A REPORT OF THREE CASES. HENRY COHEN Department of Medicine, University of Liverpool AND. C. V. HARRISON Postgraduate Medical School of London
|
|
|
- Hugh Curtis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. clin. Path. (1948), 1, 212. TEMPORAL ARTERITIS: A REPORT OF THREE CASES BY HENRY COHEN Department of Medicine, University of Liverpool AND C. V. HARRISON Postgraduate Medical School of London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION, JUNE 22, 1948) This disease, which has also been described as cranial arteritis and giant-cell arteritis, was first established as a clinical and pathological entity by Horton and others (1934), though there is evidence that single cases were described before this (Andersen, 1947). Since 1934, over seventy cases have been reported in the literature from U.S.A., Great Britain, France, and Scandinavia. These have been reviewed and analysed elsewhere in this issue (Harrison, 1948). The disease runs a characteristic clinical course, and the affected vessels have a characteristic morphology. Although the earlier recorded cases ran a completely benign course, those subsequently reported have shown that involvement of other vessels may cause blindness, cerebral damage, and even death. The three cases reported here exemplify the characteristic clinical course and morphology of the disease, and also illustrate some of its complications. Case Reports Case 1.-A coach builder, aged 72, from a country district of North Wales was admitted to hospital with a three months' history of shooting pains in both sides of his head. The pain was at first intermittent and located behind the left ear, but later it became almost continuous and spread to the front and back of the head. Six weeks before admission the pain moved to the right temple and came in bursts of great severity alternating with a continuous dull ache. Bending down made the pain worse but coughing and eating did not. During the two weeks before admission the pains had eased a little. On examination he was a well-nourished man with normal temperature and pulse; his face showed leucoderma. Both superficial temporal arteries were visibly prominent but no longer tender. There was no pulsation in eilher. Physical examination (blood pressure 148/80 mm. Hg.), blood count, electrocardiogram, and radiograph of the chest all gave negative results. A segment of the right superficial temporal artery was excised, and this appeared to relieve the pain. After nineteen days in hospital, that is, about 15 weeks after the onset of symptoms, the patient was discharged much improved. Histology (Plate VIa and b).-the lumen was reduced to a small slit by intimal proliferation, but there was no thrombosis. The intimal thickening was composed of a cellular connective tissue containing fibroblast nuclei but very few inflammatory cells. The media was intact around approximately two-thirds of the circumference and was infiltrated by a few inflammatory cells. In the remaining third it was totally replaced by a cellular infiltration of macrophages, lymphocytes, and polymorphonuclears, though there was no remaining necrotic tissue. The internal elastic lamina was fragmented, and there were a few giant cells in the vicinity of the broken elastic fibres. The adventitia was fibrosed, forming a thickened collagenous coat, and several nerves were embedded in it. It did not, however, show any appreciable cellular reaction. Case 2.-A farmer aged 65 years was admitted complaining of headaches. Six weeks before admission he felt ill and took to bed and thought that he was febrile. Soon after this he developed headaches all over his head but worse on the left side. This was aggravated by coughing and was severe enough to interfere with sleep. He had lost about 1 stone in weight since the onset of his illness. On examination he was found to be well preserved, but he showed signs of recent loss of weight. He had some pyrexia (98 to 101' F.) on admission, but this settled to normal in a few days. The temporal arteries were tortuous, thick, and tender, but pulsating. Blood pressure was 120/80 mm. Hg. Abduction of the right shoulder was limited and the right deltoid wasted. Physical examination was otherwise negative. Blood examination revealed Hb 75 per cent, red blood cells 4,400,000, white cells 12,800 per c.mm. of blood, with 73 per cent polymorphs. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 10 mm. in 1 hour (Wintrobe-corrected), the
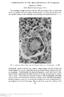
2 TEMPORAL ARTERITIS: A REPORT OF THREE CASES (a) (c) (b) 213 PLATE VI.-(a). Case 1. Transverse section of temporal artery showing extreme intimal proliferation. In the segment on the left the media is largely destroyed and the elastica is interrupted. The adventitia is fibrosed. (Verhoeff and Van Gieson, x 50.) (b). Case 1. High-power magnification of part of (a), showing the cellular infiltration spreading through media. A giant cell is shown near the left side. (Haematoxylin and eosin, x 140.) (c). Case2. Slightlyoblique section. The intima is enormously thickened and the inner fibrous and outer granulomatous layers are shown. The media is well seen near the lower border but is necrotic near the upper border. The adventitia is fibrosed, and a small nerve is visible at the extreme lower edge. (Haematoxylin and eosin, x 38.)
