ENDOCRINE DRUGS. Endocrine disorders are classified as either an over functioning or under functioning of the endocrine glands.
|
|
|
- Herbert Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENDOCRINE DRUGS Endocrine disorders are classified as either an over functioning or under functioning of the endocrine glands. Drugs that treat endocrine disorders include: a. Natural hormones and their Synthetic Analogues b. Hormone-like substances c. Drugs that stimulate or suppress hormone secretion Drugs affecting endocrine function do not cure the disease but promotes only supportive care to the client. Lifelong therapy is often indicated. ANTI DIABETIC DRUGS AND GLUCAGON ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS AND GLUCAGON Diabetes Mellitus is a condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. This may be due to either Insulin deficiency or Insulin Resistance. HOW INSULIN WORKS: Glucose cannot enter the cell without the aid of insulin Insulin binds to the receptors on the surface of the cells. This activates the glucose transport channels in the cells Glucose then is able to move from outside the cell to inside the cell through the Glucose Transport Channels Two types: 1. Type 1: Insulin dependent (body unable to produce enough insulin needed by the body) 2. Type 2: Non-Insulin Dependent (body has sufficient amount of circulating levels of insulin, but this insulin is not utilized because cells are resistant to Insulin) These are drugs that affect Serum Glucose level: a. HYPOGLYCEMIC DRUGS: lowers blood glucose levels (eg., Insulin) b. HYPERGLYCEMIC DRUGS: raises blood glucose levels (e.g., Glucagon) Hyperglycemia vs Hypoglycemia Cold and Clammy needs some Candy and Hot and Dry Sugar is High Hypoglycemia: Restlessness, Yawning, Weakness, Tremors, Pallor, Diaphoresis, Cold and Clammy Skin, Dizziness, Faintness, Slurred Speech Hyperglycemia: Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia, Warm and Flushed Dry Skin, Soft eyeballs, Kussmaul s breathing, Fruity odor of Breath INSULIN -Usually given to DM Type 1 patients but may at times be given to patients with Type 2 Diabetes -not given orally because it is broken down by gastric juices before it is absorbed in the blood stream -usual route :SUBCUTANEOUS Regular Insulin can be given INTRAVENOUSLY
2 Different Types: a. Rapid Acting: Lispro b. Short Acting: Regular Insulin c. Intermediate Acting: NPH d. Long Acting: Ultra Lente CLASSIFICATION RAPID ACTING EXAMPLES Insulin Lispro (Humalog) Insulin Aspart (Novolog) Insulin Glulisin (Avidra) Indications: a. Type 1 DM b. Type 2 DM when: Other means of controlling DM is ineffective Blood Glucose levels are elevated during periods of emotional and physical stress When Oral Antidiabetics are contraindicated or Hypersensitivity reaction occurs SHORT ACTING Onset: 15 mins or less Duration: 5 to 7 hours Regular Humalin R Novolin R Semilente Semilente Purified Pork Insulin c. Diabetic Ketoacidosis d. Hyperosmolar Non-Ketotic Acidosis e. Severe Hyperkalemia (Potassium moves together with Insulin towards the cells) What You Must Know About the Different Types of Insulin: INTERMEDIATE ACTING LONG ACTING CONSTANT ACTING Onset: mins Duration: 12-16hours Humalin N Novolin N Humalin L Lente Purified Pork Novolin L Onset 1-2 hours Duration: hours Humalin U Ultralente Onset 4-8hours Duration: 36 hours Lantus R Insulin Glargine (do not mix with other insulin) Onset: 4-8 hours Duration: 24hours Mechanism of Action: Mimics the effect of naturally occurring insulin in the body Deceleration of the breakdown of glycogen, proteins and fats and promotes storage of excess glucose as Glycogen Do not give INTERMEDIATE or LONG- ACTING Insulin in cases of coma and other emergency cases that need rapid drug actions. Insulin resistance may occur. In clients with Insulin resistance, you may use REGULAR INSULIN in large doses (500 U) to control symptoms of diabetes. DO