Muscular Channelopathies Periodic Paralysis
|
|
|
- Lucas Williamson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Periodic paralysis association Scottsdale 2017 Muscular Channelopathies Periodic Paralysis Department of Neurology Military Hospital Ulm Germany And German Air Force center of Aerospace Medicine Frank Weber Frank Lehmann-Horn, Senior Research Professor 1
2 Periodic Paralysis hypopp Thyreotoxic hyperpp ATS Age at onset < 20 ys > 20ys < 10 ys < 20 ys Attack frequency Infrequent Infrequent Frequent (several times a day) monthly Attack duration Hours to days Hours to days Min to hours hours Precipitants Exercise Carbohydrate load Stress Exercise Carbohydrate load Stress Exercise Fasting Stress K + -rich food Rest after exercise K + during attack Low Low Normal or elevated Low, normal or elevated Associated features Later onset myopathy Thyreotoxicosis Low TSH High T3, T4 Etiology Penetrance AD Inherited defect Ca 2+ -channel or Na + -channel on muscle membrane Nonpenetrance common (women) Thyreotoxicosis K + conductance (mutation K ir 2.6) Epidemiology Men more affected Highest incidence in Asian men Preventive TX Carboanhydrase inhibitors K + -sparing diuretics Euthyroid state Propanolol Myotonia (clinical, EMG) Later onset myopathy AD Inherited defect Na + -channel on muscle membrane High Sexes equally affected Carboanhydraseinhibitors Thiazide-Diuretics Inhaled beta-agonists as needed Dysmorphic features Ventricular tachycardia Long QT AD inherited defect on inward rectifier K + -channel Nonpenetrance and incomplete penetrance common Marked intrafamiliar phenotypic variation Carboanhydraseinhibitors 2
3 Episodic disorders channelopathies 3
4 Location of the channels Na v 1.4 Na + channels generate AP mutations in the voltage sensors of domains 2 and 3 cause HypoPP-2 Clinically similar to HypoPP-1 Also HyperPP Ca v 1.1 Ca 2+ channel essential for coupling of excitation- contraction all voltage sensor mutations cause HypoPP-1 4
5 4 major types of muscular ion Na + channels membrane excitability Ca 2+ channels couple membrane excitation to muscle contraction Cl - channels stabilising the resting membrane potential and help in membrane repolarization after excitation K + channels - membrane repolarization channels 5
6 Cl - channel Dominant Myotonia Pure stiffness Cl - channel Rec. Myotonia congenita Stiffness + transient weakness Ca 2+ -channel hypopp1 weakness, sensitive to low K + Na + channel Na + channel myotonia Pure stiffness stiffness K + sensitivity Muscle channelopathies Na + -channel hypopp2 weakness, sensitive to low K + Na + channel Paramyotonia congenita Stiffness, weakness, maybe K + sensitive weakness Na + -channel hyperpp weakness, sensitive to increase in K + sometimes stiffness 6 After Burge and Hanna 2011
7 Classical type of electrical excitation Other stimuli Δ Membrane potential Gating of channels Ion fluxes Other transport mechanisms
8 Classical type of electrical excitation Δ Membrane potential Gating of channels Trigger Shifts in ph, electrolyte concentration temperature Ion fluxes Other transport mechanisms
9 Free ion concentration and equilibrium potentials for mammalian skeletal muscle Ion Extracellular concentration (mm) Intracellular concentration (mm) [Ion] o /[Ion] i Equilibrium potential (mv) Na K Ca nm 15, Cl The skeletal muscles contain the largest single pool of K + in the body (75% of total). Muscular exercise releases K + serum K + 9
10 Inside the cell: high K + (140 mm), low Na + (15 mm) Outside: low K + (3-5 mm), high Na + (150 mm) At rest: high permeability for K +, low for Na + Concentration maintained by membrane pump 10
11 Basis of excitability
12 mv Basis of excitability: resting potential, dependent on [K + ] More complicated than just a deviation from E K (Nernst potential for K + ) E Goldman RT = F + P [ Na ] + [ K e ln + [ K ] i + ] e -60 paradoxical depolarization E K [ K [ K + RT = ln + F 1 10 K + [mm] 100 K + new finding: p.d. at physiological K + Paradoxical depolarization was initially explained by a block of the Na+/K+ ATPase ] ] e i 12
13 density [1/mV] density [1/mV] P1 4 mm K + Variability and functionality of P2 in normal muscle? P2 0 Healthy fibers hyperpolarised, if external K E m /mv P P1 1 mm K P1 P E m /mv P1 follows Goldman P2 ~ -60 mv 13
14 Normalized Current Electrical membrane bistability (P1, P2) and [K + ] o 1.0 P1 P P2 K 0.2 P mv At P2, most Na + channels are inactivated: no generation of action potentials K = distance from point of contact Reason for bistability and its modification by K? 14
15 Inactivation of Na + channels = no action potentials weakness = no membrane excitability = no activity in EMG 15
