Decreased Affinity of Blood for Oxygen in Patients with Low-Output Heart Failure
|
|
|
- Brooke Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Decreased Affinity of Blood for Oxygen in Patients with Low-Output Heart Failure By James Metcalfe, M.D., Dharam S. Dhindsa, Ph.D., Miles J. Edwards, M.D., and Athanasios Mourdjinis, M.D. ABSTRACT Oxygen affinity of blood was measured in 16 patients (nonsmokers) without anemia and with clinical evidence of low cardiac output. Of these patients, 12 were catheterized and showed an arteriovenous oxygen concentration difference across the lungs greater than 5 ml/100 ml. The partial pressure of oxygen required to half-saturate their blood with oxygen (P 50 ) averaged 29.4 mm Hg (SD ± 1.9). Blood from normal subjects (nonsmokers) had an average P.- l0 of 27.3 mm Hg (SD ± 0.9). The decreased oxygen affinity found in blood of patients with low levels of cardiac output is considered as a compensatory adjustment to poor tissue blood flow, promoting the diffusion of oxygen from blood in tissue capillaries to intracellular sites of utilization. ADDITIONAL KEY WORDS compensation for tissue hypoxia oxygen dissociation curve A decreased affinity for oxygen has been demonstrated in blood from patients with varied conditions including high altitude exposure (1-3), anemia of several different etiologies (4-9), and arterial hypoxemia due to either congenital heart disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (10). One physiological common denominator of these clinically dissimilar entities is an impairment in the delivery of oxygen to tissues which is reflected by a lowered oxygen tension in venous blood leaving the tissues (11). Tissue blood flow is, of course, an important link in the chain of oxygen supply which runs from the environmental air to the mitochondria. Patients with abnormally low levels of cardiac output and decreased peripheral blood flow have, like those with the other disease conditions already mentioned, a lowered oxygen concentration in mixed venous blood. This paper reports the results of studies of From the Heart Research Laboratory, Department of Medicine, University of Oregon Medical School, Portland, Oregon This study was supported in part by Training Grant HE and Research Grant HE from the National Heart Institute and by the Oregon Heart Association. Received October 28, Accepted for publication June 2, blood oxygen affinity from patients selected because of clinical and, in most cases, laboratory evidence of low cardiac output. Methods Patients were selected initially on the basis of clinical evidence of low cardiac output secondary to long-standing valvular heart disease. Patients with pulmonary or peripheral edema were excluded, as were smokers and patients whose blood oxygen capacities were lower than 17.0 ml/100 ml. Subsequently, in order to evaluate the data quantitatively, patients with clinical evidence of low cardiac output who were being subjected to cardiac catheterization were studied if the catheterization data showed an oxygen concentration difference between arterial and mixed venous blood greater than 5 ml/100 ml at rest. For each study of blood oxygen affinity, venous blood was drawn without stasis into a syringe containing a solution of sodium fluoride and heparin. Equilibrium values of oxygen hemoglobin were determined using the "mixing technique" (12) at a carbon dioxide pressure (Pco 2 ) of approximately 40 mm Hg and at 37 C. At least two values of blood oxygen pressure (Po 2 ) and ph, one between 40% and 50% saturation and the other between 50% and 60% saturation with oxygen, were determined in each study. The observed values of Po 2 were corrected to a standard plasma ph of 7.40 (13) and plotted on linear coordinates at saturation values calculated for each mixture by correcting for dissolved 47
2 48 METCALFE, DHINDSA, EDWARDS, MOURDJINIS TABLE I Cardiac Output, Arteriovenous Oxygen Concentration Differences, and Blood Oxygen Capacities of Patients with Low-Output Heart Failure with Calculated Values for P 50 Patient Cardiac output (L/min/m') Ca o, - c *o, (ml/100 ml) Oxygen capacity (ml/100 ml) Pso (mm Hg) C J. A. B. J. B. L. E. L. L. E. E. W. A. J. K. B. F. E. D. G. L. C. S. L. S. D. H. L. W. T. B.C. MEAN ± SD G.I 5.8 G.8 G G For details see text. oxygen with respect to: (a) the Po 2 value in each component of the mixture, (b) the hemoglobin concentration of the blood being studied, and (c) the Poo of the resultant mixture. No improvement in the accuracy of determining the oxygen pressure at 50% saturation (P r, 0 ) was obtained in our hands by plotting values close to 50% saturation according to Hill's equation (14). All studies were completed within 3 hours of blood withdrawal. Results As shown in Table 1, blood from patients with clinical evidence of low cardiac output and high values for arteriovenous oxygen concentration difference showed a decreased oxygen affinity (increased Pso)- The mean ± SD of P 50 values obtained by studying blood from 11 normal subjects (nonsmokers) was mm Hg (10). The corresponding value obtained on blood from the patients was 29.4 ±1.9 mm Hg. The difference is highly significant (P< 0.01). There was a normal degree of heme-heme interaction as judged by the value of Hill's n (mean 2.48 ± 0.22 [SD] compared to 2.64 ± 0.17 in blood from normal subjects) (10). Discussion The availability of oxygen to its sites of utilization in tissue cells depends upon the constancy of the external environment and also upon an integrated series of supply mechanisms which include ventilation, diffusion across the alveolocapillary membrane, transport from lungs to tissue capillaries, and diffusion from capillary blood to intracellular enzyme chains. The last of these processes is, according to evidence currently available, a passive (physical) process whose rate depends upon several physiological variables including the mean diffusion distance, the surface area for diffusion, and the gradient of oxygen tension between capillary blood and tissue cells. Present evidence (15) suggests that the level of intracellular oxygen is at most only a few millimeters of mercury, so the gradient for oxygen delivery depends largely upon the oxygen tension in capillary blood. That tension is, in turn, regulated (at a fixed rate of tissue oxygen consumption) by the rate of hemoglobin flow (the rate of blood flow multiplied by the oxygen-carrying capacity of
