The delicate balance of disease
|
|
|
- Douglas Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Play of Chance Versus Concerns Regarding Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Heart Failure and Diabetes Vani P. Sanon, MD, Saurabh Sanon, MD, Son V. Pham, MD, FACC, and Robert Chilton, DO, FACC The delicate balance of disease management versus off-target effects of treatment continues to be a vital concern to both patients and physicians. This article offers a brief overview of heart failure in diabetes and comments on the recent outcome trials of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, with a closer look at a few pathobiological concerns. The importance of safe antidiabetic treatments becomes apparent when one considers the increasing obesity and diabetes pandemics. Approximately 150,000 patients with moderate-high cardiovascular (CV) risk factor profiles are currently enrolled in trials of antidiabetic agents. Establishing the CV safety of newer antidiabetic agents, especially with respect to heart failure, remains crucial. Heart failure syndrome is a symptom complex composed of worsening shortness of breath, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, fatigue, and the well-known manifestation of ankle edema. The syndrome is characterized by physical findings of fluid retention (dependent edema), a third heart sound, rales sounds, and distension of the neck veins. In addition, heart failure is associated with chronic inflammation and a prothrombotic state. Endothelial dysfunction and proteomic and neurohormonal activation occur many months before development of the syndrome complex. 1,2 Newer areas of basic science research have identified potential prognostic indicators in chronic heart failure (mir126 and mir508-5p) that might be used as novel markers leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment of heart failure. 3,4 Heart failure has several etiologies ranging from mechanical and electrical dysfunction to structural and valvular abnormities. Moreover, the consequences of heart failure are multi-systemic and adversely affect the liver, kidneys, bone marrow, and muscle. Recent data from the Olmstead County population study 5 showed that patients with diabetes had equal amounts of systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Patients with diabetes frequently have preserved leftventricular function (a normal ejection fraction) but with a poorly compliant left ventricle that is very sensitive to volume changes. For example, people with type 2 diabetes who are exposed to an extra salt and fluid load could experience enough of an increase in circulating blood volume to place them into symptomatic heart failure. Autonomic dysfunction, glucose toxicity, and oxidative stress are believed to play a role in the development of heart failure in people with diabetes (Figure 1). The occurrence of CV events and mortality in patients with diabetes is frequently underestimated when considering heart failure in diabetes. Notably, myocardial infarction (MI), non-st elevation MI, and stroke are the leading primary endpoints of most current antidiabetic drug trials. However, heart failure may Figure 1. Diabetes and heart failure: a complex pathophysiological association. Clinical Diabetes Volume 32, Number 3,
2 Figure 2. This figure illustrates the importance of heart failure consideration in primary endpoint trials with hypoglycemic agents. A retrospective cohort study 6 with nearly 50 million lives found a high incidence of heart failure compared to the classic primary endpoints in most diabetes trials. Adapted from Ref. 6. Figure 3. This pooled data from 11 prospective cohort studies with 650,386 white adults found a significant correlation in all-cause mortality when waist circumference was combined with BMI. Note that even at a low BMI, there is an increased risk for all-cause mortality with a waist circumference > 90 cm (36 inches). Adapted from Ref. 8. need to be added or considered as a principal secondary endpoint. Recently, Juhaeri et al. 6 reported in a retrospective study encompassing > 50 million lives from Medicaid, Medicare, and 60 health maintenance organizations the incidence of heart failure, MI, and stroke in type 2 diabetes patients on insulin. The highest incidence was for heart failure (Figure 2). In addition, Bertoni et al. 7 evaluated 151,738 Medicare beneficiaries with diabetes with practically a 10-fold increase in heart failure mortality versus patients with diabetes who were free of heart failure at 60 months. In summary, the heart failure syndrome in diabetes carries an ominous outlook, and, with an increasing number of antidiabetic drugs to reduce blood glucose levels, newer trials should consider heart failure as one of the major clinical endpoints. In addition to an increasing BMI, which is frequently associated with diabetes, waist circumference should also be evaluated, even for patients with a normal weight (Figure 3). 8 Despite advances in medical and surgical therapy for the management of patients with diabetes, lifestyle modification leading to weight loss alone affords improvement in the CV risk profile, as shown in Table 1. It is possible that interventional procedures such as endobarrier or gastric bypass surgery may carry less risk for markedly obese patients who are at high risk for diabetes or who have diabetes, but these procedures also carry some degree of surgical risk. SAVOR and EXAMINE Trials Two recent DPP-4 inhibitor trials have increased discussion about hospitalizations for heart failure even though basic science studies have not noted significant heart failure concerns. The SAVOR (Saxagliptin Assessment of Vascular Outcomes Recorded in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus [TIMI-53]) trial 9 evaluated the safety and efficacy of saxagliptin on CV outcomes in patients with diabetes who are at risk for CV events. The trial was designed as a superiority trial. However, a closed testing hierarchy prespecified that a test for noninferiority of the primary composite endpoint should be completed first to preserve the alpha level, followed by a test for superiority. A total of 16,492 diabetes patients were prospectively randomized to saxagliptin 5 mg daily (2.5 mg if glomerular filtration rate [GFR] was < 50 ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) or placebo, with a mean follow-up of 2.1 years. Demographic data are shown in Table 2. The primary end- 122 Volume 32, Number 3, 2014 Clinical Diabetes