16 P1/P2 relation depends on [K + ] 0.06 Physiological Na + leak density /mv [K + ] = 1 mm [K + ] = 2.5 mm [K + ] = 4 mm E m /mv E m /mv E m /mv Additional Na + leak density /mv [K + ] = 1 mm [K + ] = 2.5 mm [K + ] = 4 mm E m /mv E m /mv E m /mv E m /mv
17 Na + channel 18
18 Leak current via ω-pore Activated by hyperpolarisation Counteracts Kir2.1 current Depolarizes and destabilizes the resting membrane potential Fraction of P2 ω-current is independent from the ion-selective α-pore 19
19 Depending on the mutation, ω-currents can bei induced by hyperpolarisation or by depolarisation, often different reaction to oral K + administration Gating pore current very small about 1% of the alpha-pore current that elicits the AP ω-current usually Na + -current, possibly also H + (external acidification, could explain why attacks preferentially occur during the recovery period following muscle exercise) 20
20 In HypoPP, all but one mutation are pointmutations that neutralize positive charged arginine in the S4 Segment of Na v 1.4 or Ca v 1.1 Arginine voltage sensor mutations in 90% of HypoPP 21
21 Bistable membrane potentials Beginning at high K + concentrations, a reduction reveals an instability of the resting potential at the limit point, LP1 (closed circles), from which a sudden transition to about 60 mv occurs. Increasing the K + concentration from low values takes the muscle fiber to another limit point, LP2 (open circles), where the system jumps back into a state with normal membrane potentials. (red line), In the presence of an omega-pore (blue line), the membrane instability occurs at mild K + reduction. Smaller omega-currents, more severe hypokalemia necessary for shift to P2. Fraction of rat diaphragm muscle fibers with normal membrane potentials after the reduction of [K+] o to different values, without (red) and with (blue) amphotericin B, a Na + and K + ionophore (= mimicking hypopp) Probability density functions give the probability of a transition from the normal to the depolarized state for responding fibers at different [K+] o. LP1 is the mode or the median of the curves. Amphotericin B causes an increment of mode, median, and SD by 1 mm, 1.5 mm, and 1.2 mm. in the presence of a small depolarizing leak current, LP1 is shifted to the right and a paradoxical depolarization is more likely to occur even at normal [K+] o 22
22 Transerve tubular system (TTS) of an adult muscle fiber Electrolyte and water dysequilibrium during paralytic attacks cause a vacuolar myopathy, a proliferation of TTS and SR Poor correlation between weakness and vacuolar myopathy
23 Hypothesis: development of muscle dystrophy normal full muscle strength 25 y. triggers CAI, aldosterone Antagonists, K + intracellular Na + accumulation and edema reversible weakness 52 y. with years fibrosis and fatty replacement irreversible weakness HypoPP family 80 y.
24 Conclusions severe mutations (= large leak): high intramuscular resting Na + reversible permanent weakness irreversible weakness, fatty muscle replacement less ictal Na + increase milder ictal hypokalemia TX: K + -sparing, Na + extruding diuretics mild mutations (= small leak): lower intramuscular resting Na + larger ictal Na + fiber swelling, compartment syndrome vacuolar myopathy larger ictal hypokalemia possibly lethal hypokalemic cardiac arrhythmia TX: ictal K + substitution
25 The principle of paradoxical depolarization upon serum K + -reduction that underlies HypoPP pathogenesis may apply to all tissues equipped with K ir channels (brain, heart, muscle, kidney, leukocytes) MS: Na + channel upregulation, redistribution, mitochondrial dysfunction 30
26 Figure 4 Higher total sodium concentrations can be detected in lesions and, to a lesser extent, in the normal-appearing white matter in patients with multiple sclerosis Source: The Lancet Neurology 2014; 13: (DOI: /S (14) ) Terms and Conditions
27 Weakness phenomenology Episodic weakness (generalized, one side, focal) Bulbar and respiratory muscles rarely affected Commonly in the morning after waking up Triggers: stress, cold, fasting (hyperpp), carbohydrate-rich meal (hypopp), exercise followed by rest Tendon reflexes depressed during the attack Later onset myopathy (hyperpp, hypopp) Not necessarily flaccid (muscles can be stiff due to influx of Na + and water) Weber Scottesdale
