Heba M Fahmy1*, Hossam M Yassin2, Islam M Muhamed1, Samar E Mohamed1, Shimaa S Hassan1. 1: Biophysics Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University
|
|
|
- Morgan Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: Heba M Fahmy1*, Hossam M Yassin2, Islam M Muhamed1, Samar E Mohamed1, Shimaa S Hassan1 1: Biophysics Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University 2: Cairo University Hospital Corresponding author: Heba Mohamed FahmyAbdelbaky heba_moh_fahmi@yahoo.com Short title: 99mTc-DMSA in dynamic renal scans. Type of article: original research Funding source: none No conflict of interest Acknowledgments: This work was supported by Biophysics Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University. Cite this article as: Fahmy HM, Yassin HM, Muhammed IM, Mohamed SE, Hassan SS. Evaluation of the efficiency of 99m Tc-DMSA as a radiopharmaceutical in dynamic renal scans. Erciyes Med J 2018; DOI: Evaluation of the efficiency of 99m Tc-DMSA as a radiopharmaceutical in dynamic renal scans Abstract Objective: In dynamic renal scans, 99m Tc-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) is copiously used and yields information about the renal blood-flow and the excretory capacity. 99m Tc-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) is utilized for static renal imaging and can likewise uncover the renal cortical structure. This work was intended to assess whether DMSA can be
2 declared as a radiopharmaceutical in dynamic renal scans or not. It scopes also on comparing the outcomes procured from DMSA with those obtained with DTPA examinations. Methods: A comparison of the information gained from the renograms of 47 subjects (normal subjects and abnormal renal function patients having: obstructive nephropathy, bilateral nephropathy, hydro-nephrosis, reduced or non-function kidney and/or atrophic kidney) that had 99m Tc-DMSA and 99m Tc-DTPA dynamic scintigraphies utilizing the same protocol. Results: A strong positive correlation had come in view on assessing of the left kidney, right kidney and the total glomerular filtration rate (GFR) from 99m Tc-DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms. In addition, estimation of the time of the peak height from 99m Tc-DTPA and 99m Tc- DMSA renograms for the right and left kidneys demonstrated non-significant varieties and strong positive correlation for both the normal subjects and patients with kidney abnormalities. Conclusion: In the light of the outcomes gained from the present investigation, it could be prescribed that 99m Tc-DMSA could be favorably replace 99m Tc- DTPA in dynamic renograms in the case of the renal conditions that had been examined in the present work. As scheduled, this will be cash and time saving, and will bring down the radiation dose to the patients. Also, the same
3 qualities of results are accomplished with both radiopharmaceuticals in normal subjects and abnormal renal function patients. Keywords: Radiopharmaceutical; GFR; DMSA; DTPA; dynamic renal imaging; static renal imaging. 1. Introduction Static and dynamic renal scans are the standard scintigraphic techniques for the assessment of renal capacities. These techniques can be proficient with distinct radiopharmaceuticals, for example: 99m Tc-dimercaptosuccinic acid ( 99m Tc-DMSA) and 99m Tc-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid ( 99m Tc-DTPA) (1,2). In dynamic renal scintigraphy, 99m Tc-DTPA is utilized to give information about the renal blood-flow and excretory function, on the other hand 99m Tc-DMSA is utilized for static renal imaging to visualize the renal cortical structure (3-5). 99m Tc-DMSA was proclaimed to be a magnificent renal imaging agent and was directed to assess the quantitative renal function (6-10). 99m Tc-DMSA could be introduced in the proximal tubular cell either by glomerular filtration and/or by direct uptake from the peritubular capillaries sicne it is largely bound to serum proteins (11-16). Lee and his partners surveyed the relative renal function in 18 rabbits with unilateral ureteral obstruction in The relative renal function was figured for 99m Tc-DMSA or 99m Tc- DTPA or 99m Tc-mercaptoacetyl triglycine ( 99m Tc-MAG-3) and they uncover that despite the fact there were conflicts between left and right kidneys, no statistical differences were noted between groups. So, they conclude that dynamic renal imaging agents ( 99m Tc-DTPA and 99m Tc- MAG-3) can be applied to assess the relative renal function rather than the static image of 99m Tc-DMSA (17). In 2011, Hülya and his co-workers compared relative renal functions
4 acquired from 99m Tc-DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA in 144 adult patients with renal diseases. The authors deduced that glomerular rate filtration (GRF) calculated with 99m Tc-DTPA might be utilized in place of static renal imaging with 99m Tc-DMSA. They proclaimed that 99m Tc-DTPA was additionaly a suitable method for the relative renal function evaluation when compared to 99m Tc-DMSA scan. 99m Tc-DTPA can be an alternative for the calculation of relative renal function without a follow up DMSA scan particularly in patients who demand renogram curve and GFR computations (18). In 2011, Zeki and his co-workers concluded that, regarding the calculation of split renal function, 99m Tc-DTPA, 99m Tc-MAG3, and 99m Tc-DMSA renal scans can be employed reliably and each method provides comparable measures (19). In 2012, Demirel and his coworkers determined the differential renal function utilizing DTPA or MAG3, the reliable outcomes were acquired in dynamic renal scan. Also, the functional condition of the kidney could be determined with these protocols. They proclaimed that MAG3 scintigraphy may be a prevalent decision in light of giving preferable data over DTPA about both the capacity of the kidneys and the structure of the renal parenchyma (20). In 2014, Tanju Çelik and his collaborators inferred that in the relative renal function evaluation, 99m Tc-DTPA was considered as a solid technique as 99m Tc-DMSA scan. The authors also suggested that 99m Tc-DTPA could be a choice for the calculation of relative renal function for patients who needs renogram curve and GFR calculations, whereas, 99m Tc-DTPA could be an alternative for the calculation of relative renal function. The authors stated that 99m Tc- DMSA was still the brilliant standard technique for the calculation of relative renal function (21). Recently, Momin and his partners looked at the relative renal functions (RRF) estimated with (99mTc-DMSA) and (99mTc-DTPA) for kidney patients between 5 months and 71 years. Fifty
5 patients including 29 males and 21 females has been chosen and applied for renography. The mean RRFs have been found to be ± 23.63% and ± 23.63%, respectively, for the left and right kidneys with 99mTc-DMSA measurement. With 99mTc-DTPA, the values were ± 23.54% and ± 23.54% for the same as in DMSA case. The authors found a significant positive correlation (r = 0.996, P < 0.001) between the RRFs estimated with the two modes. No differences were deduced between the RRFs acquired for the left and right kidneys. The mean difference between the two modes has been found to be 0.1. According to the results obtained in their study, both the 99mTc-DMSA and 99mTc-DTPA methods yield similar RRF values. The authors suggested that 99mTc-DMSA could be the superior mode for the estimation of RRF, but if the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renography were essential, 99mTc-DTPA could be the undeniable alternative (22). The current study was spearheaded on numerous other studies matching the relative renal function calculation results of 99mTc-DMSA and 99mTc-DTPA as there are no past reports (up to our knowledge) comparing between them as radiopharmaceuticals used in dynamic renal scintigraphies. The former surveys were done in groups of patients, including adult and pediatric patients. The present study incorporated a category of normal cases (either donor or not) undergoing a dynamic renal scan. The reason for which the ongoing investigation was outlined, is to assess whether 99m Tc- DMSA can be incorporated as a dynamic imaging agent and to judge its efficiency as a radiotracer instead of 99m Tc- DTPA in measuring the functionality of the urinary system. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Subjects
