CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
|
|
|
- Jeffry Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE REPORT Radiological and Pathological Correlation in nti-md5 ntibody-positive Interstitial Lung Disease: Rapidly Progressive Perilobular Opacities and Diffuse lveolar Damage Haruka Chino 1, kimasa Sekine 1, Tomohisa aba 1, Tae Iwasawa 2, Koji Okudela 3, Tamiko Takemura 4, Harumi Itoh 5, Shinji Sato 6, Yasuo Suzuki 6 and Takashi Ogura 1 bstract We herein present the first case of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD) with antimelanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MD5) antibody evaluated by surgical lung biopsy (SL). High-resolution CT scan revealed perilobular opacities, which rapidly became thicker and formed consolidation, resulting in remarkable loss of lung volume. Specimens taken from SL revealed membranous organization with alveolar occlusion, dilation of alveolar ducts, and sacs with collapsed alveoli, which are typical features of diffuse alveolar damage (DD). Rapidly progressive perilobular opacities may be characteristic of RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody and DD. Key words: rapidly-progressive interstitial lung disease, clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis, antimelanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 antibody, surgical lung biopsy, radiological and pathological correlation, perilobular opacities (Intern Med 55: , 2016) () Introduction Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (CDM), a type of dermatomyositis with clinical cutaneous features and subtle or no muscle involvement, occasionally develops into rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD) with a prevalence of 5-65% (1). nti-melanoma differentiationassociated protein 5 (MD5) antibody is a myositis-specific antibody that was identified in 2005 in the sera of patients with CDM (2), although anti-md5 antibody is also detected in some ILD patients who have clinical features suggestive of CDM, but do not fully meet the established criteria for CDM (3, 4). nti-md5 antibody is known to be strongly associated with the pathogenesis, disease activity, and an unfavorable prognosis of ILD (5). lthough differentiating between specific types of ILD remains challenging and sometimes necessitates surgical lung biopsy (SL), the aggressive clinical course of anti-md5 antibody-positive RP-ILD forces us to reconsider performing biopsies; therefore, the pathological findings remain unclear. We herein report the first case of RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody evaluatedbysl. Case Report 56-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with a 1- week history of fever and fatigue. ntibiotics had been prescribed for suspected bacterial pneumonia 1 week prior to admission to our hospital. Refractory to antibiotics, his symptoms persisted. On admission, physical examination revealed fever (body temperature, 38.0 ), and his oxygen Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kanagawa Cardiovascular and Respiratory Center, Japan, Department of Radiology, Kanagawa Cardiovascular and Respiratory Center, Japan, Department of Pathology, Yokohama City University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan, Department of Pathology, Japanese Red Cross Medical Center, Japan, iomedical Imaging Research Center, University of Fukui, Japan and Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Tokai University School of Medicine, Japan Received for publication May 20, 2015; ccepted for publication November 29, 2015 Correspondence to Dr. Haruka Chino, hchino-tky@umin.ac.jp 2241
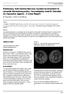
2 Intern Med 55: , 2016 C Figure 1. : Chest radiograph on admission reveals reticular shadows in the lower area of both lungs. : Ground-glass opacities are shown in the subpleural area of both upper lobes on chest CT. C: His chest CT image shows perilobular opacities in the subpleural area (arrowheads) of the lower lobes. saturation by pulse oximetry was 96% on room air; no signs of rash or muscle weakness were observed. Fine crackles were noted in the lower lung fields. Laboratory findings revealed elevated serum levels of Krebs Von den Lungen-6 [685 U/mL (normal, <500 U/mL)] and C-reactive protein [3.31 ng/ml (normal, <0.1 mg/dl)]. ntinuclear antibodies and anti-jo-1 antibody were not detected. Chest radiography revealed reticular shadows in the lower area of both lungs (Fig. 1). High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan showed slight ground-glass opacities in the upper lobes (Fig. 1) and perilobular opacities in the lower lobes (Fig. 1C). pulmonary function test did not suggest a restrictive ventilatory pattern [vital capacity (VC), 3.36 L; % expected VC, 92.6%]. ronchoalveolar lavage with a recovery rate of 66% from the right middle lobe revealed elevated levels of lymphocytes (25%) and neutrophils (4.5%). On day 26, the ground-glass opacities in the upper lobes observed on admission progressed into perilobular opacities on chest CT (Fig. 2). The area of perilobular opacities in the lower lobes observed on admission became consolidation accompanied by a loss of lung volume (Fig. 2). On day 28 after admission, video-assisted thoracoscopic SL was performed from the right S3a and S9. Histopathological findings showed acute and organizing diffuse alveolar damage (DD) without evidence of infection or malignancy (Fig. 3). Some lesions mainly consisted of widespread, poorly aerated alveoli and intra-alveolar membranous organization, which are typical features of organizing DD. Other lesions had hallmark features of acute DD, including hyaline membranes within air spaces and intra-alveolar edema with infiltration by inflammatory cells. On day 38, Krebs Von den Lungen-6 increased to 1,085 U/mL, and VC remarkably decreased from 3.36 L to 2.07 L (% expected VC, 57%). t that time, periungual erythema and erythema grenat appeared on his fingers and toes, and these eruptions evaluated by the dermatologist did not contradict the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis. lthough the creatine kinase transiently elevated just after operation, it decreased without any treatment. CDM-associated ILD was suspected according to the skin manifestations and RPILD without apparent clinical features of myositis, though the patient did not meet the criteria of CDM. The lowgrade fever persisted throughout the hospital stay, and desaturation which persisted after operation rapidly progressed with complaint of dyspnea. On day 40, methyl-prednisolone pulse therapy was initiated; however, respiratory failure progressed. HRCT revealed that the perilobular opacities were spreading extensively, forming consolidation with remarkable loss of lung volume (Fig. 2C and D). On day 42, the patient underwent treatment with tacrolimus (3 mg/day), intravenous immunoglobulin, and polymyxin- direct hemoperfusion for two successive days. Refractory to all treatment, 2242
