UNCOVERING CIRCULATING FACTORS LINKING PREDIABETES TO DIABETES. Ying Liu PhD Mar.07/2017
|
|
|
- Charity Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNCOVERING CIRCULATING FACTORS LINKING PREDIABETES TO DIABETES Ying Liu PhD Mar.07/2017
2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A MULTI-ORGAN DISEASE Initiation Stage Brain Liver Disrupted Metabolic Homeostasis Pancreas Adipose Tissue Skeletal Muscle Gut
3 DIABETES MELLITUS: A MULTI-ORGAN DISEASE Disease Stage Hyperglycemia
4 DIABETES MELLITUS Insulin Type 1 Diabetes: beta cell destruction Type 2 Diabetes: beta cell failure in respond to peripheral metabolic demands Gestational Diabetes: Insufficient beta cell function in pregnancy Red: Insulin (β cells) Green: Glucagon (α cells) Blue: Nucleus
5 DIABETES MELLITUS: A PROGRESSIVE DISEASE Compensatory Stage Disease Stage Normal Prediabetes Diabetes Severe Insulin Resistance Beta Cell Dysfunction
6 WHAT CAN WE DO??? Early Detection Prevent disease progression Therapeutic Targets Prevent loss of or restore β cell function β cell Replacement Therapy to restore β cell function Normal Prediabetes Diabetes Severe
7 WHAT CAN WE DO??? Early Detection Therapeutic Targets 1. DISCOVER Discover novel metabolites which cause β cell failure 2. PREDICT & DETECT Establish novel and sensitive biomarkers to predict and detect Diabetes
8 DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Cohort 1 Cohort 2 GDM: Toronto/Canada BMI, Age, Race Matched 3 rd trimester T2D: Shanghai/China BMI, Age, Sex Matched Prospective Cohort (2007, ,2012) One Step Diagnosis Pre-diabetes Diagnosis 75g NGT: OGTT: 24 Normal: 50 fasting: mmol/l or GDM: fasting 24 Pre-diabetes: 75 > 5.1mmol/L 75g OGTT 2hr: Diabetes: 71 1hr > 10.0 mmol/l mmol/l 2hr > 8.5 mmol/l Diabetes Diagnosis Fasting 7.0 mmol/l or Newly Diagnosed Diabetes, No 75g Drug OGTT Intervention 2hr 11 mmol/l GDM, Prediabetes and Diabetes conditions were determined based on ADA criteria (American Diabetes, 2014)
9 DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Metabolomics: Advancing Technology for Biological Discovery Blood Sample Amino Acids Nucleotides Carbohydrate Lipids
10 DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Cohort 1: Toronto GDM & Cohort 2: Shanghai T2D Up-regulation 342 metabolites Down-regulation Amino Acids Xenobiotics Amino Acids Lipids Peptides Lipids Nucleotides Prentice et. al., Cell Metabolism, 2014
11 pyroglutamine* N6-acetyllysine 3-hydroxyisobutyrate tiglyl carnitine 2-hydroxybutyrate (AHB) arginine creatine 2-aminobutyrate 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) eicosapentaenoate (EPA; 20:5n3) docosapentaenoate (n3 DPA; 22:5n3) nonadecanoate (19:0) 10-nonadecenoate (19:1n9) eicosenoate (20:1n9 or 11) dihomo-linoleate (20:2n6) arachidonate (20:4n6) docosadienoate (22:2n6) adrenate (22:4n6) 2-hydroxystearate 2-hydroxypalmitate 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2- hexanoylcarnitine octanoylcarnitine decanoylcarnitine cis-4-decenoyl carnitine laurylcarnitine 3-hydroxybutyrate (BHBA) 1-palmitoylglycerophosphoinositol* pregnenolone sulfate Prentice et. al., Cell Metabolism, 2014 Fold Change Over NGT DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Cohort 1: Toronto - GDM Cohort 2: Shanghai T2D Amino Acids Lipids
12 WHAT IS CMPF? FURAN FATTY ACID METABOLITE 3-CARBOXY-4-METHYL-5-PROPYL-2-FURANPROPANOIC ACID CMPF Furan fatty acid dibasic urofuran acids Phospholipids Cholesterol TG catabolism Spiteller Gerhard, Furan fatty acids: occurrence, synthesis, and reactions. Are furan fatty acids responsible for the cardioprotective effects of a fish diet?; Lipids; 2005 Aug;40(8):
13 CMPF IN UREMIC PATIENTS Uremia Patients Impaired Insulin Secretion CMPF Diabetes Niwa et al., 1988; Allegra et al., 1994; De Marchi et al.,1987; DeFronzo, 1978; Nakamura et al., 1985
14 DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Cohort 1: Toronto - GDM Pregnant Postpartum Prentice et. al., Cell Metabolism, 2014
15 DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Cohort 2: Shanghai T2D Prospective Cohort (2007, ,2012) Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
16 DISCOVER NOVEL METABOLITE Cohort 2: Shanghai T2D Relation between the change in CMPF levels and the risk of future diabetes development, with adjustment for Age, Sex, BMI and estimated glomerular filtration rate A large elevation in circulating CMPF concentrations is associated with increased risk of diabetes development Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
17 DIABETES MELLITUS: A PROGRESSIVE DISEASE Compensatory Stage Disease Stage Normal Prediabetes Diabetes Severe CMPF β cell dysfunction What role does CMPF play during the progression of diabetes?
