Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities
|
|
|
- Myron Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G. Bussone Ó Springer-Verlag Italia 2013 Abstract Magnetic resonance imaging in patients affected by orthostatic headache often allows the diagnosis of spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH). Nevertheless, in the last 5 years, the diagnostic and therapeutic strategy for spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) has been significantly modified. Specifically, all invasive techniques aimed at localization and demonstration of spontaneous spinal fistulas (myelography, isotopic cisternography, and so on) have been progressively abandoned. Also myelo- MR, although not an invasive exam, is no longer considered necessary to establish the most appropriate treatment. This change is due to the development and demonstration of a pathogenetic theory which considers the cerebrospinal fistula not as the primary cause of intracranial hypotension, but as the consequence of an imbalance between epidural and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressures. In a consecutive series of 80 patients, we performed a standardized epidural lumbar injection of a dense compound aimed to raise the epidural pressure irrespective of the presence and site of CSF leaks. The technique used, the long-term results of this treatment and the diagnostic pathways will be discussed. A. Franzini (&) G. Messina Department of Neurosurgery, Neurological Institute C. Besta, Via Celoria, 11, Milan, Italy angelo@angelofranzini.com L. Chiapparini Department of Neuroradiology, Neurological Institute C. Besta, Milan, Italy G. Bussone Department of Neurological Sciences, Headache Unit Fondazione IRCCS, Istituto Neurologico C. Besta, Milan, Italy Keywords Spontaneous intracranial hypotension SIH Blood patch Orthostatic headache Introduction Hospital admissions for spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) resistant to conservative treatments have increased in the last 5 years, growing from sporadic cases to more than 20 cases per year in our institute. Such increase is due to a better awareness of this syndrome [9, 10] and to an easier access to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations. SIH typically presents with postural orthostatic headache [8] which in the most severe conditions may be associated with nausea, vomiting, dizziness, diplopia, photophobia, hearing impairment, neck stiffness, blurred vision, sometimes behavioural disorders or/and abnormal movements. MRI of the brain with gadolinium injection is the imaging study of choice for patients with clinical suspect of SIH. Characteristic radiologic abnormalities [2 7] include diffuse thickening and contrast enhancement of the pachymeninges, subdural fluid collections or subdural hematomas that are frequently bilateral (Fig. 1). In the last 5 years, in our institute important changes of diagnostic pathways have been introduced. Specifically, all invasive techniques aimed at localizing and demonstrating spontaneous spinal fistulas (myelography, isotopic cisternography, and so on) have been progressively abandoned. Also myelo-mr, although not an invasive examination, is not routinely performed. This strategy is due to the development of a novel aetiopathogenetic theory which considers the cerebrospinal fistula not as the primary cause of the intracranial hypotension, but as the consequence of an imbalance between epidural and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressures [5].
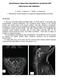
2 S152 Neurol Sci (2013) 34 (Suppl 1):S151 S155 Fig. 1 Left Axial (upper) and two coronal (lower) MRI images of two patients with SIH; notice the pachymeningeal contrast enhancement in the axial image and the subdural fluid collections in the coronal images. Right Lateral intra-procedural radiographic image showing the Tuoy needle approximating the interlaminar space of two consecutive lumbar vertebrae (upper), and the schematic localization of the blood patch compound (lower) once injected into the epidural space In 80 consecutive patients we demonstrated that, by provoking an increase in epidural pressure by injecting a dense compound into the lumbar epidural space, it is possible to obtain the recovery from this syndrome, irrespective of the demonstration and/or localization of CSF fistulas. The technique, the results of treatment and the diagnostic-therapeutic strategy will be in relation to the hypothesis of the epidural/intradural pressures imbalance. Physiopathological hypothesis Our hypothesis is based on the anatomy and physiology of the epidural veins as well as on the observation of an abnormally low spinal epidural pressure observed in patients affected by SIH. Venous drainage of the spinal epidural space is served by two main anatomical complexes. The upper thoracic plexiform venous network drains into the superior vena cava system via the radicular veins. Below L-2, the lumbar epidural venous network drains into the inferior vena cava system via a network of large radicular veins. These two systems communicate at the thoracolumbar junction [5]. Anti-reflux venous valves protect the spinal cord from the high-pressure venous waves of the vena cava system, but cannot prevent abnormally augmented venous drainage from the lumbar epidural veins. Increased venous drainage from the lumbar epidural venous system to the inferior vena cava will result in reduced volume of the emptied epidural veins and this will cause increase of the negative pressure within the epidural space, which constitutes a closed system. The negative pressure of the epidural compartment acts as an aspiration force applied to the whole dural surface, and in our opinion, will be responsible of CSF steal through the dura itself or through provoked fistulas where the