3 Intern Med 55: , 2016 C D Figure 2. Radiological course. The HRCT scan just before surgical lung biopsy (SL) (, ) and 3 weeks after the SL (C, D). : The area of the ground-glass opacity in the upper lobes on admission became perilobular opacities (arrowheads). : The area of the perilobular opacities in the lower lobes on admission shows thickening and progression into consolidation (arrowheads) accompanied by loss of lung volume. C: HRCT 3 weeks after the SL reveals thickening and increased perilobular opacities (arrowheads). D: The area of consolidation widely spread in the lower lobes (arrowheads). Figure 3. Histological findings. High-power views of right S9. : Membranous organization (arrows) in the alveolar ducts with marked intra-alveolar obliterative fibrosis. (Elastica van Gieson stain, 12 ) : Hyaline membranes, shedding of pneumocytes, and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the alveolar lumina (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, 12 ). the patient died 2 months after the first consultation. fter his death, anti-md5 antibody titers were found to be elevated. Discussion In this report, we describe the first case of RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody evaluated by SL. The evaluation of the specimen taken from the SL revealed acute and organ- 2243
4 Intern Med 55: , 2016 Table. Pathological Findings of CDM ssociated ILD with nti-md5 ntibody. ge / Gender Specimens and pathological findings Treatment Reference Year 49 F TL: cellular NSIP mpsl, immunosuppressive therapy, IVIG M utopsy: DD mpsl, IVCY, Cy, PMX M utopsy: DD with alveolar hemorrhage mpsl, IVCY, plasmapheresis F utopsy: cute and organizing DD mpsl, IVCY, Cy M utopsy: Exudative and organizing DD mpsl, IVCY, Cy round 60M TL: NSIP mpsl, IVCY, PMX, sivelestat utopsy: Organizing DD with alveolar hemorrhag 67 M TL: NSIP Not described utopsy: DD 47 F utopsy:dd with alveolar hemorrhage mpsl, immunosuppressive therapy M SL: acute and organizing DD mpsl, IVCY, Cy, PMX Our patient 2015 DD: diffuse alveolar damage, NSIP: nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, TL: transbronchial lung biopsy, SL: surgical lung biopsy, PSL: predonisolone, IVCY: intravenous cyclophosphamide, Cy: Cyclosporin, IVIG: intravenous high dose immunoglobulin C D Figure 4. Radiopathological correlation in right S3a (, ) and S9 (C, D). : HRCT shows perilobular opacities in right S3a at the time of surgical lung biopsy (SL). The square indicates the biopsy site. : panoramic view of the lung specimen from right S3a shows widespread, poorly aerated alveoli and intra-alveolar organization predominantly involving the subpleural and interlobular septal areas (arrows) (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, 1 ). C: HRCT at the time of the SL shows consolidation with loss of lung volume in the subpleural area in right S9. The square indicates the biopsy site. D: lung specimen from S9 demonstrates diffuse collapsed alveoli and membranous organization with fibrosis. izing DD in the treatment-naïve phase and clarified the radiopathological correlation. The present case provides two important clinical issues. First, it is suggested that DD is the main pathological finding in anti-md5 antibody-positive RP-ILD, considering the previous reports and the present case. This is the first case which confirms the pathological findings of RP- ILD with anti-md5 antibody. To date, there are 8 reported cases evaluating the pathological findings of RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody (Table) (6-13). ll 8 cases met the criteria of CDM and presented fatal clinical courses, despite intensive therapy. n autopsy was performed in 7 cases, with the pathological examination revealing DD, similar to the present case. However, 2 out of 7 autopsied cases were 2244
5 Intern Med 55: , 2016 also evaluated with transbronchial lung biopsy (TL), with histopathological examination showing nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). In the remaining one case evaluated only with TL, the NSIP pattern was also observed. lthough all specimens obtained by TL showed the NSIP pattern, autopsied cases demonstrated the DD pattern. In the present case, the DD pattern was also observed in the SL specimen. We believe that the mechanism underlying the discrepancy in the pathological findings between the TL and autopsy could be explained by the sample size (14). In fact, our specimens showed diverse pathological patterns. Second, perilobular opacity, which rapidly spreads and forms consolidation with remarkable loss of lung volume, is strongly suggestive of RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody and DD. In general, the typical HRCT findings of ILD with surgically proven DD pattern include bilateral symmetrical ground-glass opacity with traction bronchiectasis (15-19). However, these features are considerably different from those observed in our case: perilobular opacities were the main radiological findings, which were reported to be the common features in patients with organizing pneumonia (20). In our case, the perilobular opacities became thicker and formed consolidation during the clinical course (Fig. 1C, 2 and D). The area of the perilobular opacities pathologically corresponded to poorly aerated alveoli and intra-alveolar organization with accentuation of the subpleural and interlobular septal areas, which are the features of DD (Fig. 4 and ). Importantly, perilobular opacities were already present on admission (Fig. 1C), but rapidly spread and formed consolidation (Fig. 2 and D), which pathologically corresponded to membranous