Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn
|
|
|
- Shana Dixon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
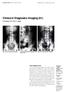
1 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 46, 314. Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn B. L. KATHEL From the Department of Urology, Alder Hey Children's Hospital; and Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool Kathel, B. L. (1971). Archives of Disease in Childhood, 46, 314. Radioisotope renography as a renal function test in the newborn. Isotope renography has been carried out in 32 babies with neurogenic bladder due to spina bifida or with other urological lesions. The tracings can be interpreted according to the standards applicable to renography in older children. Comparison of renography and intravenous urography showed a close correlation between the two tests, but renography proved to be more sensitive and informative. As renography is easily performed and since the radiation dosage is very small, it is of value in those patients where frequent assessment of the function and emptying capability of each individual kidney is required. A large amount of work has been done concerning isotope renography as a test of renal function in adults, but relatively little has been recorded about the value of the technique in infancy. The normal renogram tracing shows three phases. First, there is a sudden rise in radioactivity, then a slow rise to a peak (second phase) and subsequently a fall away (third phase) (Fig. 1). From this department, Johnston and Irving (1967) described renogram tracings from normal kidneys in children under 2 years of age. These they found to be relatively flat as compared with those obtained from older children. Winter et al. (1968) on the other hand performed renography in 26 newborn babies with presumed normal kidney function, and found that in 19 the tracings were of normal adult type; 7 showed a prolonged functional and/or excretory phase. The present contribution relates to infants under the age of 2 months. It is concerned with the analysis of renograms from kidneys with normal and abnormal function, and with the rates of elimination of radioisotope from the blood and of its accumulation in the bladder. The results are compared with the findings on intravenous pyelography and with biochemical studies. The main object of this presentation is to evaluate the test as an index of individual renal function in the newborn. Received 14 October 197. Technique Lugol's iodine solution ( 2 ml) (17 3 mg total iodine and 6-6 mg free iodine) is given orally on the night before and on the evening after the test in order to block the possible uptake of any free radioactive iodine by the thyroid. Renography is carried out 1 hours after a feed to obtain a standard level of hydration. The patient is bandaged to a crucifix splint in the prone position, a detector probe is placed over the site of each kidney, and a third is positioned over the left scapular region. The probes are connected to ratemeters and recorders. The meter range employed has been 3 and the paper speed 1 25 cm/minute. Hippuran 125I -3,uCi/kg is injected rapidly into a scalp vein. For renography in children over 2 years of age we use a dose of 25,uCi/kg and a meter range of 1. The modification in technique for newbom infants is necessary to obtain sufficient amplitude in the tracing. If necessary, the positions of the kidney probes are readjusted within a few seconds of the start of the test in order to obtain maximum deflection. The renogram tracings last from 1 to 3 minutes. At the conclusion bladder radioactivity is recorded with the baby in the supine position. All recordings reproduced by recorders are from right to left-a convention in the renographic field. The following parameters were measured from renogram curves. (1) The time interval from the injection to the peak of the tracing (Tm). (2) The time interval from the injection to the point where the curve decays to 5, of the maximum (TI). (3) The amplitude of tracing is expressed by radioactive counts per second. The parameters were compared with those obtained 314