18 CMPF AND ΒETA CELL FUNCTION Normal Prediabetes Diabetes Severe CMPF Diet Predisposed Model (DIO) Genetic Predisposed Model (Ob/Ob) Sucrose matched chow 60% high fat diet Vehicle Vehicle CMPF (6mg/kg/day) Chow DIO DIO (w/cmpf) Vehicle CMPF (6mg/kg/day) Ob/Ob Ob/Ob (w/cmpf) 6wk 2wk i.p. injection 2wk i.p. injection Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
19 CMPF AND ΒETA CELL FUNCTION Glucose Tolerance Test Insulin Secretion in-vivo Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
20 CMPF AND ΒETA CELL FUNCTION Insulin Secretion ex-vivo Elevated CMPF Impairs Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion and may Potentiate the Development of Diabetes in Rodent Models Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
21 INSULIN SECRETION IN ΒETA CELL Glucose Sensing (Glycolysis) x Metabolism x ATP production x Insulin Biosynthesis x Exocytosis x CMPF
22 CMPF: GLUCOSE SENSING (GLYCOLYSIS) Glucose Uptake Glycolysis Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) CMPF Impairs Glycolysis Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
23 CMPF: MITOCHONDRIAL METABOLISM Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
24 CMPF: MITOCHONDRIAL METABOLISM Glucose Oxidation Mitochondrial Biogenesis CMPF Impairs Glucose Metabolism without affect Mitochondrial Biogenesis Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
25 Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016 CMPF: MITOCHONDRIAL METABOLISM Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) CMPF Impairs Glucose Metabolism by Metabolic Remodeling to Enhance Fatty Acid Metabolism Fatty Acid Oxidation
26 Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016 CMPF: METABOLIC REMODELING ROS Apoptosis Advanced Glycation End-products (AGEs) CMPF Increases Advanced Glycation End-Products and Oxidative Stress
27 CMPF: INSULIN SECRETION IN ΒETA CELL Insulin Biosynthesis Insulin Exocytosis
28 CMPF: INSULIN BIOSYNTHESIS & EXOCYTOSIS Insulin Content Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
29 CMPF: INSULIN BIOSYNTHESIS & EXOCYTOSIS Transmitted Electron Microscopy (TEM) Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
30 CMPF: INSULIN BIOSYNTHESIS & EXOCYTOSIS The constitutive secretory pathway present in all cell types does not require stimulation for exocytosis Constitutive Secretory Pathway Golgi complex Regulated Secretory Pathway Secretory granules bud from the TGN as immature secretory granules (ISGs) Immature secretory granules Clathrin-coated ISCs contain missioned non-granule proteins (eg. Furin, lysosomal enzymes, etc.) ISGs remove missioned proteins and clathrin coats by budding off constitutive-like vesicles Constitutive-like vesicles Lysosome Mature secretory granules After further acidification and condensation, ISGs become mature Secretagogu e The mature granules (MSGs) are secreted via triggering by a secretagogue Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
31 CMPF: INSULIN BIOSYNTHESIS & EXOCYTOSIS Transmitted Electronic Microscopy (TEM) Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