NOT SHAKE VIAL when preparing the insulin. This causes the formation of bubbles and creates air in the syringe. Simply SWIRL THE VIAL in your palms. HUMALOG should be given 15 minutes before meals because it is rapid acting. LENTE, ULTRALENTE, and SEMILENTE may be mixed in any proportion. When mixing NPH or Lente with Regular Insulin in the same syringe, give the IMMEDIATELY to avoid loss of potency. REGULAR INSULIN may be given IV or may be incorporated with PNSS. Ensure drop rate as ordered. In mixing 2 insulins, follow the General rule: CLEAR before CLOUDY Clear: Rapid and Short Acting Cloudy: Intermediate and Long Acting
3 Drug Interactions: Some drugs interact with the capability of Insulin in promoting glucose uptake on cells while other drugs directly increase the blood glucose levels in the body: a. INCREASE HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF INSULIN: Salicylates, Alcohol and Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors b. REDUCE HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF INSULIN: Thiazide diuretics, Sympathomimetics and Corticosteroids c. Beta Adrenergic Blockers prolong the hypoglycemic effect of insulin Adverse Reactions: a. Hypoglycemia b. Somogyi effect (hypoglycemia followed by rebound hyperglycemia) c. Hypersensitivity reactions d. Lipodystrophy e. Insulin resistance a. Assess patient s blood glucose level before therapy and regularly thereafteespecially during times of stress. b. Monitor patient s uring ketone levels when glucose level is elevated. c. Monitor injection sites for lipodystrophy. d. Assess patient s and family s knowledge regarding insulin therapy. e. Do not give insulin that have granulated and have changed color. f. Check expiration of vial prior to giving insulin. g. Rotate site of injection and avoid rubbing injection site. h. Teach client to follow prescribed dietary modifications, weight reduction techniques and personal hygiene procedures. i. Review timing of injections. j. Have carbohydrates or candy ready on hand when hypoglycemia occurs. ORAL ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS Prototype Drugs: First Generation Sulfonylureas Acetohexamide Chlorpropamide Tolazamide Tolbutamide Second Generation Sulfonylureas Glimepiride Glipizide Glyburide Thiazolidinedione Drugs Pioglitazone Rosiglitazone -indicated for Type II diabetes -absorbed well in the GIT and distributed throughout the bloodstream, metabolized in the liver and excreted via the urine -has extrapancreatic function Mechanism of Action Probably stimulate pancreatic beta cells to release insulin in a patient with a minimally functioning pancreas Prevents gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis on the liver Increase receptor sites for insuling in the peripheral tissues Indications Type II diabetes if diet and exercise cannot control blood glucose levels Adverse Reactions Sulfonylureas: nausea, epigastric fullness, blood abnormalities, water retention, rash, hyponatremia, photosensitivity
4 Metformin: metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort Nursing Interventions: Assess blood glucose of patient regularly Patients transferring from insulin therapy to oral antidiabetic medications may need to have blood glucose checking TID Know when to give oral antidiabetics: SULFONYLUREAS: 30 mins.before morning meal (once dose), or 30 minutes before morning and evening meals (double-dose) METFORMIN: give together with morning and evening meals ALPHA-GLUCOSIDASE: given together with first bite of each main meal TID Inform client that therapy treats symptoms but not the disease itself Know s/sx of hyper and hypoglycemia Treat hypoglycemic episodes with a fast acting carbohydrate GLUCAGON -A hyperglycemic drug that raises blood glucose levels. A hormone produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas -glucagon causes GLYCOGENOLYSIS, a process where stored glycogen