Effects of Personal Body Armor on Functional Movement Capability
|
|
|
- Ellen Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Effects of Personal Body Armor on Functional Movement Capability COLIN D TOMES 1, and MATTHEW D. LEWIS 2 1 Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine, Bond University, Robina, QLD, AU; 2 Department of Health, Nutrition and Exercise Science, Messiah College, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA Denotes graduate student author, Denotes professional author ABSTRACT 12(6): , The Functional Movement Screen (FMS) is a tool used to assess fundamental movement patterns and has been utilized to determine movement readiness of tactical athletes. However, tactical athletes rarely perform tasks without load carriage, and limited research evaluating loaded tactical personnel via the FMS has been conducted. Therefore, the primary aim of this study was to determine if ballistic vest wear results in movement deficits as evaluated by the FMS. A convenience sample of college students (n = 31) completed test sessions in loaded and unloaded conditions. Subjects completed each FMS movement and indicated perceived effort on a Visual Analog Scale (VAS). The Sign test was used to determine difference between FMS composite and component scores collected under each condition. The level of significance was set at p < A significant (p < 0.001) difference in FMS composite scores was identified between loading conditions. Significant FMS score changes between load conditions were identified in the dominant side in-line lunge (p < 0.01), non-dominant side in-line lunge (p < 0.01), dominant shoulder mobility (p < 0.01), non-dominant shoulder mobility (p < 0.01), and non-dominant rotary stability (p = 0.01). Our data indicate ballistic vest wear reduces overall functional movement capacity, as well as mobility related to certain individual FMS components in the population examined. Additionally, results suggest subjects may better tolerate additional load carriage when completing tasks on their dominant side. These results raise important questions regarding design, fit, and task completion for tactical athletes utilizing a ballistic vest. KEY WORDS: Ergonomics, tactical personnel, movement screening, mobility, occupational fitness, load carriage INTRODUCTION The Functional Movement Screen (FMS) is an evaluation tool for quantitative, categorical assessment of fundamental movement patterns (2). Scoring is based on performance of seven movement patterns, each requiring unique combinations of balance, mobility, stability, and neuromuscular control, providing a global analysis of the dynamic body (2). In addition, the FMS helps to determine the subject s functional readiness to participate in dynamic movement patterns, an essential component of tactical athlete occupational performance (2). The FMS is also useful in the identification of neuromuscular deficits, movement asymmetries, and subsequent compensatory movement strategies (8). The current literature contains evidence linking composite scores below 14 (of a maximum score of 21) to a higher risk of non-contact
2 musculoskeletal injury (8). In order to reveal areas of deficiency within the kinetic chain, the FMS relies on a concept of proximal stability facilitating functional distal mobility in athletic activities (14). For this reason, the FMS has been utilized repeatedly in studies assessing both athletic and tactical populations with respect to their readiness for higher-level functional activity (8, 14). However, tactical athletes will rarely perform occupational tasks without load carriage, and the weight of these loads can be significant. Loads less than 3.5 kg for the general duty law enforcement officer would be unusual (14), while loads commonly reach 22 kg in specialist police (15) and exceed 40 kg in certain circumstances, such as specific forcible entry loads (14). This upward trend in load carriage weight is due not only to the increasing complexity of modern tactical engagements but increased emphasis organizations are placing on improvements in survivability (14). Given that the additional load in the form of body armor has proven to be effective in reducing fatalities in military environments, use is becoming more widespread amongst Law Enforcement Operators (LEO) (14). Current research within the military population has indicated load carriage as a causative factor in musculoskeletal injuries (10, 19, 20). Incidence of low back pain, lower limb stress fractures, neurological injuries including brachial plexus palsy, integumentary injuries including chaffing and blisters are all significantly elevated with loads exceeding 10% of the carrier s body mass or kg (19). The effect is compounded if loads are worn for more than 4 hours (19). Mission capability and performance can also be adversely affected by load carriage due to reduced carrier mobility, increased time in accomplishment of functional tasks, elevated physiological exertion on duty, and biomechanical decompensation (23). While body armor provides protection to the wearer it also imparts risk and physiological cost (1, 18, 21). While literature has extensively described the above concerns and the increasing use of body armor systems, the impact of body armor on functional performance capabilities as assessed by the FMS is still largely unknown (23). The FMS was selected for this study because it is affordable, can be used to assess large numbers of personnel in a time efficient manner, and can be easily implemented, with training, by individuals within a tactical unit (4, 14). The investigators hypothesized that a significant difference in FMS scores and perceived effort would be present between a loaded and unloaded condition in a population of healthy and physically active college students. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine if use of a ballistic vest resulted in functional movement deficits as evaluated by the FMS, and differences in perceived exertion as evaluated by a VAS, in the test population. METHODS Participants A convenience sample (n = 31) of college students, 20 males and 11 females, volunteered for participation. Collected descriptive statistics for the subjects were: age (21.29 ± 1.94 yrs.), height ( ± cm), and mass (77.09 ± kg). Exclusion criteria were as follows: musculoskeletal injury within previous six months or any chronic musculoskeletal or 537
3 neurological condition. Subject inclusion criteria were ages between 18 and 30 yrs., current regular participation in physical activity meeting American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) guidelines for healthy adults (7), and willingness to participate in two test sessions under video surveillance. All data collection was performed within the athletic training facility at the host institution. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained prior to the start of the study. Protocol The present study utilized a crossover design. Prior to participation, informed consent was obtained from volunteer subjects. Next, subjects were instructed to select two FMS trial appointments at least 24 hours apart, during which one was performed in the loaded (LD) condition, and the other in the unloaded condition (UL). The order of testing (loaded or unloaded first) was randomized via coin flip. Subjects completed a paper-based visual analog scale (VAS) following each movement under both conditions. Prior to the start of each screen, subjects were familiarized with the testing protocol using standard procedures published by the creators of the FMS (2, 3). The seven movement tasks of the FMS include the deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (ILL), active straight leg raise (ASLR), shoulder mobility test (SMT), trunk stability push-up test (TSP), and rotary stability test (RST) (2, 3). For loaded trials, the ballistic vest (Condor, Irwindale, CA) was fitted to the subject by the primary investigator. Mass of the vest was 7.1 kg, consisting of one ceramic plate in the front, one in the rear, and simulated soft plate backers. Because modern ballistic protection systems are intended to accommodate a wide variety of personnel build types and sizes, only a single size of plate and vest was necessary for this trial. Proper fit was defined as coverage by the ballistic plate at the most inferior portion of the clavicles and secure enough to the thorax to limit vest movement during testing without interfering with normal breathing. The FMS measures the motor control of fundamental movement patterns by categorizing the participant s performance on each movement (bilaterally where applicable) using a zero to three ordinal categorization (2, 3). A score of three (3) is awarded if the movement is performed as instructed, a score of two (2) is awarded if the movement is successfully completed, but with a compensatory strategy, and a score of one (1) is awarded if the individual is unable to complete the movement. A score of zero (0) is awarded if the participant experiences pain at any time during movement, regardless of overall performance (2, 3). For detailed instructions regarding the completion and scoring of each FMS component, please refer to previous publications (2, 3). At the conclusion of each exercise, subjects indicated their perceived effort on a VAS scale. The scale used was paper-based, consisting of an unlabeled 10 cm line adjacent to each exercise. Visual analog scales have previously been reported to be a reliable and valid measure of selfreported pain and fatigue (22). The left margin indicated low difficulty and the right indicated high difficulty. Scores from the seven movement patterns comprising the FMS were summed and a composite score was obtained for each subject, using the lower of the two scores for bilateral movements in the event of an asymmetry, which was then also recorded. Five of the seven movements are scored unilaterally (2, 9). Additionally, analysis was performed on dominant and non-dominant 538
