Chapter 2. Standardization of rat model for diabetic nephropathy
|
|
|
- Alfred Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Standardization of rat model for diabetic nephropathy 35
2 2.1 BACKGROUND Several animal models have been developed to elucidate the pathophysiology of DNP and to identify innovative therapies for preventing the progression of nephropathy (Marliss et al., 1983; Schmitz et al., 1992; Velasquez et al., 1995). The animals were either induced with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and were allowed to progress to nephropathy. Since DNP is a chronic disease, the most common challenge faced by several investigators is to maintain the animals in diabetic condition for a longer period of time. Although both mice and rat models are used for studying DNP, rats are generally preferred because of the longer life-span. The rat models generally used for type-2 diabetes induced nephropathy are Goto-Kakizaki and obese ZUCKER rats (Janssen et al., 1999). At the age of 14 weeks, these rats spontaneously develop diabetes and if they are maintained in hyperglycemic state for a time span of 12 months, they progressed to DNP (Popov et al., 2003; Wolf, 2003). However, nodular glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis were not observed in these rats, which are the most prominent pathological features observed in human DNP (Riley et al., 1999). Tesch et al. have found that STZ at a dose of 45, 55 and 60 mg/kg body weight has to be injected in Spontaneously Hypertensive rats (SHR), Sprague Dawley (SD) and Wistar rats respectively for inducing type-1 diabetes by damaging the pancreatic beta cells. The diabetic rats were allowed to progress to diabetic complications by maintaining them in hyperglycemic state (Tesch and Allen, 2007). Several investigators have used high dose of STZ (60 mg/kg body weight) to analyze the effect of various drugs on DNP in a shorter span of time (Tuncdemir and Ozturk, 2011; Makino et al., 2002). However, high dose of STZ is found to have non-specific toxicity on the tubular cells of kidney. So the nephropathy induced using high dose of STZ is considered to be a superimposed result of hyperglycemia and nephrotoxicity (Tay et al., 2005; Kraynak et al., 1995). Simultaneously, in few studies, albuminuria has been induced in Wistar rats even at a low dose (35 mg/kg body weight) of STZ (Kelly et al., 1998; Li et al., 2011). So there is a need for optimization of STZ dosage for inducing DNP in Wistar rats. Davis et al. have predicted that in order to prevent the animals from the nephrotoxicity of STZ, the animals have to be supplemented with long acting insulin injection. Thus the animals are 36
3 maintained in a desirable blood glucose level of mg/dl, inducing DNP (Davis et al., 2003; Tesch and Allen, 2007). This intended us to investigate if insulin supplementation is crucial for inducing DNP in Wistar rats. 37
4 2.2 MATERIALS AND METHODS CHEMICALS AND REAGENTS One Touch-Ultra Glucometer (LifeScan, USA) and long acting insulin glargine injection were procured (Lantus Solostar; Sanofi-Aventis, Germany). Streptozotocin was procured from Sigma-Aldrich, India. The kits for albumin, glucose, and urea nitrogen quantification were purchased from Span diagnostics Ltd., India. All the other reagents which are not specifically mentioned were obtained from Sisco Research Laboratories (SRL) Ltd., India. Primary antibodies against VEGF (anti-vegf, sc-152), ERK (anti- ERK, sc-7383) and NF-κB (anti-nfκb p65, sc-7151) were acquired from Santa Cruz Biotechnolgy, Inc., USA MAINTENANCE OF ANIMALS Eight weeks old male albino Wistar rats weighing g were used for the study. The rats were maintained in standard laboratory conditions and supplied with pellets and water ad libitum in VIT University animal house, Vellore. The animals were cared as per the principles of the Guide for the care and use of experimental animals and the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee approved the entire study (Approval number: VIT/IAEC/II/05/2010) STUDY 1: OPTIMIZATION OF STZ DOSAGE Thirty rats were utilized for this study and were allocated into three groups with ten rats each. The rats in all the three groups were administered i.p with STZ injection, but at three different doses. Group 1: 35 mg/kg body weight; Group 2: 45 mg/kg body weight; Group 3: 60 mg/kg body weight. The rats were kept under fasting for 16 hours before the STZ injection, and 5% sucrose was supplemented for 48 hours after the STZ injection in order to prevent the animals from fatal hypoglycemia (Tesch and Allen, 2007). The rats were observed as such for a period of three months and the mortality rate in each group was calculated. At the end of each month post-stz injection, the blood glucose level was analyzed using glucometer in the tail vein blood. The rats with a 38