on the liver are metabolized to produce glucose, thus increasing serum glucose levels. Mechanism of Action: Glycogenolysis Gluconeogenesis by mobilizing free fatty acids from fats causing lipolysis Severe hypoglycemia Nursing Interventions: Assess patient s blood glucose regularly In giving glucagon IV, use a dextrose solution together with a medication hence precipitate forms when used together with chloride solutions. Arouse lethargic patients immediately and offer fast acting carbohydrates If patient does not respond to glucaon, IV dextrose 50% may be given The pituitary gland is divided into: a. Anterior Pituitary Gland: responsible for growth &development & functioning of other endocrine glands b. Posterior Pituitary Gland: responsible for the production of hormones oxytocin and ADH ANTERIOR PITUITARY MEDICATIONS Prototype Medications: Somatotropin (Humatrope) Somatrem (Protropin) Corticotropin (ACTH) Cosyntropin (Cortrosyn) SOMATROPIN AND SOMATREM -growth hormone-like drugs Mechanism of Action -facilitates transport of Amino acids across cell membrane thus, encouraging the growth of the epiphyseal plates of long bones Indications: Dwarfism PITUITARY MEDICATIONS Drug Interactions: Oral anticoagulants: inc d risk for bleeding Should not be given to immunocompromised clients (AIDS, TB) Do not give to clients with Peptic Ulcer Disease, may cause further bleeding
5 Do not give to clients with systemic fungal infections Give with precaution to hypertensive clients (release of aldosterone causes Na retention) Note: In large amounts it may cause increased peristaltic movement, oxytocic effects and vasoconstriction leading to increased BP Drug Interactions: Note: Estrogen and oral contraceptives block the effect of cotricotropin Salicylates may increase risk of bleeding on GI if given together with corticotrophin Has the capacity to increase thyroid activity. WOF signs of hyperthyroidism WOF hypernatremia and possible HPN Hypersensitivity to pork and pork products, hence medication is a pork derivative Nursing responsibilities: Check electrolyte levels; WOF signs of hypernatremia Instruct patient of possibility of immunosuppression (e.g., sore throat, fever) Decrease sodium on diet. Avoid immunization using live vaccines POSTERIOR PITUITARY MEDICATIONS Prototype Medications: Desmopressin acetate Lypressin Vasopressin Mechanism of Action Increases water reabsorption on the distal convoluted tubules, thus decreasing urine formation Mimics the effects f ADH on the body DI Epistaxis (nasal aerosols of vasopressin) Hypersensitivity to pork and pork products Adverse Reactions Diarrhea Nausea and Vomiting HPN Uterine Cramping Nursing Responsibilities Avoid giving oral forms of vasopressin hence proteolyti enzymes of the stomach can digest medication WOF signs of fluid volume overload (e.g., increased weight gain, edema formation, crackles on lungs upon auscultation) Monitor hepatic and renal condition In giving nasal desmopressin, load medication using a straw with your mouth, flex the other tip of the straw to your nose and gently blow to spray medication on nose. No more than 3 blows at a time. ADRENAL MEDICATIONS Adrenal gland is an organ located superiorly at each kidneys. Divided into: a. Adrenal Cortex: releases glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens b. Adrenal Medulla: releases norepinephrine and epinephrine
