Imaging of DVT: A Multi-modality Overview
|
|
|
- Oswin Burns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Imaging of DVT: A Multi-modality Overview Douglas S. Katz, MD Imaging of DVT: A Multi-modality Overview STR 2010 Annual Meeting Workshop Douglas S. Katz, M.D., F.A.C.R. Vice Chair for Clinical Research and Education, and Director of Body Imaging, Winthrop-University Hospital, Mineola, NY, USA Professor of Clinical Radiology, State University of New York at Stony Brook Conflict of Interest Deputy Editor/Consultant to the Editor, Radiology Accurate clinical diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is notoriously difficult The same is true of pulmonary embolism (PE) PE and DVT are part of the same process of venous thromboembolism Most DVT is believed to begin in the calves and about 90%+ of PE are believed to originate from the deep veins of legs/pelvis usually begins around leaflets of venous valves, especially in calves, & can propagate superiorly Alternatively can form in the abdomen, pelvis, or upper thigh (e.g., due to obstruction), and then propagate inferiorly DVT is related to stasis, hypercoagulability, & trauma to the venous wall (Virchow s triad) Risk factors include: various blood disorders, malignancy, estrogen administration, dehydration, recent surgery or trauma, prolonged immobility, heart failure, mass effect on veins, obesity, pregnancy, age > 40, and prior DVT Up to 2/3 of patients with lower extremity (LE) DVT are asymptomatic Sequelae include PE & chronic venous disease The prevalence of identifiable DVT in patients with PE is variable A multi-center report of over 5000 patients with DVT shown on ultrasound (Goldhaber SZ et al. Am J Cardiol 2004): PE in 14.5%; 90% had signs/symptoms of DVT and/or PE Unilateral lower extremity DVT in 77%, bilateral in 12%; of these, 15% were isolated to the calf Upper extremity DVT in 11% Acute DVT may embolize, may resolve completely over time, or may contract/scar with residual varying degrees of occlusion/obstruction, wall thickening, and damaged/incompetent valves For decades, conventional venography was the test of choice for suspected DVT in the legs, pelvis, and inferior vena cava (IVC) (Redman HC Radiology 1988) Conventional venography: clot is identified as a filling defect or implied by complete non-filling of a vein Problems with conventional venography include (Redman HC Radiology 1988): difficulty in obtaining access, pain, contrast reactions, and paradoxical post-procedure DVT in a minority of patients; the examination is somewhat labor intensive The patient must travel to the radiology department 5-10% are technically inadequate interobserver disagreement occurs in 10%+ of examinations With the introduction of ultrasound (US), lower extremity venography now is almost never done for diagnosis alone but has occasional use for upper extremities/thoracic imaging Ultrasound Ultrasound Technique/Findings Introduced in the late 1980s Now the initial imaging test of choice for patients with signs/symptoms suggesting lower or upper extremity DVT Advantages: very high accuracy for thigh and arm evaluation for acute DVT relatively low cost portable no ionizing radiation readily repeatable Current techniques still rely primarily on compression sonography If pressure from the transducer completely collapses the vein, DVT is absent; DVT is present if the vein does not completely collapse Obtain transverse images of common femoral vein (CFV), superficial femoral vein (SFV), & popliteal vein (PV) along their courses with a 5 or 7.5 MHz linear transducer Supplement with sagittal color & spectral Doppler images (although these are usually routinely performed anyway) Color/spectral Doppler is helpful in obese patients/when imaging deep areas, especially the superficial femoral vein in the adductor canal (Lewis BD et al. Radiology 1994) Also helpful for indirect evidence of pelvic venous occlusion a monophasic waveform in the common femoral vein is a reliable indicator of proximal venous obstruction (Lin EP et al. J Ultrasound Med 2007) Augmentation did not yield any additional diagnoses of DVT in a series of almost 2000 US examinations (Lockhart ME et al. AJR 2005) Acute DVT venous distension can be present but echogenicity/visibility of clot is variable Alternative diagnoses may be identified with US e.g. hematoma, ruptured popliteal fossa cyst (Sutter ME et al. J Emerg Med) 385
2 Ultrasound Accuracy & Pitfalls Accuracy of US for DVT in the thighs of symptomatic patients approaches 100% (Fraser JD et al. Radiology 1999) However US may be limited with obese patients, with marked leg edema, & with overlying casts There is still some controversy whether to routinely image both lower extremities or only the symptomatic leg (Rosen MP et al. Semin US CT MR 1997; Lockhart ME AJR 2005); isolated contralateral DVT was rare in the latter series Most centers routinely scan both legs unless there is a good reason not to Some authors advocate a limited examination with imaging at the groin and behind the knee only (Pezzullo JA et al. Radiology 1996) Clot isolated within the thigh to the SFV has an incidence approaching 20% (Maki DD et al. AJR 2000; Katz DS et al. RadioGraphics 2002; Ford MN et al. J Clin Ultrasound 2001) so the literature does not support this practice Duplication of the SFV is very common up to 50%; if clot is present in only one of two limbs, US may be falsely-negative if only the