32 CMPF: INSULIN BIOSYNTHESIS & EXOCYTOSIS Cellular Exocytosis: Secretion Fed Fast CMPF Increases Proinsulin and Impairs Insulin Granule Maturation Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
33 Human Study 1. CMPF significantly elevated in Prediabetes and Diabetes population. 2. Rapid elevation may be a high risk for future diabetes development Animal Study 1. CMPF impairs glucose metabolism by introducing preferential fatty acid oxidation 2. CMPF induces beta cell dysfunction shown as impaired insulin secretion Rapid Elevation of CMPF May Act as a Tipping Point Towards β Cell Dysfunction During Diabetes Development Liu et. al., Cell Reports, 2016
34 ACKNOWLODGEMENTS University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital Dr. Michael Wheeler Dr. Kacey Prentice Amina Allalou Andrea Eversley Dr. Feihan Dai Kaiser Permanente Oakland, USA Dr. Erica Gunderson Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Analytical Facility for Bioactive Molecules 6 th People s Hospital, Shanghai, China Dr. Weiping Jia Dr. Wei Li Dr. Cheng Hu
35 WHAT CAN WE DO??? Early Detection Therapeutic Targets 1. DISCOVER CMPF Discover novel metabolites which cause β cell failure 2. PREDICT & DETECT Establish novel and sensitive biomarkers to predict and detect Diabetes
36 dimethylglycine aspartate glutamine N6-acetyllysine 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate kynurenine C-glycosyltryptophan* alpha-hydroxyisocaproate alpha-hydroxyisovalerate isovalerylcarnitine methylglutaroylcarnitine N-acetylmethionine alpha-ketobutyrate urea creatinine glycylvaline phenylalanylphenylalanine histidylphenylalanine glycylphenylalanine phenylalanyltryptophan gamma-glutamyltyrosine erythronate* mannose methyl-beta-glucopyranoside glucose ribitol ribose alpha-ketoglutarate malate docosapentaenoate (n3 DPA; 22:5n3) caprylate (8:0) caprate (10:0) stearate (18:0) cis-vaccenate (18:1n7) 10-nonadecenoate (19:1n9) dihomo-linoleate (20:2n6) docosadienoate (22:2n6) 2-hydroxystearate 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoate (CMPF) 17-methylstearate hydroxybutyrylcarnitine* hexanoylcarnitine decanoylcarnitine laurylcarnitine glycerol 3-phosphate (G3P) 1-palmitoylglycerophosphoethanolamine 2-docosahexaenoylglycerophosphoethanolamine* 1-myristoylglycerophosphocholine (14:0) 1-eicosatrienoylglycerophosphocholine* 1-palmitoylglycerophosphoinositol* 1-linolenoylglycerophosphocholine (18:3n3)* epiandrosterone sulfate 4-androsten-3beta,17beta-diol disulfate 2* pregn steroid monosulfate* pregnenolone sulfate inosine threonate bilirubin (E,E)* gamma-cehc Fold Change Over NGT ESTABLISH BIOMARKERS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES Glucose Amino acids Carbs Lipids Other Metabolomic Signature: it is more than just hyperglycemia Fold Change Over NGT What can we do with this data??? Amino Acids Peptides Carbs Energy
37 Allalou et. al., Diabetes, 2016 ESTABLISH SIGNATURE PANELS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES Fasting Blood Glucose/OGTT Biological Samples HbA1c Clinical Practice Guidelines Targeted MRM-MS Metabolite Identification NGT IGT MRM-MS Fingerprint Prediction of Future DM Within 5 Years Population Risk Individual Risk 10% 40-50% 0%? 100%?
