The interest in microalbuminuria originated. Cardiovascular Implications of Albuminuria. R e v i e w P a p e r.
|
|
|
- Steven Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 R e v i e w P a p e r Cardiovascular Implications of Albuminuria Katherine R. Tuttle, MD Microalbuminuria is a major independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) events in persons with diabetes or hypertension, the general population, and persons with known CVD. Although microalbuminuria is a stronger risk factor in men, women with increased albuminuria levels are also at a higher risk of CVD. Microalbuminuria is an indicator of generalized endothelial injury, a hallmark of systemic atherosclerosis. Treatments that decrease albuminuria, particularly agents that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system, reduce CVD risk in various populations, including those with and without diabetes or hypertension. Whether albuminuria should be a treatment target for CVD is not yet proven. Nevertheless, the measurement of albuminuria is clinically useful to identify high-risk individuals who should receive intensive risk factor management based on current treatment guidelines. (J Clin Hypertens. 2004;6(11 suppl 3):13 17) 2004 Le Jacq Communications, Inc. From the Research Department, the Heart Institute of Spokane and Sacred Heart Medical Center, Spokane, WA Address for correspondence: Katherine R. Tuttle, MD, Research Department, The Heart Institute of Spokane, 122 West 7th Avenue, Suite 230, Spokane, WA ktuttle@this.org ID: 4234 The interest in microalbuminuria originated with the observation that it was a marker that could be used to identify the subset of persons with diabetes who had nephropathy and were at risk of a progressive loss of renal function. Approximately 30% of persons with type 1 diabetes and 40% of those with type 2 diabetes have microalbuminuria. However, in patients with type 2 diabetes, microalbuminuria is actually a stronger predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD) than of renal outcomes (loss of glomerular filtration rate, end-stage renal disease, or death). 1 The risk of CVD death has been reported to be increased by 100% 150%, depending on the level of increase in albuminuria. 1 Microalbuminuria is also common in hypertension, occurring in about 25% of patients. Like type 2 diabetes, albuminuria is a stronger predictor of CVD than of renal outcomes in hypertension, whereas in type 1 diabetes, renal outcomes predominates as a predictor of risk (Table I). In type 2 diabetes, microalbuminuria doubles the risk of major CVD events and mortality independent of conventional risk factors (Figure 1). 2 In hypertension, most ischemic heart disease events occur in the subset of patients who have microalbuminuria (Figure 2). 3 The prevalence of microalbuminuria is about 10% in the general population. As for high-risk populations with diabetes and/or hypertension, increased levels of albuminuria also predict a marked increased risk of CVD events and deaths in the general population (Figure 3). 4,5 Microalbuminuria is associated with the metabolic syndrome, which includes the traits of abdominal obesity, glucose intolerance/hyperinsulinemia/insulin resistance, dyslipidemia (increased triglycerides/decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol), and hypertension. With increasing numbers of metabolic syndrome traits, the risk of developing microalbuminuria increases steadily. 6,7 Accordingly, the prevalence of microalbuminuria increases progressively across the spectrum from normal glucose tolerance (10%) to impaired glucose tolerance (25%), to overt type 2 diabetes (40%). This increasing prevalence parallels increasing rates of CVD events, including myocardial infarction, left ventricular hypertrophy, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, and death across the metabolic syndrome spectrum. It is important to SUPPL. 3 VOL. VI NO. XI NOVEMBER 2004 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION 13
2 Table I. Prevalence and Predictive Value of Microalbuminuria in Diabetes and Hypertension PREVALENCE PREDICTIVE VALUE FOR OUTCOME MEAN (RANGE) % CARDIOVASCULAR RENAL Hypertension 25 (5 40) ++ + Type 2 DM 40 (10 80) ++ + Type 1 DM 30 (5 50) + ++ DM=diabetes mellitus Niskanen et al., 1993 Neil et al., 1993 Stehouwer et al., 1990 Stiegler et al., 1992 Patrick et al., 1990 Subtotal Macleod et al., 1995 Total Figure 1. Association of microalbuminuria and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in type 2 diabetes. Odds ratios of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria vs. normoalbuminuria. Reprinted with permission from Arch Intern Med. 1997;157: Copyright 1997, American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Proportion without ischemic heart disease (%) Normoalbuminuria Microalbuminuria p<0.003 Relative risk Years Figure 2. Survival without ischemic heart disease in hypertensive subjects by albuminuria status. Reprinted with permission from Hypertension. 2000;35: recognize that microalbuminuria is an independent contributor to these outcomes in the various populations studied. The levels of albuminuria that predict CVD are lower than those that have traditionally been used to predict the risk of losing kidney function in diabetes (i.e., a urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) >30 mg/g). Levels of albuminuria increase progressively with the severity of coronary artery disease (Figure 4). 