Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2010, 12:27
|
|
|
- Roland Cuthbert Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Natural history of spontaneous aortic intramural hematoma progression: Six years follow-up with cardiovascular magnetic resonance Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2010, 12:27 doi: / x Xiaohai Ma Zhaoqi Zhang Zhanming Fan Lei Zhao Jing Yu ISSN X Article type Case report Submission date 7 December 2009 Acceptance date 13 May 2010 Publication date 13 May 2010 Article URL This peer-reviewed article was published immediately upon acceptance. It can be downloaded, printed and distributed freely for any purposes (see copyright notice below). Articles in Journal of Cardiovascular MR are listed in PubMed and archived at PubMed Central. For information about publishing your research in Journal of Cardiovascular MR or any BioMed Central journal, go to For information about other BioMed Central publications go to Ma et al., licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Natural history of spontaneous aortic intramural hematoma progression: Six years follow-up with cardiovascular magnetic resonance Xiaohai Ma *, Zhaoqi Zhang, Zhanming Fan, Lei Zhao, Jing Yu Deptartment of Radiology, Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, , China * Corresponding Author XM: maxi8238@gmail.com ZZ: zhaoqi5000@vip.sohu.com ZF: fanzm120@tom.com LZ: : zhaolei219@sohu.com JY: dsyujing@gmail.com 1
3 ABSTRACT We described a 6 years follow-up of a spontaneous aortic intramural hematoma (IMH) with cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) examination. Since multiple factors may play roles in the natural history of IMH, the patient experienced the course of progression, which included hematoma absorption, ulcer-like lesion, aneurysm and limited dissection. The initial and follow-up CMR examination included 3D CE MRA and non-enhanced "bright blood" pulse sequence. The inherent advantage of outstanding contrast with plain scan, which shorten the scan time and avoid potential risk of contrast agent, might make the fast gradient echo sequence as an alternative method when following stable IMH. 2
4 Background Spontaneous aortic intramural hematoma (IMH), which first described in 1920 by Krukenberg as dissection without intimal tear, results from the spontaneous rupture of the vasa vasorum of the aortic wall. IMH most frequently involves the ascending aorta (type A) or proximal descending aorta (type B). This condition presents clinically as severe chest pain radiating to the back, which is similar to aortic dissection (AD). Systemic hypertension is the leading risk factor for spontaneous IMH. Recent advances in imaging techniques have significantly improved the diagnostic accuracy and enhanced clinical understanding of IMH. The natural history of spontaneous IMH is different from classical AD and its time course of IMH can vary significantly, so early diagnosis and close follow-up is desirable. We describe a spontaneous IMH case followed for 6 years by cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR). The patient progressed through different stages, including hematoma absorption, ulcer-like lesion emergence, aneurysm enlargement and limited AD. Case History A 65-year-old female with a long history of hypertension was referred to emergency room because of acute chest pain that persisted over one day. The echocardiogram showed a widening of the lumen of the ascending aorta. A thoracic aorta CMR examination (Siemens Sonata 1.5T, Erlangen, Germany) was performed for further evaluation. The imaging protocol included three-dimension contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (3D CE MRA, TR/TE ; FOV mm; 3
5 effective thickness 1.23~1.60 mm) and true fast imaging steady-state precession (true FISP) MRI (TR/TE ms; field of view (FOV), mm; matrix, ; thickness, 6 mm). The true FISP images were acquired without cardiac gating. A stack of two-dimensional images were acquired in approximately 15~18 seconds. Each acquisition had 10 slices. Gadopentetate dimeglumine (0.1mmol/kg, Magnevist, Bayer-Schering, Germany) was administrated intravenously followed by 20 ml saline flush. An eccentric non-enhanced low signal intensity lesion around the widened ascending (50mm) and descending aorta were seen on the reconstructed 3D CE MRA and true FISP axial images. Aortic IMH (type A) combined with bilateral pleural effusion was documented (Figure 1). The symptoms ceased after conservative medical treatment. Short-term follow-up CMR examination was repeated at 1 month (Figure 2) and 3 months (Figure 3) after initial onset. The hematoma was stable at 1 month and partially absorbed at 3 months. The pleural effusion resolved entirely during the 3 months period. However, an ulcer-projection lesion (UPL) was found immediately distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery at 1month. At 3 months, the UPL had become larger and progressed into an aneurysm-like lesion. Since the patient was asymptomatic during this period, she refused surgery or intervention. At I year follow-up, CMR showed that the diameter of the ascending aorta had increased (from 50mm to 57mm) and that the aortic arch aneurysm had grown (Figure 4). Six years later, a luminal intimal flap was found at the ascending-arch of the aorta and diagnosed as limited AD (Figure 5). 4
6 Discussion There are controversial issues exist in indication of treatment of spontaneous IMH. Most studies currently recommend early surgery or interventional therapy for patients with proximal IMH and medical management for patients with distal IMH; this is similar to that of classical AD. However, others favor a conservative treatment, with initial medical management for all patients in a stable condition. Multiple factors may play roles in the natural history of spontaneous IMH, including blood pressure, vessel condition, hemodynamic changes, the wall thickness and diameter of the aorta, and even age and race [1, 2]. Moizumi et al [3] demonstrated that the aorta-related events occur equally in both types of IMH. Kaji et al [4] showed that maximum aortic diameter is predictive of progression for type A IMH with an optimal cutoff value of about 50 mm. Nishigami et al [5] reported that 18% of IMHs disappeared within 1 month and 48% within 6 months. Furthermore, those patients with an IMH that resolved or a maximal aortic diameter of <45 mm suggest good prognosis. A potential reason for progression is that aortic IMH can weaken the medial layer of aorta and increase the likelihood of fusiform aortic aneurysm or AD, especially in those with high aortic pressure or a newly emerged ulcer-like lesion. Based on short-term (<30 days) follow-up, several studies have suggested that the natural history of IMH is a dynamic process which can result in reabsorption, classical AD, or aortic rupture. Granha et al [6] reported that IMH with ulcer-like a lesion was significantly associated with disease progression, whereas IMH without an ulcer-like lesion had a reliable stable course. In a long-term study (mean follow-up 45 months) 5
7 with 68 cases, Evangelista et al [7] found that IMH most frequently evolved into aortic aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm, while complete regression without changes in the size of the aorta was observed in 30% cases. Progression to classical dissection was less common. In our 6 years of follow-up, the patient s blood pressure remained stable and no suspected symptoms occurred. However, the course of spontaneous IMH experienced hematoma absorption, ulcer-like lesion emergence, and aneurysm enlargement in the short-term and limited AD in the long-term. It verified that multiple factors may play roles in the course of disease. As a noninvasive imaging modality that does not require ionizing radiation, CMR has been preferred for the purposes of diagnosis and follow-up for IMH during the past decade [8]. The 3D CE MRA has been considered as one of the most effective techniques to diagnose aortic diseases. When combined with suitable post-processing, it can be used to differentiate primary IMH from classical AD and IMH associated with penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer (PAU). CE-MRA is a good tool for looking at the lumen but less effective at positively identifying mural haematoma, which may be missed by the unwary. Besides, emergency CMR evaluation for aortic injury or disease has not been considered practical due to prolonged examination times, especially after the rapid development of multi-detector computed tomography (CT), while CT is not suitable for long term follow-up medically stable patients because of radiation risk and the potential side effects of the associated contrast agents. Thus, researchers have focused on non-enhanced fast CMR imaging sequences to 6
