaand Beta-Adrenergic Receptors Located, Respectively, in
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2, pp. 1063-1070, October 1970 Reciprocal Hunger-Regulating Circuits Involving Alphaand Beta-Adrenergic Receptors Located, Respectively, in
COMPOSITION. A film coated tablet contains. Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan
 Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal. Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S.
 1156 Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S. Alpert The purpose of this study was to examine Na + handling and regulation
1156 Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S. Alpert The purpose of this study was to examine Na + handling and regulation
THE EFFECT OF INTRA(CEREBRO)VENTRICULAR RESERPINE ON THE ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF THE HEART, ILEUM AND HYPOTHALAMUS OF THE DOG
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 355-360. THE EFFECT OF INTRA(CEREBRO)VENTRICULAR RESERPINE ON THE ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF THE HEART, ILEUM AND HYPOTHALAMUS OF THE DOG BY C. L. MALHOTRA AND K. PRASAD From
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 355-360. THE EFFECT OF INTRA(CEREBRO)VENTRICULAR RESERPINE ON THE ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF THE HEART, ILEUM AND HYPOTHALAMUS OF THE DOG BY C. L. MALHOTRA AND K. PRASAD From
Renal Damage. Captopri 1 Ena 1 apr i 1 Kinins
 CLIN. AND EXPER.THEORY AND PRACTICE, A9(2&3), 409413 (1987) PREVENTION OF RENAL DAMAGE AND DECREASE OF URINARY KININS EXCRETION BY CHRONIC TREA"TS WITH ENALAPRIL AND CAPTOPRIL IN STROKEPRONE SPONTANEOUSLY
CLIN. AND EXPER.THEORY AND PRACTICE, A9(2&3), 409413 (1987) PREVENTION OF RENAL DAMAGE AND DECREASE OF URINARY KININS EXCRETION BY CHRONIC TREA"TS WITH ENALAPRIL AND CAPTOPRIL IN STROKEPRONE SPONTANEOUSLY
Disclosure of Relationships
 Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the rule
 Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College of Medicine and NF/SGVHS The 20-50
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College of Medicine and NF/SGVHS The 20-50
Enhanced Norepinephrine Release in Hypothalamus from Locus Coeruleus in SHR
 Enhanced Norepinephrine Release in Hypothalamus from Locus Coeruleus in SHR Shingo KAWASAKI, M.D., Kazuo TAKEDA, M.D., Motoo TANAKA, M.D., Hiroshi ITOH, M.D., Masahiro HIRATA, M.D., Tetsuo NAKATA, M.D.,
Enhanced Norepinephrine Release in Hypothalamus from Locus Coeruleus in SHR Shingo KAWASAKI, M.D., Kazuo TAKEDA, M.D., Motoo TANAKA, M.D., Hiroshi ITOH, M.D., Masahiro HIRATA, M.D., Tetsuo NAKATA, M.D.,
InteractionofInflammatoryResponseandSympatheticNervousSystemintheCentralRegulationofChronicHeartFailureinRats
 : I Surgeries and Cardiovascular System Volume 16 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
: I Surgeries and Cardiovascular System Volume 16 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 17-12-2018 A. Baroreceptor reflexes Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the walls of several large systemic arteries( specially
Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 17-12-2018 A. Baroreceptor reflexes Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the walls of several large systemic arteries( specially
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Candesartan Antihypertensive Survival Evaluation in Japan (CASE-J) Trial of Cardiovascular Events in High-Risk Hypertensive Patients
 1/5 This site became the new ClinicalTrials.gov on June 19th. Learn more. We will be updating this site in phases. This allows us to move faster and to deliver better services. Show less IMPORTANT: Listing
1/5 This site became the new ClinicalTrials.gov on June 19th. Learn more. We will be updating this site in phases. This allows us to move faster and to deliver better services. Show less IMPORTANT: Listing
Dissociation of Circulating Renin and Erythropoietin in Rats
 Dissociation of Circulating Renin and Erythropoietin in Rats By R. M. Donati, M.D., J. J. Bourgoignie, M.D., C. Kuhn, M.D., N. I. Gallagher, M.D., and H. M. Perry, Jr., M.D. Wiih ihe Assistance of Linda
Dissociation of Circulating Renin and Erythropoietin in Rats By R. M. Donati, M.D., J. J. Bourgoignie, M.D., C. Kuhn, M.D., N. I. Gallagher, M.D., and H. M. Perry, Jr., M.D. Wiih ihe Assistance of Linda
Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension Hypertension (or high blood pressure)
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension Hypertension (or high blood pressure)
Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido Boerrigter, Horng C Chen, Fernando L Martin, and John C Burnett Jr
 Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Histology and Histopathology
 Histol Histopathol (1999) 14: 45-49 http://www.ehu.es/histol-hlstopathol Histology and Histopathology Effect of hypertension and captopril treatment on the vasopressin in the rat median eminence and posterior
Histol Histopathol (1999) 14: 45-49 http://www.ehu.es/histol-hlstopathol Histology and Histopathology Effect of hypertension and captopril treatment on the vasopressin in the rat median eminence and posterior
Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic
![Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic](/thumbs/90/103241154.jpg) Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Effects of the Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist TCV-116 on Systemic and Renal Hemodynamics in Dogs with Renal Hypertension
 69 Effects of the Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist TCV-116 on Systemic and Renal Hemodynamics in Dogs with Renal Hypertension Katsuhiko Ito, Mie Shiomi, and Go Kito The effects of TCV-116,
69 Effects of the Non-Peptide Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist TCV-116 on Systemic and Renal Hemodynamics in Dogs with Renal Hypertension Katsuhiko Ito, Mie Shiomi, and Go Kito The effects of TCV-116,
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Byvalson. (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow
 Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate
 Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES
 HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT: LEPTIN IMPAIRS CARDIOVAGAL BAROREFLEX FUNCTION AT THE LEVEL OF THE SOLITARY TRACT NUCLEUS
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT: LEPTIN IMPAIRS CARDIOVAGAL BAROREFLEX FUNCTION AT THE LEVEL OF THE SOLITARY TRACT NUCLEUS Amy C. Arnold, Hossam A. Shaltout, Patricia E. Gallagher, Debra I. Diz The Hypertension & Vascular
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT: LEPTIN IMPAIRS CARDIOVAGAL BAROREFLEX FUNCTION AT THE LEVEL OF THE SOLITARY TRACT NUCLEUS Amy C. Arnold, Hossam A. Shaltout, Patricia E. Gallagher, Debra I. Diz The Hypertension & Vascular
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
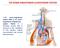 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Role of endothelin receptors in the hypertensive state of kinin B 2 knockout mice subjected to a high-salt diet
 380S Clinical Science (2002) 103 (Suppl. 48), 380S 384S (Printed in Great Britain) Role of endothelin receptors in the hypertensive state of kinin B 2 knockout mice subjected to a high-salt diet Isabelle
380S Clinical Science (2002) 103 (Suppl. 48), 380S 384S (Printed in Great Britain) Role of endothelin receptors in the hypertensive state of kinin B 2 knockout mice subjected to a high-salt diet Isabelle
A hypertensive father, but not hypertensive mother, determines blood pressure in normotensive male offspring through body mass index
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1998) 12, 441 445 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE A hypertensive father, but not hypertensive
Journal of Human Hypertension (1998) 12, 441 445 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE A hypertensive father, but not hypertensive
original contributions
 original contributions nature publishing group See reviewer commentary page 77 Upregulation of AT 1 R and inos in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla (RVLM) Is Essential for the Sympathetic Hyperactivity
original contributions nature publishing group See reviewer commentary page 77 Upregulation of AT 1 R and inos in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla (RVLM) Is Essential for the Sympathetic Hyperactivity
Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa
 Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa (project no. 04-12B) Authors Guus Akkermans, Martien Kas Preliminary data report Introduction In
Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa (project no. 04-12B) Authors Guus Akkermans, Martien Kas Preliminary data report Introduction In
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the rule
 Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
CATHETER-BASED RENAL DENERVATION INCREASES INSULIN SENSITIVITY AND IMPROVES GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN PATIENTS WITH RESISTANT HYPERTENSION
 CATHETER-BASED RENAL DENERVATION INCREASES INSULIN SENSITIVITY AND IMPROVES GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN PATIENTS WITH RESISTANT HYPERTENSION F. Mahfoud, Ch. Ukena, B. Cremers, I. Kindermann, M. Kindermann, P.