6 This work was done on 47 patients, 33 males & 14 females ranged from 14 to 73 years old, the average age was computed to be: ±2.385 & ±3.378 for males and females, respectively. The 47 subjects were divided into two primary classifications. Category 1: 18 normal subjects with relative renal function parameters in the ordinary range whether they are a donor or not. Category 2: 29 patients with different renal issues (obstructive nephropathy, bilateral nephropathy, hydro-nephrosis, reduced or non-function kidney and/or atrophic kidney). Imaging was done by utilizing two kinds of radiotracers DTPA and DMSA Renography 99m Tc-DTPA was mixed in radioisotope labs in King Fahd Unit, Cairo University Hospitals (Egypt) using a commercially available freeze-dried kit. The dose was ranged from 3.5 to 6.5 mci and was introduced to several patients with distinct renal diseases in addition to some healthy persons. Before the administration, the pre-injection syringe with straight needle was checked with two different devices: 1) Dose Calibrator (ATOMLAB 100) and 2) Gamma Camera (Siemen, Orbit, Single head), which was connected to a low-energy general-purpose parallelhole collimator. The patient was hydrated with ml of water, 30 minutes preceding the examination. The patient lay down on a bed in the supine position and the image was procured posteriorly. 99m Tc-DTPA was given through a butterfly needle into a vein and was koined by infusion of 20 ml of normal saline, then 20mg/2 ml Lasix (Frusemide). Frames of matrices were recorded with an online-computer, initially at one second for one minute and afterward at 10 seconds for 20 minutes. The post-injection syringe with a straight needle, which was detached before the injection was again counted by a
7 gamma camera in the same way as a pre-injection. Region of interest (ROI) over each kidney was assigned manually to the frame added from 1 to 3 minutes following injection. The semilunar background ROI around each kidney was characterized. The background corrected time-activity curve was produced, and the renal uptake of individual kidney for one minute after the injection (from 2 to 3 minutes) was calculated. The GFR (GFR Gates) was consequently estimated by a commercially available computer (Oddesey Pegasus Laboratories, Adac) according to the Gates' algorithm Standard protocol for the calculation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Peak time (second) The peak time is defined as the time interval from the beginning of the acquisition to the time that the curve reaches the maximum count. Half peak time (second) The half peak Time (½ peak time) is the time interval from the peak time to the time that the curve reaches half the maximum counts. For example, if the peak occurs at 400 seconds and the half peak occurs at 1600 second, then the half peak time is 1200 seconds. Note: A zero value indicates that the application did not find a half peak. Depth (cm) Uptake (%) It is the calculated depth from the body surface to the kidney s center. It is the background corrected, kidney count take-up from two to three minutes after the acquisition was started. GFR (ml/min)
8 It is the glomerular filtration rate estimated in ml/min. Total GFR (ml/min) The total GFR is the summation of the GFR for both the right and left kidneys. Normalized GFR (ml/min) The normalized GFR is normalized to the body surface area by dividing 1.73 m 2 by the body surface area. It is estimated based on the patient s height and weight, and afterward, the result is multiplied by the GFR. GFR (ml/min) = (% renal uptake ) (Equation 1) Where : is the regression coefficient (R) and : is the y-intercept (23). The percent renal uptake in Equation 1 is calculated according to the method reported by Gates (1984) as follows: % renal uptake = ( (Rt Kidney cts bkg) ( Lt Kidney cts bkg) e μx + e μx (preinj.cts postinj.cts) ) 100(Equation 2) (24) Where: (Rt Kidney cts: right kidney counts, bkg: background counts, Lt Kidney cts: left kidney counts, Pre-& Postinj. cts: pre-& post-injection counts, µ: linear attenuation coefficient of 99m Tc in soft tissue (25), Which is equal to and x is kidney depth in centimeters. From equation 2, it is unmistakably that the percent uptake of the left kidney plus the percent uptake of the right kidney, at 2 to 3 minutes, post-injection is calculated by dividing the background and depth-corrected kidney counts by the total net counts injected and multiplying the result by 100. The normalized and depth-corrected kidney counts and the total net counts are obtained from the nuclear medicine renogram study. The total net counts injected are determined by the pre-injection syringe and postinjection syringe images. The post-injection counts are then corrected for decay to
9 compensate for "excess time" between the pre-injection image and post-injection image. Ultimately, the decay-corrected, post-injection syringe counts are taken off from the preinjection syringe counts to yield the total net counts injected. The normalized and corrected kidney counts are determined from 60 seconds of data collected 2 to 3 minutes following tracer positioned in the kidney. To obtain accurate sampling of the renal uptake, a dynamic study in a matrix is acquired at 10 to 15 seconds/frame for 6 transactions, just after the administration of the tracer. A composite image is built from the dynamic study. Areas of interest are formed for each kidney and in the corresponding background areas. The background areas are then normalized to their respective renal areas and the counts in the normalized background areas are subtracted from the counts in the renal areas to obtain the normalized net kidney counts. After that, the same steps were iterated with DMSA radiotracer. Figure 1: shows an image of a patient s dynamic DMSA scan using the same protocol as in DTPA renal scans Statistical analysis Data analysis was carried out using Origin software version 6.
10 3. Results 47 patients from three different centers were reviewed and the results of all the kidney function cases were analyzed. Thirty-three of the patients were male when 14 of them were female. The age of the patients ranged between 14 and 73 and the mean age was 44.52± 2.39& ± 3.38 years for males and females, respectively. The 47 subjects were divided into2 main categories: Category 1: 18 normal subjects with relative renal function parameters in the normal range whether they are a donor or not. Category 2: 29 patients with different renal problems (obstructive nephropathy, bilateral nephropathy, hydro-nephrosis, reduced or non-function kidney and/or atrophic kidney). Imaging was done by utilizing two types of radiotracers DTPA and DMSA. The Glomerular filtration rate was computed for each category with both radiopharmaceuticals DMSA and DTPA. Estimating the mean ± standard deviation and P values for (the left kidney GFR, the right kidney GFR, the average kidney total GFR and the time to the peak height from both kidneys) for category 1 (normal subjects) and category 2 (patients with abnormal renal functions) depicted no statistical significance from 99mTc- DTPA and 99mTc- DMSA renograms at significance level 0.05 as seen in Table 1. In correlation analysis for the previously mentioned calculations, the analysis showed a strong positive correlation between 99mTc-DMSA and 99mTc-DTPA for both categories 1 and 2 as seen in Table 2. The correlation analysis for the left kidney GFR, the right kidney GFR, the kidney total GFR, the time to the peak height recorded from the left kidney and the peak height from the right kidney showed a strong positive correlation between 99mTc-DMSA and 99mTc-DTPA for
11 both categories 1 and 2 (r1= 0.96 & r2= 0.99, r1= 0.91 & r2= 0.98, r1= 0.88 & r2= 0.96, r1= 0.97 & r2= 0.89 and r1= 0.95 & r2= 0.92, respectively) as seen in (Fig. 2 (a&b), Fig. 3 (a&b), Fig. 4 (a&b), Fig. 5 (a&b) and Fig. 6 (a&b), respectively).
