C The Effect of CHDI on Behavior, Survival and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in R6/2 Huntington s Mice. Cerebricon Ltd.
|
|
|
- Eric French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cerebricon Ltd. C521-1 The Effect of on Behavior, Survival and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in R6/2 Huntington s Mice Prepared for: CHDI Inc. c/o MRSSI Inc. 35 Seventh Avenue, Suite 61 New York, NY 11 USA
2 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 6 Purpose of Study The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of treatment on body weight, survival, motor deficits, cognitive performance and volumetry of whole brain, striatum and cortex in R6/2 Huntington s mice. 6 male and female R6/2 mice (TG) (strain R62 (CHDI-1)) and 12 male and female wild-type littermate control mice (WT) were used in the study. The mice were genotyped and TG mice were randomly divided into vehicle and treated groups (female/male balance equal) whereas the WT mice received the corresponding vehicle. The twice-a-day p.o. treatment with CHDI (1 or 3 mg/kg) or vehicle started at age week 4. Body weights were measured twice a week starting at age week 4 and continued until 12 weeks of age. Motor function testing including open field and rear climbing tests were commenced at 4 weeks of age and continued at weeks 6, 8 and 12, for grip strength test at age weeks 4 and 12 and for rotarod at age weeks 4, 6 and 8. Cued two-choice swim test (Cued 2-CST) was performed at 9 weeks of age. At 13 weeks of age all the mice were subjected to in vivo T2-MRI analysis of brain, striatum and cortical volume. The mice were followed until death (=spontaneous death or fulfillment of euthanasia criteria). 7 Materials and Methods 7.1 Animals All animal experiments were carried out according to the National Institute of Health (NIH) guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals, and approved by the Ethical Committee of the National Laboratory Animal Center, Kuopio, Finland. 6 male and female R6/2 TG mice (R6/2J CAG 12 (strain R62 (CHDI-1)) and 12 male and female wild-type littermate control mice were bred at National Animal Facility Center Kuopio. The experimental groups were: 12 WT littermate control mice treated with vehicle (1 ml/kg) (p.o., BID) starting at 4 weeks of age and continuing until 23 weeks of age 2 TG mice treated with vehicle (1 ml/kg) (p.o., BID) starting at 4 weeks of age and continuing until 23 weeks of age 2 TG mice treated with (1 mg/kg, 1 ml/kg) (p.o., BID) starting at 4 weeks of age and continuing until 23 weeks of age 2 TG mice treated with (3 mg/kg, 1 ml/kg) (p.o., BID) starting at 4 weeks of age and continuing until 23 weeks of age 11(39)
3 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 7.2 Husbandry All the mice were housed in groups of up to 4 per cage (mixed genotypes, single sex), in a temperature (22±1 C) and humidity (3-7%) controlled environment with a normal light-dark cycle (7:-2:). All mice were housed in shoe-box cages with clean bedding covering the ground that is changed as frequently as needed to provide the animals with dry bedding. This basic environment was enriched with the addition of play tunnels, wooden nesting material, and plastic bones for all mice; i.e. an environmentally-enriched cage contains a Mouse Tunnel, (amber color, certified, transparent, BioServ Product# K3323) and a Petite Green Gumabone (BioServ Product # K3214) and wooden nesting material. Food (Purina Lab Diet 51) and water were available ad libitum to the mice in their home cages. R6/2 and corresponding WT mice also receive wet powdered food (Purina Lab Diet 51 mixed with water to form a paste) placed inside a cup on the floor of the cage; this additional food was replaced fresh daily and started from the time of weaning. In addition, water spouts were fitted with extensions to allow mice to easily access from floor level. 7.3 Breeding and Weaning 6 male and female R6/2 mice and 12 male and female wild-type littermate control mice (F 1 generation) were bred at FELASA compliant National Animal Facility Center Kuopio by mating (F generation) WT males (C57BL/6J, JAX) with ovarian transferred (OT) TG females (JAX). The F mice arrived at 1-12 weeks of age to allow 1 week quarantine and breeding in two consecutive weeks. Breeder animals received igloos instead of play tunnels, nylabone and cotton nestlets. Upon weaning, pups received Purina diet 51. Pups were weaned from their mothers and segregated to new cages for male and females, not exceeding 4-5 mice per cage. Ear snips were taken during the weaning process at 2-3 weeks for genotype analysis as described below. 7.4 Genotyping Mice were ear marked at the age of days and ear samples were collected at the same time for genotyping with PCR. Genotypes were determined between 15 and 21 days (weaning age) of age by PCR of ear samples. In mutant mice, the genotype was a simple PCR assay and CAG repeat length was analyzed by GeneAmp 272 Thermal Cycler sequencer. 7.5 Experimental Set Up of Mice In setting up groups for study (i.e. vehicle or compound treated), transgenic and wildtype mice were randomized into groups so that whole litters of mice did not end up in a single testing group. Mice were housed in groups of 4 and separated by sexes. In each cage, one wild-type mouse of the same gender, but different litter, was included in an attempt to provide normal social stimulation. Mice were allowed to acclimate to the experimental room for at least one hour prior to the beginning of any experiment. Mice were transported from the colony room to experimental rooms in their home cages. Experimentation was conducted in a 12(39)
4 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report blinded manner. Tail samples were taken at the end of the study for possible verification of genotypes and CAG sizes of individual mice. 7.6 General Health Status and Humane End-Points Animals were monitored twice-a-day by laboratory personnel (8 am and 16 pm). In case general health status of an animal was significantly worsened, the mouse was sacrificed by an overdose of CO 2 and decapitated. Definitions of acceptable endpoints include: weight loss of more than 25 % of the maximum, no spontaneous movements and inability to drink or eat in 24-h observation period, massive bleeding, spontaneous inflammation, missing anatomy, swelling or tumors. 7.7 Compound Delivery Compound was dissolved in 3% Propylene Glycol, 2% Solutol HS15, 5% 5mM Citrate, and administered p.o. twice-a-day starting at age week 4 and continuing until endpoint. On the days of behavioral testing the dosing was done at least 1.5 h before the test. Genotype N (F/M) Compound Dose (mg/kg) Regimen Route Dose volume (ml/kg) Wild-type 6/6 R6/2 1/1 3% Propylene Glycol, 2% Solutoll HS15, 5% 5mM Citrate BID p.o. 1 3% Propylene Glycol, 2% Solutoll HS15, 5% 5mM Citrate BID p.o. 1 R6/2 1/1 1 BID p.o. 1 R6/2 1/1 3 BID p.o. 1 Table 4. Details of the genotype, number and gender of animals (F: female, M: male) included in each treatment group, the compound, dose, dosage regime and route and volume of administration. 7.8 Body Weight and Survival Body weight was measured starting at the age of 4 weeks and two times per week on the same day (i.e. Monday and Friday) until the end of the study. This was done just prior to animals receiving doses for those days. In the case that the general health status of an animal had significantly worsened, the mouse was sacrificed by an overdose of CO 2, and decapitated. Definitions of acceptable endpoints include: no spontaneous movements and inability to drink or eat in 24-h observation period, massive bleeding, spontaneous inflammation, missing anatomy, swelling or tumors larger than 2 mm, and inability to right itself in 3 sec period. The mice were monitored until death or the fulfillment of the euthanasia criteria. No tissues were collected at the end point. 13(39)