8 address the scan time limitations. Pereles et al [9] evaluated the fast gradient echo sequence termed as truefisp, which demonstrates good contrast of the fluid flow, and shortens the examination time to less than 4 minutes. The accuracy of diagnosis for the presence of aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm was 100%. In our case, the true FISP sequence was applied in the patient s initial and follow-up examinations. The truefisp axial and/or sagittal images showed the crescent or ring- like thickening of the aortic wall due to the IMH, and displayed the low signal ring which corresponds to the intima between the aortic lumen and hematoma. The true FISP is also useful for detecting some of the complications of aortic diseases, such as pleural effusion and pericardial effusion, which is helpful in predicting the prognosis. The use of true FISP imaging is done using a non-ecg gated sequence with multiple slices, which is not ideal for evaluation of wall thickness or positively identifying haematoma (vs. laminated thrombus in an aneurysm). Tissue characterisation with ECG gated black-blood images may have been more helpful. In conclusion, the inherent contrast features of the fast gradient echo sequence without the use of a contrast agent make it a potential alternative when following stable IMH. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Author contributions XA: Literature research, manuscript preparation and editing. ZZ: Case collection. ZF: 7
9 Case collection. LZ: Manuscript preparation and editing. JY: Picture and word editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. References 1. Nienaber CA, von Kodolitsch Y, Petersen B, Loose R, Helmchen U, Haverich A, Spielmann RP. Intramural hemorrhage of the thoracic aorta: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Circulation. 1995; 92: Sawhney NS, DeMaria AN, Blanchard DG. Aortic intramural hematoma: an increasingly recognized and potentially fatal entity. Chest. 2001; 120: Moizumi Y, Komatsu T, Motoyoshi N, Tabayashi K. Clinical features and long-term outcome of type A and type B intramural hematoma of the aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004; 127: Kaji S, Nishigami K, Akasaka T, Hozumi t, Takagi T, Kawamoto T, Okura H, Shono H, Horibata Y, Honda T, Yoshida K. Prediction of progression or regression of type A aortic intramural hematoma by computed tomography. Circulation. 1999; 100: II Nishigami K, Tssuchiya T, Shono H, Horibata Y, Honda T. Disappearance of aortic intramural hematoma and its significance to the prognosis. Circulation Nov 7; 102(19 Suppl 3):III Ganaha F, Miller DC, Sugimoto K, Do YS, Minamiguchi H, Saito H, Mitchell RS, Dake MD. Prognosis of aortic intramural hematoma with and without penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer: a clinical and radiological analysis. Circulation 2002;106: Evangelista A, Dominguez R, Sebastia C, Salas A, Permanyer-Miralda G, Avegliano G, Elorz C, Gonzalez-Alujas T, Garcia Del Castillo H, Soler-Soler J. Long-term follow-up of aortic intramural hematoma predictors of outcome. Circulation. 2003; 108: Litmanovich D, Bankier AA, Cantin L, Raptopoulos V, Boiselle PM. CT and MRI in diseases of the aorta. Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193: Pereles FS, McCarthy RM, Baskaran V, Carr JC, Kapoor V, Krupinski EA, Finn JP. 8
10 Thoracic aortic dissection and aneurysm: evaluation with nonenhanced true FISP MR Angiography in less than 4 minutes. Radiology. 2002; 223:
11 Figure legends Figure 1 Initial CMR: the MIP (A) and MPR (B) images of 3D CE MRA revealed dilation of the ascending aorta and a low signal intensity non-enhanced lesion (arrow) around the ascending and descending aorta. In the true FISP axial images (C), the comparatively lower signal could be found eccentrically around both ascending and descending aorta (arrow), which was considered as hematoma. In addition, bilateral pleural effusion (asterisk) was documented. Figure 2 One month follow-up CMR: the MIP (A) and MPR (B) images revealed that the non-enhanced hematoma (arrow) became more stable compared to baseline, while an ulcer-projection lesion (UPL) was found nearby the left subclavian artery orifice. The true FISP axial images (C) were consistent with these findings and also indicated that the pleural effusion was partially absorbed. Figure 3 Three months follow-up CMR: the MIP (A), MPR (B), and true FISP axial images (C) revealed partial regression of the hematoma (arrow) and complete absorption of the pleural effusion, while the ulcer-projection lesion progressed into an aneurysm like contour (arrowhead). Figure 4 One year follow-up CMR: the MIP (A), MPR (B), and true FISP axial images (C) revealed that the aortic arch aneurysm (arrowhead) was larger than it was at the 3 months follow-up examination. A thickened aortic wall without an apparent low signal 10
12 non-enhanced hematoma could be seen, which suggested the IMH was reabsorbed. Figure 5 Six year follow-up CMR: the MIP (A) image showed the extended widening lumen of ascending aorta and aortic arch with irregular wall. The MPR (B) and true FISP sagittal (C) images displayed the luminal intimal flap (arrow) located at aortic arch that formed limited aortic dissection. The aortic arch aneurysm was still present (arrowhead). 11
13 Figure 1
14 Figure 2
15 Figure 3
16 Figure 4
17 Figure 5
ACUTE AORTIC SYNDROMES
 ACUTE AORTIC SYNDROMES AGNETA FLINCK MD, PhD Dept. of Thoracic Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital ACUTE AORTIC SYNDROMES Aortic dissection Intramural hematoma (IMH) 5-20% Penetrating atherosclerotic
ACUTE AORTIC SYNDROMES AGNETA FLINCK MD, PhD Dept. of Thoracic Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital ACUTE AORTIC SYNDROMES Aortic dissection Intramural hematoma (IMH) 5-20% Penetrating atherosclerotic
Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome
 SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
Clinical management and treatment of thoracic aortic diseases. Evolution of IMH. Luigi Lovato
 Clinical management and treatment of thoracic aortic diseases Evolution of IMH Luigi Lovato Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department Cardio-Thoracic Radiology-University Hospital S. Orsola-Malpighi Bologna-Italy
Clinical management and treatment of thoracic aortic diseases Evolution of IMH Luigi Lovato Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department Cardio-Thoracic Radiology-University Hospital S. Orsola-Malpighi Bologna-Italy
Asymptomatic Radiology / Clinical data Report / Cohort bias Referral bias. UCSF Vascular Symposium April 7-9, Acute Aortic Dissection
 Aortic Dissection: Natural History What is the Natural History of Aortic Dissection? UCSF Vascular Symposium April 7-9, 2011 Asymptomatic Radiology / Clinical data Report / Cohort bias Referral bias Stephen
Aortic Dissection: Natural History What is the Natural History of Aortic Dissection? UCSF Vascular Symposium April 7-9, 2011 Asymptomatic Radiology / Clinical data Report / Cohort bias Referral bias Stephen
Acute Aortic Syndromes
 Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Acute Aortic Syndromes Carole J. Dennie, MD Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Background Non-Traumatic Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Carole Dennie MD FRCPC Associate Professor of Radiology and Cardiology
Case Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer
 Case 12305 Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer Lopes Dias J, Costa NV, Leal C, Alves P, Bilhim T Section: Chest Imaging Published: 2014, Dec. 19 Patient: 68
Case 12305 Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer Lopes Dias J, Costa NV, Leal C, Alves P, Bilhim T Section: Chest Imaging Published: 2014, Dec. 19 Patient: 68
Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma. Leslie E. Quint, M.D.
 Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma Leslie E. Quint, M.D. 43 M Mid back pain X several months What type of aortic disease? A. Aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus B. Chronic dissection with thrombosed false
Aortic CT: Intramural Hematoma Leslie E. Quint, M.D. 43 M Mid back pain X several months What type of aortic disease? A. Aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus B. Chronic dissection with thrombosed false
Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17. Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta
 Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta Disclosures No financial disclosures Thank You Dr. Panneton for giving this lecture for me. I am stuck at Norfolk with an emergency
Animesh Rathore, MD 4/21/17 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of aorta Disclosures No financial disclosures Thank You Dr. Panneton for giving this lecture for me. I am stuck at Norfolk with an emergency
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D.
 CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
CT of Acute Thoracic Aortic Syndromes Stuart S. Sagel, M.D. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms Atherosclerotic Dissection Penetrating ulcer Mycotic Inflammatory (vasculitis) Traumatic Aortic Imaging Options Catheter
Diseases of the Aorta
 Diseases of the Aorta ASE Review 2018 Susan E Wiegers, MD, FASE, FACC Professor of Medicine My great friend Dr. Roberto Lang Disclosure None related to this presentation 1 Objectives Aneurysm Dissection
Diseases of the Aorta ASE Review 2018 Susan E Wiegers, MD, FASE, FACC Professor of Medicine My great friend Dr. Roberto Lang Disclosure None related to this presentation 1 Objectives Aneurysm Dissection
Multimodality Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta
 Multimodality Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta Steven Goldstein MD, FACC Director Noninvasive Cardiology MedStar Heart and Vascular Institute Washington Hospital Center Saturday, October 8, 2016 DISCLOSURE
Multimodality Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta Steven Goldstein MD, FACC Director Noninvasive Cardiology MedStar Heart and Vascular Institute Washington Hospital Center Saturday, October 8, 2016 DISCLOSURE
Detection of Intimal Defect by 64-Row Multidetector Computed Tomography in Patients With Acute Aortic Intramural Hematoma
 Detection of Intimal Defect by 64-Row Multidetector Computed Tomography in Patients With Acute Aortic Intramural Hematoma Takeshi Kitai, MD; Shuichiro Kaji, MD; Atsushi Yamamuro, MD; Tomoko Tani, MD; Makoto
Detection of Intimal Defect by 64-Row Multidetector Computed Tomography in Patients With Acute Aortic Intramural Hematoma Takeshi Kitai, MD; Shuichiro Kaji, MD; Atsushi Yamamuro, MD; Tomoko Tani, MD; Makoto
A Case of Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Successfully Managed with Medical Therapy. ( aortic intramural hematoma; IMH ) A ( type A IMH ) type A IMH
 A Case of Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Successfully Managed with Medical Therapy 21 A ( aortic intramural hematoma; IMH ) A ( type A IMH ) 67 20 type A IMH 20 W. H. Lin, C. Y. Chen, H. I. Yeh, and
A Case of Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Successfully Managed with Medical Therapy 21 A ( aortic intramural hematoma; IMH ) A ( type A IMH ) 67 20 type A IMH 20 W. H. Lin, C. Y. Chen, H. I. Yeh, and
IMAGING the AORTA. Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011
 IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
Acute Aortic Syndromes
 Acute Aortic Syndromes None Disclosures Smita Patel, M.B.B.S., M.R.C.P., F.R.C.R. Associate Professor, University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Objectives To review common CTA findings of acute aortic syndromes
Acute Aortic Syndromes None Disclosures Smita Patel, M.B.B.S., M.R.C.P., F.R.C.R. Associate Professor, University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI Objectives To review common CTA findings of acute aortic syndromes
Aortic intramural hematoma (IMH) has been increasingly
 Cardiovascular Surgery Outcomes of Patients With Acute Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Jae-Kwan Song, MD; Ji Hye Yim, MD; Jung-Min Ahn, MD; Dae-Hee Kim, MD; Joon-Won Kang, MD; Taek Yeon Lee, MD; Jong-Min
Cardiovascular Surgery Outcomes of Patients With Acute Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Jae-Kwan Song, MD; Ji Hye Yim, MD; Jung-Min Ahn, MD; Dae-Hee Kim, MD; Joon-Won Kang, MD; Taek Yeon Lee, MD; Jong-Min
IMH/Penetrating Aortic Ulcers/ Saccular Aneurysms: How to manage and when to intervene
 IMH/Penetrating Aortic Ulcers/ Saccular Aneurysms: How to manage and when to intervene UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium 2018 Sukgu M Han, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Clinical Surgery Co-director, Comprehensive
IMH/Penetrating Aortic Ulcers/ Saccular Aneurysms: How to manage and when to intervene UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium 2018 Sukgu M Han, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Clinical Surgery Co-director, Comprehensive
Superior vena cava obstruction caused by ascending aortic pseudoaneurysm as assessed by multi-detector row computed tomography
 Journal of Cardiology Cases (2011) 3, e98 e102 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jccase Case Report Superior vena cava obstruction caused by ascending aortic
Journal of Cardiology Cases (2011) 3, e98 e102 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jccase Case Report Superior vena cava obstruction caused by ascending aortic
MAGNETIC RESONANCE LATE GADOLINIUM ENHANCEMENT DETECTS ACUTE AORTIC INTRAMURAL HEMATOMA
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE LATE GADOLINIUM ENHANCEMENT DETECTS ACUTE AORTIC INTRAMURAL HEMATOMA Diego Perez de Arenaza, Santiago del Castillo, Marcelo Pietrani, Mariano Falconi, Juan Benger, Ezequiel Levy Yeyati,
MAGNETIC RESONANCE LATE GADOLINIUM ENHANCEMENT DETECTS ACUTE AORTIC INTRAMURAL HEMATOMA Diego Perez de Arenaza, Santiago del Castillo, Marcelo Pietrani, Mariano Falconi, Juan Benger, Ezequiel Levy Yeyati,
Diseases of Aorta: Marfan, Dissection, Atheroma
 31 st Annual State of the Art Echocardiography San Diego, CA February 20, 2018 9:00 9:20 AM 20 min Diseases of Aorta: Marfan, Dissection, Atheroma Muhamed Sarić MD, PhD, MPA Director of Noninvasive Cardiology
31 st Annual State of the Art Echocardiography San Diego, CA February 20, 2018 9:00 9:20 AM 20 min Diseases of Aorta: Marfan, Dissection, Atheroma Muhamed Sarić MD, PhD, MPA Director of Noninvasive Cardiology