3 214 HENRY COHEN AND C. V. HARRISON ~~~~~PLATE - VIL- (a). Case 2. Higher magnification of part of Plate Vlc, showing granulomatous replacement of media spreading into intima (lower ~~ ~~~~~J. ~~~~~~left). Two giant cells are seen near the top left corner. (Haematoxy- 30~~~~~~.lin and eosin, x 190.) (b). Case 3. Ael' '. ~ Transverse section just beyond a bifurcation. The greatly thickened -~~~~;Pf 41~ ~ ~ ~ ntm icopsed of loose connective tissue. The media is infiltrated by cells, and the adventitia N ~~~~~~~~~~~is fibrosed. (Verhoeff and!> Van 4' " * Gieson, x 45.) (c). Case 3. Higher intima lies to the left and the media t:r ~~~~~~~~~~~to the right, separated by a wavy black elastic lamina. Note the numerous giant cells in the media.,p~~~~~~~t ~~~~~~~ (Verhoeff and Van Gieson, x 120.) J Clin Pathol: first published as /jcp on 1 August Downloaded from on 14 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 TEMPORAL ARTERITIS: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Wassermann reaction negative, and the cerebrospinal fluid normal. A week after admission a segment of the left temporal artery was excised and this was followed by relief of the headache. A fortnight after admission, eight weeks after the onset of the illness, the patient was discharged free from pain. Six months later he died suddenly from coronary occlusion: no autopsy was performed. Histology (Plates V, VIc, and VIIa).-The lumen was reduced to a slit 0.1 x 0.5 mm. but was free from thrombus. The intima was greatly thickened and consisted of two layers. The inner was composed of mucoid connective tissue with fairly numerous fibroblast nuclei but very few inflammatory cells; the outer consisted of granulation tissue with numerous capillaries and fibroblasts and heavily infiltrated with polymorphonuclears and macrophages. The media around approximately half the circumference was necrotic; and the rest, though containing muscle fibres, was heavily infiltrated by polymorphonuclears, lymphocytes, and macrophages. The internal elastic lamina was disrupted, and there was a number of giant cells. The adventitia was fibrosed but contained few inflammatory cells. Several small nerves were embedded in the fibrous tissue. A small branch of the temporal artery included in the biopsy showed exactly the same lesion as the parent vessel. A biopsy of calf muscle did not show any vascular lesion. Case 3.-A farmer aged 69, and a neighbour of Case 2, was admitted complaining of headache and blindness in one eye. Five months before admission he developed severe pain in the right side of his head; a fortnight later he suddenly developed diplopia for five minutes and then lost the sight in the left eye. A fortnight later the pain on the right cleared up but soon returned on the left side, and he noticed a I swollen vein " in his left temple, which he said was not tender. Two months after the onset of the illness the pain returned to the right side and persisted there till admission. It was severe enough to interfere with sleep. On examination he was seen to be a wasted elderly man, apyrexial, but with a pulse rate of 100 to 120 per minute. The left superficial temporal artery was thick and tortuous but not tender. The right temporal artery was not palpable. The left eye was blind except for appreciation of light and dark; the disc was pale and there were signs of thrombosis of the central retinal artery. The blood pressure was 175/ 80 mm. Hg, and there were signs of generalized arteriosclerosis with some myocardial ischaemia. The sedimentation rate was 32 mm. in one hour (Wintrobecorrected). The blood count showed Hb 90 per cent, red blood cells 4,300,000 and white cells 6,200 per c.mm. The cerebrospinal fluid was normal. A segment of the left temporal artery was excised and this was followed by relief of his pain. He was discharged free from symptoms a fortnight after admission: five and a half months after the onset of his illness. 215 Histology (Plates IVa and b, VIIb and c).-the specimen consisted of a Y-shaped segment and was cut to show transverse sections of the two limbs. These were exactly similar. The lumen was patent but reduced to a narrow slit. The intima was greatly thickened and consisted of mucoid connective tissue with frequent fibroblast nuclei but very few inflammatory cells. The media was free from any gross necrosis but was largely destroyed by a granulomatous mass consisting of young capillaries, polymorphonuclears, lymphocytes, and a few macrophages. Giant cells were numerous. This acute inflammatory reaction spread into the immediately adjacent intima and adventitia, but only for very short distances. The internal elastic lamina was broken up into a line of short