2 Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn Ipt 9 am a 21 LEFT RIGHT.S4CfIt,Qq FIG. 1.-Normal left and right renograms, blood clearance curve, and bladder radioactivity recorded on 12th day of life. Slow clearance of tracer is shown. (This recording and those in Fig. 2, 3b, 4a and c, and 5a are to be read from right to left.) These have been rescaled in time from the originals to a paper speed of 6 cm/min in order to facilitate publication. from kidneys in children over 2 years of age. In the latter group, from our observations of 8 normal renograms, the normal range of Tm is from 2-5 to 5-5 minutes, with an average of 4 minutes and the normal - - range of Ti is from 8 2 to 19 9 minutes, with an average of 14- minutes. The neonatal renograms were classified as normal, if within these limits, and abnormal if outside the limits. Material Two groups of patients were studied. (1) 27 newborn infants with neurogenic bladder due to spina bifida. In these, intravenous pyelography was carried out within 12 days of birth. In 19 patients, radiology was performed before renography and in 8 patients afterwards. Renography was carried out between the 9th and 3th days of life. (2) 5 patients with urinary tract disorders without spina bifida. In these, renography was carried out between the 3th and 6th days. The weights of the patients in both groups varied from 2 5 kg to 4-5 kg. Results Normal kidneys. The renograms from 41 kidneys of normal pyelographic appearance from Groups 1 and 2 were assessed. In 17 of these, parameters Tm and T' both corresponded with our accepted normal standards (Fig. 1). In 2, a peak was not defined, therefore Tm was not measurable; in these, Ti was normal in 3, prolonged in 9, and not measurable in 8. In 4 instances both Tm and Te were prolonged. In the entire group Tm or Ti were prolonged either singly or together in 13 instances. The details of range and average of parameters in minutes are shown in Tables I and II. 7 - p aj z v! F z n 315 TABLE I Analysis of 41 Renograms from Normal Kidneys Pyelographically Tm (min) Ti (min) 17 Normal range 1 to5-5,average3-2 8 to 19 9, average Prolonged 5 75 to 8, average 22 to 37, average Peaks not 9 Prolonged defined 3 Normal range r4 showed 8 Not 3% decay measurable at 26 min 4 showed no Ldecay TABLE II Detailed analysis of 17 Normal Renograms from Pyelographically Normal Kidneys Tm (min) Ti (min) * * * 1 * *25 8- Weights of the patients varied from 2 * 5 kg to 4-5 kg. was carried out between 9th and 6th days of life. Renography
3 316 B. L. Kathel TABLE III Correlation Between Renograms and Intravenous Pyelograms Agreement False Positive Renogram False Negative Renogram Inter- With IVP Normal IVP Abnormal pretation IVP Renogram Abnormal Renogram Normal Uncertain 41 renograms from pyelographically normal kidneys renograms from pathological kidneys Total Bladder radioactivity in 33 renograms was within the normal range of 2 to 3 c.p.s. with an average of 25 c.p.s. (Fig. 1). In 8 renograms the range was from 3 to 15 c.p.s.; these were from the group in which the third phase was level or was slowly decaying. 41 comparisons of renograms and normal pyelograms were studied (Table III). The renograms and intravenous pyelograms corresponded in 33 normal kidneys and did not in 8. In the latter, the renogram showed delayed decay or a level third phase. These 4 patients were spina bifida babies with a raised blood urea and a distended and inexpressible bladder, suggesting urinary stasis even though the upper urinary tract was undilated on pyelography. Pathological kidneys. The renograms of 23 abnormal kidneys from Groups 1 and 2 were studied. Of these, 21 were hydronephrotic, 1 was multicystic, and 1 was congenitally dysplastic. 4 renograms relating to the multicystic kidney, the congenitally dysplastic kidney, and 2 of the hydronephrotic kidneys corresponded to the blood background, signifying no renal function. In the remaining 19 renograms, the third phase was level after the maximum in 7, rising in 5, and there was only 3% decay at 26 minutes in 7. The bladder radioactivity ranged from 18 to 3 c.p.s. with an average of 24 c.p.s. in cases of unilateral pathology. With bilateral hydronephrosis the range was from 3 to 12 c.p.s. with an average of 7 * 5 c.p.s. 23 comparisons of renograms and pyelograms of abnormal kidneys were studied (Table III). In 18, the renographic and pyelographic findings corresponded. In 2 the renograms were normal but the pyelograms showed minor dilatation of the calyces. In the remaining 3 the interpretation was difficult as it was not clear whether the tracing represented blood background radioactivity or whether there was in addition very subnormal renal function. Discussion It has long been realized that kidney function in the neonate differs from that in the older child and the adult. This is probably due mainly to anatomical and physiological differences between the age groups. In the newbom, the proximal convoluted tubules are still of primitive form and the loops of Henle are short (Smith, 1951). In addition the cuboidal epithelium lining the glomerular capsule which is present in the fetus, may persist until 2 years of age. In the newborn, the arterial blood pressure and, by presumption, the intraglomerular pressure are relatively low. Both glomerular and tubular functions are affected. The