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Thoraco-abdominal Aorta Dissection: Look Again Before You Leap
 Thoraco-abdominal Aorta Dissection: Look Again Before You Leap Abdel-Rauf Zeina 1*, Victoria Trachtengerts 1, Sobhi Abadi 2, Jacob Jarchowsky 3, Uri Soimu 1, Alicia Nachtigal 1 1. Department of Radiology,
Thoraco-abdominal Aorta Dissection: Look Again Before You Leap Abdel-Rauf Zeina 1*, Victoria Trachtengerts 1, Sobhi Abadi 2, Jacob Jarchowsky 3, Uri Soimu 1, Alicia Nachtigal 1 1. Department of Radiology,
Prognosis of Aortic Intramural Hematoma With and Without Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer. A Clinical and Radiological Analysis
 rognosis of Aortic Intramural Hematoma With and Without enetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer A Clinical and Radiological Analysis Fumikiyo Ganaha, MD; D. Craig Miller, MD; Koji Sugimoto, MD; Young Soo Do,
rognosis of Aortic Intramural Hematoma With and Without enetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer A Clinical and Radiological Analysis Fumikiyo Ganaha, MD; D. Craig Miller, MD; Koji Sugimoto, MD; Young Soo Do,
Katarzyna J. Macura 1, Frank M. Corl, Elliot K. Fishman, David A. Bluemke
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 174.110.46.171 on 02/10/18 from IP address 174.110.46.171. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved cute aortic syndromes refer to the spectrum of aortic
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 174.110.46.171 on 02/10/18 from IP address 174.110.46.171. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved cute aortic syndromes refer to the spectrum of aortic
Peter I. Kalmar, 1 Peter Oberwalder, 2 Peter Schedlbauer, 1 Jürgen Steiner, 1 and Rupert H. Portugaller Introduction. 2.
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 714914, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/714914 Case Report Secondary Aortic Dissection after Endoluminal Treatment of an Intramural Hematoma of the
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 714914, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/714914 Case Report Secondary Aortic Dissection after Endoluminal Treatment of an Intramural Hematoma of the
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION
 ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
First described by Krukenberg 1 in 1920 as aortic dissection
 Acute Type A Intramural Hematoma Analysis of Current Management Strategy Anthony Estrera, MD; Charles Miller III, PhD; Taek-Yeon Lee, MD; Paola De Rango, MD; Saad Abdullah, MD; Jon-Cecil Walkes, MD; Dianna
Acute Type A Intramural Hematoma Analysis of Current Management Strategy Anthony Estrera, MD; Charles Miller III, PhD; Taek-Yeon Lee, MD; Paola De Rango, MD; Saad Abdullah, MD; Jon-Cecil Walkes, MD; Dianna
La sindrome aortica acuta oggi
 University of Milan Thoracic Aortic Research Center La sindrome aortica acuta oggi Santi Trimarchi, MD, PhD Professore Associato di Chirurgia Vascolare, Università degli Studi di Milano Direttore, Divisione
University of Milan Thoracic Aortic Research Center La sindrome aortica acuta oggi Santi Trimarchi, MD, PhD Professore Associato di Chirurgia Vascolare, Università degli Studi di Milano Direttore, Divisione
MODERN METHODS FOR TREATING ABDOMINAL ANEURYSMS AND THORACIC AORTIC DISEASE
 MODERN METHODS FOR TREATING ABDOMINAL ANEURYSMS AND THORACIC AORTIC DISEASE AAA FACTS 200,000 New Cases Each Year Ruptured AAA = 15,000 Deaths per Year in U.S. 13th Leading Cause of Death 80% Chance of
MODERN METHODS FOR TREATING ABDOMINAL ANEURYSMS AND THORACIC AORTIC DISEASE AAA FACTS 200,000 New Cases Each Year Ruptured AAA = 15,000 Deaths per Year in U.S. 13th Leading Cause of Death 80% Chance of
Case Report CT Diagnosis of a Thoracic Aort Aneurysm with Type B Aortic Dissection Clinically Misdiagnosed as Acute Pulmonary Embolism
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 720394, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/720394 Case Report CT Diagnosis of a Thoracic Aort Aneurysm with Type B Aortic Dissection Clinically Misdiagnosed as Acute
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 720394, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/720394 Case Report CT Diagnosis of a Thoracic Aort Aneurysm with Type B Aortic Dissection Clinically Misdiagnosed as Acute
Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer
 April 2016 Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer Michael Nguyen, Harvard Medical School Year III Outline Introduction to Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcers Radiographic Features Treatment and Prognosis Patient
April 2016 Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer Michael Nguyen, Harvard Medical School Year III Outline Introduction to Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcers Radiographic Features Treatment and Prognosis Patient
Surgical indications in ascending aorta aneurysms: What do we know? Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD. Institut Mutualiste Montsouris, Paris, FRANCE
 Surgical indications in ascending aorta aneurysms: What do we know? Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD. Institut Mutualiste Montsouris, Paris, FRANCE Disclosures related to this talk : NONE 2 Clinical case A 40 year-old
Surgical indications in ascending aorta aneurysms: What do we know? Jean-Luc MONIN, MD, PhD. Institut Mutualiste Montsouris, Paris, FRANCE Disclosures related to this talk : NONE 2 Clinical case A 40 year-old
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Aorta
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Aorta William F. Armstrong M.D. Director Echocardiography Laboratory Professor of Medicine University of Michigan The Aorta: What to Evaluate Dimensions / shape Atherosclerotic
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Aorta William F. Armstrong M.D. Director Echocardiography Laboratory Professor of Medicine University of Michigan The Aorta: What to Evaluate Dimensions / shape Atherosclerotic
Χρόνιος διαχωρισμός. υπερηχοκαρδιογραφική. αορτής. παρακολούθηση ή άλλη; Α. Παπασπυρόπουλος ΕΠΙΜΕΛΗΤΗΣ ΓΝ.ΝΙΚΑΙΑΣ ΠΕΜΠΤΗ
 Χρόνιος διαχωρισμός αορτής υπερηχοκαρδιογραφική παρακολούθηση ή άλλη; Α. Παπασπυρόπουλος ΕΠΙΜΕΛΗΤΗΣ ΓΝ.ΝΙΚΑΙΑΣ ΠΕΜΠΤΗ 8-2-2018 The Normal Aorta (conduit function + control ) *Aortic expansion is about
Χρόνιος διαχωρισμός αορτής υπερηχοκαρδιογραφική παρακολούθηση ή άλλη; Α. Παπασπυρόπουλος ΕΠΙΜΕΛΗΤΗΣ ΓΝ.ΝΙΚΑΙΑΣ ΠΕΜΠΤΗ 8-2-2018 The Normal Aorta (conduit function + control ) *Aortic expansion is about
, David Stultz, MD. Aortic Dissection. David Stultz, MD October 7, 2003