6 GLUCOCORTICOIDS Mechanism of Action: Increase breakdown of proteins to amino acids, oxidize and mobilize fatty acids Increase gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis Decrease inflammatory response in the body by inhibiting the release of histamines, prostaglandis and leukotrienes Chronic inflammatory conditions Rheumatoid arthritis Systemic lupus Erythematosus Asthma Organ transplantation Urticaria Other inflammatory conditions Systemic fungal infections Immunosuppression Use cautiously on: DM and PUD caused by H. pylori Adverse Effects: Muscle wasting and weakness Impaired wound healing HPN Menstrual irregularities Cushing syndrome GI bleeding-pud Administer the lowest possible dose for glucocorticoids at a shortest possible time Mimic the normal body surge of hormones when giving glucocorticoids: Give 2/3 on AM and 1/3 on PM Monitor serum glucose levels frequently Instruct client to take drug with food Teach patient to withdraw medication slowly and not abruptly. May cause withdrawal symptoms of exhaustion, fever and diffuse muscle pain MINERALOCORTICOID Prototype drug Fludrocortizone- drug of choice Desoxycorticosterone Mechanism of action: Promote reabsorption of sodium and secondarily water on the distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys. Note: Usually given together with glucocorticoids to mimic the normal surge of hormones on the body Cortisone and Hydrocortisone use is more preferred since they have both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid properties. Immunosuppression: Systemic Fungal Infection Adverse Reactions: Hypokalemia HPN Monitor for excessive water retention: presence of excessive weight gain, edema and audible crackles Monitor for HPN Monitor electrolyte levels for hypernatremia and hypokalemia ADRENAL HORMONE INHIBITING MEDICATIONS Prototype Drugs: Aminogluthemide (Cytadron) Mitotane (Lysodren) Metyrapone (Metoprione)
7 Mechanism of Action: Inhibits the ability of the adrenal gland to secrete its G-M-A hormones Used as a temporary treatment in cases where the adrenal glands overly secretes G-M-A hormones. A permanent solution (e.g., surgery) is preferred Monitor for signs of Addison-like disorder Monitor for feelings of weakness Monitor for Hyponatremia and Hyperkalemia Sexual Disturbances may occur during therapy THYROID MEDICATIONS Thyroid gland is a gland located anteriorly to the trachea responsible for releasing hormone T3 (triidothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). These hormones are responsible for regulating body metabolic processes. THYROID HORMONE REPLACEMENT DRUGS Prototype Drugs: Levothyroxine (Synthroid) Liothyronine (Cytomel) Liotrix (Thyrolar) Mechanism of Action: Mimics the effects of naturally occurring T3 and T4 hormones in the body: a. Controls the rate of metabolism of the body b. Increase fat and carbohydrate metabolism Replacement therapy for hypothyroidism Treatment for Myxedema Coma and Thyroid cancer Contraindicated: Hypersensitivity to pork and pork derivatives Avoid using during MI and on hypoadrenal attacks Adverse Effects: Development of cardiac dysrhythmia Anxiety Sleeplessness Nursing Responsibilities Give medication 30 minutes before breakfast on empty stomach Monitor for hyperthyroidism-like effects Monitor periodic thyroid function tests Advise patient that T3 and T4 hormonal therapy could be life long ANTITHYROID MEDICATIONS Prototype Medications: Propylthiouracil (PTU) Methimazole Strong Iodine Solution Potassium Iodine Solution Mechanism of Action Increase the production or release of thyroid hormones Inhibit the production or secretion of thyroid hormones Indication Hyperthyroid state Note: Euthyroid state must last for 6-12 months before medication can be withdrawn Contraindicated during pregnancy Iodine solution hypersensitivity Drug Interactions Lithium causes increased hypothyroidism effect Potassium containing antithyroid medication can cause hyperkalemia if
8 given with other potassium carrying medications Adverse Effects HYPOTHYROID-LIKE EFFECTS: Lethargy, bradycardia, diarrhea, abdominal discomforts Monitor signs for Iodism Instruct clients that iodine solutions may cause staining of teeth. Drink medications using a straw. Monitor for serum potassium level for those clients taking potassium carrying antithyroid drugs. WOF cardiac dysrhythmias. Avoid abrupt withdrawal of medication. Achieve euthyroid state for 3 to 6 months to withdrawal.
