Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report
|
|
|
- Thomasina Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, Available online at Science and Education Publishing DOI: /ajmcr Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report Blumer V 1, Rosemberg D 2, Kaswan E 3, Lustgarten L 4,* 1 Internal Medicine, Jackson Memorial Hospital, Miami, USA 2 Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation, Centro Clinico Profesional Caracas, Caracas, Venezuela 3 Internal Medicine, Hospital de Clinicas Caracas, Caracas, Venezuela 4 Neurosurgery, Hospital de Clinicas Caracas, Caracas, Venezuela *Corresponding author: leolust@gmail.com Received August 20, 2015; Revised August 26, 2015; Accepted August 31, 2015 Abstract Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is an underdiagnosed syndrome and initially missed cause of headaches. The classical presentation is that of an orthostatic headache, mainly caused by spontaneous and difficult to detect spinal CSF leaks. The current case report describes a 38 year old female patient who presented with symptoms following a Yoga class. Despite being initially misdiagnosed, her clinical course and radiological findings made it clear that she had intracranial hypotension syndrome with bilateral chronic subdural hematomas and cerebellar descent. She responded to surgical drainage of both her subdural hematomas and conservative management for her suspected CSF leak. This case, to our knowledge, is the first report in the literature of spontaneous intracranial hypotension being caused by a Yoga class. The report highlights the fact that some cases of SIH can be difficult to diagnose as their symptoms may be very confusing. Thorough interrogation of patients is vital, as trivial efforts and some exercising activities could be the cause of spontaneous dural tears. Early recognition is important to prevent unnecessary investigations and procedures, and to minimize delay in treatment. Keywords: spontaneous intracranial hypotension, orthostatic headache, low pressure headache, CSF leak, Yoga Cite This Article: Blumer V, Rosemberg D, Kaswan E, and Lustgarten L, Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report. American Journal of Medical Case Reports, vol. 3, no. 10 (2015): doi: /ajmcr Introduction Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is an uncommon but increasingly recognized cause of headaches in young and middle-aged individuals mainly caused by spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks. Initial misdiagnosis is rather common. Orthostatic headache is the main symptom and clinical examination is usually normal. Magnetic resonance imaging shows the characteristic association of: diffuse pachymeningeal gadolinium enhancement, venous dilatation, sagging brain and bilateral subdural collections. Despite various possible explanations, the pathogenesis of this clinical entity is still a motive of debate. Conservative treatment is initially attempted and spinal epidural blood patch is reserved for those patients who fail this approach. We describe the first reported case of Yoga associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. 2. Case Report We present the interesting case of a 38-year-old Caucasian woman who was completely asymptomatic until finishing an intense Yoga class. She initially developed a diffuse and severe headache combined with cervical pain that was interpreted as a cervical muscle sprain. Given that her symptoms at the time were mainly in the neck, she was investigated with a cervical MRI that showed mild rectification with no other relevant radiological findings. She was then referred to physical therapy. As the following weeks evolved, she developed a classic orthostatic headache that improved with supine position and caffeine, and worsened when sitting or standing up. A brain MRI showed diffuse pachymeningeal gadolinium enhancement both surrounding the brain and cervical spine, with cerebellar tonsillar descent towards the foramen magnum, posterior fosa crowding, engorged cerebral venous sinuses, enlarged pituitary gland, decreased size of the ventricles and bilateral subdural fluid collections. A lumbar puncture was performed evidencing very low pressure and obtaining minimal amount of fluid. At this point, no diagnosis was reported by the treating physician and no treatment was recommended. Her symptoms continued progressing and by the time she consulted our institution for the first time, three weeks later (six weeks after the onset of her symptoms), her postural headache had significantly worsen, nonetheless, her neurological examination was unremarkable. Upon reviewing her case, we felt her symptoms were typical and consistent with intracranial hypotension syndrome and her previous radiological findings confirmed our clinical
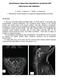
2 315 American Journal of Medical Case Reports suspicion. A repeat brain and cervical MRI (Figure 1, Figure 2) showed that both subdural collections had significantly increased in size with flattening of her sulci over the convexity and her pachymeningeal enhancement also increased in size specially at the cervical region (Figure 3). Figure 1. Gadolinium-enhanced T1 weighted MRI image demonstrating diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement and bilateral subdural fluid collections. a) Coronal view. b) Sagital image with mildly prominent pituitary gland and brain sagging Figure 2. T2 weighted MRI of the brain showing bilateral fluid collections with flattening of both hemispheres. a) axial and b) coronal views Given that her headaches had become almost unbearable and the collections had worsen, we decided to investigate the underlying cause and surgically treat them. She underwent a bilateral craniectomy and surgical drainage of her bilateral subdural collections (both under significant pressure). Her postoperative course was uneventful. A gadolinium Myelo MRI was performed trying to identify a possible CSF leak which was not demonstrated. Given that she never attempted a conservative approach with bed rest, she was discharged home under absolute bed rest and caffeine intake, with progressive tolerance to orthostatism. Her previous symptoms disappeared without further action needed and she gradually returned to her activities of daily living.