3 Table 1. Effects of Diabetes Management Strategies on Known Classic CV Risk Factors Management Strategy CRP LDL BP PPG Weight Loss Decrease in CV Events? Side Effects? SGLT-2 inhibitor? Yes Statin 0? 0 Yes (ARR 3 4%) Yes TZD ++ +/ Yes DPP-4 inhibitor No (HF?) Yes Weight loss of 10% Yes (ARR 1 2%) Hunger Endobarrier?? +?? Yes Gastric bypass Yes/SOS Yes ARR, absolute risk reduction; BP, blood pressure; CRP, C-reactive protein; LDL, LDL cholesterol; PPG, postprandial glucose; SGLT-2, sodium glucose co-transporter 2; SOS, Swedish Obese Subjects study; TZD, thiazolidinedione. Table 2. Comparison of Baseline Demographics from the SAVOR 9 and EXAMINE 10 Trials SAVOR (Stable CAD) EXAMINE (ACS) Saxagliptin Control Alogliptin Control BMI (kg/m 2 ) Duration of diabetes (years) Hypertension (%) Prior heart failure (%) Prior MI (%) Prior revascularization (%) Mean A1C (%) GFR > 60 ml/min/1.73 m 2 (%) Aspirin therapy (%) Statin therapy (%) ACE inhibitor therapy (%) ACS, acute coronary syndrome; CAD, coronary artery disease. point was a composite of CV death, MI, or ischemic stroke. The primary endpoint occurred in 613 patients in the saxagliptin group and 609 patients in the placebo group (7.3 and 7.2%, NS). The 2-year Kaplan-Meier estimate for superiority was not achieved (hazard ratio [HR] with saxagliptin 1.00, 95% CI , P = 0.99). However, noninferiority was significant at P < The major composite secondary endpoints of CV death, MI, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, coronary revascularization, and heart failure was 12.8% in the treatment arm and 12.4% in the placebo arm (2-year Kaplan-Meier estimate HR 1.02, 95% CI , P = 0.66, NS). Unfortunately, hospitalization for heart failure was significantly increased in the saxagliptin arm by 27% (HR 1.27, 95% CI , P < 0.007). The risk for primary and secondary endpoints among patients who received saxagliptin was comparable to that among patients without a history of heart failure (primary endpoint HR in the saxagliptin group 1.13, 95% CI , vs. 0.97, 95% CI , in the comparison group; secondary endpoint HR in the saxagliptin group 1.06, 95% CI , vs. 1.01, 95% CI , in the comparison group). The rate of acute and chronic pancreatitis was similar in the saxagliptin and placebo groups: 0.3 vs. 0.2% for acute pancreatitis and < 0.1 vs. 0.1% for chronic pancreatitis. The absolute risk for hospitalization for heart failure was highest among patients with a history of heart failure. However, the relative risk among patients assigned to saxagliptin was similar regardless of baseline history of heart failure (HR 1.21, 95% CI , vs. 1.32, 95% CI ). In summary, the DPP-4 inhibitor saxagliptin did not reduce CV events in diabetes Clinical Diabetes Volume 32, Number 3,
4 Figure 4. The possible off-target effect of increased heart failure hospitalizations from saxagliptin in the SAVOR trial. Higher N-terminal pro-b-type natriuretic peptide levels predicted increased risk for heart failure hospitalizations. The highest levels significantly increased this risk, but did not increase mortality. Most of the patients had a history of heart failure. Adapted from References 9 and 11. Figure 5. Patient deaths in the SAVOR trial. There was no increase in total deaths or deaths from heart failure. More patients suffered sudden cardiac death than death from heart failure. The reassuring finding of no difference in cancer deaths was supportive of safety with regard to malignancy. Adapted from Ref. 9. patients. The apparent off-target effect of increased risk for hospitalization for heart failure (best predicted by history of heart failure) will remain a question for future trials to answer in patients with stable CV disease and diabetes (Figures 4 and 5). The EXAMINE (Examination of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Alogliptin Versus Standard of Care) trial 10 was a double-blinded noninferiority trial comparing placebo to alogliptin and evaluating the impact of treatment on major CV events in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome within days before randomization. Demographic data are shown in Table 2. The primary CV endpoint was a composite of death from CV causes, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke. A total of 5,380 patients underwent randomization with a follow-up of up to 40 months (median 18 months). The primary endpoint occurred in 305 patients (11.3%) assigned to alogliptin and in 316 patients (11.8%) assigned to placebo (HR 0.96, upper boundary of the one-sided repeated confidence interval 1.16, P < for noninferiority, P = 0.32 for superiority) at 36 months of follow-up. Table 3 shows the components of the primary endpoint and additional exploratory adjudicated components. The EXAMINE trial did not find significantly increased hospitalizations for heart failure. However, there were more patient hospitalizations for heart failure in the alogliptin arm than in the placebo arm. The principal secondary endpoints of death from CV causes, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, and urgent revascularization because of unstable angina were not significant between placebo and alogliptin (13.4% [n = 359] vs. 12.7% [n = 344], P < 0.26). Hospitalization for heart failure in the alogliptin treatment arm was 106 of 2,701 events compared to 89 of 2,679 events in the placebo arm (odds ratio 1.19, 95% CI ). Figure 6 provides a comparison of the rates of hospitalization for heart failure between the SAVOR and EXAMINE trials. However, comparing these two trials in terms of heart failure may be misleading. The first concern is whether the patients in these studies had preserved left-ventricular function (low or high ejection fractions). Many patients with type 2 diabetes have preserved left-ventricular function but diastolic dysfunction. Other patients have ischemic heart disease with reduced left-ventricular function or a combination of both conditions. Understanding of heart failure in these two studies remains obscure; more data are required to fully understand the relationship between DPP-4 inhibitor therapy and heart failure. 124 Volume 32, Number 3, 2014 Clinical Diabetes
5 Conclusion Both of the SAVOR 9 and EXAMINE 10 trials failed to find CV event reduction in patients with diabetes using DPP-4 inhibitor therapy. Moreover, there was a significant increase in hospitalizations for heart failure with saxagliptin, but not with alogliptin. The reason for increased heart failure admissions with saxagliptin remains unclear, and it is possible this finding could be by Table 3. Components of the Primary Endpoint and Additional Exploratory Adjudicated Components in the EXAMINE Trial Primary endpoint: death from CV causes, non-fatal MI, and nonfatal stroke (%) Alogliptin Placebo HR NS CV death (%) NS Non-fatal MI (%) NS Non-fatal stroke (%) NS Exploratory adjudicated components: All-cause death (%) Heart failure hospitalization [% (n)] History of heart failure (%) (106) (89) 22.3 NS NS NS Figure 6. Comparison of rates of hospitalization for heart failure in the SAVOR 9 and EXAMINE 10 trials. play of chance rather than the result of other unknown off-target effects. Resolution of this issue awaits future studies to determine whether this is a problem with the DPP-4 inhibitor class, the characteristics of the specific drug within the class, or play of chance. Pending large trials such as TECOS (Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin) and CAROLINA (Cardiovascular Outcome Study of Linagliptin Versus Glimepiride in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes) 12,13 will help to answer some questions related to the possible link between hospitalization for heart failure and DPP-4 inhibitor therapy. Unfortunately, these trials have not included heart failure as a primary or principal secondary endpoint (Table 4). Potential beneficial pleotropic effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on the CV system are outlined in Figure 7. Translational consideration findings have ranged from improvement in cardiac function to increased circulating blood volume caused by neuropeptide Y mediated vasoconstriction of the microcirculation. 