4 scores individually, providing the opportunity to capture differences between component scores in addition to the composite score. The FMS has been reported to have intra-rater test-retest and inter-rater reliability of an ICC3,1 of 0.76 (95% CI: 0.63, 0.85) and an ICC2,1 of 0.74 (95% CI: 0.60, 0.83), respectively (6). Standard error of the measurement of the composite scores have fallen within 1 point, and MDC95 values of 2.1 and 2.5 points on the 21-point scale for inter-rater and intra-rater reliability, have also been reported (13). The inter-rater agreement of component scores is known to range from moderate to excellent (κw = ) (13). Statistical Analysis Data was collected and analyzed by both the primary investigator and co-author. FMS scoring was determined by the primary investigator, with discrepancies adjudicated by an experienced FMS practitioner. The Sign Test for ordinal and non-parametric data was selected for FMS component score analysis. The FMS scoring system is ordinal in nature and the Sign Test allows for identification of a simple difference between two sets of scores, in this case each FMS component in an unloaded or loaded condition. This test was performed in Minitab 17 (Minitab Inc., State College PA) on the absolute difference in scores between subjects for both the unloaded-loaded condition and dominant-non-dominant side. FMS composite scores were also analyzed via the Sign Test. VAS data was analyzed in SPSS for Mac (IBM, Armonk, NY) using a Wilcoxon Signed ranks test. RESULTS A post hoc power analysis conducted using G-Power version for Windows (5) calculated a power This was done based on the reported means and standard deviation for the FMS composite score between conditions, an alpha level of 0.05 and Cohen s dz of 1.0. No scores of 0 were recorded during the course of data collection. Significant load condition differences were identified for the In-Line Lunge (ILL) bilaterally (p < 0.01), Shoulder Mobility Test (SMT) bilaterally (p < 0.001) and the non-dominant rotary stability test (RST) (p = 0.01). For FMS scores within the same loading condition, dominant (DM) to non-dominant (ND) differences were not significant. Results of the statistical analysis for FMS data are reported in Figure
5 FMS Movement *Rotary Stability Test (ND) (LD) *Rotary Stability Test (ND) (UL) Rotary Stability Test (DM) (LD) Rotary Stability Test (DM) (UL) Trunk Stability Pushup (LD) Trunk Stability Pushup (UL) Straight Leg Raise (ND) (LD) Straight Leg Raise (ND) (UL) Straight Leg Raise (DM) (LD) Straight Leg Raise (DM) (UL) *Shoulder Mobility Test (ND) (LD) *Shoulder Mobility Test (ND) UL) *Shoulder Mobility Test (DM) (LD) *Shoulder Mobility Test (DM) (UL) *In Line Lunge (ND) (LD) *In Line Lunge (ND) (UL) *In Line Lunge (DM) (LD) *In Line Lunge (DM) (UL) Hurdle Step (ND) (LD) Hurdle Step (ND) (UL) Hurdle Step (DM) (LD) Hurdle Step (DM) (UL) Deep Squat (LD) Deep Squat (UL) 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% FMS Score 1 FMS Score 2 FMS Score 3 Figure 1. Comparison of FMS scores between load conditions. (DM) Dominant Side, (ND) Non-dominant Side, (LD) Loaded, (UL) unloaded, * indicates significant difference between loading conditions (p < 0.05) A Shapiro-Wilk test was performed on VAS data, revealing they were not normally distributed. As a result, the Wilcoxon signed ranks test was performed on the pairs of VAS data per movement to determine significance and Cohen s d analysis was then performed on those pairs of data that reached significance to determine effect size. An alpha level of.05 was selected a priori. The Deep Squat (p = 0.031, Cohen s d = 0.31 (small-medium)) and Shoulder Mobility Tests (Dominant side, p = 0.002, Cohen s d = 0.41 (small-medium), Nondominant side p = 0.001, Cohen s d = 0.54 (medium)) bilaterally reached significance. The full results can be found in Table
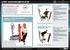
6 Table 1. Statistical analysis of VAS data. Movement Unloaded Score (Mean ± SD) Loaded Score (Mean ± SD) p-value Deep Squat 2.64 ± ± * Hurdle Step (DM) 1.41 ± ± Hurdle Step (ND) 1.57 ± ± In Line Lunge (DM) 1.88 ± ± In Line Lunge (ND) 1.92 ± ± SMT (DM) 1.71 ± ± * SMT (ND) 2.08 ± ± * SLR (DM) 1.52 ± ± SLR (ND) 1.45 ± ± TSP 2.49 ± ± RST (DM) 4.8 ± ± RST (ND) 4.39 ± ± (DM) Dominant Side, (ND) Non-dominant Side, *indicates p < 0.05 Additionally, composite FMS scores differed significantly between loading conditions as analyzed using Student s t. The mean loaded FMS score was 14 ± 2 and the mean unloaded composite FMS score was 16 ± 2 (p < 0.01, Table 2). Cohen s d analysis was performed on the composite score, yielding an effect size of 1.07 (large). For all testing, the level of significance was set at the < 0.05 level. Finally, changes in the number of movement asymmetries for each FMS movement are reported by loading condition in Table 2. Table 2. Analysis of movement asymmetries. Movement Number of Asymmetries (UL) Number of Asymmetries (LD) Percent Change HS ILL SMT SLR RST (UL) Unloaded condition, (LD) loaded condition DISCUSSION Significant functional movement deficits and increased perception of effort were present in the loaded condition. Specifically, functional capability of the upper extremity was significantly affected in all categories considered (VAS, FMS DM/ND, FMS UL/LD), indicating that a ballistic vest presents significant impairment to carrier activities involving the shoulder girdle. The large (1.07) effect size calculated for the difference between the FMS composite scores of the two loading conditions indicates a real-world change in overall FMS performance when the ballistic vest was utilized in the test population. Figure 2 demonstrates the impairment presented by the vest in shoulder range of motion. Previous research investigating this phenomenon using a 12-camera motion lab reported trunk rotation changes based on presence of vest while completing certain tasks (i.e. ammo box lift 541
7 and place) (12). The agreement of these findings suggests that the FMS may be sensitive enough as a field test to obtain reliable and valid results as compared to a more sophisticated investigative method. Figure 2. Loaded condition shoulder mobility test. The vest impairs advancement of both extremities, limiting functional range of motion and resulting in a score of 1. Figure 3. Loaded condition in-line lunge. Note that the vest may affect proper positioning of vertical down and mass applied to torso above the center of gravity may affect balance. This attempt would score a
8 Figure 4. Loaded condition rotary stability test. Mass applied to the subject by the vest may lead to unwanted trunk rotation as base of support is reduced during this activity. Changes in wearer perception during completion of FMS movements, especially the SMT (Figure 2) and DS, are more likely due to ergonomic restriction of the shoulder girdle than the resistance imparted by the mass of the vest, especially given that both movements require substantial shoulder range of motion. Previous research evaluating a fatiguing, and nonoverhead squat movement with a ballistic vest using 3D motion analysis also observed increased movement difficulty (17) suggesting that total body/le/trunk functional movement may be limited by utilization of a ballistic vest in combination with wearer perceptions. Additionally, the change in subject assessment of movement difficulty may have been partially due to the added mass of the ballistic vest. The reported small-medium effect sizes indicate a meaningful difference between load conditions beyond statistical significance. Ultimately, due to the requisite shape of common ballistic vests in providing adequate coverage, these results indicate tactical athletes may experience difficulty when attempting to access equipment carried on the back while operating in the field, or while completing overhead tasks. Therefore, training should address shoulder mobility, and particular care should be given to the shoulder joint by the multidisciplinary care team. A composite score below 14 has been reported to increase injury risk, even in elite athletes (8). More than a quarter, 27.27% (n = 6), of subjects scoring above 14 in the unloaded trial scored below 14 in the loaded condition. This evidence suggests that body armor, independent of other load carriage, may contribute to injury risk in tactical athletes due to increased perceived exertion by the wearer and functional movement restrictions as identified by the FMS. When loaded, the RST (Figure 4) FMS score decreased on the non-dominant side, and although dominant side scores decreased, the change did not reach significance. This result indicates that a larger sample size is necessary to detect dominant side changes between load conditions in the RST, or that functional movements relying on trunk stability are asymmetrically impaired when an individual is wearing a ballistic vest. This study was not without its limitations. Our participants were recruited from the university gym, and involvement was based on willingness to participate, which could introduce a 543