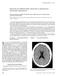
3 American Journal of Medical Case Reports 316 Figure 3. Gadolinium-enhanced T1 weighted sagital MRI image demonstrating brain sagging and posterior fossa crowding with diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement extending towards the cervical spine, being specially prominent and thick at the C2 level 3. Discussion Intracranial Hypotension may be spontaneous (no evident cause found) or provoked by interventions such as a lumbar puncture, unintentional dural puncture during spinal anesthesia, or after neurosurgical procedures. Although it is generally accepted that Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension (SIH) is due to a CSF leakage, the exact cause of the spontaneous leak remains unclear in many cases and its true incidence is therefore unknown [1,2,3,4]. When present, the leak most commonly arises from the spine, and less frequently from the skull base [1,2]. Some reports suggest that spontaneous spinal CSF leaks may be related to an underlying preexisting structural weakness of the dura rendering it more vulnerable to the effect of trivial trauma or unusual strains [1-6]. Reported triggering events include lifting small or large items, straining, stretching, coughing, positional changes, sporting activities, roller coaster rides, falls, and rarely, activities such as pilates or chiropractic manipulation [3,5,6,7,8]. Connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type II, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and isolated joint hypermobility, have also been associated with SIH [1,2]. According to the International Classification of Headache Disorders [9], a headache attributed to SIH is usually accompanied by low CSF pressure (<60 mm CSF) and/or has evidence of CSF leakage on imaging. Clinically, orthostatic (or postural) headache is the hallmark of this condition [1] typically reaching its highest intensity within a few seconds or minutes of being upright and decreasing upon lying down. It may be generalized or localized to the frontal, temporal or, most frequently, the occipital or suboccipital regions [1,6]. The severity is variable and correlates poorly with the degree of intracranial hypotension [3]. Associated symptoms may include neck pain or stiffness, nausea, vomiting, diplopia, blurred vision, tinnitus or altered hearing, facial numbness or pain [1,10,11]. There are several explanations to the headaches in SIH. The downward displacement of the brain due to loss of CSF buoyancy is the most plausible mechanism used to explain the typical headache in SIH. This forced shift causes traction on pain-sensitive structures, predominantly the dura, resulting in a headache provoked by orthostatism. The compensatory response of cerebral vasodilatation to the loss of CSF volume, evident as pachymeningeal enhancement on cranial MRI, may also contribute to pain. Alongside, this downward displacement of the brain may result in stretching of some cranial nerves; this mechanism may explain the other associated symptoms in SIH described previously [12]. Clinical presentation is often highly suggestive of the diagnosis, however, because of the nonspecific nature of the symptoms, combined with unfamiliarity with the condition, many cases probably remain undiagnosed [11]. The initial approach is a thorough clinical history of the patient s symptoms with a high index of suspicion. Imaging is used to confirm the diagnosis and to try to localize a possible leak in order to plan treatment [1,3,11,12]. Lumbar puncture is usually not necessary for the diagnosis, nevertheless, low CSF opening pressure on spinal tap is one of the diagnostic criteria suggested by the International Headache Society [9]. MRI with gadolinium enhancement is the imaging modality of choice. The most common and typical radiological findings on MRI are: subdural fluid collections, enhancement of the meninges, engorgement of venous structures (sinuses), pituitary enlargement, and downward displacement ( sagging ) of the brain. Subdural hematomas are fairly common and can be among the first findings of SIH [1,13,14,15,16]. Although MRI with gadolinium enhancement has become the first-line diagnostic radiological tool, it is not usually helpful in localizing the exact site of a CSF leak. CT myelography, radionuclide cisternography and MRI myelography with gadolinium have all been reported to be useful in detecting the site of CSF leak with varying degrees of success [6,7,16,17,18] and either one or in combination are
4 317 American Journal of Medical Case Reports commonly used in cases of SIH. When localized, the CSF leak may appear as a subtle or as a diffuse extravasation of contrast. The majority of leaks are at the cervico-thoracic junction or thoracic spine. Occasionally, multiple simultaneous CSF leaks are demonstrated on myelography at different spinal levels. Given that some of the imaging studies mentioned above may be somehow invasive, often fail to pinpoint the site of leakage [7], and in many cases do not alter our management plan, some authors believe that striving to search for a dural tear is essentially unnecessary [19]. Initial conservative management with bed rest, hydration (or, more accurately, overhydration), caffeine, and analgesia is generally the first course of action. Steroids, theophylline, abdominal binders