patent limb is seen (Screaton NJ et al. Radiology 1998; Quinlan DJ et al. Radiology 2003) Ultrasound Accuracy & Pitfalls Correctly recognizing chronic DVT (and acute on top of chronic DVT) is problematic on all non-invasive imaging modalities Up to 50% of patients on followup US for acute DVT have residual abnormalities (Murphy TP et al. Radiology 1990) Chronic DVT findings include: increased clot echogenicity irregularly thickened venous walls small caliber veins collateral veins However, these findings may not be present, the echogenicity of chronic DVT is variable, and chronic DVT may not be distinguishable from acute DVT (Murphy TP et al. Radiology 1990; Spritzer CE et al. Radiology 1998) Differentiating post-phlebitic syndrome from chronic DVT is important in symptomatic patients repeat US is very useful Obtain repeat US in patients with DVT who become asymptomatic after initial therapy, for a new future baseline, and to determine whether therapy should be continued or not (Murphy TP et al. Radiology 1990; Siragusa S et al. Blood 2008) Ultrasound Role in Patients without DVT Symptoms Ultrasound - Calves Utility of US in patients with suspected PE but without signs or symptoms of DVT is controversial (Ford MN et al. J Clin Ultrasound 2001) Previous algorithms included US after indeterminate V/Q scan or after a negative or non-diagnostic CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) study but the incidence of DVT is very variable (Girard P et al. Chest 1999; Turkstra F et al. Ann Intern Med 1997) If US is done first in patients with r/o PE, if negative then PE is not excluded, while if positive the presence of PE is assumed but not proven and if actually present the extent of PE is not known Much poorer results on US in asymptomatic patients when compared with conventional venography (e.g., patients after joint replacements) the clots are usually smaller and nonocclusive, and the incidence of calf DVT is much higher (Wells PS et al. Ann Intern Med 1995) - no proven role for US in such patients, especially if they are on DVT prophylaxis US of the calves (and pelvis) is not routinely performed at most centers because of low accuracy and the high incidence of non-diagnostic studies (Gottlieb RH et al. J Clin Ultrasound 1999) If a patient specifically reports focal pain in the calf then do attempt to image the area of pain The incidence & significance of and therapy for isolated calf DVT remains controversial Reports of up to 32% of patients with calf vein DVT propagating on serial US and up to 30% with recurrence of isolated untreated calf DVT within 3 months (Deitcher SR et al. Med Clin North Am 2003) Calf DVT has also been associated with the postphlebitic syndrome Both symptomatic and asymptomatic calf DVT seem to propagate with equal frequency (Deitcher SR et al. Med Clin North Am 2003) Ultrasound - Calves Some authors recommend follow-up thigh US at one week, particularly if patient symptoms continue but the initial US examination is negative for the thigh portion of the examination, so as to not miss calf DVT propagating to the thighs (Gottlieb RH et al. AJR 1999; Pezzullo JA et al. Radiology 1996) Not aware as to how often this is actually done, and more recent data suggests compliance is poor (McIlrath ST et al. Am J Emerg Med 2006) Incidence of calf DVT is not trivial (isolated to calves in 57% in one relatively recent series (Subramaniam RM et al. Radiology 2005)), and some patients have concurrent PE (Katz DS et al. RadioGraphics 2002; Rose SC et al. J Ultrasound Med 1994) Upper Extremity DVT Imaging The incidence of upper extremity DVT (UEDVT) is increasing due to the widespread use of central venous catheters, pacemakers, AICDs, & other devices UEDVT also may be related to hypercoagulability, malignancy, low-flow states, and effort thrombosis in athletic young people (especially men with thoracic outlet syndrome) (Volturo CA et al. Emerg Med Clin North Am 1994) Signs/symptoms of UEDVT include pain and swelling but are, as with lower extremity DVT, not specific (Joffe HU et al. Circulation 2002; Mustafa S et al. Chest 2003; Giess CS et al. J Ultrasound Med 2002) 386
3 Upper Extremity DVT Imaging Combined CT and Pulmonary Angiography The prevalence of UEDVT in oncology patients with central venous catheters is very variable, whether symptomatic or not (range 7 48%), but is higher than in non-oncology patients (Gaitini D et al. J Ultrasound Med 2006) The exact relationship of UEDVT to clinically significant PE is unknown, although the risk is estimated at 15% (Giess CS et al. J Ultrasound Med 2002) The initial test of choice is US, which is up to 95% accurate Only the symptomatic side is usually studied in contrast to lower extremity US (Lewis BD 1998) Image axillary, brachial, and internal jugular veins with compression, supplemented with color and spectral Doppler as with lower extremity US The subclavian vein is not easily compressed due to overlying clavicle so rely on color Doppler The superior vena cava and central portions of brachiocephalic veins are not routinely seen Rely on secondary signs - absence of pulsatility/respiratory variation (Giess CS et al. J Ultrasound Med 2002) Other cross-sectional imaging tests (CT & MR) are useful for further evaluation of suspected central thoracic venous thrombosis CT pulmonary angiography is the noninvasive test of choice for suspected PE Since PE and DVT are aspects of the same disease, if the deep