Oral L-Arginine Stimulates GLP-1 Secretion to Improve Glucose Tolerance in Male Mice. of L-arginine for glucose metabolism.
|
|
|
- Elwin Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B R I E F R E S E A R C H R E P O R T Oral L-Arginine Stimulates GLP-1 Secretion to Improve Glucose Tolerance in Male Mice Christoffer Clemmensen, Sanela Smajilovic, Eric P. Smith, Stephen C. Woods, Hans Bräuner-Osborne, Randy J. Seeley, David A. D Alessio, and Karen K. Ryan Division of Endocrinology Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine (C.C., E.P.S., R.J.S., D.A.D., K.K.R.), and Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neuroscience (S.C.W.), University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, Ohio 45237; and Department of Drug Design and Pharmacology (C.C., S.S., H.B.-O.), Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, DK-2100 Copenhagen, Denmark Pharmacological and surgical interventions that increase glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) action are effective to improve glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. In light of this, nutritional strategies to enhance postprandial GLP-1 secretion, particularly in the context of diet-induced obesity, may provide an alternative therapeutic approach. Importantly, recent evidence suggests the amino acid L-arginine, a well-known insulin secretagogue, can also stimulate release of GLP-1 from isolated rat intestine. Here we tested the hypothesis that oral L-arginine acts as a GLP-1 secretagogue in vivo, to augment postprandial insulin secretion and improve glucose tolerance. To test this, we administered L-arginine or vehicle by oral gavage, immediately prior to an oral glucose tolerance test in lean and diet-inducedobesemice. Inbothleanandobesemiceoral L-arginineincreasedplasmaGLP-1andinsulin and substantially improved glucose clearance. To directly assess the contribution of GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R)-signaling to these improvements, L-arginine was given to Glp1r knockout mice and their wild-type littermates. In this experiment oral L-arginine significantly augmented insulin secretion and improved glucose clearance in WT mice, but not in Glp1r knockout littermates. Taken together these findings identify L-arginine as a GLP-1 secretagogue in vivo and demonstrate that improvement of glucose tolerance by oral L-arginine depends on GLP-1R-signaling. These findings raise the intriguing possibility that L-arginine-based nutritional and/or pharmaceutical therapies may benefit glucose tolerance by improving the postprandial GLP-1 response in obese individuals. (Endocrinology 154: , 2013) Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a hormone secreted from enteroendocrine L-cells into the hepatic portal circulation in response to the ingestion of nutrients (1). GLP-1 acts at its receptor (GLP-1R) to augment glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic -cells and is essential for normal oral glucose tolerance (reviewed in Refs. 2 and 3). Therefore, developing strategies to enhance GLP-1 secretion from intestinal L cells could provide alternative therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Like carbohydrates and fats, dietary protein stimulates GLP-1 secretion (4). Moreover, oral administration of the amino acid glutamine potently ISSN Print ISSN Online Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2013 by The Endocrine Society Received June 5, Accepted August 5, First Published Online August 19, 2013 induces the release of GLP-1, thereby augmenting insulin secretion in obese- and type 2 diabetic subjects (5). Thus, at least one individual amino acid can improve oral glucose tolerance by increasing endogenous GLP-1 secretion. It is well established that the amino acid L-arginine is a potent insulin secretagogue (6). Moreover, increasing evidence supports that dietary supplementation with L-arginine improves glycemic control in multiple species (7). However, no studies have, to our knowledge, investigated a potential contribution of the GLP-1 system to the benefits of L-arginine for glucose metabolism. In the present Abbreviations: bw, body weight; DIO, diet-induced obese/obesity; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GLP-1R, GLP-1 receptor; KO, knockout; OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; WT, wild type endo.endojournals.org Endocrinology, November 2013, 154(11): doi: /en
2 doi: /en endo.endojournals.org 3979 study we tested the hypothesis that L-arginine is a GLP-1 secretagogue in vivo, and moreover that GLP-1R signaling contributes to L-arginine-mediated improvements in insulin secretion and oral glucose tolerance. Materials and Methods Animals Male C57BL/6 mice were housed in an AAALAC-approved facility with a 12-hour light, 12-hour dark cycle and allowed free access to water and standard chow or 60% high-fat diet (D12492 HFD; Research Diets), unless otherwise noted. Diet-induced obese (DIO) mice were maintained on HFD for 5 6 months prior to testing. Global Glp1r knockout (KO) mice (Glp1r CMVKO ) were generated by crossing a floxed Glp1r mouse line with CMVcre mice, followed by outbreeding of the CMVcre as previously described (8). Functional KO was validated as reported elsewhere (8). All animal procedures were approved by the University of Cincinnati Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Oral glucose tolerance tests in lean and DIO mice To investigate the role of L-arginine on glucose tolerance in both lean and obese, insulin-resistant individuals, we delivered L-arginine or vehicle orally to lean and DIO mice prior to an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). Mice were fasted for 6 hours, weighed, and separated into weight-matched groups. At 15 minutes, mice received an oral gavage containing 1 g/kg body weight (bw) L-arginine or saline (0.9% NaCl) in a 300- L volume. Although it is difficult to precisely address the physiologic relevance of this dose, we note that a similar dose of oral L-glutamine is known to act as a GLP-1 secretagogue and to improve glucose tolerance in diabetic rats (9). At 0 minutes, mice received an oral gavage containing 2 g/kg bw dextrose. Glucose was measured in blood collected from the tip of the tail vein using AccuChek glucose meters and strips (Roche) at baseline and at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 minutes. Plasma GLP-1 response to oral L-arginine in lean mice Blood for GLP-1 measurement was collected from 6-hour fasted mice. After obtaining a basal blood sample from the tip of the tail vein, mice were given an oral dose of L-arginine (1 g/kg bw), and a second blood sample was obtained at 15 minutes. Whole blood (75 L) was collected into chilled tubes containing 10 L of antiproteolytic cocktail (4.65 g EDTA 93 mg aprotinin U of heparin in 50 ml saline). Plasma was stored at 80 C until further analysis. Plasma GLP-1 and insulin response in DIO mice Blood for GLP-1 and insulin measurements was collected using a balanced crossover design conducted over 2 test days in 6-hour fasted mice. Hence each animal received both L-arginine (1 g/kg bw) and the saline control. At 15 minutes, mice received an oral gavage containing L-arginine or saline. At 0 minutes, mice received an oral gavage containing 2 g/kg bw dextrose. Whole blood (75 l) was collected from the tip of the tail vein into chilled tubes containing 10 L of antiproteolytic cocktail (4.65 g EDTA 93 mg aprotinin U of heparin in 50 ml saline), at 15,0,and15minutes.Plasmawasstored at 80 C until further analysis. Oral glucose tolerance test and L-arginine-induced insulin release in Glp1r KO and WT mice We performed an OGTT in chow-fed Glp1r KO and wild-type (WT) mice, as described above. L-Arginine-induced insulin release in chow-fed, lean Glp1r KO and WT mice was assessed in 6-hour fasted animals with free access to water. After obtaining a basal blood sample from the tail vein, mice were given an oral dose of L-arginine (1 g/kg bw), and a second blood sample was obtained at 15 minutes. Figure 1. L-Arginine Improves Glucose Tolerance in Mice. A, Blood glucose following oral L- arginine (1 g/kg) or saline to lean C57bl/6 mice 15 minutes before an OGTT (2 g glucose/kg bw) (2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n 7). B, Glucose area under the curve (AUC) (t test). C, Plasma GLP-1 (total) levels before and 15 minutes following oral gavage of L-arginine (1 g/kg) (paired t test, n 17). Data presented as mean SEM. *, P.05; ***, P.001. Measurements of GLP-1 and insulin Commercially available kits were used to measure plasma total GLP-1 (MesoScale Discovery) and insulin (ELISA, Crystal Chem), per the manufacturer s instructions.
