New daily-persistent headache and International Headache Society criteria: A retrospective analysis of 62 patients
|
|
|
- Eunice Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARTIGO ORIGINAL New daily-persistent headache and International Headache Society criteria: A retrospective analysis of 62 patients Novo critério da Sociedade Internacional de Cefaléia para cefaléia persistente e diária desde o início: análise retrospectiva de 62 pacientes Monzillo PH, Baise-Zung C, Nemoto PH, Costa AR Headache ambulatory of Discipline of Neurology of Santa Casa de São Paulo - Brazil Monzillo PH, Baise-Zung C, Nemoto PH, Costa AR. New daily-persistent headache and International Headache Society criteria: A retrospective analysis of 62 patients. Migrâneas cefaléias 2007;10(3):77-81 ABSTRACT Introduction. New Daily-Persistent Headache (NDPH) is described as a type of daily headache that becomes continuous in a short period of time (a maximum of three days). As any newly recognised headache condition, there is a paucity of reports. Therefore, its characteristics in different populations must be further described. Objectives. To describe the characteristics of NDPH in a Brazilian out-patient population. Methods. Sixty-two patients with a diagnosis of New Daily- Persistent Headache (NDPH), out of 1,348 records of outpatients regularly cared for at the Headache Clinic of Irmandade da Santa Casa de São Paulo - Brazil, had their charts reviewed. Results. Clinical characteristics were: female gender 58.1%; whole head pain=72.6%; moderate/strong intensity=93.6% and throbbing quality=43.5%. Of the 62 patients with the diagnosis of NDPH, only 19.4% did not have any clinical improvement when submitted to treatment. Diagnostic exams carried out in 56.5% of the patients contributed very little to the detection of an underlying organic substrate. Conclusion. Our results conflicted with those of the literature and with the IHS 2004 criteria regarding pain intensity, pain quality and the associated phenomena, isolated or in combinations. Perhaps the NDPH IHS 2004 diagnostic criteria should be revised. Key words: Chronic daily headaches; migraine; Chronic Tension-type headache; migraine; New daily-persistent headache; International Headache Society criteria. RESUMO Introdução. Cefaléia persistente e diária desde o início (CPDI) é descrita como um tipo de cefaléia diária que se torna continua em um curto período de tempo (máximo de três dias). Como toda condição recém-reconhecida, ainda há uma pequena quantidade de descrições. Assim sendo, suas características em diferentes populações devem ser descritas. Objetivos. Descrever as características da CPDI em uma população de pacientes brasileiros ambulatoriais. Mé- todos: Foram revisados os prontuários de 62 pacientes com o diagnóstico de CPDI, oriundos de uma população de pacientes do ambulatório de cefaléias da Irmandade da Santa Casa de São Paulo - Brasil. Resultados. As características clínicas foram: gênero feminino=58,1%; cefaléia holocraniana=72,6%; dor moderada a intensa=93,6%, qualidade pulsátil=43,5%. Dos 62 pacientes com o diagnóstico de CPDI, apenas 19,4% não apresentaram melhora ao serem submetidos a tratamento. A investigação complementar, realizada em 56,5% dos pacientes pouco contribuiu para a detecção de um substrato orgânico. Conclusão. Nossos resultados foram discordantes daqueles da literatura dos critérios da IHS de 2004, no que tange a intensidade da dor, sua qualidade e fenômenos concomitantes, isolados ou em combinação. Talvez os critérios diagnósticos da IHS/2004 devam ser revisados. Palavras alavras-chave: Cefaléia crônica diária; migrânea; cefaléia tipo-tensão crônica; cefaléia persistente e diária desde o início; critérios da International Headache Society. Migrâneas cefaléias, v.10, n.3, p.77-81, jul./ago./set
2 PAULO HÉLIO MONZILLO ET AL INTRODUCTION Vanast 2 first described New Daily-Persistent Headache (NDPH) in 1986 as a benign Chronic Daily Headache (CDH). In 1996, Silberstein and cols. 3 suggested diagnostic criteria for this entity as NDPH was not part of the 1988 IHS classification. 4 New daily-persistent headache, according to the International Headache Society (IHS 2004), 1 is described as a type of daily headache that becomes continuous in a short period of time (a maximum of three days). The pain is typically a pressing or tight non-pulsating throb, bilateral and of mild to moderate intensity. Photophobia, phonophobia, nausea and the attack intensity are not aggravated by routine physical exercises. The symptoms must be present for more than three months and not attributable to other causes. Headaches secondary to Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) hypotension, CSF hypertension, post-traumatic headache and headaches secondary to infectious clinical conditions (particularly where infecting agents are present) must always be diagnosed through appropriate investigations when suspected. In compliance with IHS 2004, NDPH can evolve during a period of time in two clinical ways: one autolimited presentation that disappears spontaneously after a few months without treatment and a chronic and normally intractable headache regardless of the therapeutic approach utilized. The IHS closes its comments suggesting that further research studies should be undertaken that better characterize its clinical features and propose possible pathophysiological mechanisms, and conclude definitively the separation from Chronic Tension-Type Headache (CTTH). Few reports are available in the literature involving large NDPH patient samples. 2,5 Its etiology remains unknown, 6 although some authors have tried to imply a temporal relationship to infectious clinical conditions, particularly Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). 7,8 We conducted a retrospective analysis of a large database of headache patients to describe the demographic data and clinical caractheristics of NDPH. PATIENTS AND METHODS We carried out a retrospective analysis consisting of a total of 1,348 records. Of this group, 241 patients presented a headache with a frequency of 15 days or more a month, for at least three months. Sixty-two patients had an NDPH diagnosis in accordance with Silberstein's proposed criteria for new daily persistent headache. 