Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
|
|
|
- Shon Harper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID , 5 pages Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Byung-chul Son, 1,2 Sang-woo Ha, 3 Si-hoon Lee, 1 and Jin-gyu Choi 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Republic of Korea 2 Catholic Neuroscience Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Republic of Korea 3 Department of Neurosurgery, Chosun University Hospital, Chosun University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea Correspondence should be addressed to Byung-chul Son; sbc@catholic.ac.kr Received 7 June 2015; Accepted 29 December 2015 Copyright 2016 Byung-chul Son et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) caused by spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks produces orthostatic headaches. Although upper arm pain or paresthesia is reportedly associated with SIH from spontaneous spinal CSF leak in the presence of orthostatic headache, low thoracic radicular pain due to spontaneous spinal CSF leak unassociated with postural headache is extremely rare. We report a 67-year-old female who presented with chronic, positional radicular right T11 pain. Computed tomography myelography showed a spontaneous lumbar spinal CSF leak at L2-3 and repeated lumbar epidural blood patches significantly alleviated chronic, positional, and lower thoracic radiculopathic pain. The authors speculate that a chronic spontaneous spinal CSF leak not severe enough to cause typical orthostatic headache or epidural CSF collection may cause local symptoms such as irritation of a remote nerve root. There might be considerable variabilities in the clinical features of SIH which can present a diagnostic challenge. 1. Introduction Most spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks are iatrogenic, occurring after lumbar puncture, epidural injection, or spinal surgery. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a posturalheadachesyndromeunrelatedtoduralpunctureanditis an uncommon but increasingly recognized clinical syndrome associated with reduced CSF pressure or CSF volume caused by spontaneous CSF leaks [1 5]. The incidence has been estimated at 5 per 100,000 per year, with a peak around 40 years of age [5]. SIH affects women more frequently than men, with a female-male ratio of approximately 2 : 1 [4, 5]. Spontaneous spinal CSF leaks are the typical cause of SIH [5, 6]. Such spontaneous CSF leaks may result from a simple dural rent or fragile arachnoid cysts, often in the presence of an underlying but previously unrecognized generalized connective tissue disorder [5 8]. An orthostatic headache is the prototypical manifestation, but other headache patterns occur as well, and associated symptoms are common [5]. When onset of such headache is spontaneous, the diagnostic challenge is created even though SIH has been recognized for more than 6 decades and the diagnosis has been greatly aided by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [4]. Typical brain MRI findings include subdural fluid collections, pachymeningeal enhancement, engorgement of venous structures, pituitary hyperemia, and downward displacement of the brain [4 11]. Because spinal CSF leaks generally do notcauseanylocalsymptoms[6],theyfrequentlyremain undetected unless actively looked for in a patient suspected of SIH [4, 5]. The precise cause of spontaneous spinal CSF leaks remains largely unknown, but an underlying structural weakness of the spinal meninges generally is suspected [6]. Until now, the symptoms and signs of SIH from spontaneous spinal CSF leak are reported to be associated with the head and the upper extremity [4, 9]. A thoracolumbar origin is extremely rare. Although a case of cervical radiculopathy causing weakness of shoulder elevation due to engorgement of the cervical epidural vein [9] and a case of
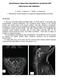