5 random blood glucose level of more than 350 mg/dl were considered diabetic and the percentage of diabetic rats in each group were calculated STUDY 2: EFFECT OF INSULIN TREATMENT ON STZ INJECTED ANIMALS EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN Thirty six rats were used for this study and were segregated into three groups with twelve rats each. The groups involved were control rats (Con), diabetic rats that were injected with 45 mg/kg body weight of STZ (STZ), diabetic rats that were supplemented daily with 2 units of long acting insulin (STZ + Ins). At the end of every two weeks, two rats from each group were placed in metabolic cages for urine collection and the urine biochemistry was analyzed on the same day of urine collection BIOCHEMICAL ANALYSES The biochemistry of the collected urine was observed using standard procedures. Albumin content was measured by Bromocresol Green method (Gendler, 1984) and the urea nitrogen content was quantified by the Diacetyl Monoxime method (Crocker, 1967) using the commercially available kits. Creatinine content was analyzed based on Jaffe method followed by Farrell and Bailey (1991) MEASUREMENT OF URINARY ALBUMIN Principle Determination of albumin in serum or urine is based on the binding ability of albumin with the dye 3,3,5,5 -tetrabromo-m-cresol-sulfonephthalein (BCG) in acidic medium (ph 4.2). The binding of albumin with BCG is formed as a blue green colored complex, which could be read at 600 nm (Doumas et al., 1971). Reagents Reagent 1: Reagent 2: BCG reagent Albumin standard (4 g/dl) 39
6 Procedure REAGENT BLANK STANDARD TEST Working reagent (R1) 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml Standard (R2) - 10 µl - Test sample µl After the addition of sample, it was mixed well and incubated at room temperature for 1 min Immediately, the absorbance of both sample and standard were measured at 600 nm Calculation Albumin concentration (gm/dl) = (OD of sample / OD of standard) X MEASUREMENT OF URINARY CREATININE Principle Creatinine present in the biological sample reacts with alkaline picrate, resulting in the formation of an orange colored complex, the intensity of which is measured at 505 nm. Protein interference from the sample is eliminated using sodium lauryl sulphate. A second absorbance reading after acidifying with 30% acetic acid corrects for non-specific chromogen in the sample (Henry et al., 1974). Reagents 1) Reagent 1: Creatinine buffer reagent 2) Reagent 2: Creatinine picrate reagent 3) Reagent 3: Creatinine standard (2 mg/dl) 4) Non-hemolyzed serum 5) Urine diluted (1:100) in saline 40
7 Procedure STANDARD TEST Working reagent 1 ml 1 ml Standard 50 µl - Sample - 50 µl Working reagent was prepared by combining equal volumes of reagent 1 and reagent 2 After the addition of sample, the initial absorbance (A1) at 30 seconds and final absorbance after 120 seconds (A2) were measured for both the sample and standard Calculation ΔA = A2 A1 Creatinine concentration (mg/dl) = (ΔAT / ΔAS) x MEASUREMENT OF URINARY UREA NITROGEN Principle In alkaline medium, urea is broken down into ammonia and carbon dioxide because of the action of urease enzyme. Ammonia liberated reacts with hypochlorite and salicylate to form dicarboxy-indophenol, which gives the color. The intensity of the color produced is directly proportional to the concentration of the urea present in the sample (Fawcett et al., 1960). Reagents 1) Reagent 1: Enzyme reagent 2) Reagent 2: Chromogen reagent 3) Reagent 3: Urea standard (40 mg/dl) 4) Non-hemolyzed serum 41
8 5) Urine diluted (1:100) in saline 6) Working reagent : Add 10 ml of distilled water to the vial containing the enzyme Procedure REAGENT BLANK STANDARD TEST Working reagent 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml Standard - 10 µl - Sample µl Mix well and incubate at 37 o C for 5 min. Reagent 2 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml It was then mixed and incubated at 37 o C for 5 min After incubation, the absorbance of both the standard and sample were measured at 600 nm ( nm) Calculation Urea concentration (mg/dl) = (OD of sample / OD of standard) x HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS Four rats from each group were sacrificed at the end of 20 and 28 weeks under mild anesthesia. Kidneys were removed carefully without any damage, washed with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), weighed and fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. The tissues were dehydrated sequentially with increasing concentrations of ethanol (70%, 80%, 90% and 100%) for 1 hour each. The tissues were treated with 100% xylene for 30 min to remove the ethanol. Paraffin wax was added to the sample and was embedded by incubating at 58 C for 2 hours. The paraffin blocks were brought back to room temperature before sectioning. Four micron sections were cut using the microtome and were mounted on glass slides. 42
9 Before staining, the slides were deparaffinised by incubating in 100% xylene twice for 3 min each. The slides were washed with decreasing concentration of ethanol (100%, 95%, 80% and 70%) for 3 min each. The slides were rehydrated by immersing the slides in distilled H 2 O for 5 min. The slides were stained with Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E), Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) and Masson Trichrome stains for histopathological analyses. The sections were then studied for the evidence of pathological changes that are observed in human diabetic nephropathy IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS Paraffin sections (4 μm thick) were cut, mounted on silanized slides, dewaxed in xylene and rehydrated in graded alcohol. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by incubating in 3% H 2 O 2 for 15 min. After washing with phosphate buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20, the slides were incubated overnight at 4ºC with primary antibodies specific for VEGF, ERK and NF-Kappa B at 1:200 dilution. The immunoreactivity was performed by incubating at room temperature for 30 min with horseradish peroxidase conjugated goat-anti-rabbit IgG antibody. 