5 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 7.9 Neurological Index The mice were observed for 1-2 minutes per mouse at 13 weeks of age. The following 3 behaviors were evaluated: Head Tremor, Head Twitch, Head Bobbing, Head Searching, Body Tremor, Body Twitch, Tail Tremor, Tail Twitch, Straub Tail, Piloerection, Shallow Respiration, Flattened Body Posture, Swollen Face, Ptosis, Irritability, Seizure, Urine Staining, Lacrimation, Salivation, Limb Splay, Catalepsy, Abnormal Gait, Tip Toe Walking, Slow Careful Movements, Excessive Grooming, Circling, Sniffing, and Chewing. In addition to the above occurrences the chronic observational phase includes excessive locomotor acitivty, loss of startle response, loss of righting reflex, dehydration and tail pinch. The assessment was performed as follows: A score of was assigned for normal features (such as locomotor activity) or for the absence of abnormal features (such as absence of piloerection); a score of 1 was given when mild abnormalities were observed; and a score of 2-3 was given when severe abnormalities were observed. All of these features were scored from simple observation of the mice in their cage, except for the startle, tail pinch and righting reflexes which are direct manipulations. To test the startle reflex, a small hand clicker was used to generate a loud popping noise and the following behaviors were identified during this process: jumping, freezing, and rapid eye blinks. For the righting reflex, each mouse was then removed from its home cage and placed on its back allowing the mouse to correct itself. Tail pinch was tested by gently squeezing the end of the tail with forceps. 7.1 Motor Function Motor function testing including open field and rear climbing tests were commenced at 4 weeks of age and continued at weeks 6, 8 and 12, for grip strength test at age weeks 4 and 12 and for rotarod at age weeks 4, 6 and 8. Compound treatment was started at 4 weeks of age after the baseline behavioral tests Rotarod Mice were tested at age weeks 4, 6 and 8 over 3 consecutive days (Wed, Thu, Fri). Each daily session included a training trial of 5 min at 4 RPM on the rotarod apparatus (AccuScan Instruments, Columbus, USA). One hour later, the animals were tested for 3 consecutive accelerating trials of 6 min with the speed changing from to 4 RPM over 36 seconds and an inter-trial interval at least 3 min. The latency to fall from the rod was recorded. Mice remaining on the rod for more than 36 s were removed and their time scored as 36 sec Grip Strength Grip strength measurement was performed according to PGI SOP at age weeks 4 and 12. The mice were tested on Monday afternoon. Mice were taken to the experimental room and, one at a time, were placed on the grip-strength apparatus (San Diego Instruments, San Diego, USA) in such a way that the animal grabs a small mesh grip with its forepaws. The entire apparatus is placed on a table top for testing. Animals are lowered to the platform and then slowly pulled away from the handle by the tail until the animal releases the handle. The equipment automatically measures the strength of the animal s grip in grams. Five scores were recorded per 14(39)
6 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report animal in consecutive sequence. testing. Mice were returned to their home cage after Open Field Test Open field test was performed according to PGI SOP at age weeks 4, 6, 8 and 12. The mice were tested on Monday at approximately 1-3 lux of red light. The mice were brought to the experimental room for at least 1 h acclimation to the experimental room conditions prior to testing. Activity chambers (Med Associates Inc, St Albans, VT; 27 x 27 x 2.3 cm) are equipped with IR beams. Mice were placed in the center of the chamber and their behavior was recorded for 3 min in 5-minute bins. Quantitative analysis was performed on the following five dependent measures: total locomotion, locomotion in the center of the open field, rearing rate in the center, total rearing frequency and velocity Rear Climbing Test Rear climbing test was performed according to PGI SOP at age weeks 4, 6, 8 and 12. The mice were tested on Tuesday. Each animal was placed into custom made pencil holder, and was scored for 5 minutes. During this period the following events were noted: 1) number of times the mouse rears without touching the mesh walls, 2) latency to climb (lifting 4 paws from the floor is labeled climbing), 3) climbing time, and 4) climbing instances Cognitive Function Cued Two-Choice Swim Test The cued two-choice swim test was performed at 9 weeks of age. Testing was conducted under low light, white light conditions. The mice were taught to swim to (acquisition), or away from (reversal), a light positioned over the escape platform. Animals were placed within a rectangular tank (76 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm) filled with water maintained at 25 C ± 1 C. The water was rendered opaque by the addition of non-toxic white paint. The escape platform was located.5 cm below the surface of the water at one end of the tank. A light source with a 25W bulb (white light), oriented toward the water, was clipped to one side of the tank above the escape platform (7 cm in diameter with the borders slanted and roughened to help the rodents climb to it). Under these conditions, the light intensity is measured as 2 lux on the illuminated side of the tank, and 3 lux on the dark side of the tank. The platform was located on the lit side of the arena across acquisition trials, although the location of the lit side within the room relative to the mouse s entry point was varied. The location of the bulb and platform was different on different trials for the same mouse. On each trial, mice were placed into the middle of the tank and allowed to swim for up to 6 sec, or until they found the platform. If an animal did not reach the platform within 6 sec, the mouse was placed on it by the experimenter and allowed to remain there for 3 sec and then removed to a pre-warmed holding cage placed on a warming pad. During all acquisition days, mice were given 8 trials per day (4 blocks of 2 trials, separated by an interblock interval of 2-3 minutes). Training continued in this way until each mouse performed at 75% correct choices for 2 consecutive days; upon reaching this criterion for successful acquisition of the task, mice were placed into the reversal phase on an individual basis. During reversal training, (4 blocks of 2 15(39)
7 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report trials per day), the platform was placed on the dark side of the tank. On each trial during testing days, the latency to reach the platform was recorded (6 seconds if the platform was not reached) and the trial was scored as either correct, incorrect or no choice. The maximum number of days of acquisition was 12 days. All mice went from acquisition into the reversal phase and the experiment was stopped when 2 consecutive days of 75% criterion was reached or after a maximum of 7 days of reversal testing. A correct choice was scored if the animal turned in the direction of the platform and successfully mounted the platform. An incorrect choice was scored if the animal swam in the direction opposite the platform. No choice was scored if the animal either did not make a choice, by swimming in the middle of the tank for the 6 sec, or turned initially toward the platform but did not mount the platform. To make a choice, a mouse had to swim within 2 cm of either end of the tank MRI MRI analysis was performed for all mice at the age of 13 weeks in a horizontal 7T magnet with bore size 16 mm (Magnex Scientific Ltd., Oxford, UK) equipped with Magnex gradient set (max. gradient strength 4 mt/m, bore 1 mm) interfaced to a Varian DirectDrive console (Varian, Inc., Palo Alto, CA) using a volume coil for transmission and surface phased array coil for receiving (Rapid Biomedical GmbH, Rimpar, Germany). Isoflurane -anesthetized mice were fixed to a head holder and positioned in the magnet bore in a standard orientation relative to gradient coils. Rectal temperature (TC-1 Temperature Controller, CWE Inc., Ardmore, PA, USA) and respiration (ECG Trigger Unit, Rapid Biomedical GmbH) were monitored throughout the study and the body temperature was kept at C. For determination of volume of brain, striatum, cortex and lateral ventricles T2-weighted multi-slice (17 continuous slices) images were acquired using fast spin-echo sequence with TR/TE eff = 3/36 ms, matrix size of 256x128, FOV of 2x2 mm 2, slice thickness of.7 mm and 8 averages. 8 Statistical Analysis All values are presented as mean ± Standard Error of Mean (SEM), and differences are considered to be statistically significant at the p <.5 level. Statistical analysis was performed using StatsDirect statistical software. Differences between group means were analyzed by 1-way-ANOVA followed by Dunnett s test (comparison to the control (=vehicle treated TG mice) group). The acquisition of the Cued two-choice swim test was analyzed using Fisher s exact test. 16(39)