28 hypopp Hypokalemic periodic paralysis estimated prevalence of 1 in 100,000 HypoPP may be familial with autosomal dominant inheritance Clinical penetrance is often incomplete, especially in women The disorder is three to four times more commonly clinically expressed in men. hypopp not confined to man, also in Burmese cats mutation in the gene that codes for the α-1 subunit of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel in skeletal muscle is found in about 70 % of patients; this mutation reduces channel availability. An aberrant pore in the voltage sensor allows a persistent inward Na + flow, which depolarizes the membrane and makes the fibers inexcitable. A mutation in the skeletal muscle sodium channel, SCN4A, is responsible for this syndrome in other families. The mutation stabilizes the inactivated state. Approximately one third of cases represent new mutations; eg phenotype with mutation of ATP1A2-gen (Gen for the Na + /K + -ATPase in the muscular membrane and in the brain) or systemic metabolic abnormalities downstream the effects on electrophysiology, e.g. abnormal AMP-activated protein kinase activation in SCN4A-Mutations (AMPK = encyme that protects the cell from lack of ATP) 33
29 What evidence suggests Periodic Paralysis? Family and own history of weakness episodes, attacks more frequent in males Normal serum K + between spells (usually in the lower range) Sensitivity to serum K + Muscle cramps/pain Permanent weakness, progressive with age Typical triggers, age of onset, serum K + alterations during spells Mutation is the final proof HypoPP: spells hours to days, response to low-na + & high-k + HyperPP: short spells, myotonia, response to low-potassium 34
30 What are triggers of HypoPP weakness spells? Stress (release of adrenaline that causes hypokalemia) Infections and vaccinations (release of inflammation factors, could be suppressed by ibuprofen) Surgery (stress, pure glucose and NaCl infusions) Cold environment Hormones adrenaline, estrogen (contained in birth control pills) Rest after strenuous work Awakening from sleep Certain food & beverages High glycemic index (GI) carbs: pasta, soft drinks (Coke), lemonade, alcohol, some juices, starch, chinese food Sodium salts (chips) (hypernatriemia causes diuresis and K + wasting; avoiding NaCl as good as med!) Cortisol (inhibits GLUT4-R, (Glucose-Transporter-R.) Certain drugs 35
31 Why are triggers so important? Helpful for DX of the phenotype Important for management (avoid the triggers) Eg misdiagnosis of conversion disorder ; stress as a trigger vs carb as a trigger 36
32 What can prevent weakness spells? - Serum K + in the high normal range or slightly above (4.5 to 5.2 mm) - Low-sodium and low-carb food - Continuous mild exercise ( keep moving ) - Warmth - Adequate physical therapy - Stress avoidance - Medication (K +, eplerenone, CAI) 37
33 Medicines for HypoPP Acute: Potassium Chronic: 1) Potassium 2) Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (Diamox, Dichlorphenamide) 3) Aldosterone Antagonists (Spironolactone, Inspra) 4) K-sparing Diuretics (Triamterene, Amiloride) 5) Beta-blockers (Propranolol) If weakness is permanent, consistent and continuous ingestion is required 38
34 How does K + work? Beneficial effects of K + K + shifts P2 to P1, increases strength & circulation Disadvantages of oral potassium ingestion Can cause stomach pain High serum peaks will cause release of aldosterone resulting in K + wasting (vicious circle) K + competes with of other substances for intestinal absorption (e.g., vitamine B12) Aim: Raise serum K + by reduced excretion! 39
35 How do Aldosterone Antagonists work? Raise serum K + (by reduced excretion) that shifts P2 fibers to P1, thereby increasing strength & circulation Old Substance: Spironolactone (major hormonal side effects such as male breast enlargement and tenderness) Relatively New Substance: Eplerenone/Inspra (minor hormonal side effects) 40
36 Important However, Serum K + in HypoPP usually is in the lower normal range (3.5 to 4.2 mm) even between spells; it is really difficult to raise it! In the attack, additional uptake of K + into the muscle! Only in case of a kidney insufficiency, additional oral K + ingestion or combination with K + -increasing drugs may cause dangerous hyperkalemia (check serum K + frequently!) 41
37 How do potassium-sparing diuretics work? Raise serum K + (by reduced excretion) that shifts P2 fibers to P1, thereby increasing strength & circulation Triamterene (Dyrenium, Dytac 50 mg/100 mg cps.) Amiloride (Midamor 5 mg tbl.) I m interested to learn more from users! 42
38 How do Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors work? Diamox shifts P2 fibers to P1 (via activation of K + channels), thereby increasing strength & circulation! As Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor (CAI), Dichlorphenamide is more potent and permeates the membrane more easily than Diamox does. 44