3 BLOOD OXYGEN AFFINITY AND HEART FAILURE I TO 0 2 Extraction - 21% Normal Patients with Low Cardiac Output Extraction 38%!*o I P0 2 mm Hg FIGURE 1 Average oxygen dissociation curves of blood from normal subjects and from patients with low levels of cardiac output determined at a temperature of 37 C. All values were corrected to a plasma ph of The increased oxygen extraction characteristic of patients with low rates of blood flow is shown. The values of Po 2 which are indicated on the curves represent mixed venous blood (see text). blood) and by the position and shape of the blood oxygen dissociation curve. Evidence has been presented, derived from comparative studies (16), for a remarkable similarity of values for oxygen tension in mixed venous blood from varied species at rest over a wide range of body sizes and rates of oxygen consumption. We have interpreted this similarity as indicating a uniformity of oxygen tension in the "average" tissue capillary of the resting animal over the recent course of evolution. It is achieved by appropriate regulation of the rate of hemoglobin flow according to the oxygen affinity of blood and the rate of oxygen consumption characteristic of each species. Changes in the oxygen affinity of blood (expressed at standard values of plasma ph and temperature) occur in humans when tissue oxygen supply is handicapped by residence at high altitude or by any of several diseases. The data presented here show that this adaptation is employed by patients whose tissue oxygen supply is compromised by low rates of blood flow secondary to heart disease. The utility of the observed change in maintaining the oxygen tension of blood in the average capillary is illustrated by Figure 1. The patients we studied extracted, on the average, 38% of the oxygen from their arterial blood during transit through peripheral tissues. This extraction contrasts with one of 21% in normal individuals (11). Because of the rightward displacement of the blood oxygen dissociation curve, the increased extraction would lower the oxygen tension in mixed venous blood from the value of 40 mm Hg which is found in normal resting humans (11) Circulation Rejearch, Vol. XXV, July 1969
4 50 METCALFE, DHINDSA, EDWARDS, MOURDJINIS to approximately 33 mm Hg. If their blood had retained a normal affinity for oxygen, the mixed venous oxygen tension would have fallen to 30 mm Hg with an oxygen extraction of 38%. Displacement of the blood oxygen dissociation curve, by itself, prevents about 30% of the fall in venous blood oxygen tension that would occur in patients with this degree of limitation of cardiac output if their blood oxygen affinity did not change. It is important to note that other mechanisms, such as changes in hydrogen ion concentration, also influence oxygen affinity. For instance, metabolic acidosis would displace the curve still further to the right, acting additively to the change reported here to support oxygen tension in tissue capillaries. We regard lowered oxygen affinity of blood as an adaptive mechanism available to the human organism when its tissues are threatened with hypoxia. A 33% increase in cardiac output would elevate mixed venous oxygen tension to 33 mm Hg without the observed change in oxygen affinity, but seems to be an unavailable or, at least, less acceptable alternative for patients with low output heart failure. A possible mechanism for changes in oxygen affinity found in blood from patients threatened with tissue hypoxia is suggested by the work of Benesch and Benesch (17), showing that deoxygenated hemoglobin removes 2, 3-diphosphoglycerate from its free state in the red cell and stimulates glycolysis to replenish the erythrocyte's stores of it and other organic phosphates. 2, 3-Diphosphoglycerate has been shown to decrease hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen (18, 19), and on the basis of these findings, we have previously postulated (10) that changes in its concentration within the erythrocyte are responsible for the changes in blood oxygen affinity seen in patients whose tissues are threatened with hypoxia, as indicated by abnormally low values for oxygen saturation in mixed venous blood. Levels of 2, 3-diphosphoglycerate have recently been shown to increase in the red cells of humans within 36 hours of beginning sojourn at high altitude (3). Although changes in its concentration within the red cell seem at present to offer the most attractive hypothesis for the changes observed in these patients with low cardiac output, other modifications in the environment of hemoglobin, such as increased acidity (20, 21), cannot be discarded as possibilities. A vital function of the circulation is to maintain an oxygen tension in peripheral capillary blood adequate to supply oxygen to intracellular sites of utilization. Capillary oxygen tension depends upon the rate of blood flow with respect to oxygen consumption and upon the respiratory characteristics of circulating blood including oxygen affinity. In considering the therapeutic management of a patient with restricted cardiac output, the oxygen affinity of blood should be regarded as subject to regulation. For example, blood stored under usual conditions shows a definite increase in oxygen affinity within a few days (22) and the high affinity persists at detectable levels for several hours after transfusion (5). Such blood, when used in the treatment of shock, is predictably less effective in delivering oxygen to tissues than blood with normal or decreased oxygen affinity would be. Similarly, exposure to carbon monoxide at levels experienced by smokers causes both an increase in blood oxygen affinity and a decrease in the concentration of functional hemoglobin (23). For both reasons, smoking jeopardizes tissue oxygen supply. Procedures for maintaining tissue oxygenation should take into account factors that influence blood's oxygen affinity as well as those that maintain blood's oxygen capacity. References 1. KEYS, A., HALL, F. G., AND GUZMAN BARRON, E. S.: Position of the oxygen dissociation curve of human blood at high altitude. Am. J. Physiol. 115: 292, HURTADO, A.: Animals in high altitudes: Resident man. In Handbook of Physiology, sec. 4. Adaptation to the Environment, edited by D. B. Dill. Washington, D. C, American Physiological Society, 1964, p LENFANT, C, TRRANCE, J., ENGLISH, E., FINCH, C. A., REYNAFABJE, C, RAMOS, J., AND FAUHA, J.: Effect of altitude on oxygen binding by