8 Weight (g) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9 Results 9.1 Body Weight The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on body weight of the R6/2 mice from 4-23 weeks of age are presented in Figure 1. No significant differences with were found at any time point in body weight (p >.5) (Fig. 1). C521-1 Body Weight Age Week Figure 1. The effects of chronic administration of on body weight from 4-23 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 17(39)
9 Latency (sec) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.2 Rotarod The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on rotarod performance of the R6/2 mice are presented in Figure 2. No significant differences with were found at any time point in rotarod latency (p >.5) (Fig. 2). C521-1 Rotarod Age Week / Test Day Figure 2. The effects of chronic administration of on rotarod performance from 4-8 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 18(39)
10 Force (g) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.3 Grip Strength The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on grip strength of the R6/2 mice are presented in Figure 3. The mice treated with 3 mg/kg of had increased grip strength at 12 weeks of age compared to vehicle-treated R6/2 mice (p <.5) (Fig. 3). C521-1 Grip Strength 1 8 * Weeks 12 Weeks Figure 3. The effects of chronic administration of on grip strength from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM 19(39)
11 Distance (cm) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.4 Open Field Total Distance Traveled The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on total distance traveled in the open field by the R6/2 mice are presented in Figure 4. The mice treated with 3 mg/kg of traveled a shorter total distance at 12 weeks of age compared to vehicle-treated R6/2 mice (p <.5) (Fig. 4). C521-1 Open Field - Distance Traveled Age Week / Session Time (min) * Figure 4. The effects of chronic administration of on total distance traveled from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 2(39)
12 Distance (cm) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Distance Traveled in Center The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on distance traveled in the center area of the open field by the R6/2 mice are presented in Figure 5. The mice treated with 3 mg/kg of traveled a shorter distance in the center area at 12 weeks of age compared to vehicle-treated R6/2 mice (p <.5) (Fig. 5). C521-1 Open Field - Distance Traveled in Center Area Age Week / Session Time (min) * Figure 5. The effects of chronic administration of on distance traveled in the center of the open field from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 21(39)
13 Rearing Rate (count / min) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Rate of Rears in Center The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on rearing rate in the center area of the open field of the R6/2 mice from are presented in Figure 6. No significant differences with were found at any time point on rearing rate in the center area (p >.5) (Fig. 6). C521-1 Open Field - Rearing Rate in Center Area Age Week Figure 6. The effects of chronic administration of on rearing rate in the center area of the open field from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 22(39)
14 Vertical Count C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Total Rearing Frequency The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on total rearing frequency in the open field of the R6/2 mice are presented in Figure 7. No significant differences with were found at any time point on total rearing frequency (p >.5) (Fig. 7). C521-1 Open Field - Total Rearing Frequency Age Week Figure 7. The effects of chronic administration of on total rearing frequency in the open field from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 23(39)
15 Average Velocity (cm / sec) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Average Velocity The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on average velocity in the open field of the R6/2 mice from are presented in Figure 8. No significant differences with were found at any time point on average velocity (p >.5) (Fig. 8). C521-1 Open Field - Average Velocity Age Week Figure 8. The effects of chronic administration of on average velocity in the open field from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 24(39)
16 Vertical Count C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.5 Rear Climbing Rearing Frequency The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on rearing frequency of the R6/2 mice in the rear climbing test are presented in Figure 9. No significant differences with were found at any time point on rearing frequency (p >.5) (Fig. 9). C521-1 Rear Climbing - Rearing Frequency Age Week Figure 9. The effects of chronic administration of on rearing frequency in the rear climbing test from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 25(39)
17 Latency (sec) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Latency to Climb The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on latency to climb of the R6/2 mice in the rear climbing test are presented in Figure 1. No significant differences with were found at any time point on latency to climb (p >.5) (Fig. 1). C521-1 Rear Climbing - Latency to Climb Age Week Figure 1. The effects of chronic administration of on latency to climb in the rear climbing test from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 26(39)
18 Time Spent Climbing (sec) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Time Spent Climbing The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on time spent climbing by the R6/2 mice in the rear climbing test are presented in Figure 11. No significant differences with were found at any time point on time spent climbing (p >.5) (Fig. 11). C521-1 Rear Climbing - Time Spent Climbing Age Week Figure 11. The effects of chronic administration of on time spent climbing in the rear climbing test from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 27(39)
19 Number of Climbing Instances C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Climbing Instances The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on climbing instances of the R6/2 mice in the rear climbing test are presented in Figure 12. No significant differences with were found at any time point on climbing instances (p >.5) (Fig. 12). C521-1 Rear Climbing - Climbing Instances Age Week Figure 12. The effects of chronic administration of on climbing instances in the rear climbing test from 4-12 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 28(39)
20 % of Mice Reaching Criterion 9.6 Cued Two-Choice Swim Test Acquisition Percent of Mice Reaching the Criterion C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on the acquisition learning of the R6/2 mice in the cued two-choice swim test are presented in Figure 13. The acquisition learning is presented as the percent of mice in each group reaching the criterion. No significant differences with were found in the acquisition learning (p >.5) (Fig. 13). C521-1 Cued Two-Choice Swim Test - Acquisition Test Day Figure 13. The effects of chronic administration of on the acquisition learning in the cued two-choice swim test at 9 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 29(39)
