Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension
|
|
|
- Morris John Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 online ML Comm CASE REPORT J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7: ISSN Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension Yong-Sang Kim, MD, Byung Moon Cho, MD, Sung-Min Cho, MD, Se-Hyuck Park, MD and Se Moon Oh, MD Department of Neurosurgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a clinical syndrome which leads to orthostatic headache due to low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) volume. Severe cases are present with nausea, vomiting, photophobia, and rarely, decreased level of consciousness and coma. The various modalities for diagnosing CSF leakage have been used, such as radionuclide cisternography (RNC), CT myelography and MRI myelography. Despites of the various modalities, the actual location of leakage is hard to find. We present two patients who underwent RNC for suspected CSF leakage after trauma and lumbar puncture. One case, site of CSF leakage was misidentified. The other case, we performed burr hole trephination with closed drainage due to progressive subdural hematoma (SDH) after epidural blood patch (EBP). This report emphasizes that intracranial hypotension presents with various clinical presentation and neuroimaging findings. (J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7: ) KEY WORDS: Intracranial hypotension ㆍ Radionuclide cisternography ㆍ Cerebrospinal fluid leak. Introduction The unique symptom of intracranial hypotension (IH) is an orthostatic headache caused by low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure and is not so rare. IH results from loss of CSF caused by a dural defect in the spine, cranial vault, or skull base. The classic orthostatic headache commences within 15 minutes, but occasionally symptoms last up to several hours, after standing or upright sitting position. The criteria of the International Classification of Headache Disorders 3) are widely used to diagnose this type of headache. These criteria require at least one of the following to confirm the diagnosis of IH; low CSF pressure; diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement of brain MR imaging; or evidence of CSF leakage on conventional myelography, CT myelography, or radionuclide cisternography (RNC). However, low CSF pressure is not always present in IH. 10) A broad spectrum of neuroimaging features has also been recognized in patients with IH, 7) particularly diffuse dural enhancement and sagging of the brain on MR imaging. 10) Received: August 22, 2011 / Revised: September 24, 2011 Accepted: September 26, 2011 Address for correspondence: Byung Moon Cho, MD Department of Neurosurgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, 150 Seongnae-gil, Gangdong-gu, Seoul , Korea Tel: , Fax: nschbm@hanmail.net However, such diagnostic abnormalities are not always detected. 15) RNC and CT myelography are the spinal imaging studies which have been used for identification of the actual site of a CSF leakage. However, in general, neurologists or neurosurgeons do not routinely perform these studies because these invasive modalities required a dural puncture, so that it may worsen the patient s condition; also there are some debates regarding appropriate timing of study. 1) At our institution, RNC is routinely performed for patients suspected of having IH. In this case series, we report two patients in whom IH was suspected. One case showed a false localizing CSF leakage, while the other case showed progressive subdural hematoma (SDH) after epidural blood patch (EBP). The purpose of this case series is to describe the clinical and imaging features of patients with IH. Case Report Case 1 A 56-year-old man was admitted to the emergency department of our hospital due to neck pain and multiple contusions after pedestrian traffic accident. Initial brain computed tomography (CT) scan was grossly normal. Two days later, he complained severe headache. Headache was aggravated by sitting or standing and relieved by lying on his bed. The headache was also accompanied by photopho- Copyright 2011 Journal of Korean Neurotraumatology Society 103
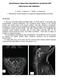
2 Intracranial Hypotension and Radionuclide Cisternography bia, nausea, tinnitus, posterior neck stiffness and progressive somnolence. Follow up brain CT scan showed widening of bilateral frontal and temporal subdural space (Figure 1A). Gadolinium-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed bilateral frontal and temporal subdural space widening and diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement, suggesting IH (Figure 1B, C, D). A subsequent RNC was performed, which revealed mild reflux of radiotracer into the lateral ventricle (Figure 2A). Normal opening pressure and xanthochromia were noted during lumbar puncture. But the supine spinal images demonstrated no evidence of a CSF leakage (Figure 2B). The radiotracer accumulation activity at the left cerebellopontine angle (CPA) cistern was seen, but it was decreased on the 24- hour delayed images (Figure 2A, C). And the both CPA cistern were shown asymmetry on the MRI (Figure 2D). These findings were a false localizing CSF leak at the left ear. In light of the negative investigations, he was managed conservatively with bed rest, hydration, and medication. Two