organization and fibrosis with the collapse of alveoli (Fig. 4C and D). The present case clearly highlights the pathological change from perilobular opacities to consolidation as mentioned above. Considering the radiological and clinical courses of the case, rapidly progressive perilobular opacities with the loss of lung volume is strongly suggestive of DD. Our results provide an important clinical implication; aggressive treatment should be started immediately without SL in patients with RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody when perilobular opacities are observed. The DD pattern is pathologically common in lung specimens from acute interstitial pneumonia (IP), which is known to be a rapidly progressive disease with a poor prognosis. Earlier intervention with intensive immunosuppressive agents was reported to improve the clinical outcome of IP (21). RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody has pathological findings similar to those of IP. In addition, similar to IP, RP-ILD with anti- MD5 antibody has been reported as a poor prognostic disease with a cumulative 6-month survival rate of approximately 50% (22, 23). Therefore, our pathological findings indicate the necessity of providing early treatment for this disease without SL in patients with RP-ILD with anti- MD5 antibody. In conclusion, we reported the first case of RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody evaluated by SL. Chest physicians should be aware that DD is the main pathological finding and present even in areas of perilobular opacities in RP-ILD with anti-md5 antibody. The present case strongly indicates the necessity to immediately initiate aggressive therapy, including steroid pulse therapy and multiple immunosuppressive drugs, when perilobular opacities are observed in RP-ILD. The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI). References 1. Fathi M, Lundberg IE. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17: , Ghazi E, Sontheimer RD, Werth VP. The importance of including amyopathic dermatomyositis in the idiopathic inflammatory myositis spectrum. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31: , Fischer, ntoniou KM, rown KK, et al; ERS/TS Task Force on Undifferentiated Forms of CTD-ILD. n official European Respiratory Society/merican Thoracic Society research statement: interstitial pneumoniawith autoimmune features. Eur Respir J 46: , Labirua, Lundberg IE. Interstitial lung disease and idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: progress and pitfalls. Curr Opin Rheumatol 22: , Sato S, Hirakata M, Kuwana M, et al. utoantibodies to a 140-kd polypeptide, CDM-140, in Japanese patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. rthritis Rheum 52: , Kumada S, Saito Y, Sogo K, et al. myopathic dermatomyositis positive for anti-140kda polypeptide antibody died from repeated acute flare up of interstitial pneumonia. Hifuka no Rinsyo (Rinsyo Derma) 50: , 2008 (in Japanese). 7. Kazuma N, Keisuke T, Shigeki N, Mio K, Ryo T, Mari N. Four cases of interstitial pneumonia associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis characterized by the anti-cdm-140 antibody. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 49: 30-36, 2011 (in Japanese, bstract in English). 8. Sakurai N, Nagai K, Tsutsumi H, Ichimiya S. nti-cdm-140 antibody-positive juvenile dermatomyositis with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease and cardiac involvement. J Rheumatol 38: , Morita Y, Kuwagata S, Kato N, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT useful for the early detection of rapidly progressive fatal interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis. Intern Med 51: , Hibino M, Nishiguchi S, kazawa K, Hikino K, Oe M. case of rapid progressive interstitial pneumonia with dermatomyositis and atypical cutaneous lesions, characterized by the anti-cdm-140 antibody. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi (nnals of The Japanese Respiratory Society) 1: 27-34, 2012 (in Japanese, bstract in English). 11. Sakai, Kita T, Ichikawa Y, Oribe Y, Miyake M, Kasahara K. case of rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonia with classic dermatomyositis with anti-cdm-140 antibody positive. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi (nnals of The Japanese Respiratory Society) 2: , 2013 (in Japanese, bstract in English). 12. Miyake M, Sakai, Nishijima C, et al. Detection of anti-cdm- 140/MD5 antibodies in patient with classic dermatomyositis developing rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. J Dermatol 41: , Sato K, Morozumi S, Takeuchi Y, Ochiai J, Mabuchi C. case of dermatomyositis with anti-cdm-140 antibody and alveolar hemorrhage. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 54: , 2245
6 Intern Med 55: , (in Japanese, bstract in English). 14. Churg, Muller NL. tlas of interstitial lung disease pathology. In: Pathology with high resolution CT correlations. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Wolters Kuwer, Obadina ET, Torrealba JM, Kanne JP. cute pulmonary injury: high-resolution CT and histopathological spectrum. r J Radiol 86: , Primack SL, Hartman TE, Ikezoe J, kira M, Sakatani M, Müller NL. cute interstitial pneumonia: radiographic and CT findings in nine patients. Radiology 188: , Parambil JG, Myers JL, ubry MC, Ryu JH. Causes and prognosis of diffuse alveolar damage diagnosed on surgicallung biopsy. Chest 132: 50-57, Ikezoe J, Johkoh T, Kohno N, Takeuchi N, Ichikado K, Nakamura H. High-resolution CT findings of lung disease in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Thorac Imaging 11: , kira M, Hara H, Sakatani M. Interstitial lung disease in association with polymyositis-dermatomyositis: long-term follow-up CT evaluation in seven patients. Radiology 210: , Ujita M, Renzoni E, Veeraraghavan S, Wells U, Hansell DM. Organizing pneumonia: perilobular pattern at thin-section CT. Radiology 232: , Suh GY, Kang EH, Chung MP, et al. Early intervention can improve clinical outcome of acute interstitial pneumonia. Chest 129: , Muro Y, Sugiura K, Hoshio K, kiyama M, Tamakoshi K. Epidemiologic study of clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and antimelanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies in central Japan. rthritis Res Ther 13: R214, Tanizawa K, Handa T, Nakashima R, et al. HRCT features of interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis with anti-cdm-140 antibody. Respir Med 105: , The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case Report