9 volunteer bias. Additionally, the Hawthorne effect may have played a role in overall performance, as participants were aware of the video recording taking place throughout each screen. Finally, our data are based on fit, but not tactically trained personnel. Because none of our participants were familiar with ballistic protection, it is quite possible that the novelty of the vest played a role in the observed FMS score differences, although if this were the case, it would be expected that VAS scores would have differed more between load conditions. Previous research has also identified that standardized load carriage mass causes a disparate ratio in load carried to body mass, disadvantaging wearers with lower body mass (11, 16), which may explain the magnitude of some of our results. Because previous research has found an association with movement asymmetry as identified by the FMS and risk of injury, even in elite athletes (8), this specific phenomenon should be investigated further in a tactically trained participant sample. Finally, it is worth noting that the large effect size between the two loading conditions for the FMS composite score may be reduced in a population of tactically trained subjects due to their familiarity and experience with completing functional movement and operational tasks while wearing a ballistic vest. Based on the results of the present study, additional research in the area of ballistic vest usage in tactical personnel is warranted. Specifically, the identified functional movement impairments suggest potential for considering tactical vest redesign in terms of mass and bulk. Due to the subjective increase in effort with some FMS tasks, further research specific to load carriage in tactical athlete fitness training programs may be indicated. The results of the present study, as well as those of previous research, indicate that usage of a tactical vest with ballistic protection impairs functional movement and exacerbates movement asymmetries, both of which have been postulated to increase on-duty injury risk. Safety of tactical personnel is of the highest priority, however, protection from external threats cannot be the only consideration; the ability to evade threats, complete operational tasks efficiently and mitigate non-threat related injury must also be considered to optimize performance and effectiveness of tactical personnel equipped with ballistic protection. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors disclose no conflicts of interest or financial arrangements related to this research. We would like to thank the Messiah College Athletic Training Department and the students of the Athletic Training Classes of 2017 and 2018, without many of which, this research would not have been possible. REFERENCES 1. Carlton SD, Carbone PD, Stierli M, Orr RM. The impact of occupational load carriage on the mobility of the tactical police officer. J Aust Strength Cond Cook G, Burton L, Hoogenboom B. Pre-participation screening: The use of fundamental movements as an assessment of function part 1. N Am J Sports Phys Ther 1(2): 62,
10 3. Cook G, Burton L, Hoogenboom B. Pre-participation screening: The use of fundamental movements as an assessment of function part 2. N Am Jour Sp Phys Ther 1(3): 132, Cook G, Burton L, Hoogenboom BJ, Voight M. Functional movement screening: The use of fundamental movements as an assessment of function - part 1. Int J Sports Phys Ther 9(3): , Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang A. -G. statistical power analyses using g*power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 41: , Gribble PA, Brigle J, Pietrosimone BG, Pfile KR, Webster KA. Intrarater reliability of the functional movement screen. J Strength Cond Res 27(4): , Haskell WL, Lee I-M, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, Macera CA, Heath GW, Thompson PD, Bauman A. Physical activity and public health: Updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 116(9): 1081, Kiesel K, Plisky PJ, Voight ML. Can serious injury in professional football be predicted by a preseason functional movement screen. N Am J Sports Phys Ther 2(3): , Kiesel K, Plisky PJ, Voight ML. Can serious injury in professional football be predicted by a preseason functional movement screen. N Am J Sports Phys Ther 2(3): , Knapik JJ, Graham BS, Rieger J, Steelman R, Pendergrass T. Activities associated with injuries in initial entry training. Mil Med 178(5): , Knapik JJ, Reynolds KL, Harman E. Soldier load carriage: Historical, physiological, biomechanical, and medical aspects. Mil Med 169(1): 45-56, Lenton G, Aisbett B, Neesham-Smith D, Carvajal A, Netto K. The effects of military body armour on trunk and hip kinematics during performance of manual handling tasks. Ergonomics 59(6): , Minick KI, Kiesel KB, Burton L, Taylor A, Plisky P, Butler RJ. Interrater reliability of the functional movement screen. J Strength Cond Res 24(2): , O'Connor FG, Deuster PA, Davis J, Pappas CG, Knapik JJ. Functional movement screening: Predicting injuries in officer candidates. Medicine Sci Sports Exerc 43(12): , Orr R, Poke D, Stierli M, Hinton B. The perceived effect of load carriage on marksmanship in the tactical athlete. J Sci Med Sport 19: e92, Orr R, Pope R, Peterson S, Hinton B, Stierli M. Leg power as an indicator of risk of injury or illness in police recruits. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(2): 237, Phillips M, Bazrgari B, Shapiro R. The effects of military body armour on the lower back and knee mechanics during toe-touch and two-legged squat tasks. Ergonomics 58(3): , Ricciardi R, Deuster PA, Talbot LA. Metabolic demands of body armor on physical performance in simulated conditions. Mil Med 173(9): , Roy TC, Knapik JJ, Ritland BM, Murphy N, Sharp MA. Risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries for soldiers deployed to Afghanistan. Aviat Space Environ Med 83(11): ,
11 20. Roy TC, Ritland BM, Sharp MA. A description of injuries in men and women while serving in Afghanistan. Mil Med 180(2): , Sell TC, Pederson JJ, Abt JP. The addition of body armor diminishes dynamic postural stability in military soldiers. Mil Med 178(1): 76-81, Stroyer J, Essendrop M, Jensen LD, Warming S, Avlund K, Schibye B. Validity and reliability of self-assessed physical fitness using visual analogue scales. Percept Mot Skills 104(2): , Tomes C, Orr RM, Pope R. The impact of body armor on physical performance of law enforcement personnel: A systematic review. Ann Occup Environ Med 29(1): 14,
The Functional Movement Screen as a Predictor of Tactical Athlete Performance
 Bond University epublications@bond Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine Publications Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine 5-17-2014 The Functional Movement Screen as a Predictor of Tactical Athlete Performance
Bond University epublications@bond Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine Publications Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine 5-17-2014 The Functional Movement Screen as a Predictor of Tactical Athlete Performance
Bond University Research Repository
 Bond University Research Repository The Functional Movement Screen as a predictor of police recruit occupational task performance Bock, Claire; Stierli, Michael; Hinton, Benjamin; Orr, Rob Marc Published
Bond University Research Repository The Functional Movement Screen as a predictor of police recruit occupational task performance Bock, Claire; Stierli, Michael; Hinton, Benjamin; Orr, Rob Marc Published
Musculoskeletal and soft tissue injuries are common
 INTERRATER AND INTRARATER RELIABILITY OF THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN CRAIG A. SMITH, 1 NICOLE J. CHIMERA, 2 NICHOLAS J. WRIGHT, 1 AND MEGHAN WARREN 1 1 Department of Physical Therapy and Athletic Training,
INTERRATER AND INTRARATER RELIABILITY OF THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN CRAIG A. SMITH, 1 NICOLE J. CHIMERA, 2 NICHOLAS J. WRIGHT, 1 AND MEGHAN WARREN 1 1 Department of Physical Therapy and Athletic Training,
A functional movement screen profile of an Australian state police force: a retrospective cohort study
 Orr et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:296 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1146-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A functional movement screen profile of an Australian state police force: a retrospective
Orr et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2016) 17:296 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1146-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A functional movement screen profile of an Australian state police force: a retrospective
FMS 4/20/16. Disclosures. Functional Movement Screen and Prior Injury in National Football League Combine Athletes.
