Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate
|
|
|
- Jeffery Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 ( Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *, ZARKA AMIN MASOODI 2, LATIEF.A. CHIESTI, SHOUKAT.A. KADLA 4 Registrar, Deptt. of e.n.t govt. Medical College Srinagar j&k India 2 Consultant gen. Medicine EX.HEAD DEPTT. ENT 4 Head Deptt. Gasteroenterology address: irfaniqbal0809@yahoo.com(i. IQBAL) To cite this article IRFAN IQBAL, ZARKA AMIN MASOODI, LATIEF.A. CHIESTI, SHOUKAT.A. KADLA. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease; How to Evaluate. Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine. Vol., No., 20, pp. 5-. Abstract Objective: To study how to evaluate Laryngopharyngeal Reflux(LPR), and to formulate management strategy. Study design: Prospective study. Material and methods: A total of 2 patients were studied and followed for a period of at least six months. The study was conducted under the following headings: ()establish the diagnosis of LPR by using Reflux Finding Score (RFS ) and Reflux Symptom Index(RSI), (2)establish diagnosis of GERD by history and endoscopy,()treat LPR by lifestyle modification and medical management using proton pump inhibitors(ppi) or surgical management. Results: Majority of patients were females (5.%) and in the age group of years.rsi was used to study symptoms and median RSI score was (7).The common symptoms were clearing of throat (97.%),lump in throat (96.2%),excess throat mucus (9.%) and heartburn (62.9%).The signs of LPR were studied by using RFS and median RFS was ().The common findings were vocal cord edema (97.%) and erythema (9.%).Symptoms of GERD were present in less than half of patients (47.6%). EGD was found to be normal in (64.8%). The most common finding on EGD was esophagitis (7.%) followed by gastritis (4.%) and hiatus hernia (8.6%). Majority of patients responded to medical management only (96.2%). RSI improved from a mean score of 7.6% at initiation of treatment to.9 at 6 months follow up. RFS improved from a mean score of.9 at pre-treatment to (.7) at 6 months follow up. Symptoms of GERD improved completely in all patients at 4 months only. Conclusion: LPR is common and RFS and RSI were used to evaluate LPR and they were reproducible and effective. GERD was present in less than half of the patients. Medical management using twice daily PPI was effective. Keyword Laryngopharyngeal Reflux, Upper Esophageal Sphingter, Reflux Finding Score, Gastroesophageal Reflux. Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is defined as the movement of gastric material into the oesophagus in the absence of belching or vomiting 5. Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) that travels proximally and penetrates the upper esophageal sphincter to enter the larynopharynx is called extra-oesophageal reflux or laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). The term LPR was adopted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery in LPR should never be considered physiologic and even a single episode of pharyngeal reflux (ph < 4.0) is diagnosti In LPR the incidence of esophagitis and the primary symptom of esophagitis i.e. heartburn, is very low (about 20-4%) 5 whereas nearly all patients with GERD report of heartburn and as many as 40% have been observed to have erosive esophagitis. Thus LPR is often called silent reflux. LPR patients are predominantly upright (daytime) refluxers Although LPR has been associated with multiple
2 6 IRFAN IQBAL et al.: Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease; How to Evaluate otolaryngologic disorders, the most common physical findings of LPR are related to laryngeal mucosal edema and injury. Laryngeal mucosal injury can result in serious pathology ranging from ulcerative disease, granulomas, subglottic stenosis to laryngopharyngeal carcinoma. However, the most common findings during laryngoscopy are related to chronic inflammatory changes. The first such finding is pseudosulcus vocalis. Analogous to the RSI, these laryngeal findings have been used to create the reflux finding score (RFS). RFS was also developed by Belafsky et al 2 as an eight item clinical screening scale for finding of laryngoscopic examination. 2. Aims and Objectives () To study the clinical presentation of laryngopharyngeal reflux. (2) To document endoscopic findings of patients with LPR (fiberoptic laryngoscopy and esophagoscopy). () To correlate LPR with GERD. (4) To formulate management strategy of LPR.. Materials and Methods The study entitled Evaluation and management of patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) and its correlation with gastroesophageal reflux (GER) was conducted in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery, SMHS Hospital of Government Medical College, Srinagar on the subjects attending Outpatient Department (OPD)... Inclusion Criteria Patients complaining of symptoms suggestive of LPR were included in the study. Subjects of all age groups were studied..2. General Study Design A total number of one hundred twelve (2) patients were studied and followed for a period of at least six (6) months. Seven (7) patients lost follow-up due to various reasons leaving a total of one hundred and five (05) patients in the study... General Study Design The study was conducted under the following headings:... To Establish the Diagnosis of LPR