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9553-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Successful Treatment of Rapidly Progressive Unclassifiable Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia with Anti-melanoma Differentiation-associated
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9553-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Successful Treatment of Rapidly Progressive Unclassifiable Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia with Anti-melanoma Differentiation-associated
Clinical Features of Anti-MDA5 Antibody-positive Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease without Signs of Dermatomyositis
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1516-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Clinical Features of Anti-MDA5 Antibody-positive Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease without Signs of Dermatomyositis Noriho
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1516-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Clinical Features of Anti-MDA5 Antibody-positive Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease without Signs of Dermatomyositis Noriho
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan
 CASE REPORT Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan Kenichiro Tokunaga 1 and Noboru Hagino 2 Abstract We performed a retrospective
CASE REPORT Dermatomyositis with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Treated with Rituximab: A Report of 3 Cases in Japan Kenichiro Tokunaga 1 and Noboru Hagino 2 Abstract We performed a retrospective
Clinical Differences Between Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis and Classic Dermatomyositis
 CHEST Clinical Differences Between Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis and Classic Dermatomyositis Hiroshi Mukae, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Ishimoto, MD; Noriho Sakamoto,
CHEST Clinical Differences Between Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis and Classic Dermatomyositis Hiroshi Mukae, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Ishimoto, MD; Noriho Sakamoto,
The Onset of Eosinophilic Pneumonia Preceding Anti-synthetase Syndrome
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8955-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Onset of Eosinophilic Pneumonia Preceding Anti-synthetase Syndrome Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Noriaki Sunaga 1,2, Chiharu
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8955-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Onset of Eosinophilic Pneumonia Preceding Anti-synthetase Syndrome Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Noriaki Sunaga 1,2, Chiharu
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates
 Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Naomi Yoshida, Shinjiro Kaieda, Kumi Tomozoe, Morihiro Tajiri, Daisuke Wakasugi, Masaki Okamoto, Masaki Tominaga, Hiroaki Ida and Tomoaki Hoshino
 CASE REPORT An Autopsy Case of Anti-melanoma Differentiation-associated Gene-5 Antibody-positive Clinical Amyopathic Dermatomyositis Complicated by Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Naomi Yoshida,
CASE REPORT An Autopsy Case of Anti-melanoma Differentiation-associated Gene-5 Antibody-positive Clinical Amyopathic Dermatomyositis Complicated by Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Naomi Yoshida,
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
T he diagnostic evaluation of a patient with
 546 REVIEW SERIES Challenges in pulmonary fibrosis? 1: Use of high resolution CT scanning of the lung for the evaluation of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Michael B Gotway, Michelle M
546 REVIEW SERIES Challenges in pulmonary fibrosis? 1: Use of high resolution CT scanning of the lung for the evaluation of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Michael B Gotway, Michelle M
PL-7 and Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies. publication is available at link.sp
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Comparison of Pulmonary Involvement PL-7 and Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies Tomonaga, Masaomi; Sakamoto, Noriho Tomoyuki; Harada, Tatsuhiko; Nakash Shintaro; Horai,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Comparison of Pulmonary Involvement PL-7 and Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies Tomonaga, Masaomi; Sakamoto, Noriho Tomoyuki; Harada, Tatsuhiko; Nakash Shintaro; Horai,
Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment
 Prague, June 2014 Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Prague, June 2014 Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
The crazy-paving pattern: A radiological-pathological correlated and illustrated overview
 The crazy-paving pattern: A radiological-pathological correlated and illustrated overview Poster No.: C-0827 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: W. F. M. De Wever, J. Coolen,
The crazy-paving pattern: A radiological-pathological correlated and illustrated overview Poster No.: C-0827 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: W. F. M. De Wever, J. Coolen,
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
CTD-related Lung Disease
 13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
Key words: CT scanners; interstitial lung diseases; polymyositis-dermatomyositis; x-ray
 Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated With Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis* Serial High-Resolution CT Findings and Functional Correlation Hiroaki Arakawa, MD; Hidehiro Yamada, MD; Yasuyuki Kurihara,
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated With Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis* Serial High-Resolution CT Findings and Functional Correlation Hiroaki Arakawa, MD; Hidehiro Yamada, MD; Yasuyuki Kurihara,
Bronkhorst colloquium Interstitiële longziekten. Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog
 Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
dermatomyositis: report of a case.