5 BLOOD OXYGEN AFFINITY AND HEART FAILURE 51 hemoglobin and on organic phosphate levels. J. Clin. Invest. 47: 2652, DILL, D. B., BOCK, A. V., VAN CAULAERT, C, FoLLINC, A., HUBXTHAL, L. M., AND HENPER- SON, L. J.: Blood as a physicochemical system: VII. Composition and respiratory exchanges of human blood during recovery from pernicious anemia. J. Biol. Chem. 78: 191, VALTIS, D. J., AND KENNEDY, A. C: Defective gas-transport function of stored red blood-cells. Lancet 1: 119, KENNEDY, A. C, AND VALTIS, D. J.: Oxygen dissociation curve in anemia of various types. J. Clin. Invest. 33: 1372, RODMAN, T., CLOSE, H. P., AND PURCELL, M. K.: Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve in anemia. Ann. Internal Med. 52: 295, SPROULE, B. J., MITCHELL, J. H., AND MILLER, W. F.: Cardiopulmonary physiological responses to heavy exercise in patients with anemia. J. Clin. Invest. 39: 378, MULHAUSEN, R., ASTRUP, P., AND KjELDSEN, K.: Oxygen affinity of hemoglobin in patients with cardiovascular diseases, anemia, and cirrhosis of the liver. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 19: 291, EDWARDS, M. J., Now, M. J., WALTERS, C.-L., AND METCALFE, J.: Improved oxygen release; an adaptation of mature red cells to hypoxia. J. Clin. Invest. 47: 1851, PAREH, J. T., JONES, W. D., AND METCALFE, J.: A quantitative comparison of oxygen transport in sheep and human subjects. Resp. Physiol. 2: 196, EDWARDS, M. J., AND MARTIN, R. J.: Mixing technique for the oxygen-hemoglobin equilibrium and Bohr effect. J. Appl. Physiol. 21: 1898, SEVERINGHAUS, J. \V.: Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve correction for temperature and ph variation in human blood. J. Appl. Physiol. 12: 485, HILL, A. V.: Possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of hemoglobin on its dissociation curves. J. Physiol. (London) 40: iv, CHANCE, B., COHEN, P., JOBSIS, F., AND SCHOENER, B.: Intracellular oxidation-reduction states in vivo. Science. 137: 499, PARER, J. T., AND METCALFE, J.: Oxygen transport by blood in relation to body size. Nature. 215: 653, BENESCH, R., AND BENESCH, R. E.: Oxygenation and ion transport in red cells. Science. 160: 83, BENESCH, R., AXD BENESCH, R. E.: Effect of organic phosphates from the human erythrocyte on the allosteric properties of hemoglobin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Coramun. 26: 162, CHANUTIN, A., AND CURNISH, R. R.: Effect of organic and inorganic phosphates on the oxygen equilibrium of human erythrocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 121: 96, DILL, D. B.: Oxygen dissociation curves for human blood at 37 C. In Handbook of Respiratory Data in Aviation. Washington, D. C, Committee on Medical Research, BARTELS, H., BETKE, K., HILPERT, P., NIEMEYER, C, AND RIEGEL, K.: Die sogenannte standard- O 0 -dissoziationskurve des gesunden erwachsenen menschen. Arch. Ges. Physiol. 272: 372, BUNN, H. F., MAY, M. H., KOCHOLATY, W. F., AND SHIELDS, C. E.: Hemoglobin function in stored blood. J. Clin. Invest. 48: 311, GOLDSMITH, J. R., AND LANDAW, S. A.: Carbon monoxide and human health. Science. 162: 1352, 1968.
3. Which of the following would be inconsistent with respiratory alkalosis? A. ph = 7.57 B. PaCO = 30 mm Hg C. ph = 7.63 D.
 Pilbeam: Mechanical Ventilation, 4 th Edition Test Bank Chapter 1: Oxygenation and Acid-Base Evaluation MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The diffusion of carbon dioxide across the alveolar capillary membrane is. A.
Pilbeam: Mechanical Ventilation, 4 th Edition Test Bank Chapter 1: Oxygenation and Acid-Base Evaluation MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The diffusion of carbon dioxide across the alveolar capillary membrane is. A.
Gas Exchange in the Tissues
 Gas Exchange in the Tissues As the systemic arterial blood enters capillaries throughout the body, it is separated from the interstitial fluid by only the thin capillary wall, which is highly permeable
Gas Exchange in the Tissues As the systemic arterial blood enters capillaries throughout the body, it is separated from the interstitial fluid by only the thin capillary wall, which is highly permeable
PBL SEMINAR. HEMOGLOBIN, O 2 -TRANSPORT and CYANOSIS An Overview
 1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR HEMOGLOBIN, O 2 -TRANSPORT and CYANOSIS
1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR HEMOGLOBIN, O 2 -TRANSPORT and CYANOSIS
P02 for Hb = HbO2 at cell
 OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVES IN SICKLE CELL ANEMIA AND IN SUBJECTS WITH THE SICKLE CELL TRAIT By MARGARET R. BECKLAKE, S. B. GRIFFITHS, M. McGREGOR, H. I. GOLDMAN, AND J. P. SCHREVE (From the Cardiopulmonary
OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVES IN SICKLE CELL ANEMIA AND IN SUBJECTS WITH THE SICKLE CELL TRAIT By MARGARET R. BECKLAKE, S. B. GRIFFITHS, M. McGREGOR, H. I. GOLDMAN, AND J. P. SCHREVE (From the Cardiopulmonary
Acute Changes in Oxyhemoglobin Affinity EFFECTS ON OXYGEN TRANSPORT AND UTILIZATION
 Acute Changes in Oxyhemoglobin Affinity EFFECTS ON OXYGEN TRANSPORT AND UTILIZATION Thomas E. Riggs,, A. William Shafer, Clarence A. Guenter J Clin Invest. 1973;52(10):2660-2663. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci107459.
Acute Changes in Oxyhemoglobin Affinity EFFECTS ON OXYGEN TRANSPORT AND UTILIZATION Thomas E. Riggs,, A. William Shafer, Clarence A. Guenter J Clin Invest. 1973;52(10):2660-2663. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci107459.
