Chapter 50 4/9/2015. Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d
|
|
|
- Oswald Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) Thyroid gland responsible for growth, development, and metabolism Parathyroid glands active in maintenance of calcium balance All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 2 Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d Adrenal glands Adrenal cortex releases mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and sex hormones Adrenal medulla releases epinephrine and norepinephrine Pancreas serves many functions, but is mainly known for insulin production Is also responsible for the production of glucagon All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 3 1
2 Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d Female sex glands Ovaries Produce estrogen and progesterone The placenta is a temporary endocrine gland Male sex glands Testes Produce testosterone All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 4 Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d Thymus gland plays an integral role in immune function Pineal glands secrete melatonin All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 5 Negative Feedback Information is constantly being exchanged between the target organs and the pituitary gland The amount of hormonal release is controlled by feedback Negative feedback means that an increase in the expected activity will lead to a decrease in the release of the hormone causing that effect All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 6 2
3 Effects of Hormones on Target Organs Anterior pituitary gland Prolactin causes the mammary glands to produce milk Posterior pituitary gland Oxytocin promotes the release of milk and stimulates uterine contractions during labor Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) causes the kidneys to conserve water by decreasing the amount of urine produced. Thyroid gland T 3 and T 4 serve to promote growth and development, maintain metabolism, and are involved in nervous function Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, secreted by the pituitary gland) controls the release of these two hormones Calcitonin decreases calcium level by causing calcium to be stored in the bones All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 7 Effects of the Hormones on Target Organs cont d Parathyroid glands Parathyroid hormone (PTH) serves as an antagonist to calcitonin PTH tends to increase calcium concentration in the blood PTH also regulates the amount of phosphorus in the blood All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 8 Effects of the Hormones on Target Organs cont d Adrenal cortex Mineralocorticoids Salt primarily involved in water and electrolyte balance, which indirectly manages blood pressure Glucocorticoids Sugar involved in glucose metabolism Sex hormones Sex control male and female sex characteristics Adrenal medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 9 3
4 Effects of the Hormones on Target Organs cont d Pancreas Insulin acts as the key that allows sugar into the cell Glucagon acts as the key to allow sugar back out of the cell Thymus gland Thymosin plays an active role in immune development Pineal gland Thought to affect mood and sleep All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 10 Hypothalamus Produces the hormones of the posterior pituitary All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 11 Acromegaly Caused by an overproduction of growth hormone Usually begins in the third to fourth decade of life Characterized by bulging forehead, bulbous nose, thick lips, and coarse facial features Patient s ability to maintain normal body function and maintain quality of life should be closely assessed Diagnosis is based largely on medical history Treatment includes dopamine agonists, somatostatin analogs, and surgery All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 12 4
5 Gigantism Overproduction of growth hormone before close of growth plates Leads to great height and size Assessment is aimed at early detection Treatment usually involves medication or surgery All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 13 Dwarfism Hypopituitary dwarfism is caused by growth hormone deficiency Assessment is aimed at early detection Diagnostic exams include CT scan and MRI Medical management involves replacement of growth hormone Nursing interventions are aimed at early detection All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 14 Diabetes Insipidus Disorder of the posterior pituitary in which ADH is deficient A decrease in ADH results in electrolyte and fluid imbalances Diabetes insipidus is characterized by significant polyuria and intense polydipsia Patients with diabetes insipidus may have a urinary output exceeding 5-20 L per 24 hours The patient is weak, tired, and lethargic Specific gravity is altered and skin turgor is poor All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 15 5
6 Diabetes Insipidus cont d Diagnosed with urine spectrometry and lab values, along with a careful history Medical management focuses on treatment ADH deficiency Nursing interventions are aimed at protecting the patient from injury Patient should be weighed daily and I&O should be monitored closely Encourage oral intake of fluids All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 16 Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH) occurs when the pituitary gland releases too much ADH As a result, excess water is reabsorbed by the kidneys Characterized by hyponatremia, hemodilution, and fluid overload Signs and symptoms include nausea, vomiting, irritability, confusion, tremors, seizures, stupor, and coma Diagnosed through urine spectrometry and lab values, with careful history Treatment includes strict fluid restriction All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 17 SIADH cont d Patient may be limited to as little as 500 ml of fluid per day Treatment is aimed at resolving underlying conditions Nursing interventions are aimed at fluid restriction and electrolyte replacement I&O should be closely monitored All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 18 6