3,3 -diaminobenzidine (Dako) was used as the chromogen for detecting the protein expression. Slides were counterstained with hematoxylin, rinsed in tap water, dehydrated, placed in xylene, and mounted. The percentage distribution and the intensity of expression of protein expression were analyzed by a semi-quantitative analysis based on the description by Indian Society of Nephrology glomeruli in the renal cortex were observed for each sample. The number of glomeruli and tubules with positive protein expression was counted and the percentage distribution was calculated. This was examined by two different pathologists who were blinded about the samples STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The data were analyzed on Graph Pad Prism 5.01 software and expressed as means ± S.D (n=4). Statistical analysis was performed by Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test to compare the three groups with respect to every month. The results were considered statistically significant, if p <
10 2.3 RESULTS After 3 months Dose of STZ (mg/kg body weight) Mortality (%) % of rats with blood glucose (> 350 mg/dl) Table 2.1: Optimization of STZ dosage The values represent the percentage mortality and rats with blood glucose of more than 350 mg/dl at the end of three months for different doses of Streptozotocin. In this preliminary study, the mortality rate was found to be very high (50%) in rats that were induced with 60 mg/kg body weight of STZ. This might have made various investigators to restrict their study period to 1-3 months (Ohtake et al., 2007; Tuncdemir and Ozturk, 2011). Simultaneously, in rats that were induced with a low dose of STZ i.e. 35 mg/kg body weight, the percentage of rats with hyperglycemia is only 33.3 though there is no mortality. However, more than 90% of the rats were maintained in hyperglycemic state with only 8.4% mortality (Table 2.1), when the rats were induced with 45 mg/kg body of STZ. This showed that 45 mg/kg body weight of STZ is more appropriate for maintaining the hyperglycemic state with less mortality, thus inducing chronic diabetic nephropathy in rats. 44
11 Urinary parameters Month 4 Month 7 Con STZ STZ + Ins Con STZ STZ + Ins Volume (ml/12 h) 3.2 ± ± 2.2 a 14.9 ± 0.8 b, * 4.3 ± ± 1.3 a 18 ± 1.3 b,n Albumin (mg/24 h) 5.4 ± ± 2.2 a 23.1 ± 1.6 c, * 4.8 ± ± 2.4 a 32 ± 2.2 b,n Creatinine (mg/dl) 1.4 ± ± 0.6 ± 0.01 a 0.02 a, ** 1.3 ± ± 0.4 ± 0.03 a 0.03 a,n Urea nitrogen (mg/dl) 9.6 ± ± 0.3 a 3.9 ± 0.4 a, ** 9.5 ± ± 0.2 a 3.6 ± 0.3 a,n Table 2.2: Effect of insulin supplementation on urine biochemistry Values represent the mean ± standard deviation of the samples (n=4). Significant difference between Con Vs STZ groups and Con Vs STZ + Ins groups: c p 0.05; b p 0.01; a p Significant difference between STZ and STZ + Ins: * p 0.05; ** p 0.01; *** p 0.001, n- not significant EFFECTS OF INSULIN INJECTION ON POLYURIA The most common symptoms of diabetes are polyuria and polydipsia. Significant increase in urine volume was observed in both diabetic rats (p< 0.001) and diabetic rats that were supplemented with insulin (p< 0.01) compared to that of control (Table 2.2). However, there was significant difference between these two groups till the end of four months. 45
12 2.3.2 EFFECT OF INSULIN INJECTION ON THE BIOMARKER OF DNP Albuminuria is the most common biomarker used for diagnosing DNP. In this study, significant increase in the urine albumin level (p< 0.001) in rats injected with STZ (Table 2.2) was observed. However, in the diabetic rats that were treated with insulin injection, significant increase in the urine albumin level (p< 0.01) was observed only from the fifth month. Simultaneously, no significant difference was observed in the urine albumin level beyond fifth month in both the STZ and STZ + Ins groups which showed that insulin supplementation could delay the progression of DNP EFFECT OF INSULIN TREATMENT ON KIDNEY DAMAGE The kidney damage is revealed by a significant decrease in the level of creatinine and urea nitrogen content in urine and DNP is no exception. In this study, significant decrease (p< 0.001) in both creatinine and urea nitrogen content was observed in urine which confirmed that the rats in both the STZ and STZ + Ins groups have progressed to DNP. Further, there was significant difference (p< 0.01) in the urine urea nitrogen and creatinine content between both the groups till the end of fifth month, which indicated that the insulin supplementation had delayed the progression of DNP (Table 2.2) PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN DIABETIC RATS PROGRESSING TO DNP On kidney histological observation, the diabetic rats showed evidence for glomerular basement membrane thickening, mesangial expansion and proliferation in more than 25% of the glomeruli at the end of 20 weeks. But there was no evidence for nodular glomerulosclerosis. Tubules showed evidence for protein re-absorption droplets which confirmed proteinuria and glycosuria in 25% of the glomeruli. On the other hand, the changes were not comparable in diabetic rats treated with insulin. At the end of 28 weeks, the diabetic rats revealed evidence for nodular glomerulosclerosis in the mesangium. Mesangial nodules were also found to be PAS positive and the Masson Trichrome stain confirmed that the mesangial nodules were not comprised of collagen (Figure 2.1). Tubules showed evidence for proteinuria and glycosuria in more than 50% of the glomeruli. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis was also observed in the blood vessels. However, interstitial fibrosis was not evident even at the end of the study. In diabetic rats 46