 Functional Movement Screen and Prior Injury in National Football League Combine Athletes Harris S. Slone, M.D., Spero G. Karas, M.D., Raj Shani, M.D., Megan East, M.A., L.A.T, O.T.C., William R. Barfield,
Functional Movement Screen and Prior Injury in National Football League Combine Athletes Harris S. Slone, M.D., Spero G. Karas, M.D., Raj Shani, M.D., Megan East, M.A., L.A.T, O.T.C., William R. Barfield,
Move2Perform Allison Behnke MS LAT ATC Jason Viel MS LAT ATC
 Move2Perform Allison Behnke MS LAT ATC Jason Viel MS LAT ATC What is Move2Perform Move2Perform is a movement measurement and analysis tool that identifies deficits and risk of injury Has been adopted by
Move2Perform Allison Behnke MS LAT ATC Jason Viel MS LAT ATC What is Move2Perform Move2Perform is a movement measurement and analysis tool that identifies deficits and risk of injury Has been adopted by
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN The Functional Movement Screen The Functional Movement Screen (FMS) is a screening tool used to evaluate seven fundamental movement patterns in individuals
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN The Functional Movement Screen The Functional Movement Screen (FMS) is a screening tool used to evaluate seven fundamental movement patterns in individuals
Frontiers in Sports Injury Prevention: The Functional Movement Screen. Gray Cook, MSPT, OCS, CSCS
 Frontiers in Sports Injury Prevention: The Functional Movement Screen Gray Cook, MSPT, OCS, CSCS Our Functional Movement History High School Athletics Bridge Gap between PPE And Performance Tests Functional
Frontiers in Sports Injury Prevention: The Functional Movement Screen Gray Cook, MSPT, OCS, CSCS Our Functional Movement History High School Athletics Bridge Gap between PPE And Performance Tests Functional
=.688, p=.492). Inter-rater reliability (ICC 3,1. =.979, p =.329), or those who reported a previous injury and those who did not (t 207
 IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN TM NORMATIVE VALUES IN A YOUNG, ACTIVE POPULATION Dr. Anthony G. Schneiders 1 Åsa Davidsson 2 Elvira Hörman 2 Prof. S. John Sullivan 1 ABSTRACT Background:
IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN TM NORMATIVE VALUES IN A YOUNG, ACTIVE POPULATION Dr. Anthony G. Schneiders 1 Åsa Davidsson 2 Elvira Hörman 2 Prof. S. John Sullivan 1 ABSTRACT Background:
Use of the Functional Movement Screen in a Tactical Population: A Review
 Use of the Functional Movement Screen in a Tactical Population: A Review Clare Bock & Robin M. Orr Abstract Background: The Functional Movement Screen is a tool used in athletic populations for predicting
Use of the Functional Movement Screen in a Tactical Population: A Review Clare Bock & Robin M. Orr Abstract Background: The Functional Movement Screen is a tool used in athletic populations for predicting
Individual Summary Report
 Individual Summary Report John, you have completed screening tests designed to determine your musculoskeletal status and injury potential. Injuries are difficult to predict, that s why we use only the
Individual Summary Report John, you have completed screening tests designed to determine your musculoskeletal status and injury potential. Injuries are difficult to predict, that s why we use only the
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer
 The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The perceived effects and comfort of various body armour systems on police officers while performing occupational tasks
 Schram et al. Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (2018) 30:15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-018-0228-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The perceived effects and comfort of various body armour
Schram et al. Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (2018) 30:15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-018-0228-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The perceived effects and comfort of various body armour
Gender Differences in Load Carriage Injuries of Australian Army Soldiers
 Bond University From the SelectedWorks of Rob Marc Orr April, 2015 Gender Differences in Load Carriage Injuries of Australian Army Soldiers Rob Marc Orr, Dr, Bond University Rodney Pope, Dr, Bond University
Bond University From the SelectedWorks of Rob Marc Orr April, 2015 Gender Differences in Load Carriage Injuries of Australian Army Soldiers Rob Marc Orr, Dr, Bond University Rodney Pope, Dr, Bond University
LEARNING OBJECTIVES PILLAR PREPARATION. Understand how the concept of the Core has evolved. Identify the components of the pillar and their function
 PILLAR PREPARATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand how the concept of the Core has evolved Identify the components of the pillar and their function Explain the concept of kinetic linking and explain its
PILLAR PREPARATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand how the concept of the Core has evolved Identify the components of the pillar and their function Explain the concept of kinetic linking and explain its
DEEP SQUAT. Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet
 APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Test-Retest and Interrater Reliability of the Functional Movement Screen
 Journal of Athletic Training 2013;48(3):331 336 doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-48.2.11 Ó by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.natajournals.org original research Test-Retest and Interrater Reliability
Journal of Athletic Training 2013;48(3):331 336 doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-48.2.11 Ó by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.natajournals.org original research Test-Retest and Interrater Reliability
Practical Implementations of Movement Screening EATA 2016
 Practical Implementations of Movement Screening EATA 2016 Dave Marchetti, MS, AT, CSCS Lock Haven University BS, Health Science/Athletic Training Salisbury University MS, Applied Health Physiology CSCS,
Practical Implementations of Movement Screening EATA 2016 Dave Marchetti, MS, AT, CSCS Lock Haven University BS, Health Science/Athletic Training Salisbury University MS, Applied Health Physiology CSCS,
Implementation of the Functional Movement Screen at Central Magnet School for Cross Country. Athletes. Lane Grizzard. Abby Graves
 Implementation of the Functional Movement Screen at Central Magnet School for Cross Country Athletes by Lane Grizzard Abby Graves A Senior Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
Implementation of the Functional Movement Screen at Central Magnet School for Cross Country Athletes by Lane Grizzard Abby Graves A Senior Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
Essentials of Coaching & Training Functional Continuums. Gray Cook Lee Burton Dan John
 Essentials of Coaching & Training Functional Continuums Gray Cook Lee Burton Dan John Historical Perspective Functional evaluation Functional exercise Movement Patterns The relationship between altered
Essentials of Coaching & Training Functional Continuums Gray Cook Lee Burton Dan John Historical Perspective Functional evaluation Functional exercise Movement Patterns The relationship between altered
The impact of body armor on physical performance of law enforcement personnel: a systematic review
 Tomes et al. Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (2017) 29:14 DOI 10.1186/s40557-017-0169-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The impact of body armor on physical performance of law enforcement
Tomes et al. Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (2017) 29:14 DOI 10.1186/s40557-017-0169-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The impact of body armor on physical performance of law enforcement
Injuries common to tactical personnel (A multidisciplinary review)
 Bond University epublications@bond Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine Publications Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine 11-8-2013 Injuries common to tactical personnel (A multidisciplinary review)
Bond University epublications@bond Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine Publications Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine 11-8-2013 Injuries common to tactical personnel (A multidisciplinary review)
Diploma in Exercise and Health Fitness. Module 2 Research Skills and Program Development in Exercise and Health Fitness
 Diploma in Exercise and Health Fitness Module 2 Research Skills and Program Development in Exercise and Health Fitness Is Functional Movement Screening (FMS) a Reliable Predictor of Musculoskeletal Injury?
Diploma in Exercise and Health Fitness Module 2 Research Skills and Program Development in Exercise and Health Fitness Is Functional Movement Screening (FMS) a Reliable Predictor of Musculoskeletal Injury?