3 Data were recorded regarding the demographic aspects, clinical characteristics of the headache attacks, as well as the presence of accompanied symptoms. More than half the patients were submitted to secondary investigations. Patients with previously diagnosed headache conditions were excluded even if they presented with a clinical picture compatible with NDPH, in order not to include CTTH or CDH bearers. We also recorded the therapeutic recommendations given at the first appointment in our out-patient clinic (abortive or prophylactic) that resulted in clinical improvement, or the treatment scheme substituted when patients did not present any improvement. RESULTS Thirty-six patients (58.1%) were female. The average age at the beginning of the symptoms was of 40.5 years, slightly lower among women (36.7) when compared to men (44.3) (Figure1). Female Male Figure1: Age at the beginning of symptoms The average time delay between initial symptoms and the first appointment at our clinic was 5.9 years. The bilateral localization of the attack occurred in 45 patients (72.6%). Pulsating-type pain was present in 43% of the patients, followed by stabbing pain in 14 (22.6%), pressing in 12 (19.4%), tightening in 4 (6.5%) and burning in 3 (4.8%). Two patients (3.2%) cited different pain types in separate attacks (tightening and pulsating) (Table 1). Strong to moderately intensive attacks were found in equal percentages (46.8%) in our sample, and mild attacks in four patients (6.4%) (Figure 2). Only 11 patients (17.7%) did not refer to any 78 Migrâneas cefaléias, v.10, n.3, p.77-81, jul./ago./set. 2007
3 NEW DAILY-PERSISTENT HEADACHE AND INTERNATIONAL HEADACHE SOCIETY CRITERIA: A RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF 62 PATIENTS Table 1. Analysis related to pain quality Pain quality N (62) % Pulsating Stabbing Pressing Tightening Burning Tightening + Pulsating Figure 2: Pain Intensity Table 2. Symptoms related to headaches Symptoms N(62) % Pt N Pn + Pt Pn + Pt + N Pn+ Pt+ N+ V N + V Pt + N Pt + Pn + O Pt + N + O Pt + Pn + D N + D Pt + Pn + N + V + O AP D Absence of symptoms Pt: photophobia; N: nausea Pn: phonophobia; V: vomit; O: osmophobia; D: dizziness; AP: autonomic phenomenae; AS: absence of symptoms symptoms associated with their attacks. All other patients presented isolated or associated symptoms that usually accompany migraine attacks. Two patients reported the presence of autonomic symptoms related to their attacks (Table 2). Fifty-five patients (56.5%) were submitted to further investigation. Within this group, it was possible to establish a factor temporally related to the initial symptoms in only three patients. Two patients reported a history of headaches after cranial-cerebral trauma and one patient had headaches following an otomastoiditis infection. Head computed tomography (Head CT-scan) was not useful in detecting abnormalities that justified the clinical symptoms. In the mastodectomized patient, the CT evidenced only a hypoattenuated area in the right temporal region adjacent to the mastoidectomy. In the remaining patients, radiological and laboratorial findings include the following: a venous angioma (right frontal) and a left frontal cavernoma, revealed by Magnetic -Ressonance Imaging (MRI). Onepatient, had a positive serology testfor HIV virus, however without an AIDS-defining clinical picture. Despite the daily frequency and the intensity of the attacks being predominantly moderate to strong, only 28 patients (45.2%) of our sample constantly and abusively used abortive medication on the occasion of their first appointment. Different prophylactic schemes were used, as monotherapy or in different combinations. It is important to point out that the majority of the patients had already used at least one of the prophylactic medicines - at the moment of their first evaluation at our clinic. The list of prophylactic medicines used by those patients during their treatments is illustrated in Table 3. Only ten patients (16.1%) remained totally asymptomatic and twelve patients (19.4%) did not respond to any of the proposed treatments. Twenty-six patients (41.9%) reported a partial improvement of symptoms; in ten of the patients the improvement obtained was related to the attack frequency, in two patients to the attack duration and in 14 patients to the pain intensity. In 14 (22.6%) records it was not possible to obtain data regarding therapeutic efficiency. Table 3. Prophylactic Medication Used Drug Number of patients (%) Amitriptyline 44 (71.0) Flunarizine 19 (30.6) Sodium Valproate 17 (27.4) Propranolol 12 (19.3) Nortriptylin 11 (17.7) Atenolol 06 (9.7) Topiramate 03 (4.8) Clorpromazin 03 (4.8) Carbamazepine 02 (3.2) Prednisone 02 (3.2) Pizotifen 02 (3.2) Oxcarbazepine 01 (1.6) Lithium Carbonate 01 (1.6) Migrâneas cefaléias, v.10, n.3, p.77-81, jul./ago./set
4 PAULO HÉLIO MONZILLO ET AL DISCUSSION Although there are few reports refering to this type of headache in the literature, the NDPH has been a part of the IHS classification since 2004, included in group 4 - Other primary headaches 1. The major characteristic of the NDPH is that the headaches are persistentfrom the onset. Although many patients can't relate the initial symptoms to any cause, a majority are able to pinpoint the start date, even though time has past. Some authors suggest that the initial headache occurs in relation to temporal viral conditions, infections, extracranial surgeries or stressing life events. 6,9,10,11,15 Li and Rozen 6 observed that more than 80% of the patients could recallthe exact date of the initial symptoms and 54% correlated the start of the symptoms to a precipitating event, generally a flu type illness. Other authors go further, linking these infectious conditions to the Influenzae 9 virus or to the Epstein-Baar 7,8 virus with the intention of attributing the NDPH to an infectious etiopathogenesis. This did not occur in any of our cases. There was no (spontaneous) mention suggesting viral infections at the time of the initial symptoms. More than half of the patients (56.5%) of our sample were submitted to imaging and laboratory exams that did little to contribute to the diagnostic elucidation. The rest of the patients did not follow the investigation protocol because they were refered to our clinic many years after the start of symptoms (average of 5.9 years). Only in three patients was it possible to link the start of the symptoms to a putative causal factor. In this analysis, we observed the predominance of female NDPH, as previously shown by the Vanast report and Li and Rozen's. In only one recent research study was it reported that males had a preponderance of NDPH. The IHS diagnostic criteria does not take into consideration the disparity between males and females. 