veins are imaged with CT immediately after the lungs, the presence/absence of DVT and the overall burden and distribution of clot can be demonstrated One-stop examination This combined protocol requires only a few extra minutes but adds images to review and radiation dose, and the dose of IV contrast needs to be higher compared with if only CTPA is performed (Katz DS et al. RadioGraphics 2002; Loud PA et al. AJR 1998) CT venography (CTV) is useful even if CTPA is positive, for identifying coexistent DVT in the thighs & pelvis; the latter reportedly increases the risk for additional emboli CTV may salvage the occasionally non-diagnostic or limited it CTPA study (Katz DS et al. RadioGraphics 2002) 7% in one MDCT series (Jones SE et al. Radiology 2005) CTVPA is still routinely performed on most of our patients undergoing CTPA unless: a) patient is pregnant; b) patient had a recent negative leg US; c) patient is young (consider latter on case-by-case basis) 3 to 3.5 minutes from the start of IV contrast for CTPA obtain consecutive 5 mm images in groups of four, with 2 to 3 cm gaps, from diaphragm to ankles Recommend contrast with at least 300 mg I/mL and use ml Clot: filling defect within a deep vein; acute DVT often expands the vein, and has associated perivenous edema/enhancement of the venous wall (Loud PA et al. AJR 1998; Loud PA et al. Radiology 2001) Prefer the survey technique and not continuous images, to reduce overall radiation burden and number of images to review Goal is to identify potentially important clot burden, but not every small DVT PIOPED II supports use of discontinuous images little difference between them and continuous images in the same 150 examinations 89% agreement, & equivalent accuracy to lower extremity sonography (Goodman LR et al. AJR 2007) Various controversies regarding CTV whether to do it, when, how, is it cost-effective, how much evidence is there to support its use (Dodd JD et al. Radiology 2007; Goodman LR et al. Radiology 2009) The more recent literature has been more mixed but is still somewhat positive towards the utility of CTV, which reflects the decreased yield of CTV (& increased radiation exposure c/w CTPA alone) Corresponds to the decreasing overall yield of CTPA, due to widespread use/over-utilization (Hunsaker AR et al. AJR 2008; Nazaroglu H et al. AJR 2009; Jones C et al. Am Surg 2008; Stein PD et al. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2009; Revel MP J Thromb Hemost 2008) CTVPA: Accuracy High accuracy has been reported for CT venography, for thigh DVT identification or exclusion (Loud PA et al. Radiology 2001; Ghaye B et al. Eur Radiol 2002; Cham MD et al. Radiology 2000 & Radiology 2005) In 308 patients 97% sensitivity & 100% specificity c/w US (Loud PA et al. Radiology 2001) Addition of CTV to CTPA has increased the overall diagnostic yield of venous thromboembolism by 20%- 27%+ in earlier series (Cham MD et al. Radiology 2005; Richman PB et al. J Thromb Haemost 2003; Ghaye B et al. Radiology 2006) CTV increased the sensitivity of CTPA alone from 83% to 90% in PIOPED II (Stein PD et al. NEJM 2006) 387
4 CTVPA: Calves and Complex Anatomy Recommend routine imaging of the calves on CT venography, although this is controversial Although as noted the clinical importance of calf DVT remains controversial, although in contrast to ultrasound, DVT is usually readily and rapidly identified or excluded on CTV CTV clearly reveals complex anatomy and pathology - e.g. superficial venous clot; clot in the profunda femoral vein in a substantial minority of patients with DVT (an area not usually imaged with US); and pelvic DVT, which may be difficult to image with US CT : Evaluation of Underlying Anatomic IVC/Iliac Vein Anomalies Contiguous multi-detector CT venography acquisition provides information on underlying anatomic abnormalities in iliofemoral DVT perform in very selected circumstances for dedicated venous imaging 45 of 56 patients with iliofemoral DVT (44 left-sided) had anatomic abnormalities evident, especially compression of the left common iliac vein by the right common iliac artery (exaggerated by a bony spur in nine) (Chang JW et al. JVIR 2004) Also use a contiguous acquisition for occasional problem solving (e.g., a dedicated CT venogram of the pelvis and/or legs after non-diagnostic US we have done this in a small number of patients in the past few years) CTVPA: Pelvic & Chronic DVT CTVPA: Accuracy and Pitfalls Report of 1745 patients DVT on 167 CTV exams (9.6%), and 23% of these had iliac vein and/or inferior vena cava involvement (Cham MD et al. RSNA 2003; published in modified form, Radiology 2005) Accurate detection of chronic DVT is also problematic as on other cross-sectional imaging studies and not well studied yet - findings parallel those on US (small veins, partial filling defects, no perivenous edema or venous wall enhancement, and calcification) A relatively small percentage of CTV studies are nondiagnostic especially in patients with poor cardiac function and/or substantial lower extremity atherosclerosis (Katz DS et al. RadioGraphics 2002; Ghaye B et al. Eur Radiol 2002; Arakawa H et al. AJR 2007) If CTPA is negative in such patients or additional information is needed regarding the lower extremities, then US should be performed US and CTV are complementary in a subset of patients MR Imaging for DVT MR for DVT imaging was first introduced in the early 1990s High accuracy of MR (i.e., MR venography, or MRV) compared with conventional venography for the pelvis and the thighs, but MR is less accurate for the calves (Cantwell CP et al. JVIR 2006) Can use spin-echo, gradient-recalled echo, and gadolinium-enhanced sequences (Evans AJ et al. AJR 1993; Polak JF et al. Semin US CT MR 1999) MR is also advantageous for imaging suspected central thoracic venous clot readily see veins compared with US, and the causes of clot, e.g. a central mass Can also find central thoracic DVT/thrombosis on CTPA MR Imaging for DVT DVT findings on MR: absent venous flow, filling defects, and (in a minority of patients) perivenous inflammation analogous to the findings on CTV MR may be superior to US and CTV for the determination of chronicity of DVT although this has not been well studied (Spritzer CE et al. Radiology 1998) MR is used as a problem-solving tool in most practices, especially for pelvic vein imaging The true frequency of pelvic DVT is underestimated with US and in pregnant patients, recent pelvic surgery, or pelvic malignancy, DVT may start in the pelvis and propagate inferiorly into the thighs (Spritzer CE et al. Radiology 2001) 388
5 MR Imaging for DVT Study of 212 patients with DVT extending proximal to the inguinal ligament on US; the patients then underwent MR (Borst-Krafek B et al. J Vasc Surg 2003) Extension to iliac veins/ivc shown in 89% Iliac veins were involved in 142 patients and the IVC in 46 patients Iliac DVT was 2X more frequent on the left compared with the right Extent of DVT had no correlation with the frequency of symptomatic PE In patients with a contraindication to iodinated contrast who can receive gadolinium can do MR pulmonary angiography and venography: obtain axial GRE images after MR pulmonary angiogram gadolinium augments MR signal in patent veins Combined MR pulmonary angiography & venography protocol increased yield by 16% c/w MRPA alone in one study (Kluge A et al. AJR 2006) Diagnostic venography is now limited to specific scenarios: prior to placement of IVC filters evaluation of central DVT in the proximal arms/chest as a prelude for intervention: thrombolysis, thrombectomy, and stent placement with indeterminate US in obese patients or a markedly swollen leg, and when other modalities do not or cannot solve the problem in suspected calf DVT in patients with negative or indeterminate US, where the findings would change management (although the latter two scenarios may be evaluated with CTV or MRV) Non-visualization of portions of the subclavian and innominate veins and of the superior vena cava as noted is a common situation with US Can easily evaluate these veins with a contrast injection into the antecubital vein or via basilic/brachial vein access with catheterization of the subclavian vein, under fluoroscopic control Diagnostic venography is performed routinely immediately prior to IVC filter placement: to evaluate for clot and venous anomalies, and also to measure the IVC to determine the type of filter to place At our institution, we routinely hand inject into the ipsilateral iliac vein when planning to place an IVC filter via the femoral approach, to evaluate for iliac DVT We then perform an IVC gram via a left iliac venous injection, to look for congenital anomalies We then perform a selective left renal venogram to check for a circumaortic renal vein, which can serve as a collateral pathway for emboli around the IVC (Beckman CF et al. AJR 1979; Phillips E 1969) Summary Ultrasound is the imaging test of choice for suspected lower or upper extremity DVT US has high accuracy in symptomatic patients for the deep thigh veins and in the arms US is less accurate for the calves and the pelvis, and in asymptomatic patients Combined CT pulmonary angiography and CT venography permits comprehensive assessment for PE and DVT, & serves as a roadmap for therapy, although the yield of CTV has decreased substantially in recent years as CTPA has been increasing used/over-utilized, and CTV is not routinely performed at many institutions/practices, although there is still evidence to support its use, especially in high risk patients MR is a helpful problemsolving test, & can also be combined with MR pulmonary angiography Conventional venography is mostly of historical interest when used solely as a diagnostic study for the lower extremities via an inguinal approach is still performed at some centers, including ours, as a road-mapping technique immediately prior to IVC filter placement of the lower and upper extremities is routinely performed as part of a variety of therapeutic procedures for DVT including thrombolysis, percutaneous thrombectomy, angioplasty, and stent placement 389
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Suspected Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis EVIDENCE TABLE
 . Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
. Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
VENOUS DOPPLER SONOGRAPHY OF THE EXTREMITIES
 VENOUS DOPPLER SONOGRAPHY OF THE EXTREMITIES The 35 th Annual Vanderbilt Diagnostic Sonography Symposium July 23-24, 2011 E. JAMES ANDREWS, JR., M.D., FACR, FACC DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY AND RADIOLOGICAL
VENOUS DOPPLER SONOGRAPHY OF THE EXTREMITIES The 35 th Annual Vanderbilt Diagnostic Sonography Symposium July 23-24, 2011 E. JAMES ANDREWS, JR., M.D., FACR, FACC DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY AND RADIOLOGICAL