The Influence of Body Armor on Balance and Movement Quality
 Original Research The Influence of Body Armor on Balance and Movement Quality ROGER O. KOLLOCK 1, DAVIS HALE 1, RACHELE VOGELPOHL 2, LOGAN KREMER *2, JOSH HORNER *2, CHRISTIAN COX *2, and MATT ALLEN *2
Original Research The Influence of Body Armor on Balance and Movement Quality ROGER O. KOLLOCK 1, DAVIS HALE 1, RACHELE VOGELPOHL 2, LOGAN KREMER *2, JOSH HORNER *2, CHRISTIAN COX *2, and MATT ALLEN *2
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Kari Babski-Reeves, PhD. Daniel Carruth, PhD. Center for Advanced Vehicular Systems Mississippi State University
 Daniel Carruth, PhD Assistant Research A i R h Professor P f Center for Advanced Vehicular Systems Mississippi State University Kari Babski-Reeves, PhD Associate Professor A i P f Industrial and Engineering
Daniel Carruth, PhD Assistant Research A i R h Professor P f Center for Advanced Vehicular Systems Mississippi State University Kari Babski-Reeves, PhD Associate Professor A i P f Industrial and Engineering
Coordination indices between lifting kinematics and kinetics
 Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering Publications Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering 2008 Coordination indices between lifting kinematics and kinetics Xu Xu North Carolina State
Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering Publications Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering 2008 Coordination indices between lifting kinematics and kinetics Xu Xu North Carolina State
ACCEPTED. Running head: Reliability of and changes in physical function and performance. Authors: Mark Waldron 1. Adrian Gray 1.
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 0./JSC.00000000000000 R-_title: The reliability of Functional Movement Screening (FMS) and in-season changes in physical function
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 0./JSC.00000000000000 R-_title: The reliability of Functional Movement Screening (FMS) and in-season changes in physical function
Bond University Research Repository
 Bond University Research Repository Comparing the Effects of Different Body Armor Systems on the Occupational Performance of Police Officers Schram, Ben; Orr, Rob Marc; Pope, Rodney R; Hinton, Benjamin;
Bond University Research Repository Comparing the Effects of Different Body Armor Systems on the Occupational Performance of Police Officers Schram, Ben; Orr, Rob Marc; Pope, Rodney R; Hinton, Benjamin;
Functional Capacity Evaluation
 OccuPro - Woodstock 1118 N. Seminary Avenue Woodstock, IL 60098 (p) (815) 337-4260 (f)(815) 337-4268 Functional Capacity Evaluation Client: John Doe Gender: Male Date of Birth: 5/14/1962 Evaluation Date:
OccuPro - Woodstock 1118 N. Seminary Avenue Woodstock, IL 60098 (p) (815) 337-4260 (f)(815) 337-4268 Functional Capacity Evaluation Client: John Doe Gender: Male Date of Birth: 5/14/1962 Evaluation Date:
Coach Development Seminar. Valencia July 2015
 Coach Development Seminar Valencia July 2015 Session Objective Measuring / Monitoring the young athlete Why do we use Postural analysis What is Coaching Essential Components of a Development Pathway What
Coach Development Seminar Valencia July 2015 Session Objective Measuring / Monitoring the young athlete Why do we use Postural analysis What is Coaching Essential Components of a Development Pathway What
THE EFFECT OF AN INTERVENTION PROGRAM ON FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN TEST SCORES IN MIXED MARTIAL ARTS ATHLETES
 THE EFFECT OF AN INTERVENTION PROGRAM ON FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN TEST SCORES IN MIXED MARTIAL ARTS ATHLETES JAMIE G. BODDEN, ROBERT A. NEEDHAM, AND NACHIAPPAN CHOCKALINGAM Center for Sport, Health and
THE EFFECT OF AN INTERVENTION PROGRAM ON FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN TEST SCORES IN MIXED MARTIAL ARTS ATHLETES JAMIE G. BODDEN, ROBERT A. NEEDHAM, AND NACHIAPPAN CHOCKALINGAM Center for Sport, Health and
MOVEMENT SCREEN DANIEL MEEK. October 2013
 AN ASSESSMENT OF THE INTRA AND INTER- RATER RELIABILITY OF THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN DANIEL MEEK A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements of Liverpool John Moores University for
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE INTRA AND INTER- RATER RELIABILITY OF THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN DANIEL MEEK A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements of Liverpool John Moores University for
In both competitive athletes and the general population,
 PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF STUDENT-ATHLETES AND GENERAL COLLEGE STUDENTS ON THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN AND THE YBALANCE TEST KATHERINE D. ENGQUIST, 1 CRAIG A. SMITH, 1,2 NICOLE J. CHIMERA, 3 AND MEGHAN
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF STUDENT-ATHLETES AND GENERAL COLLEGE STUDENTS ON THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN AND THE YBALANCE TEST KATHERINE D. ENGQUIST, 1 CRAIG A. SMITH, 1,2 NICOLE J. CHIMERA, 3 AND MEGHAN
All individuals pass through the same levels of the
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TRENDS in Sport Sciences 2017; 1(24): 31-38 ISSN 2299-9590 The impact of the corrective and stability exercises program on the quality of basic movement patterns among dance students MARTA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TRENDS in Sport Sciences 2017; 1(24): 31-38 ISSN 2299-9590 The impact of the corrective and stability exercises program on the quality of basic movement patterns among dance students MARTA
PHYSICAL PROFILING FOR GOLF. PAUL DARBY Chartered Physiotherapist And Golf Conditioning Consultant
 PHYSICAL PROFILING FOR GOLF PAUL DARBY Chartered Physiotherapist And Golf Conditioning Consultant Components of the Elite Athlete Physiological Flexibility, Strength & Power Control of Movement Technical
PHYSICAL PROFILING FOR GOLF PAUL DARBY Chartered Physiotherapist And Golf Conditioning Consultant Components of the Elite Athlete Physiological Flexibility, Strength & Power Control of Movement Technical
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials
 Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
MTI. Ruck Deep Dive: Study #2 - Ruck Training Adaptation MOUNTAIN TACTICAL INSTITUTE, JACKSON, WY MOUNTAIN MILITARY LAW ENFORCEMENT FIRE/RESCUE
 Ruck Deep Dive: Study #2 MTI MOUNTAIN TACTICAL INSTITUTE, JACKSON, WY Dedicated to maximizing athlete s outside performance. Ruck Deep Dive: Study #2 - Ruck Training Adaptation MOUNTAIN MILITARY LAW ENFORCEMENT
Ruck Deep Dive: Study #2 MTI MOUNTAIN TACTICAL INSTITUTE, JACKSON, WY Dedicated to maximizing athlete s outside performance. Ruck Deep Dive: Study #2 - Ruck Training Adaptation MOUNTAIN MILITARY LAW ENFORCEMENT
Aerobic Fitness is of Greater Importance than Strength and Power in the Load Carriage Performance of Specialist Police
 Original Research Aerobic Fitness is of Greater Importance than Strength and Power in the Load Carriage Performance of Specialist Police JEREMY ROBINSON 1, ADAM ROBERTS 1, SHANE IRVING *1, and ROBIN ORR
Original Research Aerobic Fitness is of Greater Importance than Strength and Power in the Load Carriage Performance of Specialist Police JEREMY ROBINSON 1, ADAM ROBERTS 1, SHANE IRVING *1, and ROBIN ORR
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization
 Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
5/22/2017. Discuss reliability of FMS and selected movement screens Discuss the meaning of FMS composite score results Discuss Deep Squat dysfunction
 Eric Scibek, MS, ATC, LAT, CSCS, PES Sacred Heart University Discuss reliability of FMS and selected movement screens Discuss the meaning of FMS composite score results Discuss Deep Squat dysfunction Discuss
Eric Scibek, MS, ATC, LAT, CSCS, PES Sacred Heart University Discuss reliability of FMS and selected movement screens Discuss the meaning of FMS composite score results Discuss Deep Squat dysfunction Discuss
POWERBAG. Powerbag Video / DVD Series TRAINING GUIDE
 Powerbag Video / DVD Series For more detailed Powerbag Exercise information and instruction please refer to the Powerbag Video / DVD Series All you need to know about Powerbags! Comprehensive professional
Powerbag Video / DVD Series For more detailed Powerbag Exercise information and instruction please refer to the Powerbag Video / DVD Series All you need to know about Powerbags! Comprehensive professional
2017 Coaches Clinic. Strength Development for Athletes
 2017 Coaches Clinic Strength Development for Athletes Olympic Weightlifting Implementation & Progression Dillon J. Painter, MS, USAW, CF-L1 Olympic Weightlifting Snatch Clean & Jerk Applying external load
2017 Coaches Clinic Strength Development for Athletes Olympic Weightlifting Implementation & Progression Dillon J. Painter, MS, USAW, CF-L1 Olympic Weightlifting Snatch Clean & Jerk Applying external load
The Effects of Upper -Body and Lower -Body Fatigue on Standing Balance
 The Effects of Upper -Body and Lower -Body Fatigue on Standing Balance F. Cogswell 1, B. Dietze 1, F. Huang 1 1 School of Kinesiology, The University of Western Ontario No conflicts of interest declared.