2,6,11 In our study, the average age for the onset of NDPH was 40.5 years, women had their initial headache symptoms earlier than men, and this data is in accordance with the literature. 6 This demographic data is also not mentioned in the IHS criteria. The majority of our patients presented a headache localized bilaterally, which parallels the observations by Li and Rozen, and Takase and cols. They also described the pain bilateral in accordance with the IHS criteria, although this is not obligatory. 6,11,1 Pain referred to as pulsating was reported in 43.5% of our sample. Various authors also consider this as the most common related pain. 5,6,11,12 We call attention to the fact that this conflicts directly with the current IHS 2004 classification that describes the type of pain of NDPH as being pressing or tightening but never pulsating. 1 Nearly half the sample (46.8%) classified the intensity of their attack as being strong but when combined with those who refered to the pain as moderate, the amount increases to 93.5%. Li and Rozen 6,5 had already suggested as one of the diagnostic criteria of NDPH a pain intensity variation between moderate and strong. Therefore, we question the IHS criteria that refers to the pain intensity of the NDPH as being mild, as fluctuations can occur. 1 In contradiction to the IHS 2004 criteria, 82.3% of our patients presented similar migraine attacks as opposed to CTTH, evidenced by the association of pain with: nausea, photophobia and phonophobia, isolated or in different combinations. These three symptoms were the most relevant in our experience. Our results are in total 2,6, 9,12 accordance with the literature. Few reports in the literature make a recommendation regarding the treatment of NDPH. Various therapeutic strategies were used by the patients in our out-patient clinic in monotherapy or in association. We observed clinical improvements in 36 patients (58%) and complete remission of pain symptoms in 10 patients (16.1%). That percentage of partial and complete therapeutic response is significant, considering the degree of the symptoms. Vanast 2 describes that a number of patients can improve with medical therapy treatment, however, he emphasizes that they may have difficulty accessing that treatment. Rozen also reiterates the difficulty to define the best treatment strategy for NDPH, emphasizing that succesful responses occurred in a limited amount of patients with the use of gabapentin and topiramate. 13 CONCLUSION For nearly two decades, publications are available for this intriguing type of headache. Clinical and demographic data involving large series of patients are still lacking, not to mention a total non-acquaintance of the etiopatogenesis of this entity. In this article, we emphasize that the NDPH holds a clinical similarity with migraines but cannot be confused with the CTTC, since the latter is an evolution of the Tension-Type Headache (TTH) according to the IHS 2004 diagnostic criteria. There are relevant conflicts in the clinical aspects observed in our sample research and in the literature, 2,6,9,12 80 Migrâneas cefaléias, v.10, n.3, p.77-81, jul./ago./set. 2007
5 NEW DAILY-PERSISTENT HEADACHE AND INTERNATIONAL HEADACHE SOCIETY CRITERIA: A RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF 62 PATIENTS when compared with the diagnostic criteria established by IHS 2004 such as: pain intensity, pain quality and the concomitant phenomena present in migraine attacks: nausea, photophobia and phonophobia, in an isolated way or in different combinations. Therefore we suggest that the diagnostic criteria established by IHS 2004 should be revised in the future. Additional clinical characterization and pathophysiological research must be stimulated in order to improve our understanding of this particular entity. REFERENCES 1. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd Edition. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(suppl): Vanast WJ. New daily persistent headaches: definition of a benign syndrome. Headache. 1986;26: Silberstein SD; Lipton RB; Sliwinski M. Classification of daily and near-daily headaches: field trial of revised HIS criteria. Neurology. 1996;47: Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. Classification and Diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Cephalalgia. 1988;8(supp7): Rozen TD. New daily persistent headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2003;7: Li D, Rozen TD. The clinical characteristics of new daily persistent headache. Cephalalgia. 2002;22: Diaz-Mitoma F; Vanast WJ; Tyrrel DLJ. Increased frequency of Epstein-Barr virus excretion in patients with new daily persistent headaches. The Lancet. 1987;1: Hamada T, Oshima K, Ide Y, Sakato S, Takamori M. A case of new daily persistent headache with elevated antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus (abstract). Jpn J Med. 1991;30(2):161:3. 9. Evans, RW; Rozen, TD. Etiology and treatment of new daily persistent headache. Headache. 2001;41: Takase Y, Nakano M, Tatsumi C. Primary new daily persistent Headache (NDPH): clinical characteristics of forty-three cases in Japan. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2003;43(9): Abstract. 11. Takase Y, Nakano M, Tatsumi C, Matsuyama T. Clinical features, effectiveness of drug-based treatment, and prognosis of new daily persistent headache (NDPH): 30 cases in Japan. Cephalagia. 2004;24: Goadsby, PJ; Boes, C. New daily persistent headache. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72: ii6-ii Rozen TD. Succesful treatment of new daily persistent headache with gabapentin and topiramate. Headache. 2002;42:433. Disclosure: The authors have reported no conflicts of interest Recebido: 29/08/ 2007 Aceito: 31/ Endereço paa correspondência Dr. Paulo H. Monzillo Av. Albert Einstein, 627 room 1306 São Paulo-Brazil Tel-55(11) ; Fax: 55(11) monzillo@einstein.br Migrâneas cefaléias, v.10, n.3, p.77-81, jul./ago./set
Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Daily Headache Patients Visit to University Hospital
 Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Daily Headache Patients Visit to University Hospital Jin-Kuk Do, M.D., Hee-Jong Oh, M.D., Dong-Kuck Lee, M.D. Department of Neurology, Taegu Hyosung Catholic University
Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Daily Headache Patients Visit to University Hospital Jin-Kuk Do, M.D., Hee-Jong Oh, M.D., Dong-Kuck Lee, M.D. Department of Neurology, Taegu Hyosung Catholic University
Prevalence of new daily persistent headache in the general population. The Akershus study of chronic headachecha_
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01842.x Prevalence of new daily persistent headache in the general population. The Akershus study of chronic headachecha_1842 1149..1155 RB Grande 1,2, K Aaseth 1,3, C Lundqvist
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01842.x Prevalence of new daily persistent headache in the general population. The Akershus study of chronic headachecha_1842 1149..1155 RB Grande 1,2, K Aaseth 1,3, C Lundqvist
Recurrent Headaches in Children -- An Analysis of 47 Cases
 ---------------------------------------------- Recurrent Headaches in Children -- An Analysis of Cases I H M I Hussain, MRCP Neurology Unit Paediatric Institute, Kuala Lumpur Hospital, )aian Pahang, 50586
---------------------------------------------- Recurrent Headaches in Children -- An Analysis of Cases I H M I Hussain, MRCP Neurology Unit Paediatric Institute, Kuala Lumpur Hospital, )aian Pahang, 50586
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
A review of 50 cases of bath-related headache: clinical features and possible diagnostic criteria
 VIEW AND REVIEW http://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x20180039 A review of 50 cases of bath-related headache: clinical features and possible diagnostic criteria Uma revisão de 50 casos de cefaleia relacionada
VIEW AND REVIEW http://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x20180039 A review of 50 cases of bath-related headache: clinical features and possible diagnostic criteria Uma revisão de 50 casos de cefaleia relacionada
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, II. Management of Refractory Headaches
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Differentiating Migraine from Other Headache Types to Target Treatment Peter J. Goadsby, MD, PhD
 Differentiating Migraine from Other Headache Types to Target Treatment Peter J. Goadsby, MD, PhD University of California, San Francisco San Francisco, CA King's College London London, England Learning
Differentiating Migraine from Other Headache Types to Target Treatment Peter J. Goadsby, MD, PhD University of California, San Francisco San Francisco, CA King's College London London, England Learning
New daily persistent headache: Should migrainous features be incorporated?
 Original Article New daily persistent headache: Should migrainous features be incorporated? Cephalalgia 31(15) 1561 1569! International Headache Society 2011 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article New daily persistent headache: Should migrainous features be incorporated? Cephalalgia 31(15) 1561 1569! International Headache Society 2011 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture
 Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
New Daily Persistent Headache in Children and Adolescents
 Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep (2010) 10:127 132 DOI 10.1007/s11910-010-0097-3 New Daily Persistent Headache in Children and Adolescents Eric P. Baron & A. David Rothner Published online: 24 February 2010 #
Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep (2010) 10:127 132 DOI 10.1007/s11910-010-0097-3 New Daily Persistent Headache in Children and Adolescents Eric P. Baron & A. David Rothner Published online: 24 February 2010 #
Original Article INTRODUCTION
 58 REVISTA PAULISTA DE MEDICINA Original Article Marcelo Bigal Carlos Alberto Bordini José Geraldo Speciali Headache in an emergency room in Brazil Department of Neurology, São Paulo University, School
58 REVISTA PAULISTA DE MEDICINA Original Article Marcelo Bigal Carlos Alberto Bordini José Geraldo Speciali Headache in an emergency room in Brazil Department of Neurology, São Paulo University, School
Zonisamide for migraine prophylaxis in refractory patients
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology March 2006 Zonisamide for migraine prophylaxis in refractory patients Avi Ashkenazi
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology March 2006 Zonisamide for migraine prophylaxis in refractory patients Avi Ashkenazi
Application of ICHD 2nd edition criteria for primary headaches with the aid of a computerised, structured medical record for the specialist
 J Headache Pain (2005) 6:205 210 DOI 10.1007/s10194-005-0186-x ICHD-II: EVALUATION AND PROPOSALS Paola Sarchielli Mauro Pedini Andrea Alberti Cristiana Rossi Antonio Baldi Ilenia Corbelli Paolo Calabresi
J Headache Pain (2005) 6:205 210 DOI 10.1007/s10194-005-0186-x ICHD-II: EVALUATION AND PROPOSALS Paola Sarchielli Mauro Pedini Andrea Alberti Cristiana Rossi Antonio Baldi Ilenia Corbelli Paolo Calabresi
Chief Complaint. History. History of Similar Episodes. A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache
 A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache Chief Complaint Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 10 year-old boy presented with his fifth lifetime bout of left-sided head pain followed by diplopia. Amy A. Gelfand, MD
A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache Chief Complaint Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 10 year-old boy presented with his fifth lifetime bout of left-sided head pain followed by diplopia. Amy A. Gelfand, MD
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012
 Headache and reproductive life Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012 52 years old woman, English teacher in primary school, married, mother of two, with a history of migraine without aura. Over the last 6 months
Headache and reproductive life Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012 52 years old woman, English teacher in primary school, married, mother of two, with a history of migraine without aura. Over the last 6 months
Post-infectious headache: a reactive headache?