with their viability and resistance to hemolysis ,19
 A n n a l s o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, V o l. 1, N o. 2 C o p y r i g h t 1 9 7 1, I n s t i t u t e f o r C l i n i c a l S c i e n c e In Vitro Parameters of the Integrity
A n n a l s o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, V o l. 1, N o. 2 C o p y r i g h t 1 9 7 1, I n s t i t u t e f o r C l i n i c a l S c i e n c e In Vitro Parameters of the Integrity
Dr. Puntarica Suwanprathes. Version 2007
 Dr. Puntarica Suwanprathes Version 2007 O 2 and CO 2 transport in blood Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve O 2 consumption (VO 2 ) CO 2 production (VCO 2 ) O 2 capacity O 2 content: CaO 2 or CvO 2 %saturation
Dr. Puntarica Suwanprathes Version 2007 O 2 and CO 2 transport in blood Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve O 2 consumption (VO 2 ) CO 2 production (VCO 2 ) O 2 capacity O 2 content: CaO 2 or CvO 2 %saturation
Module G: Oxygen Transport. Oxygen Transport. Dissolved Oxygen. Combined Oxygen. Topics to Cover
 Topics to Cover Module G: Oxygen Transport Oxygen Transport Oxygen Dissociation Curve Oxygen Transport Studies Tissue Hypoxia Cyanosis Polycythemia Oxygen Transport Oxygen is carried from the lungs to
Topics to Cover Module G: Oxygen Transport Oxygen Transport Oxygen Dissociation Curve Oxygen Transport Studies Tissue Hypoxia Cyanosis Polycythemia Oxygen Transport Oxygen is carried from the lungs to
Carbon Dioxide Transport. Carbon Dioxide. Carbon Dioxide Transport. Carbon Dioxide Transport - Plasma. Hydrolysis of Water
 Module H: Carbon Dioxide Transport Beachey Ch 9 & 10 Egan pp. 244-246, 281-284 Carbon Dioxide Transport At the end of today s session you will be able to : Describe the relationship free hydrogen ions
Module H: Carbon Dioxide Transport Beachey Ch 9 & 10 Egan pp. 244-246, 281-284 Carbon Dioxide Transport At the end of today s session you will be able to : Describe the relationship free hydrogen ions
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 136 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 24 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bernice Betweiler is a 73-year-old retired seamstress who has never been married. She worked in the alterations department
136 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 24 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bernice Betweiler is a 73-year-old retired seamstress who has never been married. She worked in the alterations department
Affinity in Acidosis and Alkalosis
 Regulatory Mechanisms of Hemoglobin Oxygen Affinity in Acidosis and Alkalosis A. J. BELLINGHAM, J. C. DEiTER, and C. LENFANT From the Department of Medicine and of Physiology and Biophysics, University
Regulatory Mechanisms of Hemoglobin Oxygen Affinity in Acidosis and Alkalosis A. J. BELLINGHAM, J. C. DEiTER, and C. LENFANT From the Department of Medicine and of Physiology and Biophysics, University
For many years 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (DPG) has been known to be generated
 EFFECTS OF CARBON MONOXDE ON DPG CONCENTRATONS N THE ERYTHROCYTE B. D. Dinman, M.D. lnstitute of Environmental and Zndusfrial Health and J. W. Eaton, Ph.D. and G. J. Brewer, M.D. Department of Human Genetics,
EFFECTS OF CARBON MONOXDE ON DPG CONCENTRATONS N THE ERYTHROCYTE B. D. Dinman, M.D. lnstitute of Environmental and Zndusfrial Health and J. W. Eaton, Ph.D. and G. J. Brewer, M.D. Department of Human Genetics,
The Role of Organic Phosphates in Erythrocytes on the Oxygen Dissociation of Hemoglobin
 A n n a l s o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, V o l. 1, N o. 2 C o p y r ig h t 1 9 7 1, I n s titu te f o r C lin ic a l S c ie n c e The Role of Organic Phosphates in Erythrocytes
A n n a l s o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, V o l. 1, N o. 2 C o p y r ig h t 1 9 7 1, I n s titu te f o r C lin ic a l S c ie n c e The Role of Organic Phosphates in Erythrocytes
of Keys, Hall and Barron (1). Details are given in the preceding report (6) in which the oxygen dissociation
 THE OSITION OF THE OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE OF THE BLOOD IN CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE' By MINERVA MORSE, DONALD E. CASSELS, AND MELBA HOLDER WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF FLORENCE NUMAJIRI
THE OSITION OF THE OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE OF THE BLOOD IN CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE' By MINERVA MORSE, DONALD E. CASSELS, AND MELBA HOLDER WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF FLORENCE NUMAJIRI
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Globular proteins Proteins globular fibrous
 Globular proteins Globular proteins Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. Globular
Globular proteins Globular proteins Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. Globular
Lecture 19, 04 Nov 2003 Chapter 13, Respiration, Gas Exchange, Acid-Base Balance. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003
 1 Lecture 19, 04 Nov 003 Chapter 13, Respiration, Gas Exchange, Acid-Base Balance Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology
1 Lecture 19, 04 Nov 003 Chapter 13, Respiration, Gas Exchange, Acid-Base Balance Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock. Dr Than Kyaw March 2012
 Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Respiratory Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Respiratory Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Gas exchange Gas exchange in the lungs (to capillaries) occurs by diffusion across respiratory membrane due to differences in partial
Respiratory Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Gas exchange Gas exchange in the lungs (to capillaries) occurs by diffusion across respiratory membrane due to differences in partial
prepared by Drabkin's procedure, was already noted by Havinga.4 Since DPG is a highly
 RECIPROCAL BINDING OF OXYGEN AND DIPHOSPHOGLYCERATE BY HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN* BY REINHOLD BENESCH,t RUTH E. BENESCH, AND CHI ING YU DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS AND
RECIPROCAL BINDING OF OXYGEN AND DIPHOSPHOGLYCERATE BY HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN* BY REINHOLD BENESCH,t RUTH E. BENESCH, AND CHI ING YU DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS AND