38 Allalou et. al., Diabetes, 2016 ESTABLISH SIGNATURE PANELS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES Identify metabolites associated with GDM/T2D Develop an SRM method for quantification of each metabolite Validate/quantify each metabolite in test plasma 181 metabolites chosen for testing Fatty acids Carbs Amino Acids Other Identify Ion Spectra for each metabolite and validate in blood Assay Prospective Cohort
39 Allalou et. al., Diabetes, 2016 ESTABLISH SIGNATURE PANELS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES SWIFT Prospective GDM Cohort V0: Pregnancy V1 (Baseline) PP: 6-9 weeks V2 PP: 1 year V3 PP: 2 years V4 2 years+ GDM 1035 nont2d 1010 T2D 21 nont2d 912 T2D 58 nont2d 801 T2D 47 T2D 19 By 2.5 years postpartum, 124 women (10.3%) have developed T2D
40 Intensity (x10 3 ) Intensity (x10 3 ) Allalou et. al., Diabetes, 2016 ESTABLISH SIGNATURE PANELS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES : Isoleucine T2D 2: Leucine T2D 3: Isoleucine NGT 4: Leucine NGT Time (min) Over 20 metabolites associated with future T2D status
41 Allalou et. al., Diabetes, 2016 ESTABLISH SIGNATURE PANELS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES Machine Learning: Decision Tree Algorithm PCaeC40:5 3.4 >3.4 T2D Hexose 4.9 >4.9 BCAA SM(OH)C14:1 427 > >4.4 nont2d T2D nont2d T2D
42 Sensitivity Allalou et. al., Diabetes, 2016 ESTABLISH SIGNATURE PANELS TO PREDICT AND DETECT DIABETES SWIFT Prospective GDM Cohort Machine Learning Algorithm Accurately Predicts Future T2D J48 AUC ( ) FPG AUC ( ) 2hPG AUC ( ) Specificity
43 WHAT WE HAVE ACHIEVED SO FAR??? Early Detection Therapeutic Targets 1. DISCOVER Discover novel metabolites which cause β cell failure 2. PREDICT & DETECT Establish novel and sensitive biomarkers to predict and detect Diabetes CMPF Predictive Signature Panel
44 ACKNOWLODGEMENTS University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital Dr. Michael Wheeler Dr. Kacey Prentice Amina Allalou Andrea Eversley Dr. Feihan Dai Kaiser Permanente Oakland, USA Dr. Erica Gunderson Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Canada Analytical Facility for Bioactive Molecules 6 th People s Hospital, Shanghai, China Dr. Weiping Jia Dr. Wei Li Dr. Cheng Hu
45 We need more prospective cohort to test our signature metabolite panel for future diabetes prediction!!! INTERESTED???
Metabolomic profiles of childhood obesity
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only Metabolomic profiles of childhood obesity Wei Perng, Matthew W. Gillman, Abby F. Fleisch, Ryan D. Michalek, Steven Watkins, Elvira Isganaitis, Mary-Elizabeth Patti,
Note: for non-commercial purposes only Metabolomic profiles of childhood obesity Wei Perng, Matthew W. Gillman, Abby F. Fleisch, Ryan D. Michalek, Steven Watkins, Elvira Isganaitis, Mary-Elizabeth Patti,
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
The Synovial Fluid of Post-Traumatic Ankle Arthritis Holds Many Potential Inflammatory Cytokine and Metabolite Biomarkers
 The Synovial Fluid of Post-Traumatic Ankle Arthritis Holds Many Potential Inflammatory Cytokine and Metabolite Biomarkers Samuel B. Adams, MD Lynne C. Jones, PhD Azeb Haile, BS Gregory P. Guyton, MD Stuart
The Synovial Fluid of Post-Traumatic Ankle Arthritis Holds Many Potential Inflammatory Cytokine and Metabolite Biomarkers Samuel B. Adams, MD Lynne C. Jones, PhD Azeb Haile, BS Gregory P. Guyton, MD Stuart
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester
 BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/8/e1600800/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss-of-function variants influence the human serum metabolome Bing Yu, Alexander H. Li, Ginger A. Metcalf, Donna M.
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/8/e1600800/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss-of-function variants influence the human serum metabolome Bing Yu, Alexander H. Li, Ginger A. Metcalf, Donna M.