12 4. Discussion The present work was situated on many other studies matching the relative renal function computation results of 99m Tc-DMSA and 99m Tc-DTPA.Yet, up to our knowledge, there are no reports handling with them as a radiopharmaceutical used in dynamic renal scintigraphies by using the same protocol used with 99m Tc-DTPA in dynamic renal scan. In the literature, there are many reports comparing relative renal function estimated with 99m Tc-DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA in adults and children. Nevertheless, in that respect, there is no consensus about the results. In some articles, it is emphasized that the relative renal function calculated with 99m Tc-DTPA is as reliable as 99m Tc-DMSA (18). On the other hand, in some of the works, it is declared that 99m Tc-DTPA is not as good as 99m Tc-DMSA in the relative renal function calculation (1,12). Data analysis for the present study, revealed non-significant changes between left kidney GFR, right kidney GFR, Total kidney GFR in addition, time to the peak height for the right and left kidneys in the study categories (normal subjects and abnormal renal function patients) with both tested radiopharmaceuticals 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc- DMSA during dynamic renal scans. From the current study results, it is obvious that 99mTc- DTPA and 99mTc-DMSA radiotracers can be substituted by each other without any impingement on the quality of the effects obtained during dynamic renograms. One interesting finding obtained from the current study is that using 99m Tc-DMSA in dynamic renal scintigraphies is more favored in case of patients with abnormal renal function (category 2) that in normal cases (as drawn from the higher values of the
13 correlation coefficient calculated for all the previously mentioned renograms parameters). There are some differences among DTPA and DMSA. These variations are due to discrete biological characteristics of the two radiopharmaceuticals such as methods of renal excretion, renal cell retention of radioactive material, the degree of plasma-protein bound and degree of plasma clearance. 99mTc-DMSA is taken up in the proximal tubular cells and also in the upper part of the loop of Henle (25). It has been reported that 99mTc-DMSA- protein binding is about 90% (17,29), from which they deduced that DMSA is fixed into the cortical cell while the rest of DMSA is filtered at the glomerulus. On the other hand, 99mTc-DTPA is cleared by the glomerulus (>95%) and a small fraction may be bound to protein (30). These variations in filtration through glomerulus appear clearly in normal subjects. For this reason, the values of the correlation coefficient between DTPA and DMSA in case of category 2 (patients with renal abnormalities) are stronger positive than in the case of category 1 (normal subjects) especially in case of total GFR for both kidneys (r2> r1 = 0.96>0.88). Although, in the study of Domingues and coworkers (2006) in which they estimated the relative renal functions with 99m Tc-DTPA and 99m Tc-EC were compared with the results of 99m Tc-DMSA. The authors deduced that the relative renal function estimated with technetium- 99m ethylenedicysteine ( 99m Tc-EC) was matched to 99m Tc-DMSA results, but the results of relative renal function calculated with 99m Tc-DTPA were statistically distinct, which disagree with our results (1). Our study has some limitations within which our finding need to be interpreted carefully. Foremost, the range of age tested was large which may affect the results, as GFR
14 levels vary according to the age. We too recommend categorizing the abnormal kidney function patients into further groups according to their diagnosis and re-perform the analysis to decide which is the best condition in which 99mTc-DMSA is as reliable as 99mTc-DTPA. Finally, there is a considerable external clearance by the liver and spleen, which if taken into consideration would give more and more accurate results. Conclusion Although 99m Tc-DTPA is currently the most reliable radiotracer used for dynamical renal imaging, In the light of the results acquired from the recent study, it could be recommended that, in the case of renal diseases studied in the present work (non-function right kidney, advanced nephropathy of the right kidney, nephropathy of the right kidney, reduced right kidney function, left hydronephrosis, left kidney stone, bi-lateral hydronephrosis and left loin pain). 99m Tc-DMSA could be successfully considered as a replacer to 99m Tc- DTPA in dynamic renogram with the same quality of results which will have the following avails: As Tc 99m DMSA is the most reliable mechanism for the calculation of relative renal function and in our case of replacing 99m Tc-DTPA with 99m Tc- DMSA as a radiopharmaceutical in dynamic renogram, this will give the chance for using only 99m Tc- DMSA for both types of renograms which will be a time and money-sparing where 99m Tc-DMSA is an economical and easy method to be acquired(31). Moreover, this will decrease the effort of the physicist in preparing the radiopharmaceutical material and this also will be less suffering by lowering the dose taken by patients.
15 Compliance with ethical standards Conflict of interest None. Ethical approval All procedure involved in studies involving human participants (whether donor or not) were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Role of the funding source No funding sources
16 References (1) Domingues FC, Fujikawa GY, Decker H, et al. Comparison of relative renal function measured with either 99m Tc-DTPA or 99m Tc-EC dynamic scintigraphies with that measured with 99m Tc-DMSA static scintigraphy. International Braz j Urol. 2006;32(4): (2) Bedriye BD, Tansel AB, Bekir T, et al. Comparison of DTPA and MAG3 renal scintigraphies in terms of differential renal function based on DMSA renal scintigraphy. 2012; 28:5. (3) Roman MR, Angelides S. Extrarenal uptake of99mtc-dtpa at the site of bone marrow biopsy. Ann Nucl Med. 2002; 16: (4) Song L, Yao Q, Huang X, Zhang Y. Retroperitoneal Castleman disease on 99mTc DTPA renal scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 2012, 37(10): (5) Tansel AB, Ismail C, Aziz K. Incidental DTPA and DMSA uptake during renal scanning in unknown bone metastases. Ann Nucl Med. 2005; 20(5): (6) Freitas RS, Moreno SR, Lima-Filho GL, Fonseca AS, Bernardo-Filho M. Effect of a commercial extract of Paullinia cupana (guarana) on the binding of 99mTc-DMSA on blood constituents. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007; 65(5): (7) Bazić-Đorović B, Radulović M, Šišić M, et al. Technetium-99m-dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scintigraphy can guide clinical management in congenital hydronephrosis. Hell J Nucl Med. 2017; 20:
17 (8) Yapar AF, Aydin M, Reyhan M, Yapar Z, Sukan A. The conditions for which the geometric mean method revealed a more accurate calculation of relative renal function in 99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy. Nucl Med. 2005; 26(2): (9) Hossein F. Comparison of 99mTc-DMSA renal scintigraphy with biochemical and histopathological findings in animal models of acute kidney injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017; 434(1-2): (10) Hossein F, Mohammad S, Zynab K, et al. Comparison of 99mTc-DMSA renal scintigraphy with biochemical and histopathological findings in animal models of acute kidney injury. 2017; 434(1-2): (11) Lee BH, Lee SH, Choi HJ, Kang HG, Oh SW, Lee DS, Ha IS, Choi Y, Cheong HI. Decreased renal uptake of 99mTc-DMSA in patients with tubular proteinuria. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009; 24(11): (12) Piepsz A, Ham HR. Paediatric applications of renal nuclear medicine. Semin Nucl MED. 2006; 36: (13) Kaldir M, Cosar-Alas R, Cermik TF, Yurut-Caloglu V, Saynak M, Altaner S, Caloglu M, Kocak Z, Tokatli F, Türe M, Parlar S. Amifostine Use in Radiation-Induced Kidney Damage Preclinical Evaluation with Scintigraphic and Histopathologic Parameters. Strahlenther Onkol. 2008; 184(7): (14) Jaya S, Bhagwant RM. Dimercaptosuccinic acid: A multifunctional cost effective agent for imaging and therapy. Indian J Nucl Med. 2015; 30(4): (15) Arun KRG, Kanhaiyalal A, Ashwani S, et al. Differential uptake of Tc-99m DMSA and Tc- 99m EC in renal tubular disorders: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Indian J Nucl Med. 2014; 29(3):