fragments. Only the inner part of the adventitia was included in the biopsy, but this showed some fibrous thickening. No nerves were included. Comment The present cases were all in males, though in the recorded cases there have b.en slightly more women than men (Andersen, 1947; Cooke and others, 1946). The ages of the present cases, 72, 65, 69, are in accordance with the usual findings, most recorded cases being over 60. It is of interest that our three cases were country dwellers, and two were neighbouring farmers admitted within three months of each other. Horton and others (1934) drew attention to the fact that their early cases were farmers or country dwellers, though in most of the subsequent publications the patients have either been town dwellers or this information has not been given. The duration of the disease in our cases was 15, 8, and 23 weeks, which is shorter than the average (about six months) of previously recorded cases. But it is within the range of duration of such cases, which has varied from seven or eight weeks (Hoyt and others, 1941; Sproul, 1942) up to two years' (Cooke and others, 1946). In this series Case 1 recovered completely. Case 3 also recovered but was left with blindness in his left eye. Case 2 died from myocardial infarction, six months after discharge. An autopsy was not performed, and we do not know whether death was due to arteritis affecting the coronary arteries or to coincidental atheroma. Of the published cases, a number have died within some months of discharge, mostly from myocardial ischaemia or cerebral vascular disease. (Chasnoff and Vorzimer, 1944; Curtis, 1946; Kilbourne and Wolff, 1946). Other cases (Cooke and others, 1946) have died during the course of the disease from cerebral ischaemia due to arteritis of the cranial arteries and the diagnosis confirmed at autopsy.
5 216 HENRY COHEN AND C. V. HARRISON In the first of the three cases here recorded the lesion appeared to be limited to the temporal arteries; in Case 2 the right circumflex artery was involved, and in Case 3 there was blindness in the left eye due to thrombosis of the central retinal artery. In the early reports it was suggested that the disease was a localized one, but Jennings (1938) described blindness as a complication presumably due to involvement of the retinal vessels, and similar cases have since been reported by Dick and Freeman (1940), Scott and Maxwell (1941), Cooke and others (1946), Shannon and Solomon (1945), Robertson (1947), and Curtis (1946). The cases that have come to autopsy have shown involvement of other vessels. That the disease is not a localized process is suggested by the frequent occurrence of pyrexia and pains in body and limbs, and a degree of systemic illness out of proportion to the physical findings. Case 2 of the present series was pyrexial and was sufficiently ill to take to bed. The outstanding symptom in our three cases, and in all the recorded cases, has been pain in the head. This is of great severity and is usually resistant to analgesics. Many forms of therapy have been tried but none has been constantly successful. Removal of a segment of the affected temporal artery for biopsy has quite frequently been followed by relief of pain. This was noted by Horton and Magath (1937) and has since been confirmed by numerous other workers, and from the literature it appears to be the most constantly successful form of therapy. It was certainly of value in relieving symptoms in the present three cases. It has been suggested that this is due to interruption of the accompanying nerves, and Lucien and others (1939) described such nerves embedded in the fibrosed adventitia. We have also noted nerve fibres embedded in the fibrosed adventitia of our first and second cases. Nothing is known of the aetiology of the disease and, though many of the clinical features suggest an infective cause, so far all attempts to isolate an organism have been fruitless. Nevertheless the disease presents a unifqrm pattern which differentiates it from polyarteritis nodosa or Burger's disease. It has a different anatomical and age incidence and a better prognosis. The histology of the lesions is also different though in some ways less characteristic. Almost any of the individual histological features of temporal arteritis may be found in either polyarteritis or Burger's disease, yet the whole picture is sufficiently distinctive to be recognizably different (Gilmour, 1941; Cooke and others, 1946). We are indebted to Mr. F. Beckwith for the photomicrographs. REFERENCES Andersen, T. (1947). Act. med. scand., 128, 151. Chasnoff, J., and Vorzimer, J. J. (1944). Ann. intern. Med., 20, 327. Cooke, W. T., Cloake, P. C. P., Govan, A. D. T., and