21 Daily Average Correct (%) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Reversal - Correct Choices The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on the number of correct choices of the R6/2 mice in the reversal phase of the cued two-choice swim test are presented in Figure 14. No significant differences with were found in the number of incorrect choices (p >.5) (Fig. 14). C521-1 Cued Two-Choice Swim Test - Reversal - Correct Choice Test Day Figure 14. The effects of chronic administration of on the number of correct choices in the reversal phase of the cued two-choice swim test at 9 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 3(39)
22 Daily Average Incorrect (%) Reversal - Incorrect Choices C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on the number of incorrect choices of the R6/2 mice in the reversal phase of the cued two-choice swim test are presented in Figure 15. No significant differences with were found in the number of incorrect choices (p >.5) (Fig. 15). C521-1 Cued Two-Choice Swim Test - Reversal - Incorrect Choice Test Day Figure 15. The effects of chronic administration of on the number of incorrect choices in the reversal phase of the two-choice swim test at 9 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 31(39)
23 Daily Average No Choice (%) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Reversal - No Choice The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on no choice of the R6/2 mice in the reversal phase of the cued two-choice swim test are presented in Figure 16. No significant differences with were found in no choice (p >.5) (Fig. 16). C521-1 Cued Two-Choice Swim Test - Reversal - No Choice Test Day Figure 16. The effects of chronic administration of on no choice in the reversal phase of the two-choice swim test at 9 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 32(39)
24 Daily Average Latency (%) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Reversal - Latency The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on latency of the R6/2 mice in the reversal phase of the cued two-choice swim test are presented in Figure 17. No significant differences with were found in latency (p >.5) (Fig. 17). C521-1 Cued Two-Choice Swim Test - Reversal - Latency Test Day Figure 17. The effects of chronic administration of on latency in the reversal phase of the two-choice swim test at 9 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 33(39)
25 Score C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.7 Neurological Index The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on Neurological Index of the R6/2 mice at 13 weeks of age are presented in Figure 18. No significant differences with were found in Neurological Index (p >.5) (Fig. 18). C521-1 Neurological Index Figure 18. The effects of chronic administration of on neurological index at 13 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 34(39)
26 Volume (mm 3 ) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.8 MRI Volumetry Whole Brain Volume The whole brain volume was measured at the age of 13 weeks using MRI techniques. Initially the purpose was to perform the measurements at 12 weeks of age but due to technical problems with the MRI machinery the measurements had to be postponed by one week. Due to the same reason the MR spectroscopy measurements and analysis could not be performed in this study. Total n MRI Volumetry Table 5. Number of mice used for the MRI volumetry measurements in study C The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on whole brain volume are presented in Figure 19. No significant differences with treatment were found in whole brain volumes (p >.5) (Fig. 19). C521-1 MRI Volumety - Whole Brain Figure 19. The effects of chronic administration of on whole brain volume at 13 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 35(39)
27 Volume (mm 3 ) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Striatum Volume The striatum volume was measured at the age of 13 weeks using MRI techniques. The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on striatum volume are presented in Figure 2. No significant differences with CHDI treatment were found in striatum volumes (p >.5) (Fig. 2). C521-1 MRI Volumetry - Striatum Figure 2. The effects of chronic administration of on striatum volume at 13 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 36(39)
28 Volume (mm 3 ) C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report Cortical Volume The cortical volumes were measured at the age of 13 weeks using MRI techniques. The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on cortical volumes are presented in Figure 21. No significant differences with CHDI treatment were found on cortical volumes (p >.5) (Fig. 21). C521-1 MRI Volumetry - Cortex Figure 21. The effects of chronic administration of on cortical volume at 13 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. 37(39)
29 C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report 9.9 Survival The survival of the mice was monitored until 25 weeks of age. The effects of chronic administration of (1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o., BID) on survival of the R6/2 mice is displayed as a Kaplan-Meier plot in Figure 22. The mean/median survival times of the R6/2 mice treated with vehicle was 115/16 days, with 1 mg/kg of 115/11 days, and with 3 mg/kg of 122/121 days. There were no differences in survival between the treatment groups (Logrank and Wilcoxon tests, p >.5). C521-1 Survival Plot (PL estimates) Survivor 1,,75,5,25, Times Figure 22. The effects of chronic administration of on survival until 25 weeks of age in R6/2 mice. Data are presented as Kaplan-Meier plot 38(39)
30 1 Discussion and Conclusions C521-1 R6/2 Mice Final Report As a summary, the twice-a-day oral treatment with (1 or 3 mg/kg) had no major beneficial effects on body weight, survival, motor deficits, cognitive performance, or the volume of whole brain, striatum or cortex in the R6/2 mice of Huntington s disease. However, the mice treated with 3 mg/kg of had increased grip strength at 12 weeks of age and had a decreased number of no choice on the test day two of the reversal phase of cued two-choice swim test compared to vehicle-treated R6/2 mice. Also, the mice treated with 3 mg/kg of showed decreased horizontal activity in the open field at 12 weeks of age compared to vehicle-treated R6/2 mice. 11 Storage of the Raw Data, Specimens, and the Final Report The raw data and the final report are stored in the premises of Cerebricon Ltd., Microkatu 1, FIN-7211 Kuopio, Finland until delivered to the client. ELECTRONIC ANNEXES Annex 1 C521-1 Final Report, Statistical Analyses and Excel Data Sheets (electronic files) 39(39)
Physiological normal values (Depends on age, strain, health status, type of anesthesia, etc.)
 UBC Animal Care Guidelines This SOP will be used for: Inhalational anesthesia SOP: ACC-01-2017 Rodent Anesthesia Injectable anesthesia Submitted by: Shelly McErlane both inhalational and injectable anesthesia
UBC Animal Care Guidelines This SOP will be used for: Inhalational anesthesia SOP: ACC-01-2017 Rodent Anesthesia Injectable anesthesia Submitted by: Shelly McErlane both inhalational and injectable anesthesia
How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen.
 An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
Imaging rodent behaviors
 Imaging rodent behaviors Anni-Maija Linden, PhD Institute of Biomedicine, Pharmacology 5.11.2013 Analysis of rodent behaviors? Other manipulation 2 1 Analysis of rodent behaviors Brains, other tissues,
Imaging rodent behaviors Anni-Maija Linden, PhD Institute of Biomedicine, Pharmacology 5.11.2013 Analysis of rodent behaviors? Other manipulation 2 1 Analysis of rodent behaviors Brains, other tissues,
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury
 Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC
 IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC Acoustic startle and Pre-pulse Inhibition (PPI) IMPC_ACS_003 Purpose The acoustic startle response is characterized by an exaggerated flinching response to an unexpected strong
IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC Acoustic startle and Pre-pulse Inhibition (PPI) IMPC_ACS_003 Purpose The acoustic startle response is characterized by an exaggerated flinching response to an unexpected strong
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test.
 Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life.
 Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Complexity Made Simple
 Complexity Made Simple Bussey-Saksida Touch Screen Chambers for Rats and Mice Tasks translate directly to well established monkey and human touch models e.g. CANTAB High throughput screening of multiple
Complexity Made Simple Bussey-Saksida Touch Screen Chambers for Rats and Mice Tasks translate directly to well established monkey and human touch models e.g. CANTAB High throughput screening of multiple
Ana Carneiro Survivable Stereotaxic Surgery in Mice
 Ana Carneiro Survivable Stereotaxic Surgery in Mice Adapted from: Geiger B.M., Frank L.E., Caldera-Siu A.D., Pothos E.N. (2008). Survivable Stereotaxic Surgery in Rodents. JoVE. 20. http://www.jove.com/index/details.stp?id=880,
Ana Carneiro Survivable Stereotaxic Surgery in Mice Adapted from: Geiger B.M., Frank L.E., Caldera-Siu A.D., Pothos E.N. (2008). Survivable Stereotaxic Surgery in Rodents. JoVE. 20. http://www.jove.com/index/details.stp?id=880,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
COMPARATIVE MEDICINE LABORATORY ANIMAL FACILITIES STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR RODENT SURGERY
 2.A.3 COMPARATIVE MEDICINE LABORATORY ANIMAL FACILITIES STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR RODENT SURGERY 1.0 Purpose: Post-operative infections in rodents can and do occur. Such infections, which may not
2.A.3 COMPARATIVE MEDICINE LABORATORY ANIMAL FACILITIES STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR RODENT SURGERY 1.0 Purpose: Post-operative infections in rodents can and do occur. Such infections, which may not
Complexin II is essential for normal neurological function in mice
 Complexin II is essential for normal neurological function in mice Dervila Glynn, Rachel A. Bortnick and A. Jennifer Morton* Human Molecular Genetics, 2003, Vol. 12, No. 19 2431 2448 DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddg249
Complexin II is essential for normal neurological function in mice Dervila Glynn, Rachel A. Bortnick and A. Jennifer Morton* Human Molecular Genetics, 2003, Vol. 12, No. 19 2431 2448 DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddg249
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 An acoustic startle model of sensorimotor gating, in which a weak acoustic stimulus (the pre-pulse) is used to decrease the reflex response (startle) produced by a second, more intense,
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 An acoustic startle model of sensorimotor gating, in which a weak acoustic stimulus (the pre-pulse) is used to decrease the reflex response (startle) produced by a second, more intense,
FINAL REPORT STUDY TITLE. EVALUATION OF APHRODISIAC ACTIVITY OF VigRx IN MALE ALBINO WISTAR RATS. Report No.: R401.
 FINAL REPORT STUDY TITLE EVALUATION OF APHRODISIAC ACTIVITY OF IN MALE ALBINO WISTAR RATS STUDY DIRECTOR Dr. Amit A, Ph.D. SPONSOR AIBMR Life Sciences, Inc. 4117, South Meridian, Puyallup, WA 98373 CONTENTS
FINAL REPORT STUDY TITLE EVALUATION OF APHRODISIAC ACTIVITY OF IN MALE ALBINO WISTAR RATS STUDY DIRECTOR Dr. Amit A, Ph.D. SPONSOR AIBMR Life Sciences, Inc. 4117, South Meridian, Puyallup, WA 98373 CONTENTS
Vol 6, Iss 9, May 5, 2016
 Olfactory Recognition Memory Test in Mice Stephanie A. Jacobs 1*, Fengying Huang 1, Joe Z. Tsien 1 and Wei Wei 2* 1 Department of Neurology, Brain and Behavior Discovery Institute, Medical College of Georgia,
Olfactory Recognition Memory Test in Mice Stephanie A. Jacobs 1*, Fengying Huang 1, Joe Z. Tsien 1 and Wei Wei 2* 1 Department of Neurology, Brain and Behavior Discovery Institute, Medical College of Georgia,
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
Lumbar Epidural Injections. Treatment to Reduce Pain
 Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Introductory Motor Learning and Development Lab
 Introductory Motor Learning and Development Lab Laboratory Equipment & Test Procedures. Motor learning and control historically has built its discipline through laboratory research. This has led to the
Introductory Motor Learning and Development Lab Laboratory Equipment & Test Procedures. Motor learning and control historically has built its discipline through laboratory research. This has led to the
PRODUCT STUDY TITLE DATA REQUIREMENT AUTHOR STUDY COMPLETED ON PERFORMING LABORATORY LABORATORY STUDY NUMBER
 Product Safety Laboratories 2394 Highway 130 Dayton, NJ 08810 Tel: 732.438.5100 Fax: 732.355.3275 e-mail: PSL@productsafetylabs.com PRODUCT Stalosan F STUDY TITLE Acute Dermal Toxicity Study in Rats -
Product Safety Laboratories 2394 Highway 130 Dayton, NJ 08810 Tel: 732.438.5100 Fax: 732.355.3275 e-mail: PSL@productsafetylabs.com PRODUCT Stalosan F STUDY TITLE Acute Dermal Toxicity Study in Rats -
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration.
 Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
GEMouse. Added Service Guide
 Contact mouse : mouse@macrogen.com Payment Inquiry: payment@macrogen.com Technical Support Macrogen Korea: support@macrogen.com Macrogen-Europe: support-europe@macrogen.com Update 68 GEMouse Added Service
Contact mouse : mouse@macrogen.com Payment Inquiry: payment@macrogen.com Technical Support Macrogen Korea: support@macrogen.com Macrogen-Europe: support-europe@macrogen.com Update 68 GEMouse Added Service
EXPERIMENT 26: Detection of DNA-binding Proteins using an Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay Gel shift
 EXPERIMENT 26: Detection of DNA-binding Proteins using an Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay Gel shift Remember to use sterile conditions (tips, tubes, etc.) throughout this experiment Day 1: Biotinylation
EXPERIMENT 26: Detection of DNA-binding Proteins using an Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay Gel shift Remember to use sterile conditions (tips, tubes, etc.) throughout this experiment Day 1: Biotinylation
USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series DESCRIPTION OF THE MOST IMPORTANT PROPERTIES AND THE POSSIBLE VARIATIONS AND TOLERANCES
 USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series OVERVIEW The QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series of fluids are based on a synthetic organic ester, which is the main base component, plus a number of selected additives
USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series OVERVIEW The QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series of fluids are based on a synthetic organic ester, which is the main base component, plus a number of selected additives
Animal Behavior
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Laboratory Animal Behavior 74-663 74-664 TEACHER S MANUAL World-Class Support for Science & Math This protocol has been adapted from the Advanced Placement Biology Laboratory
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Laboratory Animal Behavior 74-663 74-664 TEACHER S MANUAL World-Class Support for Science & Math This protocol has been adapted from the Advanced Placement Biology Laboratory
Patient Manual Brainsway Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
 Dr. Zahida Tayyib www.mvptms.com Patient Manual Brainsway Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder If you are considering Brainsway Deep treatment
Dr. Zahida Tayyib www.mvptms.com Patient Manual Brainsway Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder If you are considering Brainsway Deep treatment
To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
What to watch for when analyzing mouse behavior
 NEWS What to watch for when analyzing mouse behavior BY ALLA KATSNELSON 21 MARCH 2018 Tests for unusual behavior in mice are notoriously prone to operator error. Many scientists conduct or interpret them
NEWS What to watch for when analyzing mouse behavior BY ALLA KATSNELSON 21 MARCH 2018 Tests for unusual behavior in mice are notoriously prone to operator error. Many scientists conduct or interpret them
Supplementary Methods
 1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
Delayed Matching-To-Sample Test in Macaques
 C O N F I D E N T I A L Delayed Matching-To-Sample Test in Macaques DATE This study was conducted under the terms of a Materials Transfer and Services Agreement between NeuroDetective International and
C O N F I D E N T I A L Delayed Matching-To-Sample Test in Macaques DATE This study was conducted under the terms of a Materials Transfer and Services Agreement between NeuroDetective International and
Preparation Guide: Post-Offer Physical Assessment - Gas Service Representative
 Congratulations on receiving a conditional offer of employment for PG&E s Gas Service Representative position. PG&E is committed to upholding the highest standards in workplace safety. As part of that
Congratulations on receiving a conditional offer of employment for PG&E s Gas Service Representative position. PG&E is committed to upholding the highest standards in workplace safety. As part of that
Adolescent Prozac Exposure Enhances Sensitivity to Cocaine in Adulthood INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes
 EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
MB Research Laboratories
 MB Research Laboratories 1765 Wentz Road P.O. Box 178 Spinnerstown, PA 18968 phone (215) 536-4110 fax (215) 536-1816 Study Title : Single Dose Oral Toxicity in Rats Test Article : ZEOLITE PURE, Lot/Batch#
MB Research Laboratories 1765 Wentz Road P.O. Box 178 Spinnerstown, PA 18968 phone (215) 536-4110 fax (215) 536-1816 Study Title : Single Dose Oral Toxicity in Rats Test Article : ZEOLITE PURE, Lot/Batch#
Behaviors may be innate or learned. Many behaviors have both genetic and learned components.