18 (16) Balci TA, Ciftci I, Karaoglu A. Incidental DTPA and DMSA uptake during renal scanning in unknown bone metastases. Ann Nucl Med. 2006; 20(5): (17) Lee WG, Kim JH, Kim JM, et al. Renal uptakes of 99m Tc-MAG3, 99m Tc-DTPA, and 99m Tc- DMSA in rabbits with unilateral ureteral obstruction. In Vivo. 2010;24: (18) Yalçın H, Özen A, Günay EC, et al. Can 99m Tc-DTPA be used in adult patients in evaluation of relative renal function measurement as the reference 99m Tc-DMSA method? Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2011;20(1): (19) Dostbil Z, Pembegül N, Küçüköner M, et al. Comparison of split renal function measured by 99m Tc-DTPA, 99m Tc-MAG3 and 99m Tc-DMSA renal scintigraphies in paediatric age groups. Academic Journals. 2011; 3(2): (20) Demirel BB, Balci TA, Tasdemir B, et al. Comparison of DTPA and MAG3 renal scintigraphies in terms of differential renal function based on DMSA renal scintigraphy. Pak J Med Sci 2012;28(5): (21) ÇelikT,Yalçin H, Ceylan EG, et al. Comparison of the relative renal function calculated with 99m Tc-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid and 99m Tc-dimercaptosuccinic acid in children. World J Nucl MED.2014;13(3): (22) Momin MA, Abdullah MNA, Reza MS. Comparison of relative renal functions calculated with 99mTc-DTPA and 99mTc-DMSA for kidney patients of wide age ranges. Phys Med. 2018; 45: (23) Naddaf S, Azzumeea F, Fahad AM. 99mTc-DMSA Uptake in a Sister Mary Joseph's Nodule from Ovarian Cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2016; 41(12):
19 (24) Li H, Zhang X, Xu G, Wang X, Zhang C. Determination of reference intervals for creatinine and evaluation of creatinine-based estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 403(1-2): (25) Gutte H, Møller ML, Pfeifer AK, Thorup J, Borgwardt L, Borgwardt L, Kristoffersen US, Kjær A. Estimating GFR in children with 99mTc DTPA renography: a comparison with single sample 51Cr EDTA clearance. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging.2010; 30(3): (26) Alessio I, Catia O, Giannetto C, et al. Evaluation of 123I-orthoiodohippurate single kidney clearance rate by renal sequential scintigraphy in a large cohort of likely normal subjects aged between 0 and 18 years. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2006; 33(12): (27) Bradberry S, Vale A. Dimercaptosuccinic acid (succimer; DMSA) in inorganic lead poisoning. Clin Toxicol. 2009; 47(7): (28) Durand E, Prigent A. The basics of renal imaging and function studies. Q J NUCL MED. 2002; 24(4): (29) Alberto R, Abram U. 99mTc: Labelling Chemistry and Labelled Compounds. Handbook of Nuclear Chemistry (30) Gutte H, Møller ML, Pfeifer AK, Thorup J, Borgwardt L, Borgwardt L, Kristoffersen US, Kjær A. Comparison of 99mTc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging with modified MDRD equation for glomerular filtration rate estimation in Chinese patients in different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006; 22(2):
20 (31) Lezaic L, Hodolic M, Fettich J, Grmek M, Milcinski M. Reproducibility of 99mTcmercaptoacetyltriglycine renography: population comparison. Nucl Med Commun. 2008; 29(8):
21 Figure legends Fig. 1: An image of a patient s dynamic DMSA scan using the same protocol as in DTPA renal scans. Fig. 2. a: Correlation between the left kidney GFR as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 1 (normal subjects). Fig. 2. b: Correlation between the left kidney GFR as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 2(patients with abnormal renal functions). Fig. 3. a: Correlation between the right kidney GFR as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 1 (normal subjects). Fig. 3. b: Correlation between the right kidney GFR as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 2 (patients with abnormal renal functions. Fig. 4. a: Correlation between the total GFR as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc- DMSA renograms for category 1 (normal subjects). Fig. 4. b: Correlation between the total GFR as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc- DMSA renograms for category 2 (patients with abnormal renal functions). Fig. 5. a: Correlation between the time to the peak height for the left kidney as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 1 (normal subjects). Fig. 5. b: Correlation between the time to the peak height for the left kidney as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 2 (patients with abnormal renal functions).
22 Fig. 6. a: Correlation between the time to the peak height for the right kidney as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 1 (normal subjects). Fig. 6. b: Correlation between the time to the peak height for the right kidney as measured from 99m Tc- DTPA and 99m Tc-DMSA renograms for category 2 (patients with abnormal renal functions). Table legends
23 Table 1: The mean ± standard deviation and P-values of relative renal function calculated for each category. Table 2: The correlation analysis values from 99mTc- DTPA and 99mTc-DMSA renograms calculated for each category. Category 1 Category 2 Mean Value Standard Deviation P-Value Mean Value Standard Deviation P-Value DMSA DTPA Mean Left Kidney 36.80% % GFR Mean Right Kidney 46.11% % GFR Total GFR 94.01% % Time To The Peak 4.23% % Height Left Kidney Time To The Peak Height Right Kidney 4.07% % Mean Left Kidney 38.83% % GFR Mean Right Kidney 46.67% % GFR Total GFR 96.17% % Time To The Peak 4.23% % Height Left Kidney Time To The Peak Height Right Kidney 3.80% % Correlation Analysis From 99mTc- DTPA R Value For Category 1 R Value For Category 2 At Significance Level 0.05
24 And 99mTc-DMSA Renograms Left Kidney GFR Strong Positive Correlation Right Kidney GFR Strong Positive Correlation Total GFR Strong Positive Correlation Time To The Peak Height Left Kidney Strong Positive Correlation Time To The Peak Height Right Kidney Strong Positive Correlation
25
26
27
28
29
30
The correlation between effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) with renal scintigraphy 99m Tc-DTPA study
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The correlation between effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) with renal scintigraphy Tc-DTPA study To cite this
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The correlation between effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) with renal scintigraphy Tc-DTPA study To cite this
Comparison of DMSA Scan 99 m and EC Scan 99 m in Diagnosis of Cortical Defect and Differential Renal Function
 Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 6, No. 7; 2014 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Comparison of DMSA Scan 99 m and EC Scan 99 m in Diagnosis of
Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 6, No. 7; 2014 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Comparison of DMSA Scan 99 m and EC Scan 99 m in Diagnosis of
New single photon radiopharmaceuticals for renal scintigraphy
 New single photon radiopharmaceuticals for renal scintigraphy Andrew Taylor, M.D.* Malgorzata Lipowska, Ph.D.* Luigi Marzilli, Ph.D. # *Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA # Louisiana State
New single photon radiopharmaceuticals for renal scintigraphy Andrew Taylor, M.D.* Malgorzata Lipowska, Ph.D.* Luigi Marzilli, Ph.D. # *Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA # Louisiana State
Renal. Prof John Buscombe
 Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
Nuclear medicine methods in the urogenital system
 Nuclear medicine methods in the urogenital system Anatomy of the kidneys I. Anatomy of the kidneys II. The types of examinations Static examinations (scintigraphy): 1) the radiopharmaceutical is administered
Nuclear medicine methods in the urogenital system Anatomy of the kidneys I. Anatomy of the kidneys II. The types of examinations Static examinations (scintigraphy): 1) the radiopharmaceutical is administered
PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING. Dr A Brink
 PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING Dr A Brink Causes of hydronephrosis includes: Pelvi-ureteric obstruction Vesico-ureteric reflux Vesico-ureteric obstruction Posterior uretral valves Duplex kidneys Radiopharmaceutical
PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING Dr A Brink Causes of hydronephrosis includes: Pelvi-ureteric obstruction Vesico-ureteric reflux Vesico-ureteric obstruction Posterior uretral valves Duplex kidneys Radiopharmaceutical
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; March 2018: Vol.-7, Issue- 2, P
 Original article: Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction evaluation by Ethylenedicysteine Versus Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetic Acid In Technetium Tc 99m in Diuretic Renography Dr. Prarthan N Joshi, Dr. Kuldeep
Original article: Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction evaluation by Ethylenedicysteine Versus Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetic Acid In Technetium Tc 99m in Diuretic Renography Dr. Prarthan N Joshi, Dr. Kuldeep
Role of radioisotope 99m Tc and scintillation gamma camera in assessment of multiple renal functional indices using two different carriers DTPA & MDP
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov.-Dec. 2014), PP 51-57 Role of radioisotope 99m Tc and scintillation gamma camera in assessment of multiple renal
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov.-Dec. 2014), PP 51-57 Role of radioisotope 99m Tc and scintillation gamma camera in assessment of multiple renal
How to Interpret a Deterioration of Split Function?