For establishing the diagnosis of LPR, patients were subjected to a detailed history and physical examination. Symptoms of the patients were evaluated on the basis of the reflux symptom index (RSI) which is a self-administered tool developed by Belafsky et al 8. Patients were asked to use a 0 to 5 point scale to grade the following symptoms. (i) Hoarseness of voice, (ii) Throat clearing, (iii) Excess throat mucous or postnasal drip, (iv) Difficulty swallowing, (v) Coughing after eating or lying down, (vi) Breathing difficulties or chocking spells, (vii) Troublesome or annoying cough, (viii) Sensation of something sticking or a lump in the throat and (ix) Heart burn, chest pain, indigestion on standing, or acid coming up. Then laryngeal examination by indirect laryngoscopy and fiberoptic laryngoscope (FOL) / 70% rigid endoscope was done by using 5% lidocaine aerosol spray. These findings were judged on the basis of reflux finding score (RFS) which is an 8 item clinical severity scale. According to the RFS 8 LPR associated findings were rated on a variably weighted scale from 0 to 4. These findings include subglottic edema, ventricular obliteration, erythemia / hyperemia, vocal fold edema, diffuse laryngeal edema, posterior commissure hypertrophy, granuloma and thick endolaryngeal mucus. The results could range from 0 (normal) to 26 (worst possible score)...2. To Establish Diagnosis of GERD All the patients who were found to have LPR were evaluated for GERD. GERD was diagnosed on the basis of typical history like heartburn, regurgitation or dysphagia and documentation of reflux esophagitis on upper GI endoscopy with confirmation of esophagitis by biopsy.... Treatment of LPR After proper diagnosis the patients were subjected to various anti-reflux measures.... Patient Education and Behavioural Modification All patients were educated as to the nature of the problem and counselled on helpful behavioural and dietary changes. Important behavioural modifications include weight loss, smoking cessation and alcohol avoidance. Ideal dietary changes included restriction of chocolate, fat, citrus fruits, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, wines, and caffeine. Patients were advised to elevate the head end of the bed by 6-8 inches and avoid lying down hours after meals Medical Management The patients were put on proton pump inhibitors (PPI) twice daily for a period of six (6) months. The patients were followed for six (6) months at an interval of 2 months each. Improvement was assessed by again applying RFS and RSI score at 2, 4 and 6 month scores and comparing them with pretreatment scores. Investigations like esophagogastroduodenostomy (EGD) were also repeated. If patients showed improvement on subsequent followup, the drugs were titrated off. But if the patients did not show any improvement, the dose of PPI was doubled or an H 2 receptor antagonist was added.... Surgical Management Patients who failed to respond to adequate medical management were considered for surgical measures like Nissen Fundoplication 2.
3 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): Results and Observations The study group consisted of 2 patients who were Table. Reflux Symptom Index (RSI) Score of the Studied Subjects followed for at least 6 months, 7 patients lost follow-up leaving 05 patients in the study. RSI Score Total Median Hoarseness or a problem with your voice Clearing your throat Excess throat mucus or post nasal drip Difficulty swallowing food, liquid or pills Coughing after you ate or after lying down Breathing difficulties or chocking episodes Troublesome or annoying cough Lump in your throat or sensation of something sticking in throat Heartburn, chest pain, indigestion or stomach acid coming up n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % Table 2. Reflux Finding Score (RFS) in the Studied Subjects Component Score n % Total (%) Median Pseudosulcus (Subglotic Edema) (49.5) Ventricular Obliteration (57.) Erythema/Hyperemia (9.) Vocal Cord Edema (97.) Diffuse Laryngeal Edema (87.6) 2
4 8 IRFAN IQBAL et al.: Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease; How to Evaluate Component Score n % Total (%) Median Posterior Commisure Hypertrophy Granuloma/Granulation Thick Endolaryngeal Mucus (79.0) 22 (2.0) 0 7 (69.5) 2 Table. Median RFS and RSI Score Median Score Total Reflux Symptom Index Score 7 Total Reflux Finding Score Table 4. GERD symptoms in the studied subjects GERD N % Yes No Table 5. Correlation of EGD with GERD symptoms in the Studied Subjects EGD No. of Patients Percentage Normal Esophagitis 8 7. Gastritis 5 4. Haitus Hernia Total Table 6. Comparison of Initial RSI with follow-up at 2, 4, 6 months respectively RSI Mean SD p value Initial month follow-up (FU) month follow-up (FU) month follow-up (FU) Table 7. Reflux Symptom Index Score over the Study period of 6 months RSI < p value Initial month follow-up (FU) RSI < p value 4 month follow-up (FU) month follow-up (FU) Table 8. Comparison of Initial RFS with follow-up at 2, 4, 6 months respectively RFS Mean SD p value Initial month follow-up (FU) month follow-up (FU) month follow-up (FU) Table 9. Reflux Finding Score over the Study period of 6 months RFS < 7 7 p value Initial month follow-up (FU) month follow-up (FU) 6 month follow up (FU) Table 0. Comparison of Initial GERD Symptoms with the GERD at 2 month, 4 month and 6 month Follow Up Follow-up (FU) GERD 2 months Follow-up (FU) GERD 4 months Follow-up (FU) GERD 6 months Yes No n % n % Positive Negative Positive Negative Positive Negative p value