glomerular filtration rate in the neonate is low (Barnett, 194), though the precise measurements depend upon whether calculation is related to surface area or to total body water. Edelmann and Spitzer (1969) summarize that low glomerular filtration rates (GFR) in the neonatal period are due to incomplete morphological and functional development of all components involved in the process of filtration. This low GFR limits the capacity of the infant to withstand stress of loading. An adult level of GFR is reached at the age of 9 to 12 months. Grotte, Arturson, and Malmberg (1968) believe that glomerular permeability increases with the development of the nephron. With increasing age, the pore radius of the glomerular membrane, approximately 2 A in the neonatal period, increases to 4 A in the adult. The defect in tubular function in the newborn is shown by the 3% reduction in extraction of PAH as compared with the adult, by the reduction in the effective renal plasma flow as indicated by diodrast or PAH clearances, and by the inability of the newborn kidney to produce a concentrated urine. Calcagno and Rubin (1963) demonstrated that this was not due to a reduction in renal perfusion, which supports the concept of a functionally limited cortex. Our own observations of slow clearance of Hippuran 125I from the blood (Fig. 1) favour the above concept. McCance (1948) pointed out that, while
4 Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn FIG. 2.-Renograms recorded on 3th day of life in baby with an afunctional left multicystic kidney. Normal right renogram. Flat tracing on left. kidney function is adequate to maintain homeostasis in the normal infant, the kidney has little reserve capacity and may be unable to compensate for disturbances in metabolism or water balance. In 17 of the renogram tracings obtained from 41 pyelographically normal kidneys in the newborn, the parameters Tm and Ti were within the range of normality for older children (Tables I and II). Winter et al. (1968) had a similar correspondence in 19 of 26 neonatal cases. However in 14 normal neonatal kidneys in our series, Tm and/or Ti were prolonged as compared with tracings from older children. Again Winter et al. (1968) had similar findings in 7 of 26 neonatal cases. In 2 of our tracings from normal kidneys, measurement of Tm was not possible, since a clear peak at the end of the second phase was not defined. Winter et al. (1968) did not have this difficulty, probably because he used a much slower paper speed. When Tm and Ti are prolonged or when Tm cannot be measured, we believe that the level of bladder radioactivity is relevant in the interpretation of renal function. If bladder radioactivity is within the range of 2 to 3 c.p.s. the overall renal function can be assumed to be normal. On the other hand, if bladder radioactivity is below 15 c.p.s. renal function can be interpreted as subnormal provided there is no obstruction in the upper urinary tract. We have not found the blood clearance curve of tracer to be helpful as an index of renal function in the newborn since the clearance is much slower than in older children (Fig. 1). Our recent renogram tracings from newborn infants differ from those obtained by Johnston and Irving (1967). These authors noted a flat or subnormal tracing to be an invariable occurrence 317 in children under the age of 2 years. The reason for the different finding is not clear. Johnston and Irving were, however, using Hippuran 131I and the babies were examined in the supine position which may make correct positioning of the large 131I probes difficult. In the pyelographically abnormal kidneys from Groups 1 and 2, 19 hydronephrotic as a result of obstruction of varying pathogenesis, renography showed that the third phase was rising in 5, was level at the maximum in 7, and in the remaining 7 there was only 3% decay at 26 minutes. In 4 kidneys, where there was no concentration on pyelography, 1 being congenitally dysplastic, 1 multicystic, and 2 hydronephrotic, the tracings were entirely flat (Fig. 2). 64 comparisons between renography and pyelography were made; 51 renograms correlated closely with the findings on intravenous pyelography (Table III). False positive renograms, where the pyelogram was normal but the parameters of the renogram tracing were outside the accepted limits, occurred in 8 kidneys in 4 patients. These 4 babies were ill, the blood urea was raised and bladder was distended and inexpressible (Fig. 3 a and b), suggesting that renography was a better index of renal function and evacuation than pyelography. The greater prognostic value of renography as compared with pyelography was shown in the case illustrated in Fig. 4. This spina bifida baby also had a tensely" distended bladder. An intravenous pyelogram at the age of 28 days showed no upper tract dilatation, but the renogram (Fig. 4a) showed some delay in the third phase on the left side. At the age of 8 months intravenous urography showed well-marked left hydronephrosis and hydroureter (Fig. 4b), and at this