weeks later, he was discharged with no symptoms. Case 2 A 31-year-old woman was admitted to the neurosurgical department of our hospital due to severe headache [Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) was 7/10] and vomiting. Initial brain CT showed acute SDH on left cerebral hemisphere (Figure 3A). She had past medical history of operation for hemorrhoid under the spinal anesthesia 2 days ago. Headache was not improved by lying down. Gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI showed acute SDH on left cerebral hemisphere with midline shifting to right and diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement (Figure 3B, C). Lumbar puncture for RNC performed with a 24-gauge needle at the level of L3-L4, revealed an opening pressure of 11 mmh 2O and xanthochromia. RNC showed multiple CSF leakage at right anterolateral aspect and left posterolateral aspect of lower lumbar level (Figure 4A, B, C). IH was strongly suspected, and it seemed to be caused by previous spinal anesthesia. Two days after admission, 6 ml of autologous EBP was injected under fluoroscopic guidance between L4 and L5. The patient immediately experienced relief of pain. 8 hours after the EBP, her headache was improved about 5/10 on A B C D FIGURE 1. Case 1. Follow up computed tomography demonstrates widening of bilateral frontal and temporal subdural space (A). Gadolinium-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging shows bilateral frontal and temporal subdural space widening and diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement (B, C, D). A C B D FIGURE 2. Case 1. Radionuclide cisternography shows mild reflux of radiotracer into the lateral ventricle (A). Supine spinal images demonstrate no evidence of a CSF leakage (B). The radiotracer accumulation activity at the left cerebellopontine angle (CPA) cistern was seen, but that was decreased on the 24-hour delayed images (A,C). T2-weighted MRI shows asymmetry of CPA cistern (D). CSF: cerebrospinal fluid. 104 J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:
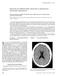
3 Yong-Sang Kim, et al. the VAS. The following day, although the postural headache was not shown, the headache persisted (VAS 4/10). A CT scan performed 2 weeks after EBP showed slightly increased volume of SDH (12 mm at maximal thickness) with aggravation of midline shifting to the right (Figure 5A). Her headache was aggravated (VAS 7/10). We performed burr hole trephination with closed drainage (Figure 5B) and her headache was immediately improved. She was discharge with no focal neurological deficits. Discussion IH is an uncommon clinical entity characterized by CSF hypovolemia due to CSF leakage and confirmed with CSF A B C FIGURE 3. Case 2. Initial brain CT shows acute subdural hematoma on left cerebral hemisphere (A). T1-weighted MRI shows acute subdural hematoma on left cerebral hemisphere with midline shifting to right and diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement (B, C). CT: computed tomography. A B C FIGURE 4. Case 2. Radionuclide cisternography shows multiple CSF leakage at right anterolateral aspect and left posterolateral aspect of lower lumbar (A, B, C). CSF: cerebrospinal fluid. FIGURE 5. Case 2. Pre-operative contrast enhanced CT at 2 weeks after EBP shows slightly increased volume of SDH with aggravation of midline shifting to the right (A), post-operative CT after burr hole trephination with closed drainage (B). CT: computed tomography, EBP: epidural blood patch, SDH: subdural hematoma. A B 105
4 Intracranial Hypotension and Radionuclide Cisternography opening pressure of less than 6 cm H 2O. Patients with IH often present with postural headache. Other symptoms are often accompanied by postural headache including posterior neck pain or stiffness, and nausea and vomiting and attributable to meningeal irritation which its incidence is approximately 50% of patients. 12) Sometimes, it also accompanied by photophobia and less commonly hypacusia and tinnitus, due to vestibulocochlear nerve traction associated with the sagging brain, or transmission of low CSF pressure to the perilymph. Secondary subdural effusions or hematomas may also be the complication of IH, which causes constant, nonpostural headaches. Causes of secondary IH include lumbar puncture, cranial or spinal surgery, and head or spine trauma. 11) Incidence of post-lumbar puncture headache is reported at 10% to 30%. In addition to meningeal diverticula, direct mechanical perforation of the dura secondary to degenerative disc-osteophyte is recognized. 16) The diagnosis of IH is difficult, thus careful history taking of patients who suffer from persistent postural headache and selection of proper diagnostic modalities are important. In 18 patients studied by Schievink, 12) 17 (94%) received an initial incorrect diagnosis and the median diagnostic delay was 5 weeks. Even some patients had undergone unnecessary invasive procedures including meningeal biopsy, a decompressive craniotomy and the evacuation of subdural fluid collections. With loss of CSF from the subarachnoid space, total intracranial blood volume is increased to counteract loss of CSF volume. This increases the results in engorgement of the epidural vertebral venous plexus, often most notable in the upper cervical spine; and enlargement and engorgement of the pituitary gland. Gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI is a useful tool for the confirmation of IH. Due to the wide variety of headache patterns, it is better to perform MRI in all patients with unexplained headaches in order to evaluate the possibility of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. However, up to 20% of patients with IH showed neither enhancement nor any other abnormalities on MRI. 13) Watanabe et al. 15) reported overall the sensitivity for IH was 83% for brain MR imaging and 94% for spinal MR imaging. But high concentration of gadolinium in the subarachnoid space may cause seizures. 