5 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5-9 Table. Treatment Effectiveness in the Studied Subjects over a period of 6 months N % Initial RSI & RFS None Both Subsided month RSI & RFS RSI Only 8 7. RFS Only None Both Subsided month RSI & RFS RSI Only 0.5 RFS Only None 2.4 Both Subsided month RSI & RFS RSI Only 2.9 None Discussion Gastric contents, refluxing through the upper esophageal sphincter are implicated as a common cause of laryngeal inflammation. As recently as the early 980s many clinicians questioned whether the backflow of gastric contents into the throat could account for laryngopharyngeal symptoms in the absence of heartburn, the primary symptom of GERD. Indeed, LPR documented by pharyngeal ph monitoring was also not reported till 986. LPR which is the retrograde movement of gastric contents into the larynx, pharynx, and upper aerodigestive tract; is now reported as an important etiological factor in the development of many inflammatory and neoplastic disorders of the upper aerodigestive tract. Improved methods of diagnosis and treatment with proton pump inhibitors have allowed for increasing recognition and control of this condition. Earlier to that, many of these head and neck symptoms were presumed to result from vagally mediated reflexes, not from LPR. Now over the past two decades, many studies have shown LPR and GERD to be two unique but related entities with different risk factors. One key distinction is that patients with classic GERD almost always have heartburn or dyspepsia as their primary symptom. In contrast most patients with LPR do not have heartburn but instead present with atypical symptoms of reflux such as hoarseness of voice, globus sensation, throat clearing. The aim of the current prospective study was to determine in patients presenting with various laryngopharyngeal symptoms to the otolaryngologist the prevalence of gastrointestinal diseases with evaluation of the success rates for specific therapies. As many as 2 patients complaining of symptoms suggestive of LPR of all age groups were included in the study, out of which 7 lost follow up leaving 05 patients for the study. In the present study, it was observed that LPR was quite common in the studied population. Among the patients having LPR females (5.%) outnumbered men (46.7 Similar observations have been reported by W. J. Issing27, Cem Bilgen5 where 6% were males and 64% females. In another study Koufman JA8 reported 5% women with LPR disease. When studied with reference to the affected age group, it was observed that the maximum number of patients were young in the age group of years with a mean age of years. This is in accordance with other studies conducted elsewhere. The mean age of the patients in the study conducted by Koufman JA8 was 49+ years while as it was years in studies conducted by Stefan Tauber27, Belafsky4 and Johnson PE4 reported affected age group of 57+7 years and 47 years respectively. The socio-demographic characteristics of the patient revealed that those patients having LPR had no significant difference with regard to the dwelling i.e. 46.7% resided in rural and 5.% in urban areas. But the number of literate people affected were more (89%) as compared to 5.2%illiterate people. This difference might be accounted to the cultural difference in identifying and reporting the disorders. To diagnose, assess severity and document improvement in patients with LPR RSI developed by Belafsky et al4 was used in the present study. RSI is a nine item reflux symptom index, a standardized instrument to qualify LPR symptoms28. Subjects are asked to grade the symptoms on a scale of 0-5, 0 signifying no problem while 5 signifying severe problem. The score ranges from A score of > was taken as abnormal and suggestive of LPR. It was found that RSI was highly reproducible. This is consistent with the study of Belafsky4. The mean RSI of the patients at the initial pretreatment visit was 7 which was comparable to that found by Belafsky 4 (mean pretreatment RSI was 9.9+.). Among the studied patients, clearing of throat (97.%) was found to be the most common symptom followed by lump in throat (96.2%). These findings are similar to the observations made in the surveys conducted by American Bronchoesophagological Association Members6, and the study conducted by Noordziji2. Koufman JA5 in his landmark study found that hoarseness of voice was present in 7%, cough 5%, globus 47%, and throat clearing in 42% subjects. This seems to vary from the present results. This might be attributed to the fact that RSI was not used to grade symptoms in their study. As we have used RSI patients even with the score of i.e. mild symptoms also get included which is not true for the above mentioned study. Similar to the RSI score the RFS score was used for assessing and grading the laryngeal signs in patients of LPR. This was also developed and validated by Belafsky2. According to this score 8 item grading system were used to assess the severity of disease. A score of > 7 is considered abnormal. The RFS is also highly reproducible as described by Belafsky2. In the present study it was found that in patients the mean RFS was which was similar to that found by Belafsky2 in his study.