5 318 B. L. Kathel.wm5* #..4 5n #1. o# ji\s ;7:caaacoaaoooaaaaaooaaoaos: l 2CLEFT iz * o o (a) I a 4 (b) FIG. 3.-Infant with spina bifida and inexpressible neurogenic bladder with urinary retention. (a) Intravenous pyelogram; undilated upper urinary tract. (b) Renogram; bilateral delayed third phase, more marked on left than right. (a) OQOcoD LEFT z 21 is -15SaWI Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 June Downloaded from -9-z (b) (c) FIG. 4.-Prognostic significance of renography. Infant with neurogenic bladder due to spina bifida. (a) Renogram on 28th day of life; some delay in emptying on left side; at this time the intravenous pyelogram was normal. (b) Intravenous pyelogram, aged 8 months; marked left hydronephrosis and hydroureter. (c) Renogram aged 8 months; severe stasis on left side. 4 19~~~~~~~~~~~ mg- 1I-- I-1-- I on 4 May 218 by guest. Protected by copyright. I- z n 4.,
6 i... s.. t-']_a *3 a 3 i4 Radioisotope Renography as a Renal Function Test in the Newborn 319 ES 3 RIGHT ~~. BHBUfluW~~~i~~Lo% 3 _ LEFT *4> iooot, 27 *#~~ ~ODa 24 K OOkl Or _ zl a~~~~~~~~~~~~~~,, -- - J TMEI IUE time the renogram was typical of severe upper tract stasis (Fig. 4c). The correlation between pyelography and renography was much closer with pathological kidneys. The renogram tracings were normal in only 2 of the 23 pathological kidneys; each of these showed only a mild degree of hydronephrosis on pyelography. The behaviour of the third phase of the renogram corresponded closely with the degree of pelvicalyceal dilatation. Severe dilatation was associated with a rising third phase (Fig. 5 a and b), moderate dilatation with a third phase parallel to the baseline, and mild dilatation with a delayed third phase. In 8 patients renography was carried out before intravenous pyelography and the expectations were confirmed. On the whole, renography correlated very well with intravenous pyelography. Intravenous pyelography has been the principal diagnostic test of individual kidney function in the newborn as with older age groups. The test allows visualization of anatomical details, but does not measure renal function since it is influenced by the state of hydration of the patient and by the concentration and the volume of contrast medium employed. Relating radiological opacity with renal function is not valid with modem contrast media and techniques. In addition the results may be inconclusive because of bowel contents obscuring the kidney on the radiograph. Isotope renography gives a qualitative index of the tubular function and emptying capability of the individual kidney. The correlation with pyelography in the S 4 tid 1 FIG. 5.-Infant with spina bifida due to neurogenic bladder. (a) Renograms, aged 12 days, showing bilateral (Iİb) rising third phases. _ (b) * l '(b) Intravenous pyelogram; gross bilateral hydronephrosis and hydroureters. o12~.3 detection of renal pathology is close. There is no special preparation required and the results are obtained quickly. It is a more sensitive test than pyelography. Renograms in the newborn can be interpreted by applying the standards from children over 2 years of age. The radiation dose with renography is only about 1/5 of that required for a single x-ray exposure (Winter, 1963). The test can, therefore, be safely and conveniently repeated in following the progress of renal function over a lengthy period of time. The great value of renography lies, in our view, in the follow-up of children who will require repeated and fairly frequent assessment of the function and drainage capability of each individual kidney. As such it can be of great use in the management and care of the child with neurogenic bladder due to spina bifida. I am grateful to Mr. J. H. Johnston for his encouragement and advice in the preparation of this report. REFERENCES Barnett, H. L. (194). Renal physiology in infants and children. I. Method for estimation of glomerular filtration rate. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 44, 654. Calcagno, P. L., and Rubin, M. I. (1963). Renal extraction of paraaminohippurate in infants and children. journal of Clinical Investigation, 42, Edelmann, C. M., Jr., and Spitzer, A. (1969). The maturing kidney: a modem view of well-balanced infants with imbalanced nephrons. journal of Pediatrics, 75, 59. Grotte, G., Arturson, G., and Malmberg, P. (1968). Maturation of kidney function. Proceedings of the XIIth International Congress of Pediatrics, Mexico, 3, 32.