 Aortic Dissection David Stultz, MD October 7, 2003 Background Incidence of 1 in 2000 in US Early mortality of 1%/hour for proximal dissection Two theories of formation Breach of intimal layer of aorta
Aortic Dissection David Stultz, MD October 7, 2003 Background Incidence of 1 in 2000 in US Early mortality of 1%/hour for proximal dissection Two theories of formation Breach of intimal layer of aorta
Remarkable progress has been made in recent years
 Intramural Hematoma and Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer of the Aorta Thoralf M. Sundt, MD Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota Intramural hematoma and penetrating aortic
Intramural Hematoma and Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer of the Aorta Thoralf M. Sundt, MD Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota Intramural hematoma and penetrating aortic
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Study of aortic ulcer by using MDCTA
 Study of aortic ulcer by using MDCTA Poster No.: C-3085 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Vascular Authors: L. Saba, R. Sanfilippo, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, R. Montisci, G. Mallarini; Cagliari/IT
Study of aortic ulcer by using MDCTA Poster No.: C-3085 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Vascular Authors: L. Saba, R. Sanfilippo, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, R. Montisci, G. Mallarini; Cagliari/IT
New ASE Guidelines: What you must know
 New ASE Guidelines: What you must know Federico M Asch MD, FASE, FACC Chair, ASE Guidelines and Standards Committee Medstar Washington Hospital Center Medstar Health Research Institute Georgetown University
New ASE Guidelines: What you must know Federico M Asch MD, FASE, FACC Chair, ASE Guidelines and Standards Committee Medstar Washington Hospital Center Medstar Health Research Institute Georgetown University
The potential value of intravascular ultrasound imaging in diagnosis of aortic intramural hematoma
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2011) 8: 224 229 2011 IGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Articles Open Access The potential value of intravascular ultrasound imaging in diagnosis of aortic
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2011) 8: 224 229 2011 IGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Articles Open Access The potential value of intravascular ultrasound imaging in diagnosis of aortic
Acute Aortic Syndromes
 Acute Aortic Syndromes Michael H. Picard, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures For everything you need to know about the aorta see Circulation 2010;121:e266-e369 And.
Acute Aortic Syndromes Michael H. Picard, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures For everything you need to know about the aorta see Circulation 2010;121:e266-e369 And.
Jean Jeudy, MD. Disease is very old, and nothing about it has changed. It is we who change as we learn to recognize what was formerly imperceptible.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology D e p a r t m e n t o f D i a g n o s t i c R a d i o l o g y T h e A c u t e A o r t i c S y n d r o m e s Jean Jeudy, MD BB aa lltt iimm oo rr e e,, MM aa rr yy llaa
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology D e p a r t m e n t o f D i a g n o s t i c R a d i o l o g y T h e A c u t e A o r t i c S y n d r o m e s Jean Jeudy, MD BB aa lltt iimm oo rr e e,, MM aa rr yy llaa
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Aortic intramural hematoma (IMH) has been recognized
 Long-Term Prognosis of Patients With Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Shuichiro Kaji, MD; Takashi Akasaka, MD; Yoko Horibata, MD; Kazuhiro Nishigami, MD; Hiroyuki Shono, MD; Minako Katayama, MD; Atsushi
Long-Term Prognosis of Patients With Type A Aortic Intramural Hematoma Shuichiro Kaji, MD; Takashi Akasaka, MD; Yoko Horibata, MD; Kazuhiro Nishigami, MD; Hiroyuki Shono, MD; Minako Katayama, MD; Atsushi
Tortuosity of the Descending Thoracic Aorta Simulating Dissection on Transesophageal Echocardiography
 CASE REPORTS Tortuosity of the Descending Thoracic Aorta Simulating Dissection on Transesophageal Echocardiography Edward S. Katz, MD, Robert M. Applebaum, MD, James P. Earls, MD, Glenn Krinsky, MD, Jeffrey
CASE REPORTS Tortuosity of the Descending Thoracic Aorta Simulating Dissection on Transesophageal Echocardiography Edward S. Katz, MD, Robert M. Applebaum, MD, James P. Earls, MD, Glenn Krinsky, MD, Jeffrey
Case 8036 Multiple penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers
 Case 8036 Multiple penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers Santiago I, Seco M, Curvo-Semedo L Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2010, Feb. 22 Patient: 78 year(s), male Clinical History A 78-year-old hypertensive
Case 8036 Multiple penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers Santiago I, Seco M, Curvo-Semedo L Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2010, Feb. 22 Patient: 78 year(s), male Clinical History A 78-year-old hypertensive
Orthogonal Measurement of Thoracic Aorta Luminal Diameter Using ECG-Gated High- Resolution Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 26:1480 1485 (2007) Original Research Orthogonal Measurement of Thoracic Aorta Luminal Diameter Using ECG-Gated High- Resolution Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography William
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 26:1480 1485 (2007) Original Research Orthogonal Measurement of Thoracic Aorta Luminal Diameter Using ECG-Gated High- Resolution Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography William
Disclosures: Acute Aortic Syndrome. A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO
 Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Acute Aortic Syndrome Disclosures: A. Michael Borkon, M.D. Director of CV Surgery Mid America Heart Institute Saint Luke s Hospital Kansas City, MO No financial relationships to disclose 1 Acute Aortic
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Follow-up of Aortic Dissection: How, How Often, Which Consequences Euro Echo 2011
 Follow-up of Aortic Dissection: How, How Often, Which Consequences Euro Echo 2011 Susan E. Wiegers, MD, FASE Director of Clinical Echocardiography Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Disclosure
Follow-up of Aortic Dissection: How, How Often, Which Consequences Euro Echo 2011 Susan E. Wiegers, MD, FASE Director of Clinical Echocardiography Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Disclosure
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance
 Trends in Emergency ortic Imaging Determining optimal imaging techniques for each patient. Y PERRY CHOI, MD, ND HMID MOJIIN, MD Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play vital