Diabetes Mellitus. Raja Nursing Instructor. Acknowledgement: Badil 09/03/2016
 Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Chapter 43. Endocrine System. Negative Feedback. Hypothalamus and Pituitary Glands
 Chapter 43 Drugs for Pituitary, Thyroid, and Adrenal Disorders Endocrine System Consists of glands that secrete hormones Maintains homeostasis using hormones as chemical messengers Secreted in response
Chapter 43 Drugs for Pituitary, Thyroid, and Adrenal Disorders Endocrine System Consists of glands that secrete hormones Maintains homeostasis using hormones as chemical messengers Secreted in response
CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013
 A & P Review CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013 Endocrine Anterior pituitary Growth hormone: long bone growth Thyroid stimulating hormone: growth, thyroid secretion Adrenocorticotropic hormone: growth,
A & P Review CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013 Endocrine Anterior pituitary Growth hormone: long bone growth Thyroid stimulating hormone: growth, thyroid secretion Adrenocorticotropic hormone: growth,
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
I. General Considerations
 1 2 3 I. General Considerations A. Type I ( Juvenile Onset or IDDM) IDDM results from autoimmune destruction of beta cells inability to secrete insulin --> ketone formation --> DKA 4 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
1 2 3 I. General Considerations A. Type I ( Juvenile Onset or IDDM) IDDM results from autoimmune destruction of beta cells inability to secrete insulin --> ketone formation --> DKA 4 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7
 Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7 1. A long- acting insulin, like Lantus is for? A. When the next meal is within 30-60 minutes of the injection B. Over night use or for ½ of the day often combined
Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7 1. A long- acting insulin, like Lantus is for? A. When the next meal is within 30-60 minutes of the injection B. Over night use or for ½ of the day often combined
CEBU NORMAL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING
 CEBU NORMAL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING Unit XI Overview By: Domino Butron Puson This chapter discusses the different hormones and steroids used in medical therapy. Unlike many other categories of medications,
CEBU NORMAL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING Unit XI Overview By: Domino Butron Puson This chapter discusses the different hormones and steroids used in medical therapy. Unlike many other categories of medications,
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar
 9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
Care of patients with endocrine system disorders
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department Application of Adult Health Nursing Skills ( NUR 317 ) Care of patients with endocrine system disorders Prepared by Mrs: Alwah M. Alkathiri
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department Application of Adult Health Nursing Skills ( NUR 317 ) Care of patients with endocrine system disorders Prepared by Mrs: Alwah M. Alkathiri
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Chapter 50 4/9/2015. Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d
 Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary
Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts:
 Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
INSULIN OVERVIEW. Type Brand Name Onset Peak Duration Role in glucose management Page Rapid-Acting lispro min. 3-5 hrs min.
 INSULIN OVERVIEW Type Brand Name Onset Peak Duration Role in glucose management Page Rapid-Acting lispro Humalog 15-30 min 30-90 min 3-5 hrs aspart glulisine Short-Acting Regular insulin NovoLog Apidra
INSULIN OVERVIEW Type Brand Name Onset Peak Duration Role in glucose management Page Rapid-Acting lispro Humalog 15-30 min 30-90 min 3-5 hrs aspart glulisine Short-Acting Regular insulin NovoLog Apidra
Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery
 Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Girish P. Joshi, MB BS, MD, FFARCSI Anesthesia & Analgesia
Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Girish P. Joshi, MB BS, MD, FFARCSI Anesthesia & Analgesia
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM. Objectives A & P 8/11/2011
 PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
Blood Glucose Monitoring
 Blood Glucose Monitoring What is Glucose? A simple sugar that enters the diet as part of sucrose, lactose, or maltose Part of a polysaccharide called dietary starch Most of the body s energy comes from
Blood Glucose Monitoring What is Glucose? A simple sugar that enters the diet as part of sucrose, lactose, or maltose Part of a polysaccharide called dietary starch Most of the body s energy comes from
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
To provide nursing staff with guidelines for the safe and appropriate administration of insulin.
 SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
Monitor patient s ability to self-administer insulin. (To evaluate safe administration of drug.)
 Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Adrenal gland And Pancreas
 Adrenal gland And Pancreas Structure Cortex Glucocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Mineralocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Sex steroids Medulla Catecholamines Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal
Adrenal gland And Pancreas Structure Cortex Glucocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Mineralocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Sex steroids Medulla Catecholamines Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Diabetes Oral Agents Pharmacology. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre-Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 Diabetes Oral Agents Pharmacology University of Hawai i Hilo Pre-Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 Learning Objectives Understand the role of the utilization of free
Diabetes Oral Agents Pharmacology University of Hawai i Hilo Pre-Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 Learning Objectives Understand the role of the utilization of free
The Metabolic System. Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs. The Endocrine System
 Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 44, (pp 1154-1189) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult
Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 44, (pp 1154-1189) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult
The Endocrine System. Lipid-Soluble Hormones. Bio217 Sp14 Unit 5. Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27
 Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
DIABETES. Mary Bruskewitz APNP, MS, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes. November 2013
 DIABETES Mary Bruskewitz APNP, MS, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes November 2013 mbruskewitz@outlook.com Objectives Part 1 Overview of Endocrine Physiology Pathophysiology of Diabetes Diabetes
DIABETES Mary Bruskewitz APNP, MS, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes November 2013 mbruskewitz@outlook.com Objectives Part 1 Overview of Endocrine Physiology Pathophysiology of Diabetes Diabetes
Hypoglycemia in congenital hyperinsulinism
 How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Corticosteroids. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital,
 Corticosteroids Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, http://aagha.kau.edu.sa History 1855 Addison's disease 1856 Adrenal glands essential
Corticosteroids Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, http://aagha.kau.edu.sa History 1855 Addison's disease 1856 Adrenal glands essential
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com
 1 Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com 2 Disclaimer Medicine and nursing are continuously changing practices. The author and publisher have reviewed all information in this book with resources believed
1 Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com 2 Disclaimer Medicine and nursing are continuously changing practices. The author and publisher have reviewed all information in this book with resources believed
THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS
 THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS They are two glands, present above the kidneys. One adrenal gland is sufficient for human beings/mammals (example: we also have two kidneys but one is sufficient). The Adrenal
THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS They are two glands, present above the kidneys. One adrenal gland is sufficient for human beings/mammals (example: we also have two kidneys but one is sufficient). The Adrenal
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
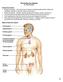 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Metformin Hydrochloride
 Metformin Hydrochloride 500 mg, 850 mg, 500 mg LA and 750 mg LA Tablet Description Informet is a preparation of metformin hydrochloride that belongs to a biguanide class of oral antidiabetic drugs. Metformin
Metformin Hydrochloride 500 mg, 850 mg, 500 mg LA and 750 mg LA Tablet Description Informet is a preparation of metformin hydrochloride that belongs to a biguanide class of oral antidiabetic drugs. Metformin
Corticosteroids. Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Biophysics Dr.Susan Abdulkadir Farhadi MSc Pharmacology
 Corticosteroids Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Biophysics Dr.Susan Abdulkadir Farhadi MSc Pharmacology Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be
Corticosteroids Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Biophysics Dr.Susan Abdulkadir Farhadi MSc Pharmacology Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Slide #2 : - Local hormones : so they're released locally and work as hormones ; used to maintain homeostasis.
 Firstly, the doctor wasn't very clear about the deleted slides ; when we find out exactly we will upload them on the group, so don't worry. ** Set of slides #1 :- Slide #2 : - Local hormones : so they're
Firstly, the doctor wasn't very clear about the deleted slides ; when we find out exactly we will upload them on the group, so don't worry. ** Set of slides #1 :- Slide #2 : - Local hormones : so they're
Combining Complex Pathophysiologic Concepts: Diabetes Mellitus
 Chapter 18 Combining Complex Pathophysiologic Concepts: Diabetes Mellitus KEY TERMS dawn phenomenon diabetes mellitus endocrine pancreas exocrine pancreas hyperglycemia hyperketonemia hypoglycemia insulin
Chapter 18 Combining Complex Pathophysiologic Concepts: Diabetes Mellitus KEY TERMS dawn phenomenon diabetes mellitus endocrine pancreas exocrine pancreas hyperglycemia hyperketonemia hypoglycemia insulin
Hypoglycemia. When recognized early, hypoglycemia can be treated successfully.