Colbeck, J. C. (1946). Quart J. Med., n.s. 15, 47. Curtis, H. C. (1946). Amer. J. Med., 1, 437. Dick, G. F., and Freeman, G. (1940). J. Amer. med. Ass., 114, 645. Gilmour, J. R. (1941). J. Path. Bact., 53, 263. Harrison, C. V. (1948). J. clin. Path., 1, 197. Horton, B. T., Magath, T. B., and Brown, G. E. (1934). Arch. intern. Med., 53, 400. Horton, B. T., and Magath, T. B. (1937). Proc. Mayo Clin., 12, 548. Hoyt, L. H., Perera, G. A., and Kauvar, A. J. (1941). New Engl. J. Med., 225, 283. Jennings, G. H. (1938). Lancet, 1, 424. Kilbourne, E. D., and Wolff, H. G. (1946). Ann. intern. Med., 24, 1. Lucien, M., Mathieu, L., and Verain, M. (1939). Arch. Mal. Coeur, 32, 603. Robertson, K. (1947). Brit. med. J., 2, 168. Scott, T., and Maxwell, E. S. (1941). Internat. Clin., 2, 220. Shannon, E. W., and Solomon, J. (1945). J. Amer. med. Ass., 127,647. Sproul, E. E. (1942). N.Y.St. J. Med., 42, 345. J Clin Pathol: first published as /jcp on 1 August Downloaded from on 14 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
COMMUNICATIONS. ARTERITIS*t CILIARY ARTERY INVOLVEMENT IN GIANT CELL. generalized vascular disease was emphasized by Cooke, Cloake, Govan, and
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 505 COMMUNICATIONS CILIARY ARTERY INVOLVEMENT IN GIANT CELL ARTERITIS*t BY P. A. MAcFAUL Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THIS condition
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 505 COMMUNICATIONS CILIARY ARTERY INVOLVEMENT IN GIANT CELL ARTERITIS*t BY P. A. MAcFAUL Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THIS condition
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Giant Cell Arteritis
 Brit. Heart J., 1968, 30, 840. Dissecting Aneurysm of the Aorta due to Giant Cell Arteritis M. HARRIS From the Department of Pathology, University of Bristol Giant cell arteritis is a rare cause of dissecting
Brit. Heart J., 1968, 30, 840. Dissecting Aneurysm of the Aorta due to Giant Cell Arteritis M. HARRIS From the Department of Pathology, University of Bristol Giant cell arteritis is a rare cause of dissecting
MITRAL STENOSIS AND HYPERTENSION
 MITRAL STENOSIS AND HYPERTENSION IAN R. BY GRAY From University College Hospital Received April 15 1953 Hypertension is often found in cases of mitral stenosis but reports of the frequency of the association
MITRAL STENOSIS AND HYPERTENSION IAN R. BY GRAY From University College Hospital Received April 15 1953 Hypertension is often found in cases of mitral stenosis but reports of the frequency of the association
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION
 Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 481-485 Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy S. R. KENDEEL AND J. A. J. FERRIS' From the Department ofpathology, University of Newcastle
J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 481-485 Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy S. R. KENDEEL AND J. A. J. FERRIS' From the Department ofpathology, University of Newcastle
CARCINOMA OF ESOPHAGUS PERFORATING THE AORTA*
 CARCINOMA OF ESOPHAGUS PERFORATING THE AORTA* HERBERT J. SCHATTENBERG AND JOSEPH ZISKIND From the Department of Pathology, Graduate School, Tulane University, and the Charity Hospital, New Orleans Perforation
CARCINOMA OF ESOPHAGUS PERFORATING THE AORTA* HERBERT J. SCHATTENBERG AND JOSEPH ZISKIND From the Department of Pathology, Graduate School, Tulane University, and the Charity Hospital, New Orleans Perforation
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
POLYARTERITIS NODOSA AFTER RESECTION
 Thorax (1957), 12, 258. INTESTINAL VASCULAR LESIONS SIMULATING POLYARTERITIS NODOSA AFTER RESECTION OF COARCTATION OF THE AORTA BY R. L. HURT AND W. J. HANBURY From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London (RECEIVED
Thorax (1957), 12, 258. INTESTINAL VASCULAR LESIONS SIMULATING POLYARTERITIS NODOSA AFTER RESECTION OF COARCTATION OF THE AORTA BY R. L. HURT AND W. J. HANBURY From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London (RECEIVED
THE INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL FACTORS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPHERAL ARTERIES AND
 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 199. THE INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL FACTORS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPHERAL ARTERIES AND THE LOCALIZATION OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University,
J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 199. THE INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL FACTORS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PERIPHERAL ARTERIES AND THE LOCALIZATION OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University,