Trends in Emergency ortic Imaging Determining optimal imaging techniques for each patient. Y PERRY CHOI, MD, ND HMID MOJIIN, MD Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play vital
According to Vilacosta et al,
 Review Article Hellenic J Cardiol 2015; 56: 169-180 Imaging of Acute Aortic Syndrome: Advantages, Disadvantages and Pitfalls Efstratios Apostolakis 1, Nikolaos A. Papakonstantinou 2, Nikolaos G. Baikoussis
Review Article Hellenic J Cardiol 2015; 56: 169-180 Imaging of Acute Aortic Syndrome: Advantages, Disadvantages and Pitfalls Efstratios Apostolakis 1, Nikolaos A. Papakonstantinou 2, Nikolaos G. Baikoussis
Management of Acute Aortic Syndromes. M. Grabenwoger, MD Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery Hospital Hietzing, Vienna, Austria
 Management of Acute Aortic Syndromes M. Grabenwoger, MD Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery Hospital Hietzing, Vienna, Austria I have nothing to disclose. Acute Aortic Syndromes Acute Aortic Dissection Type
Management of Acute Aortic Syndromes M. Grabenwoger, MD Dept. of Cardiovascular Surgery Hospital Hietzing, Vienna, Austria I have nothing to disclose. Acute Aortic Syndromes Acute Aortic Dissection Type
AORTIC ANEURYSM. howmed.net
 AORTIC ANEURYSM howmed.net ANATOMY It is important to understand the anatomy of the aorta Need to know the extent of the aneurysm Need to know the vessels involved This helps with Medical or Surgical management
AORTIC ANEURYSM howmed.net ANATOMY It is important to understand the anatomy of the aorta Need to know the extent of the aneurysm Need to know the vessels involved This helps with Medical or Surgical management
Transluminal Stent-graft Placement endovascular surgery
 13 545 551 2004 Transluminal Stent-graft Placement endovascular surgery 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 3 2 1 1996 11Transluminal Stent-graft Placement TSGP 6 82 TSGP T42 O TSGP Th10 T 26 O 5 T 3 O 23T 6 O 2 T 47 A15B17B15O
13 545 551 2004 Transluminal Stent-graft Placement endovascular surgery 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 3 2 1 1996 11Transluminal Stent-graft Placement TSGP 6 82 TSGP T42 O TSGP Th10 T 26 O 5 T 3 O 23T 6 O 2 T 47 A15B17B15O
Ταξινόµηση οξέων αορτικών συνδρόµων
 !!!!!!!!!! ΕΑΑΑ Ταξινόµηση οξέων αορτικών συνδρόµων Acute aortic syndromes The common denominator of AAS is disruption of the media layer of the aorta with Bleeding within IMH, Bleeding along the aortic
!!!!!!!!!! ΕΑΑΑ Ταξινόµηση οξέων αορτικών συνδρόµων Acute aortic syndromes The common denominator of AAS is disruption of the media layer of the aorta with Bleeding within IMH, Bleeding along the aortic
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
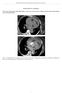 SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
2014 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis & Treatment of AORTIC DISEASES
 2014 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis & Treatment of AORTIC DISEASES Prof. Fausto J. Pinto, FESC, FACC, FASE President, ESC University Hospital Sta Maria University of Lisbon, Portugal Professor Fausto
2014 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis & Treatment of AORTIC DISEASES Prof. Fausto J. Pinto, FESC, FACC, FASE President, ESC University Hospital Sta Maria University of Lisbon, Portugal Professor Fausto
Vascular Intervention
 10 : 389-393, 2001 B Vascular Intervention 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 2 1 1997 7 2000 4 B 29 19 10 50 84 66.1 stent graft S/G primary entry stenting S/G 12 4 2 1 1 40 mm 8 1 MOF 1 endoleak + 11 91.6% 10 stenting
10 : 389-393, 2001 B Vascular Intervention 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 2 1 1997 7 2000 4 B 29 19 10 50 84 66.1 stent graft S/G primary entry stenting S/G 12 4 2 1 1 40 mm 8 1 MOF 1 endoleak + 11 91.6% 10 stenting
CT angiography in type I acute aortic dissection complicated with malperfusion - a visual review of obstruciton patterns
 CT angiography in type I acute aortic dissection complicated with malperfusion - a visual review of obstruciton patterns Eneva M. St. Ekaterna University Hospital Report objectives 1. Review malperfusion
CT angiography in type I acute aortic dissection complicated with malperfusion - a visual review of obstruciton patterns Eneva M. St. Ekaterna University Hospital Report objectives 1. Review malperfusion
Richard L. Hallett, MD
 SCCT 2015 LAS VEGAS, NV 18 JULY 2015 Richard L. Hallett, MD Chief, Cardiovascular Imaging Northwest Radiology Network Indianapolis St. Vincent Heart Center of Indiana Adjunct Assistant Professor of Radiology
SCCT 2015 LAS VEGAS, NV 18 JULY 2015 Richard L. Hallett, MD Chief, Cardiovascular Imaging Northwest Radiology Network Indianapolis St. Vincent Heart Center of Indiana Adjunct Assistant Professor of Radiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Penetrating Atherosclerotic Aortic Ulcer: Documentation by Transesophageal Echocardiography
 JACC Vol. 32, No. 1 July 1998:83 9 83 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Penetrating Atherosclerotic rtic Ulcer: Documentation by Transesophageal Echocardiography ISIDRE VILACOSTA, MD, JOSÉ ALBERTO SAN ROMÁN, MD,* PALOMA
JACC Vol. 32, No. 1 July 1998:83 9 83 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Penetrating Atherosclerotic rtic Ulcer: Documentation by Transesophageal Echocardiography ISIDRE VILACOSTA, MD, JOSÉ ALBERTO SAN ROMÁN, MD,* PALOMA
Typical and atypical imaging of thoracic and abdominal aortic rupture
 Typical and atypical imaging of thoracic and abdominal aortic rupture Poster No.: C-0453 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Isogai, T. Ichihara, T. Inoue, T. Kanamori ; Asahi/JP,
Typical and atypical imaging of thoracic and abdominal aortic rupture Poster No.: C-0453 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Isogai, T. Ichihara, T. Inoue, T. Kanamori ; Asahi/JP,
Long-term Follow-up of Aortic Intramural Hematomas and Penetrating Ulcers
 Long-term Follow-up of Aortic Intramural Hematomas and Penetrating Ulcers Alan S. Chou, BA, Bulat A. Ziganshin, MD, Paris Charilaou, MD, Maryann Tranquilli, RN, John A. Rizzo, PhD, John A. Elefteriades,
Long-term Follow-up of Aortic Intramural Hematomas and Penetrating Ulcers Alan S. Chou, BA, Bulat A. Ziganshin, MD, Paris Charilaou, MD, Maryann Tranquilli, RN, John A. Rizzo, PhD, John A. Elefteriades,
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor. Cardiothoracic Radiology
 New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor Cardiothoracic Radiology Disclosure I have no disclosure pertinent to this presentation.