7 Disorders of the Thyroid Gland Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Thyroid cancer Goiter All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 19 Hyperthyroidism Also called Graves disease Results in an increased production of T 3 and T 4, which leads to exaggerated metabolic processes Symptoms include weight loss, nervousness, insomnia, shortness of breath Objective data includes VS changes, increased BP, tachycardia, hair becomes fine and brittle, diarrhea T 3 and T 4 levels are measured to diagnose All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 20 Hyperthyroidism cont d Ablation therapy using radioactive iodine is the gold standard for treating hyperthyroidism Treated medically with propylthiouracil or Tapazole Surgery may also be used to treat Nursing interventions include Diet therapy Increase vitamin intake Teaching foods that aid in easing the burden of Graves disease Provide preoperative and postoperative care All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 21 7
8 Thyroidectomy Removal of the thyroid Postoperatively, the nurse should Monitor the airway Monitor carpopedal spasms, Chvostek s sign, and Trousseau s sign Monitor for thyroid storm All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 22 Signs of Hypocalcemia As a result of thyroidectomy, one or more parathyroid glands may be inadvertently removed This can result in hypocalcemia Signs of hypocalcemia include Carpopedal spasms muscle spasms of the wrist and feet Chvostek s sign Trousseau s sign All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 23 Hypothyroidism A state that occurs when the thyroid fails to secrete sufficient hormones Signs and symptoms include weight gain, fluid gain, mood swings, infertility, depression Diagnosed by assessing TSH, T 3, T 4, and FT 4 levels Medical management is aimed at replacing thyroid hormones Nursing interventions are aimed at keeping the patient comfortable and preventing complications All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 24 8
9 Simple Goiter Enlarged thyroid gland Characterized by overt thyroid dysfunction Symptoms include dysphagia, hoarseness, and dyspnea Objective data includes increased goiter size, voice changes, decreased food intake Diagnosis is made through lab values of T 3, T 4, and TSH Medical management is aimed at replacing iodine Nursing interventions are aimed at patient teaching and postoperative care for the patient who undergoes thyroidectomy All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 25 Cancer of the Thyroid Relatively rare malignancy Affects about 25 per 1,000,000 people Risk factors include diets low in iodine, women in their 40s and 50s, and radiation exposure Characterized by a firm, fixed, small, rounded, painless mass or nodule that is felt over the thyroid gland Diagnosed when a thyroid scan shows a cold nodule Treatment is usually a total thyroidectomy All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 26 Hyperparathyroidism Overactivity of the parathyroid glands, which increases production of PTH The primary clinical manifestation is hypercalcemia Assessment findings include skeletal pain, fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, pathologic fractures, dysrhythmias Assessed via radiography, lab levels, and history Usually treated via surgical intervention Nursing interventions are aimed at restoring and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 27 9
10 Hypoparathyroidism cont d Occurs when PTH is decreased Characterized by a decreased serum calcium level and increased serum phosphorus level May be characterized by Laryngeal stridor Muscle spasms Chvostek s sign Hypocalcemic tetany All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 28 Hypoparathyroidism cont d Diagnosis is made by assessing laboratory calcium, PTH, and phosphorus levels Medical management is aimed at replacing calcium Vitamin D is also given orally Patient should be provided education about eating foods that are high in calcium All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 29 Cushing s Syndrome (Adrenal Hyperfunction) Caused by increased corticosteroids, especially glucocorticoids Signs and symptoms include Weight gain Accumulation of adipose tissue in the trunk, face, and cervical spine Hypokalemia Hyperglycemia All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
11 Addison s Disease (Adrenal Hypofunction) Most commonly caused by an autoimmune response The patient should be assessed for weakness, vertigo, syncope, and postural hypotension The patient also usually experiences weight loss, vomiting, and diarrhea Medical therapy is aimed at replacing steroids, usually with hydrocortisone Nursing interventions are aimed at improving circulatory status, maintaining accurate I&O, and daily weights All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 31 Diabetes Mellitus (DM) DM Type I: Most commonly referred to as insulin-dependent diabetes DM Type II: More commonly linked to sedentary lifestyle and lack of activity Insulin sensitivity may be decreased, the patient may not produce enough insulin, or a combination of both All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 32 Signs and Symptoms of DM DM is characterized by three cardinal signs and symptoms Polydipsia Polyphagia Polyuria All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