Bedside Ultrasound for Detection of Deep Vein Thrombosis: the Two-Point Compression Method
 Bedside Ultrasound for Detection of Deep Vein Thrombosis: the Two-Point Compression Method Tom Ashar MD RDMS a, Krishnaraj Jayarama DO, Raymond Yun MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Newark Beth Israel
Bedside Ultrasound for Detection of Deep Vein Thrombosis: the Two-Point Compression Method Tom Ashar MD RDMS a, Krishnaraj Jayarama DO, Raymond Yun MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Newark Beth Israel
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULARTECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULARTECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy. John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
 Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Illustrative Clinical Scenario 32 year old female 34 weeks pregnant with recent onset shortness of breath and central chest pain
Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Illustrative Clinical Scenario 32 year old female 34 weeks pregnant with recent onset shortness of breath and central chest pain
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex. Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016
 Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016 Patricia A. (Tish) Poe, BA RVT FSVU Director of Quality Assurance Navix Diagnostix Patricia A. Poe
Upper Extremity Venous Duplex Michigan Sonographers Society Fall Ultrasound Symposium October 15, 2016 Patricia A. (Tish) Poe, BA RVT FSVU Director of Quality Assurance Navix Diagnostix Patricia A. Poe
Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism
 Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric Tseng MD MScCH, University of
Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric Tseng MD MScCH, University of
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach
 Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D20 Statement on Peripheral Venous Ultrasound
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D20 Statement on Peripheral Venous Ultrasound Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D20 Statement on Peripheral Venous Ultrasound Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Clinical Guide - Suspected PE (Reviewed 2006)
 Clinical Guide - Suspected (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: B. Geerts Secondary Developers: C. Demers, C. Kearon Background Investigation of patients with suspected pulmonary emboli () remains problematic
Clinical Guide - Suspected (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: B. Geerts Secondary Developers: C. Demers, C. Kearon Background Investigation of patients with suspected pulmonary emboli () remains problematic
Surgical approach for DVT. Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Duplex ultrasound is first-line imaging for all
 Our Protocol for Transabdominal Pelvic Vein Duplex Ultrasound A summary of s protocol for pelvic vein duplex ultrasonography, including equipment, patient positioning, ultrasound settings, and technique.
Our Protocol for Transabdominal Pelvic Vein Duplex Ultrasound A summary of s protocol for pelvic vein duplex ultrasonography, including equipment, patient positioning, ultrasound settings, and technique.
A rare case of May-Thurner-like syndrome in an elderly lady
 CASE REPORT A rare case of May-Thurner-like syndrome in an elderly lady Chris Pui Yan Yee 1, Kapil Sahnan 2, Robert Hywel Thomas 1, Kaji Sritharan 1 1. Department of Vascular Surgery, St Mary's Hospital,
CASE REPORT A rare case of May-Thurner-like syndrome in an elderly lady Chris Pui Yan Yee 1, Kapil Sahnan 2, Robert Hywel Thomas 1, Kaji Sritharan 1 1. Department of Vascular Surgery, St Mary's Hospital,
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Bedside Emergency Ultrasound For Deep Venous Thrombosis
 Bedside Emergency Ultrasound For Deep Venous Thrombosis Michael Blaivas, MD, MBA(candidate) FACEP, FAIUM Professor of Medicine University of South Carolina School of Medicine AIUM Third Vice President
Bedside Emergency Ultrasound For Deep Venous Thrombosis Michael Blaivas, MD, MBA(candidate) FACEP, FAIUM Professor of Medicine University of South Carolina School of Medicine AIUM Third Vice President
BC Vascular Day. Contents. November 3, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3. Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6. Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8
 BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
Deep Vein Thrombosis: Can a Second Sonographic Examination Be Avoided?
 Alfonsa Friera 1 Nuria R. Giménez 2 Paloma Caballero 1 Pilar S. Moliní 2 Carmen Suárez 2 Received August 15, 2001; accepted after revision October 16, 2001. 1 Radiology Department, Hospital de la Princesa,
Alfonsa Friera 1 Nuria R. Giménez 2 Paloma Caballero 1 Pilar S. Moliní 2 Carmen Suárez 2 Received August 15, 2001; accepted after revision October 16, 2001. 1 Radiology Department, Hospital de la Princesa,
ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED
 ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED Ralph Wang UCSF Department of Emergency Medicine 53 yo f c/o left leg swelling recent cholecystectomy its midnight how do you manage this patient?
ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED Ralph Wang UCSF Department of Emergency Medicine 53 yo f c/o left leg swelling recent cholecystectomy its midnight how do you manage this patient?
BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND. Deep Vein Thrombosis. Probe used
 BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND Part 2 Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis Kishore Kumar Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, CMC, Vellore Summary: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a problem encountered in
BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND Part 2 Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis Kishore Kumar Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, CMC, Vellore Summary: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a problem encountered in
A A U
 PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
MRA/MRV CASE REVIEW. Carlos Avila R.T.(R)(MR)(CT)
 MRA/MRV CASE REVIEW Carlos Avila R.T.(R)(MR)(CT) Carlso Avila, RT (R)(MR) No relevant financial relationship reported MRA/MRV Magnetic resonance angiography: noninvasive examination performed to evaluate
MRA/MRV CASE REVIEW Carlos Avila R.T.(R)(MR)(CT) Carlso Avila, RT (R)(MR) No relevant financial relationship reported MRA/MRV Magnetic resonance angiography: noninvasive examination performed to evaluate
Starting with deep venous treatment
 Starting with deep venous treatment Carsten Arnoldussen, MD Interventional Radiologist Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht VieCuri Medical Centre, Venlo The Netherlands Background Maastricht
Starting with deep venous treatment Carsten Arnoldussen, MD Interventional Radiologist Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht VieCuri Medical Centre, Venlo The Netherlands Background Maastricht
Bedside Ultrasound for DVT. Linear Probe. Leg Veins
 Bedside Ultrasound for DVT J. Christian Fox, MD, RDMS, FAAEM, FAIUM Director of Emergency Ultrasound Fellowship University of California, Irvine Jchrsitianfox@gmail.com Linear Probe High frequency transducer
Bedside Ultrasound for DVT J. Christian Fox, MD, RDMS, FAAEM, FAIUM Director of Emergency Ultrasound Fellowship University of California, Irvine Jchrsitianfox@gmail.com Linear Probe High frequency transducer
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Pulmonary Emboli without Leg Symptoms, May-Thurner syndrome. Case Report and Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 Pulmonary Emboli without Leg Symptoms, May-Thurner syndrome. Case Report and Review A Hamo, M Alyaseen, F Alkhankan, T Gress Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 Pulmonary Emboli without Leg Symptoms, May-Thurner syndrome. Case Report and Review A Hamo, M Alyaseen, F Alkhankan, T Gress Citation
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. predictive value for compression ultrasonography. for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Outpatients
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Predictive Value of Compression Ultrasonography for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Outpatients Clinical Implications of the Site of Vein Noncompressibility Brian G. Birdwell,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Predictive Value of Compression Ultrasonography for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Outpatients Clinical Implications of the Site of Vein Noncompressibility Brian G. Birdwell,
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
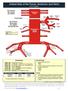 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI
 Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth
 Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth Naveed Saqib, MD Assistant Professor Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science
Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth Naveed Saqib, MD Assistant Professor Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ, Dalsing MC, Eklof BG, Gillespie DL, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:
 Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ,
Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ,
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
Ultrasonography and Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism
 Ultrasonography and Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism Brenda K. Zierler, PhD Abstract Venous thromboembolism (VTE) consists of two related conditions: pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis
Ultrasonography and Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism Brenda K. Zierler, PhD Abstract Venous thromboembolism (VTE) consists of two related conditions: pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis
Sample page. POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com.
 2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND. CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center
 LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center Learning Objectives Setup and patient positioning for optimizing success
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center Learning Objectives Setup and patient positioning for optimizing success
NOTE: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Risk Factors
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in the deep leg vein. It is a very serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in the deep leg vein. It is a very serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein
 Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
As with any intervention, selection of an appropriate
 DVT: ccess Decisions for Interventions ssessing the advantages and disadvantages of venous access options is crucial for safe and successful DVT intervention. Y JOHN. KUFMN, MD, MS, FSIR, FH, FCIRSE, EIR
DVT: ccess Decisions for Interventions ssessing the advantages and disadvantages of venous access options is crucial for safe and successful DVT intervention. Y JOHN. KUFMN, MD, MS, FSIR, FH, FCIRSE, EIR
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus
 Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Case 1:
 12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
Diagnostic Algorithms in VTE
 Diagnostic Algorithms in VTE Mark H. Meissner, MD Department of Surgery University of Washington School of Medicine Overutilization of Venous Duplex U/S 1983-1993 (Zweibel et al, Australasian Rad, 1995)
Diagnostic Algorithms in VTE Mark H. Meissner, MD Department of Surgery University of Washington School of Medicine Overutilization of Venous Duplex U/S 1983-1993 (Zweibel et al, Australasian Rad, 1995)
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Patients with suspected DVT of the lower limb how to exam the patient
 Patients with suspected DVT of the lower limb how to exam the patient Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2015, Oslo Content Anatomy and pathophysiology
Patients with suspected DVT of the lower limb how to exam the patient Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2015, Oslo Content Anatomy and pathophysiology
Detection of deep venous thrombosis on CT venography: Comparison of dose of contrast material
 Detection of deep venous thrombosis on CT venography: Comparison of dose of contrast material Poster No.: C-1140 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Contrast Media Authors: T. Ichikawa,
Detection of deep venous thrombosis on CT venography: Comparison of dose of contrast material Poster No.: C-1140 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Contrast Media Authors: T. Ichikawa,
DVT and Pulmonary Embolus. Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
 DVT and Pulmonary Embolus Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview Structure of deep and superficial venous system of upper
DVT and Pulmonary Embolus Dr Piers Blombery BSc(Biomed), MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA Consultant Haematologist Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview Structure of deep and superficial venous system of upper
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event?