RUPTURED AORTIC VALVE WITH MYCOTIC
 RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
 Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
False aneurysm of the pulmonary artery with
 Thorax (1964), 19, 449. False aneurysm of pulmonary artery with peripheral venous thrombosis Aneurysms of pulmonary artery are usually of its extrapulmonary portion (Boyd and Mc- Gavack, 1939; Deterling
Thorax (1964), 19, 449. False aneurysm of pulmonary artery with peripheral venous thrombosis Aneurysms of pulmonary artery are usually of its extrapulmonary portion (Boyd and Mc- Gavack, 1939; Deterling
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms
 J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS
 J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
Giant cell arteritis
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1974) 50, 265-269. R. G. TURNER M.B., B.S. J. HENRY M.B., B.S. Giant cell arteritis A. I. FRIEDMANN F.R.C.S. D. GERAINT JAMES M.D., F.R.C.P. The Medical Ophthalmology
Postgraduate Medical Journal (May 1974) 50, 265-269. R. G. TURNER M.B., B.S. J. HENRY M.B., B.S. Giant cell arteritis A. I. FRIEDMANN F.R.C.S. D. GERAINT JAMES M.D., F.R.C.P. The Medical Ophthalmology
OPHTHALMIC MANIFESTATIONS OF TEMPORAL
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1952) 36, 615. OPHTHALMIC MANIFESTATIONS OF TEMPORAL ARTERITIS* BY GERALD PARSONS-SMITH Western Ophthalmic Hospital, London TEMPORAL arteritis is the name given to a local and systemic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1952) 36, 615. OPHTHALMIC MANIFESTATIONS OF TEMPORAL ARTERITIS* BY GERALD PARSONS-SMITH Western Ophthalmic Hospital, London TEMPORAL arteritis is the name given to a local and systemic
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
BLOOD PRESSURE AND OLD AGE
 BLOOD PRESSURE AND OLD AGE BY TREVOR H. HOWELL From the Royal Hospital, Chelsea Received June 20, 1942 Twenty years ago, Thompson and Todd (1922) published an article entitled "Old age and blood pressure
BLOOD PRESSURE AND OLD AGE BY TREVOR H. HOWELL From the Royal Hospital, Chelsea Received June 20, 1942 Twenty years ago, Thompson and Todd (1922) published an article entitled "Old age and blood pressure
TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK -
 Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
Vol. 11, No. 2. June, 1970. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL TRANSIENT LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK - A CASE REPORT 86 By L.S. Chew (Medical Unit III, General Hospital, Singapore) INTRODUCTION It is generally believed
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Patient with Daily Headache NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION HEADACHE DISORDERS. R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP. Professor of Medicine (Neurology)
 Patient with Daily Headache NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) 2nd edition (ICHD-II) Learning Issues Headaches in the elderly
Patient with Daily Headache NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) 2nd edition (ICHD-II) Learning Issues Headaches in the elderly
SUDDEN BLINDNESS IN CRANIAL ARTERITIS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 204. SUDDEN BLINDNESS IN CRANIAL ARTERITIS* BY Western Ophthalmic Hospital (St. Mary's Hospital), London THAT vision may be affected during an attack of cranial arteritis is
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 204. SUDDEN BLINDNESS IN CRANIAL ARTERITIS* BY Western Ophthalmic Hospital (St. Mary's Hospital), London THAT vision may be affected during an attack of cranial arteritis is
Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism
 1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
1510 JACC Vol. 12, No, 6 December 1988:1510--4 Calcified Aortic Sinotubular Ridge: A Source of Coronary Ostial Stenosis or Embolism KEVIN J. TVETER, MD, JESSE E. EDWARDS, MD, FACC St, Paul, Minnesota This
Temporal arteritis in a large necropsy series
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 30, 224 Temporal arteritis in a large necropsy series GOREL OSTBERG From the University Department of Pathology, Malmo General Hospital, S 214 01 Malmo, Sweden Temporal arteritis
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 30, 224 Temporal arteritis in a large necropsy series GOREL OSTBERG From the University Department of Pathology, Malmo General Hospital, S 214 01 Malmo, Sweden Temporal arteritis
Vasculitis Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie
 Vasculitis 08-21-2018 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Agenda Anatomy and histology Vasculitis: Chapel Hill Classification Examples Giant cell arteritis Single organ vasculitis Artery or Vein?