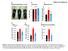
3 3980 Clemmensen et al L-Arg and GLP-1 in Glucose Metabolism Endocrinology, November 2013, 154(11): Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism Version 5.0c (GraphPad Software) or SigmaStat 3.1 (SYSTAT). Data were analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA (RM ANOVA) with Tukey s post hoc test or by paired, two-tailed Student s t test, as appropriate. In all cases Results are presented as mean SEM. Results Oral L-arginine improves glucose tolerance and increases plasma GLP-1 and insulin In both lean and DIO mice, oral administration of L- arginine 15 minutes prior to an OGTT significantly improved glucose tolerance relative to controls (Figure 1, A and B; Figure 2, A and B). Coincident with this, oral L- arginine elicited GLP-1 secretion in both lean and DIO mice. Among lean mice, oral administration of L-arginine significantly increased total plasma GLP-1 (tglp-1) within 15 minutes (Figure 1C) (P.001, pg/ml at 0 minutes, pg/ml at 15 minutes). Likewise, among DIO mice, the plasma total GLP-1 response ( tglp-1) was significantly increased 15 minutes following oral administration of L-arginine (P.01, pg/ml at 15 minutes, pg/ml at 0 minutes), compared with oral saline [ pg/ml at 15 minutes, pg/ml at 0 minutes]. This was further enhanced by an oral gavage of dextrose (P.001, pg/ml vs pg/ml at 15 minutes) (Figure 2C). Consistent with the improved glucose tolerance the plasma insulin response ( insulin) to 2 g/kg bw oral dextrose was significantly enhanced by prior administration of L-arginine relative to saline in DIO mice [ pg/ml at 15 minutes, pg/ml at 0 minutes, pg/ml at 15 minutes, P.01 and pg/ml at 15 minutes, pg/ml at 0 minutes, pg/ml at 15 minutes, respectively] (Figure 2D). Effect of oral L-arginine on insulin levels and glucose tolerance in Glp1r-deficient mice Assessment of plasma insulin levels in chow-fed lean Glp1r KO and WT mice following oral gavage of L-arginine revealed a significant increase in plasma insulin in Figure 2. L-Arginine Induces GLP-1 Secretion and Improves Glucose Tolerance in DIO Mice. A, Blood glucose following oral gavage of L-arginine (1g/kg) or saline to DIO C57bl/6 mice 15 minutes before an OGTT (2 g glucose/kg bw) (2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n 4 5). B, Glucose area under the curve (AUC) (t test). C, Plasma total-glp-1 response ( tglp-1) to oral gavage of L-arginine or saline 15 minutes prior to an OGTT (2 g dextrose/kg bw) in DIO mice (2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n 9). D, Plasma insulin response ( insulin) following oral gavage of L-arginine or saline 15 minutes prior to an OGTT (2 g glucose/kg bw) in DIO mice (2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n 9). Data presented as mean SEM. *, P.05; **, P.01; ***, P.001.
4 doi: /en endo.endojournals.org 3981 WT mice 15 minutes following L-arginine administration (P.01, pg/ml at 0 minutes, pg/ml at 15 minutes) (Figure 3, A and B) but no effect of L-arginine on plasma insulin levels in Glp1r KO mice ( pg/ml at 0 minutes, pg/ml at 15 minutes) (Figure 3, A and B). Oral gavage of L-arginine 15 minutes prior to an OGTT significantly improved glucose tolerance in WT mice (P.01) (Figure 4, A and C), but had no significant effect on glucose tolerance in Glp1r KO mice (Figure 4, B and C). Although we observed no significant impairment in oral glucose tolerance associated with Glp1r deficiency per se in this experiment, consistent with previous reports (10), a mild impairment was observed when this cohort of mice was challenged with a higher dose of glucose (2.5 g/kg bw) (data not shown). Figure 3. The GLP-1R Is Necessary for L-Arginine-Induced Insulin Secretion. A, Mean change of plasma insulin from baselines to 15 minutes after L-arginine administration (paired t test). B, Individual plasma insulin levels before and 15 minutes following oral gavage of L-arginine in lean WT and Glp1r KO mice (paired t test, n 7 9). Data presented as mean SEM. **, P.01. Figure 4. The GLP-1R Is Necessary for L-Arginine-Induced Improvements in Glucose Tolerance. Blood glucose following oral gavage of L-arginine (1 g/kg) or saline to lean WT (A) and Glp1r KO (B) mice 15 minutes before an OGTT (2 g glucose/kg bw) (2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n 8 9). C, Glucose area under the curve (AUC) (2-way repeated measures ANOVA, n 8 9). Data presented as mean SEM. **, P.01; ***, P.001. Discussion The present data demonstrate that oral administration of L-arginine acutely improves glucose tolerance in both lean and DIO mice. Moreover, L-arginine potently increases plasma concentrations of GLP-1, suggesting that GLP-1R signaling may contribute to its insulinotropic action. Consistent with this possibility, in mice with genetic disruption of Glp1r, the effect of L-arginine to induce insulin secretion and to improve glucose tolerance is significantly blunted. These findings reveal a novel role for L-arginine to improve glucose tolerance indirectly, via GLP-1 action, and may have implications for the treatment of T2DM. Previous studies investigating the possibility that L-arginine acts as a GLP-1 secretagogue, either in vitro (11) or ex vivo (12), have generated conflicting results. First, Reimann et al. (11) investigated the individual effects of multiple L- -amino acids to stimulate GLP-1 secretion from GLUTag cells, an immortalized murine enteroendocrine cell line that expresses GLP-1. They reported that L-glutamine, but not L-arginine, potently stimulates GLP-1 secretion. Conversely, Mace et al (12) reported that L-arginine elicits GLP-1 release from isolated loops of rat small intestine (12). Together with the present observation that L-arginine elicits GLP-1 release in vivo, these data suggest the effect of L-arginine on the L cell may require an intact intestinal environment or that GLUTag cells do not mimic L cells in all aspects. Additional studies will be necessary to parse the mechanisms by which L-arginine elicits GLP-1 secretion and the contribution of the extracellular environment. Relevant to this, we did not observe a significant effect of D-arginine to elicit GLP-1 secretion (data not shown), suggesting
5 3982 Clemmensen et al L-Arg and GLP-1 in Glucose Metabolism Endocrinology, November 2013, 154(11): the metabolism of L-arginine or stereo-specific interaction with a receptor or a transporter may be necessary for its effects. Similar to other nutrients, in vivo L- -amino acidmediated enteroendocrine release of incretin hormones is likely to involve both G protein-coupled receptor-dependent and -independent, pathways (12 14). The diminished effect of L-arginine to elicit insulin secretion and improve oral glucose tolerance in Glp1r KO mice implicates GLP-1 signaling in the -cell response to this amino acid. Whereas acute iv administration of L- arginine has a direct effect to stimulate islet hormone secretion (15, 16), the effect of oral L-arginine on glucose tolerance and insulin release requires intact GLP-1 signaling and thus appears to be indirect. The GLP-1 incretin effect has traditionally been ascribed to effects on intestinal L cells elicited by ingested carbohydrate, but the findings reported here support the involvement of gut hormones to link protein ingestion with insulin secretion. This has also been recently suggested in studies of humans consuming meals of specific macronutrient composition (17). Also, we have recently reported