39 Side effects of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Nausea and dizziness at the beginning (take it with food and start with low dose and increase gradually) Paresthesias Strange taste (do not take carbonated drinks) Kidney Stones can be avoided by K + -citrate! 46
40 How do Beta Blockers work? Beta1-Blockers indirectly inhibit Aldosterone examples: Metoprolol, Bisoprolol, Atenolol Beta2-Blockers assist in avoiding stress-triggered weakness spells examples for Nonselective-Beta Blockers: Propranolol, Timolol, Bupranolol Adverse effects: reduce heart rate and blood pressure Beta-Blockers are widely accepted for Thyrotoxic HypoPP but so far not for Familial HypoPP 47
41 My belief: If long-term medication is required, combine 2 meds of different groups at low-dose, e.g. Dichlorphenamide and an aldosterone antagonist, and try to keep additional K + as low as possible. The low doses of each med will keep adverse effects minimal. 48
42 Modification of HypoPP by sexual hormones Majority of females report premenstrual symptoms (uterus cramps, muscle weakness) Some report worsening with birth control pills (usually contain both estrogen + progesterone) Majority report improvement during pregnancy (increase in progesterone), those might benefit from a progesterone-only pill 49
43 What drugs worsen HypoPP? Drugs reducing neuromuscular transmission, i.e. those contraindicated when myasthenic: Muscle Relaxants, Antibiotics like aminoglycosides, macrolides, fluoroquinolones Drugs causing hypokalemia (& hypophosphatemia): Albuterol (and other beta-2 sympathicomimetics against asthma), Penicillin, Cortisol, most diuretics, laxatives, Liquorice, Bactrim Drugs causing muscle ischemia (Epinephrine) Myotoxic substances such as Statins (recommended only to HypoPP with high infarction risk)
44 What does determine the individual prognosis? 1) Type of mutation The 2 extreme ends of the HypoPP spectrum: severe hypokalemia during spell may cause arrhythmia but no progressive weakness mild or no hypokalemia but progressive weakness 2) Genetic background (family) 3) Environmental factors, e.g. life-long strong physical work favours development of permanent weakness 51
45 hyperpp pathophysiology hyperpp, the Na + channel closes too slowly, Na + ions continue to leak into the muscle cell oversensitivity and stiffness in the muscle (myotonia) If the channel remains open, the muscle will become desensitized and paralyzed During the episode of muscle weakness or paralysis, K + ions are released from the muscle [K + ] o 52
46 Different effects of HypoPP and HyperPP mutations explain contrary clinical features Glucose HypoPP HyperPP K + -rich food Low K + aberrant pore external + High K + central pore Hypokalemia leads to transient hyperpolarization followed by sustained depolarization (weak) mv mm NaMS Jurkat-Rott et al. PNAS internal 0-5 na/mm 2-15 Hyperkalemia induces slight depolarization which opens channels that can t inactivate 53
47 Vicious circle in hyperpp K + extracellular depolarization Na + channel opening K + efflux myotonia paralysis 54
48 Features of hyperkalemic PP (hyperpp) transmission: autosomal dominantly prevalence: 1:200,000 onset of disease: clinical features: frequency of attacks: provocative factors: childhood or puberty attacks of generalized muscle weakness ictal increase in serum potassium EMG myotonia progressive myopathy daily for minutes to hours K + rich food, fasting, cooling, mental stress, pregnancy resting periods after exercise red: new; blue: contrary Weber to Scottsdale hypopp
49 HyperPP TX no ω-pore, but deficient Na + channel inactivation Acute attacks often do not require treatment, as they are brief. Some patients can abort attacks with sugar or mild exercise Stimulation of the Na + -K + -pump, increasing K + transport into cells (continous mild exercise, carbohydrate ingestion, inhaled beta adrenergic agonists (eg, one to two puffs of 0.1 mg albuterol)) intravenous calcium Thiazid-diuretics, CAI 57
50 58
51 View from Ulm University of Ulm Munster and the Alpes
KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) oral tablet
 KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Anaesthesia pearls and pitfalls in periodic paralysis
 Biannual Meeting of the PPA Orlando, FL, 2013 Anaesthesia pearls and pitfalls in periodic paralysis Department of Neurology Military Hospital Ulm Germany Frank Weber Frank Lehmann Horn, Senior Research
Biannual Meeting of the PPA Orlando, FL, 2013 Anaesthesia pearls and pitfalls in periodic paralysis Department of Neurology Military Hospital Ulm Germany Frank Weber Frank Lehmann Horn, Senior Research
Primary Periodic Paralysis. A Complex Disorder. A Challenging Diagnosis.