 J Headache Pain (2011) 12:467 473 DOI 10.1007/s10194-011-0346-0 ORIGINAL Post-infectious headache: a reactive headache? Sanjay Prakash Niyati Patel Purva Golwala Rushad Patell Received: 21 March 2011 /
J Headache Pain (2011) 12:467 473 DOI 10.1007/s10194-011-0346-0 ORIGINAL Post-infectious headache: a reactive headache? Sanjay Prakash Niyati Patel Purva Golwala Rushad Patell Received: 21 March 2011 /
Clinical profile of patients with chronic headache in a tertiary care hospital
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Senthil C et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Aug;3(3):721-726 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20162524
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Senthil C et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Aug;3(3):721-726 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20162524
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
6/2/2017. Objectives. Statement of Problem: Migraine Headaches Are Common. Chronic Headache In Pediatrics, Botox and Beyond
 Chronic Headache In Pediatrics, Botox and Beyond Ken Mack MD PhD Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Understand pediatric chronic headache presentations Review evidence for the treatment of chronic
Chronic Headache In Pediatrics, Botox and Beyond Ken Mack MD PhD Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Understand pediatric chronic headache presentations Review evidence for the treatment of chronic
Does repeated subcutaneous administration of sumatriptan produce an unfavorable evolution in cluster headache?
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:110 114 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0078-5 ORIGINAL Virginie Dousset Virginie Chrysostome Bruno Ruiz S. Irachabal Magalie Lafittau Françoise Radat Bruno Brochet Patrick Henry Does repeated
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:110 114 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0078-5 ORIGINAL Virginie Dousset Virginie Chrysostome Bruno Ruiz S. Irachabal Magalie Lafittau Françoise Radat Bruno Brochet Patrick Henry Does repeated
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention
 Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Atypical presentations of cluster headache
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Nee Kong CHEW, Chong Tin TAN, Heng Thay CHONG, Yau Hoong CHAN, Kuoh Ren CHONG, Hee Hong LAM, Yan Beng NGE, Chek Tung NGO.
 Neurol J Southeast Asia 2001; 6 : 13 17 Ramadan headache Nee Kong CHEW, Chong Tin TAN, Heng Thay CHONG, Yau Hoong CHAN, Kuoh Ren CHONG, Hee Hong LAM, Yan Beng NGE, Chek Tung NGO. Department of Medicine,
Neurol J Southeast Asia 2001; 6 : 13 17 Ramadan headache Nee Kong CHEW, Chong Tin TAN, Heng Thay CHONG, Yau Hoong CHAN, Kuoh Ren CHONG, Hee Hong LAM, Yan Beng NGE, Chek Tung NGO. Department of Medicine,
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Headache. Karen Thaxter
 Headache Karen Thaxter An eight year old girl is taken to her paediatrician because she has been complaining of almost daily pain at the back of her head for the past 4 months. She states that each headache
Headache Karen Thaxter An eight year old girl is taken to her paediatrician because she has been complaining of almost daily pain at the back of her head for the past 4 months. She states that each headache
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Who discovers the cutaneous melanoma * Quem descobre o melanoma cutâneo *
 244 Clinical, Epidemiological, Laboratory and Therapeutic Investigation Who discovers the cutaneous melanoma * Quem descobre o melanoma cutâneo * Marcus Maia 1 Marianne Basso 2 Abstract: BACKGROUND - In
244 Clinical, Epidemiological, Laboratory and Therapeutic Investigation Who discovers the cutaneous melanoma * Quem descobre o melanoma cutâneo * Marcus Maia 1 Marianne Basso 2 Abstract: BACKGROUND - In
PPH AND BIOLOGICAL GLUE IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH RISK OF BLEEDING IN STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY
 PPH AND BIOLOGICAL GLUE IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH RISK OF BLEEDING IN STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
PPH AND BIOLOGICAL GLUE IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH RISK OF BLEEDING IN STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Migraine Migraine Age Specific Prevalence in the United States. Headache International Headache Society Classification
 28 Primary Care Medicine Principles and Practice 29 October 28 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification
28 Primary Care Medicine Principles and Practice 29 October 28 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification
Inpatient Treatment of Status Migraine With Dihydroergotamine in Children and Adolescents
 Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b
 UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. No relevant financial relationships
 Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
UNDERSTANDING CHRONIC MIGRAINE. Learn about diagnosis, management, and treatment options for this headache condition
 UNDERSTANDING CHRONIC MIGRAINE Learn about diagnosis, management, and treatment options for this headache condition 1 What We re Going to Cover Today The symptoms and phases of migraine Differences between
UNDERSTANDING CHRONIC MIGRAINE Learn about diagnosis, management, and treatment options for this headache condition 1 What We re Going to Cover Today The symptoms and phases of migraine Differences between
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
Coexistence of migraine and idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema
 / GX'~C1~.. Coexistence of migraine and idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema Ninan T. Mathew, MD; K. Ravishankar, MD; and Luis C. Sanin, MD!