2 2 Pain Research and Management (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 1: Computed tomography (CT) myelograms showing spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks. (a) Bilateral CSF leaks (arrows) at L2-3 levels. (b) A contrast-filling nerve root sheath (arrows) at left T12-L1 level. (c) A coronal reconstruction image showing bilateral contrast-filling nerve root sheaths (arrows) at T1 level. (d) A small amount of contrast leak (arrow) in left T10 epidural space. paresthesia in the upper extremity [4] have been reportedly associated with SIH, an isolated presentation of unilateral low thoracic radiculopathic pain from spontaneous CSF leak without typical positional headache has not been reported. We report a case of spontaneous lumbar CSF leak presenting as a chronic, intractable, positional, unilateral lower thoracic radiculopathic pain, not associated with the typical symptom of orthostatic headache. 2. Case Presentation A 67-year-old female presented with a 12-month history of chronic radicular pain along the course of right T11. The pain was described as mainly aching, with extreme severity (7-8/10 on the numeral rating scale (NRS) ranging from 0 to 10). It was aggravated with position change from lying to sitting, and daily activity and walking did not influence the pain. There was no precipitating event before the onset of right thoracic pain and its onset was insidious. The pain was not relieved with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tramadol (300 mg/day), and 20 mg oxycodone b.i.d. and was so agonizing that treatment with repeated injections of diclofenac sodium and on a regular schedule of epidural blocks, intercostal blocks of T11, and tender point injections was done two times a week for a year. However, repeated blocks were unsuccessful. She underwent right-sided L4-5 hemilaminectomy because the pain radiated to the lateral flank and was misdiagnosed as lumbar stenosis 5 months after pain onset. Hemilaminectomy was not effective. Finally, she was referred to our outpatient clinic under the diagnosis of failed back surgery syndrome. On examination, the pain was typically present along the course of the right T11 dermatome from the lower trunk radiating to the right lower abdomen. There was no sensory disturbance including right T11 dermatome and right leg, and no allodynia, tenderness, or limitation of motion of low back and trunk was observed. Laboratory examinations were normal including the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and blood sugar level (95 mg/dl). A Congo red stain of the abdominal fat to rule out amyloidosis was negative. Plain X-rays of lower thoracic and lumbar spine were unremarkable and no pathologic lesion to explain right T11 pain was found in the MRI of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine. Electromyography including nerve conduction study revealed no evidence of radiculopathy or peripheral neuropathy. As an evaluation for failed back surgery syndrome, myelography computed tomography (CT) was performed. There was no lesion found causing right T11 pain. However, a prominent CSF leak was noted bilaterally at the level of L2-3 (Figure 1(a)) and contrast-filling nerve root sheath was identified at left T12 (Figure 1(b)), left L1 (Figure 1(c)), and bilateral T1. A small amount of epidural contrast leakage was found at the T10 level (Figure 1(d)). There was no pseudomeningocele or CSF leak at the laminectomized L4-5 level. Under suspicion of spontaneous spinal CSF leak, lumbar CSF examination was done 2 days later with adequate hydration. The CSF opening pressure was 8 cmh 2 Ointherecumbent position. The CSF examination showed 10 cells/mm 3 and a protein level of 35 mg/dl. No erythrocytes were found. On the basis of the CT myelographic finding of a CSF leak, the provisional diagnosis was spontaneous spinal CSF
3 Pain Research and Management 3 leak causing low thoracic radiculopathic pain. Considering thechronicityandmedicalintractabilityoftheradicularpain, combined with the radiological finding of spontaneous CSF leaks, an epidural blood patch (EBP) with 15 ml of autologous blood was performed at the L1-2 level. Immediately after the blood patch, she reported about 30% relief of T11 radicular pain (4 6 on NRS-11). A repeat lumbar EBP was performed one week later, which achieved an additional 30% pain relief (2 5 on NRS-11), and a total of 60% pain relief over baseline was achieved. At 2 weeks after the blood patch, myelographic CT and enhanced lumbar spine MRI were performed to assess the degree of spinal CSF leaks. There was no identifiable CSF leak at the L2-3 level. However, contrast-filling in bilateral nerve root sheaths without CSF leak was identified at T12-L1, L2-3, and L3-4 levels. The small amount of epidural contrast leakage at the level of T10 had disappeared. In the repeated enhanced lumbar spine MRI, there was no typical finding of spontaneous CSF leak, such as epidural CSF collection. However, subtle epidural enhancement was noted from T10 to L3, and a remnant of the