 European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 686 690 How to Interpret a Deterioration of Split Function? A. Piepsz a, *, K. Ismaili b, M. Hall b, F. Collier c, M. Tondeur a, H. Ham d a Department of Radioisotopes,
European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 686 690 How to Interpret a Deterioration of Split Function? A. Piepsz a, *, K. Ismaili b, M. Hall b, F. Collier c, M. Tondeur a, H. Ham d a Department of Radioisotopes,
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom. Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium
 Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
GFR Determination by a Modification of the Gates Method: The Conventional Renal Examination with a Semi-Automated GFR Measurement
 GFR Determination by a Modification of the Gates Method: The Conventional Renal Examination with a Semi-Automated GFR Measurement Erol M. Beytas, Sharon M. Hamblen, Michael W. Hanson, and F. Dever Thomas
GFR Determination by a Modification of the Gates Method: The Conventional Renal Examination with a Semi-Automated GFR Measurement Erol M. Beytas, Sharon M. Hamblen, Michael W. Hanson, and F. Dever Thomas
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Introduction George N. Sfakianakis MD Professor
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Introduction George N. Sfakianakis MD Professor
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses)
 weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
Estimation of Absolute Renal Uptake of 99m Tc DMSA in Potential Kidney Donors and its Accuracy in Determination of Split Function
 Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 9, No. 1 June 2014 Page 55 of 65 Original Article Estimation of Absolute Renal Uptake of 99m Tc DMSA in Potential Kidney Donors and its Accuracy in Determination of Split Function
Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 9, No. 1 June 2014 Page 55 of 65 Original Article Estimation of Absolute Renal Uptake of 99m Tc DMSA in Potential Kidney Donors and its Accuracy in Determination of Split Function
DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR (DRI) EFFECT ON GFR AND USE IN RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS SCREENING
 DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR (DRI) EFFECT ON GFR AND USE IN RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS SCREENING Harold Thomas Pretorius, MD, PhD, Nichole Richards, and Michael Harrell Abstract Objective: A new method using a nuclear
DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR (DRI) EFFECT ON GFR AND USE IN RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS SCREENING Harold Thomas Pretorius, MD, PhD, Nichole Richards, and Michael Harrell Abstract Objective: A new method using a nuclear
Influence of hydration status in normal subjects: fractional analysis of parameters of Tc-99m DTPA and Tc-99m MAG 3 renography
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 1, 1 7, 2005 Influence of hydration status in normal subjects: fractional analysis of parameters of Tc-99m DTPA and Tc-99m MAG 3 renography Hyun
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 1, 1 7, 2005 Influence of hydration status in normal subjects: fractional analysis of parameters of Tc-99m DTPA and Tc-99m MAG 3 renography Hyun
Comparative Study Between 99m Tc-MDP and 99m Tc-DTPA as a Predictor For Renal Function
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 7(2): 360-367, 2013 ISSN 1991-8178 Comparative Study Between 99m Tc-MDP and 99m Tc-DTPA as a Predictor For Renal Function 1 W.M. Khalil, 2 Hany A. Shousha,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 7(2): 360-367, 2013 ISSN 1991-8178 Comparative Study Between 99m Tc-MDP and 99m Tc-DTPA as a Predictor For Renal Function 1 W.M. Khalil, 2 Hany A. Shousha,
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010
 RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010 Alive patient RA + tracers Tc-99m(86%) + MAG 3 DMSA (DTPA) T½ = 6,5h Gamma camera ect. Radio-active
RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010 Alive patient RA + tracers Tc-99m(86%) + MAG 3 DMSA (DTPA) T½ = 6,5h Gamma camera ect. Radio-active
Validation of El-Minia Equation for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
 Kidney Diseases Validation of El-Minia Equation for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Osama El Minshawy, 1 Eman El-Bassuoni 2 Original Paper 1 Department
Kidney Diseases Validation of El-Minia Equation for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Osama El Minshawy, 1 Eman El-Bassuoni 2 Original Paper 1 Department
KEY words: adult, humans, radioisotope renography, reproducibility of results, radiopharmaceuticals, technetium Tc 99m-ethylenedicysteine
 Nuclear Medicine Review 2015, 18, 1: 29 34 DOI: 10.5603/NMR.2015.0007 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Original Preliminary assessment of interand intraobserver reproducibility, and normative values
Nuclear Medicine Review 2015, 18, 1: 29 34 DOI: 10.5603/NMR.2015.0007 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Original Preliminary assessment of interand intraobserver reproducibility, and normative values
SNMMI Procedure Standard/EANM Practice Guideline for Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy in Adults with Suspected Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction 1.
 SNMMI Procedure Standard/EANM Practice Guideline for Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy in Adults with Suspected Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction 1.0 Andrew T. Taylor 1 (Chair), M. Donald Blaufox 2, David C. Brandon
SNMMI Procedure Standard/EANM Practice Guideline for Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy in Adults with Suspected Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction 1.0 Andrew T. Taylor 1 (Chair), M. Donald Blaufox 2, David C. Brandon
Estimation of Split Renal Function With 99m Tc-DMSA SPECT: Comparison Between 3D Volumetric Assessment and 2D Coronal Projection Imaging
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Cao et al. SPECT of Renal Function Pediatric Imaging Original Research Xinhua Cao Xiaoyin Xu Frederick D. Grant, S. Ted Treves Cao X, Xu X, Grant FD, Treves ST Keywords:
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Cao et al. SPECT of Renal Function Pediatric Imaging Original Research Xinhua Cao Xiaoyin Xu Frederick D. Grant, S. Ted Treves Cao X, Xu X, Grant FD, Treves ST Keywords:
Dynamic Renal Scintigraphy
 Dynamic Renal Scintigraphy JP Esser, Meander Medical Centre, Amersfoort 1. Introduction Patients referred for renography either have partial kidney obstruction or no obstruction. Partial obstruction is
Dynamic Renal Scintigraphy JP Esser, Meander Medical Centre, Amersfoort 1. Introduction Patients referred for renography either have partial kidney obstruction or no obstruction. Partial obstruction is
Division of Nuclear Medicine Procedure / Protocol University Hospital and The American Center
 KIDNEY FLOW / FUNCTION WITH DIURETIC CPT CODE: 78708 UPDATED: FEBRUARY 2017 Indications: The scan is designed to differentiate dilated renal collecting systems (calyces, pelves, or ureters) from obstructed
KIDNEY FLOW / FUNCTION WITH DIURETIC CPT CODE: 78708 UPDATED: FEBRUARY 2017 Indications: The scan is designed to differentiate dilated renal collecting systems (calyces, pelves, or ureters) from obstructed
*Department of Radiology, JR Sapporo General Hospital **Department of Pediatrics, Fussa Metropolitan Hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 8, 541 548, 2002 The single-plasma-sample method for determining the glomerular filtration rate with Tc-99m-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 8, 541 548, 2002 The single-plasma-sample method for determining the glomerular filtration rate with Tc-99m-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid
Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153
 APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
How to cite this article: Dharmalingam Citation will be A, included Pawar
 Original Article Tc-99m Ethylenedicysteine and Tc-99m Dimercaptosuccinic Acid Scintigraphy-Comparison of the Two for Detection of Scarring and Differential Cortical Function Abstract Context: The differential
Original Article Tc-99m Ethylenedicysteine and Tc-99m Dimercaptosuccinic Acid Scintigraphy-Comparison of the Two for Detection of Scarring and Differential Cortical Function Abstract Context: The differential
University Clinical Centre Ljubljana, Children's hospital Ljubljana, Radiology Unit
 University Clinical Centre Ljubljana, Children's hospital Ljubljana, Radiology Unit Usporedba dinamičke scintigrafije bubrega naspram Funkcionalne MR urografije - naša iskustva Zagreb, 2014 US - ultrasound
University Clinical Centre Ljubljana, Children's hospital Ljubljana, Radiology Unit Usporedba dinamičke scintigrafije bubrega naspram Funkcionalne MR urografije - naša iskustva Zagreb, 2014 US - ultrasound
IART and EBRT, an innovative approach
 External beam radiotherapy and nuclear medicine therapy: which kind of integration? Mahila Ferrari mahila.ferrari ferrari@ieo.it A different NM and RT integration... Radionuclide therapy combined to EBRT
External beam radiotherapy and nuclear medicine therapy: which kind of integration? Mahila Ferrari mahila.ferrari ferrari@ieo.it A different NM and RT integration... Radionuclide therapy combined to EBRT
THE SNMMI AND EANM PROCEDURAL GUIDELINES FOR DIURESIS RENOGRAPHY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN.