 Living-donor lobar lung transplanta Titleinterstitial pneumonia associated w dermatomyositis: report of a case., Tsuyoshi; Bando, Toru; Fujin Author(s) Fengshi; Sasano, Hajime; Yukawa, Na Tsuneyo; Date,
Living-donor lobar lung transplanta Titleinterstitial pneumonia associated w dermatomyositis: report of a case., Tsuyoshi; Bando, Toru; Fujin Author(s) Fengshi; Sasano, Hajime; Yukawa, Na Tsuneyo; Date,
HRCT in Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis. Where are the lymphatics? Anatomic distribution
 Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Correspondence should be addressed to Yasuhiro Shimojima;
 Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 5386797, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5386797 Case Report Effective Administration of Rituximab in Anti-MDA5 Antibody Positive Dermatomyositis
Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 5386797, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5386797 Case Report Effective Administration of Rituximab in Anti-MDA5 Antibody Positive Dermatomyositis
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Case Report Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Keisuke Murata 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Norimitsu Kasahara 1, Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Satoshi Nunomura 2, Nozomi
Case Report Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Keisuke Murata 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Norimitsu Kasahara 1, Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Satoshi Nunomura 2, Nozomi
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Spectrum of High-Resolution CT and Pathologic Findings
 CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis
 Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 1005 1012 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00038806 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis T. Suda*, T. Fujisawa*, N. Enomoto*,
Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 1005 1012 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00038806 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis T. Suda*, T. Fujisawa*, N. Enomoto*,
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of pulmonary diseases
 The 1578 th Chest Conference/ 3 rd Biennial Clinical- Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Radiologic-pathologic correlation of pulmonary diseases Harumi Itoh, M.D. University of Fukui, Japan Centriacinar
The 1578 th Chest Conference/ 3 rd Biennial Clinical- Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Radiologic-pathologic correlation of pulmonary diseases Harumi Itoh, M.D. University of Fukui, Japan Centriacinar
Case 1 : Question. 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random
 Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Rapidly Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Following the Onset of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Sjögren s Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report
 CASE REPORT Rapidly Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Following the Onset of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Sjögren s Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report Yusuke Tomita 1,2, Shunsuke Mori 3, Nobuyuki Arima 4,
CASE REPORT Rapidly Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Following the Onset of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Sjögren s Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report Yusuke Tomita 1,2, Shunsuke Mori 3, Nobuyuki Arima 4,
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Initial presentation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as an acute exacerbation
 Respiratory Medicine CME (2008) 1, 43 47 respiratory MEDICINE CME CASE REPORT Initial presentation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as an acute exacerbation Krishna M. Sundar a,b,, Dixie L. Harris a a
Respiratory Medicine CME (2008) 1, 43 47 respiratory MEDICINE CME CASE REPORT Initial presentation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as an acute exacerbation Krishna M. Sundar a,b,, Dixie L. Harris a a
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte
 IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Clinical significance of serum surfactant protein D (SP-D) in patients with polymyositisudermatomyositis: correlation with interstitial lung disease
 Rheumatology 2002;41:1268 1272 Clinical significance of serum surfactant protein D (SP-D) in patients with polymyositisudermatomyositis: correlation with interstitial lung disease H. Ihn, Y. Asano, M.
Rheumatology 2002;41:1268 1272 Clinical significance of serum surfactant protein D (SP-D) in patients with polymyositisudermatomyositis: correlation with interstitial lung disease H. Ihn, Y. Asano, M.