14 The optimal management of patients with diabetes who remain at risk for heart failure in addition to a plethora of other CV problems deserves due attention. Additional research will be Table 4. Ongoing, Prospective Clinical Trials of DPP-4 Inhibitors With CV Outcomes DPP-4 Inhibitor Trial Design Patient Characteristics Linagliptin CAROLINA n = 6,000 5 mg glimepiride vs. 1 4 mg linagliptin Noninferiority and superiority trial Sitagliptin TECOS n = 14, or 100 mg sitagliptin vs. placebo Noninferiority trial A1C %, high CV risk A1C %, history of cardiovascular disease Primary Endpoint Time to first occurrence of nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or CV death Time to first confirmed CV event (nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for unstable angina) Clinical Diabetes Volume 32, Number 3,
6 Figure 7. Potential beneficial cellular pleotropic effects of DPP-4 inhibitors. Antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory, and atheroprotective effects are key players in the CV arena. *Makdissi A, Ghanim H, Vora M, Green K, Abuaysheh S, Chaudhuri A, Dhindsa S, Dandona P: Sitagliptin exerts an antinflammatory action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97: , required to clarify the role of novel agents such as DPP-4 inhibitors. References 1 McMurray JJ: Clinical practice: systolic heart failure. N Engl J Med 362: , McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA: Heart failure. Lancet 365: , Qiang L, Hong L, Ningfu W, Huaihong C, Jing W: Expression of mir-126 and mir-508-5p in endothelial progenitor cells is associated with the prognosis of chronic heart failure patients. Int J Cardiol 168: , Wang HW, Huang TS, Lo HH, Huang PH: Deficiency of the microrna-31 microrna-720 pathway in the plasma and endothelial progenitor cells from patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34: , Dandamudi S, Slusser J, Mahoney DW, Redfield MM, Rodeheffer RJ, Chen HH: The prevalence of diabetic cardiomyopathy: a population based study in Olmsted County, MN. J Card Fail. Electronically published ahead of print on 24 February 2014 (doi: /j.cardfail ) 6 Juhaeri J, Gao S, Dai WS: Incidence rates of heart failure, stroke, and acute myocardial infarction among type 2 diabetic patients using insulin glargine and other insulin. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 18: , Bertoni AG, Hundley WG, Massing MW, Bonds DE, Burke GL, Goff DC Jr: Heart failure prevalence, incidence, and mortality in the elderly with diabetes. Diabetes Care 27: , Cerhan JR, Moore SC, Jacobs EJ: A pooled analysis of waist circumference and mortality in 650,000 adults. Mayo Clin Proc 89: , Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, Steg PG, Davidson J, Hirshberg B, Ohman P, Frederich R, Wiviott SD, Hoffman EB, Cavender MA, Udell JA, Desai NR, Mosenzon O, McGuire DK, Ray KK, Leiter LA, Raz I, for the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Steering Committee and Investigators: Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 369: , White WB, Cannon CP, Heller SR, Nissen SE, Bergenstal RM, Bakris GL, Perez AT, Fleck PR, Mehta CR, Kupfer S, Wilson C, Cushman WC, Zannad F, for the EXAMINE Investigators: Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 369: , Bhatt DL, on behalf of the SAVOR- TIMI 53 Steering Committee and Investigators: Saxagliptin Assessment of Vascular Outcomes Recorded in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (SAVOR) TIMI 53. Presentation delivered at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes 49th annual meeting on 26 September 2013 in Barcelona, Spain 12 Sitagliptin cardiovascular outcome study (MK ) (TECOS). Available from ?term=NCT &rank=1. Accessed 15 April CAROLINA: Cardiovascular Outcome Study of Linagliptin Versus Glimeperide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Available from 24?term=NCT &rank=1. Accessed 15 April Evanson KW, Stone AJ, Hammond AL, Kluess HA: Neuropeptide Y overflow and metabolism in skeletal muscle arterioles. J Physiol 589: , 2011 Vani P. Sanon, MD, is a fellow in the Division of Cardiology at the University of Texas Health Science Center in San Antonio. Saurabh Sanon, MD, is an interventional fellow in the Division of Cardiovascular Diseases at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. Son V. Pham, MD, FACC, is the chief of cardiology at the Audie L. Murphy Veterans Affairs Hospital in San Antonio. Robert Chilton, DO, FACC, is a professor in the Division of Cardiology at the University of Texas Health Science Center and the Audie L. Murphy Veterans Affairs Hospital in San Antonio. 126 Volume 32, Number 3, 2014 Clinical Diabetes
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content McGuire DK, Van de Werf F, Armstrong PW, et al; Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes With Sitagliptin (TECOS) Study Group. Association between sitagliptin use and heart
Supplementary Online Content McGuire DK, Van de Werf F, Armstrong PW, et al; Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes With Sitagliptin (TECOS) Study Group. Association between sitagliptin use and heart
Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes
 Biomarkers 2018 Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
Biomarkers 2018 Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA
 ON ISSUES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES JUNE 2015 Coverage of data from ADA 2015, June 5 9 in Boston, Massachusetts No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA First Cardiovascular
ON ISSUES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES JUNE 2015 Coverage of data from ADA 2015, June 5 9 in Boston, Massachusetts No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA First Cardiovascular
LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes
 LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Presented at DSBS seminar on mediation analysis August 18 th Søren Rasmussen, Novo Nordisk. LEADER CV outcome study To determine the effect
LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Presented at DSBS seminar on mediation analysis August 18 th Søren Rasmussen, Novo Nordisk. LEADER CV outcome study To determine the effect
LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD. Will this change the guidelines?
 LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD Will this change the guidelines? Objectives 1. Discuss current guidelines for prevention of CHD in diabetes. 2. Discuss the FDA Guidance for Industry regarding evaluating
LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD Will this change the guidelines? Objectives 1. Discuss current guidelines for prevention of CHD in diabetes. 2. Discuss the FDA Guidance for Industry regarding evaluating
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016
 Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
Fasting or non fasting?
 Vascular harmony Robert Chilton Professor of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center Director of Cardiac Catheterization labs Director of clinical proteomics Which is best to measure Lower continues
Vascular harmony Robert Chilton Professor of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center Director of Cardiac Catheterization labs Director of clinical proteomics Which is best to measure Lower continues
Drug Class Monograph
 Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy
 Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials 2018 Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Blevins has disclosed that he has received grant support
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials 2018 Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Blevins has disclosed that he has received grant support
Case Presentation. Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer
 Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
 Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice
 Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice Biykem Bozkurt, MD, FACC The Mary and Gordon Cain Chair & Professor of Medicine Medical Care Line Executive, DeBakey VA Medical Center, Director, Winters Center for
Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice Biykem Bozkurt, MD, FACC The Mary and Gordon Cain Chair & Professor of Medicine Medical Care Line Executive, DeBakey VA Medical Center, Director, Winters Center for
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
Soo LIM, MD, PHD Internal Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Soo LIM, MD, PHD Internal Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Agenda Association between Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Importance of HbA1c Management esp. High risk patients
Soo LIM, MD, PHD Internal Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Agenda Association between Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Importance of HbA1c Management esp. High risk patients
Clinical Trial Synopsis TL-OPI-518, NCT#
 Clinical Trial Synopsis, NCT# 00225264 Title of Study: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Comparator-Controlled Study in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Comparing the Effects of Pioglitazone HCl vs Glimepiride
Clinical Trial Synopsis, NCT# 00225264 Title of Study: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Comparator-Controlled Study in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Comparing the Effects of Pioglitazone HCl vs Glimepiride
Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists
 Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists Robert R. Henry, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Relevant Conflict
Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists Robert R. Henry, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Relevant Conflict
Diabetes and Heart Failure: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors
 22 nd Annual Heart Failure 2018 Symposium Diabetes and Heart Failure: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
22 nd Annual Heart Failure 2018 Symposium Diabetes and Heart Failure: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
Rikshospitalet, University of Oslo
 Rikshospitalet, University of Oslo Preventing heart failure by preventing coronary artery disease progression European Society of Cardiology Dyslipidemia 29.08.2010 Objectives The trends in cardiovascular
Rikshospitalet, University of Oslo Preventing heart failure by preventing coronary artery disease progression European Society of Cardiology Dyslipidemia 29.08.2010 Objectives The trends in cardiovascular
New Strategies for Cardiovascular Risk reduction in Diabetes
 New Strategies for Cardiovascular Risk reduction in Diabetes Dr. Godwin LEUNG Tat Chi MB ChB(HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (Medicine) FRCP (Glasg), FACC Specialist in Cardiology % event as first CV event
New Strategies for Cardiovascular Risk reduction in Diabetes Dr. Godwin LEUNG Tat Chi MB ChB(HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (Medicine) FRCP (Glasg), FACC Specialist in Cardiology % event as first CV event
OBJECTIVE RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS RESULTS CONCLUSIONS. Diabetes Care Volume 39, July CARDIOVASCULAR AND METABOLIC RISK
 Diabetes Care Volume 39, July 2016 1267 Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Recent Acute Coronary Syndromes From the EXAMINE Trial Diabetes Care 2016;39:1267 1273 DOI: 10.2337/dc16-0303
Diabetes Care Volume 39, July 2016 1267 Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Recent Acute Coronary Syndromes From the EXAMINE Trial Diabetes Care 2016;39:1267 1273 DOI: 10.2337/dc16-0303
01/09/2017. Outline. SGLT 2 inhibitor? Diabetes Patients: Complex and Heterogeneous. Association between diabetes and cardiovascular events
 MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the. impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood.
 Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
CANVAS Program Independent commentary
 CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP
 Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research InsAtute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research InsAtute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link?
 Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link? Denise Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS AQ Cardiology 1 Erika Hellenbart, PharmD, BCPS 2 Jennifer D Souza, PharmD, CDE, BC ADM
Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link? Denise Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS AQ Cardiology 1 Erika Hellenbart, PharmD, BCPS 2 Jennifer D Souza, PharmD, CDE, BC ADM
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS
 The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial)
 CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial) William B. White, MD, for the CARES Investigators Calhoun Cardiology Center University
CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial) William B. White, MD, for the CARES Investigators Calhoun Cardiology Center University
A: Epidemiology update. Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups
 A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare
 Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Antihypertensive Trial Design ALLHAT
 1 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Major Outcomes in High Risk Hypertensive Patients Randomized to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Calcium Channel Blocker vs Diuretic National Institutes
1 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Major Outcomes in High Risk Hypertensive Patients Randomized to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Calcium Channel Blocker vs Diuretic National Institutes
Cardiovascular disease and diabetes Vascular harmony
 Cardiovascular disease and diabetes 2018 Vascular harmony Robert Chilton Professor of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center Director of Cardiac Catheterization labs Director of clinical proteomics
Cardiovascular disease and diabetes 2018 Vascular harmony Robert Chilton Professor of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center Director of Cardiac Catheterization labs Director of clinical proteomics
Lowering blood pressure (BP) in patients with type 2
 Average Clinician-Measured Blood Pressures and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Ischemic Heart Disease in the EXAMINE Trial William B. White, MD; Fatima Jalil, MD;
Average Clinician-Measured Blood Pressures and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Ischemic Heart Disease in the EXAMINE Trial William B. White, MD; Fatima Jalil, MD;
HFpEF, Mito or Realidad?
 HFpEF, Mito or Realidad? Ileana L. Piña, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology/Population Health Associate Chief for Academic Affairs -- Cardiology Montefiore-Einstein Medical Center Bronx, NY
HFpEF, Mito or Realidad? Ileana L. Piña, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology/Population Health Associate Chief for Academic Affairs -- Cardiology Montefiore-Einstein Medical Center Bronx, NY
CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management. Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH
 CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH Case 49 y female with the following medical problems DM typ2 Hypertension
CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH Case 49 y female with the following medical problems DM typ2 Hypertension
HEART FAILURE AND DIABETES MELLITUS: DANGEROUS LIASONS MICHEL KOMAJDA, MD
 HEART FAILURE AND DIABETES MELLITUS: DANGEROUS LIASONS MICHEL KOMAJDA, MD Author affiliations: Department of Cardiology, Hôpital Saint Joseph, Paris, France Address for correspondence: Michel Komajda,
HEART FAILURE AND DIABETES MELLITUS: DANGEROUS LIASONS MICHEL KOMAJDA, MD Author affiliations: Department of Cardiology, Hôpital Saint Joseph, Paris, France Address for correspondence: Michel Komajda,
Trial to Reduce. Aranesp* Therapy. Cardiovascular Events with
 Trial to Reduce Cardiovascular Events with Aranesp* Therapy John J.V. McMurray, Hajime Uno, Petr Jarolim, Akshay S. Desai, Dick de Zeeuw, Kai-Uwe Eckardt, Peter Ivanovich, Andrew S. Levey, Eldrin F. Lewis,
Trial to Reduce Cardiovascular Events with Aranesp* Therapy John J.V. McMurray, Hajime Uno, Petr Jarolim, Akshay S. Desai, Dick de Zeeuw, Kai-Uwe Eckardt, Peter Ivanovich, Andrew S. Levey, Eldrin F. Lewis,
Type 2 diabetes affects an estimated 25.8 million
 Hosp Pharm 2014;49(8):697 701 2014 Thomas Land Publishers, Inc. www.hospital-pharmacy.com doi: 10.1310/hpj4908-697 Cardiovascular Therapeutics Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk: Are Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4
Hosp Pharm 2014;49(8):697 701 2014 Thomas Land Publishers, Inc. www.hospital-pharmacy.com doi: 10.1310/hpj4908-697 Cardiovascular Therapeutics Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk: Are Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4
GALECTIN-3 PREDICTS LONG TERM CARDIOVASCULAR DEATH IN HIGH-RISK CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE PATIENTS
 GALECTIN-3 PREDICTS LONG TERM CARDIOVASCULAR DEATH IN HIGH-RISK CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE PATIENTS Table of Contents List of authors pag 2 Supplemental figure I pag 3 Supplemental figure II pag 4 Supplemental
GALECTIN-3 PREDICTS LONG TERM CARDIOVASCULAR DEATH IN HIGH-RISK CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE PATIENTS Table of Contents List of authors pag 2 Supplemental figure I pag 3 Supplemental figure II pag 4 Supplemental
JUPITER NEJM Poll. Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The JUPITER Study
 Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
Impatto dei farmaci antidiabetici sullo scompenso cardiaco
 Impatto dei farmaci antidiabetici sullo scompenso cardiaco Riccardo Candido S.S.D. Gestione Rete Diabetologica Aziendale Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Integrata di Triste Il sottoscritto Riccardo Candido
Impatto dei farmaci antidiabetici sullo scompenso cardiaco Riccardo Candido S.S.D. Gestione Rete Diabetologica Aziendale Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Integrata di Triste Il sottoscritto Riccardo Candido
Empagliflozin (Jardiance ) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the EMPA REG OUTCOME study
 Empagliflozin (Jardiance ) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the EMPA REG OUTCOME study POSITION STATEMENT: Clinicians should continue to follow MHRA advice and NICE technology appraisal guidance
Empagliflozin (Jardiance ) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the EMPA REG OUTCOME study POSITION STATEMENT: Clinicians should continue to follow MHRA advice and NICE technology appraisal guidance
Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs
 Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs Professor Guntram Schernthaner Medical University of Vienna, Austria guntram.schernthaner@meduniwien.ac.at Agenda Glucose
Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs Professor Guntram Schernthaner Medical University of Vienna, Austria guntram.schernthaner@meduniwien.ac.at Agenda Glucose
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Udell JA, Cavender MA, Bhatt DL, Chatterjee
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Udell JA, Cavender MA, Bhatt DL, Chatterjee
Online Appendix (JACC )
 Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Diabetes and the Heart
 Diabetes and the Heart Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 6, 2012 Outline Screening for diabetes in patients with CAD Screening for CAD in patients with
Diabetes and the Heart Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 6, 2012 Outline Screening for diabetes in patients with CAD Screening for CAD in patients with
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention
 CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle. Dr Bernard SAMIA. KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration
 GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial)
 CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial) William B. White, MD for the CARES Investigators Calhoun Cardiology Center University
CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial) William B. White, MD for the CARES Investigators Calhoun Cardiology Center University
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology
 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Disclosures In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Disclosures In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the
Causes of death in Diabetes
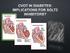 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Metformin. Sulfonylurea. Thiazolidinedione. Insulin
 동아의대내분비내과박미경 Metformin Sulfonylurea Thiazolidinedione Insulin 요약 markers of inflammation (hs-crp, TNF-a) markers of impaired endothelial function (VFW, scams, tpa, PAI-1) LDL-C, fasting and postprandial
동아의대내분비내과박미경 Metformin Sulfonylurea Thiazolidinedione Insulin 요약 markers of inflammation (hs-crp, TNF-a) markers of impaired endothelial function (VFW, scams, tpa, PAI-1) LDL-C, fasting and postprandial
Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications
 Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications Nathan Woolever, Pharm.D., Resident Pharmacist Pharmacy Grand Rounds November 6 th, 2018 Franciscan Healthcare La Crosse, WI 2017
Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications Nathan Woolever, Pharm.D., Resident Pharmacist Pharmacy Grand Rounds November 6 th, 2018 Franciscan Healthcare La Crosse, WI 2017
Cedars Sinai Diabetes. Michael A. Weber
 Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Trials Enrolled subjects Findings Fox et al. 2014, SIGNIFY 1
 Appendix 5 (as supplied by the authors): Published trials on the effect of ivabradine on outcomes including mortality in patients with different cardiovascular diseases Trials Enrolled subjects Findings
Appendix 5 (as supplied by the authors): Published trials on the effect of ivabradine on outcomes including mortality in patients with different cardiovascular diseases Trials Enrolled subjects Findings
Using DOACs in CAD Patients in Sinus Ryhthm Results of the ATLAS ACS 2, COMPASS and COMMANDER-HF Trials
 Using DOACs in CAD Patients in Sinus Ryhthm Results of the ATLAS ACS 2, COMPASS and COMMANDER-HF Trials 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La
Using DOACs in CAD Patients in Sinus Ryhthm Results of the ATLAS ACS 2, COMPASS and COMMANDER-HF Trials 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La
Alogliptin after Acute Coronary Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 original article after Acute Coronary Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes William B. White, M.D., Christopher P. Cannon, M.D., Simon R. Heller, M.D., Steven E. Nissen, M.D., Richard M. Bergenstal,
original article after Acute Coronary Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes William B. White, M.D., Christopher P. Cannon, M.D., Simon R. Heller, M.D., Steven E. Nissen, M.D., Richard M. Bergenstal,
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes. Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013
 Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013 Residual Vascular Risk in People with Diabetes 2 Analyses based on 530,083 participants
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013 Residual Vascular Risk in People with Diabetes 2 Analyses based on 530,083 participants
HEART FAILURE IN WOMEN. Marian Limacher, MD Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Florida
 HEART FAILURE IN WOMEN Marian Limacher, MD Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Florida Outline Epidemiology Clinical Overview Why HF is such a challenge State of the Field Heart Failure Adjudication
HEART FAILURE IN WOMEN Marian Limacher, MD Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Florida Outline Epidemiology Clinical Overview Why HF is such a challenge State of the Field Heart Failure Adjudication
Efficacy of beta-blockers in heart failure patients with atrial fibrillation: An individual patient data meta-analysis
 Efficacy of beta-blockers in heart failure patients with atrial fibrillation: An individual patient data meta-analysis Dipak Kotecha, MD PhD on behalf of the Selection of slides presented at the European
Efficacy of beta-blockers in heart failure patients with atrial fibrillation: An individual patient data meta-analysis Dipak Kotecha, MD PhD on behalf of the Selection of slides presented at the European
Evaluating the Cardiovascular Benefits of Antidiabetic Medications
 Evaluating the Cardiovascular Benefits of Antidiabetic Medications Target Audience: Pharmacists ACPE#: 0202-0000-18-054-L01-P Activity Type: Application-based Disclosures Stuart T. Haines has no relevant
Evaluating the Cardiovascular Benefits of Antidiabetic Medications Target Audience: Pharmacists ACPE#: 0202-0000-18-054-L01-P Activity Type: Application-based Disclosures Stuart T. Haines has no relevant
DPP-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: a new safety issue of a safe drug Nam Hoon Kim
 DPP-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: a new safety issue of a safe drug Nam Hoon Kim Endocrinology of Metabolism, Korea University College of Medicine Conflict of interest disclosure None
DPP-4 inhibitor use and risk of diabetic retinopathy: a new safety issue of a safe drug Nam Hoon Kim Endocrinology of Metabolism, Korea University College of Medicine Conflict of interest disclosure None
Dapagliflozin and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58
 Dapagliflozin and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58 Marc P. Bonaca MD MPH for the DECLARE TIMI 58 Investigators American College of Cardiology March 2019