 Primary Periodic Paralysis A Complex Disorder. A Challenging Diagnosis. A Complex Disorder A Group of Rare Channelopathies With Varying Subtypes and Triggers Primary periodic paralysis causes recurrent,
Primary Periodic Paralysis A Complex Disorder. A Challenging Diagnosis. A Complex Disorder A Group of Rare Channelopathies With Varying Subtypes and Triggers Primary periodic paralysis causes recurrent,
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
5 th Annual Conference of the Periodic Paralysis Association. October 24-25, 2003
 5 th Annual Conference of the Periodic Paralysis Association October 24-25, 2003 Las Vegas, Nevada EMS Orientation to the Periodic Paralyses By Jacob Levitt, M.D. Medical Director, Periodic Paralysis Association
5 th Annual Conference of the Periodic Paralysis Association October 24-25, 2003 Las Vegas, Nevada EMS Orientation to the Periodic Paralyses By Jacob Levitt, M.D. Medical Director, Periodic Paralysis Association
Hypokalaemic periodic paralysis: In these attacks the blood potassium is low
 Periodic paralyses The ability we have to control and move the muscles in our body depends upon the passage of electrical signals along the nerves and into our muscles. The periodic paralyses are conditions
Periodic paralyses The ability we have to control and move the muscles in our body depends upon the passage of electrical signals along the nerves and into our muscles. The periodic paralyses are conditions
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES
 THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
Challenges in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis
 Periodic Paralysis Association: Annual Meeting Challenges in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis Robert C. Griggs, M.D. Professor of Neurology, Professor of Medicine, Pathology
Periodic Paralysis Association: Annual Meeting Challenges in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis Robert C. Griggs, M.D. Professor of Neurology, Professor of Medicine, Pathology
Managing Periodic Paralysis 101
 Managing Periodic Paralysis 101 Jacob Levitt, MD, FAAD President, Periodic Paralysis Association; Vice Chairman and Associate Professor of Dermatology, The Mount Sinai Medical Center, New York, NY Hypokalemic
Managing Periodic Paralysis 101 Jacob Levitt, MD, FAAD President, Periodic Paralysis Association; Vice Chairman and Associate Professor of Dermatology, The Mount Sinai Medical Center, New York, NY Hypokalemic
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
dichlorphenamide (Keveyis )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
PRINCIPLES OF DIURETIC ACTIONS:
 DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
PHYSIOLOGY 2. The effect of Cl ions on neurological is not specified, especially in adults. However, some new studies show effects on infants.
 PHYSIOLOGY 2 Effect of K Ions on the RMP INCREASED (Hyperkalemia):-hyperpolarized because of more incurrent K+, SO the RMP will be at new level further from the Threshold, so the probability to have an
PHYSIOLOGY 2 Effect of K Ions on the RMP INCREASED (Hyperkalemia):-hyperpolarized because of more incurrent K+, SO the RMP will be at new level further from the Threshold, so the probability to have an
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 15, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Voltage Gated Ion Channels
 Voltage Gated Ion Channels The Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Ion
Voltage Gated Ion Channels The Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Ion
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 18, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
FIBER TYPES - oxidative metabolism is the main form here - ATPase activity is relatively low
 Cardiac Muscle Physiology Special characteristics of cardiac muscle - Branching and interdigitating cells - At their ends, they are connected by INTERCALATED DISCS - The discs are always at the Z-lines
Cardiac Muscle Physiology Special characteristics of cardiac muscle - Branching and interdigitating cells - At their ends, they are connected by INTERCALATED DISCS - The discs are always at the Z-lines
Introduction. Circulation
 Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Resting Membrane Potential & Goldman Equation
 Resting Membrane Potential & Goldman Equation V m RT F log P K P K [ K [ K ] o ] i P P Na Na [ Na [ Na ] ] o i P P cl cl [ Cl [ Cl ] ] o i P = permeability at rest: P K : P Na : P Cl = 1.0 : 0.04 : 0.45
Resting Membrane Potential & Goldman Equation V m RT F log P K P K [ K [ K ] o ] i P P Na Na [ Na [ Na ] ] o i P P cl cl [ Cl [ Cl ] ] o i P = permeability at rest: P K : P Na : P Cl = 1.0 : 0.04 : 0.45
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis- A case report
 Case report DOI: https://doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201704.0101 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis-
Case report DOI: https://doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201704.0101 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis-
Fundamentals of Pharmacology
 Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Ch. 3: Cells & Their Environment
 Ch. 3: Cells & Their Environment OBJECTIVES: 1. To distinguish different cellular (fluid) compartments 2. Understand movement of substances across cell membranes (passive vs active) 3. To recognize different
Ch. 3: Cells & Their Environment OBJECTIVES: 1. To distinguish different cellular (fluid) compartments 2. Understand movement of substances across cell membranes (passive vs active) 3. To recognize different
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
NEURONS Chapter Neurons: specialized cells of the nervous system 2. Nerves: bundles of neuron axons 3. Nervous systems
 NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
A Summary Review o f the Diagnosis and Pathology o f the Prim ary Familial Periodic Paralyses
 Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, Vol. 5, N o. 3 Copyright 1975, Institute for Clinical Science A Summary Review o f the Diagnosis and Pathology o f the Prim ary Familial Periodic Paralyses KARL
Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, Vol. 5, N o. 3 Copyright 1975, Institute for Clinical Science A Summary Review o f the Diagnosis and Pathology o f the Prim ary Familial Periodic Paralyses KARL
Muscle Channelopathies
 Queen Square Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases Muscle Channelopathies Professor Michael G Hanna 25.3.17 What is a skeletal muscle channelopathy? Muscle and nerves communicate by electrical signals Electrical
Queen Square Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases Muscle Channelopathies Professor Michael G Hanna 25.3.17 What is a skeletal muscle channelopathy? Muscle and nerves communicate by electrical signals Electrical