HOW TO DEFINE GOOD BIOMARKERS OF HEALTH? Suzan Wopereis
 HOW TO DEFINE GOOD BIOMARKERS OF HEALTH? Suzan Wopereis My personal objective: identification of biomarkers of (optimal) health Biomarker Definition: a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated
HOW TO DEFINE GOOD BIOMARKERS OF HEALTH? Suzan Wopereis My personal objective: identification of biomarkers of (optimal) health Biomarker Definition: a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated
23.1 Lipid Metabolism in Animals. Chapter 23. Micelles Lipid Metabolism in. Animals. Overview of Digestion Lipid Metabolism in
 Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM
 Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
glucose glucose 6-phospho fructose 6-phosphate fructose 1,6-bisphosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
 Cells glucose glucose glucose 6-phospho glycogen pentose phosphate T 1-phosphate 6-phosphate gluconate CC T CC+PD-1 pathway Isobar: fructose 1,6-diphosphate; glucose 1,6-diphosphate DHAP lactate fructose
Cells glucose glucose glucose 6-phospho glycogen pentose phosphate T 1-phosphate 6-phosphate gluconate CC T CC+PD-1 pathway Isobar: fructose 1,6-diphosphate; glucose 1,6-diphosphate DHAP lactate fructose
Effects of Histidine Supplementation on Global Serum and Urine 1 H NMR-based. Metabolomics and Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Obese Women from a
 Supporting information for Effects of Histidine Supplementation on Global Serum and Urine 1 H NMR-based Metabolomics and Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Obese Women from a Randomized Controlled Study Shanshan
Supporting information for Effects of Histidine Supplementation on Global Serum and Urine 1 H NMR-based Metabolomics and Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Obese Women from a Randomized Controlled Study Shanshan
Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism. Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross
 Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cellular Respiration Set of reactions that take place during the conversion of nutrients into ATP Intricate regulatory relationship between several
Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cellular Respiration Set of reactions that take place during the conversion of nutrients into ATP Intricate regulatory relationship between several
Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
 Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry
 1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
Cellular Respiration Other Metabolites & Control of Respiration. AP Biology
 Cellular Respiration Other Metabolites & Control of Respiration Cellular respiration: Beyond glucose: Other carbohydrates: Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates fuels. polysaccharides glucose
Cellular Respiration Other Metabolites & Control of Respiration Cellular respiration: Beyond glucose: Other carbohydrates: Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates fuels. polysaccharides glucose
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln
 The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
2. When a muscle depletes its supply of ATP, the next molecule used as an energy source is: a) pyruvate b) muscle glycogen c) blood glucose d) GTP
 Chapter 34: Carbohydrate Metabolism Multiple Choice 1. The synthesis of glycogen from glucose is known as: a) glycogenolysis b) gluconeogenesis c) glycogenesis d) the Embden-Myerhof pathway 2. When a muscle
Chapter 34: Carbohydrate Metabolism Multiple Choice 1. The synthesis of glycogen from glucose is known as: a) glycogenolysis b) gluconeogenesis c) glycogenesis d) the Embden-Myerhof pathway 2. When a muscle
Organic Molecules. 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1
 Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Metabolomic profiling was performed by Metabolon (Durham, NC) as previously
 Supplemental Methods: Metabolomic profiling Metabolomic profiling was performed by Metabolon (Durham, NC) as previously described [1, 2] using ultra high performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass
Supplemental Methods: Metabolomic profiling Metabolomic profiling was performed by Metabolon (Durham, NC) as previously described [1, 2] using ultra high performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
a tidal wave of chronic illness
 Using organic acids to resolve chief complaints and improve quality of life in chronically ill patients Part IV Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Summer
Using organic acids to resolve chief complaints and improve quality of life in chronically ill patients Part IV Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Summer
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids
 Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS
 Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS Alternate Fuel Sources When glucose levels are low Proteins and Triglycerides will be metabolized Tissues will use different fuel sources depending on:
Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS Alternate Fuel Sources When glucose levels are low Proteins and Triglycerides will be metabolized Tissues will use different fuel sources depending on:
associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences with preventive measures
 Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
Normal Fuel Metabolism Five phases of fuel homeostasis have been described A. Phase I is the fed state (0 to 3.9 hours after meal/food consumption),
 Normal Fuel Metabolism Five phases of fuel homeostasis have been described A. Phase I is the fed state (0 to 3.9 hours after meal/food consumption), in which blood glucose predominantly originates from
Normal Fuel Metabolism Five phases of fuel homeostasis have been described A. Phase I is the fed state (0 to 3.9 hours after meal/food consumption), in which blood glucose predominantly originates from
Metabolomic Data Analysis with MetaboAnalystR