The Effects of Upper -Body and Lower -Body Fatigue on Standing Balance F. Cogswell 1, B. Dietze 1, F. Huang 1 1 School of Kinesiology, The University of Western Ontario No conflicts of interest declared.
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
SHARKS TAKING A BITE OUT OF ATHLETIC INJURIES
 SHARKS TAKING A BITE OUT OF ATHLETIC INJURIES Peter A. Sprague, PT, DPT, OCS Associate Professor Physical Therapy Department College of Healthcare Sciences Nova Southeastern University NSU SPORTS MEDICINE
SHARKS TAKING A BITE OUT OF ATHLETIC INJURIES Peter A. Sprague, PT, DPT, OCS Associate Professor Physical Therapy Department College of Healthcare Sciences Nova Southeastern University NSU SPORTS MEDICINE
T he necessity for dynamic warmup ABSTRACT
 The Core Mobility Series: A Dynamic Warm-up Tool Mitch Hauschildt, MA, ATC, CSCS, 1 Brett McQueen, MS, ATC, LAT, 2 and Geoffrey Stanford 1 1 Missouri State University, Springfield, MO; and 2 Rocky Mountain
The Core Mobility Series: A Dynamic Warm-up Tool Mitch Hauschildt, MA, ATC, CSCS, 1 Brett McQueen, MS, ATC, LAT, 2 and Geoffrey Stanford 1 1 Missouri State University, Springfield, MO; and 2 Rocky Mountain
Athletic performance in professional sport is widely
 INTEGRATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN INTO THE NATIONAL HOCKEY LEAGUE COMBINE CHIP P. ROWAN, 1 CHRISTIANE KUROPKAT, 2 ROBERT J. GUMIENIAK, 1 NORMAN GLEDHILL, 1 AND VERONICA K. JAMNIK 1 1 Human
INTEGRATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREEN INTO THE NATIONAL HOCKEY LEAGUE COMBINE CHIP P. ROWAN, 1 CHRISTIANE KUROPKAT, 2 ROBERT J. GUMIENIAK, 1 NORMAN GLEDHILL, 1 AND VERONICA K. JAMNIK 1 1 Human
Title: Aerobic Fitness is of Greater Importance Than Strength and Power in the Load Carriage Performance of Specialist Police
 Title: Aerobic Fitness is of Greater Importance Than Strength and Power in the Load Carriage Performance of Specialist Police Authors: JEREMY ROBINSON 1, ADAM ROBERTS 1, SHANE IRVING *1, and ROBIN ORR
Title: Aerobic Fitness is of Greater Importance Than Strength and Power in the Load Carriage Performance of Specialist Police Authors: JEREMY ROBINSON 1, ADAM ROBERTS 1, SHANE IRVING *1, and ROBIN ORR
Discuss the training tradition and how it has influenced preparation for athletes.
 MOVEMENT BASED PHILOSOPHY AN APPROACH TO PROGRAM DESIGN LEARNING OBJECTIVES Discuss the training tradition and how it has influenced preparation for athletes. Introduce the key concepts behind movement
MOVEMENT BASED PHILOSOPHY AN APPROACH TO PROGRAM DESIGN LEARNING OBJECTIVES Discuss the training tradition and how it has influenced preparation for athletes. Introduce the key concepts behind movement
Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation
 Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation BRADY L. TRIPP, PhD, LAT, ATC Florida International University Key Points As evidence accumulates, so does our appreciation of the integral roles that
Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation BRADY L. TRIPP, PhD, LAT, ATC Florida International University Key Points As evidence accumulates, so does our appreciation of the integral roles that
Journal of Occupational Health J-STAGE Publication Advance (June 14, 2018) Article author(s). CC BY-NC-SA 4.0(
 Profiling the Metabolic Fitness of a Special Operations Police Unit Danny Maupin, Jeremy Robinson, Thomas Wills, Shane Irving, Ben Schram, Rob Orr Bond Institute of Health and Sport, Bond University, Gold
Profiling the Metabolic Fitness of a Special Operations Police Unit Danny Maupin, Jeremy Robinson, Thomas Wills, Shane Irving, Ben Schram, Rob Orr Bond Institute of Health and Sport, Bond University, Gold
Functional Assessment of The Lower Kinetic Chain
 1 2 Functional Assessment of The Lower Kinetic Chain UCSF Primary Care Sports Medicine Course San Francisco December 11 th, 2015 Michelle Cappello, PT, SCS, MSPT Ryan Sargent, MBA, MS, ATC Introduction
1 2 Functional Assessment of The Lower Kinetic Chain UCSF Primary Care Sports Medicine Course San Francisco December 11 th, 2015 Michelle Cappello, PT, SCS, MSPT Ryan Sargent, MBA, MS, ATC Introduction
TRAINING GUIDE G O L F P E R F O R M A N C E T R A C K
 TRAINING GUIDE G O L F P E R F O R M A N C E T R A C K ABOUT Crossover Symmetry provides equipment, education, and training for athletes who want to end shoulder pain and increase strength. Our systems
TRAINING GUIDE G O L F P E R F O R M A N C E T R A C K ABOUT Crossover Symmetry provides equipment, education, and training for athletes who want to end shoulder pain and increase strength. Our systems
The Causes of Early Hip Extension in the Golf Swing
 The Causes of Early Hip Extension in the Golf Swing Hypothesis: Our hypothesis for this research is when a golfer fails any of Leg Lowering, Toe Touch, or Overhead Deep Squat tests early hip extension
The Causes of Early Hip Extension in the Golf Swing Hypothesis: Our hypothesis for this research is when a golfer fails any of Leg Lowering, Toe Touch, or Overhead Deep Squat tests early hip extension
Section: Original Research Report. Article Title: The Effect of Core Stability Training on Functional Movement Patterns in Collegiate Athletes
 Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the. The article appears here in its accepted, peer-reviewed form, as it was provided by the submitting author. It has not been copyedited,
Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the. The article appears here in its accepted, peer-reviewed form, as it was provided by the submitting author. It has not been copyedited,
HEAVY-DUTY TRAINING BAG INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND EXERCISE GUIDE
 HEAVY-DUTY TRAINING BAG INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND EXERCISE GUIDE IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ!» Consult your healthcare professional before beginning this or any type of exercise program.» Recommended for athletes
HEAVY-DUTY TRAINING BAG INSTRUCTION MANUAL AND EXERCISE GUIDE IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ!» Consult your healthcare professional before beginning this or any type of exercise program.» Recommended for athletes
Digital Human Modeling of Non-Occupational Risk Factors for
 Digital Human Modeling of Non-Occupational Risk Factors for Manufacturing Breakout Work Session Task Design 2014 Iowa Governor s Safety & Health Conference Cedar Rapids, IA ; November 7, 2013 1 st International
Digital Human Modeling of Non-Occupational Risk Factors for Manufacturing Breakout Work Session Task Design 2014 Iowa Governor s Safety & Health Conference Cedar Rapids, IA ; November 7, 2013 1 st International