3. Which statement is false about anatomical dead space?
 Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Blood Gases, ph, Acid- Base Balance
 Blood Gases, ph, Acid- Base Balance Blood Gases Acid-Base Physiology Clinical Acid-Base Disturbances Blood Gases Respiratory Gas Exchange Chemical Control of Respiration Dyshemoglobins Oxygen Transport
Blood Gases, ph, Acid- Base Balance Blood Gases Acid-Base Physiology Clinical Acid-Base Disturbances Blood Gases Respiratory Gas Exchange Chemical Control of Respiration Dyshemoglobins Oxygen Transport
sounds are distant with inspiratory crackles. He sits on the edge of his chair, leaning forward, with both hands on his
 I NTE R P R ETI N G A R T E R I A L B L O O D G A S E S : EASY AS A B C Take this step-by-step approach to demystify the parameters of oxygenation, ventilation, acid-base balance. BY WILLIAM C. PRUITT,
I NTE R P R ETI N G A R T E R I A L B L O O D G A S E S : EASY AS A B C Take this step-by-step approach to demystify the parameters of oxygenation, ventilation, acid-base balance. BY WILLIAM C. PRUITT,
There are number of parameters which are measured: ph Oxygen (O 2 ) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Bicarbonate (HCO 3 -) AaDO 2 O 2 Content O 2 Saturation
 Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) A blood gas is exactly that...it measures the dissolved gases in your bloodstream. This provides one of the best measurements of what is known as the acid-base balance. The body
Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) A blood gas is exactly that...it measures the dissolved gases in your bloodstream. This provides one of the best measurements of what is known as the acid-base balance. The body
Acids, Bases, and Salts
 Acid / Base Balance Objectives Define an acid, a base, and the measure of ph. Discuss acid/base balance, the effects of acidosis or alkalosis on the body, and the mechanisms in place to maintain balance
Acid / Base Balance Objectives Define an acid, a base, and the measure of ph. Discuss acid/base balance, the effects of acidosis or alkalosis on the body, and the mechanisms in place to maintain balance
OpenStax-CNX module: m Transport of Gases. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46545 1 Transport of Gases OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46545 1 Transport of Gases OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Critical Care Monitoring. Assessing the Adequacy of Tissue Oxygenation. Tissue Oxygenation - Step 1. Tissue Oxygenation
 Critical Care Monitoring 1 Assessing the Adequacy of Tissue oxygenation is the end-product of many complex steps 2 - Step 1 Oxygen must be made available to alveoli 3 1 - Step 2 Oxygen must cross the alveolarcapillary
Critical Care Monitoring 1 Assessing the Adequacy of Tissue oxygenation is the end-product of many complex steps 2 - Step 1 Oxygen must be made available to alveoli 3 1 - Step 2 Oxygen must cross the alveolarcapillary
Appendix D An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires:
 Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Haemoglobin Revision. May minutes. 85 marks. Page 1 of 32
 Haemoglobin Revision May 103 97 minutes 85 marks Page 1 of 3 Q1. (a) The graph shows a dissociation curve for human haemoglobin at ph 7.4. The position of the curve is different at ph 7.. (i) (ii) Sketch
Haemoglobin Revision May 103 97 minutes 85 marks Page 1 of 3 Q1. (a) The graph shows a dissociation curve for human haemoglobin at ph 7.4. The position of the curve is different at ph 7.. (i) (ii) Sketch
ALCO Regulations. Protocol pg. 47
 For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
CIRCULATION IN CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE*
 THE EFFECT OF CARBON DIOXIDE ON THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IN CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE* BY R. J. SHEPHARD From The Cardiac Department, Guy's Hospital Received July 26, 1954 The response of the pulmonary
THE EFFECT OF CARBON DIOXIDE ON THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION IN CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE* BY R. J. SHEPHARD From The Cardiac Department, Guy's Hospital Received July 26, 1954 The response of the pulmonary
i-stat Alinity v Utilization Guide
 istat Alinity v Utilization Guide The istat Alinity v delivers blood gas, acidbase, electrolyte, chemistry, and hematology measurements in a completely portable, handheld package. Accuracy is ensured by
istat Alinity v Utilization Guide The istat Alinity v delivers blood gas, acidbase, electrolyte, chemistry, and hematology measurements in a completely portable, handheld package. Accuracy is ensured by
Studies of the circulation and pulmonary function
 THE ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES, THE OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE, AND THE ACID-BASE BALANCE IN POLYCYTHEMIA VERA 1 By DONALD E. CASSELS AND MINERVA MORSE (From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Chicago
THE ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES, THE OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE, AND THE ACID-BASE BALANCE IN POLYCYTHEMIA VERA 1 By DONALD E. CASSELS AND MINERVA MORSE (From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Chicago
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
OXYGENATION AND ACID- BASE EVALUATION. Chapter 1
 OXYGENATION AND ACID- BASE EVALUATION Chapter 1 MECHANICAL VENTILATION Used when patients are unable to sustain the level of ventilation necessary to maintain the gas exchange functions Artificial support
OXYGENATION AND ACID- BASE EVALUATION Chapter 1 MECHANICAL VENTILATION Used when patients are unable to sustain the level of ventilation necessary to maintain the gas exchange functions Artificial support
Chapter 7. Heme proteins Cooperativity Bohr effect
 Chapter 7 Heme proteins Cooperativity Bohr effect Hemoglobin is a red blood cell protein that transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin is an allosteric protein that displays cooperativity
Chapter 7 Heme proteins Cooperativity Bohr effect Hemoglobin is a red blood cell protein that transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin is an allosteric protein that displays cooperativity
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4
 Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
i-stat Alinity v Utilization Guide
 istat Alinity v Utilization Guide The istat Alinity v delivers blood gas, acidbase, electrolyte, chemistry, and hematology results in a completely portable, handheld package. Accuracy is ensured by extensive
istat Alinity v Utilization Guide The istat Alinity v delivers blood gas, acidbase, electrolyte, chemistry, and hematology results in a completely portable, handheld package. Accuracy is ensured by extensive
Acid - base equilibrium