6 0 IRFAN IQBAL et al.: Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease; How to Evaluate In the present study, vocal cord edema was the most common finding (97.%) followed by erythema (9.%), diffuse laryngeal edema (87.6%), and posterior commisure hypertrophy (79%). These findings are consistent with other studies conducted elsewhere in the world. The prevalence of symptoms of GERD in our patients of LPR was quite less (47.6%). This shows that more than half of the patients with LPR showed no symptoms of GERD. This is consistent with almost all the studies done to compare GERD and LPR. In the large series of patients described by Koufman 5 only 4% had symptoms of GERD which is comparable to the findings in the present study. This emphasizes the difference between GERD and LPR. LPR is therefore sometimes termed as silent reflux. The patterns, mechanism, manifestation and treatment of LPR and GERD all differ significantly and the gastroenterology model of GERD does not apply to LPR. The laryngeal epithelium is more susceptible to reflex related injury than esophageal epithelium. In all the patients of LPR endoscopy of the upper GI system was done to find any abnormalities. We found that 64.8% of patients had absolutely normal EGD. The most common abnormality was that of esophagitis which was present in 4% of patients. The next common finding was antral gastritis present in 9% and hiatal hernia in 7% of patients. The world literature seems to agree on the fact that a large percentage of patients of LPR do not have signs and symptoms of GERD. Koufman JA 8 documented esophagitis in 2% of subjects while in the study conducted by Stefan Tauber 27 the prevalence of esophagitis was 4%. 6. Treatment The patients were given treatment in three phases: 6.. Dietary and Life Style Modification Low fat, high protein diet is recommended for patients with GERD, thus it is recommended that fats, chocolates, mints, carbonated beverages and caffeine are to be avoided. Similarly ethanol and use of tobacco are both discouraged because these agents adversely influence several pathophysiologic GER mechanisms. No food or drink within hours of recumbency is also recommended. The life style modification include elvation of the bed or sleeping on a wedge. This has shown to improve acid clearance time in two-third of patients. The patients were instructed to avoid wearing corsets, high belts, and tight fitting clothing which increase the abdominal pressure Medical Management The patients were treated with PPIs like Omperazole, Pantoperazole, Rabeprazole. These are H + K + inhibitors (hydrogen ion blocker). The last stage of hydrogen ion production in the acid clearing pathway within the parietal cell is a hydrogen ion pump in which potassium is exchanged for hydrogen. This step is carried out by H + K + ATPase. PPIs act on this final step in the stimulating process of acid secretion and totally inhibits both stimulated and basal acid secretion. In this study, the patients were treated with twice a day of PPI in accordance with various studies conducted on LPR patients,8,9,0,5,8,9,2o,2,24,0. The efficacy of using the increased dose of PPI was shown in studies conducted by Koufman 5,8, Belafsky, Pach W 2, Peghini PL 24, Noordziji JP 20, Katz 9, Wetscher GJ 0, Eherer AJ 8, Fass 0, El-Seray 9. When compared at 0, 2, 4 and 6 months it was that the mean RSI improved from 7.6% at pre-treatment to 4.0 at 2 months follow up, 8.2 at 4 months and.9 at 6 months follow up. Similarly when RFS was compared at 0, 2, 4 and 6 months it was found that mean RFS improve from.9% at pretreatment level to.7 at 6 months follow up. These studies were consistent with that done by Bilgen 5 who documented a mean RFS score of at 6 months interval.the subjects were followed for 6 months after an interval of every 2 months. The parameters that were followed were RSI, RFS, symptoms of GERD and EGD findings At 6 months reviewing all the patients, it was found that.8% (4) had no improvement signs and symptoms of LPR. This was documented by Amin MR. These patients were considered for surgical management2,,22,29. In various studies like that conducted by Westcott CJ29, Hunter GJ, Oelschlager22, Fuch2 surgical management was found to be helpful for treating symptoms of LPR. In this study, empirical trial of PPIs was also used to diagnose LPR5,8 The duration of empiric treatment was 2 months5. The trial of PPI for diagnosing has been shown to be an effective means of diagnosing LPR. It has been proven to be an alternative to ambulatory double probe ph monitoring for diagnosing LPR. This was suggested by Bilgen5 and Koufman8 in their studies. Hence it is concluded that maximum number of patients of LPR improved with PPI but the dose of PPI required was high i.e. twice daily dosage and they required the treatment for a larger duration i.e. for 6 months period. This was attributed to the fact that as few as episodes per week has been shown to be associated with development of significant disease the difference appears to be due to the fact that the extrinsic and intrinsic differences of the laryngeal epithelial are much weaker than the esophagus since none of the PPI s exert intragastric and suppression for more than 6.8 hours patients with LPR treated with PPI requires at least twice daily dosing5,8. References [] Amin MR, Postma GN, Johnson P, Koufman JA. Proton pump inhibitors resistance in the treatment of LPR. Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg 200; 25: [2] Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score. Laryngoscope 200; : -7.