Vasculitis 08-21-2018 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Agenda Anatomy and histology Vasculitis: Chapel Hill Classification Examples Giant cell arteritis Single organ vasculitis Artery or Vein?
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS. photocoagulation of the rabbit's retina.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A. OLUSEGUN FAYEMI, M.D.* Department of Pathology, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York 129
Pulmonary Vascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus A. OLUSEGUN FAYEMI, M.D.* Department of Pathology, The Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York 129
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Incidence and significance of coronary artery calcification
 British Heart journal, I974, 36, 499-506. Incidence and significance of coronary artery calcification J. H. McCarthy and F. J. Palmer From the Departments of Pathology and Radiology, Prince Henry Hospital,
British Heart journal, I974, 36, 499-506. Incidence and significance of coronary artery calcification J. H. McCarthy and F. J. Palmer From the Departments of Pathology and Radiology, Prince Henry Hospital,
Temporal arteritis. Occurrence of ocular complications 7 years after diagnosis. University of Edinburgh, and Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 584 Temporal arteritis Occurrence of ocular complications 7 years after diagnosis JAMES F. CULLEN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Edinburgh, and Royal Infirmary
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 584 Temporal arteritis Occurrence of ocular complications 7 years after diagnosis JAMES F. CULLEN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Edinburgh, and Royal Infirmary
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
THE popliteal artery is the second most common site of aneurysm. The
 POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
CASE NOTES SCLEROSING LIPO-GRANULOMA IN THE ORBIT* fluctuation, and no transillumination. The skin was bound down to the mass which
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1958) 42, 697. CASE NOTES SCLEROSING LIPO-GRANULOMA IN THE ORBIT* BY G. B. DAVIES AND P. L. WONG The Royal Eye Hospital, Surbiton, Surrey THIS case is reported as a mass in the lower
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1958) 42, 697. CASE NOTES SCLEROSING LIPO-GRANULOMA IN THE ORBIT* BY G. B. DAVIES AND P. L. WONG The Royal Eye Hospital, Surbiton, Surrey THIS case is reported as a mass in the lower
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION)
 Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION) Your doctor thinks you have suffered an episode of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION). This is the most common cause of sudden decreased vision in patients
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION) Your doctor thinks you have suffered an episode of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION). This is the most common cause of sudden decreased vision in patients
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
PAPILLIFEROUS TUMOURS OF THE HEART VALVES
 PAPILLIFEROUS TUMOURS OF THE HEART VALVES BY D. HEATH, P. V. BEST,* and B. T. DAVIS From the Department ofpathology, The University of Birmingham Received March 21, 1960 After the first year of life the
PAPILLIFEROUS TUMOURS OF THE HEART VALVES BY D. HEATH, P. V. BEST,* and B. T. DAVIS From the Department ofpathology, The University of Birmingham Received March 21, 1960 After the first year of life the
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis
 J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 668-675 Infected infarcts of the testis: A study of 18 cases preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis D. O'B. HOURIHANE From the Central Histopathology Laboratory of the Federated
J. clin. Path., 1970, 23, 668-675 Infected infarcts of the testis: A study of 18 cases preceded by pyogenic epididymoorchitis D. O'B. HOURIHANE From the Central Histopathology Laboratory of the Federated
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Renal vein thrombosis in cases of polyarteritis
 J. cliii. Path. (1959), 22, 395-400 Renal vein thrombosis in cases of polyarteritis nodosa and of the Henoch-Schoenlein syndrome M. E. J. BEARD AND D. J. E. TAYLOR From the Group Pathology Laboratory,
J. cliii. Path. (1959), 22, 395-400 Renal vein thrombosis in cases of polyarteritis nodosa and of the Henoch-Schoenlein syndrome M. E. J. BEARD AND D. J. E. TAYLOR From the Group Pathology Laboratory,
AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS BRACHIAL ARTERY AND ITS BRANCHES: HISTOLOGICAL BASIS AND ITS CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Ashwini C and Vasantha Kuberappa, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Ashwini C and Vasantha Kuberappa, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved AN UNUSUAL TORTUOUS
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
RENAL BIOPSIES IN HYPERTENSION
 RENAL BOPSES N HYPERTENSON BY R. H. HEPTNSTALL From the Department of Pathology, St. Mary's Hospital Received June 2, 1953 The examination of a piece of kidney cortex taken during sympathectomy for hypertension
RENAL BOPSES N HYPERTENSON BY R. H. HEPTNSTALL From the Department of Pathology, St. Mary's Hospital Received June 2, 1953 The examination of a piece of kidney cortex taken during sympathectomy for hypertension
Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma
 Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
OBSERVATIONS ON THE GROWTH OF REFRIGERATED. By ADRIAN E. FLATT, M.A., M.B.(Cantab.)