13 that were treated with insulin, though there was evidence for mild mesangial expansion, well formed PAS positive mesangial nodules were conspicuously absent with no change in glomerular basement membrane. The tubules revealed evidence for glycosuria and protein re-absorption droplets in 25% of the cortical surface examined. Figure 2.1: Kidney histological observation Figure showing the kidney histological images of control (Con), diabetic (STZ) and diabetic rats treated with insulin (STZ + Ins) at the end of 28 weeks using H&E, PAS and Masson Trichrome staining (Magnification x400). 47
14 Figure 2.2: Immunohistochemical observation of VEGF, ERK and NF-κB Figure showing the immunohistochemical expression of VEGF, ERK and NF-κB in control (Con), diabetic (STZ), diabetic rats treated with insulin (STZ + Ins) at the end of 28 weeks (Magnification x400). 48
15 2.3.5 ALTERATION OF PROTEIN EXPRESSIONS THAT MEDIATE THE PROGRESSION OF DNP ERK and NF-κB were expressed in the cytoplasm and nucleus of occasional tubules (< 5% of the cortical surface) in the control group. In diabetic rats, there was a marked increase in the expression (> 50%) of both these markers in the proximal convoluted tubules in terms of intensity and distribution (Figure 2.2). Further, intense expression for ERK was observed in the glomerular mesangium while NF-κB was not expressed in the glomerulus. The expression of both ERK and NF-κB was observed mainly in the cortical region with no expression in the medullary region. In diabetic rats treated with insulin, though there was an increase in the expression of both the proteins, the increase was not that significant (< 25%). In diabetic rats, significant increase in the expression (> 50%) of VEGF was observed in the proximal convoluted tubule. However, in diabetic rats treated with insulin, the expression was very focal in distribution (< 5%) with marked reduction in intensity. 49
16 2.4 DISCUSSION Though several pathophysiological mechanisms have been predicted for DNP, hyperglycemia is considered to play the lead role in setting the stage for kidney damage in diabetic patients (Rosario and Prabhakar, 2006). So, it was predicted that for inducing DNP in animal models, the animals have to be maintained in the hyperglycemic condition. STZ, which is well known for inducing diabetes, has been used at different doses for inducing DNP in animal models (Tesch and Allen, 2007). But, there are few drawbacks in using STZ for inducing DNP. Low dose of STZ was not sufficient to induce nephropathy and at higher dosage, the animals encountered nephrotoxicity rather than nephropathy (Kraynak et al., 1995; Kelly et al., 1998). Since it was found that nephropathy could be induced only at high dose of STZ, it was predicted that the mortality in diabetic animals could be reduced by supplementing insulin injections (Tesch and Allen, 2007; Davis et al., 2003). But insulin supplementation could not be utilized in all situations. When the effect of a drug on nephropathy has to be studied, insulin supplementation might hamper the results. Further, the chance for insulin to interact with the drug and with the metabolism is higher, thus confounding the outcome. Since insulin and the drug of interest are supplemented on a daily basis, the mechanistic biological activity of the drug cannot be elucidated. This made us to investigate whether insulin supplementation is essential for inducing nephropathy in diabetic rats. In our study, the changes in urine biochemistry such as albumin, creatinine and urea nitrogen content were observed at the end of every month after the induction of diabetes. It was found that the urinary biochemical changes observed at the end of fourth month in diabetic rats were observed only at the end of seven months in diabetic rats supplemented with insulin (Table 2.2). As speculated, insulin supplementation delayed the progression of nephropathy. This was further substantiated by the histological and immunohistochemical examinations of the kidney. At the end of seven months, the diabetic rats showed evidence for glomerular basement membrane thickening, nodular glomerulosclerosis, mesangial expansion and tubular changes such as proteinuria and glycosuria (Figure 2.1). This confirmed that the animal model established showed all the prominent histological changes that are observed in human diabetic nephropathy. 50
17 However, in diabetic rats supplemented with insulin, though there were severe tubular changes such as proteinuria and glycosuria, the glomerular changes such as mesangial expansion and basement membrane thickening were less prominent. In spite of the hyperglycemic state, which was maintained by insulin supplementation, the rats did not show evidence for all the pathological changes even at the end of seven months. In hyperglycemic condition, there is evidence for the formation of advanced glycation end product in diabetic patients. AGE products are found to activate several cytokines and growth factors including TGF-β and VEGF in the tubules. The upregulation of these growth factors enhances ERK activation, thus aggravating the progression of DNP (Cellier et al., 2003). VEGF has the ability to stimulate collagen and fibronectin expression, causing mesangial expansion and proteinuria (Hovind et al., 2000). Since inflammation has been proven to mediate the progression of DNP, treatments inhibiting the upregulation of VEGF and ERK have been shown to improve renal damage in diabetic patients (Chen et al., 2011). In our study, more than 50% increase in the