or corsets have also been used with inconclusive evidence of efficacy [4,7,20]. Despite the subdural collections being a frequent component in these patients, the decision to surgically drain them as the mainstay of treatment is still controversial [13,14,21]. They seem to occur secondary to the tearing of small bridging veins caused by the downward traction on the brain as the CSF volume decreases and usually respond to conservative management. Nonetheless, patients with clinically important or enlarging subdural hematomas or progressive debilitating symptoms seem to have a more defined indication to proceed with surgery and may require neurosurgical intervention [12,20]. For those patients that fail to respond to conservative management, an epidural blood patch (EBP) is the mainstay of treatment [7,14,20,22,23,24,25]. This procedure involves injecting autologous blood into the epidural space, increasing the total volume within the spinal canal and thus raising the CSF pressure. Patients often refer immediate relief of their symptoms. The mechanism of action is believed to be twofold. The first is an immediate volume replacement, and the second is the sealing of the dural defect, which may be delayed from the first action [6]. If the location of the leak has been identified, the blood patch can be targeted accordingly at that spinal level. Otherwise, a blind injection into the lumbar spine is often successful [7,12,20,24], or even injecting at different sites has been done with favorable results [1,26,27]. It is worth mentioning at this point that the hypothesis involving intravenous hypotension as the pathogenesis in developing SIH is of particular importance. The loss of pressure inside the venous system may create a differential pressure gradient between venous and CSF compartments, possibly disrupting the dura at one or even several locations. Furthermore, this theory may also explain the success of unselective (or blind) epidural blood patches producing tamponage in the epidural space as well as compressing the leakage sites. [28]. Alternative treatments in special situations or when EBP fails include epidural saline infusions, epidural fibrin glue, fibrin glue and blood, and even epidural infusion of dextran (rarely practiced) [4,20]. However, the effectiveness of these measures has not been well established due to limited data. Surgical repair is a last resource treatment only when conservative treatment fails and the source of the leak has been clearly identified. 4. Conclusion Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a common but unrecognized cause of headaches. Initial misdiagnosis is frequent and patients tend to suffer progressive and debilitating symptoms before a clear diagnosis is made. Early recognition and clinical awareness of spontaneous intracranial hypotension is therefore important to prevent unnecessary investigations and a delay in treatment. Yoga may be a risk factor for the development of a spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak in certain patients. References [1] Schievink, W. Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks and Intracranial Hypotension. JAMA. 2006;295: [2] Frank L, Paxson A, Brake J. Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - A Case Report. J Emerg Med. 2005; 28(4): [3] Schievink W, Deline C. Headache Secondary to Intracranial Hypotension. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2014; 18:457. [4] Mokri B. Spontaneous CSF Leaks - Low CSF Volume Syndromes. Neurol Clin. 2014; 32: [5] Davis J, Yanny I, Chatu S, et al. Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak following a pilates class: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014; 8: 456. [6] Spears, R. Low-Pressure/Spinal Fluid Leak Headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2014; 18:425. [7] Lahoria R, Allport L, Glenn D, et al. Spontaneous low pressure headache A review and illustrative patient. J Clin Neurosci. 2012; 19: [8] Tuchin P. A systematic literature review of intracranial hypotension following chiropractic. Int J Clin Pract. 2014; 68(3): [9] International Headache Society Classification Subcommittee. International classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 2013; 33(9): [10] Scott S, Davenport R. Low pressure headaches caused by spontaneous intracranial hypotension. BMJ. 2014; 349:6219. [11] Malone R, Love J. Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Case Report and Relevant Review of the Literature. J Emerg Med. 2007; 32 (4): [12] Yoon S, Chung Y, Yoon B, et al. Clinical experiences with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: A proposal of a diagnostic approach and treatment. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011; 113: [13] Chen H, Huang C, Hseu S, et al. Bilateral Subdural Hematomas Caused by Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension. J Chin Med Assoc 2008;71(3): [14] Kim B, Jung Y, Kim M, et al. Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Case Treated with Epidural Blood Patch on C1-2. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2001; 50: [15] Watanabe A, Horikoshi T, Uchida M, et al. Diagnostic value of spinal MR imaging in spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30: [16] Schievink WI. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. Cephalalgia. 2008; 28: [17] Schievink WI, Meyer FB, Atkinson JLD, et al: Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension. J Neurosurg. 1996; 84: [18] Schievink WI, Morreale VM, Atkinson JLD, et al: Surgical treatment of spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. J Neurosurg. 1998; 88: [19] Bousser MG. Headache in spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid hypotension. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2005; 161(6-7): [20] Mokri B. Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks. Headache. 2013; 53 (7): [21] Warnick W, Neal J. Beyond Spinal Headache: Prophylaxis and Treatment of Low-Pressure Headache Syndromes. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007;32:
5 American Journal of Medical Case Reports 318 [22] Kantor D, Silberstein S. Cervical epidural blood patch for low CSF pressure headaches. Neurology. 2005; 65(1): [23] Madsen SA, Fomsgaard JS, Jensen R. Epidural blood patch for refractory low CSF pressure headache: a pilot study. Headache Pain. 2011; 12: [24] Shrikrishna D, Green C, Wood D, et al. Life-threatening spontaneous intracranial hypotension responding to epidural blood patch. BJA. 2006; 97(5): 750. [25] Ferraro F, Marano E, Petruzzi J, et al. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension and epidural blood patch: a report involving seven cases. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2013; 41(3): [26] Beleña JM, Nuñez M, Yuste J, et al. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome treated with a double epidural blood patch. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012; 56(10): [27] Ohtonari T, Ota S, Nishihara N, et al. A novel technique of multiple-site epidural blood patch administration for the treatment of cerebrospinal fluid hypovolemia. J Neurosurg. 2012; 116(5): [28] Franzini A, Messina G, Nazzi V, et al. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome: a novel speculative physiopathological hypothesis and a novel patch method in a series of 28 consecutive patients. J Neurosurg. 2010;112(2):300-6.
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman
 Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
Remembering Donald J. Dalessio, MD The Headache Clinic Featuring the Baylor Scott & White Headache Clinic in Temple, Texas.
 Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities
 DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
Low PRESSURE Headaches. What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah
 Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension
 online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
While some patients with SIH recover without intervention
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory headache due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report
 DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch
 J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch
 LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache
 Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension
 Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission
 Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report
 Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects.
 Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a syndrome characterized
 Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal
 Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) classically
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
Time-Dependent Changes in Dural Enhancement Associated With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report
 Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Definition by ICHD: 7.2 Headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure (see ICHD 3 rd edition beta version Cephalalgia 2013; 33(9): )
 Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Intracranial hypotension after trauma
 Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES
 2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
 Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension
 Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Postdural Puncture Headache
 2015 Annual Meeting and Workshops Postdural Puncture Headache Christopher L. Wu, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, Maryland Disclosures No financial conflicts of
2015 Annual Meeting and Workshops Postdural Puncture Headache Christopher L. Wu, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, Maryland Disclosures No financial conflicts of
Post-Dural Puncture Headache. Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel
 Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH), also
 CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai. Interventional Options
 10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of:
 This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of: Severe bilateral subdural hematomas as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture for possible Alzheimers disease Reference: Verslegers Lieven,
This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of: Severe bilateral subdural hematomas as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture for possible Alzheimers disease Reference: Verslegers Lieven,
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
CSF Leaks. Abnormal communication between the subarachnoid space and the tympanomastoid space or nasal cavity. Presenting symptoms:
 CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
Lumbar puncture. Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml): <1h
 Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks. Bahram Mokri, MD
 Headache 2013 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/head.12149 Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks
Headache 2013 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/head.12149 Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Spontaneous Low Pressure, Low CSF Volume Headaches: Spontaneous CSF Leaks
Spinal Imaging Findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Anesthesiology ROUNDS. The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture Headache. Anesthesia. Volume 8, Issue 5
 2010 Volume 8, Issue 5 Anesthesiology ROUNDS A PHYSICIAN LEARNING RESOURCE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL AND McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTIES OF MEDICINE The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture
2010 Volume 8, Issue 5 Anesthesiology ROUNDS A PHYSICIAN LEARNING RESOURCE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL AND McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTIES OF MEDICINE The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture
Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics
 Appendix 2: Case Report Form EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics Case Report Form Please fill each relevant step carefully Step 1. From Epidural
Appendix 2: Case Report Form EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics Case Report Form Please fill each relevant step carefully Step 1. From Epidural
Internal Carotid Artery Dissection
 May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report and review of literature
 Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Review Article. Abstract. Introduction. Pathophysiology:
 Pathophysiology and management of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension A Review Nadir Ali Syed, 1 Farhan Arshad Mirza, 2 Aqueel Hussain Pabaney, 3 Rameez-ul-Hassan 4 Review Article Department of Neurology,
Pathophysiology and management of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension A Review Nadir Ali Syed, 1 Farhan Arshad Mirza, 2 Aqueel Hussain Pabaney, 3 Rameez-ul-Hassan 4 Review Article Department of Neurology,
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome in a Patient With Marfan Syndrome and Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 632 April 2008 secondary causes of intracranial hypertension can be lifethreatening. Review of the imaging studies by an experienced neuro-radiologist is of paramount importance. Low threshold for repeat
632 April 2008 secondary causes of intracranial hypertension can be lifethreatening. Review of the imaging studies by an experienced neuro-radiologist is of paramount importance. Low threshold for repeat
Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review
 Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1897 1904 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review Shruti G. Kapoor, MD, MPH* and Shihab Ahmed, MBBS, MPH *Department of Anesthesiology,
Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1897 1904 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review Shruti G. Kapoor, MD, MPH* and Shihab Ahmed, MBBS, MPH *Department of Anesthesiology,
1242 Intracranial Hypertension After CSF Leaks Mayo Clin Proc, November 2002, Vol 77 indium In 111 cisternography and CT myelography. These studies sh
 Mayo Clin Proc, November 2002, Vol 77 Intracranial Hypertension After CSF Leaks 1241 Case Report Intracranial Hypertension After Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks BAHRAM MOKRI, MD Four
Mayo Clin Proc, November 2002, Vol 77 Intracranial Hypertension After CSF Leaks 1241 Case Report Intracranial Hypertension After Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks BAHRAM MOKRI, MD Four
Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
Meningioma tumor. Meningiomas are named according to their location (Fig. 1) and cause various symptoms: > 1
 Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
Chiari malformations. A fact sheet for patients and carers
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
Dural Puncture Headache: How to Prevent It and What to Do When It Happens Kathleen A. Smith, M.D. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC
 Session: L125 Session: L338 Dural Puncture Headache: How to Prevent It and What to Do When It Happens Kathleen A. Smith, M.D. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC Disclosures: This presenter has
Session: L125 Session: L338 Dural Puncture Headache: How to Prevent It and What to Do When It Happens Kathleen A. Smith, M.D. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC Disclosures: This presenter has
Chiari bridges review Chiari Treatments & Potential Pitfalls
 Chiari bridges review Chiari Treatments & Potential Pitfalls Once diagnosed, you will usually be referred to a specialist (not a Chiari Specialist, but an everyday, run-of-the-mill neurologist or neurosurgeon).
Chiari bridges review Chiari Treatments & Potential Pitfalls Once diagnosed, you will usually be referred to a specialist (not a Chiari Specialist, but an everyday, run-of-the-mill neurologist or neurosurgeon).