12 Assessment of the Patient with DM Subjective data The three Ps Nocturia Weakness Fatigue Blurred vision Objective data Slow wound healing Hyperglycemia Weight loss Muscle wasting All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 34 Diagnostic Exams for DM Any random blood glucose greater than 200 Fasting blood glucose greater than 126 Elevated results on an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 35 Treatment Triad for DM Diet Exercise Medications All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
13 Nursing Interventions and Patient Teaching Nursing interventions and patient teaching are aimed at Diet education Exercise education Medication for dosage, type, route All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 37 Hyperglycemia Condition of elevated blood glucose associated with DM Fasting blood glucose >126 Random blood glucose >200 All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 38 Hypoglycemia Blood glucose level less than normal Caused by administration of excessive insulin, excessive secretion of insulin, or dietary deficiency Signs and symptoms include faintness, hunger, excessive perspiration, irritability, trembling Treatment is aimed at replacing glucose in the body by Oral intake IV intake IM injection All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
14 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with type I DM Caused by lack of insulin and/or increased sugar intake Onset is hours to days Patient is hot, dry, and flushed and has fruity breath Kussmaul s respirations Treated with insulin and limited intake All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 40 Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Coma Caused by inadequate insulin or oral hypoglycemic intake Onset is days Usually occurs in type 2 diabetes Patient is hot and dry Characterized by lethargy and decreased LOC Treatment includes large amounts of IV fluid and insulin All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 41 DM Triad of Treatment Diet Exercise Nutrition All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
15 Diet Low concentrated sweets Moderate carbs Low fat High protein Small meals with frequent snacks All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 43 Exercise Improves insulin sensitivity Improves insulin production Improves cardiovascular health All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 44 Medications Insulin Oral hypoglycemic agents All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
16 Oral Hypoglycemic Agents Sulfonylureas, Meglitinide, and thiazolidinediones improve insulin production and increase insulin sensitivity Biguanides decrease hepatic glucose production and increase insulin sensitivity Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors delay carbohydrate absorption All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 46 Insulin Rapid- or short-acting has a short onset and peak of action Mixed is a combination of short-acting and long-acting Intermediate acting generally has an onset of about 30 minutes and a 6-12 hour effect Long-acting has a long duration All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 47 Insulin Administration Preparation of Insulin Wash hands Assemble equipment Turn insulin vial in hands Clean rubber stopper with alcohol Insert air into vial Withdraw insulin Inspect for air bubbles All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
17 Insulin Administration cont d Two Insulins Following procedure described earlier. First withdraw regular insulin Then withdraw longer-acting insulin All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 49 Insulin Administration cont d Insulin Injection Don gloves Clean injection site Quickly insert needle in subcutaneous tissue Inject insulin slowly Dispose of syringe appropriately All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 50 Short-Term DM Complications Hypoglycemia HHNC DKA All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
18 Long-Term DM Complications Blindness Kidney disease Heart disease Poor circulation All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Hormones by location
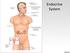 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth
 9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth Hormonal Regulation of Growth Pituitary gland regulates growth and development Thyroid gland regulates metabolic rate (exception: some hormones for growth and development)
9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth Hormonal Regulation of Growth Pituitary gland regulates growth and development Thyroid gland regulates metabolic rate (exception: some hormones for growth and development)
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27
 Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013
 A & P Review CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013 Endocrine Anterior pituitary Growth hormone: long bone growth Thyroid stimulating hormone: growth, thyroid secretion Adrenocorticotropic hormone: growth,
A & P Review CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013 Endocrine Anterior pituitary Growth hormone: long bone growth Thyroid stimulating hormone: growth, thyroid secretion Adrenocorticotropic hormone: growth,