8 In a study of people undergoing elective coronary angiography, the average ACR was 10 mg/g in patients with normal arteries and 31 mg/g in individuals with severe (generally 3- vessel) coronary artery disease. 8 ACR values were intermediate in patients with less severe degrees of coronary artery disease. Similarly, the risk of CVD events is increased at levels of albuminuria traditionally considered to be within the normal range. 9 Although still a matter of study and debate, ACR levels >15 mg/g can be considered indicative of increased CVD risk. Some studies have suggested that the ACR cut off for increased CVD risk may be even lower. For the first time, recent recommendations from the Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure 10 recognize both microalbuminuria and a glomerular filtration rate of <60 ml/min as major CVD risk factors. The accumulating evidence indicates that microalbuminuria appears to be a stronger risk factor in men than in women; microalbuminuria occurs more frequently and is more closely associated with CVD and renal outcomes in men. Microalbuminuria is, however, also an important risk factor in women. In a large population-based study, women with albuminuria levels in the highest compared with the lowest quintile had a greatly increased risk of CVD mortality over 20 years. 11 Another population-based study found that the risk of microalbuminuria was increased about twofold with the administration of exogenous estrogen both in postmenopausal women (due to hormone replacement therapy) and premenopausal women (due to oral contraceptive use). 12 Risk was also related to dose and duration of estrogen use in that study. Such information adds to the concerns about the administration of estrogen, particularly in individuals who are already at a high CVD risk. MICROALBUMINURIA AS A WINDOW TO THE CIRCULATION: MECHANISTIC CONSIDERATIONS Although increases in albuminuria have long been known to reflect progressive kidney damage, this marker also appears to be an excellent indicator of the status of circulation at large. Increased amounts of albumin are lost in the urine when endothelial cells are damaged in the glomerulus. This damage may be the result of multiple pathways to injury, including hyperglycemia, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. The glomerulus is a unique capillary structure that has an arteriole on both its afferent and efferent ends (Figure 5). By contrast, all other capillary circulations have an arteriole in the afferent position with a venule on the efferent side. The unique structure of the glomerulus 14 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION SUPPL. 3 VOL. VI NO. XI NOVEMBER 2004
3 Table II. Why Does Albuminuria Reflect the Status of the Circulation? Arterial and Glomerular Injury CELL PROLIFERATE MIGRATE PHENOTYPE CHANGE GROWTH FACTORS INCREASE MATRIX ADHESION CHEMOTAXIS THROMBOSIS Endothelial Platelet Macrophages Smooth muscle Mesangial results in a higher blood pressure than in typical capillaries, as well as other characteristics with similarities to vessels of the arterial circulation. At a cellular level, damage to the glomerulus and to arteries can be viewed as parallel biological processes (Table II). Regardless of the inciting cause of injury, the responses of the various cells involved in both athero- and glomerulosclerosis are largely shared. After the initial endothelial injury, a cascade of pro-sclerotic events ensues. In particular, the smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis behave much like their corresponding contractile cell in the glomerulus, the mesangial cell. Both of these cell types proliferate, migrate from the subendothelial location to the vessel lumen, change phenotype, and secrete growth factors and matrix proteins. Several lines of evidence support a functionalstructural relationship between microalbuminuria and endothelial damage. In patients with systemic atherosclerosis, the transvascular escape rate of albumin is directly related to the amount of albumin lost in the urine. 13 This observation has been interpreted to indicate generalized leakiness to the macromolecules, which reflects widespread vascular damage. Furthermore, persons with elevated urinary albumin levels have impaired endothelial function (decreased flow-associated dilation after brachial artery occlusion), even when diabetes and hypertension are absent. 14 In summary, microalbuminuria is an indicator of generalized endothelial injury, a hallmark of systemic atherosclerosis. Hazard ratio Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (mg/g) Microalbuminuria range Urinary albumin concentration (mg/l) Figure 3. Risk of cardiovascular death by albuminuria level in the general population. Reprinted with permission from Circulation. 2002;106: * 25 * 31 Absent Mild Moderate Severe Figure 4. Urinary albumin and severity of coronary artery disease. *p=0.027 vs. Absent and Mild groups Reprinted from Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;34: Copyright 1999, with permission from the National Kidney Foundation. 