that long-term dietary supplementation with L-arginine improves glucose metabolism in mice exposed to a low-protein diet (18). Additional studies will be necessary to determine the contribution of the GLP-1 system to the benefits of this chronic intervention and to further explore a potential physiological role for this amino acid in glucose metabolism. Several effective pharmaceutical treatments for T2DM target the GLP-1 system, by either inhibiting its rapid clearance by dipeptidyl-peptidase IV or using dipeptidylpeptidase IV-resistant GLP-1 mimetics (2). Developing strategies to enhance GLP-1 secretion from intestinal L cells, particularly in the context of DIO, could provide an alternative approach. The present findings raise the possibility that either dietary supplementation with L-arginine and/or L-arginine-based therapies may be effective to increase GLP-1 secretion in humans. Such an intervention would have the benefit of increasing GLP-1 concentration locally near GLP-1R-positive afferent neurons, thought to contribute to the metabolic benefits of GLP-1 (19, 20). In summary, our data demonstrate a novel role for oral L-arginine to regulate glucose metabolism indirectly by inducing GLP-1 release. Additionally, we demonstrate a pronounced effect of oral L-arginine to enhance glucose clearance in both lean and obese animals, underlining that nutritional-based strategies aiming to improve endogenous GLP-1 release may provide an alternative therapeutic approach to aid metabolic disorders. Acknowledgments We thank Dana Buesing, Todd Greer, Radhakrishna Krishna, William Li, and Sonia Lipp for expert technical assistance. Address all correspondence and requests for reprints to: Karen K. Ryan, 2170 East Galbraith Road, A125, Cincinnati, Ohio karen.ryan@uc.edu. C.C., S.S., and H.B.O. were supported by the UNIK: Food Fitness and Pharma for Health and Disease research program; S.S. was supported by the Carlsberg foundation; H.B.O. was supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation; S.C.W. was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant DK017844; R.J.S. was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant DK093848; K.K.R. was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant HL Disclosure Summary: D.A.D. consults for Amylin, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Zealand and has research support from Ethicon Endo-Surgery and MannKind; R.J.S. has consultancies, research support, or is a paid speaker with the following companies: Ethicon Endo-Surgery/Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Novartis, Angiochem, Zafgen, Takeda, Ablaris, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and Zealand Pharma. References 1. Kreymann B, Williams G, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR. Glucagon-like peptide : a physiological incretin in man. Lancet. 1987; 2(8571): Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(4): Baggio LL, Drucker DJ. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(6): Ma J, Stevens JE, Cukier K, et al. Effects of a protein preload on gastric emptying, glycemia, and gut hormones after a carbohydrate meal in diet-controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(9): Greenfield JR, Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, et al. Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89(1): Floyd JC, Jr., Fajans SS, Conn JW, Knopf RF, Rull J. Stimulation of insulin secretion by amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1966;45(9): McKnight JR, Satterfield MC, Jobgen WS, et al. Beneficial effects of L-arginine on reducing obesity: potential mechanisms and important implications for human health. Amino Acids. 2010;39(2): Wilson-Perez HE, Chambers AP, Ryan KK, et al. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy is effective in two genetic mouse models of glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor deficiency. Diabetes. 2013;62(7): Badole SL, Bagul PP, Mahamuni SP, et al. Oral L-glutamine increases active GLP-1 (7-36) amide secretion and improves glycemic control in stretpozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;203(2): Hansotia T, Baggio LL, Delmeire D, et al. Double incretin receptor knockout (DIRKO) mice reveal an essential role for the enteroinsular axis in transducing the glucoregulatory actions of DPP-IV inhibitors. Diabetes. 2004;53(5): Reimann F, Williams L, da Silva Xavier G, Rutter GA, Gribble FM. Glutamine potently stimulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from GLUTag cells. Diabetologia. 2004;47(9): Mace OJ, Schindler M, Patel S. The regulation of K- and L-cell activity by GLUT2 and the calcium-sensing receptor CasR in rat small intestine. J Physiol. 2012;590(Pt 12):
6 doi: /en endo.endojournals.org Oya M, Kitaguchi T, Pais R, Reimann F, Gribble F, Tsuboi T. The G protein-coupled receptor family C group 6 subtype A (GPRC6A) receptor is involved in amino acid-induced glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from GLUTag cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(7): Reimann F, Tolhurst G, Gribble FM. G-protein-coupled receptors in intestinal chemosensation. Cell Metab. 2012;15(4): Palmer JP, Walter RM, Ensinck JW. Arginine-stimulated acute phase of insulin and glucagon secretion. I. in normal man. Diabetes. 1975;24(8): Smajilovic S, Clemmensen C, Johansen LD, et al. The L- -amino acid receptor GPRC6A is expressed in the islets of Langerhans but is not involved in L-arginine-induced insulin release. Amino Acids. 2013;44(2): Carrel G, Egli L, Tran C, et al. Contributions of fat and protein to the incretin effect of a mixed meal. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94(4): Clemmensen C, Madsen AN, Smajilovic S, Holst B, Bräuner-Osborne H. L-Arginine improves multiple physiological parameters in mice exposed to diet-induced metabolic disturbances. Amino Acids. 2012;43(3): Vahl TP, Tauchi M, Durler TS, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors expressed on nerve terminals in the portal vein mediate the effects of endogenous GLP-1 on glucose tolerance in rats. Endocrinology. 2007;148(10): Williams DL. Minireview: finding the sweet spot: peripheral versus central glucagon-like peptide 1 action in feeding and glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2009;150(7): Plan to Attend Endocrine Board Review September 2-3, 2014, San Francisco, California
The Mediterranean Diet: HOW and WHY It Works So Well for T2DM
 The Mediterranean Diet: HOW and WHY It Works So Well for T2DM Susan L. Barlow, RD, CDE. Objectives 1. Discuss the effects of meal size on GLP-1 concentrations. 2. Compare and contrast the specific effects
The Mediterranean Diet: HOW and WHY It Works So Well for T2DM Susan L. Barlow, RD, CDE. Objectives 1. Discuss the effects of meal size on GLP-1 concentrations. 2. Compare and contrast the specific effects
Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function
 Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function Background. Following meal ingestion, several hormones are released from the gastrointestinal tract. Some
Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function Background. Following meal ingestion, several hormones are released from the gastrointestinal tract. Some
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Bariatric surgery, such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