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM. Objectives A & P 8/11/2011
 PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com
 1 Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com 2 Disclaimer Medicine and nursing are continuously changing practices. The author and publisher have reviewed all information in this book with resources believed
1 Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com 2 Disclaimer Medicine and nursing are continuously changing practices. The author and publisher have reviewed all information in this book with resources believed
The Endocrine System. Lipid-Soluble Hormones. Bio217 Sp14 Unit 5. Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
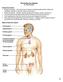 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Metabolic System. Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs. The Endocrine System
 Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 44, (pp 1154-1189) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult
Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 44, (pp 1154-1189) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 25. Diabetic Emergencies
 Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT
 PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and
PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Hormones. Regulation. Endocrine System. What Do Endocrine Glands Release (Secrete)? Endocrine System
 Endocrine System Function: Endocrine System - For glands to release products into bloodstream to deliver messages throughout the body. Regulation Is the control & coordination of other life functions to
Endocrine System Function: Endocrine System - For glands to release products into bloodstream to deliver messages throughout the body. Regulation Is the control & coordination of other life functions to
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes?
 Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System
 Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH
 J 1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH NURSING MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION: THEORETICAL SKILLS and KNOWLEDGE, SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES, CRITICAL THINKING, HEALTHCARE PROMOTION,
J 1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH NURSING MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION: THEORETICAL SKILLS and KNOWLEDGE, SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES, CRITICAL THINKING, HEALTHCARE PROMOTION,
Target cells only respond to specific signals Different target cells have different kinds of receptors in their membranes or cytoplasm
 1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss the characteristics of hormones. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. Look at the location and the functions
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss the characteristics of hormones. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. Look at the location and the functions
Pathophysiology of the th E d n ocr i ne S S t ys em B. Marinov, MD, PhD Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus
 Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Hormones. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
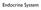 Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Endocrine System. True or False
 True or False Endocrine System Some overweight people actually eat very little; their excess weight is caused by glands A woman who becomes anxious and depressed just before menstruating is suffering from
True or False Endocrine System Some overweight people actually eat very little; their excess weight is caused by glands A woman who becomes anxious and depressed just before menstruating is suffering from
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Hormonal Regula8on of Homeostasis
 Hormonal Regula8on of Homeostasis Chapter 13 (MH) 15 (N) MH: 436 N: 470 MH: 436 N: 470 Glands and hormones Endocrine glands secrete chemical messengers called hormones Hormones are delivered to target
Hormonal Regula8on of Homeostasis Chapter 13 (MH) 15 (N) MH: 436 N: 470 MH: 436 N: 470 Glands and hormones Endocrine glands secrete chemical messengers called hormones Hormones are delivered to target
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System
 Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
BIOLOGY. CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition. Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor. CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation
 BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
The Endocrine System Unit 7
 General Functions of the Endocrine System Coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals (hormones) The Endocrine System Unit 7 Effects
General Functions of the Endocrine System Coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals (hormones) The Endocrine System Unit 7 Effects
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Pathology of the Endocrine System
 Pathology of the Endocrine System นายแพทย ดร.ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร 4 เมษายน พ.ศ. 2557 Topics Introduction Diseases of the Endocrine glands Pituitary gland
Pathology of the Endocrine System นายแพทย ดร.ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร 4 เมษายน พ.ศ. 2557 Topics Introduction Diseases of the Endocrine glands Pituitary gland
Endocrine system pathology
 Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