7 32 B. L. Kathel Johnston, J. H., and Irving, I. M. (1967). Experiences with radioisotope renography in children. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 42, 583. McCance, R. A. (1948). Renal function in early life. Physiological Review, 28, 331. Smith, H. W. (1951). The Kidney: Structure and Function in Health and Disease, p Oxford University Press, New York. Winter, C. C. (1963). Radioisotope Renography: A Kidney Function Test Performed with Radioisotope-Labeled Agents. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore. Winter, C. C., Elliott, J., Grace, D., and Robertson, A. (1968). Radioisotoperenography in the assessment of renal function in the newborn. Journal of Urology, 1, 99. Correspondence to Mr. B. L. Kathel, Department of Urology, Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Eaton Road, Liverpool L12 2AP. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 June Downloaded from on 4 May 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom. Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium
 Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
The Use of the 113Hippuran Renogram in the Detection of Disparate Kidney Function in Hypertensive Patients
 The Use of the 11Hippuran Renogram in the Detection of Disparate Kidney Function in Hypertensive Patients By RICHARD P. WEDEEN, M.D., EDWARD LITTMAN, M.D., MARVIN F. LEVIrr, M.D., AND MARVIN H. GOLDSTEIN,
The Use of the 11Hippuran Renogram in the Detection of Disparate Kidney Function in Hypertensive Patients By RICHARD P. WEDEEN, M.D., EDWARD LITTMAN, M.D., MARVIN F. LEVIrr, M.D., AND MARVIN H. GOLDSTEIN,
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING. Dr A Brink
 PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING Dr A Brink Causes of hydronephrosis includes: Pelvi-ureteric obstruction Vesico-ureteric reflux Vesico-ureteric obstruction Posterior uretral valves Duplex kidneys Radiopharmaceutical
PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING Dr A Brink Causes of hydronephrosis includes: Pelvi-ureteric obstruction Vesico-ureteric reflux Vesico-ureteric obstruction Posterior uretral valves Duplex kidneys Radiopharmaceutical
Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 531. Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney G. L. ROLLESTON, T. M. J. MALING, and C. J. HODSON* From the Department of Radiology, Christchurch Hospital and
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 531. Intrarenal reflux and the scarred kidney G. L. ROLLESTON, T. M. J. MALING, and C. J. HODSON* From the Department of Radiology, Christchurch Hospital and
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
R adio logical investigations of urinary system
 R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Renal. Prof John Buscombe
 Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 176-180 Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism MALGORZATA BORZYSKOWSKI AND B G R NEVILLE Evelina Children's Department, Guy's Hospital, London SUMMARY The
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 176-180 Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism MALGORZATA BORZYSKOWSKI AND B G R NEVILLE Evelina Children's Department, Guy's Hospital, London SUMMARY The
Nuclear medicine methods in the urogenital system
 Nuclear medicine methods in the urogenital system Anatomy of the kidneys I. Anatomy of the kidneys II. The types of examinations Static examinations (scintigraphy): 1) the radiopharmaceutical is administered
Nuclear medicine methods in the urogenital system Anatomy of the kidneys I. Anatomy of the kidneys II. The types of examinations Static examinations (scintigraphy): 1) the radiopharmaceutical is administered
INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS
 1 INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS The working-group consists of: Fin Biering-Sørensen representing the Executive Committee of The International
1 INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS The working-group consists of: Fin Biering-Sørensen representing the Executive Committee of The International
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
 MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010
 RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010 Alive patient RA + tracers Tc-99m(86%) + MAG 3 DMSA (DTPA) T½ = 6,5h Gamma camera ect. Radio-active
RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010 Alive patient RA + tracers Tc-99m(86%) + MAG 3 DMSA (DTPA) T½ = 6,5h Gamma camera ect. Radio-active
Pediatric Ure-Radiology*
 Pediatric Ure-Radiology* HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina "Routine" radiologic studies do not, often enough, concentrate
Pediatric Ure-Radiology* HERMAN GROSSMAN, M.D. Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina "Routine" radiologic studies do not, often enough, concentrate