 B R I E F R E S E A R C H R E P O R T -Cell Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Contributes to Improved Glucose Tolerance After Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Darline Garibay, Anne K. McGavigan, Seon A. Lee,
B R I E F R E S E A R C H R E P O R T -Cell Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Contributes to Improved Glucose Tolerance After Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Darline Garibay, Anne K. McGavigan, Seon A. Lee,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Diabetologia. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans
 The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
Voglibose, an Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitor, to Increase Active Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Levels
 PharmSight TM DOI: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.09.22 Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology www.mcpharmacol.com Voglibose, an Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitor, to Increase Active Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Levels Yusuke
PharmSight TM DOI: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.09.22 Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology www.mcpharmacol.com Voglibose, an Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitor, to Increase Active Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Levels Yusuke
Scope. History. History. Incretins. Incretin-based Therapy and DPP-4 Inhibitors
 Plasma Glucose (mg/dl) Plasma Insulin (pmol/l) Incretin-based Therapy and Inhibitors Scope Mechanism of action ผศ.ดร.นพ.ว ระเดช พ ศประเสร ฐ สาขาว ชาโภชนว ทยาคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล
Plasma Glucose (mg/dl) Plasma Insulin (pmol/l) Incretin-based Therapy and Inhibitors Scope Mechanism of action ผศ.ดร.นพ.ว ระเดช พ ศประเสร ฐ สาขาว ชาโภชนว ทยาคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล
New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM
 Dale Clayton MHSc, MD, FRCPC Dalhousie University/Capital Health April 28, 2011 New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM The science of today, is the technology of tomorrow. Edward Teller American Physicist
Dale Clayton MHSc, MD, FRCPC Dalhousie University/Capital Health April 28, 2011 New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM The science of today, is the technology of tomorrow. Edward Teller American Physicist
Targeting simultaneously GLP-1, GIP and glucagon receptors : a new paradigm for treating obesity and diabetes
 SHORT COMMENT FOR NATURE REVIEWS ENDOCRINOLOGY Targeting simultaneously GLP-1, GIP and glucagon receptors : a new paradigm for treating obesity and diabetes André J. SCHEEN (1), Nicolas PAQUOT (2) (1)
SHORT COMMENT FOR NATURE REVIEWS ENDOCRINOLOGY Targeting simultaneously GLP-1, GIP and glucagon receptors : a new paradigm for treating obesity and diabetes André J. SCHEEN (1), Nicolas PAQUOT (2) (1)
My Journey in Endocrinology. Samuel Cataland M.D
 My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery but not vertical sleeve gastrectomy decreases bone mass in male rats
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery but not vertical sleeve gastrectomy decreases bone mass in male rats 1 Kerstin Stemmer, 2 Maximilian Bielohuby, 3 Bernadette E. Grayson, 3 Denovan P.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery but not vertical sleeve gastrectomy decreases bone mass in male rats 1 Kerstin Stemmer, 2 Maximilian Bielohuby, 3 Bernadette E. Grayson, 3 Denovan P.
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE. CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010
 Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Gut hormones KHATTAB
 Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice.
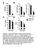 Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP
 Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
7/31/2009. G.Y. Prince Used Cars 10 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland Drive..later that day. Would you buy a car without taking it for a spin first?
 7/31/29 My Anna will love it! Who needs a test drive? Or a Warranty? It looked great in the lot! Do mean to say that you never actually test drove the car? G.Y. Prince Used Cars 1 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland
7/31/29 My Anna will love it! Who needs a test drive? Or a Warranty? It looked great in the lot! Do mean to say that you never actually test drove the car? G.Y. Prince Used Cars 1 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland
Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects 1 4
 Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects 1 4 Jerry R Greenfield, I Sadaf Farooqi, Julia M Keogh, Elana
Oral glutamine increases circulating glucagon-like peptide 1, glucagon, and insulin concentrations in lean, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects 1 4 Jerry R Greenfield, I Sadaf Farooqi, Julia M Keogh, Elana
GLP-1 agonists. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA. Objectives. Scope of Problem: Obesity. Background. Pathophysiology of T2DM
 Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA Objectives Identify patients in the pediatric population with T2DM that would potentially benefit from the use of GLP-1 RA Discuss changes in glycemic outcomes
Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA Objectives Identify patients in the pediatric population with T2DM that would potentially benefit from the use of GLP-1 RA Discuss changes in glycemic outcomes
Appetite, Glycemia and Entero-Insular Hormone Responses Differ Between Oral, Gastric-Remnant and Duodenal Administration of a Mixed Meal Test After
 Appetite, Glycemia and Entero-Insular Hormone Responses Differ Between Oral, Gastric-Remnant and Duodenal Administration of a Mixed Meal Test After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass June 2018 How a surgical complication
Appetite, Glycemia and Entero-Insular Hormone Responses Differ Between Oral, Gastric-Remnant and Duodenal Administration of a Mixed Meal Test After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass June 2018 How a surgical complication
Megan Lawless. Journal Club. January 20 th, 2011
 Megan Lawless Journal Club January 20 th, 2011 Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences September 2007 Abstract
Megan Lawless Journal Club January 20 th, 2011 Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences September 2007 Abstract
Zurich Open Repository and Archive. The dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor NVP-DPP728 reduces plasma glucagon concentration in cats
 University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2009 The dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor NVP-DPP728 reduces plasma glucagon concentration
University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2009 The dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor NVP-DPP728 reduces plasma glucagon concentration
28 Regulation of Fasting and Post-
 28 Regulation of Fasting and Post- Prandial Glucose Metabolism Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes, endogenous glucose production, splanchnic glucose uptake, gluconeo-genesis, glycogenolysis, glucose effectiveness.
28 Regulation of Fasting and Post- Prandial Glucose Metabolism Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes, endogenous glucose production, splanchnic glucose uptake, gluconeo-genesis, glycogenolysis, glucose effectiveness.