8 SHOULD MICROALBUMINURIA BE A THERAPEUTIC TARGET? Based on the evidence relating microalbuminuria to CVD and renal risk and the availability of treatments to reduce albuminuria, it has been argued that the reduction of albuminuria should be a therapeutic target. Observational data indicate that people with type 2 diabetes who do not demonstrate a progressive increase in albuminuria are more likely to survive. 15 As reviewed elsewhere by Bakris 16 in this issue of The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, a number of studies have shown that a reduction in albuminuria, or overt proteinuria, correlates with improved renal survival and predicts better renal function. Although less data are available for CVD, similar trends are emerging. When albuminuria is reduced by treatment, in particular with inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system using a regimen based on angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, rates of major CVD events decrease in parallel. These observations have been made in various populations, including those with SUPPL. 3 VOL. VI NO. XI NOVEMBER 2004 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION 15
4 Mesangial cell Endothelial cell Efferent arteriole Juxtaglomerular apparatus Capillary loop Afferent arteriole Figure 5. Glomerular structure Reprinted from Tuttle KR, Stein JH. Diabetic nephropathy. Current Concepts. Kalamazoo, MI: The Upjohn Company; With permission of Pfizer Inc. and without diabetes or hypertension. 17,18 Such data are suggestive that albuminuria can be used to assess a response to treatment and to optimize therapy based on individual responsiveness. At present, however, this concept should be viewed as a hypothesis that is not yet conclusive for CVD. To confirm this hypothesis, future studies should be performed with the reduction of albuminuria as the therapeutic target and CVD events as the main outcome. In the meantime, the measurement of albuminuria is clinically valuable to identify high-risk individuals who should receive intensive risk factor management based on current treatment guidelines. The therapy of microalbuminuria is focused on the management of hypertension and renin-angiotensin-system inhibition, as reviewed by Toto 19 and Weir 20 elsewhere in this issue, however, other therapies also show promise. These therapies include strict glycemic control in diabetes, lipid lowering with statins, the limitation of dietary protein, and aspirin. A similar multifactorial approach in people with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria reduced rates of major CVD and renal events by 50% 60%. 21 Thus the treatment of patients with microalbuminuria should include attention to the spectrum of major CVD risk factors. Whether albuminuria can be used to indicate responsiveness to multiple risk factor intervention, and whether it reflects a responsiveness to specific treatment components, remain to be determined. Nevertheless, high-risk patients with microalbuminuria clearly benefit from strategies known to reduce CVD risk. CONCLUSIONS Microalbuminuria is a major, independent risk factor for CVD events in various groups including persons with diabetes or hypertension, the general population, and individuals with prevalent CVD. Microalbuminuria appears to be a stronger risk factor in men than in women, however, women with increased albuminuria levels are also at higher risk, and exogenous estrogen therapy raises the odds of microalbuminuria by about two-fold. Microalbuminuria is an indicator of generalized endothelial injury, a hallmark of systemic atherosclerosis. Treatments that decrease albuminuria, particularly with agents that inhibit the reninangiotensin system, reduce CVD risk in various populations including individuals with and without diabetes or hypertension. Whether albuminuria should be a treatment target to reduce CVD risk, however, has not yet been proven. In the meantime, the measurement of albuminuria is clinically valuable to identify high-risk individuals who should receive intensive risk factor management based on current treatment guidelines. REFERENCES 1 Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984;310: Dinneen SF, Gerstein HC. The association of microalbuminuria and mortality in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157: Jensen JS, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S, et al. Arterial hypertension, microalbuminuria, and risk of ischemic heart disease. Hypertension. 2000;35: Hillege HL, Fidler V, Diercks GF, et al. Prevention of Renal and Vascular End Stage Disease (PREVEND) Study Group. Urinary albumin excretion predicts cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality in general population. Circulation. 2002;106: Romundstad S, Holmen J, Kvenild K, et al. Microalbuminuria and all-cause mortality in 2,089 apparently healthy individuals: a 4.4 year follow-up study. The Nord-Trondelag Health Study (HUNT), Norway. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42: Chen J, Muntner P, Hamm LL, et al. The metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in U.S. adults. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140: Hoehner CM, Greenlund KJ, Righ-Najarian S, et al. Association of the insulin resistance syndrome and microalbuminuria among nondiabetic native Americans. The Inter-Tribal Heart Project. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13: Tuttle KR, Puhlman ME, Cooney SK, et al. Urinary albumin and insulin as predictors of coronary artery disease: an angiographic study. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;34: Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, et al. HOPE Study Investigators. Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA. 2001;286: The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. The JNC 7 Report. JAMA. 2003;289: Roest M, Banga JD, Janssen WM, et al. Excessive urinary albumin levels are associated with future cardiovascular mortality in postmenopausal women. Circulation. 2001;103: Monster TB, Janssen WM, de Jong PE, et al. Oral contraceptive use and hormone replacement therapy are associated with microalbuminuria. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161: THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION SUPPL. 3 VOL. VI NO. XI NOVEMBER 2004
5 13 Jensen JS. Renal and systemic transvascular albumin leakage in severe atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15: Clausen P, Jensen JS, Jensen G, et al. Elevated urinary albumin excretion is associated with impaired arterial dilatory capacity in clinically healthy subjects. Circulation. 2001;103: Spoelstra-de Man AM, Brouwer CB, Stehouwer CD, et al. Rapid progression of albumin excretion as an independent predictor of cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care. 2001;24: Bakris GL. Implications of albuminuria on kidney disease progression. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2004;6(11 suppl 3): Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuew D, et al. for the RENAAL Study Investigators. Effect of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345: Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000;355: Toto RD. Microalbuminuria: definition, detection and clinical significance. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2004;6(11 suppl 3): Weir MR. Dietary salt, blood pressure, and microalbuminuria. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2004;6(11 suppl 3): Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348: SUPPL. 3 VOL. VI NO. XI NOVEMBER 2004 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION 17
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the major cause. Microalbuminuria: Definition, Detection, and Clinical Significance. R e v i e w P a p e r
 R e v i e w P a p e r Microalbuminuria: Definition, Detection, and Clinical Significance Robert D. Toto, MD Proteinuria is a sign of abnormal excretion of protein by the kidney but is a nonspecific term
R e v i e w P a p e r Microalbuminuria: Definition, Detection, and Clinical Significance Robert D. Toto, MD Proteinuria is a sign of abnormal excretion of protein by the kidney but is a nonspecific term
Microalbuminuria As Predictor Of Severity Of Coronary Artery Disease In Non-Diabetic Patients:
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiology Volume 9 Number 1 Microalbuminuria As Predictor Of Severity Of Coronary Artery Disease In Non-Diabetic Patients: F Aziz, S Penupolu, S Doddi, A Alok, S Pervaiz,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiology Volume 9 Number 1 Microalbuminuria As Predictor Of Severity Of Coronary Artery Disease In Non-Diabetic Patients: F Aziz, S Penupolu, S Doddi, A Alok, S Pervaiz,
According to the US Renal Data System,
 DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY * Mohamed G. Atta, MD ABSTRACT *Based on a presentation given by Dr Atta at a CME dinner symposium for family physicians. Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, Johns
DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY * Mohamed G. Atta, MD ABSTRACT *Based on a presentation given by Dr Atta at a CME dinner symposium for family physicians. Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, Johns
Numerous epidemiologic studies have shown an association
 SYMPOSIUM ARTICLE Cardiorenal Risk Factors Barry M. Wall, MD Abstract: The chronic renocardiac syndrome, in which chronic kidney disease (CKD) contributes to impairment of cardiac function or structure,
SYMPOSIUM ARTICLE Cardiorenal Risk Factors Barry M. Wall, MD Abstract: The chronic renocardiac syndrome, in which chronic kidney disease (CKD) contributes to impairment of cardiac function or structure,
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan
 Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Kidney and heart: dangerous liaisons. Luis M. RUILOPE (Madrid, Spain)
 Kidney and heart: dangerous liaisons Luis M. RUILOPE (Madrid, Spain) Type 2 diabetes and renal disease: impact on cardiovascular outcomes The "heavyweights" of modifiable CVD risk factors Hypertension
Kidney and heart: dangerous liaisons Luis M. RUILOPE (Madrid, Spain) Type 2 diabetes and renal disease: impact on cardiovascular outcomes The "heavyweights" of modifiable CVD risk factors Hypertension
Massimo Cirillo, Cinzia Lombardi, Giancarlo Bilancio, Daniela Chiricone, Davide Stellato, and Natale G. De Santo
 Urinary Albumin and Cardiovascular Profile in the Middle-Aged Population Massimo Cirillo, Cinzia Lombardi, Giancarlo Bilancio, Daniela Chiricone, Davide Stellato, and Natale G. De Santo The moderate increase
Urinary Albumin and Cardiovascular Profile in the Middle-Aged Population Massimo Cirillo, Cinzia Lombardi, Giancarlo Bilancio, Daniela Chiricone, Davide Stellato, and Natale G. De Santo The moderate increase
Diabetes and kidney disease.