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary continence in open myelomeningocele
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1977, 52, 703-707 Urinary continence in open myelomeningocele ROGER J. BRERETON*, R. B. ZACHARY, AND JAMES VISTER* From the Department ofpaediatric Surgery, Children's
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1977, 52, 703-707 Urinary continence in open myelomeningocele ROGER J. BRERETON*, R. B. ZACHARY, AND JAMES VISTER* From the Department ofpaediatric Surgery, Children's
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones
 4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses)
 weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
Nephrographic and Pyelographic Analysis of CT Urography: Principles, Patterns, and Pathophysiology
 Genitourinary Imaging Review Wolin et al. CT Urography Principles, Patterns, and Genitourinary Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Ely A. Wolin 1 David S. Hartman J. Ryan Olson Wolin EA, Hartman DS, Olson JR Keywords:
Genitourinary Imaging Review Wolin et al. CT Urography Principles, Patterns, and Genitourinary Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Ely A. Wolin 1 David S. Hartman J. Ryan Olson Wolin EA, Hartman DS, Olson JR Keywords:
Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
 Scan for mobile link. Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an x-ray exam that uses an injection of contrast material to evaluate your kidneys, ureters and bladder and help diagnose
Scan for mobile link. Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an x-ray exam that uses an injection of contrast material to evaluate your kidneys, ureters and bladder and help diagnose
Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra
 Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
EXCRETORY SYSTEM E. F. G. H.
 XRTORY SYSTM 1. Label the following parts of the nephron in the diagram below:..... F. G. H. I. J. K. L. 2. Identify the following as either True or False: There is a greater osmotic concentration in the
XRTORY SYSTM 1. Label the following parts of the nephron in the diagram below:..... F. G. H. I. J. K. L. 2. Identify the following as either True or False: There is a greater osmotic concentration in the
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA
 Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
The Excretory System
 The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Prenatal Hydronephrosis
 Prenatal Hydronephrosis What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis is dilation of the kidney, specifically the renal pelvis (place where urine is stored after its production). This can be the result of an
Prenatal Hydronephrosis What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis is dilation of the kidney, specifically the renal pelvis (place where urine is stored after its production). This can be the result of an
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Calculus Induced Hydroureteronephrosis Obstructive Syndrome in a Patient with Two
 CASE REPORT ISSN: 2467-9151OPEN ACCESS Calculus Induced Hydroureteronephrosis Obstructive Syndrome in a Patient with Two Separate Pelvicalcyeal System in Right Side with Bifid Ureter: A Rare Clinical Entity
CASE REPORT ISSN: 2467-9151OPEN ACCESS Calculus Induced Hydroureteronephrosis Obstructive Syndrome in a Patient with Two Separate Pelvicalcyeal System in Right Side with Bifid Ureter: A Rare Clinical Entity
16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children
 16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
The excretory system
 Key Words The excretory system haemoglobin Convoluted tubule Loop of Henle nephron ureter/-s sweat glands Bowman s capsule Glomerulus cholesterol Bladder Excretion is the removal of the waste products
Key Words The excretory system haemoglobin Convoluted tubule Loop of Henle nephron ureter/-s sweat glands Bowman s capsule Glomerulus cholesterol Bladder Excretion is the removal of the waste products
Dynamic Renal Scintigraphy
 Dynamic Renal Scintigraphy JP Esser, Meander Medical Centre, Amersfoort 1. Introduction Patients referred for renography either have partial kidney obstruction or no obstruction. Partial obstruction is
Dynamic Renal Scintigraphy JP Esser, Meander Medical Centre, Amersfoort 1. Introduction Patients referred for renography either have partial kidney obstruction or no obstruction. Partial obstruction is
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Urinary System VASTACCESS, INC.
 Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound. Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I
 Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Medicine, Cambridge, England, and Wuppertal, B.A.O.R.