expression of both VEGF and ERK was observed in diabetic rats (Figure 2.2), which evinced that the diabetic rats have encountered chronic nephropathy. However, in diabetic rats supplemented with insulin, only a 25% increase in the expression of ERK and NF-Kappa was observed (Figure 2.2). The results supported the urinary biochemical changes such as albumin, creatinine and urea nitrogen observed in our study. Since NF-κB regulates the expression of several cytokines and matrix proteins involved in inflammation, it is considered to play a major role in mediating renal injury (Guijarro and Egido, 2001). In animal models of nephropathy, an increased expression of NF-κB has been reported in the tubules and glomeruli (Gomez-Garre et al., 2001). However, in our study, though there was an increased expression of NF-κB in the tubules, the increase was found to be insignificant in the glomeruli. This suggests that NF-κB may not play a direct role in mesangial injury in STZ injected diabetic rats. 51
18 2.5 CONCLUSION From the results, we conclude that there is no need of insulin supplementation for inducing DNP, when the rats are induced with an optimal dose of 45 mg/kg body weight of STZ. Further, the studies that are focused on the therapeutic targets for DNP should maintain the diabetic animals for a minimum period of three months for the animals to attain the pathological changes pertaining to the early stages of DNP. Once the rat model for DNP was established, the query for investigation was that, What is the level of expression of CD36 in different pathological stages of DNP? 52
Effect of long acting insulin supplementation on diabetic nephropathy in Wistar rats
 Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol.50, December 2012 pp. 867-874 Effect of long acting insulin supplementation on diabetic nephropathy in Wistar rats Shiju Thomas Michael a, Rajesh Nachiappa Ganesh
Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol.50, December 2012 pp. 867-874 Effect of long acting insulin supplementation on diabetic nephropathy in Wistar rats Shiju Thomas Michael a, Rajesh Nachiappa Ganesh
Diabetic Nephropathy in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) Rats
 The Open Diabetes Journal, 2011, 4, 45-49 45 Diabetic Nephropathy in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) Rats Takeshi Ohta * and Tomohiko Sasase Open Access Biological/Pharmacological Research Laboratories,
The Open Diabetes Journal, 2011, 4, 45-49 45 Diabetic Nephropathy in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) Rats Takeshi Ohta * and Tomohiko Sasase Open Access Biological/Pharmacological Research Laboratories,
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Ordering Physician. Collected REVISED REPORT. Performed. IgG IF, Renal MCR. Lambda IF, Renal MCR. C1q IF, Renal. MCR Albumin IF, Renal MCR
 RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats
 Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats Stenio Fiorelli¹, Camille F França¹, Carlos Alberto Basílio
Oxidative Stress Unify the Pathophysiological Mechanism of Experimental Hypertension and Diabetes of Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke-Prone Rats Stenio Fiorelli¹, Camille F França¹, Carlos Alberto Basílio
RENOPROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF COMBINED ALISKIREN AND VALSARTAN IN PROGRESSIVE DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY IN RATS
 Research Article RENOPROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF COMBINED ALISKIREN AND VALSARTAN IN PROGRESSIVE DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY IN RATS Hemanth Kumar. Nyathani, Prashanth. Srirangam*, Vidya Sagar Jinugu Vaagdevi College
Research Article RENOPROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF COMBINED ALISKIREN AND VALSARTAN IN PROGRESSIVE DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY IN RATS Hemanth Kumar. Nyathani, Prashanth. Srirangam*, Vidya Sagar Jinugu Vaagdevi College
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
HRP cytochemistry. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany
 HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Relationship between renal injury and the antagonistic roles of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2
 Relationship between renal injury and the antagonistic roles of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2 C. Ma, H. Xin, X.-Y. Jiang, Y.-X. Wang and Y.-S. Zhang Key Laboratory of Animal Physiology and
Relationship between renal injury and the antagonistic roles of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2 C. Ma, H. Xin, X.-Y. Jiang, Y.-X. Wang and Y.-S. Zhang Key Laboratory of Animal Physiology and
Estimation of Serum Urea. BCH472 [Practical] 1
![Estimation of Serum Urea. BCH472 [Practical] 1 Estimation of Serum Urea. BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/86/93847865.jpg) Estimation of Serum Urea BCH472 [Practical] 1 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory product of protein metabolism. It is formed by urea cycle
Estimation of Serum Urea BCH472 [Practical] 1 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory product of protein metabolism. It is formed by urea cycle
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
BCH 447. Estimation of Serum Urea
 BCH 447 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 Objective: Estimation of Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum sample. 2 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory
BCH 447 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 Objective: Estimation of Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum sample. 2 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory
Appendix 1. A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for
 Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model. Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications. SDT fatty rats. SDT fatty rats
 Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model rats Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications rats Background and Origin In 24, Dr. Masuyama and Dr. Shinohara (Research Laboratories of Torii Pharmaceutical Co.,
Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model rats Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications rats Background and Origin In 24, Dr. Masuyama and Dr. Shinohara (Research Laboratories of Torii Pharmaceutical Co.,
Estimation of Serum Urea
 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory product of protein metabolism. It is formed by urea cycle in the liver from
Estimation of Serum Urea 1 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory product of protein metabolism. It is formed by urea cycle in the liver from
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University
 Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on
 Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1
 BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS Glucose Assay Kit Manual Catalog #: 5611-01 BIOO Scientific Corp. 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Procedure Overview... 1 Required Materials
BIOO RESEARCH PRODUCTS Glucose Assay Kit Manual Catalog #: 5611-01 BIOO Scientific Corp. 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Procedure Overview... 1 Required Materials
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM. The cases we will cover are:
 THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
THE URINARY SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the urinary system. Diseases of the kidney can be broken down into diseases that affect the glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood
CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT OF UREA AND URIC ACID IN BLOOD SERUM
 79 CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT OF UREA AND URIC ACID IN BLOOD SERUM 5.1 INTRODUCTION Urea and Uric acid are the metabolic nitrogenous wastes present in the body that can be measured in blood and urine. Serum
79 CHAPTER 5 MEASUREMENT OF UREA AND URIC ACID IN BLOOD SERUM 5.1 INTRODUCTION Urea and Uric acid are the metabolic nitrogenous wastes present in the body that can be measured in blood and urine. Serum
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
Urea Nitrogen (BUN) detection Kit
 K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Urea Nitrogen (BUN) detection Kit For the quantitative determination of urea nitrogen in saliva and TCM Cat. No. KT-747 For Research Use Only.
K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Urea Nitrogen (BUN) detection Kit For the quantitative determination of urea nitrogen in saliva and TCM Cat. No. KT-747 For Research Use Only.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Diabetic Nephropathy. Introduction/Clinical Setting. Pathologic Findings Light Microscopy. J. Charles Jennette
 12 Diabetic Nephropathy J. Charles Jennette Introduction/Clinical Setting Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome in a patient with diabetes mellitus that is characterized by persistent albuminuria,
12 Diabetic Nephropathy J. Charles Jennette Introduction/Clinical Setting Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome in a patient with diabetes mellitus that is characterized by persistent albuminuria,
Glucose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 03. Intended for research use only.
 Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1648 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1648 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance. BCH472 [Practical] 1
![Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance. BCH472 [Practical] 1 Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance. BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/73/68933269.jpg) Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance BCH472 [Practical] 1 -Kidney functions: - The kidneys serve three essential functions: 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic
Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance BCH472 [Practical] 1 -Kidney functions: - The kidneys serve three essential functions: 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy
 Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and inflammatory factors of rats with diabetic nephropathy J. Guan 1,2, L. Long 1, Y.-Q. Chen 1, Y. Yin 1, L. Li 1, C.-X. Zhang 1, L. Deng 1 and L.-H. Tian
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
-26- MATERIALS AND METHODS
 -26- MATERIALS AND METHODS The pollutant : Sevin (1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate) was used at a concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/l. At these concentrations, the insecticide was completely soluble in water.
-26- MATERIALS AND METHODS The pollutant : Sevin (1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate) was used at a concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/l. At these concentrations, the insecticide was completely soluble in water.
SODIUM TUNGSTATE; EFFECT OF SODIUM TUNGSTATE ON KIDNEY OF STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RABBIT.