Characterization of GLP-1 Effects on -Cell Function After Meal Ingestion in Humans
 Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Characterization of GLP-1 Effects on -Cell Function After Meal Ingestion in Humans BO AHRÉN, MD, PHD 1 JENS J. HOLST, MD, PHD 2 ANDREA
Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Characterization of GLP-1 Effects on -Cell Function After Meal Ingestion in Humans BO AHRÉN, MD, PHD 1 JENS J. HOLST, MD, PHD 2 ANDREA
Blood glucose concentrations in healthy humans
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Glycemia on Plasma Incretins and the Incretin Effect During Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Marzieh Salehi, 1 Benedict Aulinger, 1 and David A. D Alessio 1,2 The incretin effect,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Glycemia on Plasma Incretins and the Incretin Effect During Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Marzieh Salehi, 1 Benedict Aulinger, 1 and David A. D Alessio 1,2 The incretin effect,
22 Emerging Therapies for
 22 Emerging Therapies for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Siddharth N Shah Abstract: The prevalence of Diabetes is progressively increasing world-wide and the growth of the disease in our country is phenomenal.
22 Emerging Therapies for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Siddharth N Shah Abstract: The prevalence of Diabetes is progressively increasing world-wide and the growth of the disease in our country is phenomenal.
Diabetes: What is the scope of the problem?
 Diabetes: What is the scope of the problem? Elizabeth R. Seaquist MD Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes Department of Medicine Director, General Clinical Research Center Pennock Family Chair in Diabetes
Diabetes: What is the scope of the problem? Elizabeth R. Seaquist MD Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes Department of Medicine Director, General Clinical Research Center Pennock Family Chair in Diabetes
Update on GLP-1 Past Present Future
 Update on GLP-1 p Past Present Future Effects of GLP-1: Glucose Metabolism and Nutritional Balance L-Cells: Glp-1 release Betacellfollowing ingestion Stress Increases satiety reduces appetite Betacell-
Update on GLP-1 p Past Present Future Effects of GLP-1: Glucose Metabolism and Nutritional Balance L-Cells: Glp-1 release Betacellfollowing ingestion Stress Increases satiety reduces appetite Betacell-
EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS. Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008
 EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008 THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Exocrine pancreas Endocrine pancreas THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS EXOCRINE
EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008 THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Exocrine pancreas Endocrine pancreas THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS EXOCRINE
Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital
 Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
EXENDIN-4 IS A 39-amino acid reptilian peptide that
 0021-972X/04/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 89(7):3469 3473 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-032001 Exendin-4 Normalized Postcibal
0021-972X/04/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 89(7):3469 3473 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-032001 Exendin-4 Normalized Postcibal
Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing L cell and cell glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion
 Supplementary online material to Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing L cell and cell glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion Helga Ellingsgaard 1, Irina Hauselmann 1, Beat Schuler 2, Abdella
Supplementary online material to Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing L cell and cell glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion Helga Ellingsgaard 1, Irina Hauselmann 1, Beat Schuler 2, Abdella
GLUCAGON LIKE PEPTIDE (GLP) 1 AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES, WEIGHT CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR PROTECTION.
 GLUCAGON LIKE PEPTIDE (GLP) 1 AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES, WEIGHT CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR PROTECTION. Patricia Garnica MS, ANP-BC, CDE, CDTC Inpatient Diabetes Nurse Practitioner North
GLUCAGON LIKE PEPTIDE (GLP) 1 AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES, WEIGHT CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR PROTECTION. Patricia Garnica MS, ANP-BC, CDE, CDTC Inpatient Diabetes Nurse Practitioner North
SELECTED ABSTRACTS AND POSTER PRESENTATIONS
 SELECTED ABSTRACTS AND POSTER PRESENTATIONS The following summaries are based on abstracts and posters presented at the American Diabetes Association s 65th Annual Scientific Sessions held in San Diego,
SELECTED ABSTRACTS AND POSTER PRESENTATIONS The following summaries are based on abstracts and posters presented at the American Diabetes Association s 65th Annual Scientific Sessions held in San Diego,
adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K[ Citation Journal of Diabetes Investigation ( modifications or adaptations are ma
 Fructose induces glucose-dependent Titleglucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K[ Seino, Yusuke; Ogata, Hidetada; Mae Author(s) Takako; Iida, Atsushi; Harada, Nori Susumu;
Fructose induces glucose-dependent Titleglucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K[ Seino, Yusuke; Ogata, Hidetada; Mae Author(s) Takako; Iida, Atsushi; Harada, Nori Susumu;
Full title: The effect of encapsulated glutamine on gut peptide secretion in human volunteers
 Original Article Full title: The effect of encapsulated glutamine on gut peptide secretion in human volunteers Authors: Claire L Meek 1,2 Hannah B Lewis 1 Bensi Vergese 1 Adrian Park 2 Frank Reimann 1
Original Article Full title: The effect of encapsulated glutamine on gut peptide secretion in human volunteers Authors: Claire L Meek 1,2 Hannah B Lewis 1 Bensi Vergese 1 Adrian Park 2 Frank Reimann 1
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes Prof. Marc Y. Donath
 Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery. Goal of Treating T2DM. Remission of T2DM with Bariatric
 Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery Number (in Millions) of Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 198 25 The number of Americans with diabetes increased from 5.6 to 15.8 million Guilherme
Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery Number (in Millions) of Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 198 25 The number of Americans with diabetes increased from 5.6 to 15.8 million Guilherme
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Role of incretins in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
 Role of incretins in the treatment of type 2 diabetes Jens Juul Holst Department of Medical Physiology Panum Institute University of Copenhagen Denmark Diabetes & Obesity Spanish Society of Internal Medicine
Role of incretins in the treatment of type 2 diabetes Jens Juul Holst Department of Medical Physiology Panum Institute University of Copenhagen Denmark Diabetes & Obesity Spanish Society of Internal Medicine
Bariatric Surgery MM /11/2001. HMO; PPO; QUEST 05/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient; Inpatient
 Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 05/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient;
Bariatric Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.003 09/11/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 05/01/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient;
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Case. Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare
 Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview. Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU
 Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Changing Diabetes: The time is now!