 Metabolomic Data Analysis with MetaboAnalystR Name: guest623839008349489450 February 7, 2018 1 Background Understanding the functional importance of metabolites in untargeted metabolomics is limited due
Metabolomic Data Analysis with MetaboAnalystR Name: guest623839008349489450 February 7, 2018 1 Background Understanding the functional importance of metabolites in untargeted metabolomics is limited due
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING
 HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
Lipid Metabolism * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46462 1 Lipid Metabolism * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m46462 1 Lipid Metabolism * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM. Pancreatic secretions ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Insulin
 18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003
 CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003 1. A cell in an active, catabolic state has a. a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD + ) ratio b. a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD + ) ratio c. a
CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003 1. A cell in an active, catabolic state has a. a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD + ) ratio b. a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD + ) ratio c. a
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals. By Scott Magee, MD, FACE
 Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Hormones and Target Tissues
 Hormones and Target Tissues The hypothalamus is the coordination center of the endocrine system Hypothalamus is a small region of the forebrain in animals with skulls It receives and integrates nerve signals
Hormones and Target Tissues The hypothalamus is the coordination center of the endocrine system Hypothalamus is a small region of the forebrain in animals with skulls It receives and integrates nerve signals
Lipids Carbohydrate Protein. Fatty Acids Glycerol. Mono/di-saccarides. Aminoacids. Fat Liver Muscle. Triglycerides Glycogen Protein
 Lipids Carbohydrate Protein Fatty Acids Glycerol Mono/di-saccarides Fat Liver Muscle Aminoacids Triglycerides Glycogen Protein Microvascular Macrovascular Diabetes-specific Diabetes-enhanced HbA1c 5.7(6.0)
Lipids Carbohydrate Protein Fatty Acids Glycerol Mono/di-saccarides Fat Liver Muscle Aminoacids Triglycerides Glycogen Protein Microvascular Macrovascular Diabetes-specific Diabetes-enhanced HbA1c 5.7(6.0)
Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004
 Name Write your name on the back of the exam Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004 This examination consists of forty-four questions, each having 2 points. The remaining
Name Write your name on the back of the exam Physiological Chemistry II Exam IV Dr. Melissa Kelley April 13, 2004 This examination consists of forty-four questions, each having 2 points. The remaining
A Predictive Metabolic Signature for the Transition From Gestational Diabetes Mellitus to Type 2 Diabetes
 Diabetes Volume 65, September 2016 2529 Amina Allalou, 1 Amarnadh Nalla, 2,3 Kacey J. Prentice, 3 Ying Liu, 3 Ming Zhang, 3 Feihan F. Dai, 3 Xian Ning, 4 Lucy R. Osborne, 1,5 Brian J. Cox, 3,6 Erica P.
Diabetes Volume 65, September 2016 2529 Amina Allalou, 1 Amarnadh Nalla, 2,3 Kacey J. Prentice, 3 Ying Liu, 3 Ming Zhang, 3 Feihan F. Dai, 3 Xian Ning, 4 Lucy R. Osborne, 1,5 Brian J. Cox, 3,6 Erica P.
Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1
 Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1 Song, Dae-Kyu Department of Physiology & Chronic Disease Research Center Keimyung University School of Medicine 2800 dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, 704-701, Korea
Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1 Song, Dae-Kyu Department of Physiology & Chronic Disease Research Center Keimyung University School of Medicine 2800 dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, 704-701, Korea
Metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disorders and potential. biomarkers associated with the developmental toxicity of
 Supplementary information for Metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disorders and potential biomarkers associated with the developmental toxicity of tetrabromobisphenol A and tetrachlorobisphenol A Guozhu
Supplementary information for Metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disorders and potential biomarkers associated with the developmental toxicity of tetrabromobisphenol A and tetrachlorobisphenol A Guozhu
Biological Molecules. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids
 Biological Molecules Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules Always contain Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) Carbon is missing four electrons Capable of forming 4 covalent bonds
Biological Molecules Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules Always contain Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) Carbon is missing four electrons Capable of forming 4 covalent bonds
Supplementary materials
 Supplementary materials Metabolic phenotyping for monitoring ovarian cancer patients Chaofu Ke a, Ang Li a, Yan Hou a, Meng Sun b, Kai Yang a, Jinlong Cheng c, Jingtao Wang a, Tingting Ge c, Fan Zhang
Supplementary materials Metabolic phenotyping for monitoring ovarian cancer patients Chaofu Ke a, Ang Li a, Yan Hou a, Meng Sun b, Kai Yang a, Jinlong Cheng c, Jingtao Wang a, Tingting Ge c, Fan Zhang
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes Prof. Marc Y. Donath
 Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Intermediary metabolism. Eva Samcová
 Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia
Supplementary Online Content Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL, et al. Effect of liraglutide treatment on prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia
Bio Metabolism. Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry. Chloroplasts and mitochondria. What is food?
 Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry 1 Chloroplasts and mitochondria Heat Carbohydrate O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Chloroplast Mitochondria 2 What is food? Proteins - polymers of amino acids Carbohydrates
Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry 1 Chloroplasts and mitochondria Heat Carbohydrate O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Chloroplast Mitochondria 2 What is food? Proteins - polymers of amino acids Carbohydrates
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
Using the Organic Acids Test Part 5 Dr. Jeff Moss
 Using organic acids to resolve chief complaints and improve quality of life in chronically ill patients Part V Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Summer
Using organic acids to resolve chief complaints and improve quality of life in chronically ill patients Part V Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Summer
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY. BI 28 Second Midterm Examination April 3, 2007
 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm Examination April 3, 2007 Name SIS # Make sure that your name or SIS # is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with your exam after
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm Examination April 3, 2007 Name SIS # Make sure that your name or SIS # is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with your exam after
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages)
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages) READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #1, 100 points (7 pages) READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis [2]
![1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis [2] 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis [2]](/thumbs/80/81464401.jpg) 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. (i) Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis.... [2] Describe how negative feedback is used to control blood glucose concentration.
1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. (i) Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis.... [2] Describe how negative feedback is used to control blood glucose concentration.
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style. Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
ANATOMY OF A METABOLIC CRISIS: FAOD-style Mark S. Korson, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Anabolic Eating well Calories eaten > body s needs BRAIN uses GLUCOSE MUSCLE uses GLUCOSE
Tutorial 27: Metabolism, Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain
 Tutorial 27: Metabolism, Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain Goals: To be able to describe the overall catabolic pathways for food molecules. To understand what bonds are hydrolyzed in the digestion
Tutorial 27: Metabolism, Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain Goals: To be able to describe the overall catabolic pathways for food molecules. To understand what bonds are hydrolyzed in the digestion
Lipid Metabolism. Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals
 Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
4. Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules? a. 2. d. 5
 1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
Screening and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan
 Screening and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan Hung-Yuan Li, MD, MMSc, PhD Attending Physician, Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Associate Professor,
Screening and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan Hung-Yuan Li, MD, MMSc, PhD Attending Physician, Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Associate Professor,
Biomolecules. Organic compounds of life
 Biomolecules Organic compounds of life TEKS 9A: Students will Compare the structure and function of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids 9D: Students
Biomolecules Organic compounds of life TEKS 9A: Students will Compare the structure and function of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids 9D: Students
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP
 2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There s got to be a better way!
2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There s got to be a better way!
EB Education Revision Guide. How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation
 EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation Blood Glucose Regulation a) Why your body regulates glucose levels What you need to know about Homeostasis: Part
EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation Blood Glucose Regulation a) Why your body regulates glucose levels What you need to know about Homeostasis: Part
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine
 Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Lynne A. Wolfe, MS, ACNP, PNP, BC Department of Genetics Yale School of Medicine Harvey Levy, MD Mark Korson, MD Piero Rinaldo, MD, PhD Larry Sweetman, PhD K. Michael Gibson, PhD Charlie Roe, MD Jerry
Energy metabolism - the overview
 Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
/ The following functional group is a. Aldehyde c. Carboxyl b. Ketone d. Amino
 Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Urea impairs b cell glycolysis and insulin secretion in chronic kidney disease
 Urea impairs b cell glycolysis and insulin secretion in chronic kidney disease Laetitia Koppe,, Julien Ghislain, Vincent Poitout J Clin Invest. 2016;126(9):3598-3612. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci86181.
Urea impairs b cell glycolysis and insulin secretion in chronic kidney disease Laetitia Koppe,, Julien Ghislain, Vincent Poitout J Clin Invest. 2016;126(9):3598-3612. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci86181.