injected epidural blood patch was observed. After achieving about 60% pain relief, she was discharged and was maintained with medication (10 mg oxycodone b.i.d., 400 mg gabapentin t.i.d., 50 mg tramadol/acetaminophen t.i.d., and 10 mg amitriptyline hs/a day). A repeated myelographic CT was performed 3 months after the first EBP showed the same findings obtained in the second myelographic CT, bilateral contrast-filling nerve root sheaths without CSF leak evident at the T12-L1, L2-3, and L3-4, L4-5 levels. An additional blood patch was not performed as the patient could tolerate low thoracic pain (NRS 2 4/10). Thus, the pain in this patient which was of 12 months duration and severe was relieved after two epidural blood patches to a mild to moderate level (2 4 on NRS-11) at 12-month follow-up. 3. Discussion 3.1. Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension (SIH) and Spontaneous CSF Leaks. Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a clinical syndrome in which absolute or relative hypovolemia of CSF results in various clinical symptoms [2]. Causes of IH can be either spontaneous or secondary to lumbar puncture, spine surgery, and chiropractic manipulation [1, 3, 9, 12, 13]. Many patients with IH present without known predisposing factors or a major trauma, and the condition has been called spontaneous IH (SIH). SIH is caused by spontaneous CSF leaks and is characterized by orthostatic headache (i.e., headache aggravated with standing up and relieved by lying down). Associated neurologic symptoms include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, photophobia, cranial nerve palsies such as diplopia, tinnitus, hearing disturbance, stiffness, and back pain, and radicular symptoms, such as pain or paresthesia of the upper extremity [4, 5, 9]. True radicular symptoms, such as pain and paresthesia, are extremely rare. Despite recent awareness of SIH by physicians, the diagnosis of SIH can be missed initially and the diagnostic delay is significant [4]. In a series of 18 consecutive series of SIH [4], 17 (94%) were initially given incorrect diagnoses, including migraine, meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cervical strain, and cervical radiculopathy [4]. This exposes patients to risks associated with treatment for the disorders that mimic SIH; the importance of increasing awareness of SIH causing headache has been stressed [4, 11] Differential Diagnosis. As a differential diagnosis of isolated T11 radiculopathic pain, both structural lesions and nonstructural peripheral neuropathic pain should be taken into account. For structural lesions such as foraminal stenosis or disc pathology, there was no obvious pathologic lesion possibly abutting the right T11 root on both MRI and myelographic CT scans. A radionuclide bone scintigraphy was negative and a neoplasm or benign tumor involving peripheral nerve root was also excluded with an enhanced MRI study. Diverse peripheral neuropathic lesion or systemic metabolic disease could involve a thoracic nerve root. Most commonly, diabetic neuropathy, nonvesicular form of herpes zoster (zoster sine herpete, ZSH), or sarcoid infiltration of nerve root could be considered. A syndrome of painful unilateral or symmetrical multiple neuropathy tends to occur in older patients with relatively mild or even unrecognized diabetes [14]. However, the patient did not show a history of diabetes and blood sugar level was normal. Diabetic amyotrophy typically involves lumbar roots and can cause severe aching pain with superimposed lancinating jabs. Although zoster sine herpete (ZSH) could manifest as chronic nonvesicular thoracic radiculopathy [15, 16], this patient did not show hyperaesthesia or allodynia to light touch which are the characteristics of ZSH. There was no granulomatous lesion in the chest, skin, and the eye which could be suspected for sarcoid infiltration and the test for systemic amyloidosis was negative also. Other possibilities of radiating pain caused by intra-abdominal or retroperitoneal pathologywereruledoutbyanabdominalctscanduring evaluation. In this case, we believe radicular pain occurred because of spontaneous CSF leak without headache Cause of Right T11 Pain from Spontaneous CSF Leak. Spontaneous CSF leak as a cause of the right T11 radicular pain in the present case may be questioned because there has been no reported case of SIH causing lower thoracic radiculopathy. Furthermore, there was no orthostatic headache. No typical enhanced MRI of the