 OBSERVATIONS ON THE GROWTH OF REFRIGERATED SKIN GRAFTS By ADRIAN E. FLATT, M.A., M.B.(Cantab.) DURING the last thirty years several comments have appeared in the literature concerning the effects of cooling
OBSERVATIONS ON THE GROWTH OF REFRIGERATED SKIN GRAFTS By ADRIAN E. FLATT, M.A., M.B.(Cantab.) DURING the last thirty years several comments have appeared in the literature concerning the effects of cooling
Vasculitis. Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology. Vasculitis
 Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Ischaemic strictures of the small intestine in Nigeria
 Gut, 1977, 18, 266-273 Ischaemic strictures of the small intestine in Nigeria S. G. SUBBUSWAMY,1 AND F. I. IWEZE From the Departments ofpathology and Surgery, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria SUMMARY
Gut, 1977, 18, 266-273 Ischaemic strictures of the small intestine in Nigeria S. G. SUBBUSWAMY,1 AND F. I. IWEZE From the Departments ofpathology and Surgery, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria SUMMARY
COR PULMONALE IN COAL-WORKER'S PNEUMOCONIOSIS
 COR PULMONALE IN COAL-WORKER'S PNEUMOCONIOSIS From the Institute of Pathology, BY A. L. WELLS* Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff Received September 26, 1953 Attention has been drawn to the occurrence
COR PULMONALE IN COAL-WORKER'S PNEUMOCONIOSIS From the Institute of Pathology, BY A. L. WELLS* Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff Received September 26, 1953 Attention has been drawn to the occurrence
Collateral arteries in pulmonary atresia with
 Collateral arteries in pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect A precarious blood supply SHEILA G HAWORTH* Br HeartJ 1980; 44: 5-13 From the Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Institute of Child
Collateral arteries in pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect A precarious blood supply SHEILA G HAWORTH* Br HeartJ 1980; 44: 5-13 From the Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Institute of Child
INTRAMURAL VESSELS AND ENDOTHELIAL CELLS
 594 INTRAMURAL VESSELS AND ENDOTHELIAL CELLS IN THE WALLS OF SCLEROSED RETINAL ARTERIES *t BY ARNOLD LOEWENSTEIN Fromz the Tennent Institute, Glasgow (Prof. W1. J. B. Riddell). ARTERIO-SCLEROTIC vessels
594 INTRAMURAL VESSELS AND ENDOTHELIAL CELLS IN THE WALLS OF SCLEROSED RETINAL ARTERIES *t BY ARNOLD LOEWENSTEIN Fromz the Tennent Institute, Glasgow (Prof. W1. J. B. Riddell). ARTERIO-SCLEROTIC vessels
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
PRIMARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN THREE SIBS
 PRIMARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN THREE SIBS BY P. N. COLEMAN, A. W. B. EDMUNDS, AND J. TREGILLUS From the Friarage Hospital, Northallerton, and the Memorial Hospital, Darlington Received January 4, 1958
PRIMARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN THREE SIBS BY P. N. COLEMAN, A. W. B. EDMUNDS, AND J. TREGILLUS From the Friarage Hospital, Northallerton, and the Memorial Hospital, Darlington Received January 4, 1958
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system.
 LAB 3: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cases we will cover are: A. Atherosclerosis Refer to virtual slide p_8, should
LAB 3: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cases we will cover are: A. Atherosclerosis Refer to virtual slide p_8, should
CASE NOTES. nephritis, and diabetes. ACUTE RETINAL VASCULAR PROLIFERATION* Duke-Elder (1940), who states that it depends essentially on two factors;
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 179. CASE NOTES ACUTE RETINAL VASCULAR PROLIFERATION* BY JOHN A. CHIVERS Dartford and Orpington Hospital Groups, Kent THs condition is described under its usual title retinitis
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 179. CASE NOTES ACUTE RETINAL VASCULAR PROLIFERATION* BY JOHN A. CHIVERS Dartford and Orpington Hospital Groups, Kent THs condition is described under its usual title retinitis
Histology of the Cardiac System. Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department
 Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Anatomy of Human Coronary Arterial Pulsation
 24 J Anat. Soc. India 52(1) 24-27 (2003) Anatomy of Human Coronary Arterial Pulsation Kumar, Keshaw Department of Anatomy, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi. INDIA Abstract.