Type 1 Diabetes 2/23/2015. Endocrine System Hormones. Living with Type 1 Diabetes
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Living with Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes results from the autoimmune destruction of the insulin- producing beta-cells in the pancreas. The lack of insulin leads to
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Living with Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes results from the autoimmune destruction of the insulin- producing beta-cells in the pancreas. The lack of insulin leads to
Metabolic integration and Regulation
 Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
BPA exposure during pregnancy: risk for gestational diabetes and diabetes following pregnancy
 BPA exposure during pregnancy: risk for gestational diabetes and diabetes following pregnancy Paloma Alonso-Magdalena Applied Biology Department and CIBERDEM, Miguel Hernández University, Elche, Spain
BPA exposure during pregnancy: risk for gestational diabetes and diabetes following pregnancy Paloma Alonso-Magdalena Applied Biology Department and CIBERDEM, Miguel Hernández University, Elche, Spain
History of Investigation
 Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Metabolomics and systems biology approaches to study health and disease. Matej Oreši
 Metabolomics and systems biology approaches to study health and disease Matej Oreši 14.12.2011 1/19/2012 2 Biomarker concept in domain of human health [Wikipedia definition] A substance used as an indicator
Metabolomics and systems biology approaches to study health and disease Matej Oreši 14.12.2011 1/19/2012 2 Biomarker concept in domain of human health [Wikipedia definition] A substance used as an indicator
What is the Warburg Effect
 What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
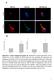 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
METABOLISM CATABOLIC Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
 Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae.
 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Nutrigenomics / Nutrigenetics How our DNA will Shape our Diets in the Future Personalized nutrition based on OMICS approaches
 Nutrigenomics / Nutrigenetics How our DNA will Shape our Diets in the Future Personalized nutrition based on OMICS approaches Iwona Rudkowska, PhD, Registered Dietitian Assistant Professor and Researcher
Nutrigenomics / Nutrigenetics How our DNA will Shape our Diets in the Future Personalized nutrition based on OMICS approaches Iwona Rudkowska, PhD, Registered Dietitian Assistant Professor and Researcher
Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma NO Retention time Metabolites Level
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Table S1. Identified metabolites in rats plasma NO Retention time Metabolites Level
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Org/Biochem Final Lec Form, Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6
 Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Current Trends in Diagnosis and Management of Gestational Diabetes
 Current Trends in Diagnosis and Management of Gestational Diabetes Shreela Mishra, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Fresno Medical Education Program 2/2/2019 Disclosures No disclosures 2/2/19 Objectives
Current Trends in Diagnosis and Management of Gestational Diabetes Shreela Mishra, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Fresno Medical Education Program 2/2/2019 Disclosures No disclosures 2/2/19 Objectives
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Carbohydrate Metabolism
 Chapter 34 Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is important for both plants and animals. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison,
Chapter 34 Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is important for both plants and animals. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison,
Hormones and Homeostasis
 Hormones and Homeostasis The endocrine system is a system of organs that releases chemical message molecules, called hormones, into the blood. Unlike the nervous system whose action helps the body react
Hormones and Homeostasis The endocrine system is a system of organs that releases chemical message molecules, called hormones, into the blood. Unlike the nervous system whose action helps the body react
Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life
 Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life A. Important Inorganic Molecules Water 1. Explain why water is considered a polar molecule. The partial negative charge of the oxygen and the
Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life A. Important Inorganic Molecules Water 1. Explain why water is considered a polar molecule. The partial negative charge of the oxygen and the
Macro molecule = is all the reactions that take place in cells, the sum of all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism Anabolism:
 Macromolecule Macro molecule = molecule that is built up from smaller units The smaller single subunits that make up macromolecules are known as Joining two or more single units together form a M is all
Macromolecule Macro molecule = molecule that is built up from smaller units The smaller single subunits that make up macromolecules are known as Joining two or more single units together form a M is all
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
Glycolysis Part 2. BCH 340 lecture 4
 Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
Metabolism of proteins and amino acids
 BIOQUÍMICA E BIOLOGIA CELULAR António Ascensão, José Magalhães Metabolism of proteins and amino acids Faculdade de Desporto, Universidade do Porto, 1º Ciclo, 1º Ano 202_2013 Humans degradation of ingested
BIOQUÍMICA E BIOLOGIA CELULAR António Ascensão, José Magalhães Metabolism of proteins and amino acids Faculdade de Desporto, Universidade do Porto, 1º Ciclo, 1º Ano 202_2013 Humans degradation of ingested