brain was able to be obtained and CSF pressure was normal. The only positive finding that supports the diagnosis of SIH due to spontaneous CSF leak is CT myelographic evidence of CSF leak in the thoracolumbar junction area and subsequent improvement of radicular pain after EBPs. However, considerable variability of the clinical features of SIH has been reported [4 6, 8]. Although an orthostatic, positional headache is a typical symptom of spontaneous CSF leak, absence of orthostatic headache in spite of typical meningeal enhancement on brain MRI and low CSF pressure has been reported. Mokri et al. [17] reported three patients two with overdraining CSF shunts and one with proven CSF
4 4 Pain Research and Management leak with typical pachymeningeal enhancement but without headache. Hochman and Naidich [18] also reported two patients with overdraining, long-standing ventricular shunts without any headache despite typical diffuse meningeal enhancement and documented low CSF pressure on lumbar puncture. Some patients deny having any headache, usuallywhenothersymptomsofsih,suchasposteriorneck pain, nausea, and photophobia, predominate the clinical picture [5]. Regarding typical MRI finding of pachymeningeal enhancement, up to 20% of patients with SIH never develop enhancement, or any of the other abnormalities on brain MRI [13,19,20].Unfortunately,wecouldnotexaminethebrain MRI in the present case, as the patient refused to have this test as her complaint was only low thoracic pain. It is known that CSF opening pressure in SIH is typically less than 60 mmh 2 O (reference range, mmh 2 O), which can be unmeasurable or even negative [21]. However, some patients with SIH have consistently normal CSF pressure [5, 6]. Indeed, the CT myelographic findings of spontaneous CSF leak in the current case were an unexpected finding during evaluation of right T11 radicular pain. Spontaneous CSFleakwasmostprominentatL2-3andtherewasascant amount of epidural contrast leak at T10. The CSF leaks at L2-3 and T10 disappeared after EBP with concomitant pain relief. In addition, multiple areas of contrast-filling nerve rootsheathswereobservedontheleftsideoft12-l1,left L1, and bilateral T1 in initial examination. However, the areas with contrast-filling nerve root sheaths were found bilaterally at the level of T12-L1, L2-3, and L3-4 in the second examination and bilaterally in T12-L1, L2-3, L3-4, and L4-5 in the follow-up examination at 3 months. The exact significance of contrast-filling along the course of the nerverootsheathisuncertain.wethinkthereisapossibility that these changes may implicate an underlying structural weakness of spinal meninges, which causes spontaneous spinal CSF leak [6, 9], and sealing of spinal CSF leak might induce some redistribution of intraspinal CSF pressure. In this patient, contrast-filling was prominent in the left T12- L1 and this had become prominent in the right T12-L1 in the follow-up myelographic CT. Relatively less attention is typically given to spinal MRI in the diagnosis of SIH, mainly because it is not particularly effective in localizing the CSF leak [5]. However, many spinal MRI manifestations of SIH have now been described, such as dilated epidural or intradural veins, dural enhancement, meningeal diverticula, epidural CSF collections, and collapse of the dural sac [10, 12, 18, 22 25]. In this case, the initial spinalmriwasnotinformativebecausetherewasnoclinical suspicion of spontaneous spinal CSF leak. MRI did not reveal characteristic signs of spinal CSF leak, such as epidural CSF collection or pseudomeningocele, or a dilated epidural vein causing compression of low thoracic nerve root. Enhancement was not performed. The enhanced spine MRI taken 2 weeks after the initial EBP again showed no typical findings of spontaneous CSF leak. However, on enhancement study in this occasion, subtle leptomeningeal enhancement was found from the T12 to L3 level. It seems that the severity of the spontaneous CSF leak in the present case was obviously milder than those reported in theliterature.thiscsfleakwasnotsevereenoughtocausean orthostatic headache and typical spinal MRI findings of a CSF collectionepidurallyandinparaspinalmuscles[3,22,23]. However, there were definite spontaneous CSF leaks at the L2-3 level and a chronic, low thoracic radiculopathic pain of 12-month duration, which showed a positional pain and which responded to L1-2 epidural blood patch. We speculate that a less severe type of spontaneous spinal CSF leak might