Tactical Athlete Symposium: Physical Therapists Working with Firefighters, Law Enforcement, and Military personnel
 Tactical Athlete Symposium: Physical Therapists Working with Firefighters, Law Enforcement, and Military personnel Combined Sections Meeting 2016 Anaheim, California, February 17-20, 2016 Description:
Tactical Athlete Symposium: Physical Therapists Working with Firefighters, Law Enforcement, and Military personnel Combined Sections Meeting 2016 Anaheim, California, February 17-20, 2016 Description:
IJSPT CLINICAL COMMENTARY ABSTRACT
 IJSPT CLINICAL COMMENTARY FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREENING: THE USE OF FUNDAMENTAL MOVEMENTS AS AN ASSESSMENT OF FUNCTION-PART 2 Gray Cook, PT, OCS 1 Lee Burton PhD, ATC 2 Barbara J. Hoogenboom, PT, EdD,
IJSPT CLINICAL COMMENTARY FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT SCREENING: THE USE OF FUNDAMENTAL MOVEMENTS AS AN ASSESSMENT OF FUNCTION-PART 2 Gray Cook, PT, OCS 1 Lee Burton PhD, ATC 2 Barbara J. Hoogenboom, PT, EdD,
Most Dangerous Man! FACTS ON STREGNTH. Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
 FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
Muscular Training This is a sample session for strength, endurance & power training exercises
 Muscular Training This is a sample session for strength, endurance & power training exercises Presenter: Leslie McAdam CCAA Trainer Education Coordinator lbrown59@uwo.ca 519-661-1607 1-866-661-1603 X81607
Muscular Training This is a sample session for strength, endurance & power training exercises Presenter: Leslie McAdam CCAA Trainer Education Coordinator lbrown59@uwo.ca 519-661-1607 1-866-661-1603 X81607
 Our goal is to improve the health and safety of firefighters, law enforcement officials, and military personnel by improving their strength and cardio condition. Our customized programs are crafted to
Our goal is to improve the health and safety of firefighters, law enforcement officials, and military personnel by improving their strength and cardio condition. Our customized programs are crafted to
RELATIVE EXERCISE INTENSITY, HEART RATE, OXYGEN CONSUMPTION, AND CALORIC EXPENDITURE WHEN EXERCISING ON VARIOUS NON-IMPACT CARDIO TRAINERS
 RELATIVE EXERCISE INTENSITY, HEART RATE, OXYGEN CONSUMPTION, AND CALORIC EXPENDITURE WHEN EXERCISING ON VARIOUS NON-IMPACT CARDIO TRAINERS Kirsten Hendrickson, B.S. John P. Porcari, Ph.D. Carl Foster,
RELATIVE EXERCISE INTENSITY, HEART RATE, OXYGEN CONSUMPTION, AND CALORIC EXPENDITURE WHEN EXERCISING ON VARIOUS NON-IMPACT CARDIO TRAINERS Kirsten Hendrickson, B.S. John P. Porcari, Ph.D. Carl Foster,
Anaerobic Metabolism Model Weight Training Guide
 Richwoods High School Women s Track & Field Anaerobic Metabolism 400-800 Model Weight Training Guide SINGLE EFFORT MAXIMUM LIFT CONVERSION CHART To estimate single repetition maximum, locate the cross
Richwoods High School Women s Track & Field Anaerobic Metabolism 400-800 Model Weight Training Guide SINGLE EFFORT MAXIMUM LIFT CONVERSION CHART To estimate single repetition maximum, locate the cross
TRAINING GUIDE S H O U L D E R H E A L T H & P E R F O R M A N C E P A R T N E R W I T H
 TRAINING GUIDE S H O U L D E R PA R T N E R W I T H H E A L T H & P E R F O R M A N C E ABOUT Crossover Symmetry provides equipment, education, and training for athletes who want to end shoulder pain and
TRAINING GUIDE S H O U L D E R PA R T N E R W I T H H E A L T H & P E R F O R M A N C E ABOUT Crossover Symmetry provides equipment, education, and training for athletes who want to end shoulder pain and
The Influence of Corrective Exercises on Functional Movement Screen and Physical Fitness Performance in Army ROTC Cadets
 Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Theses and Dissertations 3-14-2017 The Influence of Corrective Exercises on Functional Movement Screen and Physical Fitness Performance in Army ROTC
Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Theses and Dissertations 3-14-2017 The Influence of Corrective Exercises on Functional Movement Screen and Physical Fitness Performance in Army ROTC
Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards.
 Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards. Prepared by Engineering and Human Performance Lab Department of
Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards. Prepared by Engineering and Human Performance Lab Department of
EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT. Prepared By:
 EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT Prepared By: Dr. Tyler Brown, Principal Investigator Wyatt Ihmels, Graduate Research Assistant Research
EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT Prepared By: Dr. Tyler Brown, Principal Investigator Wyatt Ihmels, Graduate Research Assistant Research
Effects of special exercise programs on functional movement screen scores and injury prevention in preprofessional young football players
 Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2017;13(5):535-540 Effects of special exercise programs on functional movement screen scores and injury prevention in preprofessional young football
Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2017;13(5):535-540 Effects of special exercise programs on functional movement screen scores and injury prevention in preprofessional young football
BENCH, SQUAT, DEADLIFT
 BENCH, SQUAT, DEADLIFT By: Chad Andracki What do the words bench, squat, and deadlift mean? Where do they come from? Who does these things? Is there a specific way to do these movements? What happens if
BENCH, SQUAT, DEADLIFT By: Chad Andracki What do the words bench, squat, and deadlift mean? Where do they come from? Who does these things? Is there a specific way to do these movements? What happens if
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention. Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS
 ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
S trength and conditioning professionals ABSTRACT
 Strength and Power Profiling of Athletes: Selecting Tests and How to Use the Information for Program Design Michael R. McGuigan, PhD, CSCS*D, 1 Stuart J. Cormack, PhD, 2 and Nicholas D. Gill, PhD 1,3 1
Strength and Power Profiling of Athletes: Selecting Tests and How to Use the Information for Program Design Michael R. McGuigan, PhD, CSCS*D, 1 Stuart J. Cormack, PhD, 2 and Nicholas D. Gill, PhD 1,3 1
MELDING EXPLOSIVE POWER WITH TECHNIQUES IN THE LONG JUMP. Explosive Strength IS THE RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT AT THE START OF A MUSCLE CONTRACTION.