 Diabetes and kidney disease. What are the implications? Can it be prevented? Nice 18 june 2010 Lars G Weiss. M.D. Ph.D. Department of Neprology Central Hospital Karlstad Sweden Diabetic nephropathy vs
Diabetes and kidney disease. What are the implications? Can it be prevented? Nice 18 june 2010 Lars G Weiss. M.D. Ph.D. Department of Neprology Central Hospital Karlstad Sweden Diabetic nephropathy vs
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
Pattern of urinary albumin excretion in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
 Pattern of urinary albumin excretion in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients Elsheba Mathew 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Gomathi KG 3*,
Pattern of urinary albumin excretion in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients Elsheba Mathew 1, Jayadevan Sreedharan 2, Jayakumary Muttappallymyalil 2, Gomathi KG 3*,
Morbidity & Mortality from Chronic Kidney Disease
 Morbidity & Mortality from Chronic Kidney Disease Dr. Lam Man-Fai ( 林萬斐醫生 ) Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor MBBS, MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM, PDipID (HK), FRCP (Edin, Glasg) Hong Kong Renal Registry Report
Morbidity & Mortality from Chronic Kidney Disease Dr. Lam Man-Fai ( 林萬斐醫生 ) Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor MBBS, MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM, PDipID (HK), FRCP (Edin, Glasg) Hong Kong Renal Registry Report
E.Ritz Heidelberg (Germany)
 Predictive capacity of renal function in cardiovascular disease E.Ritz Heidelberg (Germany) If a cure is not achieved, the kidneys will pass on the disease to the heart Huang Ti Nei Ching Su Wen The Yellow
Predictive capacity of renal function in cardiovascular disease E.Ritz Heidelberg (Germany) If a cure is not achieved, the kidneys will pass on the disease to the heart Huang Ti Nei Ching Su Wen The Yellow
University of Groningen. C-reactive protein and albuminuria Stuveling, Erik Marcel
 University of Groningen C-reactive protein and albuminuria Stuveling, Erik Marcel IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen C-reactive protein and albuminuria Stuveling, Erik Marcel IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease
 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease Nestoras Mathioudakis, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism September 30, 2013 1 The ABCs of cardiovascular
Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease Nestoras Mathioudakis, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism September 30, 2013 1 The ABCs of cardiovascular
Management of Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Calcium Channel Blockers. Robert D. Toto, MD
 R e v i e w P a p e r Management of Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Calcium Channel Blockers Robert D. Toto, MD Both the prevalence and incidence of end-stage renal disease have been increasing
R e v i e w P a p e r Management of Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Calcium Channel Blockers Robert D. Toto, MD Both the prevalence and incidence of end-stage renal disease have been increasing
Development of Renal Disease in People at High Cardiovascular Risk: Results of the HOPE Randomized Study
 J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 641 647, 2003 Development of Renal Disease in People at High Cardiovascular Risk: Results of the HOPE Randomized Study JOHANNES F. E. MANN, HERTZEL C. GERSTEIN, QI-LONG YI, EVA M.
J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 641 647, 2003 Development of Renal Disease in People at High Cardiovascular Risk: Results of the HOPE Randomized Study JOHANNES F. E. MANN, HERTZEL C. GERSTEIN, QI-LONG YI, EVA M.
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
Guest Speaker Evaluations Viewer Call-In Thanks to our Sponsors: Phone: Fax: Public Health Live T 2 B 2
 Public Health Live T 2 B 2 Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetes: Early Identification and Intervention Guest Speaker Joseph Vassalotti, MD, FASN Chief Medical Officer National Kidney Foundation Thanks to
Public Health Live T 2 B 2 Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetes: Early Identification and Intervention Guest Speaker Joseph Vassalotti, MD, FASN Chief Medical Officer National Kidney Foundation Thanks to
ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: What s the Evidence?
 Reviews ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: What s the Evidence? George L. Bakris, MD; 1 and Matthew Weir, MD 2 Although angiotensin-converting
Reviews ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: What s the Evidence? George L. Bakris, MD; 1 and Matthew Weir, MD 2 Although angiotensin-converting
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009
 Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA
 ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
Eugene Barrett M.D., Ph.D. University of Virginia 6/18/2007. Diagnosis and what is it Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG
 Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
MISE AU POINT/IN-DEPTH REVIEW INCREASED URINARY ALBUMIN EXCRETION Définition, prevalence, clinical significance and therapeutic implications
 MISE AU POINT/IN-DEPTH REVIEW INCREASED URINARY ALBUMIN EXCRETION Définition, prevalence, clinical significance and therapeutic implications Adel E. BIRBARI, Najla DAOUK, Ahmed FAWAZ Birbari AE, Daouk
MISE AU POINT/IN-DEPTH REVIEW INCREASED URINARY ALBUMIN EXCRETION Définition, prevalence, clinical significance and therapeutic implications Adel E. BIRBARI, Najla DAOUK, Ahmed FAWAZ Birbari AE, Daouk
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
TELMISARTAN IN IN ISOLATED SYSTOLIC HYPERTENSION
 Chapter 3 The angiotensin II receptor antagonist telmisartan reduces urinary albumin excretion in patients with isolated systolic hypertension: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled
Chapter 3 The angiotensin II receptor antagonist telmisartan reduces urinary albumin excretion in patients with isolated systolic hypertension: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
A: Epidemiology update. Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups
 A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has received
 Participant Follow-up in the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) After Initial Detection Allan J. Collins, MD, FACP, 1,2 Suying Li, PhD, 1 Shu-Cheng Chen, MS, 1 and Joseph A. Vassalotti, MD 3,4 Background:
Participant Follow-up in the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) After Initial Detection Allan J. Collins, MD, FACP, 1,2 Suying Li, PhD, 1 Shu-Cheng Chen, MS, 1 and Joseph A. Vassalotti, MD 3,4 Background:
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment GUIDELINES
 ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
The hypertensive kidney and its Management