 182 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, i82-i86 6I2.46I.62 PHOSPHATE CLEARANCES IN INFANTS AND ADULTS BY R. F. A. DEAN AND R. A. McCANCE From the Medical Research Council, Department. of Experimental Medicine, Cambridge,
182 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, i82-i86 6I2.46I.62 PHOSPHATE CLEARANCES IN INFANTS AND ADULTS BY R. F. A. DEAN AND R. A. McCANCE From the Medical Research Council, Department. of Experimental Medicine, Cambridge,
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
URINARY TRACT DUPLICATION IN CHILDHOOD
 URINARY TRACT DUPLICATION IN CHILDHOOD The incidence of duplication of the urinary tract has variously been estimated by different authors to be between the extremes of 0-6% (Campbell, 1951) and 6% (Thompson
URINARY TRACT DUPLICATION IN CHILDHOOD The incidence of duplication of the urinary tract has variously been estimated by different authors to be between the extremes of 0-6% (Campbell, 1951) and 6% (Thompson
BIOL 2402 Renal Function
 BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61)
 Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(5) : 233-237 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61) K B J Sheah, S K H Yip, V T Joseph Fig. 1a Control abdominal radiograph. Fig. 1b Coned oblique
Singapore Med J 2001 Vol 42(5) : 233-237 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (61) K B J Sheah, S K H Yip, V T Joseph Fig. 1a Control abdominal radiograph. Fig. 1b Coned oblique
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
WHAT TO CALL HYPOPLASTIC KIDNEY?*
 WHAT TO CALL HYPOPLASTIC KIDNEY?* Among the congenital abnormalities of the urinary tract, the term hypoplastic kidney is one of the least well defined and also one of the most widely used. Certain abnormal
WHAT TO CALL HYPOPLASTIC KIDNEY?* Among the congenital abnormalities of the urinary tract, the term hypoplastic kidney is one of the least well defined and also one of the most widely used. Certain abnormal
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Lab 19 The Urinary System
 Lab 19 The Urinary System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the micro- and macroscopic anatomy of the kidney. Track the blood flow in and out of the kidney. Compare blood, glomerular filtrate,
Lab 19 The Urinary System Laboratory Objectives Identify and describe the micro- and macroscopic anatomy of the kidney. Track the blood flow in and out of the kidney. Compare blood, glomerular filtrate,
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Introduction George N. Sfakianakis MD Professor
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Introduction George N. Sfakianakis MD Professor
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN*
 THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
Pages Renal A&P Renal Blood Flow The Nephron Urine Formation Homeostatic Imbalances & Treatment
 CH. 25-URINARY SYSTEM Pages 960-994 Renal A&P Renal Blood Flow The Nephron Urine Formation Homeostatic Imbalances & Treatment 2009- First public case of water intoxication (hyponatremia); Jury awarded
CH. 25-URINARY SYSTEM Pages 960-994 Renal A&P Renal Blood Flow The Nephron Urine Formation Homeostatic Imbalances & Treatment 2009- First public case of water intoxication (hyponatremia); Jury awarded
Vesicoureteral Reflux
 What is the normal urinary tract? The kidneys filter the blood and extract waste products from the blood to make urine. Urine passes from the kidneys, down the ureters, and into the bladder for storage
What is the normal urinary tract? The kidneys filter the blood and extract waste products from the blood to make urine. Urine passes from the kidneys, down the ureters, and into the bladder for storage
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
Fractional excretion of uric acid in infancy and childhood
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 878. Fractional excretion of uric acid in infancy and childhood Index of tubular maturation J. H. PASSWELL, M. MODAN, M. BRISH, S. ORDA, and H. BOICHIS From
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 878. Fractional excretion of uric acid in infancy and childhood Index of tubular maturation J. H. PASSWELL, M. MODAN, M. BRISH, S. ORDA, and H. BOICHIS From
network of thin-walled capillaries closely surrounded by a pear-shaped epithelial membrane called the Bowman s capsule
 Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. ANTENATAL HYRONEPHROSIS UROLOGICAL ASPECTS Dr Gianantonio Manzoni, FEAPU FRCS U.O.
G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. ANTENATAL HYRONEPHROSIS UROLOGICAL ASPECTS Dr Gianantonio Manzoni, FEAPU FRCS U.O.
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
Nuclear medicine in renal scarring
 Paediatric NM General principles Need to image in a child friendly department Maybe use of play therapist to help explain the procedure Reduce activities as weight a proportion of 70kg adult with 10% minimum
Paediatric NM General principles Need to image in a child friendly department Maybe use of play therapist to help explain the procedure Reduce activities as weight a proportion of 70kg adult with 10% minimum