 Animal Behavior AP Biology Lab 11: (consider using http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab11/intro.html to help you with this lab) Introduction Animals exhibit a variety of behaviors,
Animal Behavior AP Biology Lab 11: (consider using http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab11/intro.html to help you with this lab) Introduction Animals exhibit a variety of behaviors,
Senior Assessment Form
 1 [Senior Assessment Form] Senior Assessment Form Client name: Patient name: Signalment: Date: Use this form to guide a discussion with the owner about the health of their pet. Select the most appropriate
1 [Senior Assessment Form] Senior Assessment Form Client name: Patient name: Signalment: Date: Use this form to guide a discussion with the owner about the health of their pet. Select the most appropriate
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
Higher National Unit specification: general information. Strength and Conditioning for Sports Performance
 Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FX9T 35 Superclass: MD Publication date: October 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The purpose of
Higher National Unit specification: general information Unit code: FX9T 35 Superclass: MD Publication date: October 2011 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 01 Unit purpose The purpose of
STUDIES OF WHEEL-RUNNING REINFORCEMENT: PARAMETERS OF HERRNSTEIN S (1970) RESPONSE-STRENGTH EQUATION VARY WITH SCHEDULE ORDER TERRY W.
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR 2000, 73, 319 331 NUMBER 3(MAY) STUDIES OF WHEEL-RUNNING REINFORCEMENT: PARAMETERS OF HERRNSTEIN S (1970) RESPONSE-STRENGTH EQUATION VARY WITH SCHEDULE
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR 2000, 73, 319 331 NUMBER 3(MAY) STUDIES OF WHEEL-RUNNING REINFORCEMENT: PARAMETERS OF HERRNSTEIN S (1970) RESPONSE-STRENGTH EQUATION VARY WITH SCHEDULE
AN ACUTE ORAL TOXICITY STUDY IN RATS WITH ADVANTRA Z
 AN ACUTE ORAL TOXICITY STUDY IN RATS WITH ADVANTRA Z AMENDED FINAL REPORT Author Deborah A Douds, M.S. Original Study Completion Date July 8, 1997 Amended Study Completion Date November 19, 1997 Performing
AN ACUTE ORAL TOXICITY STUDY IN RATS WITH ADVANTRA Z AMENDED FINAL REPORT Author Deborah A Douds, M.S. Original Study Completion Date July 8, 1997 Amended Study Completion Date November 19, 1997 Performing
Limbic system outline
 Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Pathology Specimen Handling Requirements
 CONWAY REGIONAL HEALTH SYSTEM CLINICAL LABORATORY Pathology Specimen Handling Requirements POLICY: Tissue or body fluids, etc. removed or collected during any procedure for purposes of Pathologist examination
CONWAY REGIONAL HEALTH SYSTEM CLINICAL LABORATORY Pathology Specimen Handling Requirements POLICY: Tissue or body fluids, etc. removed or collected during any procedure for purposes of Pathologist examination
Postoperative Days 1-7
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
CROSSMODAL PLASTICITY IN SPECIFIC AUDITORY CORTICES UNDERLIES VISUAL COMPENSATIONS IN THE DEAF "
 Supplementary Online Materials To complement: CROSSMODAL PLASTICITY IN SPECIFIC AUDITORY CORTICES UNDERLIES VISUAL COMPENSATIONS IN THE DEAF " Stephen G. Lomber, M. Alex Meredith, and Andrej Kral 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Online Materials To complement: CROSSMODAL PLASTICITY IN SPECIFIC AUDITORY CORTICES UNDERLIES VISUAL COMPENSATIONS IN THE DEAF " Stephen G. Lomber, M. Alex Meredith, and Andrej Kral 1 Supplementary
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
NEONATAL RODENTS SURVIVAL SURGERY
 MCGILL UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY ANIMAL CARE COMMITTEE UACC Standard Operating Procedure # 11 October 2005 version NEONATAL RODENTS SURVIVAL SURGERY 1. INTRODUCTION Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) provide
MCGILL UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY ANIMAL CARE COMMITTEE UACC Standard Operating Procedure # 11 October 2005 version NEONATAL RODENTS SURVIVAL SURGERY 1. INTRODUCTION Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) provide
Drexel University Animal Care and Use Committee Policy for Assigning Pain and Distress Categories on IACUC Protocols
 Drexel University Animal Care and Use Committee Policy for Assigning Pain and Distress Categories on IACUC Protocols OBJECTIVE: Drexel University (DU) Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC)
Drexel University Animal Care and Use Committee Policy for Assigning Pain and Distress Categories on IACUC Protocols OBJECTIVE: Drexel University (DU) Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC)
Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION. Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition. A Senior Honors Thesis
 Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION Alcohol on Object Recognition 1 Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the
Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION Alcohol on Object Recognition 1 Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
First mouse model of Timothy syndrome debuts
 NEWS First mouse model of Timothy syndrome debuts BY VIRGINIA HUGHES 5 SEPTEMBER 2011 1 / 5 Cold shoulder: Mice carrying the Timothy syndrome mutation tend to spend more time near an empty cage (red areas),
NEWS First mouse model of Timothy syndrome debuts BY VIRGINIA HUGHES 5 SEPTEMBER 2011 1 / 5 Cold shoulder: Mice carrying the Timothy syndrome mutation tend to spend more time near an empty cage (red areas),
ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS
 37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
Lesson 1: Types of ECG s
 Electrocardiography Lesson 1: Types of ECG s Objectives: Distinguish between a single-channel ECG machine and a multi-channel machine. Distinguish between a manual ECG machine and an automatic ECG machine.