New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor Cardiothoracic Radiology Disclosure I have no disclosure pertinent to this presentation.
Management of intramural hematoma and penetrating ulcers - what is different? D.Böckler University Hospital Heidelberg, Germany
 Management of intramural hematoma and penetrating ulcers - what is different? D.Böckler University Hospital Heidelberg, Germany Disclosure Speaker name: Dittmar Böckler I have the following potential conflicts
Management of intramural hematoma and penetrating ulcers - what is different? D.Böckler University Hospital Heidelberg, Germany Disclosure Speaker name: Dittmar Böckler I have the following potential conflicts
Acute aortic syndrome : Comprehensive MDCT evaluation
 Acute aortic syndrome : Comprehensive MDCT evaluation Poster No.: C-2290 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ilic, Z. Badnjar, D. Raceta Masic, D. Raicevic, V. Vujovic ; 1 1 2 2 2
Acute aortic syndrome : Comprehensive MDCT evaluation Poster No.: C-2290 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ilic, Z. Badnjar, D. Raceta Masic, D. Raicevic, V. Vujovic ; 1 1 2 2 2
Haemodynamically unstable patient with chest trauma
 HR J Clinical Case - Test Yourself Interventional Haemodynamically unstable patient with chest trauma Dimitrios Tomais, Theodoros Kratimenos, Dimosthenis Farsaris Interventional Radiology Unit, Radiology
HR J Clinical Case - Test Yourself Interventional Haemodynamically unstable patient with chest trauma Dimitrios Tomais, Theodoros Kratimenos, Dimosthenis Farsaris Interventional Radiology Unit, Radiology
ON FLOW DYNAMICS IN TYPE B AORTIC DISSECTION (TBAD)
 ON FLOW DYNAMICS IN TYPE B AORTIC DISSECTION (TBAD) A. Rabin 1, R. Karmeli 1, P. Bar-Yoseph 2 1- Vascular & Endovascular surgery department Hadassah university hospital, Jerusalem, Israel 2- Mechanical
ON FLOW DYNAMICS IN TYPE B AORTIC DISSECTION (TBAD) A. Rabin 1, R. Karmeli 1, P. Bar-Yoseph 2 1- Vascular & Endovascular surgery department Hadassah university hospital, Jerusalem, Israel 2- Mechanical
The Radiologist s role in Acute Aortic Syndrome.
 The Radiologist s role in Acute Aortic Syndrome. Poster No.: C-1525 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Quintana de la Cruz, M. M. Rienda, F. Jiménez Aragón, E. Domínguez Ferreras,
The Radiologist s role in Acute Aortic Syndrome. Poster No.: C-1525 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Quintana de la Cruz, M. M. Rienda, F. Jiménez Aragón, E. Domínguez Ferreras,
Acute aortic syndrome
 Keynote Lecture Series Acute aortic syndrome Joel S. Corvera Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health, Indianapolis, IN, USA Correspondence
Keynote Lecture Series Acute aortic syndrome Joel S. Corvera Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health, Indianapolis, IN, USA Correspondence
Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Multimodality Imaging in Aortic Diseases:
 Multimodality Imaging in Aortic Diseases: Federico M Asch MD, FASE, FACC Chair, ASE Guidelines and Standards Committee MedStar Washington Hospital Center MedStar Health Research Institute Georgetown University
Multimodality Imaging in Aortic Diseases: Federico M Asch MD, FASE, FACC Chair, ASE Guidelines and Standards Committee MedStar Washington Hospital Center MedStar Health Research Institute Georgetown University
Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications. Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University
 Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University No disclosures Disclosures Goals and Objectives To review CT technique
Post-Op Aorta: Differentiating Normal Post-Op vs. Complications Linda C. Chu, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Johns Hopkins University No disclosures Disclosures Goals and Objectives To review CT technique
Acute Aortic Syndrome: Beyond aortic dissection.