24 J Anat. Soc. India 52(1) 24-27 (2003) Anatomy of Human Coronary Arterial Pulsation Kumar, Keshaw Department of Anatomy, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi. INDIA Abstract.
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse
 Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 2005 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-30, 2005
 Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
Pathology of Vulnerable Plaque Angioplasty Summit 25 TCT Asia Pacific, Seoul, April 28-3, 25 Renu Virmani, MD CVPath, A Research Service of the International Registry of Pathology Gaithersburg, MD Plaque
FURTHER STUDIES OF THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE BIRD'S HEART
 FURTHER STUDIES OF THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE BIRD'S HEART By FRANCIS DAVIES, M.D. (LONDON) Anatomy Department, University College, London INTRODUCTION T1HE histological investigation of the conducting
FURTHER STUDIES OF THE CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE BIRD'S HEART By FRANCIS DAVIES, M.D. (LONDON) Anatomy Department, University College, London INTRODUCTION T1HE histological investigation of the conducting
CUTANEOUS PETECHIAE IN FATAL CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
 J. clin. Path. (1958), 11, 391. CUTANEOUS PETECHAE N FATAL CORONARY ARTERY DSEASE BY L. M. GERLS From the Department of Pathology, Grimsby General Hospital n the clinical recognition of myocardial ischaemia,
J. clin. Path. (1958), 11, 391. CUTANEOUS PETECHAE N FATAL CORONARY ARTERY DSEASE BY L. M. GERLS From the Department of Pathology, Grimsby General Hospital n the clinical recognition of myocardial ischaemia,
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA
 NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
NOTE ON THE PATHOLOGY OF MORTON'S METATARSALGIA MAJOR LESTER S. KING, M.C., A.U.S. From the Laboratory Service of the William Beaumont General Hospital, El Paso, Texas Until relatively recently, the immediate
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1
 POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
/ Edward Cecil Williams, B.A., M.B. Cantab., / Physician, to the Royal Hospital for Sick Children and Women, Bristol.
 NOTES ON A CASE OF LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA IN A CHILD AGED THREE YEARS. / Edward Cecil Williams, B.A., M.B. Cantab., / Physician, to the Royal Hospital for Sick Children and Women, Bristol. The lymphatic type
NOTES ON A CASE OF LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA IN A CHILD AGED THREE YEARS. / Edward Cecil Williams, B.A., M.B. Cantab., / Physician, to the Royal Hospital for Sick Children and Women, Bristol. The lymphatic type
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART. I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine
 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY
 40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to:
 Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Control material was obtained in cases in which necropsy was performed and in which there was no history of peripheral vascular disease or
 Blood Vessels of the Skin in Chronic Venous Insufficiency By MYRON H. KULWIN, M.D., AND EDGAR A. HINES, JR., M.D. This study concerns ain evaluation of the anatomicopathologic changes found in blood vessels
Blood Vessels of the Skin in Chronic Venous Insufficiency By MYRON H. KULWIN, M.D., AND EDGAR A. HINES, JR., M.D. This study concerns ain evaluation of the anatomicopathologic changes found in blood vessels
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome
 J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
J. clin. Path. (1967), 2, 117 Histological features of the nephrotic syndrome associated with quartan malaria J. W. KIBUKAMUSOKE AND M. S. R. HUTT From the Makerere University College Medical School and
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
A CASE OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY HAEMOSIDEROSIS WITH MYOCARDITIS
 A CASE OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY HAEMOSIDEROSIS WITH MYOCARDITIS BY S. CAMPBELL and C. A. J. MACAFEE From the Royal Belfast Hospital.for Sick Children ana the Department of Pathology. the Queen's University
A CASE OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY HAEMOSIDEROSIS WITH MYOCARDITIS BY S. CAMPBELL and C. A. J. MACAFEE From the Royal Belfast Hospital.for Sick Children ana the Department of Pathology. the Queen's University