Electrocardiography Lesson 1: Types of ECG s Objectives: Distinguish between a single-channel ECG machine and a multi-channel machine. Distinguish between a manual ECG machine and an automatic ECG machine.
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD
 EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
Pharmacological study
 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY Pharmacology is one of the cornerstones of the drug discovery process. The medicinal chemist may create the candidate compound, but the pharmacologist is the one who tests it for
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY Pharmacology is one of the cornerstones of the drug discovery process. The medicinal chemist may create the candidate compound, but the pharmacologist is the one who tests it for
The In Bed Workout or the Getting Up Routine
 The In Bed Workout or the Getting Up Routine This is a great way to wake up and make good use of time. Just think, instead of lying there wasting 10 minutes thinking about getting up, you can complete
The In Bed Workout or the Getting Up Routine This is a great way to wake up and make good use of time. Just think, instead of lying there wasting 10 minutes thinking about getting up, you can complete
AviagenBrief. Evaluating Comparative Broiler Performance through Trials INTRODUCTION KEY CONSIDERATIONS. November 2018
 AviagenBrief Evaluating Comparative Broiler Performance through Trials INTRODUCTION November 2018 Carefully planned broiler trials will allow the customer to clearly evaluate the effect of the treatment,
AviagenBrief Evaluating Comparative Broiler Performance through Trials INTRODUCTION November 2018 Carefully planned broiler trials will allow the customer to clearly evaluate the effect of the treatment,
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life
 Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Surgical Instructions. Wisdom Tooth TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY
 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY Surgical Instructions Wisdom Tooth 1000 North Curtis Road, Suite 103 Boise, ID 83706 Phone: 208-343-0909 Fax: 208-343-6282 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY AFTER
TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY Surgical Instructions Wisdom Tooth 1000 North Curtis Road, Suite 103 Boise, ID 83706 Phone: 208-343-0909 Fax: 208-343-6282 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY AFTER
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
USER MANUAL CAUTION. MADE IN CHINA 2015 Body Action Enterprise Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
 USER MANUAL CAUTION MADE IN CHINA 05 Body Action Enterprise Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. READ ALL PRECAUTIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL BEFORE USING THIS EQUIPMENT AND KEEP THIS FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
USER MANUAL CAUTION MADE IN CHINA 05 Body Action Enterprise Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. READ ALL PRECAUTIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL BEFORE USING THIS EQUIPMENT AND KEEP THIS FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Herdman Dizziness Questionnaire 1
 Violand and McNerney, P.A. Physical Therapists 5024 Dorsey Hall Drive, Suite 103 Ellicott City, MD 21042 Phone: 410 740-1047 Fax: 410 740-2280 Herdman Dizziness Questionnaire 1 Name: Age: Date: Present
Violand and McNerney, P.A. Physical Therapists 5024 Dorsey Hall Drive, Suite 103 Ellicott City, MD 21042 Phone: 410 740-1047 Fax: 410 740-2280 Herdman Dizziness Questionnaire 1 Name: Age: Date: Present
Age at Puberty and First Litter Size in Early and Late Paired Rats 2
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 34, 322-3 26 (1986) Age at Puberty and First Litter Size in Early and Late Paired Rats 2 ALIDA M. EVANS Cancer Prevention Program 1300 University Avenue-7C University of Wisconsin
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 34, 322-3 26 (1986) Age at Puberty and First Litter Size in Early and Late Paired Rats 2 ALIDA M. EVANS Cancer Prevention Program 1300 University Avenue-7C University of Wisconsin
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD
 EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
HENDERSONVILLE FIRE DEPARTMENT VOLUNTARY PREP CLASSES FOR PHYSICAL AGILITY TESTING
 HENDERSONVILLE FIRE DEPARTMENT VOLUNTARY PREP CLASSES FOR PHYSICAL AGILITY TESTING In order to assist applicants in preparing for the Physical Agility Test, the Hendersonville Fire Department is offering
HENDERSONVILLE FIRE DEPARTMENT VOLUNTARY PREP CLASSES FOR PHYSICAL AGILITY TESTING In order to assist applicants in preparing for the Physical Agility Test, the Hendersonville Fire Department is offering
RiGO801 Laboratory Requirements
 RiGO801 Laboratory Requirements 2015-11-25 Air Conditioning According to EN 13032 1 and LM-79-08 the temperature in the environment of the DUT needs to be 25 C +/- 1 C during the measurement. EN 13032-4
RiGO801 Laboratory Requirements 2015-11-25 Air Conditioning According to EN 13032 1 and LM-79-08 the temperature in the environment of the DUT needs to be 25 C +/- 1 C during the measurement. EN 13032-4
Sample Report Only - NOT INTENDED FOR USE
 Project Title: Evaluation of 3 Formulations of [Product] when applied directly onto [Species]. Sample Report Only - NOT INTENDED FOR USE Project Code: [Code] Test Date(s): October 5, 2006 October 7, 2006
Project Title: Evaluation of 3 Formulations of [Product] when applied directly onto [Species]. Sample Report Only - NOT INTENDED FOR USE Project Code: [Code] Test Date(s): October 5, 2006 October 7, 2006
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 The glucose tolerance test measures the clearance of an intraperitoneally injected glucose load from the body. Animals are fasted for approximately 16 hours, a solution of glucose is administered
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 The glucose tolerance test measures the clearance of an intraperitoneally injected glucose load from the body. Animals are fasted for approximately 16 hours, a solution of glucose is administered
Primate Observation Form (Use the back for continuations or additional observations)
 Primate Observation Form (Use the back for continuations or additional observations) Observer: Zoo: Date of observation: Time observation began: Time observation ended: Common name of primate: Scientific
Primate Observation Form (Use the back for continuations or additional observations) Observer: Zoo: Date of observation: Time observation began: Time observation ended: Common name of primate: Scientific
- -. I ANIMAL BEHAVIOR
 LAB L- - -. I ANIMAL BEHAVIOR OVERVIEW In this lab you will observe some aspects of animal behavior. 1. In Exercise 11A you will observe pillbugs and design an experiment to investigate their responses
LAB L- - -. I ANIMAL BEHAVIOR OVERVIEW In this lab you will observe some aspects of animal behavior. 1. In Exercise 11A you will observe pillbugs and design an experiment to investigate their responses
Exercise, Physical Therapy and Fall Prevention
 Exercise, Physical Therapy and Fall Prevention University of Davis Medical Center Rosy Chow Neuro Clinical Specialist Physical Therapist Outline of Talk Role of Physical Therapy in care of people with
Exercise, Physical Therapy and Fall Prevention University of Davis Medical Center Rosy Chow Neuro Clinical Specialist Physical Therapist Outline of Talk Role of Physical Therapy in care of people with
Post Operative Instructions: Wisdom Teeth
 The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and swelling can be minimized if the instructions
The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and swelling can be minimized if the instructions
Cognitive and behavioral assessment in experimental stroke research: will it prove useful?