Cardiac Properties MCQ
 Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Neuromuscular Junction
 Muscle Relaxants Neuromuscular Junction Cholinergic antagonists Neuromuscular-blocking agents (mostly nicotinic antagonists): interfere with transmission of efferent impulses to skeletal muscles. These
Muscle Relaxants Neuromuscular Junction Cholinergic antagonists Neuromuscular-blocking agents (mostly nicotinic antagonists): interfere with transmission of efferent impulses to skeletal muscles. These
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e
 Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 03: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 1 Slide 2 Cytosolic
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 03: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 1 Slide 2 Cytosolic
NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS
 NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Pharmacology and Toxicology Smith 742, 828-2127, Email: eishac@vcu.edu Learning Objectives: 1. Understand the physiology of the
NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING AGENTS Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Associate Professor, Pharmacology and Toxicology Smith 742, 828-2127, Email: eishac@vcu.edu Learning Objectives: 1. Understand the physiology of the
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
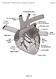 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Normal range of serum potassium is meq/l true hyperkalemia manifests clinically as : Clinical presentation : muscle and cardiac dysfunction
 Potassium Disorders hyperkalemia Potassium is mainly an cation? What is the major physiological role of potassium in the body? What is the major regulatory system of serum potassium level? Which part of
Potassium Disorders hyperkalemia Potassium is mainly an cation? What is the major physiological role of potassium in the body? What is the major regulatory system of serum potassium level? Which part of
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation. Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine
 Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Potassium A NNA VINNIKOVA, M. D.
 Potassium A NNA VINNIOVA, M. D. DIVISION OF NEPHROLOGY Graphics by permission from The Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Companion, S. Faubel and J. Topf, http://www.pbfluids.com Do you want to hear a Sodium
Potassium A NNA VINNIOVA, M. D. DIVISION OF NEPHROLOGY Graphics by permission from The Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Companion, S. Faubel and J. Topf, http://www.pbfluids.com Do you want to hear a Sodium
Low Efficacy Diuretics. Potassium sparing diuretics. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Osmotic diuretics. Miscellaneous
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 18, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 18, 2019 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 18, 2019 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
Objectives. Functions of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle. Smooth Muscle Contraction: Mechanism. Latch state. Smooth muscle contraction
 Objectives Functions of smooth muscle Sompol Tapechum,, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj hospital อธ บายล กษณะการหดต วของกล ามเน อเร ยบได อธ บายกลไกและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการหดต
Objectives Functions of smooth muscle Sompol Tapechum,, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj hospital อธ บายล กษณะการหดต วของกล ามเน อเร ยบได อธ บายกลไกและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการหดต
Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).
![Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside). Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).](/thumbs/80/80478709.jpg) 1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE
 NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
Local Anesthetics. Xiaoping Du Room E417 MSB Department of Pharmacology Phone (312) ;
 Local Anesthetics Xiaoping Du Room E417 MSB Department of Pharmacology Phone (312)355 0237; Email: xdu@uic.edu Summary: Local anesthetics are drugs used to prevent or relieve pain in the specific regions
Local Anesthetics Xiaoping Du Room E417 MSB Department of Pharmacology Phone (312)355 0237; Email: xdu@uic.edu Summary: Local anesthetics are drugs used to prevent or relieve pain in the specific regions
Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj. Abdullah Nimer. Loai Zghoul
 2 Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj Abdullah Nimer Loai Zghoul At the end of this sheet you should be able to understand the general characteristics of action potential and some of its clinical applications
2 Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj Abdullah Nimer Loai Zghoul At the end of this sheet you should be able to understand the general characteristics of action potential and some of its clinical applications
Gene annotation for heart rhythm. 1. Control of heart rate 2. Action Potential 3. Ion channels and transporters 4. Arrhythmia 5.
 Gene annotation for heart rhythm 1. Control of heart rate 2. Action Potential 3. Ion channels and transporters 4. Arrhythmia 5. EC coupling Control of heart rate Autonomic regulation of heart function
Gene annotation for heart rhythm 1. Control of heart rate 2. Action Potential 3. Ion channels and transporters 4. Arrhythmia 5. EC coupling Control of heart rate Autonomic regulation of heart function
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected by Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Doctor Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptors are targeted by drugs, the question now is how do these drugs
number 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected by Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Doctor Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptors are targeted by drugs, the question now is how do these drugs
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED. Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics
 Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Cardiac Muscle Physiology. Physiology Sheet # 8
 15 8 1 We have three types of muscles in our body: 1. Skeletal muscles. 2. Cardiac muscle. 3. Smooth muscles. The cardiovascular system consists of : Heart, cardiac vessels. The wall of the Heart has three
15 8 1 We have three types of muscles in our body: 1. Skeletal muscles. 2. Cardiac muscle. 3. Smooth muscles. The cardiovascular system consists of : Heart, cardiac vessels. The wall of the Heart has three
Questions. Question 1!