7 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- [] Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. LPR symptoms improve before changes in physical findings. Laryngoscope 200; (6): [4] Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index. Journal of Voice 2002; 6: [5] Bilgen C, Ogut F, Kesimili-Dinc H, Kirazli T, Bor S. The comparison of an empiric proton pump inhibitor trial vs. 24 hour double probe ph monitoring in laryngopharyngeal reflux. The Journal of Laryngology and Otology 200; 7: [6] Book DT, Rhee JS, Toohill RJ, Smith TL. Perspectives in laryngopharyngeal reflux: an international survey. Laryngoscope 2000; 2: [7] DeMeester TR, Johnson LF, Joseph GJ, Toscano MS, Hall AW, Skinner DB. Patterns of gastroesophageal reflux in health and disease. Ann Surg 976; 84: [8] Eherer AJ, Habermann W, Hammer HF, Kiesler K, Friedrich G, Krejs GJ. Effect of pantoprazole on the course of refluxassociated laryngitis: a placebo-controlled double blind cross over study. Scand J Gastroenterol 200; 8: [9] El Seraj HB, Lee P, Buchner A, Inadomi JM, Gavin M, McCarthy DM. Lansoprazole treatment of patients with chronic idiopathic laryngitis: a placebo-controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 200; 96: [0] Fass R. Empirical trials in treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis 2000; 8: [] Ford CN. Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux. JAMA 2005; 294; [2] Fuchs KH, Breithaupt W, Feinn M, Maroske J, Hammer I. laparoscopic Nissen repair: indications, techniques and long-term benefits. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2005; 90: [] Hunter JG, Trus Ted L, Branum GD, Waring J. Patrick, Wood WC. A physiological approach to laproscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 996; 22: [4] Johnson PE, Kaufman JA, Nowah LJ, Belafsky PC, Postma GN. Ambulatory 24 hour double probe PH monitoring. The importance of monometry. Laryngoscope 200; : [5] Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestation of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24 hour ph monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope 99; 0: -78. [6] Koufman JA, Amin MR, Panetti M. Prevalence of reflux in consecutive patients with laryngeal and voice disorders. Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg 2000; 2: 85-8 [7] Koufman JA, Aviv JE, Casiano RR, Shaw GY. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: Position statement of the committee on speech, voice and swallowing disorders of the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surgery 2002; 27: 2-5. [8] Koufman JA, Belafsky PC, Bach KK, Daniel E, Postma GN. Prevalence of esophagitis in patients with PH-documented laryngopharyngeal reflux. Laryngoscope 2002; 2: [9] Katz PO, Castell DO. Medical therapy of supra-esophageal gastroesophgeal reflux disease. Am J Med 2000; 08(suppl 4a): 70S-77S. [20] Noordziji JP, Khidr A, Evans BA et al. Evaluation of Omperazole in the treatment of reflux laryngitis: a prospective placebo-controlled randomized double-blind study. Laryngoscope 200; : [2] Noordzij JP, Khidr A, Desper E, Meek RB, Reibel JF, Levine PA. Correlation of ph probe-measured laryngopharyngeal reflux with symptoms and signs of reflux laryngitis. Laryngoscope 2002; 2: [22] Oelsclager BK, Eubanks TR, Oleynikov D, Pope C, Pellegrini CA. Symptomatic and physiologic outcomes after operative treatment for extraesophageal reflux. Surg Endosc 2002; 6: [2] Park W, Hicks DM, Khandwala F, Richter Vaezi MF. Laryngopharyngeal reflux; prospective cohort study evaluating optimal dose of PPI therapy and pretherapy predictors of response. Laryngoscope 2005; 5(7): [24] Peghini PL, Katz PO, Bracy NA, et al. Noctural recovery of gastric acid secretion with twice daily dosing of PPI. Am J Gastroenterol 998; 9: [25] Postma GN. Ambulatory PH monitoring methodology. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2000; 09(0, Suppl 84): 0-4. [26] Postma GN, Tomek MS, Belafsky PC, Koufman JA. Esophageal motor function in laryngopharyngeal reflux is superior to that of classic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 200; 0(2): 4-6. [27] Tauber S, Gross M. Issing WJ. Association of laryngopharyngeal symptoms with gastroestophageal reflux disease. Laryngoscope 2002; 2: [28] Tutuian R, Castell DO. Diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Current opinion in otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery 2004; 2: [29] Westcott CJ, Hopkins MB, Bach K, Postma GN, Belasfsky PC, Koufman JA. Fundoplication for LPR disease. J Am Coll Surg 2004; 99(): 2-0. [0] Wetscher GJ, Gadenstaetter M, Klingler PJ et al. Efficacy of medical therapy and antireflux surgery to prevent Barett s metaplasia in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 200; 24:
Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease with Special Reference to Video Endoscopic Findings
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. or dysphagia may alert a physician to the possibility of LPR. 1,2 Laryngeal findings
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis ABSTRACT
 THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors in the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
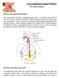 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux
 The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2013), 127, 590 594. JLO (1984) Limited, 2013 doi:10.1017/s0022215113000832 MAIN ARTICLE The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients
The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2013), 127, 590 594. JLO (1984) Limited, 2013 doi:10.1017/s0022215113000832 MAIN ARTICLE The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
 Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Lansoprazole Treatment of Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis: A Placebo-Controlled Trial
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation
 The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and Assessment
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX
 CLINICAL REVIEW CLINICIAN S CORNER Evaluation and Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Charles N. Ford, MD LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX (LPR) is the result of retrograde flow of gastric contents to the laryngopharynx,