3 dura is particularly thin or fenestrated (such as in the cervical radicular pockets). Low venous pressure within the inferior vena cava system is amplified by the muscles pumping blood during standing and walking and these actions are well known to worsen SIH. Following these considerations, we argued that a rise in the epidural pressure would abolish the aspiration effect on the dural surface and so, also abolish the CSF steal. In other words, only a significant pressure gradient between the intradural pressure (positive) and the epidural pressure (negative) will maintain the CSF outflow and CSF loss trough the venous system. When the gradient between the two compartments is nill, the passage of CSF will also be nill. So we decided to introduce within the epidural lumbar space a dense compound aimed to obtain the increase in the epidural pressure and a partial segmental compression of the lumbar epidural vein to obtain further and stable reduction of the venous drainage to the inferior cava system. Our hypotheses have been extensively published and discussed [5] and is schematically represented in Fig. 2. The following considerations are stressed: The site of the CSF leak is not influential because in any case the cause of the disease is the negative epidural pressure maintained by the lumbar venous drainage toward the inferior cava system. The conventional blood patch or the blood patch in the Trendelenburg position is effective [1, 3, 4, 11], because the injection of blood within the epidural space modifies the pressure gradients between the epidural and intradural compartments but, in our opinion, it is not necessary that blood actually reaches the site of the fistula [6]. The optimal procedure would be aimed at increasing the epidural pressure instead of closing the CSF leak. So we introduced a blood patch procedure based on the injection of a dense compound within the lumbar epidural space, irrespective of the actual site of the CSF leak [5]. Following the first results in a preliminary series of 28 patients and the demonstration that the lumbar procedure was effective in presence of cervical demonstrated CSF leaks [6], we definitively abandoned all the diagnostic procedures aimed at searching the site of CSF leaks and introduced a standard procedure for all patients affected by SIH. Patients and methods Technique Five ml of fibrin glue is mixed with 5 ml of homologous blood and 3 ml of hydrosoluble contrast medium. The resulting viscous compound is then injected into the epidural space at L1 2 or lower levels under fluoroscopic control with the patient lying prone. The epidural needle connected to a syringe filled with saline solution is left in place for a few minutes to balance the epidural pressure with the atmospheric pressure (*15 20 ml of saline is usually aspirated spontaneously within the epidural space due to the negative epidural pressure). Then the compound is injected under fluoroscopic guidance (Fig. 1). The day after the procedure the patient can be discharged from hospital and will return to normal working and social activities in few weeks. Patient series S153 Between 2000 and 2011, 80 patients (mean age 42, range years, 44 females) have been admitted to our institution because of SIH resistant to conservative treatments for at least 2 months. In all patients the heralding and prominent symptom of the disease was headache and/or neck pain appearing or worsening within 15 min after sitting or standing. In addition to these symptoms, some patients complained nausea (19 patients), tinnitus (29 patients), hypoacusia (45 patients). Mild endocrine dysfunction related to ADH deficiency was present in two cases. One patient complained a severe behaviour disorder with anhedonia, apathia and depression while one patient complained parkinsonian rest tremor (both patients recovered from symptoms few weeks after the blood patch procedure). The median time elapsed between symptom s onset and diagnosis was 4 months (from 15 days to 45 months). Brain MRI features were: diffuse thickening and linear enhancement of the pachymeninges along the convexities, the cerebral falx, the tentorium and the clivus (79 cases), intradural fluid collections or hematomas (15 cases), sagging of the brain with caudal diencephalic displacement, descent and enlargement of the pons, flattening of the peripontine cisterns and, in some case, downward tonsillar displacement (6 cases). Additional findings included pituitary enlargement and engorgement of the dural venous sinuses. One of these findings was observed in almost all the patients of this series. In most of the patients spinal MRI findings included: epidural fluid collections within the spinal canal and engorgement of the venous plexuses in the cervical epidural anterior space. The search for CSF leak has been performed by MRI myelograms in 39 patients and by isotopic myelography in 14 cases. The CSF leak has been demonstrated in four patients within the cervical (2 patients), thoracic (1 patients) and lumbar (1 patient) spinal segments. In these series the search for the CSF
4 S154 Neurol Sci (2013) 34 (Suppl 1):S151 S155 Fig. 2 Schematic representation of the three spinal compartments as axial spinal lumbar sections: violet veins, yellow epidural space, blue CSF, black dots roots, red blood patch compound At the bottom are represented the relative pressures of the considered compartments with the same colour code. a Steady state of the normal condition with volumes (upper) and pressures (bottom) in equilibrium. b In conditions of abnormal venous drainage the veins are emptied by the blood aspiration from the cava system and veins volume is reduced (upper) provoking a negative pressure in the spinal closed system. CSF leaves the dural sac due to the existing pressure gradient between the intradural positive pressure compartment and the epidural negative pressure compartment (represented at the bottom of the figure). c The CSF that escaped from the dural sac is absorbed by the epidural veins and leaves definitively the system through the inferior vena cava system. The steal of CSF is responsible of the volume reduction of