 Questions Question 1 In a laboratory, scientists often study neurons in isolation, outside of a living creature, in a dish. In this setting, one can have a good deal of control over the local ionic environment
Questions Question 1 In a laboratory, scientists often study neurons in isolation, outside of a living creature, in a dish. In this setting, one can have a good deal of control over the local ionic environment
Membrane Structure, Resting membrane potential, Action potential. Biophysics seminar
 Membrane Structure, Resting membrane potential, Action potential Biophysics seminar 09.09.2013. Membrane structure Biological membranes consists of lipids and proteins to bind with non-covalent bond. Phospholipids
Membrane Structure, Resting membrane potential, Action potential Biophysics seminar 09.09.2013. Membrane structure Biological membranes consists of lipids and proteins to bind with non-covalent bond. Phospholipids
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 19, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 19, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 19, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
PROGRESSION OF SYMPTOMS AND DIFFERENCES IN THE RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT SKELETAL MUSCLES TO HYPERKALEMIC PERIODIC PARALYSIS.
 PROGRESSION OF SYMPTOMS AND DIFFERENCES IN THE RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT SKELETAL MUSCLES TO THE M1592V MUTATION OF Na V1.4 THAT CAUSES HYPERKALEMIC PERIODIC PARALYSIS By Shiemaa Khogali Thesis submitted to
PROGRESSION OF SYMPTOMS AND DIFFERENCES IN THE RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT SKELETAL MUSCLES TO THE M1592V MUTATION OF Na V1.4 THAT CAUSES HYPERKALEMIC PERIODIC PARALYSIS By Shiemaa Khogali Thesis submitted to
Therapeutics of Diuretics
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140
 هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
آالء العجرمي أسامة الخضر. Faisal Muhammad
 16 آالء العجرمي أسامة الخضر Faisal Muhammad 1. Summary for what taken : *changes in permeability of ions: 1. During phase 0: changes happen due to the influx of Na+, the permeability of Na ions increase
16 آالء العجرمي أسامة الخضر Faisal Muhammad 1. Summary for what taken : *changes in permeability of ions: 1. During phase 0: changes happen due to the influx of Na+, the permeability of Na ions increase
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Rare Monogenic Disorders. Function. Pathophysiology
 Rare Monogenic Disorders Function Pathophysiology Protein Gene Episodic Nervous System Diseases Migraine Epilepsy Periodic Paralysis LQTS Episodic Ataxia Paroxysmal Dyskinesias Phenotypes Muscle diseases
Rare Monogenic Disorders Function Pathophysiology Protein Gene Episodic Nervous System Diseases Migraine Epilepsy Periodic Paralysis LQTS Episodic Ataxia Paroxysmal Dyskinesias Phenotypes Muscle diseases
Drugs Used in Heart Failure. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Electrical Properties of Neurons. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Electrical Properties of Neurons Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Communication Neurons communicate with other cells, often over long distances. The electrical
Electrical Properties of Neurons Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Communication Neurons communicate with other cells, often over long distances. The electrical
Contemporary Nutrition 6 th. th ed. Chapter 9 Minerals
 Contemporary Nutrition 6 th th ed. Chapter 9 Minerals Minerals Various functions in the body Major Minerals Require >100 mg /day Calcium, phosphorus Trace Minerals Require < 100 mg/day Iron, zinc Bioavailability
Contemporary Nutrition 6 th th ed. Chapter 9 Minerals Minerals Various functions in the body Major Minerals Require >100 mg /day Calcium, phosphorus Trace Minerals Require < 100 mg/day Iron, zinc Bioavailability
Cellular Messengers. Intracellular Communication
 Cellular Messengers Intracellular Communication Most common cellular communication is done through extracellular chemical messengers: Ligands Specific in function 1. Paracrines Local messengers (neighboring
Cellular Messengers Intracellular Communication Most common cellular communication is done through extracellular chemical messengers: Ligands Specific in function 1. Paracrines Local messengers (neighboring
Transport through biological membranes. Christine Carrington Biochemistry Unit Apr 2010
 Transport through biological membranes Christine Carrington Biochemistry Unit Apr 2010 Biological membranes Membranes control the structures and environments of the compartments they define and thereby
Transport through biological membranes Christine Carrington Biochemistry Unit Apr 2010 Biological membranes Membranes control the structures and environments of the compartments they define and thereby
Antiepileptic agents
 Antiepileptic agents Excessive excitability of neurons in the CNS Abnormal function of ion channels Spread through neural networks Abnormal neural activity leads to abnormal motor activity Suppression
Antiepileptic agents Excessive excitability of neurons in the CNS Abnormal function of ion channels Spread through neural networks Abnormal neural activity leads to abnormal motor activity Suppression
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
Title Page. The skeletal muscle channelopathies: phenotype, genotype and pathogenesis. Emma Louise Matthews UCL. Submission for PhD examination
 Title Page The skeletal muscle channelopathies: phenotype, genotype and pathogenesis Emma Louise Matthews UCL Submission for PhD examination Declaration I, Emma Louise Matthews confirm that the work presented