 Acid base equilibrium ph concept ph = log [H + ] ph [H+] 1 100 mmol/l D = 90 mmol/l 2 10 mmol/l D = 9 mmol/l 3 1 mmol/l 2 ph = log [H + ] 3 ph ph = log [H + ] ph of capillary blood norm: 7,35 7,45 Sorensen
Acid base equilibrium ph concept ph = log [H + ] ph [H+] 1 100 mmol/l D = 90 mmol/l 2 10 mmol/l D = 9 mmol/l 3 1 mmol/l 2 ph = log [H + ] 3 ph ph = log [H + ] ph of capillary blood norm: 7,35 7,45 Sorensen
Mechanical Ventilation. Assessing the Adequacy of Tissue Oxygenation. Tissue Oxygenation - Step 1. Tissue Oxygenation
 1 Mechanical Ventilation Assessing the Adequacy of 2 Tissue oxygenation is the end-product of many complex steps - Step 1 3 Oxygen must be made available to alveoli 1 - Step 2 4 Oxygen must cross the alveolarcapillary
1 Mechanical Ventilation Assessing the Adequacy of 2 Tissue oxygenation is the end-product of many complex steps - Step 1 3 Oxygen must be made available to alveoli 1 - Step 2 4 Oxygen must cross the alveolarcapillary
RESP-1320: ACID-BASE AND HEMODYNAMICS
 RESP-1320: Acid-Base and Hemodynamics 1 RESP-1320: ACID-BASE AND HEMODYNAMICS Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:RESP-1320 : Acid-Base and Hemodynamics Board of Trustees: 2017-01-26 Academic Term: 2017-08-24
RESP-1320: Acid-Base and Hemodynamics 1 RESP-1320: ACID-BASE AND HEMODYNAMICS Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:RESP-1320 : Acid-Base and Hemodynamics Board of Trustees: 2017-01-26 Academic Term: 2017-08-24
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE
 UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
Exercise Respiratory system Ventilation rate matches work rate Not a limiting factor Elite athletes
 Respiratory Exercise Response Chapter 11 Exercise Respiratory system Ventilation rate matches work rate Not a limiting factor Elite athletes Submaximal (
Respiratory Exercise Response Chapter 11 Exercise Respiratory system Ventilation rate matches work rate Not a limiting factor Elite athletes Submaximal (
Oxygen and CO 2 transport. Biochemistry II
 Oxygen and CO 2 transport 2 Acid- base balance Biochemistry II Lecture 9 2008 (J.S.) 1 Transport of O 2 and CO 2 O 2 INSPIRED AIR CO 2 EXPIRED AIR HCO 3 + HHb + Lungs HbO 2 + H + + HCO 3 HbO 2 + H 2 O
Oxygen and CO 2 transport 2 Acid- base balance Biochemistry II Lecture 9 2008 (J.S.) 1 Transport of O 2 and CO 2 O 2 INSPIRED AIR CO 2 EXPIRED AIR HCO 3 + HHb + Lungs HbO 2 + H + + HCO 3 HbO 2 + H 2 O
Appendix E Choose the sign or symptom that best indicates severe respiratory distress.
 Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
i. Zone 1 = dead space ii. Zone 2 = ventilation = perfusion (ideal situation) iii. Zone 3 = shunt
 Respiratory Review I. Oxygen transport a. Oxygen content of blood i. Dissolved oxygen =.003 x PaO 2, per 100 ml plasma 1. Henry s Law ii. Oxygen on hemoglobin = 1.34 ml x sat x Hgb iii. CaO 2 = Dissolved
Respiratory Review I. Oxygen transport a. Oxygen content of blood i. Dissolved oxygen =.003 x PaO 2, per 100 ml plasma 1. Henry s Law ii. Oxygen on hemoglobin = 1.34 ml x sat x Hgb iii. CaO 2 = Dissolved
Carbon Dioxide Transport and Acid-Base Balance
 CHAPTER 7 Carbon Dioxide Transport and Acid-Base Balance Carbon Dioxide Transport Dioxide Transport In plasma: Carbamino compound (bound to protein) Bicarbonate Dissolved CO 2 CO 2 Is Converted to HCO
CHAPTER 7 Carbon Dioxide Transport and Acid-Base Balance Carbon Dioxide Transport Dioxide Transport In plasma: Carbamino compound (bound to protein) Bicarbonate Dissolved CO 2 CO 2 Is Converted to HCO
Oxygenation. Chapter 45. Re'eda Almashagba 1
 Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016
 LH8 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SRB3008 Date: Monday
LH8 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SRB3008 Date: Monday
Acid-Base 1, 2, and 3 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Acid-Base 1, 2, and 3 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The relationship between hydrogen ion concentration and ph. 2. Production of acid
Acid-Base 1, 2, and 3 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The relationship between hydrogen ion concentration and ph. 2. Production of acid
1. Hemoglobin and the Movement of Oxygen. Respirator system/biochemistry
 1. Hemoglobin and the Movement of Oxygen Respirator system/biochemistry YOU MUST BE ABLE TO: Hemoglobin and the Movement of Oxygen specific aims 1. Compare structure of myoglobin and hemoglobin 2. Understand
1. Hemoglobin and the Movement of Oxygen Respirator system/biochemistry YOU MUST BE ABLE TO: Hemoglobin and the Movement of Oxygen specific aims 1. Compare structure of myoglobin and hemoglobin 2. Understand
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Control of Ventilation [2]
![Control of Ventilation [2] Control of Ventilation [2]](/thumbs/83/87644191.jpg) Control of Ventilation [2] สรช ย ศร ส มะ พบ., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล มหาว ทยาล ยมห ดล Describe the effects of alterations in chemical stimuli, their mechanisms and response to
Control of Ventilation [2] สรช ย ศร ส มะ พบ., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล มหาว ทยาล ยมห ดล Describe the effects of alterations in chemical stimuli, their mechanisms and response to
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD
 BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
Biology A-level: Transport. Blood. Page 1 of 22 1/18/2009. Red blood cells
 Page 1 of 22 Home A-level Biology Transport Blood Biology A-level: Transport Blood Just over half of the blood volume is made up of a pale yellow fluid called plasma. The rest of the blood is made up of
Page 1 of 22 Home A-level Biology Transport Blood Biology A-level: Transport Blood Just over half of the blood volume is made up of a pale yellow fluid called plasma. The rest of the blood is made up of
Neaam Al-Bahadili. Rana J. Rahhal. Mamoun Ahram
 5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
Maternal and Fetal Physiology
 Background Maternal and Fetal Physiology Anderson Lo, DO Fellow, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine SEMCME Fetal Assessment Course July 20, 2018 Oxygen pathway Mother Placenta
Background Maternal and Fetal Physiology Anderson Lo, DO Fellow, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine SEMCME Fetal Assessment Course July 20, 2018 Oxygen pathway Mother Placenta
Physiological Causes of Abnormal ABG s
 Physiological Causes of Abnormal ABG s Major Student Performance Objective 1 1. The student will be able to discuss causes for various types of blood gas results. 2. They will also be required to discuss
Physiological Causes of Abnormal ABG s Major Student Performance Objective 1 1. The student will be able to discuss causes for various types of blood gas results. 2. They will also be required to discuss
Lecture 10. Circulatory systems; flow dynamics, flow regulation in response to environmental and internal conditions.