5) Although MRI has become a first-line diagnostic measure, RNC and CT myelography are particularly useful in identifying CSF leaks and studying CSF circulation. 8,17,18) The sensitivity of RNC is lower in case of small leakage. Even when direct findings of tracer extravasation are not visualized, Morioka et al. 9) reported that indirect findings on RNC, renal and bladder activity, poor propagation of radiotracer to the convexities, can be useful in determining the presence of leak as well as follow-up monitoring after treatment. In the first case, the radiotracer accumulation activity at the left CPA cistern was seen; this finding should not be mistaken for identification of actual site of CSF leakage (Figure 2A) because of decreased radiotracer accumulation activity was seen on the 24-hour delayed images (Figure 2C). Furthermore, the both CPA cistern were shown asymmetry on the MRI (Figure 2D). These findings were false localizing finding of CSF leakage at the left ear. Yoon et al. 18) reported 15 of 24 cases could not reveal the leakage site. Most patients treated by EBP and showed remarkable improvement. Occasionally CSF pressure within the normal range has been documented in some patients with IH. Orthostatic headache can occur without evidence of IH or detectable CSF leak despite extensive diagnostic testing. Some cases of IH were resolved spontaneously; thus conservative treatment consisting of bed rest, oral caffeine, and hydration may make sense initially to treat the symptoms during waiting for spontaneous closure of the leakage site. One study showing relief of headache in 75% of patients compared with a control group treated with intravenous saline. 14) Once the diagnosis of IH is made, EBP is recommended if conservative treatments fail to reduce symptoms. The appropriate injection site of EBP is controversial. Some authors reported that the location of EBP is not important, but others suggested that accurate injection on the leakage site is more effective. 1,4) Progressive SDH after EBP for IH is extremely rare, there are only three reported cases (Figure 5A, B). 2,6,14) Interestingly, all three cases (including our patient) complained of a persistent nonpostural headache after disappearance of the postural headache. This change of symptom suggests that persistent nonpostural headache after EBP might be predictive clue of progressive SDH and that an early CT scan should be performed. Conclusion Although the incidence of IH is not so high, it is an important clinical entity to which the clinicians should pay attention. Delayed diagnosis of IH may cause prolongation of symptomatic period and exposes patients to unnecessary, high-risk diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. This report emphasizes that secondary IH can present with various clinical presentations and neuroimaging findings. It also points that the clinicians is to be attentive to alterations of patients symptoms, in order to prompt manage- 106 J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc 2011;7:
5 Yong-Sang Kim, et al. ment of secondary events during the treatment of IH, such as progression of SDH. The authors have no financial conflicts of interest. REFERENCES 1) Berroir S, Loisel B, Ducros A, Boukobza M, Tzourio C, Valade D, et al. Early epidural blood patch in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology 63: , ) Fujimaki H, Saito N, Tosaka M, Tanaka Y, Horiguchi K, Sasaki T. Cerebrospinal fluid leak demonstrated by three-dimensional computed tomographic myelography in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Surg Neurol 58: ; discussion , ) Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 24 Suppl 1:9-160, ) Kantor D, Silberstein SD. Cervical epidural blood patch for low CSF pressure headaches. Neurology 65:1138, ) Li L, Gao FQ, Zhang B, Luo BN, Yang ZY, Zhao J. Overdosage of intrathecal gadolinium and neurological response. Clin Radiol 63: , ) Mikawa S, Ebina T. [Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicating subdural hematoma: unilateral oculomotor nerve palsy caused by epidural blood patch]. No Shinkei Geka 29: , ) Mokri B. Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol 16: , ) Mokri B, Low PA. Orthostatic headaches without CSF leak in postural tachycardia syndrome. Neurology 61: , ) Morioka T, Aoki T, Tomoda Y, Takahashi H, Kakeda S, Takeshita I, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension syndrome: usefulness of indirect findings in radionuclide cisternography for detection and treatment monitoring. Clin Nucl Med 33: , ) Paldino M, Mogilner AY, Tenner MS. Intracranial hypotension syndrome: a comprehensive review. Neurosurg Focus 15:ECP2, ) Raskin NH. Lumbar puncture headache: a review. Headache 30: , ) Schievink WI. Misdiagnosis of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Arch Neurol 60: , ) Schoffer KL, Benstead TJ, Grant I. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension in the absence of magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities. Can J Neurol Sci 29: , ) Takeuchi S, Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Hayakawa T, Otani N, Yoshino Y, et al. Progressive subdural hematomas after epidural blood patch for spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J Anesth 24: , ) Watanabe A, Horikoshi T, Uchida M, Koizumi H, Yagishita T, Kinouchi H. Diagnostic value of spinal MR imaging in spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30: , ) Winter SC, Maartens NF, Anslow P, Teddy PJ. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to thoracic disc herniation. Case report. J Neurosurg 96: , ) Yoo HM, Kim SJ, Choi CG, Lee DH, Lee JH, Suh DC, et al. Detection of CSF leak in spinal CSF leak syndrome using MR myelography: correlation with radioisotope cisternography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29: , ) Yoon SH, Chung YS, Yoon BW, Kim JE, Paek SH, Kim DG. Clinical experiences with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a proposal of a diagnostic approach and treatment. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113: ,
Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3775-z CASE STUDY Open Access Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage Yake Zheng 1, Yajun Lian 1*, Chuanjie Wu 1, Chen
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman
 Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
Sudden Headache and visual disturbances in a young woman A. Soupart, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine BSIM, December 12, 2014 48 years old woman with Sudden Headache 7/2014 * Admitted for Headache
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Following a Yoga Class: A Case Report
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 10, 314-318 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/3/10/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-3-10-3 Spontaneous Intracranial
Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch
 J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
J Neurosurg Spine 9:000 000, 9:483 487, 2008 Occult cervical (C1 2) dural tear causing bilateral recurrent subdural hematomas and repaired with cervical epidural blood patch Case report As o k u m a r
Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities
 DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
DOI 10.1007/s10072-013-1364-2 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension: evolution of the therapeutic and diagnostic modalities Angelo Franzini G. Messina L. Chiapparini G.
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch
 LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
LV-EBP: Record-setting large volume epidural blood patch Michael D. Staudt Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine, Western University London Health Sciences Centre, London,
While some patients with SIH recover without intervention
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P.H. Luetmer K.M. Schwartz L.J. Eckel C.H. Hunt R.E. Carter F.E. Diehn When Should I Do Dynamic CT Myelography? Predicting Fast Spinal CSF Leaks in Patients with Spontaneous Intracranial
Low PRESSURE Headaches. What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah
 Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Low PRESSURE Headaches aka Low CSF volume headache: What they area and what can you do? Kathleen B. Digre MD University of Utah Disclosure: I have a part ownership on a patent for thin filmed technology
Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report
 NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
NNQ Intracranial Hypotension Concurrent Presented with Pseudo-Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Transverse Sinus Thrombosis: A Case Report Chieh-Yang Cheng 1, Che-Chuan Wang 1, Tai-Yuan Chen 2, Jinn-Rung Kuo
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache
 Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Differential Diagnosis of Orthostatic Headache MORRIS LEVIN, MD PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY CHIEF, DIVISION OF HEADACHE MEDICINE, UCSF Disclosures Consulting for Amgen, Lilly, Allergan, Supernus, Pernix No
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Complications of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Poster No.: C-0890 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Endo, Y. Kubo, M. Ida; Tokyo/JP Hemorrhage, Embolism / Thrombosis,
Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E1115-E1122 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Epidural Blood Patch for the Treatment of Spontaneous and Iatrogenic Orthostatic Headache Yun So, MD, Jung Min Park, MD, Pil-moo
Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory headache due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report
 DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
DOI 0.86/s40064-06-975- RESEARCH Efficacy of epidural blood patch with fibrin glue additive in refractory due to intracranial hypotension: preliminary report Justin Elwood *, Misha Dewan 2, Jolene Smith
Remembering Donald J. Dalessio, MD The Headache Clinic Featuring the Baylor Scott & White Headache Clinic in Temple, Texas.
 Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak An Under-recognized Cause of Headache More common than expected, why is this type of headache so often misdiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed? Challenging the One Size
Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53, 207 212, 2013 Floating Dural Sac Sign is a Sensitive Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding of Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Takaaki HOSOYA, 1 Jun HATAZAWA,
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension
 Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Mechanisms of Headache in Intracranial Hypotension Stephen D Silberstein, MD Jefferson Headache Center Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA Stephen D. Silberstein, MD, FACP Director, Jefferson
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report
 Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicated with cerebral venous thrombosis and subdural effusion: a case report Murali Krishna Menon 1, Thara Prathap 2, Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal 3 1
Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote Spontaneous Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 4798465, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4798465 Case Report The Relief of Unilateral Painful Thoracic Radiculopathy without Headache from Remote
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Intracranial hypotension after trauma
 Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
Sarrafzadeh et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Intracranial hypotension after trauma Asita S Sarrafzadeh 1*, Stephanie A Hopf 1, Oliver P Gautschi 1, Ana-Paula
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission
 Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report
 Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
Spinal MRI findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension - Case Report Poster No.: P-0105 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: M. Tzalonikou, D. KECHAGIAS, A. Plomaritoglou, A. 1 1 2
This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of:
 This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of: Severe bilateral subdural hematomas as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture for possible Alzheimers disease Reference: Verslegers Lieven,
This item is the archived peer-reviewed author-version of: Severe bilateral subdural hematomas as a complication of diagnostic lumbar puncture for possible Alzheimers disease Reference: Verslegers Lieven,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.76380 Received: 15.05.2017 Accepted: 27.07.2017 Published: 22.05.2018 http://www.polradiol.com Case report Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive
Spinal CSF leak syndrome is a rare disorder characterized
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.-M. Yoo S.J. Kim C.G. Choi D.H. Lee J.H. Lee D.C. Suh J.W. Choi K.S. Jeong S.J. Chung J.S. Kim S.-C. Yun Detection of CSF Leak in Spinal CSF Leak Syndrome Using MR Myelography: Correlation
Lumbar puncture. Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml): <1h
 Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a syndrome characterized
 Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
Case Report 293 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in a Patient with Reversible Pachymeningeal Enhancement and Brain Descent Yu-Lung Tseng, MD; Yung-Yee Chang, MD; Min-Yu Lan, MD; Hsiu-Shan Wu, MD; Jia-Shou
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION
 PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) classically
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:732 736, 2015 Intrathecal preservative-free normal saline challenge magnetic resonance myelography for the identification of cerebrospinal fluid leaks in spontaneous intracranial
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects.
 Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
Postdural puncture headache preventing the impossible, treating the symptoms, evaluating long term effects. Marc Van de Velde, MD, PhD Professor of Anaesthesia, Catholic University Leuven (KUL) Chair Department
Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 4, 339 343, 2005 Detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension with radionuclide cisternography and blood activity monitoring
 Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Ian Carroll MD, MS https://med.stanford.edu/profiles/ian-carroll CarrollCSFleak@gmail.com SIH and/or POTS? Disclosures No Conflicts of Interest This work is supported by the Considine CSF Leaks Fund Thank
Anesthesiology ROUNDS. The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture Headache. Anesthesia. Volume 8, Issue 5
 2010 Volume 8, Issue 5 Anesthesiology ROUNDS A PHYSICIAN LEARNING RESOURCE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL AND McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTIES OF MEDICINE The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture
2010 Volume 8, Issue 5 Anesthesiology ROUNDS A PHYSICIAN LEARNING RESOURCE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF MONTREAL AND McGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTIES OF MEDICINE The Epidural Blood Patch: Beyond the Post-dural Puncture
POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY
 Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
Nagoya postoperative Med. J., chronic subdural hematoma after aneurysmal clipping 13 POSTOPERATIVE CHRONIC SUBDURAL HEMATOMA FOLLOWING CLIP- PING SURGERY TAKAYUKI OHNO, M.D., YUSUKE NISHIKAWA, M.D., KIMINORI
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
Definition by ICHD: 7.2 Headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure (see ICHD 3 rd edition beta version Cephalalgia 2013; 33(9): )
 Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Low pressure Headache syndromes 2016: Kathleen Digre MD, University of Utah Objectives 1) List the clinical manifestations of CSF hypovolemic headaches 2) list 4 predisposing factors to low pressure headaches
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal
 Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
Supine Digital Subtraction Myelography for the Demonstration of a Dorsal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: A Technical Note Michael Carstensen 1*, Navjot
EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics
 Appendix 2: Case Report Form EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics Case Report Form Please fill each relevant step carefully Step 1. From Epidural
Appendix 2: Case Report Form EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics Case Report Form Please fill each relevant step carefully Step 1. From Epidural
A New Mechanism of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage after Lumboperitoneal Shunt: A Theory of Shunt Side Hole Case Report