/ GX'~C1~.. Coexistence of migraine and idiopathic intracranial hypertension without papilledema Ninan T. Mathew, MD; K. Ravishankar, MD; and Luis C. Sanin, MD!
PROPRANOLOL vs FLUNARIZINE vs FLUNARIZINE PLUS PROPRANOLOL IN MIGRAINE WITHOUT AURA PROPHYLAXIS
 PROPRANOLOL vs FLUNARIZINE vs FLUNARIZINE PLUS PROPRANOLOL IN MIGRAINE WITHOUT AURA PROPHYLAXIS A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL CARLOS ALBERTO BORDINI*, MARCO ANTÔNIO ARRUDA ** MARCELO CEDRINHO CICIARELLI**, JOSÉ
PROPRANOLOL vs FLUNARIZINE vs FLUNARIZINE PLUS PROPRANOLOL IN MIGRAINE WITHOUT AURA PROPHYLAXIS A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL CARLOS ALBERTO BORDINI*, MARCO ANTÔNIO ARRUDA ** MARCELO CEDRINHO CICIARELLI**, JOSÉ
Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in Children
 original ARTICLE Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in Children How to Cite this Article: Nejad Biglari H, Karimzadeh P, Mohammadi Kord-kheyli M, Hashemi SM. Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in
original ARTICLE Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in Children How to Cite this Article: Nejad Biglari H, Karimzadeh P, Mohammadi Kord-kheyli M, Hashemi SM. Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Cluster headache in women: clinical characteristics and comparison with cluster headache in men
 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:613 617 613 Department of Neurology, JeVerson Headache Center, Thomas University Hospital, 111 South 11th Street, Gibbon Building, Suite 8130, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:613 617 613 Department of Neurology, JeVerson Headache Center, Thomas University Hospital, 111 South 11th Street, Gibbon Building, Suite 8130, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Is Topiramate Effective in Preventing Pediatric Migraines?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Topiramate Effective in Preventing
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Topiramate Effective in Preventing
Classification of headaches
 Classification of headaches Jasna Zidverc Trajković Headache center Headache in adults: 1-year prevalence 13.4 Kryst 35.9 Miranda 28.7 Jaillard 87.3 O Brien 63.1 Wiehe 37.3 Lavados 59.7 Schwartz 76.0 Boardman
Classification of headaches Jasna Zidverc Trajković Headache center Headache in adults: 1-year prevalence 13.4 Kryst 35.9 Miranda 28.7 Jaillard 87.3 O Brien 63.1 Wiehe 37.3 Lavados 59.7 Schwartz 76.0 Boardman
Disease Description and Statistics Current State: Medicare Denial of Coverage Expert Opinion Clinical Studies Gap in Medical Care Cost to US
 Oxygen Therapy Disease Description and Statistics Current State: Medicare Denial of Coverage Expert Opinion Clinical Studies Gap in Medical Care Cost to US Taxpayers Recommendations Cluster headaches are
Oxygen Therapy Disease Description and Statistics Current State: Medicare Denial of Coverage Expert Opinion Clinical Studies Gap in Medical Care Cost to US Taxpayers Recommendations Cluster headaches are
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Tension-type Headaches
 Stress-related Diseases Tension-type Headaches JMAJ 45(5): 202 206, 2002 Koji TSUBOI Professor, Department of Psychosomatic Medicine, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Tension-type headaches
Stress-related Diseases Tension-type Headaches JMAJ 45(5): 202 206, 2002 Koji TSUBOI Professor, Department of Psychosomatic Medicine, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Tension-type headaches
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
PREVALENCE BY HEADACHE TYPE
 CLINICAL CLUES AND CLINICAL RULES: PRIMARY VS SECONDARY HEADACHE * Based on a presentation by David W. Dodick, MD ABSTRACT Headache is a common condition, accounting for many specialist office visits annually.
CLINICAL CLUES AND CLINICAL RULES: PRIMARY VS SECONDARY HEADACHE * Based on a presentation by David W. Dodick, MD ABSTRACT Headache is a common condition, accounting for many specialist office visits annually.
Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II
 Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II Richard B. Lipton, MD; Seymour Diamond, MD; Michael Reed, PhD; Merle L. Diamond, MD; Walter F. Stewart, MPH, PhD Objective.
Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II Richard B. Lipton, MD; Seymour Diamond, MD; Michael Reed, PhD; Merle L. Diamond, MD; Walter F. Stewart, MPH, PhD Objective.