cause intracranial hypotension and subsequent stretching or irritation of a lower thoracic root which would result in chronic radicular pain. Assuming that thoracic radicular pain unassociated with anatomical pathology presents without positional headache, clinical suspicion of spontaneous CSF leak would not be possible in daily clinical practice if spinal MRI does not show an extensive epidural fluid collection or paraspinal CSF extension. As shown in present case, spontaneous spinal CSF leak as a cause of unexplained, chronic thoracic radicular pain inevitably requires a process of diagnosis of exclusion. We suggest that if unexplained thoracic radicular pain presents without orthostatic headache, even without the brain and spinal findings of SIH, spontaneous spinal CSF leak should be included in the list of differential diagnosis. 4. Conclusion The occurrence of cervical unilateral radiculopathic pain caused by spontaneous spinal CSF leak has been reported in association with a typical orthostatic headache. The development of an isolated chronic lower unilateral thoracic radicular pain without orthostatic headache may be a rare manifestation of a remotely located spontaneous CSF leak. Asshowninourcase,disablinglowerthoracicunilateral radicular pain of 12-month duration from an L2-3 CSF leak responded at 12-month follow-up after two epidural blood patches. We speculate that a chronic, milder pattern of spontaneous spinal CSF leak may cause a radicular pain without typical symptoms of intracranial hypotension. Spontaneous spinal CSF leak may have a different presentation of remote radicular pain and presents a variability to the clinical features of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Acronyms CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid EBP: Epidural blood patch Myelographic CT: Myelography computed tomography SIH: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Competing Interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests regarding this paper. References [1] K. Miyazawa, Y. Shiga, T. Hasegawa et al., CSF hypovolemia vs. intracranial hypotension in spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome, Neurology,vol.60,no.6,pp ,2003.
5 Pain Research and Management 5 [2] B. Mokri, Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leaks: from intracranial hypotension to cerebrospinal fluid hypovolemia evolution of a concept, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, vol. 74, no. 11, pp , [3] M. Paldino, A. Y. Mogilner, and M. S. Tenner, Intracranial hypotension syndrome: a comprehensive review, Neurosurgical Focus,vol.15,no.6,articleECP2,2003. [4] W. I. Schievink, Misdiagnosis of spontaneous intracranial hypotension, Archives of Neurology, vol. 60, no. 12, pp , [5] W. I. Schievink, Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension, The the American Medical Association,vol.295,no.19,pp ,2006. [6]W.I.Schievink,F.B.Meyer,J.L.D.Atkinson,andB.Mokri, Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension, Neurosurgery, vol. 84, no. 4, pp , [7] W. I. Schievink and V. E. Torres, Spinal meningeal diverticula in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, The Lancet, vol.349,no.9060,pp ,1997. [8]I.Schrijver,W.I.Schievink,M.Godfrey,F.B.Meyer,and U. Francke, Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and minor skeletal features of Marfan syndrome: a microfibrillopathy, Neurosurgery,vol.96,no.3,pp ,2002. [9] S. Albayram, B. A. Wasserman, D. M. Yousem, and R. Wityk, Intracranial hypotension as a cause of radiculopathy from cervical epidural venous engorgement: case report, American Neuroradiology,vol.23,no.4,pp ,2002. [10] W.P.DillonandR.A.Fishman, Somelessonslearnedaboutthe diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension, American Neuroradiology, vol.19,no.6,pp , [11] P. J. Goadsby and C. Boes, New daily persistent headache, Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry,vol.72,supplement 2,pp ,2002. [12]M.T.Burtis,J.L.Ulmer,G.A.Miller,A.C.Barboli,S.A. Koss, and W. D. Brown, Intradural spinal vein enlargement in craniospinal hypotension, American Neuroradiology, vol.26,no.1,pp.34 38,2005. [13] J. Inamasu and B. H. Guiot, Intracranial hypotension with spinal pathology, Spine Journal,vol.6,no. 5,pp ,2006. [14]A.H.RopperandR.H.Brown, Diseaseoftheperipheral nerves, in Adams and Victor s Principles of Neurology, A. H. Ropper and R. H. Brown, Eds., pp , McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, USA, 8th