CLINICAL REVIEW CLINICIAN S CORNER Evaluation and Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Charles N. Ford, MD LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX (LPR) is the result of retrograde flow of gastric contents to the laryngopharynx,
Epidemiology Classic Symptoms of GERD
 Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Patient information. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4
 Patient information Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4 You have been diagnosed with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), otherwise known as extra-oesophageal reflux
Patient information Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4 You have been diagnosed with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), otherwise known as extra-oesophageal reflux
Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
Diverged Otorhinolaryngological Manifestations of Reflux Disease in Indian Condition: A Base Line Data Generation
 Suddhasheel Roy, Rajiv Kumar Jain Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1114 Diverged Otorhinolaryngological Manifestations of Reflux Disease in Indian Condition: A Base Line Data Generation 1 Suddhasheel
Suddhasheel Roy, Rajiv Kumar Jain Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1114 Diverged Otorhinolaryngological Manifestations of Reflux Disease in Indian Condition: A Base Line Data Generation 1 Suddhasheel
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION
 DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors
 REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Silent reflux (also known as LPR or EOR)
 ENT - Information for patients Silent reflux (also known as LPR or EOR) Introduction This leaflet explains what your condition is, why it happens, what the symptoms are and how it can be managed. If there
ENT - Information for patients Silent reflux (also known as LPR or EOR) Introduction This leaflet explains what your condition is, why it happens, what the symptoms are and how it can be managed. If there
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
Dysphagia Questionnaire. Referring Doctor:
 Dysphagia Questionnaire Name: Date of Birth: Address: Referring Doctor: Diagnosis: Phone number: Email: What are your complaints regarding your swallowing: Date and onset of swallowing problems: Please
Dysphagia Questionnaire Name: Date of Birth: Address: Referring Doctor: Diagnosis: Phone number: Email: What are your complaints regarding your swallowing: Date and onset of swallowing problems: Please
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL
 LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL A randomized, open label, three arm parallel design, single-site study, comparing the effects of esomeprazole and alginate on top of lifestyle guidance
LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL A randomized, open label, three arm parallel design, single-site study, comparing the effects of esomeprazole and alginate on top of lifestyle guidance
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Outline. Outline. Definition. Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Definitions
 Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Original Article. K Semmanaselvan 1, Qayum I Mukaddam 2, Manoj Naik 3. Abstract
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 63 July 2015 27 Original Article An Open Label, Prospective, Single Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 63 July 2015 27 Original Article An Open Label, Prospective, Single Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
Silent Reflux. Adult Speech & Language Therapy Macclesfield District General Hospital
 Silent Reflux Adult Speech & Language Therapy 01625 661067 Macclesfield District General Hospital @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11067 Published: Jan 2019 Review: 31/12/2021 Page 1 Introduction Reflux is
Silent Reflux Adult Speech & Language Therapy 01625 661067 Macclesfield District General Hospital @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11067 Published: Jan 2019 Review: 31/12/2021 Page 1 Introduction Reflux is
Gastro esophageal reflux disease DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF
 Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Medicine. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 1. Introduction. 2. Methods OPEN
 Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Medicine Efficacy of acid suppression therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease-related chronic laryngitis Yue Yang, PhD a,b, Haitao Wu, PhD a,b, Jian Zhou, PhD a,b,
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Medicine Efficacy of acid suppression therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease-related chronic laryngitis Yue Yang, PhD a,b, Haitao Wu, PhD a,b, Jian Zhou, PhD a,b,
Hiatus Hernia. Endoscopy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS
 MEDICINĂ, no 2, 2011 ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS Monica Voineag 1,2, Vasile Costinescu 3, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 3 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr
MEDICINĂ, no 2, 2011 ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS Monica Voineag 1,2, Vasile Costinescu 3, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 3 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 LPRD? Joseph L. Russell, MD Faculty Advisor: Michael P. Underbrink, MD, MBA, FAC Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck urgery The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation November
LPRD? Joseph L. Russell, MD Faculty Advisor: Michael P. Underbrink, MD, MBA, FAC Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck urgery The University of Texas Medical Branch Grand Rounds Presentation November
Heartburn Overview. Causes & Risk Factors
 Return to Web version Heartburn Overview What is heartburn? Despite its name, heartburn doesn't affect the heart. Heartburn is a burning feeling in the lower chest, along with a sour or bitter taste in