Dapagliflozin and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58 Marc P. Bonaca MD MPH for the DECLARE TIMI 58 Investigators American College of Cardiology March 2019
Preventive Cardiology Scientific evidence
 Preventive Cardiology Scientific evidence Professor David A Wood Garfield Weston Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine International Centre for Circulatory Health Imperial College London Primary prevention
Preventive Cardiology Scientific evidence Professor David A Wood Garfield Weston Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine International Centre for Circulatory Health Imperial College London Primary prevention
Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
 EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS diabetes Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Introduction People with type 2 diabetes
EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS diabetes Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Introduction People with type 2 diabetes
New evidences in heart failure: the GISSI-HF trial. Aldo P Maggioni, MD ANMCO Research Center Firenze, Italy
 New evidences in heart failure: the GISSI-HF trial Aldo P Maggioni, MD ANMCO Research Center Firenze, Italy % Improving survival in chronic HF and LV systolic dysfunction: 1 year all-cause mortality 20
New evidences in heart failure: the GISSI-HF trial Aldo P Maggioni, MD ANMCO Research Center Firenze, Italy % Improving survival in chronic HF and LV systolic dysfunction: 1 year all-cause mortality 20
Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials
 Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials Rajiv Roy, MD Endocrinology Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group Background Between 1990 and 2010: Incidence of
Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials Rajiv Roy, MD Endocrinology Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group Background Between 1990 and 2010: Incidence of
Clinical and Economic Value of Rivaroxaban in Coronary Artery Disease
 CHRISTOPHER B. GRANGER, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine; Director, Cardiac Care Unit Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC Clinical and Economic Value of Rivaroxaban
CHRISTOPHER B. GRANGER, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine; Director, Cardiac Care Unit Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC Clinical and Economic Value of Rivaroxaban
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula
 T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
7 th Munich Vascular Conference
 7 th Munich Vascular Conference Secondary prevention of major cardiovascular events in patients with CHD or PAD - What can we learn from EUCLID and COMPASS, evaluating Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor and Univ.-Prof.
7 th Munich Vascular Conference Secondary prevention of major cardiovascular events in patients with CHD or PAD - What can we learn from EUCLID and COMPASS, evaluating Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor and Univ.-Prof.
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF INCRETIN-BASED ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC DRUGS RELATIVE TO TREATMENT ALTERNATIVES IN OLDER ADULTS. Mugdha Gokhale.
 CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF INCRETIN-BASED ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC DRUGS RELATIVE TO TREATMENT ALTERNATIVES IN OLDER ADULTS Mugdha Gokhale A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF INCRETIN-BASED ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC DRUGS RELATIVE TO TREATMENT ALTERNATIVES IN OLDER ADULTS Mugdha Gokhale A dissertation submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina
The Changing Landscape of Managing Patients with PAD- Update on the Evidence and Practice of Care in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
 Interventional Cardiology and Cath Labs The Changing Landscape of Managing Patients with PAD- Update on the Evidence and Practice of Care in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Manesh R. Patel MD Chief,
Interventional Cardiology and Cath Labs The Changing Landscape of Managing Patients with PAD- Update on the Evidence and Practice of Care in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Manesh R. Patel MD Chief,
Methods. Background and Objectives STRADIVARIUS
 STRADIVARIUS Effect of on Progression of Atherosclerosis in Patients with Abdominal Obesity and Coronary Artery Disease Steven E. Nissen MD Stephen J. Nicholls MBBS PhD, Kathy Wolski MPH, Josep Rodés-Cabau
STRADIVARIUS Effect of on Progression of Atherosclerosis in Patients with Abdominal Obesity and Coronary Artery Disease Steven E. Nissen MD Stephen J. Nicholls MBBS PhD, Kathy Wolski MPH, Josep Rodés-Cabau
Beta-blockers in Patients with Mid-range Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after AMI Improved Clinical Outcomes
 Beta-blockers in Patients with Mid-range Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after AMI Improved Clinical Outcomes Seung-Jae Joo and other KAMIR-NIH investigators Department of Cardiology, Jeju National
Beta-blockers in Patients with Mid-range Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after AMI Improved Clinical Outcomes Seung-Jae Joo and other KAMIR-NIH investigators Department of Cardiology, Jeju National
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
New Drug Evaluation: lixisenatide injection, subcutaneous
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
What oral antiplatelet therapy would you choose? a) ASA alone b) ASA + Clopidogrel c) ASA + Prasugrel d) ASA + Ticagrelor
 76 year old female Prior Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, Smoking On Hydrochlorothiazide, Atorvastatin New onset chest discomfort; 2 episodes in past 24 hours Heart rate 122/min; BP 170/92 mm Hg, Killip Class
76 year old female Prior Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, Smoking On Hydrochlorothiazide, Atorvastatin New onset chest discomfort; 2 episodes in past 24 hours Heart rate 122/min; BP 170/92 mm Hg, Killip Class
GSK Medicine: Study Number: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials
 Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Louis Kuritzky MD Clinical Assistant Professor Emeritus Department of Community Health and Family Medicine College of Medicine
Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Louis Kuritzky MD Clinical Assistant Professor Emeritus Department of Community Health and Family Medicine College of Medicine
John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam
 Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