edition, [15] D.H.Gilden,R.R.Wright,S.A.Schneck,J.M.GwaltneyJr.,and R. Mahalingam, Zoster sine herpete, a clinical variant, Annals of Neurology,vol.35,no.5,pp ,1994. [16] D.R.MayoandJ.Booss, Varicellazoster associatedneurologic disease without skin lesions, Archives of Neurology, vol. 46, no. 3, pp , [17] B. Mokri, J. L. D. Atkinson, and D. G. Piepgras, Absent headache despite CSF volume depletion (intracranial hypotension), Neurology,vol.55,no.11,pp ,2000. [18] M. S. Hochman and T. P. Naidich, Diffuse meningeal enhancement in patients with overdraining, long-standing ventricular shunts, Neurology,vol.52, no.2,pp , [19] W. I. Schievink and J. Tourje, Intracranial hypotension without meningeal enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging: case report, Neurosurgery, vol. 92, no. 3, pp , [20] K. L. Schoffer, T. J. Benstead, and I. Grant, Spontaneous intracranial hypotension in the absence of magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities, Canadian Neurological Sciences,vol.29,no.3,pp ,2002. [21] T. A. Rando and R. A. Fishman, Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: report of two cases and review of the literature, Neurology,vol.42,no.3,pp ,1992. [22] C.-J. Chen, T.-H. Lee, H.-L. Hsu, Y.-C. Tseung, Y.-C. Wong, and L.-J. Wang, Spinal MR findings in spontaneous intracranial hypotension, Neuroradiology, vol. 44, no. 12, pp , [23] L. Chiapparini, L. Farina, L. D Incerti et al., Spinal radiological findings in nine patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension, Neuroradiology, vol. 44,no. 2, pp , [24] N. N. Moayeri, J. W. Henson, P. W. Schaefer, and N. T. Zervas, Spinal dural enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: report of threecasesandreviewoftheliterature, Neurosurgery, vol. 88, no. 5, pp , [25] B.M.Rabin,S.Roychowdhury,J.R.Meyer,B.A.Cohen,K.D. LaPat,andE.J.Russell, Spontaneousintracranialhypotension: spinal MR findings, American Neuroradiology, vol. 19, no. 6, pp , 1998.
6 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman
 Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension
 online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
 Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Case Report Synovial Cyst Mimicking an Intraspinal Sacral Mass
 , Article ID 953579, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/953579 Case Report Synovial Cyst Mimicking an Intraspinal Sacral Mass Jason Hoover 1,2 and Stephen Pirris 3 1 The Texas Brain and Spine Institute,
, Article ID 953579, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/953579 Case Report Synovial Cyst Mimicking an Intraspinal Sacral Mass Jason Hoover 1,2 and Stephen Pirris 3 1 The Texas Brain and Spine Institute,
While some patients with SIH recover without intervention
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention Demonstrated on MRI
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch
 J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report
 Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities
 DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache
 Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Low PRESSURE Headaches. What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah
 Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory headache due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report
 DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal
 Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Report Three Cases of Neoplastic Meningitis Initially Diagnosed with Infectious Meningitis in Emergency Department
 Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 561475, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/561475 Case Report Three Cases of Neoplastic Meningitis Initially Diagnosed with Infectious Meningitis
Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 561475, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/561475 Case Report Three Cases of Neoplastic Meningitis Initially Diagnosed with Infectious Meningitis
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension
 Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report and review of literature
 Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Spinal Imaging Findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
Spinal CSF leak syndrome is a rare disorder characterized
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Remembering Donald J. Dalessio, MD The Headache Clinic Featuring the Baylor Scott & White Headache Clinic in Temple, Texas.
 Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch
 LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a syndrome characterized
 Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report
 Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) classically
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
The spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) syndrome
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
Time-Dependent Changes in Dural Enhancement Associated With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 131962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/131962 Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report F. Koech,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 131962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/131962 Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report F. Koech,
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Kanji Mori, Kazuya Nishizawa, Akira Nakamura, and Shinji Imai. 1. Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Case Report Atypical Presentation of Idiopathic Bilateral Optic Perineuritis in a Young Patient
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 6741925, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6741925 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Idiopathic Bilateral Optic Perineuritis in
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 6741925, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6741925 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Idiopathic Bilateral Optic Perineuritis in
Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 328103, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/328103 Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 328103, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/328103 Case Report Pneumocephalus Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula as a Complication of Spinal Surgery: A Case
Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of the Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Medical Affairs Policy
 Medical Affairs Policy Service: Back Pain Procedures-Epidural Injection (Caudal Epidural, Selective Nerve Root Block, Interlaminar, Transforaminal, Translaminar Epidural Injection) PUM 250-0015-1706 Medical
Medical Affairs Policy Service: Back Pain Procedures-Epidural Injection (Caudal Epidural, Selective Nerve Root Block, Interlaminar, Transforaminal, Translaminar Epidural Injection) PUM 250-0015-1706 Medical
Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report
 Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension
 Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Cervical Spine in Baseball
 Cervical Spine in Baseball Robert G Watkins, IV, MD Co-Director, Marina Spine Center Marina del Rey, CA Vice Chief of Staff Cedars-Marina del Rey Hospital Disclosures n Pioneer / RTI Consulting, Royalties
Cervical Spine in Baseball Robert G Watkins, IV, MD Co-Director, Marina Spine Center Marina del Rey, CA Vice Chief of Staff Cedars-Marina del Rey Hospital Disclosures n Pioneer / RTI Consulting, Royalties
Review Article. Abstract. Introduction. Pathophysiology:
 Pathophysiology and management of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension A Review Nadir Ali Syed, 1 Farhan Arshad Mirza, 2 Aqueel Hussain Pabaney, 3 Rameez-ul-Hassan 4 Review Article Department of Neurology,
Pathophysiology and management of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension A Review Nadir Ali Syed, 1 Farhan Arshad Mirza, 2 Aqueel Hussain Pabaney, 3 Rameez-ul-Hassan 4 Review Article Department of Neurology,
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome in a Patient With Marfan Syndrome and Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 632 April 2008 secondary causes of intracranial hypertension can be lifethreatening. Review of the imaging studies by an experienced neuro-radiologist is of paramount importance. Low threshold for repeat
632 April 2008 secondary causes of intracranial hypertension can be lifethreatening. Review of the imaging studies by an experienced neuro-radiologist is of paramount importance. Low threshold for repeat
Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai. Interventional Options
 10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Case Report Calcific Tendonitis of the Longus Colli Muscle: A Noninfectious Cause of Retropharyngeal Fluid Collection
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 286190, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/286190 Case Report Calcific Tendonitis of the Longus Colli Muscle: A Noninfectious Cause of Retropharyngeal Fluid
Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 286190, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/286190 Case Report Calcific Tendonitis of the Longus Colli Muscle: A Noninfectious Cause of Retropharyngeal Fluid
Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic Left Lung
 Volume 2013, Article ID 620120, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/620120 Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic
Volume 2013, Article ID 620120, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/620120 Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at (sent 5/9/17) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Clinical Study The Incidence and Management of Pleural Injuries Occurring during Open Nephrectomy
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 948906, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/948906 Clinical Study The Incidence and Management of Pleural Injuries Occurring during Open Nephrectomy Ali Fuat Atmaca, Abdullah
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 948906, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/948906 Clinical Study The Incidence and Management of Pleural Injuries Occurring during Open Nephrectomy Ali Fuat Atmaca, Abdullah
Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission
 Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Case Report Spontaneous Rapid Resolution of Acute Epidural Hematoma in Childhood
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 956849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/956849 Case Report Spontaneous Rapid Resolution of Acute Epidural Hematoma in Childhood Ismail GülGen, 1
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 956849, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/956849 Case Report Spontaneous Rapid Resolution of Acute Epidural Hematoma in Childhood Ismail GülGen, 1
Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery Shunt Narrowing
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 779 783 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.146 Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction Aaron Bayne 1, Brad Koslin 2, and Siamak Daneshmand