 Hypoglycemia Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized early, hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized early, hypoglycemia
Adrenal Hormone Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone
 Adrenal gland Adrenal Hormone Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone Cortex 80 % Glucocorticoids Cortisol Sex hormones Androgen Medulla 20% Catecholamines E, NE 1 2 Adrenal cortex hormones Glucocorticoid Mineralocorticoids
Adrenal gland Adrenal Hormone Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone Cortex 80 % Glucocorticoids Cortisol Sex hormones Androgen Medulla 20% Catecholamines E, NE 1 2 Adrenal cortex hormones Glucocorticoid Mineralocorticoids
Xultophy 100/3.6. (insulin degludec, liraglutide) New Product Slideshow
 Xultophy 100/3.6 (insulin degludec, liraglutide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Xultophy Generic name: Insulin degludec, liraglutide Pharmacological class: Human insulin analog + glucagon-like
Xultophy 100/3.6 (insulin degludec, liraglutide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Xultophy Generic name: Insulin degludec, liraglutide Pharmacological class: Human insulin analog + glucagon-like
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
The endocrine system is made up of a complex group of glands that secrete hormones.
 1 10. Endocrinology I MEDCHEM 535 Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry Endocrinology The endocrine system is made up of a complex group of glands that secrete hormones. These hormones control reproduction, metabolism,
1 10. Endocrinology I MEDCHEM 535 Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry Endocrinology The endocrine system is made up of a complex group of glands that secrete hormones. These hormones control reproduction, metabolism,
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Dextran 40 (Gentran 40)
 Assess for presence/history of hypovolemia, shock, venous thrombosis. Assess vital signs: Hypovolemic shock secondary to surgery, burns, hemorrhage, other serious condition PT and PTT abnormalities Venous
Assess for presence/history of hypovolemia, shock, venous thrombosis. Assess vital signs: Hypovolemic shock secondary to surgery, burns, hemorrhage, other serious condition PT and PTT abnormalities Venous
Adrenal Gland Disorders
 1 Adrenal Gland Disorders Adrenal cortex steroid hormones (corticosteroids) 1. Glucocorticoids Regulate metabolism and blood glucose Critical to physiologic stress response 2. Mineralocorticoids Regulate
1 Adrenal Gland Disorders Adrenal cortex steroid hormones (corticosteroids) 1. Glucocorticoids Regulate metabolism and blood glucose Critical to physiologic stress response 2. Mineralocorticoids Regulate
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Diabetic Emergencies. Chapter 15
 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter 15 Diabetes- is a disorder of glucose metabolism or difficulty metabolizing carbohydrates, fats and proteins Full name is diabetes mellitus which refers to the presence of
Diabetic Emergencies Chapter 15 Diabetes- is a disorder of glucose metabolism or difficulty metabolizing carbohydrates, fats and proteins Full name is diabetes mellitus which refers to the presence of
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 25. Diabetic Emergencies
 Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY
 HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY In contrast to the hormones of the anterior lobe of the pituitary, those of the posterior lobe, vasopressin and oxytocin, are not
HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES OF THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY In contrast to the hormones of the anterior lobe of the pituitary, those of the posterior lobe, vasopressin and oxytocin, are not
Chapter 24 Diabetes Mellitus
 Chapter 24 Diabetes Mellitus Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Acute Effects of Diabetes Mellitus Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: Early Stages Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus:
Chapter 24 Diabetes Mellitus Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Acute Effects of Diabetes Mellitus Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: Early Stages Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus:
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
REGULAR HUMAN INSULIN
 HUMULIN R Eli Lilly 10 ml Vial (1000 Units per vial) REGULAR INSULIN HUMAN INJECTION, USP (rdna ORIGIN) 100 UNITS PER ML (U-100) WARNINGS THIS LILLY HUMAN INSULIN PRODUCT DIFFERS FROM ANIMAL-SOURCE INSULINS