Preventive treatment of migraine. Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 Preventive treatment of migraine Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA No disclosures Disclosures Many preventive treatments for migraine are not FDA-approved
Preventive treatment of migraine Rebecca Burch, MD Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA No disclosures Disclosures Many preventive treatments for migraine are not FDA-approved
Venlafaxine versus amitriptyline in the prophylactic treatment of migraine: randomized, double-blind, crossover study
 Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 107 (2004) 44 48 Venlafaxine versus amitriptyline in the prophylactic treatment of migraine: randomized, double-blind, crossover study Serpil Bulut a,, M. Said Berilgen
Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 107 (2004) 44 48 Venlafaxine versus amitriptyline in the prophylactic treatment of migraine: randomized, double-blind, crossover study Serpil Bulut a,, M. Said Berilgen
Headache evaluation and management after concussion. Assistant Professor
 Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
ARTICLE DOI: / X
 DOI: 10.1590/0004-282X20140148 ARTICLE Amitriptyline and aerobic exercise or amitriptyline alone in the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized comparative study Amitriptilina e exercício aeróbico
DOI: 10.1590/0004-282X20140148 ARTICLE Amitriptyline and aerobic exercise or amitriptyline alone in the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized comparative study Amitriptilina e exercício aeróbico
11. HEADACHE 1. Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH
 11. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language
11. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language
Comorbidities of Migraine
 Comorbidities of Migraine Richard B. Lipton, MD Edwin S Lowe Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, Montefiore Headache Center Albert Einstein College of Medicine Overview What is comorbidity?
Comorbidities of Migraine Richard B. Lipton, MD Edwin S Lowe Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, Montefiore Headache Center Albert Einstein College of Medicine Overview What is comorbidity?
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
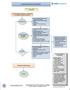 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania: differential diagnosis
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 2004254244248Original ArticleCH and PH: differential diagnosisj Zidverc-Trajkovic et al. Cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania:
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 2004254244248Original ArticleCH and PH: differential diagnosisj Zidverc-Trajkovic et al. Cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania:
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Specific features of migraine syndrome in children
 J Headache Pain (2006) 7:206 210 DOI 10.1007/s10194-006-0312-4 RAPID COMMUNICATION Marija Knezevic-Pogancev Specific features of migraine syndrome in children Received: 16 April 2006 Accepted in revised
J Headache Pain (2006) 7:206 210 DOI 10.1007/s10194-006-0312-4 RAPID COMMUNICATION Marija Knezevic-Pogancev Specific features of migraine syndrome in children Received: 16 April 2006 Accepted in revised
Migraine much more than just a headache
 Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Combination of pharmacotherapy and lidocaine analgesic block of the peripheral trigeminal branches for trigeminal neuralgia: a pilot study
 ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/0004-282X20150077 Combination of pharmacotherapy and lidocaine analgesic block of the peripheral trigeminal branches for trigeminal neuralgia: a pilot study Combinação de farmacoterapia
ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/0004-282X20150077 Combination of pharmacotherapy and lidocaine analgesic block of the peripheral trigeminal branches for trigeminal neuralgia: a pilot study Combinação de farmacoterapia
Diagnosing headache. The clinician should approach the diagnosis of. Secondary headache. Primary headache. Blue and red flag headaches
 Headache THEME Diagnosing headache BACKGROUND A systematic approach to the diagnosis of primary and secondary headache disorders requires the measurement of the frequency and the duration of headache.
Headache THEME Diagnosing headache BACKGROUND A systematic approach to the diagnosis of primary and secondary headache disorders requires the measurement of the frequency and the duration of headache.
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Frequency Domain Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Tension Type Headache: A Case Control
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Frequency Domain Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Tension Type Headache: A Case Control
Specific Objectives A. Topics to be lectured and discussed at the plenary sessions
 Specific Objectives A. Topics to be lectured and discussed at the plenary sessions 0. Introduction: Good morning ICHD-III! Let s start at the very beginning. When you read you begin with A-B-C, so when
Specific Objectives A. Topics to be lectured and discussed at the plenary sessions 0. Introduction: Good morning ICHD-III! Let s start at the very beginning. When you read you begin with A-B-C, so when
Article. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2011;69(1):79-84
 Article Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2011;69(1):79-84 ABSTRACT Background: Ventricular drainage has played an important role in the management of traumatic brain-injured patients. The aim of the present study was
Article Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2011;69(1):79-84 ABSTRACT Background: Ventricular drainage has played an important role in the management of traumatic brain-injured patients. The aim of the present study was
Intraoperative frozen section assessment in the evaluation of axillary sentinel lymph node in breast cancer
 J Bras Patol Med Lab v. 48 n. 5 p. 369-373 outubro 2012 artigo original original paper Intraoperative frozen section assessment in the evaluation of axillary sentinel lymph node in breast cancer Primeira
J Bras Patol Med Lab v. 48 n. 5 p. 369-373 outubro 2012 artigo original original paper Intraoperative frozen section assessment in the evaluation of axillary sentinel lymph node in breast cancer Primeira
Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION. Headaches HEADACHE DISORDERS. R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP
 Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION Headaches of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada 2nd edition (ICHD-II)
Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION Headaches of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada 2nd edition (ICHD-II)
Frequency of types of headache in the tertiary care center of the Hospital das Clínicas of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, MG, Brazil
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of types of headache in the tertiary care center of the Hospital das Clínicas of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, MG, Brazil Ariovaldo Alberto da Silva Junior 1, Rafael
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of types of headache in the tertiary care center of the Hospital das Clínicas of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, MG, Brazil Ariovaldo Alberto da Silva Junior 1, Rafael
Learning objectives 6/20/2018
 Cognitive impairment of patients with chronic migraine, in a neuropsychological assessment, does not depend on the use of topiramate or comorbidities Ferreira KS, MD, PhD Professor, Neurology Clinic, Medicine
Cognitive impairment of patients with chronic migraine, in a neuropsychological assessment, does not depend on the use of topiramate or comorbidities Ferreira KS, MD, PhD Professor, Neurology Clinic, Medicine
Tension-Type Headache
 Chronic Headache Tension-Type Headache Its mechanism and treatment JMAJ 47(3): 130 134, 2004 Manabu SAKUTA Chief Professor, First Internal Medicine (Neurology), Kyorin University Abstract: Tension-type
Chronic Headache Tension-Type Headache Its mechanism and treatment JMAJ 47(3): 130 134, 2004 Manabu SAKUTA Chief Professor, First Internal Medicine (Neurology), Kyorin University Abstract: Tension-type
A new questionnaire for assessment of adverse events associated with triptans: methods of assessment influence the results. Preliminary results
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S112 S116 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0123-4 Michele Feleppa Fred D. Sheftell Luciana Ciannella Amedeo D Alessio Giancarlo Apice Nino N. Capobianco Donato M.T. Saracino Walter Di Iorio
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S112 S116 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0123-4 Michele Feleppa Fred D. Sheftell Luciana Ciannella Amedeo D Alessio Giancarlo Apice Nino N. Capobianco Donato M.T. Saracino Walter Di Iorio
1. On how many days in the last 3 months did you miss work or school because of your headaches?
 The Migraine Disability Assessment Test The MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) questionnaire was put together to help you measure the impact your headaches have on your life. The information on this
The Migraine Disability Assessment Test The MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) questionnaire was put together to help you measure the impact your headaches have on your life. The information on this
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
Subject: CGRP Inhibitors
 ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Archived: 08/01/18 09-J2000-98 Original Effective Date: 06/15/18 Reviewed: 05/09/18 Revised: 08/01/18 Next Review: ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Subject: CGRP Inhibitors THIS
ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Archived: 08/01/18 09-J2000-98 Original Effective Date: 06/15/18 Reviewed: 05/09/18 Revised: 08/01/18 Next Review: ARCHIVED (NOT ACTIVE RETIRED) Subject: CGRP Inhibitors THIS
Quality of life of chronic renal patients on hemodialysis in Marília, SP, Brazil
 Original Article Artigo Original Quality of life of chronic renal patients on hemodialysis in Marília, SP, Brazil A qualidade de vida dos pacientes renais crônicos em hemodiálise na região de Marília,
Original Article Artigo Original Quality of life of chronic renal patients on hemodialysis in Marília, SP, Brazil A qualidade de vida dos pacientes renais crônicos em hemodiálise na região de Marília,
Neurotrophic factors in tension-type headache
 ARTICLE DOI: 0.590/0004-282X2050000 Neurotrophic factors in tension-type headache Fatores neurotróficos na cefaleia do tipo tensional Renan B. Domingues, Halina Duarte, Natália P. Rocha 2, Antonio L. Teixeira,2
ARTICLE DOI: 0.590/0004-282X2050000 Neurotrophic factors in tension-type headache Fatores neurotróficos na cefaleia do tipo tensional Renan B. Domingues, Halina Duarte, Natália P. Rocha 2, Antonio L. Teixeira,2
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
This policy addresses only the type B formulation rimabotulinumtoxinb marketed as Myobloc.
 RimabotulinumtoxinB NDC CODE(S) 10454-0710-XX Myobloc 2500 UNIT/0.5ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0711-XX Myobloc 5000 UNIT/ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0712-XX Myobloc 10000 UNIT/2ML
RimabotulinumtoxinB NDC CODE(S) 10454-0710-XX Myobloc 2500 UNIT/0.5ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0711-XX Myobloc 5000 UNIT/ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0712-XX Myobloc 10000 UNIT/2ML
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis.
 Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
1/25/2018 ARE CGRP ANTAGONISTS ANY BETTER THAN CURRENT EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENTS? Disclosures: Objectives: Headache Division
 ARE CGRP ANTAGONISTS ANY BETTER THAN CURRENT EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENTS? Lawrence C Newman, MD, FAHS, FAAN Clinical Professor of Neurology Disclosures: Advisory Board: Alder, Allergan, Amgen, Lilly, Supernus,
ARE CGRP ANTAGONISTS ANY BETTER THAN CURRENT EVIDENCE BASED TREATMENTS? Lawrence C Newman, MD, FAHS, FAAN Clinical Professor of Neurology Disclosures: Advisory Board: Alder, Allergan, Amgen, Lilly, Supernus,
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MIGRAINE HEADACHE PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT 1ST EDITION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MIGRAINE HEADACHE PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT 1ST EDITION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 migraine headache prevention and management 1st edition migraine headache prevention and pdf
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MIGRAINE HEADACHE PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT 1ST EDITION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 migraine headache prevention and management 1st edition migraine headache prevention and pdf