 89 th ASMA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING DALLAS- May 6-10, 2018 What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event? S BISCONTE (1), V MARICOURT
89 th ASMA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING DALLAS- May 6-10, 2018 What is the real place of venous echo Doppler in aircrew member flying rehabilitation after a thromboembolism event? S BISCONTE (1), V MARICOURT
Pulmonary Embolism..Diagnostic Approach and Algorithm. Tolulope Adesiyun Harvard Medical School, Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Pulmonary Embolism..Diagnostic Approach and Algorithm Tolulope Adesiyun Harvard Medical School, Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism Pulmonary Embolus (PE): Thrombus originating
Pulmonary Embolism..Diagnostic Approach and Algorithm Tolulope Adesiyun Harvard Medical School, Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism Pulmonary Embolus (PE): Thrombus originating
PE and DVT. Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP
 PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2016
 STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Vascular Sonography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Vascular Sonography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
Vascular Sonography Examination
 Vascular Sonography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Vascular Sonography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
Vascular Sonography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Vascular Sonography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
New Criteria for Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Interpretation: A Basis for Optimal Interaction with Helical CT Angiography 1
 1206 July-August 2000 RG Volume 20 Number 4 New Criteria for Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Interpretation: A Basis for Optimal Interaction with Helical CT Angiography 1 Alexander Gottschalk, MD Introduction
1206 July-August 2000 RG Volume 20 Number 4 New Criteria for Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Interpretation: A Basis for Optimal Interaction with Helical CT Angiography 1 Alexander Gottschalk, MD Introduction
What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis?
 What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis? Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, University of Thessalia, Greece Chairman,
What is the impact of Superficial Vein Thrombosis? Athanasios D. Giannoukas MD, MSc(Lond.), PhD(Lond.), FEBVS Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine, University of Thessalia, Greece Chairman,
Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound. Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons)
 Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons) Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Venous Deep System Common Iliac External/Internal Iliac Common Femoral Femoral
Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons) Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Venous Deep System Common Iliac External/Internal Iliac Common Femoral Femoral
Copy Here. The Easy One.. What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Deep Venous Thrombosis Spectrum
 What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Mitchell J. Silver DO FACC FSVM RPVI Director, Center for Critical Limb Care Riverside Methodist Hospital Ohio Health Heart and
What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Mitchell J. Silver DO FACC FSVM RPVI Director, Center for Critical Limb Care Riverside Methodist Hospital Ohio Health Heart and
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
EKOS. Interventional Vascular 3 February, Imagine where we can go.
 EKOS Interventional Vascular 3 February, 2015 Imagine where we can go. Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to you may contain certain projections and other
EKOS Interventional Vascular 3 February, 2015 Imagine where we can go. Forward-looking statement This presentation and information communicated verbally to you may contain certain projections and other
Treatment of Chronic DVT with EKOS: Reproducing ACCESS PTS Data in Every Day Clinical Practice
 Treatment of Chronic DVT with EKOS: Reproducing ACCESS PTS Data in Every Day Clinical Practice Mert Dumantepe, MD Acibadem Altunizade Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey Department of Cardiovascular Surgery Disclosure
Treatment of Chronic DVT with EKOS: Reproducing ACCESS PTS Data in Every Day Clinical Practice Mert Dumantepe, MD Acibadem Altunizade Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey Department of Cardiovascular Surgery Disclosure
Image Formation (10) 2 Evaluation and Selection of Representative Images (10)
 STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Vascular Sonography The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists
STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Vascular Sonography The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists
Thrombolysis in PE. Outline. Disclosure. Overview on Pulmonary Embolism. Hot Topics in Emergency Medicine 2012 Midyear Clinical Meeting
 Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Imaging, it s central role in planning and guiding intervention. Prof. Luis Izquierdo. MD, PhD, FEBVS
 Imaging, it s central role in planning and guiding intervention Prof. Luis Izquierdo. MD, PhD, FEBVS IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These materials are intended to describe common clinical considerations and procedural
Imaging, it s central role in planning and guiding intervention Prof. Luis Izquierdo. MD, PhD, FEBVS IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These materials are intended to describe common clinical considerations and procedural
Clinical Guide - Inferior Vena Cava Filters (Reviewed 2006)
 Clinical Guide - Inferior Vena Cava Filters (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: V. Oliva Secondary Developers: W. Geerts Background The treatment of choice for deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary
Clinical Guide - Inferior Vena Cava Filters (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: V. Oliva Secondary Developers: W. Geerts Background The treatment of choice for deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary
Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline
 Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Normal Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Evaluate normal anatomy, perfusion, function 2 Pathology, Perfusion,
Vascular Technology Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Normal Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Evaluate normal anatomy, perfusion, function 2 Pathology, Perfusion,
Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein
 416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
416507JDMXXX10.1177/8756479311416507Wash ko et al.journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Pseudothrombosis of the Subclavian Vein Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 27(5) 231 235 The Author(s) 2011
Management of an Unusual Iliac Fossa Venous Plexus
 Management of an Unusual Iliac Fossa Venous Plexus Irwin M Best, Emory University Journal Title: Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume: Volume 2011, Number 2011 Publisher: 2011-11-22, Pages 1-4 Type
Management of an Unusual Iliac Fossa Venous Plexus Irwin M Best, Emory University Journal Title: Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume: Volume 2011, Number 2011 Publisher: 2011-11-22, Pages 1-4 Type
Venous interventions in DVT
 Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
For exam: VL DUPLEX EXTREMITY VEINS UNILAT LT
 For exam: VL DUPLEX EXTREMITY VEINS UNILAT LT - 8870390 METHOD/TECHNIQUE: The veins of the left upper extremity were studied at multiple For exam: VL DUPLEX EXTREMITY VEINS UNILAT RT - 8870400 METHOD/TECHNIQUE:
For exam: VL DUPLEX EXTREMITY VEINS UNILAT LT - 8870390 METHOD/TECHNIQUE: The veins of the left upper extremity were studied at multiple For exam: VL DUPLEX EXTREMITY VEINS UNILAT RT - 8870400 METHOD/TECHNIQUE:
Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology
 Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome Left CIV compressed by right CIA Virchow 1851: DVT L>R May and Thurner 1954: venous spurs Cockett and Thomas 1965:
Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome Left CIV compressed by right CIA Virchow 1851: DVT L>R May and Thurner 1954: venous spurs Cockett and Thomas 1965:
Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease
 none Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease David Rigberg, M.D. Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery University of California Los Angeles Chronic Venous Occlusive Disease Chronic
none Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease David Rigberg, M.D. Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery University of California Los Angeles Chronic Venous Occlusive Disease Chronic
Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D.