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a debilitating
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE MR Myelography for Identification of Spinal CSF Leak in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension J.L. Chazen, J.F. Talbott, J.E. Lantos, and W.P. Dillon ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE MR Myelography for Identification of Spinal CSF Leak in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension J.L. Chazen, J.F. Talbott, J.E. Lantos, and W.P. Dillon ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
POSTPARTUM MANAGEMENT OF DURAL PUNCTURE
 Document Ref: MAT 0145 WOMEN AND CHILDREN S and CLINICAL SUPPORT SERVICES DIVISION Clinical Guideline POSTPARTUM MANAGEMENT OF DURAL PUNCTURE For use in: (Clinical Area) For use by: (Staff Group) Distributed
Document Ref: MAT 0145 WOMEN AND CHILDREN S and CLINICAL SUPPORT SERVICES DIVISION Clinical Guideline POSTPARTUM MANAGEMENT OF DURAL PUNCTURE For use in: (Clinical Area) For use by: (Staff Group) Distributed
PDPH: To Patch or Not to Patch
 PDPH: To Patch or Not to Patch Moderators: 1. Kim Strupp, MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology, Children s Hospital Colorado/University of Colorado, Aurora, CO 2. Debnath Chatterjee, MD Associate
PDPH: To Patch or Not to Patch Moderators: 1. Kim Strupp, MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology, Children s Hospital Colorado/University of Colorado, Aurora, CO 2. Debnath Chatterjee, MD Associate
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Spinal CSF leak syndrome is a rare disorder characterized
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Incidental durotomy during spine surgery occurs in. Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks
 J Neurosurg Spine 21:805 810, 2014 AANS, 2014 Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks Clinical article Frank Mihlon, M.D., Peter G. Kranz, M.D., Andreia
J Neurosurg Spine 21:805 810, 2014 AANS, 2014 Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks Clinical article Frank Mihlon, M.D., Peter G. Kranz, M.D., Andreia
The spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) syndrome
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
Frank Rosemeier. MD, MRCP(UK), MRCA, DipPEC(SA) Attending Anesthesiologist. JLR Medical Group
 Postdural Puncture Headaches A Contemporary Update Frank Rosemeier MD, MRCP(UK), MRCA, DipPEC(SA) Attending Anesthesiologist JLR Medical Group Maitland, FL Why should we care? Mother want to feel well
Postdural Puncture Headaches A Contemporary Update Frank Rosemeier MD, MRCP(UK), MRCA, DipPEC(SA) Attending Anesthesiologist JLR Medical Group Maitland, FL Why should we care? Mother want to feel well
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
Diagnostic imaging and clinical features of intracranial hypotension review of literature
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.72970 Received: 20.03.2017 ccepted: 24.03.2017 Published: 20.01.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Review article Diagnostic imaging and clinical features of intracranial
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.72970 Received: 20.03.2017 ccepted: 24.03.2017 Published: 20.01.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Review article Diagnostic imaging and clinical features of intracranial
EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics
 Appendix 3: Pre-study Questionnaire EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics All questions in this questionnaire relate to the situation in 2014
Appendix 3: Pre-study Questionnaire EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics All questions in this questionnaire relate to the situation in 2014
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Cranio-cervical decompression. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION
 PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
NEURO QUIZ 45 EHLERS DANLOS SYNDROME
 NEURO QUIZ 45 EHLERS DANLOS SYNDROME Verghese Cherian, MD, FFARCSI Penn State Hershey Medical Center, Hershey Quiz Team Shobana Rajan, M.D Suneeta Gollapudy, M.D Angele Marie Theard, M.D START 1. Regarding
NEURO QUIZ 45 EHLERS DANLOS SYNDROME Verghese Cherian, MD, FFARCSI Penn State Hershey Medical Center, Hershey Quiz Team Shobana Rajan, M.D Suneeta Gollapudy, M.D Angele Marie Theard, M.D START 1. Regarding
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES
 TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
Acute subdural hematoma as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture: case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Acute subdural hematoma as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture: case report Luis Rafael Moscote-Salazar 1, Andres M. Rubiano
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Acute subdural hematoma as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture: case report Luis Rafael Moscote-Salazar 1, Andres M. Rubiano
NMH happens when there is an abnormal reflex interaction between the heart and the brain, although both are structurally normal.
 Neurally mediated hypotension: is also known as: the fainting reflex, neurocardiogenic syncope, vasodepressor syncope, the vaso-vagal reflex, and autonomic dysfunction. (Hypotension= low blood pressure,
Neurally mediated hypotension: is also known as: the fainting reflex, neurocardiogenic syncope, vasodepressor syncope, the vaso-vagal reflex, and autonomic dysfunction. (Hypotension= low blood pressure,
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults
 Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM
 TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point
 Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH
 5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH The retrosigmoid approach provides good access to the cerebellopontine angle. It is by far simpler and faster with much less need for bone removal than other more extensive lateral
5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH The retrosigmoid approach provides good access to the cerebellopontine angle. It is by far simpler and faster with much less need for bone removal than other more extensive lateral
The Ehlers Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a mixed group of. Neurological and Spinal Manifestations of the Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes FOR NON-EXPERTS
 The Ehlers-Danlos Society P.O. Box 87463 Montgomery Village, MD 20886 USA Phone: +1 410-670-7577 The Ehlers-Danlos Society - Europe Office 7 35-37 Ludgate Hill London EC4M 7JN UK Phone: +44 203 887 6132
The Ehlers-Danlos Society P.O. Box 87463 Montgomery Village, MD 20886 USA Phone: +1 410-670-7577 The Ehlers-Danlos Society - Europe Office 7 35-37 Ludgate Hill London EC4M 7JN UK Phone: +44 203 887 6132