 The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and professional organization founded in 1954 to promote the science, technology, and practical application
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and professional organization founded in 1954 to promote the science, technology, and practical application
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin) Overview Indications The successively demonstrates hepatic perfusion, hepatocyte clearance, hepatic
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure SPHINCTER OF ODDI STUDY (Tc-99m-Mebrofenin) Overview Indications The successively demonstrates hepatic perfusion, hepatocyte clearance, hepatic
Nuclear medicine in renal scarring
 Paediatric NM General principles Need to image in a child friendly department Maybe use of play therapist to help explain the procedure Reduce activities as weight a proportion of 70kg adult with 10% minimum
Paediatric NM General principles Need to image in a child friendly department Maybe use of play therapist to help explain the procedure Reduce activities as weight a proportion of 70kg adult with 10% minimum
RADIONUCLIDES METHODS IN VITRO clearance measurement methods
 ISCORN, Mikulov, 2010 Tuesday May 11 th 10 30-11 30 RADIONUCLIDES METHODS IN VITRO clearance measurement methods Emmanuel DURAND Question 1 What is the best index for renal function? (one choice only)
ISCORN, Mikulov, 2010 Tuesday May 11 th 10 30-11 30 RADIONUCLIDES METHODS IN VITRO clearance measurement methods Emmanuel DURAND Question 1 What is the best index for renal function? (one choice only)
Scintiphotography Transplants
 Scintiphotography Transplants In Evaluation of Renal HALCOTT T. HADEN, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology and Medicine, Chief. Nuclear Medicine Section, McGuire VA Hospital, Richmond. Virginia Renal
Scintiphotography Transplants In Evaluation of Renal HALCOTT T. HADEN, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology and Medicine, Chief. Nuclear Medicine Section, McGuire VA Hospital, Richmond. Virginia Renal
Renal Function and Associated Laboratory Tests
 Renal Function and Associated Laboratory Tests Contents Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)... 2 Cockroft-Gault Calculation of Creatinine Clearance... 3 Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Serum Creatinine (SCr)
Renal Function and Associated Laboratory Tests Contents Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)... 2 Cockroft-Gault Calculation of Creatinine Clearance... 3 Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Serum Creatinine (SCr)
INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS
 1 INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS The working-group consists of: Fin Biering-Sørensen representing the Executive Committee of The International
1 INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS The working-group consists of: Fin Biering-Sørensen representing the Executive Committee of The International
Reassessment of the reproducibility of Technetium-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine renal clearance
 Nuclear Medicine Review 2005 Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 15 20 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Original Reassessment of the reproducibility of Technetium-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine renal clearance Carlos
Nuclear Medicine Review 2005 Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 15 20 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Original Reassessment of the reproducibility of Technetium-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine renal clearance Carlos
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Evaluation of dilated upper renal tracts by technetium-99m ethylenedicysteine F+0 diuresis renography in infants and children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 18, No. 8, 681 687, 2004 Evaluation of dilated upper renal tracts by technetium-99m ethylenedicysteine F+0 diuresis renography in infants and children Madhavi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 18, No. 8, 681 687, 2004 Evaluation of dilated upper renal tracts by technetium-99m ethylenedicysteine F+0 diuresis renography in infants and children Madhavi
Nuclear Medicine Investigations
 Chapter 4 Nuclear Medicine Investigations Introduction Nuclear medicine techniques are integral to modern urological practice and can be used to investigate almost any organ in the body. Urological usage
Chapter 4 Nuclear Medicine Investigations Introduction Nuclear medicine techniques are integral to modern urological practice and can be used to investigate almost any organ in the body. Urological usage
Radiation Detection and Measurement
 Radiation Detection and Measurement Range of charged particles (e.g.,!: µm; ": mm) Range of high energy photons (cm) Two main types of interactions of high energy photons Compton scatter Photoelectric
Radiation Detection and Measurement Range of charged particles (e.g.,!: µm; ": mm) Range of high energy photons (cm) Two main types of interactions of high energy photons Compton scatter Photoelectric
Validation of IAEA Software Package for the Analysis of Scintigraphic Renal Dynamic Studies
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of IAEA Software Package for the Analysis of Scintigraphic Renal Dynamic Studies Parameters of Renal Transit in Children With Renal Pelvic Dilatation Slobodanka Lj. Beatovic,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of IAEA Software Package for the Analysis of Scintigraphic Renal Dynamic Studies Parameters of Renal Transit in Children With Renal Pelvic Dilatation Slobodanka Lj. Beatovic,
Εκηίμηζη ηης μεθρικής λειηοσργίας Ε. Μωραλίδης
 Εκηίμηζη ηης μεθρικής λειηοσργίας Ε. Μωραλίδης Ιατρική Σχολή ΑΠΘ Νοσοκομείο ΑΧΕΠA Θεσσαλομίκη Kidney in body homeostasis Excretory function Uremic toxins removal Vascular volume maintainance Fluid-electrolyte
Εκηίμηζη ηης μεθρικής λειηοσργίας Ε. Μωραλίδης Ιατρική Σχολή ΑΠΘ Νοσοκομείο ΑΧΕΠA Θεσσαλομίκη Kidney in body homeostasis Excretory function Uremic toxins removal Vascular volume maintainance Fluid-electrolyte
The kidney. (Pseudo) Practical questions. The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis. for questions Ella
 The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility
 Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 8, No. 2, December 2013 1 Editorial Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility Taalab, Kh; and Mohsen, Z Department of Nuclear Medicine, International Medical Center;
Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 8, No. 2, December 2013 1 Editorial Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility Taalab, Kh; and Mohsen, Z Department of Nuclear Medicine, International Medical Center;
The estimation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) for renal split function with 99m Tc-DTPA Alamgir Hossain a*, Bedarul Islam a, Chanchal K.