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4256 1. MBBS, DCP, M.Phil. Assistant Professor, Multan Medical and Dental College Multan. 2. MBBS, M.Phil. Associate Professor, 3. MBBS, M.Phil. Assistant
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4256 1. MBBS, DCP, M.Phil. Assistant Professor, Multan Medical and Dental College Multan. 2. MBBS, M.Phil. Associate Professor, 3. MBBS, M.Phil. Assistant
Urinary Collagen IV EIA
 Urinary Collagen IV EIA Enzyme Immunoassay Instructions for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures ACTIF 3-27-3 Kyodo, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 1560052 JAPAN TEL&FAX: +81(0)3-6413-1860
Urinary Collagen IV EIA Enzyme Immunoassay Instructions for Use FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures ACTIF 3-27-3 Kyodo, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 1560052 JAPAN TEL&FAX: +81(0)3-6413-1860
Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy. Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI
 Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI Group Members Mount Sinai: Phenotyping, Molecular Pathology & Validation Erwin
Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI Group Members Mount Sinai: Phenotyping, Molecular Pathology & Validation Erwin
Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
Reagent Set DAS ELISA, Alkaline phosphatase label SRA 22001, SRA 23203, SRA 27703, SRA & SRA ToRSV, ArMV, GFLV, AnFBV and PDV
 List of contents Lot number Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
List of contents Lot number Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Effects of Triptergium Glycosides on Expressions of MCP- 1 and CTGF in Rats with Early Diabetic Nephropathy
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research January 2016; 15 (1): 55-64 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research January 2016; 15 (1): 55-64 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report:
 Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Report on Pathology. Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques
 Report on Pathology Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques Prepared for: Client Name Client Address January 1, 2013 Prepared by: Charter Preclinical Services 21 Main St.,
Report on Pathology Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques Prepared for: Client Name Client Address January 1, 2013 Prepared by: Charter Preclinical Services 21 Main St.,
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο
 Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Σ. ΓΟΥΜΕΝΟΣ Νεφρολογικό και Μεταμοσχευτικό Κέντρο Πανεπιστημιακό Νοσοκομείο Πατρών Causes of chronic
Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Σ. ΓΟΥΜΕΝΟΣ Νεφρολογικό και Μεταμοσχευτικό Κέντρο Πανεπιστημιακό Νοσοκομείο Πατρών Causes of chronic
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
 Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
Quantitative protein estimation of Urine
 Quantitative protein estimation of Urine 1 In a healthy renal and urinary tract system, the urine contains no protein or only trace amounts. The presence of increased amounts of protein in the urine can
Quantitative protein estimation of Urine 1 In a healthy renal and urinary tract system, the urine contains no protein or only trace amounts. The presence of increased amounts of protein in the urine can
BCH472 [Practical] 1
![BCH472 [Practical] 1 BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/90/103504023.jpg) BCH472 [Practical] 1 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic products and toxins from the blood and excreting them through the urine. 2. They regulate the body s fluid status, electrolyte balance,
BCH472 [Practical] 1 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic products and toxins from the blood and excreting them through the urine. 2. They regulate the body s fluid status, electrolyte balance,
References. Plasma renin activity (PRA) PRA was measured by a radioimmunoassay kit (Wallac, Tokyo, Japan).
 Detailed Methods Experiment I enos / mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, USA). C57BL/6J mice on the same genetic background were purchased from KBT Oriental (Hamamatsu, Japan). Eleven-week-old
Detailed Methods Experiment I enos / mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, USA). C57BL/6J mice on the same genetic background were purchased from KBT Oriental (Hamamatsu, Japan). Eleven-week-old
SIV p27 Antigen ELISA Catalog Number:
 INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is for research use only and is not intended for in vitro diagnostic use. The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is an enzyme linked immunoassay used to detect
INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is for research use only and is not intended for in vitro diagnostic use. The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is an enzyme linked immunoassay used to detect
Longitudinal Validation Study: Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes as a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brown Norway Rats
 Longitudinal Validation Study: Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes as a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brown Norway Rats Robin Dean, Robert Sukhu, Leslie Nemeth, Qin Zhang, Isaac Hakim, Ali Ebramhimnejad,
Longitudinal Validation Study: Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes as a Model of Diabetic Retinopathy in Brown Norway Rats Robin Dean, Robert Sukhu, Leslie Nemeth, Qin Zhang, Isaac Hakim, Ali Ebramhimnejad,
Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways
![Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways](/thumbs/96/128474991.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
MATERIALS AND METHOD
 Chapter - 3 Histomorphology, Ecology and Biochemistry of leaf galls of Ficus glomerata Roxb. induced by Pauropsylla depressa Crawford. MATERIALS AND METHOD Field observations were confined in Saharanpur
Chapter - 3 Histomorphology, Ecology and Biochemistry of leaf galls of Ficus glomerata Roxb. induced by Pauropsylla depressa Crawford. MATERIALS AND METHOD Field observations were confined in Saharanpur
complemented with SipA ( SipA/pSipA) or SL1344 WT for 48 hours, after which the
 P-gp expression (% of control) 12 1 8 6 4 2 * * Untreated SipA SipA/pSipA WT Supplementary Figure 1. SipA modulates the expression of P-gp in healthy murine intestinal epithelium in vivo. Salmonella Typhimurium
P-gp expression (% of control) 12 1 8 6 4 2 * * Untreated SipA SipA/pSipA WT Supplementary Figure 1. SipA modulates the expression of P-gp in healthy murine intestinal epithelium in vivo. Salmonella Typhimurium
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 04. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Human Creatinine Urinary Detection Kit
 Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA
 Practical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA A practical manual Tamas Csont, MD, PhD Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 1 BACKGROUND
Practical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA A practical manual Tamas Csont, MD, PhD Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 1 BACKGROUND
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Blood Urea Nitrogen Enzymatic Kit Manual Catalog #:
 Blood Urea Nitrogen Enzymatic Kit Manual Catalog #: 5602-01 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 Product Description... 2 Procedure Overview... 2 Kit Contents, Storage and Shelf Life... 3 Required
Blood Urea Nitrogen Enzymatic Kit Manual Catalog #: 5602-01 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 Product Description... 2 Procedure Overview... 2 Kit Contents, Storage and Shelf Life... 3 Required
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents. Amal Alamri
 Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing Low-vacuum scanning electron microscope
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2017 Vol. 9 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2017 Vol. 9 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Examination of the light microscopic slide of renal biopsy specimens by utilizing
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
CASE 3 AN UNUSUAL CASE OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
 CASE 3 AN UNUSUAL CASE OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME Dr Seethalekshmy N.V., Dr.Annie Jojo, Dr Hiran K.R., Amrita institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala Case history 34 year old gentleman Nephrotic range
CASE 3 AN UNUSUAL CASE OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME Dr Seethalekshmy N.V., Dr.Annie Jojo, Dr Hiran K.R., Amrita institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala Case history 34 year old gentleman Nephrotic range
associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences with preventive measures
 Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Increased oxidative and glyco-oxidative stress has
 Overexpression of Cu 2 /Zn 2 Superoxide Dismutase Protects Against Early Diabetic Glomerular Injury in Transgenic Mice Patricia A. Craven, 1 Mona F. Melhem, 2 Stephen L. Phillips, 3 and Frederick R. DeRubertis
Overexpression of Cu 2 /Zn 2 Superoxide Dismutase Protects Against Early Diabetic Glomerular Injury in Transgenic Mice Patricia A. Craven, 1 Mona F. Melhem, 2 Stephen L. Phillips, 3 and Frederick R. DeRubertis
HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA Catalog Number:
 INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA is supplied for research purposes only. It is not intended for use in the diagnosis or prognosis of disease, or for screening and may not be used as a
INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA is supplied for research purposes only. It is not intended for use in the diagnosis or prognosis of disease, or for screening and may not be used as a
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
CHAPTER 2 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
 EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS * D Ramakrishna 1, G Vidyasagar 2, K Pavan Kumar 1, I Madhusudhana Reddy 3, VSS S Gupta Atyam 4 1
EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS * D Ramakrishna 1, G Vidyasagar 2, K Pavan Kumar 1, I Madhusudhana Reddy 3, VSS S Gupta Atyam 4 1
Uric acid correlates with the severity of histopathological parameters in IgA nephropathy
 NDT Advance Access published November 30, 2004 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2004) 1 of 7 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh584 Original Article Uric acid correlates with the severity of histopathological parameters in IgA
NDT Advance Access published November 30, 2004 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2004) 1 of 7 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh584 Original Article Uric acid correlates with the severity of histopathological parameters in IgA
Severity of tubulointerstitial inflammation and prognosis in immunoglobulin A nephropathy
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology original article Severity of tubulointerstitial inflammation and prognosis in immunoglobulin A nephropathy JM Myllymäki 1,
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology original article Severity of tubulointerstitial inflammation and prognosis in immunoglobulin A nephropathy JM Myllymäki 1,
HBeAg and HBeAg Ab ELISA Kit
 HBeAg and HBeAg Ab ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0290 96 assays Version: 17 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3
HBeAg and HBeAg Ab ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0290 96 assays Version: 17 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Pathology of endocrine pancreas. By: Shifaa Alqa qa
 Pathology of endocrine pancreas By: Shifaa Alqa qa major cell types: Beta ----- insulin Alpha ----- glucagon Delta ----- somatostatin PP (pancreatic polypeptide) cells ------ VIP DIABETES MELLITUS Normal
Pathology of endocrine pancreas By: Shifaa Alqa qa major cell types: Beta ----- insulin Alpha ----- glucagon Delta ----- somatostatin PP (pancreatic polypeptide) cells ------ VIP DIABETES MELLITUS Normal
GLP-2 ELISA. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples.
 GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
Date... Name... Group... Urine sample (Tube No 2)
 Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Glucose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 07. Intended for research use only.
 Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0831 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0831 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
Hosta virus X ELISA KIT
 Hosta virus X ELISA KIT Cat. No.:DEIA9256 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use The Hosta virus X ELISA KIT is used to detect HVX in both leaves and roots of hosta plants. Reagents And Materials Provided 1. Capture
Hosta virus X ELISA KIT Cat. No.:DEIA9256 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use The Hosta virus X ELISA KIT is used to detect HVX in both leaves and roots of hosta plants. Reagents And Materials Provided 1. Capture
Fructose-6-Phosphate Colorimetric Assay Kit
 Fructose-6-Phosphate Colorimetric Assay Kit Catalog No. KM0060 Detection and Quantification of Fructose-6-Phosphate Concentrations in Biological Samples. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Fructose-6-Phosphate Colorimetric Assay Kit Catalog No. KM0060 Detection and Quantification of Fructose-6-Phosphate Concentrations in Biological Samples. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
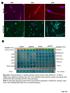 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