 Acute Aortic Syndrome: Beyond aortic dissection. Poster No.: C-2204 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Rodriguez Ortega, A. Sánchez Tovar, M. Santillana, I. 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 ARTERO,
Acute Aortic Syndrome: Beyond aortic dissection. Poster No.: C-2204 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Rodriguez Ortega, A. Sánchez Tovar, M. Santillana, I. 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 ARTERO,
Aortic Dissection Without Intimal Tear: Case Report and Findings on Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Aortic Dissection Without Intimal Tear: Case Report and Findings on Transesophageal Echocardiography James P. Eichelberger, MD, Rochester, New York Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) relies on the
Aortic Dissection Without Intimal Tear: Case Report and Findings on Transesophageal Echocardiography James P. Eichelberger, MD, Rochester, New York Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) relies on the
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Late False Lumen Expansion Predicted by Preoperative Blood Flow Simulation in a Patient with Chronic Type B Aortic Dissection
 Accepted Manuscript Late False Lumen Expansion Predicted by Preoperative Blood Flow Simulation in a Patient with Chronic Type B Aortic Dissection Chikara Ueki, MD, Hiroshi Tsuneyoshi, MD, PhD PII: S0022-5223(18)32652-7
Accepted Manuscript Late False Lumen Expansion Predicted by Preoperative Blood Flow Simulation in a Patient with Chronic Type B Aortic Dissection Chikara Ueki, MD, Hiroshi Tsuneyoshi, MD, PhD PII: S0022-5223(18)32652-7
La dissection aortique de type B : Dépistage et Suivi
 La dissection aortique de type B : Dépistage et Suivi Philippe Cluzel Département d Imagerie Cardiovasculaire et de Radiologie Interventionnelle et Thoracique (DICVRIT) Sorbonne Université Médecine, UMR
La dissection aortique de type B : Dépistage et Suivi Philippe Cluzel Département d Imagerie Cardiovasculaire et de Radiologie Interventionnelle et Thoracique (DICVRIT) Sorbonne Université Médecine, UMR
Internal Carotid Artery Dissection
 May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION
 The Essence of Aortic Dissection THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION Aortic dissection can be classified as acute if it s onset has been less than 14 days or chronic if its onset has been more than 14 days. Mortality
The Essence of Aortic Dissection THORACIC AORTIC DISSECTION Aortic dissection can be classified as acute if it s onset has been less than 14 days or chronic if its onset has been more than 14 days. Mortality
CARDIAC MRI. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Overview
 CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
 Accepted Manuscript Chronic type A dissection: when to operate? Francois Dagenais, MD PII: S0022-5223(18)33131-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.11.032 Reference: YMTC 13781 To appear in: The
Accepted Manuscript Chronic type A dissection: when to operate? Francois Dagenais, MD PII: S0022-5223(18)33131-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.11.032 Reference: YMTC 13781 To appear in: The
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management. TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida
 AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES
 NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
Mohit Bhasin MD. Aortic Imaging and Follow-up
 Mohit Bhasin MD Aortic Imaging and Follow-up "There is no condition more conducive to clinical humility than aneurysm of the aorta. William Osler 55 yo F suddenly develops ventricular fibrillation Defibrillated
Mohit Bhasin MD Aortic Imaging and Follow-up "There is no condition more conducive to clinical humility than aneurysm of the aorta. William Osler 55 yo F suddenly develops ventricular fibrillation Defibrillated
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Treatment of acute type B aortic dissection: Current status
 MEET Cannes, 18. - 21.06.2009 Treatment of acute type B aortic dissection: Current status Christoph A. Nienaber, MD, FACC University of Rostock Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiology christoph.nienaber@med.uni-rostock.de
MEET Cannes, 18. - 21.06.2009 Treatment of acute type B aortic dissection: Current status Christoph A. Nienaber, MD, FACC University of Rostock Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiology christoph.nienaber@med.uni-rostock.de
Total Endovascular Repair Type A Dissection. Eric Herget Interventional Radiology
 Total Endovascular Repair Type A Dissection Eric Herget Interventional Radiology 65 year old male Acute Type A Dissection Severe Aortic Regurgitation No co-morbidities Management? Part II Evolving Global
Total Endovascular Repair Type A Dissection Eric Herget Interventional Radiology 65 year old male Acute Type A Dissection Severe Aortic Regurgitation No co-morbidities Management? Part II Evolving Global
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
ΟΞΤ ΑΟΡΣΙΚΟ ΤΝΔΡΟΜΟ. Υωτεινή Λαζαρίδου Καρδιολόγος ΕΒ Νοσοκομείο Άγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη
 Η ΗΧΩΚΑΡΔΙΟΓΡΑΦΙΑ ΣΩΝ ΕΠΕΙΓΟΝΣΩΝ ΠΕΡΙΣΑΣΙΚΩΝ ΣΑ ΕΞΩΣΕΡΙΚΑ ΙΑΣΡΕΙΑ ΟΞΤ ΑΟΡΣΙΚΟ ΤΝΔΡΟΜΟ Υωτεινή Λαζαρίδου Καρδιολόγος ΕΒ Νοσοκομείο Άγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) Acute aortic syndrome
Η ΗΧΩΚΑΡΔΙΟΓΡΑΦΙΑ ΣΩΝ ΕΠΕΙΓΟΝΣΩΝ ΠΕΡΙΣΑΣΙΚΩΝ ΣΑ ΕΞΩΣΕΡΙΚΑ ΙΑΣΡΕΙΑ ΟΞΤ ΑΟΡΣΙΚΟ ΤΝΔΡΟΜΟ Υωτεινή Λαζαρίδου Καρδιολόγος ΕΒ Νοσοκομείο Άγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) Acute aortic syndrome
CT and MRI in Diseases of the Aorta
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Review Litmanovich et al. CT and MRI in Diseases of the orta Vascular and Interventional Radiology Review FOCUS ON: Diana Litmanovich 1 lexander. ankier Luce Cantin
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Review Litmanovich et al. CT and MRI in Diseases of the orta Vascular and Interventional Radiology Review FOCUS ON: Diana Litmanovich 1 lexander. ankier Luce Cantin
Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of the aorta
 Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of the aorta James A. Harris, MD, Kostaki G. Bis, MD, John L. Glover, MD, Phillip J. Bendick, PhD, Anil Shetty, PhD, and O. William Brown, MD, RDyal Oak, Mich. Purpose:
Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of the aorta James A. Harris, MD, Kostaki G. Bis, MD, John L. Glover, MD, Phillip J. Bendick, PhD, Anil Shetty, PhD, and O. William Brown, MD, RDyal Oak, Mich. Purpose:
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Medicine doi: To be assigned Early view version published: October
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Medicine doi: To be assigned Early view version published: October
Aortic dissection (AD) is a dynamic pathology
 Optimal Imaging for Aortic Dissection Choosing the best imaging modality to assess aortic dissection based on each patient s unique clinical factors. BY YOUNG-WOOK KIM, MD; YANG-JIN PARK, MD; AND DUK-KYUNG
Optimal Imaging for Aortic Dissection Choosing the best imaging modality to assess aortic dissection based on each patient s unique clinical factors. BY YOUNG-WOOK KIM, MD; YANG-JIN PARK, MD; AND DUK-KYUNG