HUMULIN R Eli Lilly 10 ml Vial (1000 Units per vial) REGULAR INSULIN HUMAN INJECTION, USP (rdna ORIGIN) 100 UNITS PER ML (U-100) WARNINGS THIS LILLY HUMAN INSULIN PRODUCT DIFFERS FROM ANIMAL-SOURCE INSULINS
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Thyroid Gland. Chapter 18 Part 2. Thyroid gland. Thyroid Gland. Thyroid Gland. Parathyroid Gland. Adrenal Gland. Pancreas
 Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Oral and Injectable Medication Options for Diabetes Treatment
 Oral and Injectable Medication Options for Diabetes Treatment Presented by: Dr. Daphne E. Smith, Pharm.D., CDE Clinical Assistant Professor/Clinical Pharmacist-University of Illinois at Chicago College
Oral and Injectable Medication Options for Diabetes Treatment Presented by: Dr. Daphne E. Smith, Pharm.D., CDE Clinical Assistant Professor/Clinical Pharmacist-University of Illinois at Chicago College
Medically Compromised Patients (Part II)
 Medically Compromised Patients (Part II) Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI Endocrine Disorders I. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Definition (WHO): - Chronic disease due to absolute or relative lack of insulin
Medically Compromised Patients (Part II) Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI Endocrine Disorders I. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Definition (WHO): - Chronic disease due to absolute or relative lack of insulin
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Diabetes Review. October 31, Dr. Don Eby Tracy Gaunt Dwayne Cottel
 Diabetes Review October 31, 2012 Dr. Don Eby Tracy Gaunt Dwayne Cottel Diabetes Review Learning Objectives: Describe the anatomy and physiology of the pancreas Describe the effects of hormones on the maintenance
Diabetes Review October 31, 2012 Dr. Don Eby Tracy Gaunt Dwayne Cottel Diabetes Review Learning Objectives: Describe the anatomy and physiology of the pancreas Describe the effects of hormones on the maintenance
AACN PCCN Review. Endocrine
 AACN PCCN Review Endocrine Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com Endocrine I. INTRODUCTION Disorders
AACN PCCN Review Endocrine Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com Endocrine I. INTRODUCTION Disorders
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
PHARMACOLOGY. Dentalelle tutoring DENTALELLE TUTORING -
 PHARMACOLOGY Dentalelle tutoring 1 HORMONES Transported by the blood to target organs. Help maintain homeostasis by regulating body functions. 2 PITUITARY HORMONES 3 ANTERIOR The pituitary gland is located
PHARMACOLOGY Dentalelle tutoring 1 HORMONES Transported by the blood to target organs. Help maintain homeostasis by regulating body functions. 2 PITUITARY HORMONES 3 ANTERIOR The pituitary gland is located
Nursing Care of the Resident with Diabetes Mellitus
 Nursing Care of the Resident with Diabetes Mellitus Level III Definitions Diabetes is a disorder in which there is relative or absolute lack of insulin. Among other things, glucose (sugar) from food cannot
Nursing Care of the Resident with Diabetes Mellitus Level III Definitions Diabetes is a disorder in which there is relative or absolute lack of insulin. Among other things, glucose (sugar) from food cannot
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017
 CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM
 Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Thyroid, Antithyroid, and Parathyroid Preparations. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Thyroid, Antithyroid, and Parathyroid Preparations. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Thyroid, Antithyroid, and Parathyroid Preparations. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1.
DIPRIAN 80 mg Tablets
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER DIPRIAN 80 mg Tablets GLICLAZIDE This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet for a medicine, which outlines
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER DIPRIAN 80 mg Tablets GLICLAZIDE This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet for a medicine, which outlines
Type I Type II Insulin Resistance
 Insulin An aqueous hormonal solution made in the pancreas. Affects metabolism by allowing glucose to leave the blood and enter the body cells, preventing hyperglycemia. It is measured in units, e.g. 100
Insulin An aqueous hormonal solution made in the pancreas. Affects metabolism by allowing glucose to leave the blood and enter the body cells, preventing hyperglycemia. It is measured in units, e.g. 100
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