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 779 783 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.146 Bilateral Segmental Testicular Infarction Aaron Bayne 1, Brad Koslin 2, and Siamak Daneshmand
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Transdural Nerve Rootlet Entrapment in the Intervertebral Disc Space through Minimal Dural Tear : Report of 4 Cases
 www.jkns.or.kr J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 52-56, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.1.52 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2013 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Case Report
www.jkns.or.kr J Korean Neurosurg Soc 53 : 52-56, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.1.52 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2013 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Case Report
Overview. Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord. Anatomy of the dura. Anatomy of the arachnoid. Anatomy of the spinal meninges
 European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN
 A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN W Singleton, D Ramnarine, N Patel, C Wigfield Department of Neurological Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol, UK Introduction We present
A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN W Singleton, D Ramnarine, N Patel, C Wigfield Department of Neurological Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol, UK Introduction We present
Case Report Subacute Subdural Hematoma in a Patient with Bilateral DBS Electrodes
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 390727, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/390727 Case Report Subacute Subdural Hematoma in a Patient with Bilateral DBS Electrodes Ha
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 390727, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/390727 Case Report Subacute Subdural Hematoma in a Patient with Bilateral DBS Electrodes Ha
DISORDERS OF THE SPINE TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET
 DISORDERS OF THE SPINE TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET Short form FOR REPRESENTATIVE USE ONLY REPRESENTATIVE S NAME AND ADDRESS REPRESENTATIVE S TELEPHONE REPRESENTATIVE S EMAIL PHYSICIAN S NAME AND ADDRESS
DISORDERS OF THE SPINE TREATING PHYSICIAN DATA SHEET Short form FOR REPRESENTATIVE USE ONLY REPRESENTATIVE S NAME AND ADDRESS REPRESENTATIVE S TELEPHONE REPRESENTATIVE S EMAIL PHYSICIAN S NAME AND ADDRESS
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5263248, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5263248 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case Susumu
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5263248, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5263248 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case Susumu
Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management
 THIEME Original Article 15 Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management Vernon Velho 1 Sachin Guthe 1 Pravin Survashe 1 Poonam
THIEME Original Article 15 Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management Vernon Velho 1 Sachin Guthe 1 Pravin Survashe 1 Poonam
Case Report Crossed Renal Ectopia without Fusion An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 728531, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/728531 Case Report Crossed Renal Ectopia without Fusion An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain: A Case Report D. P. Ramaema,
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 728531, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/728531 Case Report Crossed Renal Ectopia without Fusion An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain: A Case Report D. P. Ramaema,
Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome
 Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V?
 Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Isolated Cranial Nerve-III Palsy Secondary to Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Medicine Isolated Cranial Nerve-III Palsy Secondary to Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Hussam A. Yacoub MD Lehigh Valley Health
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Medicine Isolated Cranial Nerve-III Palsy Secondary to Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Hussam A. Yacoub MD Lehigh Valley Health
Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral Fracture: Two Case Reports of Curved Femurs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Synovial cyst of spinal facet
 Case report CHUN C. KAO, M.D., STEFAN S. WINKLER, M.D., AND J. H. TURNER, M.D. Sections of Neurosurgery, Radiology, and Pathology, Madison Veterans Administration Hospital, and University of Wisconsin,
Case report CHUN C. KAO, M.D., STEFAN S. WINKLER, M.D., AND J. H. TURNER, M.D. Sections of Neurosurgery, Radiology, and Pathology, Madison Veterans Administration Hospital, and University of Wisconsin,
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
 What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) What is Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumour
What is IIH? Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) What is Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension? Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as benign intracranial hypertension or pseudotumour
Regional Pain Syndromes: Neck and Low Back
 Regional Pain Syndromes: Neck and Low Back Srinivas Nalamachu, MD Disclosures Consultant/Independent Contractor/Honoraria: Ferring 1 Learning Objectives Identify the most common painful conditions in the
Regional Pain Syndromes: Neck and Low Back Srinivas Nalamachu, MD Disclosures Consultant/Independent Contractor/Honoraria: Ferring 1 Learning Objectives Identify the most common painful conditions in the
Clinical and Radiological Findings of Nerve Root Herniation after Discectomy of Lumbar Disc Herniation
 www.jkns.or.kr J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52 : 62-66, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.1.62 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2012 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Case Report
www.jkns.or.kr J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52 : 62-66, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.1.62 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2012 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Case Report
Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects.
 Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