Title Page The skeletal muscle channelopathies: phenotype, genotype and pathogenesis Emma Louise Matthews UCL Submission for PhD examination Declaration I, Emma Louise Matthews confirm that the work presented
Nerve. (2) Duration of the stimulus A certain period can give response. The Strength - Duration Curve
 Nerve Neuron (nerve cell) is the structural unit of nervous system. Nerve is formed of large numbers of nerve fibers. Types of nerve fibers Myelinated nerve fibers Covered by myelin sheath interrupted
Nerve Neuron (nerve cell) is the structural unit of nervous system. Nerve is formed of large numbers of nerve fibers. Types of nerve fibers Myelinated nerve fibers Covered by myelin sheath interrupted
numbe r Done by Corrected Docto Alia Shatnawi
 numbe r 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Docto Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptor targets by the drugs, the question now how these drugs work on
numbe r 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Docto Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptor targets by the drugs, the question now how these drugs work on
Chapter 3 Neurotransmitter release
 NEUROPHYSIOLOGIE CELLULAIRE CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 Neurotransmitter release In chapter 3, we proose 3 videos: Observation Calcium Channel, Ca 2+ Unitary and Total Currents Ca 2+ and Neurotransmitter
NEUROPHYSIOLOGIE CELLULAIRE CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 Neurotransmitter release In chapter 3, we proose 3 videos: Observation Calcium Channel, Ca 2+ Unitary and Total Currents Ca 2+ and Neurotransmitter
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1/31/2018 1
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1/31/2018 1 Normal conduction pathway: 1- SA node generates action potential and delivers it to the atria and the AV node 2- The AV node delivers the impulse to purkinje fibers Other
Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1/31/2018 1 Normal conduction pathway: 1- SA node generates action potential and delivers it to the atria and the AV node 2- The AV node delivers the impulse to purkinje fibers Other
BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11
 BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11 External signal is received and converted to another form to elicit a response 1 Lecture Outline 1. Types of intercellular
BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11 External signal is received and converted to another form to elicit a response 1 Lecture Outline 1. Types of intercellular
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
Body water content. Fluid compartments. Regulation of water output. Water balance and ECF osmolallty. Regulation of water intake
 Body water content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; females 50% This difference reflects
Body water content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; females 50% This difference reflects
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
Muscle cramping the connection between diet
 Muscle cramping the connection between diet Fluid Imbalances and Dehydration Whether fluid imbalances and mild dehydration can trigger muscle cramping is open to debate. Although we know that muscle cramps
Muscle cramping the connection between diet Fluid Imbalances and Dehydration Whether fluid imbalances and mild dehydration can trigger muscle cramping is open to debate. Although we know that muscle cramps
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Arrhythmias. Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium.
 Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
membranes membrane functions basic structure membrane functions chapter 11-12
 membranes chapter - membrane functions Ca + hormone IP H + HO compartmentalization intracellular compartments scaffold for biochemical activities organize enzymes selectively permeable membrane allows
membranes chapter - membrane functions Ca + hormone IP H + HO compartmentalization intracellular compartments scaffold for biochemical activities organize enzymes selectively permeable membrane allows
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview
 Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
APs & Synapses. Review & outline. Thought experiment. Inside. Outside
 Review & outline APs & Synapses Chapters 2 & 3 Cells of the nervous system The blood brain barrier Membrane potential (at rest = -70mV) Sodium potassium pump Concentration Electrical Action potentials
Review & outline APs & Synapses Chapters 2 & 3 Cells of the nervous system The blood brain barrier Membrane potential (at rest = -70mV) Sodium potassium pump Concentration Electrical Action potentials
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU
 Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY APRIL 21, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 21, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- APRIL 21, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There is
Mechanisms of cold sensitivity of paramyotonia congenita mutation R1448H and overlap syndrome mutation M1360V
 J Physiol (2003), 547.3, pp. 691 698 DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.033928 The Physiological Society 2003 www.jphysiol.org Mechanisms of cold sensitivity of paramyotonia congenita mutation R1448H and overlap
J Physiol (2003), 547.3, pp. 691 698 DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.033928 The Physiological Society 2003 www.jphysiol.org Mechanisms of cold sensitivity of paramyotonia congenita mutation R1448H and overlap