 Case Report Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) xx, xxx xxx, 20xx doi: 10.2176/nmc.cr2013-0067 Online November 20, 2013 A New Mechanism of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage after Lumboperitoneal Shunt: A Theory of Shunt
Case Report Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) xx, xxx xxx, 20xx doi: 10.2176/nmc.cr2013-0067 Online November 20, 2013 A New Mechanism of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage after Lumboperitoneal Shunt: A Theory of Shunt
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
The spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) syndrome
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Albayram F. Kilic H. Ozer S. Baghaki N. Kocer C. Islak Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Cisternography to Evaluate Dural Leaks in Intracranial Hypotension Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: We
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES
 2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
2017 BASIC RECOGNIZING AND EVALUATING LOW PRESSURE HEADACHE SYNDROMES Kathleen Digre, MD University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT Headache is the most common symptom associated with changes of intracranial
Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series
 CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
CASE REPORT Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea as the Presenting Symptom of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Series Hossein Ghalaenovi 1, Maziar Azar 1, Morteza Taheri 1, Mahdi Safdarian
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome with extracranial vein dilatation C. Heine 1, H. Altinova 1, T. Pietilä 1, LC Stavrinou 1 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Evangelical Hospital Bielefeld, Germany
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Post-Dural Puncture Headache. Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel
 Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Post-Dural Puncture Headache Dr. Jacobs Aurélie Krans Anesthesie 18/03/2016 Kliniek St.-Jan, Brussel I - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY August Bier (intrathecal cocaïn1898)! first 2 cases PDPH CSF leak trough dura mater
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point
 Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Goals. Objectives
 Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F1
 05.04.2016 By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F1 Objectives Introduction Materials and methods Results Discussion Algorithm Conclusion Introduction Risk of meningitis, which has been reported
05.04.2016 By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F1 Objectives Introduction Materials and methods Results Discussion Algorithm Conclusion Introduction Risk of meningitis, which has been reported
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach
 Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension The first 1111 patients: A practical approach WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery Department of Neurosurgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
CSF Leaks. Abnormal communication between the subarachnoid space and the tympanomastoid space or nasal cavity. Presenting symptoms:
 CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
CSF Leaks Steven Wright, M.D. Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, M.D. The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2005 CSF Leaks Abnormal communication
Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report
 Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
Fujiwara et al. JA Clinical Reports (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-016-0073-2 CASE REPORT Transforaminal epidural blood patch for intractable spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak: a case report Open Access
HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI, M.D., PH.D., TAKEO TANISHIMA, M.D., PH.D., Clinical Material and Methods
 J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report and review of literature
 Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Available online at Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 1:153-157 Iatrogenic lumbar Pseudomeningocele: A case report
Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults
 Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures. imaging (MRI) to evaluate lesions of the temporal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures Richard M. Jones, MD; Michael I. Rothman, MD; William C. Gray, MD; Gregg H. Zoarski, MD; Douglas E. Mattox, MD Objective: To determine the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Temporal Lobe Injury in Temporal Bone Fractures Richard M. Jones, MD; Michael I. Rothman, MD; William C. Gray, MD; Gregg H. Zoarski, MD; Douglas E. Mattox, MD Objective: To determine the
Time-Dependent Changes in Dural Enhancement Associated With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Peter G. Kranz 1 Timothy J. mrhein Kingshuk Roy Choudhury Teerath Peter Tanpitukpongse Linda
Clinical Outcome of Borderline Subdural Hematoma with 5-9 mm Thickness and/or Midline Shift 2-5 mm
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/300 Clinical Outcome of Borderline Subdural Hematoma with 5-9 mm Thickness and/or Midline Shift 2-5 mm Raja S Vignesh
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/300 Clinical Outcome of Borderline Subdural Hematoma with 5-9 mm Thickness and/or Midline Shift 2-5 mm Raja S Vignesh
Chronic Subdural Hematoma in Young Adult: An Age Comparison Study
 online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:6-11 ISSN 2234-8999 Chronic Subdural Hematoma in Young Adult: An Age Comparison Study Yu Deok Won, MD 1, Hyeong-Joong Yi, MD 1, Young Jun Lee,
online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:6-11 ISSN 2234-8999 Chronic Subdural Hematoma in Young Adult: An Age Comparison Study Yu Deok Won, MD 1, Hyeong-Joong Yi, MD 1, Young Jun Lee,
Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal Cord without Evidence of Spinal Cord Herniation or an Intradural Mass
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Introduction. Chang-Gi Yeo, MD 1, Woo-Yeol Jeon, MD 2, Seong-Ho Kim, MD 1, Oh-Lyong Kim, MD 1, and Min-Su Kim, MD 1 CLINICAL ARTICLE
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2016;12(2):101-106 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.101 The Effectiveness of Subdural Drains Using Urokinase after Burr Hole
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2016;12(2):101-106 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.101 The Effectiveness of Subdural Drains Using Urokinase after Burr Hole
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH), also
 CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
CASE REPORT J Neurosurg 129:205 210, 2018 Multilevel, ultra-large-volume epidural blood patch for the treatment of neurocognitive decline associated with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2011 Sep;18(3): Originally published online September 30, 2011;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Acute Spontaneous Cervical Spinal Epidural Hematoma with Spontaneous Resolution -A Case Report- Young-Do Koh, M.D.,Seung Hwan Kook, M.D. J Korean Soc Spine Surg
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Acute Spontaneous Cervical Spinal Epidural Hematoma with Spontaneous Resolution -A Case Report- Young-Do Koh, M.D.,Seung Hwan Kook, M.D. J Korean Soc Spine Surg
PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]
![PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center] PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]](/thumbs/89/98821167.jpg) Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
CHRONIC HEADACHE AFTER CRANIO-CERVICAL TRAUMA HYPOTHETICAL PATHOMECHANISM BASED UPON NEUROANATOMICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 June 27, 2007 EU RO PE AN JOUR NAL OF MED I CAL RE SEARCH 249 Eur J Med Res (2007) 12: 249-254 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2007 CHRONIC HEADACHE AFTER CRANIO-CERVICAL TRAUMA HYPOTHETICAL PATHOMECHANISM BASED
June 27, 2007 EU RO PE AN JOUR NAL OF MED I CAL RE SEARCH 249 Eur J Med Res (2007) 12: 249-254 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2007 CHRONIC HEADACHE AFTER CRANIO-CERVICAL TRAUMA HYPOTHETICAL PATHOMECHANISM BASED
Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Correspondence should be addressed to Sorayouth Chumnanvej;
 Neurology Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 2737028, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2737028 Research Article Assessment and Predicting Factors of Repeated Brain Computed Tomography
Neurology Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 2737028, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2737028 Research Article Assessment and Predicting Factors of Repeated Brain Computed Tomography
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is a debilitating
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE MR Myelography for Identification of Spinal CSF Leak in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension J.L. Chazen, J.F. Talbott, J.E. Lantos, and W.P. Dillon ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE MR Myelography for Identification of Spinal CSF Leak in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension J.L. Chazen, J.F. Talbott, J.E. Lantos, and W.P. Dillon ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
TBI are twice as common in males High potential for poor outcome Deaths occur at three points in time after injury
 Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Maxillofacial Fracture: Report of 2 Cases
 Shimane J. Med. Sci., Vol.35 pp.15-19, 2018 Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Maxillofacial Fracture: Report of 2 Cases Takashi KOIKE 1,2, Takahiro KANNO 2, Masaaki KARINO 2, Aya YOSHINO 2, Joji SEKINE
Shimane J. Med. Sci., Vol.35 pp.15-19, 2018 Chronic Subdural Hematoma Following Maxillofacial Fracture: Report of 2 Cases Takashi KOIKE 1,2, Takahiro KANNO 2, Masaaki KARINO 2, Aya YOSHINO 2, Joji SEKINE
Intracranial hypotension syndrome: A radiologist's approach to the "saggy" brain
 Intracranial hypotension syndrome: A radiologist's approach to the "saggy" brain Poster No.: C-1124 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Naval Baudin, J. J. Sánchez Fernández, P. Puyalto
Intracranial hypotension syndrome: A radiologist's approach to the "saggy" brain Poster No.: C-1124 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Naval Baudin, J. J. Sánchez Fernández, P. Puyalto
Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:120-124 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.120 Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:120-124 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.120 Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Contrast mimicking a subarachnoid hemorrhage after lumbar percutaneous epidural neuroplasty: a case report
 Oh et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:88 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Contrast mimicking a subarachnoid hemorrhage after lumbar percutaneous epidural neuroplasty:
Oh et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:88 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Contrast mimicking a subarachnoid hemorrhage after lumbar percutaneous epidural neuroplasty:
Spinal Imaging Findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Medina et al. MRI and CT of Intracranial Hypotension Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jocelyn H. Medina 1 Kevin brams 2 Steven
Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension
 J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
J Neurosurg 103:608 613, 2005 Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension WOUTER I. SCHIEVINK, M.D., M. MARCEL MAYA, M.D., FRANKLIN G. MOSER, M.D., AND JAMES TOURJE,
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review
 Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1897 1904 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review Shruti G. Kapoor, MD, MPH* and Shihab Ahmed, MBBS, MPH *Department of Anesthesiology,
Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1897 1904 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Articles Cervical Epidural Blood Patch A Literature Review Shruti G. Kapoor, MD, MPH* and Shihab Ahmed, MBBS, MPH *Department of Anesthesiology,
Drainage of an acute spinal epidural hematoma that developed without risk factors in the thoracic spine using epidural needle -A case report-
 Anesth Pain Med 2017; 12: 266-270 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.266 Case Report http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.266&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-07-25 pissn 1975-5171
Anesth Pain Med 2017; 12: 266-270 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.266 Case Report http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.266&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-07-25 pissn 1975-5171
EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics
 Appendix 3: Pre-study Questionnaire EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics All questions in this questionnaire relate to the situation in 2014
Appendix 3: Pre-study Questionnaire EPiMAP Obstetrics European Practices in the Management of Accidental Dural Puncture in Obstetrics All questions in this questionnaire relate to the situation in 2014
Lumbar puncture-related cerebrospinal fluid leakage on magnetic resonance myelography: is it a clinically significant finding?