The radiological differential diagnosis of the UIP pattern
 5th International Conference on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Modena, 2015, June 12th The radiological differential diagnosis of the UIP pattern Simon Walsh King s College Hospital Foundation Trust London,
5th International Conference on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Modena, 2015, June 12th The radiological differential diagnosis of the UIP pattern Simon Walsh King s College Hospital Foundation Trust London,
9/15/11. Dr. Vivien Hsu Director, UMDNJ Scleroderma Program New Brunswick, NJ September Scleroderma. Hard skin
 Dr. Vivien Hsu Director, UMDNJ Scleroderma Program New Brunswick, NJ September 2011 Scleroderma Hard skin 1 No diagnostic test for scleroderma Pathogenesis is unknown prominent features of disease reflect
Dr. Vivien Hsu Director, UMDNJ Scleroderma Program New Brunswick, NJ September 2011 Scleroderma Hard skin 1 No diagnostic test for scleroderma Pathogenesis is unknown prominent features of disease reflect
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Imaging: how to recognise idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 REVIEW IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS Imaging: how to recognise idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Anand Devaraj Affiliations: Dept of Radiology, St George s Hospital, London, UK. Correspondence: Anand Devaraj,
REVIEW IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS Imaging: how to recognise idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Anand Devaraj Affiliations: Dept of Radiology, St George s Hospital, London, UK. Correspondence: Anand Devaraj,
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Evidence Review: Title. Month/ Year. Evidence Review:
 Evidence Review: Title Month/ Year Evidence Review: Rituximab for connective tissue disease associated interstitial lung disease October 2014 Standard Operating Procedure: NHS England Evidence Review:
Evidence Review: Title Month/ Year Evidence Review: Rituximab for connective tissue disease associated interstitial lung disease October 2014 Standard Operating Procedure: NHS England Evidence Review:
Case 1: Question. 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule
 HRCT WORK SHOP Case 1 Case 1: Question 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule Case 1: Question 1.2 What is the diagnosis? 1. Hypersensitivity
HRCT WORK SHOP Case 1 Case 1: Question 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule Case 1: Question 1.2 What is the diagnosis? 1. Hypersensitivity
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Acute Exacerbation of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia After Resection of Lung Cancer
 Acute Exacerbation of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia After Resection of Lung Cancer Hiroaki Sugiura, MD, Atsuya Takeda, MD, PhD, Toshiko Hoshi, MD, PhD, Yoshinori Kawabata, MD, Koichi Sayama, MD, PhD, Masahiro
Acute Exacerbation of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia After Resection of Lung Cancer Hiroaki Sugiura, MD, Atsuya Takeda, MD, PhD, Toshiko Hoshi, MD, PhD, Yoshinori Kawabata, MD, Koichi Sayama, MD, PhD, Masahiro
An Autopsy Case of Lepidic Pulmonary Metastasis. from cholangiocarcinoma.
 CSE REPORT n utopsy Case of Lepidic Pulmonary Metastasis from Cholangiocarcinoma Yohsuke Nagayoshi 1,2, Kazuko Yamamoto 1,2, Satoru Hashimoto 1, Keiko Hisatomi 1, Seiji oi 1, Seiji Nagashima 1, Hirokazu
CSE REPORT n utopsy Case of Lepidic Pulmonary Metastasis from Cholangiocarcinoma Yohsuke Nagayoshi 1,2, Kazuko Yamamoto 1,2, Satoru Hashimoto 1, Keiko Hisatomi 1, Seiji oi 1, Seiji Nagashima 1, Hirokazu
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy
 Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
Overview of Diagnostic Autoantibodies in Inflammatory Myopathy Minoru Satoh, M.D., Ph.D. Research Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology University of Florida
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case Report
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1142-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Analysis of Surgical Lung Biopsy and Explanted Lung Specimens Sheds Light on the Pathological Progression of Chronic Bird-related
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1142-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Analysis of Surgical Lung Biopsy and Explanted Lung Specimens Sheds Light on the Pathological Progression of Chronic Bird-related
Department of Anaesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seonam University College of Medicine, Namwon, Korea
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.473 Rapid Progression of Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification and Alveolar Hemorrhage in a Patient with Chronic Renal Failure and Primary
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.473 Rapid Progression of Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification and Alveolar Hemorrhage in a Patient with Chronic Renal Failure and Primary
International consensus statement on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
Diffuse Interstitial Lung Diseases: Is There Really Anything New?
 : Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
: Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after smoking cessation
 Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 453 461 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015506 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after
Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 453 461 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015506 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs) are a group of
 SYMPOSIA C. Isabela S. Silva, MD, PhD and Nestor L. Müller, MD, PhD Abstract: The idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs) are a group of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases of unknown etiology characterized
SYMPOSIA C. Isabela S. Silva, MD, PhD and Nestor L. Müller, MD, PhD Abstract: The idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs) are a group of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases of unknown etiology characterized
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia: comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis
 Original Article Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia: comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis Xia Li 1, Chang Chen 2, Jinfu Xu 1, Jinming Liu 1, Xianghua
Original Article Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia: comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis Xia Li 1, Chang Chen 2, Jinfu Xu 1, Jinming Liu 1, Xianghua
Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases
 CASE REPORT Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases Nobuhiko Nagata 1, Kentaro Watanabe 2, Michihiro Yoshimi 3, Hiroshi Okabayashi 4, Katsuo Sueishi 5, Kentaro
CASE REPORT Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases Nobuhiko Nagata 1, Kentaro Watanabe 2, Michihiro Yoshimi 3, Hiroshi Okabayashi 4, Katsuo Sueishi 5, Kentaro
Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation
 http://www.jhltonline.org FEATURED ARTICLES Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation Masaaki Sato, MD, PhD, a,b David M. Hwang, MD, PhD, a Thomas K. Waddell, MD,
http://www.jhltonline.org FEATURED ARTICLES Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation Masaaki Sato, MD, PhD, a,b David M. Hwang, MD, PhD, a Thomas K. Waddell, MD,
Original Article. Keywords: Systemic sclerosis (SSc); mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD); interstitial lung disease (ILD); biomarker
 Original Article Serum KL-6 and surfactant protein-d as monitoring and predictive markers of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease Hideaki Yamakawa
Original Article Serum KL-6 and surfactant protein-d as monitoring and predictive markers of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease Hideaki Yamakawa
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases. Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Influence of Smoking in Interstitial Pneumonia Presenting with a Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of Smoking in Interstitial Pneumonia Presenting with a Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern Tetsuro Sawata, Masashi Bando, Masayuki Nakayama, Naoko Mato, Hideaki Yamasawa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of Smoking in Interstitial Pneumonia Presenting with a Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern Tetsuro Sawata, Masashi Bando, Masayuki Nakayama, Naoko Mato, Hideaki Yamasawa
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than
 TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker. Michael B. Gotway, MD
 August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ USA Clinical History: A 55 year old woman presented
August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ USA Clinical History: A 55 year old woman presented
Fatal Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Associated with Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: An Autopsy Case Report
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1144-18 Intern Med 57: 3619-3624, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Fatal Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Associated with Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: An Autopsy
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1144-18 Intern Med 57: 3619-3624, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Fatal Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Associated with Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: An Autopsy
myopathy and interstitial lung dise
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case of primary Sjögren's syndrom myopathy and interstitial lung dise Koga, Tomohiro; Kouhisa, Yukiko; Na Akinari; Motomura, Masakatsu; Kawak
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case of primary Sjögren's syndrom myopathy and interstitial lung dise Koga, Tomohiro; Kouhisa, Yukiko; Na Akinari; Motomura, Masakatsu; Kawak
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest
 Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
2009 H1N1 Influenza Infection: Spectrum Of Chest CT Findings, With Radiologic- Pathologic Correlation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 2009 H1N1 Influenza Infection: Spectrum Of Chest CT Findings, With Radiologic- Pathologic Correlation A Nachiappan, E Weihe, B Akkanti, V
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 2009 H1N1 Influenza Infection: Spectrum Of Chest CT Findings, With Radiologic- Pathologic Correlation A Nachiappan, E Weihe, B Akkanti, V
Interstitial lung disease in clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis with and without anti-mda-5 antibody: to lump or split?
 Ikeda et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2015) 15:159 DOI 10.1186/s12890-015-0154-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Interstitial lung disease in clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis with and without anti-mda-5
Ikeda et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2015) 15:159 DOI 10.1186/s12890-015-0154-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Interstitial lung disease in clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis with and without anti-mda-5
Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions
 Review Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Clinical Radiology and Case Reports Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions D souza M *, Rajiah P, Khan A and Irion K Department
Review Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Clinical Radiology and Case Reports Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions D souza M *, Rajiah P, Khan A and Irion K Department
Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis
 19 th Congress of APSR PG of Lung Cancer (ESAP): Update of Lung Cancer Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis Kazuma Kishi, M.D. Department of Respiratory Medicine,
19 th Congress of APSR PG of Lung Cancer (ESAP): Update of Lung Cancer Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis Kazuma Kishi, M.D. Department of Respiratory Medicine,
Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9338-17 Intern Med 57: 1281-1285, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient Yuki Hosono, Nobuhiko Sawa,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9338-17 Intern Med 57: 1281-1285, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient Yuki Hosono, Nobuhiko Sawa,
IPF - Inquadramento clinico
 IPF - Inquadramento clinico Sergio Harari Unità Operativa di Pneumologia UTIR Servizio di Fisiopat. Resp. e Emodinamica Polmonare Ospedale S. Giuseppe, Milano Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal
IPF - Inquadramento clinico Sergio Harari Unità Operativa di Pneumologia UTIR Servizio di Fisiopat. Resp. e Emodinamica Polmonare Ospedale S. Giuseppe, Milano Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal
USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS
 USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS Brestas P., Vergadis V., Emmanouil E., Malagari K. 2 nd Dept of Radiology, University of Athens, Greece ABSTRACT
USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS Brestas P., Vergadis V., Emmanouil E., Malagari K. 2 nd Dept of Radiology, University of Athens, Greece ABSTRACT
Three Cases of Non-specific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated with Primary Lung Cancer
 CASE REPORT Three Cases of Non-specific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated with Primary Lung Cancer Toshio SATO, Ichiro YAMADORI, Jiro FUJITA*, Noboru HAMADA, Toshiro YONEI, Shuji BANDOH*, Yuji OHTSUKI**
CASE REPORT Three Cases of Non-specific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated with Primary Lung Cancer Toshio SATO, Ichiro YAMADORI, Jiro FUJITA*, Noboru HAMADA, Toshiro YONEI, Shuji BANDOH*, Yuji OHTSUKI**
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (Esbriet /pirfenidone, Ofev /nintedanib)
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (Esbriet /pirfenidone, Ofev /nintedanib)
Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 1
 Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 1 Kee Hyuk Yang, M.D., Yo Won Choi, M.D., Seok Chol Jeon, M.D., Choong Ki Park, M.D., Kyung in Joo, M.D., Chang Kok Hahm, M.D., Seung Ro Lee, M.D.
Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 1 Kee Hyuk Yang, M.D., Yo Won Choi, M.D., Seok Chol Jeon, M.D., Choong Ki Park, M.D., Kyung in Joo, M.D., Chang Kok Hahm, M.D., Seung Ro Lee, M.D.
Overview of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Therapy
 Overview of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Therapy Jeff Swigris, DO, MS Director, ILD Program National Jewish Health Disclosures Speaker - Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech Objectives Describe
Overview of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Therapy Jeff Swigris, DO, MS Director, ILD Program National Jewish Health Disclosures Speaker - Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech Objectives Describe
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014
 Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Comparison of clinical course of polymyositis and dermatomyositis :a follow-up study in Tokushima University
 9 ORIGINAL Comparison of clinical course of polymyositis and dermatomyositis :a follow-up study in Tokushima University Hospital Kenji Tani, Reiko Tomioka,KeikoSato, Chiyuki Furukawa, Takeshi Nakajima,
9 ORIGINAL Comparison of clinical course of polymyositis and dermatomyositis :a follow-up study in Tokushima University Hospital Kenji Tani, Reiko Tomioka,KeikoSato, Chiyuki Furukawa, Takeshi Nakajima,
Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
Bilateral Diffuse Radiation Pneumonitis Caused by Unilateral Thoracic Irradiation: A Case Report
 J Lung Cancer 2012;11(2):97-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2012.11.2.97 Bilateral Diffuse Radiation Pneumonitis Caused by Unilateral Thoracic Irradiation: A Case Report Radiation therapy is one of the
J Lung Cancer 2012;11(2):97-101 http://dx.doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2012.11.2.97 Bilateral Diffuse Radiation Pneumonitis Caused by Unilateral Thoracic Irradiation: A Case Report Radiation therapy is one of the
Two Series of Familial Cases With Unclassified Interstitial Pneumonia With Fibrosis
 Case Report Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012 July;4(4):240-244. http://dx.doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.4.240 pissn 2092-7355 eissn 2092-7363 Two Series of Familial Cases With Unclassified Interstitial Pneumonia
Case Report Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012 July;4(4):240-244. http://dx.doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.4.240 pissn 2092-7355 eissn 2092-7363 Two Series of Familial Cases With Unclassified Interstitial Pneumonia
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases
 Outline A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Outline A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II
 Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I. December 5, 2012
 SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
Myositis and Your Lungs
 Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
Myositis and Your Lungs 2013 TMA Annual Patient Meeting Louisville, Kentucky Chester V. Oddis, MD University of Pittsburgh Director, Myositis Center Myositis Heterogeneous group of autoimmune syndromes
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Thin-Section CT Findings in 32 Immunocompromised Patients with Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia Who Do Not Have AIDS
 Tomás Franquet 1,2 Kyung S. Lee 3 Nestor L. Müller 1 Received January 27, 2003; accepted after revision April 21, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Vancouver Hospital and Health Sciences Center and University
Tomás Franquet 1,2 Kyung S. Lee 3 Nestor L. Müller 1 Received January 27, 2003; accepted after revision April 21, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Vancouver Hospital and Health Sciences Center and University
Subpleural Honeycombing on High Resolution Computed Tomography is Risk Factor for Fatal Pneumonitis
 Subpleural Honeycombing on High Resolution Computed Tomography is Risk Factor for Fatal Pneumonitis Hiroyuki Ito, MD, Haruhiko Nakayama, MD, Masahiro Tsuboi, MD, MD, Yoichi Kameda, MD, Tomoyuki Yokose,
Subpleural Honeycombing on High Resolution Computed Tomography is Risk Factor for Fatal Pneumonitis Hiroyuki Ito, MD, Haruhiko Nakayama, MD, Masahiro Tsuboi, MD, MD, Yoichi Kameda, MD, Tomoyuki Yokose,