 The hypertensive kidney and its Management Dr H0 Chung Ping Hypertension Management Seminar 20061124 Hypertensive kidney Kidney damage asymptomatic till late stage Viscous cycle to augment renal damage
The hypertensive kidney and its Management Dr H0 Chung Ping Hypertension Management Seminar 20061124 Hypertensive kidney Kidney damage asymptomatic till late stage Viscous cycle to augment renal damage
The retinal renin-angiotensin system: implications for therapy in diabetic retinopathy
 (2002) 16, S42 S46 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh : implications for therapy in diabetic retinopathy AK Sjølie 1 and N Chaturvedi 2 1 Department
(2002) 16, S42 S46 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh : implications for therapy in diabetic retinopathy AK Sjølie 1 and N Chaturvedi 2 1 Department
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS
 Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Reversal of Microalbuminuria A Causative Factor of Diabetic Nephropathy is Achieved with ACE Inhibitors than Strict Glycemic Control
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2013; 4(5): 923-928 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reversal of Microalbuminuria A Causative Factor
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2013; 4(5): 923-928 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reversal of Microalbuminuria A Causative Factor
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Higher levels of Urinary Albumin Excretion within the Normal Range Predict Faster Decline in Glomerular Filtration Rate in Diabetic Patients
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online May 12, 2009 Albuminuria and GFR Decline in Diabetes Higher levels of Urinary Albumin Excretion within the Normal Range Predict Faster Decline in
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online May 12, 2009 Albuminuria and GFR Decline in Diabetes Higher levels of Urinary Albumin Excretion within the Normal Range Predict Faster Decline in
ACEIs / ARBs NDHP dihydropyridine ( DHP ) ACEIs ARBs ACEIs ARBs NDHP. ( GFR ) 60 ml/min/1.73m ( chronic kidney disease, CKD )
 005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
Lessons learned from AASK (African-American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension)
 Lessons learned from AASK (African-American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension) Janice P. Lea, MD, MSc, FASN Professor of Medicine Chief Medical Director of Emory Dialysis ASH Clinical Specialist
Lessons learned from AASK (African-American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension) Janice P. Lea, MD, MSc, FASN Professor of Medicine Chief Medical Director of Emory Dialysis ASH Clinical Specialist
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Heart Failure Clin 2 (2006) 101 105 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACE inhibitors, in diabetic hypertension, 30 31 Adipokines, cardiovascular events related to, 6 Advanced
Heart Failure Clin 2 (2006) 101 105 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACE inhibitors, in diabetic hypertension, 30 31 Adipokines, cardiovascular events related to, 6 Advanced
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018
 Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
CARDIO-RENAL SYNDROME
 CARDIO-RENAL SYNDROME Luis M Ruilope Athens, October 216 DISCLOSURES: ADVISOR/SPEAKER for Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, BMS, Daiichi-Sankyo, Esteve, GSK Janssen, Lacer, Medtronic, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Relypsa,
CARDIO-RENAL SYNDROME Luis M Ruilope Athens, October 216 DISCLOSURES: ADVISOR/SPEAKER for Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, BMS, Daiichi-Sankyo, Esteve, GSK Janssen, Lacer, Medtronic, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Relypsa,
Diabetes is not only the single most common
 R e v i e w P a p e r : C M E Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetics: An Important, Overlooked Cardiovascular Risk Factor Matthew R. Weir, MD The presence of microalbumin in the urine of persons with type
R e v i e w P a p e r : C M E Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetics: An Important, Overlooked Cardiovascular Risk Factor Matthew R. Weir, MD The presence of microalbumin in the urine of persons with type
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE. Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota
 SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
Microvascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes
 Microvascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine The Course
Microvascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine The Course
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
RENAAL, IRMA-2 and IDNT. Three featured trials linking a disease spectrum IDNT RENAAL. Death IRMA 2
 Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease. Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010
 Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Classification of CKD by Diagnosis
 Classification of CKD by Diagnosis Diabetic Kidney Disease Glomerular diseases (autoimmune diseases, systemic infections, drugs, neoplasia) Vascular diseases (renal artery disease, hypertension, microangiopathy)
Classification of CKD by Diagnosis Diabetic Kidney Disease Glomerular diseases (autoimmune diseases, systemic infections, drugs, neoplasia) Vascular diseases (renal artery disease, hypertension, microangiopathy)
Kidney Disease, Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk
 1 Kidney Disease, Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk George Bakris, MD, FAHA, FASN Professor of Medicine Director, Hypertensive Diseases Unit The University of Chicago-Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago,
1 Kidney Disease, Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk George Bakris, MD, FAHA, FASN Professor of Medicine Director, Hypertensive Diseases Unit The University of Chicago-Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago,
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression
 Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression Arasu Gopinath, MD Clinical Nephrologist, Medical Director, Jordan Landing Dialysis Center Objectives: Identify the most important risks
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression Arasu Gopinath, MD Clinical Nephrologist, Medical Director, Jordan Landing Dialysis Center Objectives: Identify the most important risks
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART. Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009
 TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ. Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH
 ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH Hypertension Co-Morbidities HTN Commonly Clusters with Other Risk
ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH Hypertension Co-Morbidities HTN Commonly Clusters with Other Risk
Albuminuria, not only a cardiovascular/renal risk marker, but also a target for treatment?