 Midwest Cardiovascular Research Foundation Welcomes DANITA HARRISON, ARNP Ms. Harrison discloses speaking relationships with Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Pfizer. Changing Diabetes: The time is now! Danita Harrison
Midwest Cardiovascular Research Foundation Welcomes DANITA HARRISON, ARNP Ms. Harrison discloses speaking relationships with Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Pfizer. Changing Diabetes: The time is now! Danita Harrison
type 2 diabetes is a surgical disease
 M. Lannoo, MD, University Hospitals Leuven Walter Pories claimed in 1992 type 2 diabetes is a surgical disease Buchwald et al. conducted a large meta-analysis THE FIRST OBSERVATIONS W. Pories 500 patients
M. Lannoo, MD, University Hospitals Leuven Walter Pories claimed in 1992 type 2 diabetes is a surgical disease Buchwald et al. conducted a large meta-analysis THE FIRST OBSERVATIONS W. Pories 500 patients
British Journal of Nutrition
 , page 1 of 5 q The Authors 2013 doi:10.1017/s0007114513000731 Endogenous plasma glucagon-like peptide-1 following acute dietary fibre consumption Caroline L. Bodinham*, Najlaa M. Al-Mana, Leanne Smith
, page 1 of 5 q The Authors 2013 doi:10.1017/s0007114513000731 Endogenous plasma glucagon-like peptide-1 following acute dietary fibre consumption Caroline L. Bodinham*, Najlaa M. Al-Mana, Leanne Smith
GLP-1 receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes A rationale drug. development. Bo Ahrén
 PROF. BO AHREN (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-9804-5340) Article type : Mini Review GLP-1 receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes A rationale drug development Bo Ahrén Department of Clinical Sciences Lund, Lund University,
PROF. BO AHREN (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-9804-5340) Article type : Mini Review GLP-1 receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes A rationale drug development Bo Ahrén Department of Clinical Sciences Lund, Lund University,
Hyperglycaemia increases dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity in diabetes mellitus
 Diabetologia (2005) 48: 1168 1172 DOI 10.1007/s00125-005-1749-8 ARTICLE E. Mannucci. L. Pala. S. Ciani. G. Bardini. A. Pezzatini. I. Sposato. F. Cremasco. A. Ognibene. C. M. Rotella Hyperglycaemia increases
Diabetologia (2005) 48: 1168 1172 DOI 10.1007/s00125-005-1749-8 ARTICLE E. Mannucci. L. Pala. S. Ciani. G. Bardini. A. Pezzatini. I. Sposato. F. Cremasco. A. Ognibene. C. M. Rotella Hyperglycaemia increases
Sweetness and Glycaemic Regulation. (A focus on gut related and physiological aspects) John McLaughlin Manchester University
 Sweetness and Glycaemic Regulation (A focus on gut related and physiological aspects) John McLaughlin Manchester University Disclosures No personal conflicts of interest Funding from BBSRC, including Cargill
Sweetness and Glycaemic Regulation (A focus on gut related and physiological aspects) John McLaughlin Manchester University Disclosures No personal conflicts of interest Funding from BBSRC, including Cargill
Metformin activates a duodenal Ampk-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose production
 activates a duodenal Ampk-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose Frank A. Duca, Clémence D. Côté, Brittany A. Rasmussen, Melika Zadeh-Tahmasebi, Guy A. Rutter, Beatrice M. Filippi & Tony K.T. Lam Supplementary
activates a duodenal Ampk-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose Frank A. Duca, Clémence D. Côté, Brittany A. Rasmussen, Melika Zadeh-Tahmasebi, Guy A. Rutter, Beatrice M. Filippi & Tony K.T. Lam Supplementary
Soliqua (insulin glargine and lixisenatide), Xultophy (insulin degludec and liraglutide)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.48 Subject: Insulin GLP-1 Combinations Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Insulin GLP-1
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.48 Subject: Insulin GLP-1 Combinations Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Insulin GLP-1
GPR119 Regulates Murine Glucose Homeostasis Through Incretin Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms
 GPR119 Regulates Murine Glucose Homeostasis Through Incretin Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms Grace Flock, Dianne Holland, Yutaka Seino and Daniel J. Drucker Endocrinology 2011 152:374-383
GPR119 Regulates Murine Glucose Homeostasis Through Incretin Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms Grace Flock, Dianne Holland, Yutaka Seino and Daniel J. Drucker Endocrinology 2011 152:374-383
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors. Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018
 Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018 Objectives For each drug class: Identify the overall place in therapy Explain the mechanism of action
Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018 Objectives For each drug class: Identify the overall place in therapy Explain the mechanism of action
BARIATRIC SURGERY AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
 BARIATRIC SURGERY AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS George Vl Valsamakis European Scope Fellow Obesity Visiting iti Associate Prof Warwick Medical School Diabetes is an increasing healthcare epidemic throughout
BARIATRIC SURGERY AND TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS George Vl Valsamakis European Scope Fellow Obesity Visiting iti Associate Prof Warwick Medical School Diabetes is an increasing healthcare epidemic throughout
Agonists at GPR119 mediate secretion of GLP-1 from mouse enteroendocrine cells through glucoseindependent
 2799..2807 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01754.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1754 Agonists at GPR119 mediate secretion of GLP-1 from mouse enteroendocrine cells
2799..2807 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01754.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1754 Agonists at GPR119 mediate secretion of GLP-1 from mouse enteroendocrine cells
Normal Fuel Metabolism Five phases of fuel homeostasis have been described A. Phase I is the fed state (0 to 3.9 hours after meal/food consumption),
 Normal Fuel Metabolism Five phases of fuel homeostasis have been described A. Phase I is the fed state (0 to 3.9 hours after meal/food consumption), in which blood glucose predominantly originates from
Normal Fuel Metabolism Five phases of fuel homeostasis have been described A. Phase I is the fed state (0 to 3.9 hours after meal/food consumption), in which blood glucose predominantly originates from
Exendin-4-mediated cell proliferation in beta-cells: focusing on the transcription factors
 Exendin-4-mediated cell proliferation in beta-cells: focusing on the transcription factors Seo-Yoon Chang, Jae Min Cho, Yang-Hyeok Jo, Myung-Jun Kim Departments of Physiology, College of Medicine, The
Exendin-4-mediated cell proliferation in beta-cells: focusing on the transcription factors Seo-Yoon Chang, Jae Min Cho, Yang-Hyeok Jo, Myung-Jun Kim Departments of Physiology, College of Medicine, The
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
MULTI-ARRAY. 1-Plate Kit 5-Plate Kit 25-Plate Kit
 MESO SCALE DISCOVERY MULTI-ARRAY Assay System Active GLP-1 (ver. 2) Assay Kit 1-Plate Kit 5-Plate Kit 25-Plate Kit K150JWC-1 K150JWC-2 K150JWC-4 MESO SCALE DISCOVERY MESO SCALE DISCOVERY MESO SCALE DISCOVERY
MESO SCALE DISCOVERY MULTI-ARRAY Assay System Active GLP-1 (ver. 2) Assay Kit 1-Plate Kit 5-Plate Kit 25-Plate Kit K150JWC-1 K150JWC-2 K150JWC-4 MESO SCALE DISCOVERY MESO SCALE DISCOVERY MESO SCALE DISCOVERY
Drug Class Monograph
 Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
The augmenting effect on insulin secretion by oral versus intravenous glucose is exaggerated by high-fat diet in mice
 181 The augmenting effect on insulin secretion by oral versus intravenous glucose is exaggerated by high-fat diet in mice Bo Ahrén, Maria Sörhede Winzell and Giovanni Pacini 1 Department of Clinical Sciences,
181 The augmenting effect on insulin secretion by oral versus intravenous glucose is exaggerated by high-fat diet in mice Bo Ahrén, Maria Sörhede Winzell and Giovanni Pacini 1 Department of Clinical Sciences,
An integrated glucose homeostasis model of glucose, insulin, C-peptide, GLP-1, GIP and glucagon in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes
 An integrated glucose homeostasis model of glucose, insulin, C-peptide, GLP-1, GIP and glucagon in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes Oskar Alskär, Jonatan Bagger, Rikke Røge, Kanji Komatsu,