 Lecture 10 Circulatory systems; flow dynamics, flow regulation in response to environmental and internal conditions Professor Simchon Influence of P O2 on Hemoglobin Saturation Hemoglobin saturation plotted
Lecture 10 Circulatory systems; flow dynamics, flow regulation in response to environmental and internal conditions Professor Simchon Influence of P O2 on Hemoglobin Saturation Hemoglobin saturation plotted
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 6.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 17, 26, 27, 31, 33, 37, 40 42, 44, 45, 51, 58 6.2 Describe the basic roles and structures
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 6.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 17, 26, 27, 31, 33, 37, 40 42, 44, 45, 51, 58 6.2 Describe the basic roles and structures
Neaam Al-Bahadili. Rana J. Rahhal. Mamoun Ahram
 5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
a. Describe the physiological consequences of intermittent positive pressure ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure.
 B. 10 Applied Respiratory Physiology a. Describe the physiological consequences of intermittent positive pressure ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure. Intermittent positive pressure ventilation
B. 10 Applied Respiratory Physiology a. Describe the physiological consequences of intermittent positive pressure ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure. Intermittent positive pressure ventilation
Control of Respiration
 Control of Respiration Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction The basic rhythm of breathing is
Control of Respiration Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction The basic rhythm of breathing is
Pediatric Code Blue. Goals of Resuscitation. Focus Conference November Ensure organ perfusion
 Pediatric Code Blue Focus Conference November 2015 Duane C. Williams, MD Pediatric Critical Care Department of Pediatrics Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Goals of Resuscitation Ensure organ perfusion
Pediatric Code Blue Focus Conference November 2015 Duane C. Williams, MD Pediatric Critical Care Department of Pediatrics Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Goals of Resuscitation Ensure organ perfusion
OXYGEN SATURATION OF STERNAL MARROW BLOOD IN POLYCYTHEMIA VERA
 OXYGEN SATURATION OF STERNAL MARROW BLOOD IN POLYCYTHEMIA VERA Bernard M. Schwartz, Daniel Stats J Clin Invest. 1949;28(4):736-740. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci102125. Research Article Find the latest version:
OXYGEN SATURATION OF STERNAL MARROW BLOOD IN POLYCYTHEMIA VERA Bernard M. Schwartz, Daniel Stats J Clin Invest. 1949;28(4):736-740. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci102125. Research Article Find the latest version:
Principles of Fluid Balance
 Principles of Fluid Balance I. The Cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes A. Water 1. Total body water (TBW) = 60% of total body weight 2. Fluid Compartments in the Body a. Intracellular Compartment
Principles of Fluid Balance I. The Cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes A. Water 1. Total body water (TBW) = 60% of total body weight 2. Fluid Compartments in the Body a. Intracellular Compartment
The equilibrium between basis and acid can be calculated and termed as the equilibrium constant = Ka. (sometimes referred as the dissociation constant
 Acid base balance Dobroslav Hájek dhajek@med.muni.cz May 2004 The equilibrium between basis and acid can be calculated and termed as the equilibrium constant = Ka. (sometimes referred as the dissociation
Acid base balance Dobroslav Hájek dhajek@med.muni.cz May 2004 The equilibrium between basis and acid can be calculated and termed as the equilibrium constant = Ka. (sometimes referred as the dissociation
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology
 Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Lecture 5. Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Lecture 5 Myoglobin & Hemoglobin Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin - Myoglobin and Hemoglobin are (metalloprotein containing a heme prosthetic group). hemeproteins - Function as
Lecture 5 Myoglobin & Hemoglobin Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin - Myoglobin and Hemoglobin are (metalloprotein containing a heme prosthetic group). hemeproteins - Function as
Bell Work. b. is wrong because combining two glucose molecules requires energy, it does not release energy
 Bell Work How is energy made available to the cell to move large starch molecules across the cell membrane through the process of endocytosis? a. removing a phosphate from ATP b. combining two glucose
Bell Work How is energy made available to the cell to move large starch molecules across the cell membrane through the process of endocytosis? a. removing a phosphate from ATP b. combining two glucose
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
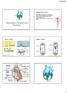 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Each event in Table 5.1 is immediately followed by one of the events listed in Table 5.2.
 1 (a) Table 5.1 and Table 5.2 list events that occur during the cardiac cycle. Each event in Table 5.1 is immediately followed by one of the events listed in Table 5.2. Complete Table 5.1 by inserting
1 (a) Table 5.1 and Table 5.2 list events that occur during the cardiac cycle. Each event in Table 5.1 is immediately followed by one of the events listed in Table 5.2. Complete Table 5.1 by inserting
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings
 Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
How Does Pulse Oximetry Work? SpO2 Sensors Absorption at the Sensor Site Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
 SpO2 Monitoring Contents 1 Introduction 1 What is SpO 2? How Does Pulse Oximetry Work? SpO2 Sensors Absorption at the Sensor Site Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve 5 How Do I Use SpO2? Choosing a Sensor
SpO2 Monitoring Contents 1 Introduction 1 What is SpO 2? How Does Pulse Oximetry Work? SpO2 Sensors Absorption at the Sensor Site Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve 5 How Do I Use SpO2? Choosing a Sensor
GAS EXCHANGE IB TOPIC 6.4 CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM. Terminal bronchiole Nasal cavity. Pharynx Left lung Alveoli.