 The estimation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) for renal split function with 99m Tc-DTPA Alamgir Hossain a*, Bedarul Islam a, Chanchal K. Ckaki a, Samirun Kumar Shaha b, Shariful I. Chowdhury c a Department
The estimation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) for renal split function with 99m Tc-DTPA Alamgir Hossain a*, Bedarul Islam a, Chanchal K. Ckaki a, Samirun Kumar Shaha b, Shariful I. Chowdhury c a Department
PHA5128 Dose Optimization II Case Study I Spring 2013
 Silsamicin is an investigational compound being evaluated for its antimicrobial effect. The route of administration for this drug is via intravenous bolus. Approximately 99.9% of this drug is eliminated
Silsamicin is an investigational compound being evaluated for its antimicrobial effect. The route of administration for this drug is via intravenous bolus. Approximately 99.9% of this drug is eliminated
GLUCEPTATE. Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION
 27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
Evaluation of renal function using excretion urography and renal scintigraphy
 Original Article Evaluation of renal function using excretion urography and renal scintigraphy Mariam Elawad Almuk, Mohammad Elfadil Mohamed Garelnabi 1, Abd Elmonem Saeed Ahamd 2, Mazin Babikir Abdullah
Original Article Evaluation of renal function using excretion urography and renal scintigraphy Mariam Elawad Almuk, Mohammad Elfadil Mohamed Garelnabi 1, Abd Elmonem Saeed Ahamd 2, Mazin Babikir Abdullah
Internal Dosimetry of Human Brain for 99m tc and 131 I Using Nuclear Imaging in Bangladesh
 Sri Lankan Journal of Physics, Vol. 6 (2005) 33-41 Institute of Physics - Sri Lanka Internal Dosimetry of Human Brain for 99m tc and 131 I Using Nuclear Imaging in Bangladesh M. M. Alam a, M. I. Kabir
Sri Lankan Journal of Physics, Vol. 6 (2005) 33-41 Institute of Physics - Sri Lanka Internal Dosimetry of Human Brain for 99m tc and 131 I Using Nuclear Imaging in Bangladesh M. M. Alam a, M. I. Kabir
R: March, E D T P A. Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection. DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use
 R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Imaging Core Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure
 Imaging Core Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure Patient Preparation and FDG Administration Procedure for ACRIN FDG-PET Scans 1.0 PURPOSE To outline the procedure for patient preparation and for 18
Imaging Core Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure Patient Preparation and FDG Administration Procedure for ACRIN FDG-PET Scans 1.0 PURPOSE To outline the procedure for patient preparation and for 18
Information for patients having an isotope kidney (renal) scan (also known as a DMSA scan)
 Information for patients having an isotope kidney (renal) scan (also known as a DMSA scan) The leaflet tells you about having an isotope kidney (renal) scan. It is also known as a DMSA scan. It explains
Information for patients having an isotope kidney (renal) scan (also known as a DMSA scan) The leaflet tells you about having an isotope kidney (renal) scan. It is also known as a DMSA scan. It explains
Expert systems for diuresis renography Andrew Taylor, MD Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA
 Expert systems for diuresis renography Andrew Taylor, MD Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA Collaborators Ernest V. Garcia, PhD Amita Manatunga, PhD Jose Binonngo, PhD Jieqiong Bao, MS Russell Folks, CNMT
Expert systems for diuresis renography Andrew Taylor, MD Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA Collaborators Ernest V. Garcia, PhD Amita Manatunga, PhD Jose Binonngo, PhD Jieqiong Bao, MS Russell Folks, CNMT
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Renal function vs chemotherapy dosing
 Renal function vs chemotherapy dosing Jenny Casanova Senior Clinical Pharmacist Repatriation General Hospital Daw Park 1 Methods of estimating renal function Cockcroft-Gault (1976) C-G using ideal vs actual
Renal function vs chemotherapy dosing Jenny Casanova Senior Clinical Pharmacist Repatriation General Hospital Daw Park 1 Methods of estimating renal function Cockcroft-Gault (1976) C-G using ideal vs actual
Optimization of a routine method for bone marrow dose estimation in
 Optimization of a routine method for bone marrow dose estimation in 177 Lu-EDTMP therapy- Experience in Uruguay. Teran. M 1, Paolino.A 2, Coppe.F 2, Nuñez M 2, Hermida J C 2, Gaudiano.J 2 1 Cátedra de
Optimization of a routine method for bone marrow dose estimation in 177 Lu-EDTMP therapy- Experience in Uruguay. Teran. M 1, Paolino.A 2, Coppe.F 2, Nuñez M 2, Hermida J C 2, Gaudiano.J 2 1 Cátedra de
Physical Bases : Which Isotopes?
 Physical Bases : Which Isotopes? S. Gnesin Institute of Radiation Physics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland 1/53 Theranostic Bruxelles, 2 Octobrer 2017 Theranostic : use of diagnostic
Physical Bases : Which Isotopes? S. Gnesin Institute of Radiation Physics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland 1/53 Theranostic Bruxelles, 2 Octobrer 2017 Theranostic : use of diagnostic
Original Article. YAN QI, 1 PANPAN HU, 2 YUANSHENG XIE, 1 KAI WEI, 1,3 MEILING JIN, 1,3 GUANGYU MA, 4 QINGGANG LI, 1 BAIXUAN XU 4 and XIANGMEI CHEN 1
 Nephrology 21 (2016) 499 505 Original Article Glomerular filtration rate measured by 99m Tc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging is significantly lower than that estimated by the CKD-EPI equation in horseshoe kidney
Nephrology 21 (2016) 499 505 Original Article Glomerular filtration rate measured by 99m Tc-DTPA renal dynamic imaging is significantly lower than that estimated by the CKD-EPI equation in horseshoe kidney
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate)
 Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
The SNMMI and EANM Procedural Guidelines for Diuresis Renography in Infants and Children
 SPECIAL CONTRIBUTION The SNMMI and EANM Procedural Guidelines for Diuresis Renography in Infants and Children Massoud Majd 1, Zvi Bar-Sever 2, Ana Isabel Santos 3, and Diego De Palma 4 1 SNMMI Pediatric
SPECIAL CONTRIBUTION The SNMMI and EANM Procedural Guidelines for Diuresis Renography in Infants and Children Massoud Majd 1, Zvi Bar-Sever 2, Ana Isabel Santos 3, and Diego De Palma 4 1 SNMMI Pediatric
--Manuscript Draft-- University of Saskatchewan Royal University Hospital Saskatoon, Saskatchewan CANADA. Gary R Conrad, M.D.
 European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging A simple method for determining split renal function from dynamic mtc-mag scintigraphic data --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title:
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging A simple method for determining split renal function from dynamic mtc-mag scintigraphic data --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title:
Gastrointestinal tract
 Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Paediatrics. John Buscombe
 Paediatrics John Buscombe Renal disease n Use of most radiopharmaceuticals limited as excreted via kidneys n However some role for infection specific studies in no-working kidneys Eg Infected polycystic
Paediatrics John Buscombe Renal disease n Use of most radiopharmaceuticals limited as excreted via kidneys n However some role for infection specific studies in no-working kidneys Eg Infected polycystic
Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 46, 314. Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn B. L. KATHEL From the Department of Urology, Alder Hey Children's Hospital; and Institute
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 46, 314. Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn B. L. KATHEL From the Department of Urology, Alder Hey Children's Hospital; and Institute
METROLOGY TO SUPPORT INNOVATION IN MOLECULAR RADIOTHERAPY. Glenn Flux
 METROLOGY TO SUPPORT INNOVATION IN MOLECULAR RADIOTHERAPY Glenn Flux Head of Radioisotope Physics Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK CGPM 2018 glenn.flux@icr.ac.uk Overview
METROLOGY TO SUPPORT INNOVATION IN MOLECULAR RADIOTHERAPY Glenn Flux Head of Radioisotope Physics Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK CGPM 2018 glenn.flux@icr.ac.uk Overview
Effective Renal Plasma Flow Determination Using Technetium 99m MAG 3 : Comparison of Two Camera Techniques with the Tauxe Method
 Effective Renal Plasma Flow Determination Using Technetium 99m MAG 3 : Comparison of Two Camera Techniques with the Tauxe Method Alberto J. Arroyo Division of Nuclear Medicine, St. Vincent Medical Center,
Effective Renal Plasma Flow Determination Using Technetium 99m MAG 3 : Comparison of Two Camera Techniques with the Tauxe Method Alberto J. Arroyo Division of Nuclear Medicine, St. Vincent Medical Center,
The Effect of Administered Activity on Patient Radiation dose and Image Quality in SPECT at Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital
 2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 1 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology The Effect of Administered Activity on Patient Radiation dose and Image Quality in SPECT
2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 1 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology The Effect of Administered Activity on Patient Radiation dose and Image Quality in SPECT
16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children
 16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients
 Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 291 295, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh079 Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients G.
Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 291 295, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh079 Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients G.
Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris
 Single nephron GFR Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril 2018 Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris Introdution Glomerular filtration and SNGFR
Single nephron GFR Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril 2018 Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris Introdution Glomerular filtration and SNGFR
Primary hyperparathyroidism (HPT) has an incidence of
 Dual-Phase Tc-Sestamibi Imaging: Its Utility in Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Use of Immediate/ Delayed Image Ratios to Improve Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism Leonie Gordon, MD; William Burkhalter, MD;
Dual-Phase Tc-Sestamibi Imaging: Its Utility in Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Use of Immediate/ Delayed Image Ratios to Improve Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism Leonie Gordon, MD; William Burkhalter, MD;
TUBULAR SECRETION (Tc-99m MAG3)
 NUCLEAR MEDICINE SERVICES SUBJECT: RENAL MAG-3 ONLY STUDY TUBULAR SECRETION (Tc-99m MAG3) Overview Indications Tc-99m MAG3 is a technetium-labeled compound with many of the functional properties of I-131
NUCLEAR MEDICINE SERVICES SUBJECT: RENAL MAG-3 ONLY STUDY TUBULAR SECRETION (Tc-99m MAG3) Overview Indications Tc-99m MAG3 is a technetium-labeled compound with many of the functional properties of I-131
Thyroid remnant volume and Radioiodine ablation in Differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thyroid remnant volume and Radioiodine ablation in Differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Md. Sayedur Rahman Miah, Md. Reajul Islam, Tanjim Siddika Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thyroid remnant volume and Radioiodine ablation in Differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Md. Sayedur Rahman Miah, Md. Reajul Islam, Tanjim Siddika Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences,
Glomerular Filtration Rate. Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC
 Glomerular Filtration Rate Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): Amount of blood that is filtered per unit time through glomeruli. It is a measure of the function of kidneys. The
Glomerular Filtration Rate Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): Amount of blood that is filtered per unit time through glomeruli. It is a measure of the function of kidneys. The
Case 4: 27 yr-old woman with history of kidney stones and hyperparathyroidism.
 Case 4: 27 yr-old woman with history of kidney stones and hyperparathyroidism. Giuliano Mariani Regional Center of Nuclear Medicine, University of Pisa Medical School, Pisa (Italy) Hyperparathyroidism
Case 4: 27 yr-old woman with history of kidney stones and hyperparathyroidism. Giuliano Mariani Regional Center of Nuclear Medicine, University of Pisa Medical School, Pisa (Italy) Hyperparathyroidism
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Can modifications of the MDRD formula improve the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in renal allograft recipients?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (7) 22: 361 3615 doi:1.193/ndt/gfm282 Advance Access publication 22 September 7 Original Article Can modifications of the MDRD formula improve the estimation of glomerular filtration
Nephrol Dial Transplant (7) 22: 361 3615 doi:1.193/ndt/gfm282 Advance Access publication 22 September 7 Original Article Can modifications of the MDRD formula improve the estimation of glomerular filtration
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
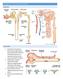 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Life Science Journal 2014;11(10)
 Performance of CKD-EPI versus MDRD among Diabetic Egyptians Khaled Abou-Seif, Yahya Makkeyah, Maha Behairy and Mohamed Mostafa Ali Internal Medicine & Nephrology Department, Ain Shams University Mahabehairy80@gmail.com
Performance of CKD-EPI versus MDRD among Diabetic Egyptians Khaled Abou-Seif, Yahya Makkeyah, Maha Behairy and Mohamed Mostafa Ali Internal Medicine & Nephrology Department, Ain Shams University Mahabehairy80@gmail.com
Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates
![Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates](/thumbs/87/95592963.jpg) Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates Molecular Imaging Branch, NIMH Bldg. 1 Rm. B3-10 September 6 th, 2006 The
Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates Molecular Imaging Branch, NIMH Bldg. 1 Rm. B3-10 September 6 th, 2006 The
Catheter Related Artifacts on Bone Scans: Report of Two Cases. Introduction
 21 Iran J Nucl Med 2006; Vol 14, No 25 Catheter Related Artifacts on Bone Scans: Report of Two Cases M. Eftekhari MD 1&2, A. Gholamrezanezhad MD 1, S. Izadyar MD 2, J. Esmaili MD 2, S. Mirpour MD 1, M.
21 Iran J Nucl Med 2006; Vol 14, No 25 Catheter Related Artifacts on Bone Scans: Report of Two Cases M. Eftekhari MD 1&2, A. Gholamrezanezhad MD 1, S. Izadyar MD 2, J. Esmaili MD 2, S. Mirpour MD 1, M.
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Diagnosis of Renovascular Hypertension
 Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Diagnosis of Renovascular Hypertension version 3.0, approved June 20, 2003 Authors: Andrew T. Taylor, Jr., MD (Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta,
Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Diagnosis of Renovascular Hypertension version 3.0, approved June 20, 2003 Authors: Andrew T. Taylor, Jr., MD (Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta,
Human Creatinine Urinary Detection Kit
 Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
99mTc dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan in patients with established radiological renal scarring
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 1315-1319 99mTc dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan in patients with established radiological renal scarring J M SMELLIE,* P J SHAW,t N P PRESCOD,* AND H M BANTOCKt
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 1315-1319 99mTc dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan in patients with established radiological renal scarring J M SMELLIE,* P J SHAW,t N P PRESCOD,* AND H M BANTOCKt
OTHER NON-CARDIAC USES OF Tc-99m CARDIAC AGENTS Tc-99m Sestamibi for parathyroid imaging, breast tumor imaging, and imaging of other malignant tumors.
 DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD Contact me at lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology Lecture 3 Renal Clearance and Glomerular Filtration Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d Amount
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD Contact me at lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology Lecture 3 Renal Clearance and Glomerular Filtration Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d Amount
Renal Impairment From Dettli to Guideline: What can we learn?
 Renal Impairment From Dettli to Guideline: What can we learn? SocraMetrics GmbH Mainzerhofplatz 14 99084 Erfurt phone: ++49-361-6020526 fax: ++49-361-6020525 e-mail: meinolf.wonnemann@socrametrics.de SocraMetrics
Renal Impairment From Dettli to Guideline: What can we learn? SocraMetrics GmbH Mainzerhofplatz 14 99084 Erfurt phone: ++49-361-6020526 fax: ++49-361-6020525 e-mail: meinolf.wonnemann@socrametrics.de SocraMetrics
KEYWORDS: nuclear medicine; gamma camera; radiopharmaceutical activities.
 Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in the First Six Months of the Gamma Camera Use in the Clinical Center of Montenegro - Podgorica Nevenka Antovic
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in the First Six Months of the Gamma Camera Use in the Clinical Center of Montenegro - Podgorica Nevenka Antovic
Comparison of Serum Cystatin C and Creatinine Levels to Evaluate Early Renal Function after Kidney Transplantation
 IJMS Vol 34, No 2, June 2009 Original Article Comparison of Serum Cystatin C and Creatinine Levels to Evaluate Early Renal Function after Kidney Transplantation Reza Hekmat, Hamid Eshraghi Abstract Background:
IJMS Vol 34, No 2, June 2009 Original Article Comparison of Serum Cystatin C and Creatinine Levels to Evaluate Early Renal Function after Kidney Transplantation Reza Hekmat, Hamid Eshraghi Abstract Background:
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of Diuretic Renography in the Evaluation of Obstructed Hydronephrosis after Pediatric Pyeloplasty
 Original Article 344 The Role of Diuretic Renography in the Evaluation of Obstructed Hydronephrosis after Pediatric Pyeloplasty Ta-Min Wang, MD; Phei-Lang Chang, MD; Pan-Fu Kao 1, MD; Ming-Li Hsieh, MD;
Original Article 344 The Role of Diuretic Renography in the Evaluation of Obstructed Hydronephrosis after Pediatric Pyeloplasty Ta-Min Wang, MD; Phei-Lang Chang, MD; Pan-Fu Kao 1, MD; Ming-Li Hsieh, MD;
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Technical Considerations in Zevalin Radioimmunotherapy Kathy Thomas, MHA, CNMT City of Hope National Medical Center
 Technical Considerations in Zevalin Radioimmunotherapy Kathy Thomas, MHA, CNMT City of Hope National Medical Center Technical Considerations in Zevalin Radioimmunotherapy Objectives: Explain the technical
Technical Considerations in Zevalin Radioimmunotherapy Kathy Thomas, MHA, CNMT City of Hope National Medical Center Technical Considerations in Zevalin Radioimmunotherapy Objectives: Explain the technical