 In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
In low-risk patients with isolated calf DVT (IDDVT), what is the morbidity risk of treating with repeat ultrasound/observation versus anticoagulation? Discussion Leader: Doug Bias, M.D. Clinical Scenario:
Amanda Phillips, RVT
 Amanda Phillips, RVT Cockett Syndrome Iliac vein compression syndrome http://www.ardms.org/volunteer-now/clearly-connected/pages/may-thurner-syndrome-what-sonographers-should-know.aspx Compression of Lt
Amanda Phillips, RVT Cockett Syndrome Iliac vein compression syndrome http://www.ardms.org/volunteer-now/clearly-connected/pages/may-thurner-syndrome-what-sonographers-should-know.aspx Compression of Lt
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski. Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008
 Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008 History of Vena Cava Filters Virchow-1846-Proposes PE originate from veins
Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008 History of Vena Cava Filters Virchow-1846-Proposes PE originate from veins
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Policy #: 291 Latest Review Date: February 2013
 Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Lower Extremity Venous Insufficiency Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Insufficiency Evaluation This Protocol was prepared by members of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound (SVU) as a template
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Venous Insufficiency Evaluation This Protocol was prepared by members of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound (SVU) as a template
REVIEW ON PULMONARY EMBOLISM
 REVIEW ON PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Shashi Kumar Yadav, Prof. Xiao Wei, Roshan Kumar Yadav, Sanjay Kumar Verma and Deepika Dhakal * Department of Medicine, Clinical College of Yangtze University, The first
REVIEW ON PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Shashi Kumar Yadav, Prof. Xiao Wei, Roshan Kumar Yadav, Sanjay Kumar Verma and Deepika Dhakal * Department of Medicine, Clinical College of Yangtze University, The first
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
Background & Indications Probe Selection
 Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Venous Doppler Sonography of the Extremities: A Window to Pathology of the Thorax, Abdomen, and Pelvis
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology linical Perspective Selis and Kadakia Doppler Sonography of the Extremities Vascular and Interventional Radiology linical Perspective Downloaded from www.ajronline.org
Vascular and Interventional Radiology linical Perspective Selis and Kadakia Doppler Sonography of the Extremities Vascular and Interventional Radiology linical Perspective Downloaded from www.ajronline.org
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline
 Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
VIVO-EU Results: Prospective European Study of the Zilver Vena TM Venous Stent in the Treatment of Symptomatic Iliofemoral Venous Outflow Obstruction
 VIVO-EU Results: Prospective European Study of the Zilver Vena TM Venous Stent in the Treatment of Symptomatic Iliofemoral Venous Outflow Obstruction Gerard J O Sullivan, M.D. and Jennifer McCann-Brown,
VIVO-EU Results: Prospective European Study of the Zilver Vena TM Venous Stent in the Treatment of Symptomatic Iliofemoral Venous Outflow Obstruction Gerard J O Sullivan, M.D. and Jennifer McCann-Brown,
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC 1 st workshop: update to VTE guidelines in 2016 2 nd workshop: VTE controversies + new horizons André Roussin MD, FRCP, CSPQ CHUM
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
MR and CT venography for imaging venous obstruction
 MR and CT venography for imaging venous obstruction Hendrik von Tengg-Kobligk University Hospitals Inselspital Bern Hendrik.vonTengg@insel.ch Disclosure Speaker name:...hendrik von Tengg-Kobligk... I have
MR and CT venography for imaging venous obstruction Hendrik von Tengg-Kobligk University Hospitals Inselspital Bern Hendrik.vonTengg@insel.ch Disclosure Speaker name:...hendrik von Tengg-Kobligk... I have
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Arterial Access for Diagnosis and Intervention T-Woei Tan, MD, FACS
 Arterial Access for Diagnosis and Intervention T-Woei Tan, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Vascular Endovascular Surgery Louisiana State University Health - Shreveport Disclosures None Objective
Arterial Access for Diagnosis and Intervention T-Woei Tan, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Vascular Endovascular Surgery Louisiana State University Health - Shreveport Disclosures None Objective
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