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1)
 Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN DEPT. OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY MEDICAL STUDENTS FALL 2014/2015 (lecture 1)
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN DEPT. OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY MEDICAL STUDENTS FALL 2014/2015 (lecture 1) Textbook of medical physiology, by A.C. Guyton and John E, Hall, Twelfth Edition,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN DEPT. OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY MEDICAL STUDENTS FALL 2014/2015 (lecture 1) Textbook of medical physiology, by A.C. Guyton and John E, Hall, Twelfth Edition,
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Capillary Action and Blood Components. Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation
 Capillary Action and Blood Components Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation 1 Remember. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only pass through single file Important because they are the
Capillary Action and Blood Components Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation 1 Remember. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only pass through single file Important because they are the
ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
Renal physiology V. Regulation of acid-base balance. Dr Alida Koorts BMS
 Renal physiology V Regulation of acidbase balance Dr Alida Koorts BMS 712 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Hydrogen ions (H + ): Concentration and origin Concentration in arterial blood, resting: [H
Renal physiology V Regulation of acidbase balance Dr Alida Koorts BMS 712 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Hydrogen ions (H + ): Concentration and origin Concentration in arterial blood, resting: [H
Chapter 38: Pulmonary Circulation, Pulmonary Edema, Pleural Fluid UNIT VII. Slides by Robert L. Hester, PhD
 UNIT VII Chapter 38: Pulmonary Circulation, Pulmonary Edema, Pleural Fluid Slides by Robert L. Hester, PhD Objectives Describe the pulmonary circulation Describe the pulmonary blood pressures List the
UNIT VII Chapter 38: Pulmonary Circulation, Pulmonary Edema, Pleural Fluid Slides by Robert L. Hester, PhD Objectives Describe the pulmonary circulation Describe the pulmonary blood pressures List the
Objectives. Blood Buffers. Definitions. Strong/Weak Acids. Fixed (Non-Volatile) Acids. Module H Malley pages
 Blood Buffers Module H Malley pages 120-126 Objectives Define a buffer system and differentiate between the buffering systems present in the body. Given an arterial blood-gas result, determine the degree
Blood Buffers Module H Malley pages 120-126 Objectives Define a buffer system and differentiate between the buffering systems present in the body. Given an arterial blood-gas result, determine the degree
Factors affecting oxygen dissociation curve
 P a g e 1 Factors affecting oxygen dissociation curve As you know, hemoglobin contains 4 heme molecules that bind 4 oxygen molecules (8 atoms). These 4 heme molecules, however, do not bind oxygen all at
P a g e 1 Factors affecting oxygen dissociation curve As you know, hemoglobin contains 4 heme molecules that bind 4 oxygen molecules (8 atoms). These 4 heme molecules, however, do not bind oxygen all at
Acid-base management during hypothermic CPB alpha-stat and ph-stat models of blood gas interpretation
 Acid-base management during hypothermic CPB alpha-stat and ph-stat models of blood gas interpretation Michael Kremke Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
Acid-base management during hypothermic CPB alpha-stat and ph-stat models of blood gas interpretation Michael Kremke Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis
 Arterial Blood Gas Analysis L Lester www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Drawn from radial or femoral arteries. Invasive procedure Caution must be taken with patient on anticoagulants ph: 7.35-7.45
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis L Lester www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Drawn from radial or femoral arteries. Invasive procedure Caution must be taken with patient on anticoagulants ph: 7.35-7.45
individuals who are not in excellent physical condition. Since Under these circumstances some factor, or factors, additional to the
 THE EFFECT OF BREATHING OXYGEN-ENRICHED AIR DURING EXERCISE UPON PULMONARY VENTILATION AND UPON THE LACTIC ACID CONTENT OF BLOOD AND URINE BY A. W. HEWLETT, G. D. BARNEIT KN J. K. LEWIS (From The Department
THE EFFECT OF BREATHING OXYGEN-ENRICHED AIR DURING EXERCISE UPON PULMONARY VENTILATION AND UPON THE LACTIC ACID CONTENT OF BLOOD AND URINE BY A. W. HEWLETT, G. D. BARNEIT KN J. K. LEWIS (From The Department
Red blood cell transfusions Risks, benefits, and surprises
 SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education Presentation Date: 19 th January 2016 www.cure4kids.org Red blood cell transfusions Risks, benefits, and surprises Scott Howard, MD, MSc Professor, Universidad de Memphis,
SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education Presentation Date: 19 th January 2016 www.cure4kids.org Red blood cell transfusions Risks, benefits, and surprises Scott Howard, MD, MSc Professor, Universidad de Memphis,
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Hierarchy of Biological Organization
 Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN TGESBIOLOGY ISC 11
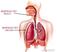 RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN Difference between dry and wet cough Irritation of respiratory tract Due to dust or smoke Accumulation of mucus Due to infections The respiratory tract Tracheal epithelium
RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN Difference between dry and wet cough Irritation of respiratory tract Due to dust or smoke Accumulation of mucus Due to infections The respiratory tract Tracheal epithelium
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES PART 1 BACK TO BASICS SSR OLIVIA ELSWORTH SEPT 2017
 ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES PART 1 BACK TO BASICS SSR OLIVIA ELSWORTH SEPT 2017 WHAT INFORMATION DOES AN ABG GIVE US? ph = measure of hydrogen ion concentration (acidity or alkalinity) PaCO2 = partial pressure
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES PART 1 BACK TO BASICS SSR OLIVIA ELSWORTH SEPT 2017 WHAT INFORMATION DOES AN ABG GIVE US? ph = measure of hydrogen ion concentration (acidity or alkalinity) PaCO2 = partial pressure
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL ACID-BASE BALANCE SECTION SIX Version 1.1 2010 Update PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL OBJECTIVES: ACID-BASE BALANCE The objectives indicate what you should
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL ACID-BASE BALANCE SECTION SIX Version 1.1 2010 Update PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL OBJECTIVES: ACID-BASE BALANCE The objectives indicate what you should
Energy sources in skeletal muscle
 Energy sources in skeletal muscle Pathway Rate Extent ATP/glucose 1. Direct phosphorylation Extremely fast Very limited - 2. Glycolisis Very fast limited 2-3 3. Oxidative phosphorylation Slow Unlimited
Energy sources in skeletal muscle Pathway Rate Extent ATP/glucose 1. Direct phosphorylation Extremely fast Very limited - 2. Glycolisis Very fast limited 2-3 3. Oxidative phosphorylation Slow Unlimited
Omar Sami. Mustafa Khader. Yanal Shafaqouj
 8 Omar Sami Mustafa Khader Yanal Shafaqouj Let us retrieve our discussion about the ventilation-perfusion ratio (V/Q). - When (V/Q) is Zero this means that no ventilation is taking place, V is Zero; bronchial
8 Omar Sami Mustafa Khader Yanal Shafaqouj Let us retrieve our discussion about the ventilation-perfusion ratio (V/Q). - When (V/Q) is Zero this means that no ventilation is taking place, V is Zero; bronchial