CATHETER-BASED RENAL DENERVATION INCREASES INSULIN SENSITIVITY AND IMPROVES GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN PATIENTS WITH RESISTANT HYPERTENSION F. Mahfoud, Ch. Ukena, B. Cremers, I. Kindermann, M. Kindermann, P.
Data Alert #2... Bi o l o g y Work i n g Gro u p. Subject: HOPE: New validation for the importance of tissue ACE inhibition
 Vascular Bi o l o g y Work i n g Gro u p c/o Medical Education Consultants, In c. 25 Sy l van Road South, We s t p o rt, CT 06880 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiovascular
Vascular Bi o l o g y Work i n g Gro u p c/o Medical Education Consultants, In c. 25 Sy l van Road South, We s t p o rt, CT 06880 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiovascular
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
Potassium Feeding Reduces Hyperactive Central Nervous System Pressor Responses in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats AND JUNICHI IWAI, M.D.
 Potassium Feeding Reduces Hyperactive Central Nervous System Pressor Responses in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats ATSUO GOTO, M.D., Louis TOBIAN, M.D., AND JUNICHI IWAI, M.D. SUMMARY Dahl showed that feeding
Potassium Feeding Reduces Hyperactive Central Nervous System Pressor Responses in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats ATSUO GOTO, M.D., Louis TOBIAN, M.D., AND JUNICHI IWAI, M.D. SUMMARY Dahl showed that feeding
Dr Doris M. W Kinuthia
 Dr Doris M. W Kinuthia Objectives Normal blood pressures in children Measurement of blood pressure in children Aetiology of Hypertension in children Evaluation of children with hypertension Treatment of
Dr Doris M. W Kinuthia Objectives Normal blood pressures in children Measurement of blood pressure in children Aetiology of Hypertension in children Evaluation of children with hypertension Treatment of
Baroreflex sensitivity and the blood pressure response to -blockade
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 185 190 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Baroreflex sensitivity and the blood pressure
Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 185 190 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Baroreflex sensitivity and the blood pressure
Recently, Mullins et al
 687 Increased Vascular Angiotensin Formation in Female Rats Harboring the Mouse Ren-2 Gene Karl F. Hilgers, Jorg Peters, Roland Veelken, Martin Sommer, Gerhard Rupprecht, Detlev Ganten, Friedrich C. Luft,
687 Increased Vascular Angiotensin Formation in Female Rats Harboring the Mouse Ren-2 Gene Karl F. Hilgers, Jorg Peters, Roland Veelken, Martin Sommer, Gerhard Rupprecht, Detlev Ganten, Friedrich C. Luft,
Plasma sodium and hypertension
 Kidney International, Vol. 66 (2004), pp. 2454 2466 COMMENTARY Plasma sodium and hypertension HUGH E. DE WARDENER,FENG J. HE, and GRAHAM A. MACGREGOR Department of Clinical Chemistry, Imperial College,
Kidney International, Vol. 66 (2004), pp. 2454 2466 COMMENTARY Plasma sodium and hypertension HUGH E. DE WARDENER,FENG J. HE, and GRAHAM A. MACGREGOR Department of Clinical Chemistry, Imperial College,
In unilateral renovascular hypertension (RVH), prostaglandin
 Scientific Contributions Prostaglandin I 2 /E 2 Ratios in Unilateral Renovascular Hypertension of Different Severities Masahito Imanishi, Tetsu Tsuji, Satoko Nakamura, Makoto Takamiya Abstract Differences
Scientific Contributions Prostaglandin I 2 /E 2 Ratios in Unilateral Renovascular Hypertension of Different Severities Masahito Imanishi, Tetsu Tsuji, Satoko Nakamura, Makoto Takamiya Abstract Differences
Peptides 30 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Peptides. journal homepage:
 Peptides 30 (2009) 1921 1927 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Peptides journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/peptides Angiotensin-(1-7) antagonist, A-779, microinjection into the caudal ventrolateral
Peptides 30 (2009) 1921 1927 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Peptides journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/peptides Angiotensin-(1-7) antagonist, A-779, microinjection into the caudal ventrolateral
Exam KEY. NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 23, 2015 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 23, 2015 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) Arterial and venous blood samples are taken, and other physiological measures are obtained, from a
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 23, 2015 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) Arterial and venous blood samples are taken, and other physiological measures are obtained, from a
BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles (n = 5). (C) Plasma norepinephrine
 Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
Kanazawa, et al. Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 DS rats had congestive heart failure. (A) DR and DS rat hearts. (B) QRT-PCR analysis of BNP mrna expression in DR and DS rat left ventricles
Management of Hypertension. M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine
 Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Jun FUJII, M.D., Akira SEKI, M.D.,* and Toshiyuki TANAKA, M.D.*
 Peri-Ureteric Collateral Vessels in Rabbits with Experimental Renal Hypertension Jun FUJII, M.D., Akira SEKI, M.D.,* and Toshiyuki TANAKA, M.D.* SUMMARY The development of collaterals to an ischemic kidney
Peri-Ureteric Collateral Vessels in Rabbits with Experimental Renal Hypertension Jun FUJII, M.D., Akira SEKI, M.D.,* and Toshiyuki TANAKA, M.D.* SUMMARY The development of collaterals to an ischemic kidney
Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome
 RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
Subjects. Thirty-five adult male Lister Hooded rats (Charles River, Kent, UK),
 Supplemental Material: Subjects. Thirty-five adult male Lister Hooded rats (Charles River, Kent, UK), weighing between 280 300 g at the beginning of the experiment, were housed singly in holding rooms
Supplemental Material: Subjects. Thirty-five adult male Lister Hooded rats (Charles River, Kent, UK), weighing between 280 300 g at the beginning of the experiment, were housed singly in holding rooms
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Suppression of Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System during Dental Surgery in Hypertensive Patients
 207 Original Article Suppression of Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System during Dental Surgery in Hypertensive Patients Keiko MIURA, Kiyoshi MATSUMURA*, Yoshito NAKAMURA*, Minoru KAJIYAMA, and Yutaka TAKATA*
207 Original Article Suppression of Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System during Dental Surgery in Hypertensive Patients Keiko MIURA, Kiyoshi MATSUMURA*, Yoshito NAKAMURA*, Minoru KAJIYAMA, and Yutaka TAKATA*
2. Langendorff Heart
 2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8. Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital
 Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Losartan Reduces Central and Peripheral Sympathetic Nerve Activity in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Hypertension
 Losartan Reduces Central and Peripheral Sympathetic Nerve Activity in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Hypertension Shaohua Ye, Huiquin Zhong, Vu Ngoc Duong, Vito M. Campese Abstract We have developed a new model
Losartan Reduces Central and Peripheral Sympathetic Nerve Activity in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Hypertension Shaohua Ye, Huiquin Zhong, Vu Ngoc Duong, Vito M. Campese Abstract We have developed a new model
Renal Artery Denervation New Concepts in Hypertension Treatment
 Renal Artery Denervation New Concepts in Hypertension Treatment Istanbul Course of Interventional Cardiology J. Weil Medizinische Klinik II Kardiologie, Angiologie und internistische Intensivmedizin Universitätsklinikum,
Renal Artery Denervation New Concepts in Hypertension Treatment Istanbul Course of Interventional Cardiology J. Weil Medizinische Klinik II Kardiologie, Angiologie und internistische Intensivmedizin Universitätsklinikum,
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates angiotensin signaling in the hypothalamus to increase blood pressure in rats
 Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 38: H612 H622, 215. First published January 9, 215; doi:1.1152/ajpheart.776.214. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates angiotensin signaling in the hypothalamus to
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 38: H612 H622, 215. First published January 9, 215; doi:1.1152/ajpheart.776.214. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates angiotensin signaling in the hypothalamus to
HISTAMINE INHIBITS EATING WITHOUT ALTERING POSTPRANDIAL SATIETY IN RATS KELLY TSCHANTZ
 HISTAMINE INHIBITS EATING WITHOUT ALTERING POSTPRANDIAL SATIETY IN RATS KELLY TSCHANTZ Abstract Exogenous histamine decreases food intake and injection of H-1 antagonists increases food intake in rats.
HISTAMINE INHIBITS EATING WITHOUT ALTERING POSTPRANDIAL SATIETY IN RATS KELLY TSCHANTZ Abstract Exogenous histamine decreases food intake and injection of H-1 antagonists increases food intake in rats.