 Sakurai et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2013, 13:35 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lumbar puncture-related cerebrospinal fluid leakage on magnetic resonance myelography: is it a clinically significant finding?
Sakurai et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2013, 13:35 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lumbar puncture-related cerebrospinal fluid leakage on magnetic resonance myelography: is it a clinically significant finding?
Efficacy of neuroendoscopic evacuation of traumatic intracerebral or intracerebellar hematoma
 Original Contribution Kitasato Med J 2017; 47: 141-147 Efficacy of neuroendoscopic evacuation of traumatic intracerebral or intracerebellar hematoma Hiroyuki Koizumi, 1,2 Daisuke Yamamoto, 1 Yasushi Asari,
Original Contribution Kitasato Med J 2017; 47: 141-147 Efficacy of neuroendoscopic evacuation of traumatic intracerebral or intracerebellar hematoma Hiroyuki Koizumi, 1,2 Daisuke Yamamoto, 1 Yasushi Asari,
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Analysis of Prognostic Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma
 online ML Comm 0CLINICAL ARTICLE0 J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2008;4:14-18 ISSN 1738-8708 Analysis of Prognostic Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma Young-Il Kim, MD, Jung-Hoon Lee, MD, Seung-Won Park,
online ML Comm 0CLINICAL ARTICLE0 J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2008;4:14-18 ISSN 1738-8708 Analysis of Prognostic Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma Young-Il Kim, MD, Jung-Hoon Lee, MD, Seung-Won Park,
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Frank Rosemeier. MD, MRCP(UK), MRCA, DipPEC(SA) Attending Anesthesiologist. JLR Medical Group
 Postdural Puncture Headaches A Contemporary Update Frank Rosemeier MD, MRCP(UK), MRCA, DipPEC(SA) Attending Anesthesiologist JLR Medical Group Maitland, FL Why should we care? Mother want to feel well
Postdural Puncture Headaches A Contemporary Update Frank Rosemeier MD, MRCP(UK), MRCA, DipPEC(SA) Attending Anesthesiologist JLR Medical Group Maitland, FL Why should we care? Mother want to feel well
Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Incidental durotomy during spine surgery occurs in. Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks
 J Neurosurg Spine 21:805 810, 2014 AANS, 2014 Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks Clinical article Frank Mihlon, M.D., Peter G. Kranz, M.D., Andreia
J Neurosurg Spine 21:805 810, 2014 AANS, 2014 Computed tomography guided epidural patching of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks Clinical article Frank Mihlon, M.D., Peter G. Kranz, M.D., Andreia
Concussion. Concussion is a disturbance of brain function caused by a direct or indirect force to the head.
 Concussion Concussion is a disturbance of brain function caused by a direct or indirect force to the head. Disturbances of brain tissue is largely related to neurometabolic dysfunction rather then structural
Concussion Concussion is a disturbance of brain function caused by a direct or indirect force to the head. Disturbances of brain tissue is largely related to neurometabolic dysfunction rather then structural
Intracranial Vasospasm without Intracranial Hemorrhage due to Acute Spontaneous Spinal Subdural Hematoma
 Exp Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;24(4):366-370. pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Case Report Intracranial Vasospasm without Intracranial Hemorrhage due to Acute Spontaneous Spinal Subdural Hematoma Jung-Hwan Oh
Exp Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;24(4):366-370. pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Case Report Intracranial Vasospasm without Intracranial Hemorrhage due to Acute Spontaneous Spinal Subdural Hematoma Jung-Hwan Oh
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