 Kidney International, Vol. 66, Supplement 92 (2004), pp. S2 S6 Albuminuria, not only a cardiovascular/renal risk marker, but also a target for treatment? DICK DE ZEEUW Department of Clinical Pharmacology,
Kidney International, Vol. 66, Supplement 92 (2004), pp. S2 S6 Albuminuria, not only a cardiovascular/renal risk marker, but also a target for treatment? DICK DE ZEEUW Department of Clinical Pharmacology,
Cedars Sinai Diabetes. Michael A. Weber
 Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
The study of correlation of silent myocardial ischemia with microalbuminuria in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Dua HS et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Dec;4(6):1506-1512 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20175120
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Dua HS et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Dec;4(6):1506-1512 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20175120
Educational and behavioral interventions hitherto published
 Treatment of High-Risk Patients with Diabetes: Motivation and Teaching Intervention: A Randomized, Prospective 8-Year Follow-Up Study Rita Rachmani, Inna Slavacheski, Maya Berla, Ronni Frommer-Shapira,
Treatment of High-Risk Patients with Diabetes: Motivation and Teaching Intervention: A Randomized, Prospective 8-Year Follow-Up Study Rita Rachmani, Inna Slavacheski, Maya Berla, Ronni Frommer-Shapira,
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Renal Protection Staying on Target
 Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting. Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA
 Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
hypertension Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath
 hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
AGING KIDNEY IN HIV DISEASE
 AGING KIDNEY IN HIV DISEASE Michael G. Shlipak, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Chief, General Internal Medicine, San Francisco VA Medical Center Kidney, Aging and HIV
AGING KIDNEY IN HIV DISEASE Michael G. Shlipak, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Chief, General Internal Medicine, San Francisco VA Medical Center Kidney, Aging and HIV
Cardiovascular and renal outcome in subjects with K/DOQI stage 1 3 chronic kidney disease: the importance of urinary albumin excretion
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 3851 3858 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn356 Advance Access publication 18 July 2008 Original Article Cardiovascular and renal outcome in subjects with K/DOQI stage 1 3 chronic
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 3851 3858 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn356 Advance Access publication 18 July 2008 Original Article Cardiovascular and renal outcome in subjects with K/DOQI stage 1 3 chronic
JOSHUA K. KAYIMA INTERLINKING CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND OBESITY
 INTERLINKING CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND OBESITY JOSHUA K. KAYIMA ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DEPT. OF CLINICAL MEDICINE AND THERAPEUTICS UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI Introduction According to
INTERLINKING CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND OBESITY JOSHUA K. KAYIMA ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR DEPT. OF CLINICAL MEDICINE AND THERAPEUTICS UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI Introduction According to
Reducing proteinuria
 Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Hypertension is a major risk factor for
 OPTIMAL RISK MANAGEMENT OF THE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE RISK FACTORS * Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, FACC ABSTRACT To determine the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with hypertension, it
OPTIMAL RISK MANAGEMENT OF THE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE RISK FACTORS * Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, FACC ABSTRACT To determine the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with hypertension, it
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula
 T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
DISCLOSURE PHARMACIST OBJECTIVES 9/30/2014 JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES. I have nothing to disclose.
 JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES Tiffany Dickey, PharmD Assistant Professor, UAMS COP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Mercy Hospital Northwest AR DISCLOSURE I
JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES Tiffany Dickey, PharmD Assistant Professor, UAMS COP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Mercy Hospital Northwest AR DISCLOSURE I
Mingming Liu 1,2, Yan Liang 1*, Jun Zhu 1, Yanmin Yang 1, Wenfang Ma 1 and Guozheng Zhang 1
 Liu et al. Clinical Hypertension (2018) 24:12 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40885-018-0095-3 RESEARCH Open Access Albumin-to-creatinine ratio as a predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization of congestive
Liu et al. Clinical Hypertension (2018) 24:12 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40885-018-0095-3 RESEARCH Open Access Albumin-to-creatinine ratio as a predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization of congestive
The Burden of the Diabetic Heart
 The Burden of the Diabetic Heart Dr. Ghaida Kaddaha (MBBS, MRCP-UK, FRCP-london) Diabetes Unit Rashid Hospital Dubai U.A.E Risk of CVD in Diabetes Morbidity and mortality from CVD is 2-4 fold higher than
The Burden of the Diabetic Heart Dr. Ghaida Kaddaha (MBBS, MRCP-UK, FRCP-london) Diabetes Unit Rashid Hospital Dubai U.A.E Risk of CVD in Diabetes Morbidity and mortality from CVD is 2-4 fold higher than
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population
 Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable?
 Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Disclosures. Outline. Outline 5/23/17 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Metabolic Syndrome. Bill Roberts, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pathology University of Utah
 Metabolic Syndrome Bill Roberts, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pathology University of Utah Objectives Be able to outline the pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome Be able to list diagnostic criteria for
Metabolic Syndrome Bill Roberts, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pathology University of Utah Objectives Be able to outline the pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome Be able to list diagnostic criteria for
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. 5. Classification of chronic kidney disease based on evaluation of kidney function
 5. Classification of chronic kidney disease based on evaluation of kidney function Date written: April 2005 Final submission: May 2005 GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence
5. Classification of chronic kidney disease based on evaluation of kidney function Date written: April 2005 Final submission: May 2005 GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Disclosures. Outline. Outline 7/27/2017 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
23-Jun-15. Albuminuria Renal and Cardiovascular Consequences A history of progress since ,490,000. Kidney Center, UMC Groningen
 Kidney function (egfr in ml/min) Albuminuria (mg/hr) Incidentie ESRD (%) 3-Jun- Number of patients worldwide that receives kidney replacement therapy Albuminuria Renal and Cardiovascular Consequences A
Kidney function (egfr in ml/min) Albuminuria (mg/hr) Incidentie ESRD (%) 3-Jun- Number of patients worldwide that receives kidney replacement therapy Albuminuria Renal and Cardiovascular Consequences A
DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications
 DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications Lihteh Wu MD Asociados de Mácula, Vítreo y Retina de Costa Rica San José, Costa Rica LW65@cornell.edu Disclosures Dr Wu has received lecture fees from
DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications Lihteh Wu MD Asociados de Mácula, Vítreo y Retina de Costa Rica San José, Costa Rica LW65@cornell.edu Disclosures Dr Wu has received lecture fees from
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
Indiana Medicaid Drug Utilization Review Board Newsletter
 Indiana Medicaid Drug Utilization Review Board Newsletter Volume 12 Issue 4 October 2009 Indiana Medicaid DUR Board Room W382 Indiana State Government Center, South 402 West Washington Street Indianapolis,
Indiana Medicaid Drug Utilization Review Board Newsletter Volume 12 Issue 4 October 2009 Indiana Medicaid DUR Board Room W382 Indiana State Government Center, South 402 West Washington Street Indianapolis,
Kerry Cooper M.D. Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center April 30, 2009
 Kerry Cooper M.D. Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center April 30, 2009 DR. KERRY COOPER IS ON THE SPEAKER BUREAU OF AMGEN, ABBOTT, GENZYME, SHIRE, AND BMS DR. COOPER IS ALSO INVOLVED IN CLINICAL
Kerry Cooper M.D. Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center April 30, 2009 DR. KERRY COOPER IS ON THE SPEAKER BUREAU OF AMGEN, ABBOTT, GENZYME, SHIRE, AND BMS DR. COOPER IS ALSO INVOLVED IN CLINICAL
Inflammation in Renal Disease
 Inflammation in Renal Disease Donald G. Vidt, MD Inflammation is a component of the major modifiable risk factors in renal disease. Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-crp) levels have been
Inflammation in Renal Disease Donald G. Vidt, MD Inflammation is a component of the major modifiable risk factors in renal disease. Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-crp) levels have been
Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective
 Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Reframe the Paradigm of Hypertension treatment Focus on Diabetes
 Reframe the Paradigm of Hypertension treatment Focus on Diabetes Paola Atallah, MD Lecturer of Clinical Medicine SGUMC EDL monthly meeting October 25,2016 Overview Physiopathology of hypertension Classification
Reframe the Paradigm of Hypertension treatment Focus on Diabetes Paola Atallah, MD Lecturer of Clinical Medicine SGUMC EDL monthly meeting October 25,2016 Overview Physiopathology of hypertension Classification
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
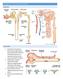 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Published trials point to a detrimental relationship
 ANEMIA, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE: THE CLINICAL TRIALS Steven Fishbane, MD* ABSTRACT Clinical trials have shown a strong detrimental relationship among anemia, chronic kidney disease
ANEMIA, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE: THE CLINICAL TRIALS Steven Fishbane, MD* ABSTRACT Clinical trials have shown a strong detrimental relationship among anemia, chronic kidney disease
DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
Macrovascular Residual Risk. What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy?
 Macrovascular Residual Risk What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy? Defining Residual Vascular Risk The risk of macrovascular events and microvascular complications which persists
Macrovascular Residual Risk What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy? Defining Residual Vascular Risk The risk of macrovascular events and microvascular complications which persists
Clinical Approach to Achieving Treatment Targets: Case Vignette Discussion
 Clinical Approach to Achieving Treatment Targets: Case Vignette Discussion Om P. Ganda, MD; Kirit Tolia, MD, FACE Postcardiac Follow-up in a 66-Year-Old Man Slide 1. Dr. Ganda: Now we will present a case
Clinical Approach to Achieving Treatment Targets: Case Vignette Discussion Om P. Ganda, MD; Kirit Tolia, MD, FACE Postcardiac Follow-up in a 66-Year-Old Man Slide 1. Dr. Ganda: Now we will present a case

 www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to
www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to