 MELDING EXPLOSIVE POWER WITH TECHNIQUES IN THE LONG JUMP Jake Jacoby Jumps Coach University of Louisville jake.jacoby@louisville.edu Explosive Strength IS THE RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT AT THE START OF
MELDING EXPLOSIVE POWER WITH TECHNIQUES IN THE LONG JUMP Jake Jacoby Jumps Coach University of Louisville jake.jacoby@louisville.edu Explosive Strength IS THE RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT AT THE START OF
American Council on Exercise
 American Council on Exercise February 23, 2015 Fitnovatives Blog Exercise Progressions for Clients Who Are Overweight or Are Affected by Obesity While there is no single right way to train clients who
American Council on Exercise February 23, 2015 Fitnovatives Blog Exercise Progressions for Clients Who Are Overweight or Are Affected by Obesity While there is no single right way to train clients who
The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl. Sarah DoBroka Wilson, PT, SCS Ron Weathers, PT, DPT, ATC, LAT
 The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson, PT, SCS Ron Weathers, PT, DPT, ATC, LAT Page 1 of 6 The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson PT, SCS Ron Weathers PT, DPT,
The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson, PT, SCS Ron Weathers, PT, DPT, ATC, LAT Page 1 of 6 The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson PT, SCS Ron Weathers PT, DPT,
Strength and Conditioning in Tactical Athletes With Low Back Pain Scott D. Carow, PT, DSc, OCS, SCS
 Strength and Conditioning in Tactical Athletes With Low Back Pain Scott D. Carow, PT, DSc, OCS, SCS The views expressed in this presentation do not reflect the official policy or position of the US Army
Strength and Conditioning in Tactical Athletes With Low Back Pain Scott D. Carow, PT, DSc, OCS, SCS The views expressed in this presentation do not reflect the official policy or position of the US Army
Section: Original Research Report
 Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the. The article appears here in its accepted, peer-reviewed form, as it was provided by the submitting author. It has not been copyedited,
Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the. The article appears here in its accepted, peer-reviewed form, as it was provided by the submitting author. It has not been copyedited,
30/30 Challenge Program Overview
 30/30 Challenge Program Overview The Ontario Minor Hockey Association (OMHA) is proud to present the 30/30 Challenge, part of the OMHA s Players Club presented by Bauer Hockey. This program was created
30/30 Challenge Program Overview The Ontario Minor Hockey Association (OMHA) is proud to present the 30/30 Challenge, part of the OMHA s Players Club presented by Bauer Hockey. This program was created
Ottumwa Police Department
 Ottumwa Police Department Minimum Requirements for placement on the eligibility list: Be at least eighteen years of age; Citizen of the United States; Good moral character; Uncorrected vision of not less
Ottumwa Police Department Minimum Requirements for placement on the eligibility list: Be at least eighteen years of age; Citizen of the United States; Good moral character; Uncorrected vision of not less
THE STRENGTH WORKOUT FOR RUNNERS
 THE H T G N E R ST T U O K R O W S R E N N U R FOR n a d r By Jo D M, l z t e D. M Runners love running. They don t like getting hurt. That s why it s so important for every runner to strength train. Strong,
THE H T G N E R ST T U O K R O W S R E N N U R FOR n a d r By Jo D M, l z t e D. M Runners love running. They don t like getting hurt. That s why it s so important for every runner to strength train. Strong,
President s Day Pitching Camp
 President s Day Pitching Camp EXTENDED Warm - Up *Ages 13-18* Sleeper Stretch The sleeper stretch is a great flexibility stretch for the shoulder joint. It will help increase flexibility. In this stretch,
President s Day Pitching Camp EXTENDED Warm - Up *Ages 13-18* Sleeper Stretch The sleeper stretch is a great flexibility stretch for the shoulder joint. It will help increase flexibility. In this stretch,
Guidance Tool: Manual Handling
 Guidance Tool: Manual Handling Please tick the relevant boxes to ensure you follow the correct procedures. Manual Handling Risk Assessments completed for Hazardous Activities Employee made aware of the
Guidance Tool: Manual Handling Please tick the relevant boxes to ensure you follow the correct procedures. Manual Handling Risk Assessments completed for Hazardous Activities Employee made aware of the
Session Title: Plyometrics for Everyone Presented by: Jonathan Ross,
 Introduction Many athletic movements as well as many everyday life movements require explosive and/or rapid muscle actions that require rapid rates of force production or power in addition to high levels
Introduction Many athletic movements as well as many everyday life movements require explosive and/or rapid muscle actions that require rapid rates of force production or power in addition to high levels
Speed & Power Development for HS Track & Field
 Speed & Power Development for HS Track & Field Tim O Neill Head Coach Davenport Assumption HS USATF Level 2 Sprints/Hurdles/Relays, Throws, Jumps and Endurance @Assumptiontrack toneill@power-lift.com 641-757-7934
Speed & Power Development for HS Track & Field Tim O Neill Head Coach Davenport Assumption HS USATF Level 2 Sprints/Hurdles/Relays, Throws, Jumps and Endurance @Assumptiontrack toneill@power-lift.com 641-757-7934
Long-term Training Adaptations in Elite Male Volleyball Players
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2011 2011 Long-term Training Adaptations in Elite Male Volleyball Players Jeremy Sheppard Edith Cowan University Robert Newton Edith Cowan University
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2011 2011 Long-term Training Adaptations in Elite Male Volleyball Players Jeremy Sheppard Edith Cowan University Robert Newton Edith Cowan University
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
Copyright 2010 by Dave Schmitz All Rights Reserved
 Copyright 2010 by Dave Schmitz All Rights Reserved No portion of this manual may be used, reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including fax, photocopy, recording
Copyright 2010 by Dave Schmitz All Rights Reserved No portion of this manual may be used, reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including fax, photocopy, recording
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH
 NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
Rehabilitation of Low Back Injuries in Football Players
 Rehabilitation of Low Back Injuries in Football Players By Albi Gilmer, OCS, Cert MDT Typical Lumbar Injuries in Football Players Seen in Rehab Disc Injuries Lumbar Instability Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis
Rehabilitation of Low Back Injuries in Football Players By Albi Gilmer, OCS, Cert MDT Typical Lumbar Injuries in Football Players Seen in Rehab Disc Injuries Lumbar Instability Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis
Wayne Strube PT, DPT FUNCTIONAL TRAINING AND REHAB
 Wayne Strube PT, DPT FUNCTIONAL TRAINING AND REHAB DISCLAIMER The view(s) expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the official policy or position of Brooke Army Medical Center, the
Wayne Strube PT, DPT FUNCTIONAL TRAINING AND REHAB DISCLAIMER The view(s) expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the official policy or position of Brooke Army Medical Center, the
Diane Vives, MS, CSCS, *D Owner, Fit4Austin, Austin, TX Member of the Board of Directors, NSCA
 Diane Vives, MS, CSCS, *D Owner, Fit4Austin, Austin, TX Member of the Board of Directors, NSCA 1. Introduction a. Through my experience as a strength coach over the last 11 years, I have often been faced
Diane Vives, MS, CSCS, *D Owner, Fit4Austin, Austin, TX Member of the Board of Directors, NSCA 1. Introduction a. Through my experience as a strength coach over the last 11 years, I have often been faced
MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING
 MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING Kimitake Sato Department of Exercise and Sport Science, Center of Excellence for Sport Science and Coach Education, East Tennessee State
MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING Kimitake Sato Department of Exercise and Sport Science, Center of Excellence for Sport Science and Coach Education, East Tennessee State
Tips for Teaching the 3 Core Bulgarian Bag Movement Patterns
 Tips for Teaching the 3 Core Bulgarian Bag Movement Patterns The following tips will help you work with details and fine points of taking someone through the instruction process for the 3 core fundamental
Tips for Teaching the 3 Core Bulgarian Bag Movement Patterns The following tips will help you work with details and fine points of taking someone through the instruction process for the 3 core fundamental
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
STEP HURDLE LADDER IMPORTANT INFORMATION PLEASE READ AND KEEP DISCLAIMER
 STEP HURDLE LADDER IMPORTANT INFORMATION PLEASE READ AND KEEP DISCLAIMER The following guidelines should be observed when using the Step Hurdle Ladder. Always consult your physician before participating
STEP HURDLE LADDER IMPORTANT INFORMATION PLEASE READ AND KEEP DISCLAIMER The following guidelines should be observed when using the Step Hurdle Ladder. Always consult your physician before participating
DES MOINES REGIONAL POLICE ACADEMY COOPER ASSESSMENT PREPARATION GUIDE
 DES MOINES REGIONAL POLICE ACADEMY COOPER ASSESSMENT PREPARATION GUIDE The Cooper Assessment uses a battery of tests to identify an individual s ability to perform functions associated with law enforcement
DES MOINES REGIONAL POLICE ACADEMY COOPER ASSESSMENT PREPARATION GUIDE The Cooper Assessment uses a battery of tests to identify an individual s ability to perform functions associated with law enforcement
Injury prediction in Division-I collegiate crosscountry runners using functional movement tests
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Theses and Dissertations 2013 Injury prediction in Division-I collegiate crosscountry runners using functional movement tests Samuel
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Theses and Dissertations 2013 Injury prediction in Division-I collegiate crosscountry runners using functional movement tests Samuel
Preseason functional movement screen component tests predict severe contact injuries in professional rugby union players
 Preseason functional movement screen component tests predict severe contact injuries in professional rugby union players Jason C. Tee, 1,* Jannie F.G. Klingbiel, 2 Robert Collins, 2,3 Mike I. Lambert,
Preseason functional movement screen component tests predict severe contact injuries in professional rugby union players Jason C. Tee, 1,* Jannie F.G. Klingbiel, 2 Robert Collins, 2,3 Mike I. Lambert,