2/11/2017. Weighing the Heavy Cardiovascular Burden of Obesity and the Obesity Paradox. Disclosures. Carl J. Lavie, MD, FACC, FACP, FCCP
 Weighing the Heavy Cardiovascular Burden of Obesity and the Obesity Paradox Carl J. Lavie, MD, FACC, FACP, FCCP Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Cardiac Rehabilitation and Preventive Cardiology
Weighing the Heavy Cardiovascular Burden of Obesity and the Obesity Paradox Carl J. Lavie, MD, FACC, FACP, FCCP Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Cardiac Rehabilitation and Preventive Cardiology
PROCORALAN MAKING A STRONG ENTRY TO THE NEW ESC GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEART FAILURE
 Press Release Issued on behalf of Servier Date: June 6, 2012 PROCORALAN MAKING A STRONG ENTRY TO THE NEW ESC GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEART FAILURE The new ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and
Press Release Issued on behalf of Servier Date: June 6, 2012 PROCORALAN MAKING A STRONG ENTRY TO THE NEW ESC GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF HEART FAILURE The new ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
Prasugrel vs. Ticagrelor in ACS/PCI Which one to choose? V. Voudris MD FESC FACC 2 nd Cardiology Division Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center
 Prasugrel vs. Ticagrelor in ACS/PCI Which one to choose? V. Voudris MD FESC FACC 2 nd Cardiology Division Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center Hospitalizations in the U.S. Due to ACS Acute Coronary Syndromes
Prasugrel vs. Ticagrelor in ACS/PCI Which one to choose? V. Voudris MD FESC FACC 2 nd Cardiology Division Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center Hospitalizations in the U.S. Due to ACS Acute Coronary Syndromes
Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes
 Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Radha J. Sarma, MBBS, FACP. FACC. FAHA. FASE Professor of Internal Medicine Western University of Health Sciences. Director, Heart and Vascular Center Western
Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Radha J. Sarma, MBBS, FACP. FACC. FAHA. FASE Professor of Internal Medicine Western University of Health Sciences. Director, Heart and Vascular Center Western
Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk: the role of GLP-1
 Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk: the role of GLP-1 Dr Isidora Kitsou-Mylona, PhD Novo Nordisk Regional Medical Advisor Business Area Africa, Gulf & India Disclaimer I am an employee of Novo Nordisk
Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk: the role of GLP-1 Dr Isidora Kitsou-Mylona, PhD Novo Nordisk Regional Medical Advisor Business Area Africa, Gulf & India Disclaimer I am an employee of Novo Nordisk
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Antiplatelet Therapy in Primary CVD Prevention and Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Καρακώστας Γεώργιος Διευθυντής Καρδιολογικής Κλινικής, Γ.Ν.
 Antiplatelet Therapy in Primary CVD Prevention and Stable Coronary Artery Disease Καρακώστας Γεώργιος Διευθυντής Καρδιολογικής Κλινικής, Γ.Ν.Κιλκίς Primary CVD Prevention A co-ordinated set of actions,
Antiplatelet Therapy in Primary CVD Prevention and Stable Coronary Artery Disease Καρακώστας Γεώργιος Διευθυντής Καρδιολογικής Κλινικής, Γ.Ν.Κιλκίς Primary CVD Prevention A co-ordinated set of actions,
Diabetes and Heart Failure: Challenges and Opportunities
 AHA Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure Webinar Diabetes and Heart Failure: Challenges and Opportunities Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA
AHA Get With The Guidelines-Heart Failure Webinar Diabetes and Heart Failure: Challenges and Opportunities Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA
The JUPITER trial: What does it tell us? Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC January 24, 2009
 The JUPITER trial: What does it tell us? Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC January 24, 2009 Learning Objectives 1. Understand the role of statin therapy in the primary and secondary prevention of stroke 2. Explain
The JUPITER trial: What does it tell us? Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCPC January 24, 2009 Learning Objectives 1. Understand the role of statin therapy in the primary and secondary prevention of stroke 2. Explain
Managing Dyslipidemia in Disclosures. Learning Objectives 03/05/2018. Speaker Disclosures
 Managing Dyslipidemia in 2018 Glen J. Pearson, BSc, BScPhm, PharmD, FCSHP, FCCS Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) Co-Director, Cardiac Transplant Clinic; Associate Chair, Health Research Ethics Boards;
Managing Dyslipidemia in 2018 Glen J. Pearson, BSc, BScPhm, PharmD, FCSHP, FCCS Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) Co-Director, Cardiac Transplant Clinic; Associate Chair, Health Research Ethics Boards;
Lipid Management 2013 Statin Benefit Groups
 Clinical Integration Steering Committee Clinical Integration Chronic Disease Management Work Group Lipid Management 2013 Statin Benefit Groups Approved by Board Chair Signature Name (Please Print) Date
Clinical Integration Steering Committee Clinical Integration Chronic Disease Management Work Group Lipid Management 2013 Statin Benefit Groups Approved by Board Chair Signature Name (Please Print) Date
Diabetic Patients: Current Evidence of Revascularization
 Diabetic Patients: Current Evidence of Revascularization Alexandra J. Lansky, MD Yale University School of Medicine University College of London The Problem with Diabetic Patients Endothelial dysfunction
Diabetic Patients: Current Evidence of Revascularization Alexandra J. Lansky, MD Yale University School of Medicine University College of London The Problem with Diabetic Patients Endothelial dysfunction
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
Is Lower Better for LDL or is there a Sweet Spot
 Is Lower Better for LDL or is there a Sweet Spot ALAN S BROWN MD, FACC FNLA FAHA FASPC DIRECTOR, DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL, PARK RIDGE, ILLINOIS DIRECTOR OF CARDIOLOGY,
Is Lower Better for LDL or is there a Sweet Spot ALAN S BROWN MD, FACC FNLA FAHA FASPC DIRECTOR, DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY ADVOCATE LUTHERAN GENERAL HOSPITAL, PARK RIDGE, ILLINOIS DIRECTOR OF CARDIOLOGY,
Disclosures. Dr. Scirica has also served as a consultant for Lexicon, Arena, Gilead, and Eisai.
 Disclosures Benjamin M. Scirica, MD, MPH, is employed by the TIMI Study Group, which has received research grants from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb,
Disclosures Benjamin M. Scirica, MD, MPH, is employed by the TIMI Study Group, which has received research grants from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb,