 PERGAMON Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 25 (2001) 325342 Review Cognitive and behavioral assessment in experimental stroke research: will it prove useful? A. Courtney DeVries a,b, *, Randy J. Nelson
PERGAMON Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 25 (2001) 325342 Review Cognitive and behavioral assessment in experimental stroke research: will it prove useful? A. Courtney DeVries a,b, *, Randy J. Nelson
Learn the Ropes! By Buddy Lee Date Released : 28 Jun 2007
 Page 1 of 6 close Learn the Ropes! By Buddy Lee Date Released : 28 Jun 2007 You ve probably avoided rope jumping as a form of exercise because you ve heard it was high impact and difficult to learn. But
Page 1 of 6 close Learn the Ropes! By Buddy Lee Date Released : 28 Jun 2007 You ve probably avoided rope jumping as a form of exercise because you ve heard it was high impact and difficult to learn. But
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rett Syndrome Mutation MeCP2 T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
P301S Mutant Human Tau Transgenic Mice Manifest Early Symptoms of Human Tauopathies with Dementia and Altered Sensorimotor Gating
 P301S Mutant Human Tau Transgenic Mice Manifest Early Symptoms of Human Tauopathies with Dementia and Altered Sensorimotor Gating Hiroki Takeuchi 1,2., Michiyo Iba 3., Haruhisa Inoue 2,4 *, Makoto Higuchi
P301S Mutant Human Tau Transgenic Mice Manifest Early Symptoms of Human Tauopathies with Dementia and Altered Sensorimotor Gating Hiroki Takeuchi 1,2., Michiyo Iba 3., Haruhisa Inoue 2,4 *, Makoto Higuchi
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
Dissection and Contraction of Frog Heart
 Dissection and Contraction of Frog Heart Rob MacLeod and Alex Brownell (aabrownell@yahoo.com) March 4, 2006 1 Purpose and Background 1.1 Purpose: To examine the anatomy and basic contractile physiology
Dissection and Contraction of Frog Heart Rob MacLeod and Alex Brownell (aabrownell@yahoo.com) March 4, 2006 1 Purpose and Background 1.1 Purpose: To examine the anatomy and basic contractile physiology
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
A Night of Frogging, by X. Bernal (revised 2006 MJR)
 1 A Night of Frogging, by X. Bernal... 2000 (revised 2006 MJR) 1930 Meet froggers Discuss the previous night s tests, any problems with the chamber, computer, etc. Bring up any interesting developments
1 A Night of Frogging, by X. Bernal... 2000 (revised 2006 MJR) 1930 Meet froggers Discuss the previous night s tests, any problems with the chamber, computer, etc. Bring up any interesting developments
ADULT - PHASE 6. ACTIVATEye PART A PART B SMALL SIDED GAMES SNAKE RUNS KNEE TO ELBOW STATIC BEAR CRAWL 5 TO 10 MINUTES
 PART A SMALL SIDED GAMES For the first 5 to 10 minutes of training, while players arrive, use small-sided games to get players moving, to keep them warm and to act as a pulse raiser exercise. Groups should
PART A SMALL SIDED GAMES For the first 5 to 10 minutes of training, while players arrive, use small-sided games to get players moving, to keep them warm and to act as a pulse raiser exercise. Groups should
TASK ANALYSIS REPORT. Job role
 TASK ANALYSIS REPORT Job role Hours of work Workplace/ location Equipment/tools Description of normal task Office Based Role 8:30am 5:00pm, 45 minute lunchbreak, ability for flexi time hours 8:15am 5:00pm
TASK ANALYSIS REPORT Job role Hours of work Workplace/ location Equipment/tools Description of normal task Office Based Role 8:30am 5:00pm, 45 minute lunchbreak, ability for flexi time hours 8:15am 5:00pm
Supplementary Materials
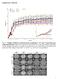 Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Prisoner of Echo. 45 minutes. A sound wave needs a medium through which it is transmitted.
 LESSON ACTIVITY: Prisoner of Echo Prisoner of Echo is a physical science learning game aligned to Common Core and Next Generation Science standards. Partner with Jenkins, a helpful but slightly snarky
LESSON ACTIVITY: Prisoner of Echo Prisoner of Echo is a physical science learning game aligned to Common Core and Next Generation Science standards. Partner with Jenkins, a helpful but slightly snarky
Instructions for Patients Following Vitreoretinal Surgery Who Need to Posture
 Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Vitreoretinal Services Information for Patients Instructions for Patients Following Vitreoretinal Surgery Who Need to Posture Patient name: Hospital Number: Consultant: Surgery
Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Vitreoretinal Services Information for Patients Instructions for Patients Following Vitreoretinal Surgery Who Need to Posture Patient name: Hospital Number: Consultant: Surgery
WORLD OSTRICH ASSOCIATION UNDERSTANDING AND CONTROLING AVIAN INFLUENZA RISKS IN OSTRICH
 UNDERSTANDING AND CONTROLING AVIAN INFLUENZA RISKS IN OSTRICH Introduction There are many good web sites containing information on Avian Influenza and offering guidelines on measures to be taken to protect
UNDERSTANDING AND CONTROLING AVIAN INFLUENZA RISKS IN OSTRICH Introduction There are many good web sites containing information on Avian Influenza and offering guidelines on measures to be taken to protect
EMMA health monitoring procedures
 EMMA health monitoring procedures Brief description of housing system, health monitoring programme and health status of the EMMA SPF live colonies Type of facility Animals distributed by EMMA are bred
EMMA health monitoring procedures Brief description of housing system, health monitoring programme and health status of the EMMA SPF live colonies Type of facility Animals distributed by EMMA are bred
ROWER. An indoor rowing machine that delivers a seamless group training experience
 ROWER An indoor rowing machine that delivers a seamless group training experience The biggest challenge was to change the perception of contemporary rowing exercise. We knew that the rower originated from
ROWER An indoor rowing machine that delivers a seamless group training experience The biggest challenge was to change the perception of contemporary rowing exercise. We knew that the rower originated from
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE
 CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE INDICATIONS FOR USE The LATERA Absorbable Nasal Implant is indicated for supporting upper and lower lateral nasal cartilage. CAUTION: Federal law restricts
CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE INDICATIONS FOR USE The LATERA Absorbable Nasal Implant is indicated for supporting upper and lower lateral nasal cartilage. CAUTION: Federal law restricts