An integrated glucose homeostasis model of glucose, insulin, C-peptide, GLP-1, GIP and glucagon in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes Oskar Alskär, Jonatan Bagger, Rikke Røge, Kanji Komatsu,
T2DM is a global epidemic with
 : a new option for the management of type 2 diabetes Marc Evans MRCP, MD, Consultant Diabetologist, Llandough Hospital, Cardiff Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of diabetes mellitus (T2DM) present
: a new option for the management of type 2 diabetes Marc Evans MRCP, MD, Consultant Diabetologist, Llandough Hospital, Cardiff Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of diabetes mellitus (T2DM) present
Data from an epidemiologic analysis of
 CLINICAL TRIAL RESULTS OF GLP-1 RELATED AGENTS: THE EARLY EVIDENCE Lawrence Blonde, MD, FACP, FACE ABSTRACT Although it is well known that lowering A 1c (also known as glycated hemoglobin) is associated
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULTS OF GLP-1 RELATED AGENTS: THE EARLY EVIDENCE Lawrence Blonde, MD, FACP, FACE ABSTRACT Although it is well known that lowering A 1c (also known as glycated hemoglobin) is associated
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) Agonists (Byetta, Bydureon, Tanzeum, Trulicity, Victoza ) Step Therapy and Quantity Limit Criteria Program Summary
 OBJECTIVE The intent of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) s (Byetta/exenatide, Bydureon/ exenatide extended-release, Tanzeum/albiglutide, Trulicity/dulaglutide, and Victoza/liraglutide) Step Therapy
OBJECTIVE The intent of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) s (Byetta/exenatide, Bydureon/ exenatide extended-release, Tanzeum/albiglutide, Trulicity/dulaglutide, and Victoza/liraglutide) Step Therapy
Motility Conference Ghrelin
 Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Product Theaters. Light refreshments provided by the American Diabetes Association will be served to the first 300 attendees.
 Product Theaters Product Theaters, located in the rear of the Exhibit Hall, offer informative sessions focusing on particular products or a single facet of diabetes. Product Theater sessions do not provide
Product Theaters Product Theaters, located in the rear of the Exhibit Hall, offer informative sessions focusing on particular products or a single facet of diabetes. Product Theater sessions do not provide
Abstract. Effect of sitagliptin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Introduction. Abbas Mahdi Rahmah
 Effect of sitagliptin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes Abbas Mahdi Rahmah Correspondence: Dr. Abbas Mahdi Rahmah Consultant Endocrinologist, FRCP (Edin) Director of Iraqi National Diabetes
Effect of sitagliptin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes Abbas Mahdi Rahmah Correspondence: Dr. Abbas Mahdi Rahmah Consultant Endocrinologist, FRCP (Edin) Director of Iraqi National Diabetes
Extrapancreatic incretin receptors modulate glucose homeostasis, body weight, and energy expenditure
 Research article Extrapancreatic incretin receptors modulate glucose homeostasis, body weight, and energy expenditure Tanya Hansotia, 1 Adriano Maida, 1 Grace Flock, 1 Yuichiro Yamada, 2 Katsushi Tsukiyama,
Research article Extrapancreatic incretin receptors modulate glucose homeostasis, body weight, and energy expenditure Tanya Hansotia, 1 Adriano Maida, 1 Grace Flock, 1 Yuichiro Yamada, 2 Katsushi Tsukiyama,
a b c Physical appearance of mice Lean mass Adipocyte size d e f
 LFD HFD LFD HFD Area under curve (GTT) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD Area under curve (ITT) HFD-VSL#3 Liver TG content (% l) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD + VSL#3 Lean mass (gm) Mean adipocyte
LFD HFD LFD HFD Area under curve (GTT) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD Area under curve (ITT) HFD-VSL#3 Liver TG content (% l) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD + VSL#3 Lean mass (gm) Mean adipocyte
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Defining the Role of GLP-1 in the Enteroinsulinar Axis in Type 2 Diabetes Using DPP-4 Inhibition and GLP-1 Receptor Blockade
 Diabetes Volume 63, March 2014 1079 Benedikt A. Aulinger, 1 Anne Bedorf, 1 Gabriele Kutscherauer, 1 Jocelyn de Heer, 1 Jens J. Holst, 2 Burkhard Göke, 1 and Jörg Schirra 1 Defining the Role of GLP-1 in
Diabetes Volume 63, March 2014 1079 Benedikt A. Aulinger, 1 Anne Bedorf, 1 Gabriele Kutscherauer, 1 Jocelyn de Heer, 1 Jens J. Holst, 2 Burkhard Göke, 1 and Jörg Schirra 1 Defining the Role of GLP-1 in
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
DPP-4 inhibitor. The new class drug for Diabetes
 DPP-4 inhibitor The new class drug for Diabetes 1 Cause of Death in Korea 1 st ; Neoplasm 2 nd ; Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd ; Cerebrovascular Disease Diabetes 2 Incidence of Fatal or Nonfatal MI During
DPP-4 inhibitor The new class drug for Diabetes 1 Cause of Death in Korea 1 st ; Neoplasm 2 nd ; Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd ; Cerebrovascular Disease Diabetes 2 Incidence of Fatal or Nonfatal MI During
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition by Vildagliptin and the Effect on Insulin Secretion and Action in Response to Meal Ingestion in Type 2 Diabetes
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition by Vildagliptin and the Effect on Insulin Secretion and Action in Response to Meal
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition by Vildagliptin and the Effect on Insulin Secretion and Action in Response to Meal
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle. Dr Bernard SAMIA. KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration
 GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis. Keith Sharkey
 Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis Keith Sharkey Department of Physiology & Pharmacology University of Calgary Dr. Keith Sharkey Financial Interest
Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis Keith Sharkey Department of Physiology & Pharmacology University of Calgary Dr. Keith Sharkey Financial Interest
ROLE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITOR IN GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY
 ROLE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITOR IN GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY An Article Review By Dr.Shaikh Khalid Anwar, India (PG Diploma in Diabetes, MMSc in Diabetology Student
ROLE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITOR IN GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY An Article Review By Dr.Shaikh Khalid Anwar, India (PG Diploma in Diabetes, MMSc in Diabetology Student
PANDER KO mice on high-fat diet are glucose intolerant yet resistant to fasting hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia
 FEBS Letters 585 (2011) 1345 1349 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org PANDER KO mice on high-fat diet are glucose intolerant yet resistant to fasting hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia Claudia E. Robert-Cooperman
FEBS Letters 585 (2011) 1345 1349 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org PANDER KO mice on high-fat diet are glucose intolerant yet resistant to fasting hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia Claudia E. Robert-Cooperman
Therapeutic strategy to reduce Glucagon secretion
 Clinical focus on glucagon: α-cell as a companion of β-cell Therapeutic strategy to reduce Glucagon secretion Sunghwan Suh Dong-A University Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific
Clinical focus on glucagon: α-cell as a companion of β-cell Therapeutic strategy to reduce Glucagon secretion Sunghwan Suh Dong-A University Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific
Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Augments Glucagon Responses to Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes
 72 Diabetes Volume 64, January 2015 Mikkel Christensen, 1,2 Salvatore Calanna, 1,3 Alexander H. Sparre-Ulrich, 1,4 Peter L. Kristensen, 5 Mette M. Rosenkilde, 4 Jens Faber, 6 Francesco Purrello, 3 Gerrit
72 Diabetes Volume 64, January 2015 Mikkel Christensen, 1,2 Salvatore Calanna, 1,3 Alexander H. Sparre-Ulrich, 1,4 Peter L. Kristensen, 5 Mette M. Rosenkilde, 4 Jens Faber, 6 Francesco Purrello, 3 Gerrit
Div. of Endocrinology and Metabolism Konyang University, School of Medicine. Byung-Joon Kim M.D., Ph.D.