the intradural compartment and is so responsible for the whole syndrome. d The dense compound injected within the epidural space (the so called blood patch ) rises the epidural pressure (yellow column at bottom of the figure) inverting the pressure gradient between the intradural and epidural compartments e The veins (violet) remain collapsed by the blood patch and the new CSF production gradually replaces the CSF steal. In this phase hydration and steroids may be helpful to increase and restore CSF volume (colour figure online) leaks was mainly performed between 2000 and 2005, while in the last 5 years diagnostic workup has gradually been modified and spinal studies have been abandoned because of the adoption of the above-mentioned standardized blood patch procedure always being performed within the lumbar region. Results and discussion After the first blood patch procedure 87 % of patients obtained complete symptom regression within 3 months. In 13 % of patients the first EPB was not effective and a second treatment has been performed reaching a global
5 success rate of 90 %. So 10 % of patients could not be cured by the blood patch procedure and subsequently developed chronic tensive headache refractory to drugs and characterized by the progressive disappearance of the postural changes typical of the SIH. Only 2 out of 15 patients with convexity fluid collections (Fig. 1) requested surgical evacuation after the BP procedure. Finally, it has to be remarked that 25 % of patients had recurrence of the disease within 2 8 years after the BP procedure, which was then was successfully repeated. Some topics from our experience in the reported series are remarked: All patients at hospital admission were highly invalidated and after the blood patch procedures 90 % returned to normal life in few weeks. None of our patients needed open surgery to repair CSF leak. There is no need to search the radiological evidence and site of the CSF leak; in fact brain MRI and clinical data are enough to establish the diagnosis of SIH. The therapeutic mechanism of the epidural lumbar blood patch is related to the rise of the spinal epidural pressure and to the correction of the negative balance between CSF and epidural space. The success rate of EBP in patients who underwent diagnostic procedures aimed to discover the CSF leak (47 %) and the success rate in patients who underwent lumbar EBP following the clinical and brain MRI data was the same. In conclusion, lumbar BP was effective independently of the severity of the disease and the site of the CSF leak, thus confirming that the negative epidural pressure plays a major role in the pathogenesis of SIH. Epidural lumbar blood patch is the procedure of choice for SIH when conservative treatments failed. Anyway 10 % of patients develop chronic headache syndromes in spite of repeated BP procedures. Acknowledgments We gratefully acknowledgement Eliana Mea MD for the support. Conflict of interest We certify that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article. References S Berroir S, Loisel B, Ducros A, Boukobza M, Tzourio C, Valade D, Bousser MG (2004) Early epidural blood patch in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology 63(10): Chiapparini L, Ciceri E, Nappini S, Castellani MR, Mea E, Bussone G, Leone M, Savoiardo M (2004) Headache and intracranial hypotension: neuroradiological findings. Neurol Sci 25(Suppl 3): Dillo W, Hollenhorst J, Brassel F, von Hof-Strobach K, Heidenreich F, Johannes S (2002) Successful treatment of a spontaneous cervical cerebrospinal fluid leak with a CT guided epidural blood patch. J Neurol 249: Ferrante E, Arpino I, Citterio A, Wetzl R, Savino A (2010) Epidural blood patch in Trendelenburg position pre-medicated with acetazolamide to treat spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Eur J Neurol 17(5): Franzini A, Messina G, Nazzi V, Mea E, Leone M, Chiapparini L, Broggi G, Bussone G (2010) Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome: a novel speculative physiopathological hypothesis and a novel patch method in a series of 28 consecutive patients. J Neurosurg 112: Franzini A, Zekaj E, Messina G, Mea E, Broggi G (2010) Intracranial spontaneous hypotension associated with CSF cervical leakage successfully treated by lumbar epidural blood patch. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 152(11): Mea E, Franzini A, D Amico D, Leone M, Cecchini AP, Tullo V, Chiapparini L, Bussone G (2011) Treatment of alterations in CSF dynamics. Neurol Sci. 32(Suppl 1): Mokri B (2003) Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol 16: Rai A, Rosen C, Carpenter J, Miele V (2005) Epidural blood patch at C2: diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(10): Schievink WI (2000) Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks: a review. Neurosurg Focus 9(1) (review) 11. Sencakova D, Mokri B, McClelland RL (2001) The efficacy of epidural blood patch in spontaneous CSF leaks. Neurology 57:
Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory headache due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report
 DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
While some patients with SIH recover without intervention
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman
 Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension
 online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:103-107 ISSN 1738-8708 Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park,
Intracranial hypotension after trauma
 Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch
 LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report
 Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch
 J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
Low PRESSURE Headaches. What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah
 Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Remembering Donald J. Dalessio, MD The Headache Clinic Featuring the Baylor Scott & White Headache Clinic in Temple, Texas.
 Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a debilitating
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE MR Myelography for Identification of Spinal CSF Leak in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension J.L. Chazen, J.F. Talbott, J.E. Lantos, and W.P. Dillon ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE MR Myelography for Identification of Spinal CSF Leak in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension J.L. Chazen, J.F. Talbott, J.E. Lantos, and W.P. Dillon ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) classically
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
Time-Dependent Changes in Dural Enhancement Associated With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review
 Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1897 1904 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review Shruti G. Kapoor, MD, MPH* and Shihab Ahmed, MBBS, MPH *Department of Anesthesiology,
Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1897 1904 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review Shruti G. Kapoor, MD, MPH* and Shihab Ahmed, MBBS, MPH *Department of Anesthesiology,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache
 Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal
 Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a syndrome characterized
 Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission
 Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension
 Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
 Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Spinal Imaging Findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension
 Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Radiological Findings on MRI in Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-1678 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VELASCO, P. Redondo Buil, N. Sanchez Rubio, N. A. Abbas 1 2 2 2 2 3
Incidental durotomy during spine surgery occurs in. Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks
 J Neurosurg Spine 21:805 810, 2014 AANS, 2014 Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks Clinical article Frank Mihlon, M.D., Peter G. Kranz, M.D., Andreia
J Neurosurg Spine 21:805 810, 2014 AANS, 2014 Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks Clinical article Frank Mihlon, M.D., Peter G. Kranz, M.D., Andreia
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report
 Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai. Interventional Options
 10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
10/20/2017 Current & Evolving Percutaneous Treatment Approaches: Cedars-Sinai Charles Luoy and Marcel Maya Cedars Sinai Blood Patch Single level Bilevel Targeted Fibrin Glue Interventional Options 1 10/20/2017
Spinal CSF leak syndrome is a rare disorder characterized
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
The spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) syndrome
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Adachi S. Mugikura A. Shibata E. Kawaguchi T. Sato S. Takahashi Relative Decrease in Signal Intensity of Subcortical White Matter in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension on Fluid-Attenuated
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Pure cervical radiculopathy due to spontaneous spinal epidural haematoma (SSEH): report of a case solved conservatively
 Eur Spine J (2006) 15 (Suppl. 5): S569 S573 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0023-6 CASE REPORT Carlos Villas Alvaro Silva Matı as Alfonso Pure cervical radiculopathy due to spontaneous spinal epidural haematoma
Eur Spine J (2006) 15 (Suppl. 5): S569 S573 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0023-6 CASE REPORT Carlos Villas Alvaro Silva Matı as Alfonso Pure cervical radiculopathy due to spontaneous spinal epidural haematoma
Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
Advanced Animal Imaging Ryan Harrell BS, BS, CNMT
 Advanced Animal Imaging Ryan Harrell BS, BS, CNMT It is a specialized form of x -ray that helps veterinarians determine damage to th e spinal cord. A myelogram can help determine if there is a serious
Advanced Animal Imaging Ryan Harrell BS, BS, CNMT It is a specialized form of x -ray that helps veterinarians determine damage to th e spinal cord. A myelogram can help determine if there is a serious
SIH: Trials and Research Endeavors. Tim Amrhein, MD Assistant Professor of Neuroradiology Duke University Medical
 SIH: Trials and Research Endeavors Tim Amrhein, MD Assistant Professor of Neuroradiology Duke University Medical Center @TimAmrheinMD Disclosures No relevant disclosures RSNA Research Scholar Grant ASNR
SIH: Trials and Research Endeavors Tim Amrhein, MD Assistant Professor of Neuroradiology Duke University Medical Center @TimAmrheinMD Disclosures No relevant disclosures RSNA Research Scholar Grant ASNR
Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report
 Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Intracranial hypotension
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XVIII 3: 279 285 279 Intracranial hypotension Şt.M. Iencean Neurosurgery, Emergency Clinical Hospital Prof. Dr. N. Oblu Iaşi, Romania Abstract The intracranial hypotension
Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XVIII 3: 279 285 279 Intracranial hypotension Şt.M. Iencean Neurosurgery, Emergency Clinical Hospital Prof. Dr. N. Oblu Iaşi, Romania Abstract The intracranial hypotension
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point
 Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Intracranial hypotension syndrome: A radiologist's approach to the "saggy" brain
 Intracranial hypotension syndrome: A radiologist's approach to the "saggy" brain Poster No.: C-1124 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Naval Baudin, J. J. Sánchez Fernández, P. Puyalto
Intracranial hypotension syndrome: A radiologist's approach to the "saggy" brain Poster No.: C-1124 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Naval Baudin, J. J. Sánchez Fernández, P. Puyalto
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH), also
 CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects.
 Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics
 Appendix 2: Case Report Form EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics Case Report Form Please fill each relevant step carefully Step 1. From Epidural
Appendix 2: Case Report Form EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics Case Report Form Please fill each relevant step carefully Step 1. From Epidural
This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of:
 This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of: Severe bilateral subdural hematomas as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture for possible Alzheimers disease Reference: Verslegers Lieven,
This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of: Severe bilateral subdural hematomas as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture for possible Alzheimers disease Reference: Verslegers Lieven,
Definition by ICHD: 7.2 Headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure (see ICHD 3 rd edition beta version Cephalalgia 2013; 33(9): )
 Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report and review of literature
 Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Recommendations for Management
 REVIEW ARTICLE Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Recommendations for Management Farnaz Amoozegar, Darryl Guglielmin, William Hu, Denise Chan, Werner J. Becker ABSTRACT: A literature search found no
REVIEW ARTICLE Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Recommendations for Management Farnaz Amoozegar, Darryl Guglielmin, William Hu, Denise Chan, Werner J. Becker ABSTRACT: A literature search found no
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES
 2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Cervical Epidural Injection
 Cervical Epidural Injection The Cervical Vertebrae The cervical vertebrae are the bones that support your neck and head. They form the top part of your spine. The tunnel made by these vertebrae is called
Cervical Epidural Injection The Cervical Vertebrae The cervical vertebrae are the bones that support your neck and head. They form the top part of your spine. The tunnel made by these vertebrae is called
Lumbar drains. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Lumbar drains Information for patients Neurosurgery Why do I need drainage of my cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? The brain and spinal cord are bathed in clear fluid like a baby in the womb. This cerebrospinal
Lumbar drains Information for patients Neurosurgery Why do I need drainage of my cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? The brain and spinal cord are bathed in clear fluid like a baby in the womb. This cerebrospinal
Anesthesiology ROUNDS. The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture Headache. Anesthesia. Volume 8, Issue 5
 2010 Volume 8, Issue 5 Anesthesiology ROUNDS A PHYSICIAN LEARNING RESOURCE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL AND McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTIES OF MEDICINE The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture
2010 Volume 8, Issue 5 Anesthesiology ROUNDS A PHYSICIAN LEARNING RESOURCE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL AND McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTIES OF MEDICINE The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 2778 N. Webb Rd. Wichita, KS 67226 Phone: (316) 631-1600 Fax: (316) 631-1617 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Epidural Steroid Injections 2778 N. Webb Rd. Wichita, KS 67226 Phone: (316) 631-1600 Fax: (316) 631-1617 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Utilizing real-time contrast medium to detect the fistula of giant spinal arachnoid cyst and treat with minimal invasive surgery
 Ying et al. BMC Surgery (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-019-0475-y CASE REPORT Open Access Utilizing real-time contrast medium to detect the fistula of giant spinal arachnoid cyst and treat
Ying et al. BMC Surgery (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-019-0475-y CASE REPORT Open Access Utilizing real-time contrast medium to detect the fistula of giant spinal arachnoid cyst and treat
Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY
 Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
Unit #3: Dry Lab A. David A. Morton, Ph.D.
 Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
S. Inagawa, N. Yoshimura, Y. Ito; Niigata/JP spinal sacral areteriovenous fistulae, CTA, MRA /ecr2010/C-2581
 Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
CSF Leaks. Abnormal communication between the subarachnoid space and the tympanomastoid space or nasal cavity. Presenting symptoms:
 CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN
 A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN W Singleton, D Ramnarine, N Patel, C Wigfield Department of Neurological Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol, UK Introduction We present
A NOVEL CAUSE FOR CAUDA- EQUINA SYNDROME WITH A NEW RADIOLOGICAL SIGN W Singleton, D Ramnarine, N Patel, C Wigfield Department of Neurological Surgery, Frenchay Hospital, Bristol, UK Introduction We present
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgety, and Psychiatry 1995;59:511-515 51 SHORT REPORT Neuroradiology S A Renowden Neurology, Radcliffe Infirmary NHS Trust, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK R Gregory N Hyman
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgety, and Psychiatry 1995;59:511-515 51 SHORT REPORT Neuroradiology S A Renowden Neurology, Radcliffe Infirmary NHS Trust, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK R Gregory N Hyman
Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series
 CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
1242 Intracranial Hypertension After CSF Leaks Mayo Clin Proc, November 2002, Vol 77 indium In 111 cisternography and CT myelography. These studies sh
 Mayo Clin Proc, November 2002, Vol 77 Intracranial Hypertension After CSF Leaks 1241 Case Report Intracranial Hypertension After Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks BAHRAM MOKRI, MD Four
Mayo Clin Proc, November 2002, Vol 77 Intracranial Hypertension After CSF Leaks 1241 Case Report Intracranial Hypertension After Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks BAHRAM MOKRI, MD Four
Hydrocephalus 1/16/2015. Hydrocephalus. Functions of Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Flow of CSF
 Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome in a Patient With Marfan Syndrome and Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 632 April 2008 secondary causes of intracranial hypertension can be lifethreatening. Review of the imaging studies by an experienced neuro-radiologist is of paramount importance. Low threshold for repeat
632 April 2008 secondary causes of intracranial hypertension can be lifethreatening. Review of the imaging studies by an experienced neuro-radiologist is of paramount importance. Low threshold for repeat
Cervical laminectomy for spinal cord compression. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Cervical laminectomy for spinal cord compression Information for patients Neurosurgery What is a compression of the spinal cord and how has it been caused? The bones in our back are called vertebras and
Cervical laminectomy for spinal cord compression Information for patients Neurosurgery What is a compression of the spinal cord and how has it been caused? The bones in our back are called vertebras and
Successful Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Headache With Fluoroscopically Guided Epidural Blood Patch: A Report of Four Cases
 Successful Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Headache With Fluoroscopically Guided Epidural Blood Patch: A Report of Four Cases Salim M. Hayek, MD, PhD, Maher Fattouh, MD, Teresa Dews,
Successful Treatment of Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Headache With Fluoroscopically Guided Epidural Blood Patch: A Report of Four Cases Salim M. Hayek, MD, PhD, Maher Fattouh, MD, Teresa Dews,
Spinal and para-spinal plexiform neurofibromas in NF1 patients, a clinical-radiological correlation study
 Spinal and para-spinal plexiform neurofibromas in NF1 patients, a clinical-radiological correlation study Poster No.: C-1846 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Mauda-Havakuk, B. Shofty,
Spinal and para-spinal plexiform neurofibromas in NF1 patients, a clinical-radiological correlation study Poster No.: C-1846 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Mauda-Havakuk, B. Shofty,
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Post-Dural Puncture Headache. Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel
 Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION
 PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
Case Report Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in Two Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine, Article ID 528268, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/528268 Case Report Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in Two Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine, Article ID 528268, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/528268 Case Report Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in Two Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Diagnostic imaging and clinical features of intracranial hypotension review of literature
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.72970 Received: 20.03.2017 ccepted: 24.03.2017 Published: 20.01.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Review article Diagnostic imaging and clinical features of intracranial
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.72970 Received: 20.03.2017 ccepted: 24.03.2017 Published: 20.01.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Review article Diagnostic imaging and clinical features of intracranial
3. A plane is an imaginary line dividing the body into.
 CHAPTER 2 Multiple Choice Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Knowing the exact body region where pain is located can help a physician determine the.
CHAPTER 2 Multiple Choice Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Knowing the exact body region where pain is located can help a physician determine the.
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