Return to Web version Heartburn Overview What is heartburn? Despite its name, heartburn doesn't affect the heart. Heartburn is a burning feeling in the lower chest, along with a sour or bitter taste in
Frequency of Barrett Esophagus in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Original Article Frequency of Barrett Esophagus in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease From Military Hospital, Rawalpindi Obaid Ullah Khan, Abdul Rasheed Correspondence: Dr. Abdul
Original Article Frequency of Barrett Esophagus in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease From Military Hospital, Rawalpindi Obaid Ullah Khan, Abdul Rasheed Correspondence: Dr. Abdul
Acid reflux treatment for hoarseness (Protocol)
 Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane protocol, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 200, Issue 2 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane protocol, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 200, Issue 2 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal Mechanoreceptor Response
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh
 IJOPL Original article Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1107 Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh 1
IJOPL Original article Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1107 Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh 1
Speaker disclosure. Objectives. GERD: Who and When to Treat 7/21/2015
 GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Heartburn, also referred to acid reflux, happens when stomach acid flows back (refluxes) into your esophagus.
 WHILE almost everyone experiences mild heartburn from time to time and many individuals have some antacids or another medication on hand for its relief, talk to your doctor, if you have heartburn more
WHILE almost everyone experiences mild heartburn from time to time and many individuals have some antacids or another medication on hand for its relief, talk to your doctor, if you have heartburn more
Heartburn. Understanding and Treating. Heal n Cure For appointments call
 A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Understanding and Treating Heartburn What is Heartburn? It begins as a burning pain in the middle of your chest, behind the breastbone, often after a big meal. The burning
A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Understanding and Treating Heartburn What is Heartburn? It begins as a burning pain in the middle of your chest, behind the breastbone, often after a big meal. The burning
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training
 Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
Evergreen Speech & Hearing Clinic, Inc. Transforming Lives Through Improved Communication Since 1979
 Audiology Hearing Testing VRA VNG/VEMP OAE BAER/ECochG Hearing Aids Cochlear/Bone Implants Tinnitus CAPD EHDDI Speech-Language Pathology Language Voice Accent Modification Autism Evaluation & Treatment
Audiology Hearing Testing VRA VNG/VEMP OAE BAER/ECochG Hearing Aids Cochlear/Bone Implants Tinnitus CAPD EHDDI Speech-Language Pathology Language Voice Accent Modification Autism Evaluation & Treatment
4/24/2015. History of Reflux Surgery. Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux
 Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
GERD. gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD LPRD GERD. gastroesophageal reflux ; GER GERD
 114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acid-reflux-gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-in-adults-...
 Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
LPRD? Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease? November 2013
 TITLE: Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease? (LPRD?) SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, Department of Otolaryngology, The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB Health) DATE: November 26, 2013 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
TITLE: Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease? (LPRD?) SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, Department of Otolaryngology, The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB Health) DATE: November 26, 2013 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
*OC4501* OC-4567 NORTHWEST CLINIC FOR VOICE AND SWALLOWING NEW PATIENT INTAKE. Patient Name: Primary Care Provider: Provider Specialty:
 OC4501 Oregon Health & Science University *OC4501* Page 1 of 6 Patient Name: Primary Care Provider: Address: Other Provider: Address: Provider Specialty: Preferred Pharmacy: Please briefly describe the
OC4501 Oregon Health & Science University *OC4501* Page 1 of 6 Patient Name: Primary Care Provider: Address: Other Provider: Address: Provider Specialty: Preferred Pharmacy: Please briefly describe the
Extraesophageal GERD: Fact or Fiction?
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Optimizing the Upper GI: Mind, Mouth, and Stomach What Can Go Wrong With Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo
 Optimizing the Upper GI: Mind, Mouth, and Stomach What Can Go Wrong With Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship
Optimizing the Upper GI: Mind, Mouth, and Stomach What Can Go Wrong With Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship
Dysphagia. Conflicts of Interest
 Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Composite ph Predicts Esomeprazole Response in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Without Typical Reflux Syndrome
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Composite ph Predicts Esomeprazole Response in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Without Typical Reflux Syndrome Han-Chung
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Composite ph Predicts Esomeprazole Response in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Without Typical Reflux Syndrome Han-Chung
GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions. Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University
 GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University How to Maximize Your PPI Treatment? Improve compliance and adherance Fass R. Am J Gastroenterol.
GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University How to Maximize Your PPI Treatment? Improve compliance and adherance Fass R. Am J Gastroenterol.
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE. William M. Brady
 Drugs of Today 1998, 34(1): 25-30 Copyright PROUS SCIENCE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE William M. Brady Section of General Internal Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
Drugs of Today 1998, 34(1): 25-30 Copyright PROUS SCIENCE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE William M. Brady Section of General Internal Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
Is Rabeprazole A Safe Treatment for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children Ages 1-16 years?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Rabeprazole A Safe Treatment for Gastroesophageal
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Rabeprazole A Safe Treatment for Gastroesophageal
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that
 Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease
 CHAPTER 1 Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease M.ASHOKKUMAR DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY SRM UNIVERSITY ** Click on the arrow at the bottom right to move forward ** ** The arrow at the
CHAPTER 1 Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease M.ASHOKKUMAR DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY SRM UNIVERSITY ** Click on the arrow at the bottom right to move forward ** ** The arrow at the
Traditional Reflux Parameters and Not Impedance Monitoring Predict Outcome After Fundoplication in Extraesophageal Reflux
 The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Traditional Reflux Parameters and Not Impedance Monitoring Predict Outcome After Fundoplication in Extraesophageal
The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Traditional Reflux Parameters and Not Impedance Monitoring Predict Outcome After Fundoplication in Extraesophageal
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Effective Health Care
 Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Management Strategies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Executive Summary Background Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), defined as weekly heartburn
Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Management Strategies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Executive Summary Background Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), defined as weekly heartburn
EGD. John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008
 EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus
 Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
James Paget University Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Hiatus hernia. Patient Information
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, What is the Diagnosis and Treatment?
 NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, PPI REFRACTORY REFLUX: What is the Diagnosis and Treatment? Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc, FACG Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and
NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, PPI REFRACTORY REFLUX: What is the Diagnosis and Treatment? Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc, FACG Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls
 GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang
TBURN TBURN BURN ARTBURN EARTBURN EART HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST
 TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia
 Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
QUICK QUERIES. Topical Questions, Sound Answers
 QUICK QUERIES Topical Questions, Sound Answers Dyspepsia: An Evidence-Based Approach Alan B. R. Thomson, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG Presented at the University of Alberta s Medical Grand Rounds, University
QUICK QUERIES Topical Questions, Sound Answers Dyspepsia: An Evidence-Based Approach Alan B. R. Thomson, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG Presented at the University of Alberta s Medical Grand Rounds, University
For this session on the esophagus, I have selected three conditions that are somewhat related, namely gastro esophageal reflux disease, which from
 1 For this session on the esophagus, I have selected three conditions that are somewhat related, namely gastro esophageal reflux disease, which from here on I would refer to as GERD, eosinophilic esophagitis,
1 For this session on the esophagus, I have selected three conditions that are somewhat related, namely gastro esophageal reflux disease, which from here on I would refer to as GERD, eosinophilic esophagitis,
Acid reflux treatment for hoarseness (Review)
 Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2007, Issue 3 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2007, Issue 3 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS
 Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy C.S.QUA*,C.H.WONG*,K.GOPALA &K.L.GOH* *Division of Gastroenterology
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy C.S.QUA*,C.H.WONG*,K.GOPALA &K.L.GOH* *Division of Gastroenterology
Acidic and Non-Acidic Reflux During Sleep Under Conditions of Powerful Acid Suppression*
 Original Research SLEEP MEDICINE Acidic and Non-Acidic Reflux During Sleep Under Conditions of Powerful Acid Suppression* William C. Orr, PhD; Andrea Craddock, PhD; and Suanne Goodrich, PhD Background:
Original Research SLEEP MEDICINE Acidic and Non-Acidic Reflux During Sleep Under Conditions of Powerful Acid Suppression* William C. Orr, PhD; Andrea Craddock, PhD; and Suanne Goodrich, PhD Background:
Medical Policy Manual. Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November 2012 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014 Policy No: 186 Effective Date: May 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November 2012 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014 Policy No: 186 Effective Date: May 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children
 Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Mette Pedersen * The Medical Centre, Voice Unit, Østergade 18, 3, 1100 Copenhagen, Denmark
 Journal of Rhinolaryngo-Otologies, 2014, 2, 67-73 67 Acoustical Voice Measurements did Change after Treatment in Patients with Laryngo-Pharyngeal Reflux: A Prospective Randomized Study Including MDVP (Laryngograph
Journal of Rhinolaryngo-Otologies, 2014, 2, 67-73 67 Acoustical Voice Measurements did Change after Treatment in Patients with Laryngo-Pharyngeal Reflux: A Prospective Randomized Study Including MDVP (Laryngograph
SURGERY LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
AGA SECTION. Gastroenterology 2016;150:
 Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