 Diabetes and Thyroid Center Div. of Endocrinology and Metabolism Konyang University, School of Medicine Byung-Joon Kim M.D., Ph.D. Background Incretin effect and GLP 1 Receptor in L cells TGR5 receptor
Diabetes and Thyroid Center Div. of Endocrinology and Metabolism Konyang University, School of Medicine Byung-Joon Kim M.D., Ph.D. Background Incretin effect and GLP 1 Receptor in L cells TGR5 receptor
GLP-1 released to the mesenteric lymph duct in mice: Effects of glucose and fat.
 GLP-1 released to the mesenteric lymph duct in mice: Effects of glucose and fat. Ohlsson, Lena; Kohan, Alison B; Tso, Patrick; Ahrén, Bo Published in: Regulatory Peptides DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2014.02.001
GLP-1 released to the mesenteric lymph duct in mice: Effects of glucose and fat. Ohlsson, Lena; Kohan, Alison B; Tso, Patrick; Ahrén, Bo Published in: Regulatory Peptides DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2014.02.001
Non-nutritive sweeteners: no class effect on the glycemic or appetite responses to ingested glucose
 Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014 May ; 68(5): 629 631. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2014.19. Non-nutritive sweeteners: no class effect on the glycemic
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014 May ; 68(5): 629 631. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2014.19. Non-nutritive sweeteners: no class effect on the glycemic
Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice
 Diabetologia (211) 4:339 349 DOI 1.17/s12-1-1937-z ARTICLE Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice A. Maida & B. J.
Diabetologia (211) 4:339 349 DOI 1.17/s12-1-1937-z ARTICLE Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice A. Maida & B. J.
Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice
 DOI.7/s125--1937-z ARTICLE Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice A. Maida & B. J. Lamont & X. Cao & D. J. Drucker
DOI.7/s125--1937-z ARTICLE Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice A. Maida & B. J. Lamont & X. Cao & D. J. Drucker
Personalized therapeutics in diabetes
 Personalized therapeutics in diabetes Leen M. t Hart Molecular Cell Biology & Molecular Epidemiology Leiden University Medical Center Epidemiology & Biostatistics VU University Medical Center Diabetes
Personalized therapeutics in diabetes Leen M. t Hart Molecular Cell Biology & Molecular Epidemiology Leiden University Medical Center Epidemiology & Biostatistics VU University Medical Center Diabetes
Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction as a lean model of bariatric surgery
 Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases ] (2018) 00 00 Original article Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction as a lean model of bariatric surgery Geoffrey P. Roberts, M.A. (Cantab), B.M., B.Ch.,
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases ] (2018) 00 00 Original article Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y reconstruction as a lean model of bariatric surgery Geoffrey P. Roberts, M.A. (Cantab), B.M., B.Ch.,
Objectives. Define satiety and satiation Summarize the satiety cascade Describe potential dietary interventions aimed at improving satiety
 Foods that Fill Monica Esquivel PhD RDN Assistant Professor, Dietetics Program Director Department of Human Nutrition, Food and Animal Sciences November 8, 2017 Objectives Define satiety and satiation
Foods that Fill Monica Esquivel PhD RDN Assistant Professor, Dietetics Program Director Department of Human Nutrition, Food and Animal Sciences November 8, 2017 Objectives Define satiety and satiation
INJECTABLE THERAPIES IN DIABETES. Barbara Ann McKee Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 INJECTABLE THERAPIES IN DIABETES Barbara Ann McKee Diabetes Specialist Nurse 1 Aims of the session Describe the different injectable agents for diabetes and when they would be used. Describe some common
INJECTABLE THERAPIES IN DIABETES Barbara Ann McKee Diabetes Specialist Nurse 1 Aims of the session Describe the different injectable agents for diabetes and when they would be used. Describe some common
Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes
 9/23/215 Multiple, Complex Pathophysiological Abnmalities in T2DM incretin effect gut carbohydrate delivery & absption pancreatic insulin secretion pancreatic glucagon secretion HYPERGLYCEMIA? Pathogenesis
9/23/215 Multiple, Complex Pathophysiological Abnmalities in T2DM incretin effect gut carbohydrate delivery & absption pancreatic insulin secretion pancreatic glucagon secretion HYPERGLYCEMIA? Pathogenesis
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Is obesity a brain disorder? What is the evidence to support obesity is a brain disorder? Environmental, biological, and behavioral issues Over
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Is obesity a brain disorder? What is the evidence to support obesity is a brain disorder? Environmental, biological, and behavioral issues Over
ROLE OF TASTE IN METABOLIC CONTROL OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
 Progress report ROLE OF TASTE IN METABOLIC CONTROL OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Dr Gianluca Tornese, MD, PhD Background The sense of taste is one of the main factors that determine the choice of food and
Progress report ROLE OF TASTE IN METABOLIC CONTROL OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Dr Gianluca Tornese, MD, PhD Background The sense of taste is one of the main factors that determine the choice of food and
Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment. Session 2: Individualizing Therapy
 Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment Session 2: Individualizing Therapy Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism
Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment Session 2: Individualizing Therapy Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism
Preserved insulin secretory capacity and weight loss are the predominant predictors
 Page 1 of 23 Preserved insulin secretory capacity and weight loss are the predominant predictors of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Kim T. Nguyen,
Page 1 of 23 Preserved insulin secretory capacity and weight loss are the predominant predictors of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Kim T. Nguyen,
