Review Article. Current Concepts CONTINUOUS HEMOFILTRATION IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
|
|
|
- Corey Evans
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Current Concepts CONTINUOUS HEMOFILTRATION IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE RENAL FAILURE L.G. FORNI, M.B., PH.D., AND P.J. HILTON, M.D. ACUTE renal failure that requires renal therapy is a relatively common condition, with an annual incidence of at least 30 cases per 1 million population. 1 Historically, the of renal function in acute renal failure has involved techniques also employed in the treatment of end-stage chronic renal failure intermittent hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. 2,3 was first described in 1977 as a means of removing extracellular from s with edema refractory to diuretic agents. 4 Continuous hemofiltration, combined with the administration of an appropriate, is now recognized as a form of renal- therapy in acute renal failure. The technique is widely used in intensive care units for the treatment of acute renal failure, although intermittent hemodialysis continues to be used for s with acute renal failure but without multiorgan failure. BASIC PRINCIPLES has many superficial similarities to hemodialysis. In both techniques, access to the circulation is required and blood passes through an extracorporeal circuit that includes either a dialyzer or a hemofilter. However, the mechanisms by which the composition of the blood is modified differ markedly (Fig. 1). During dialysis (Fig. 1, upper panel), blood flows along one side of a semipermeable membrane as a solution of crystalloids is pumped along the other side of the membrane against the direction of the blood flow. Small molecules diffuse across the membrane from regions of greater concentration to regions of lesser concentration, and the composition of the dialysis is designed to produce as near From St. Thomas Hospital, London SE1 7EH, United Kingdom, where reprint requests should be addressed to Dr. Hilton. 1997, Massachusetts Medical Society. normalization of the plasma as possible. Thus, the sodium concentration of the dialysis is physiologic, but the potassium concentration is lower than that of normal plasma in order to establish a gradient from plasma to the that promotes the removal of potassium ions from the s blood. The concentrations of substances that are to be removed completely (such as urea, creatinine, and phosphate) are zero in the dialysis. The removal of salt and water is achieved by the creation of a transmembrane pressure gradient (with lower pressure in the dialysis- compartment). According to the laws of diffusion, the larger the molecule, the slower will be its rate of transfer across the membrane. A small molecule, such as urea (60 daltons), is cleared efficiently, and a larger molecule, such as creatinine (113 daltons), less well. ions have such low rates of clearance that hyperphosphatemia is always a problem for s on intermittent dialysis. Dialysis has no similarity to the normal physiologic processes of the kidney, but it is effective, and many s have lived for decades entirely dependent on intermittent hemodialysis. 5 (Fig. 1, lower panel) works in a different manner. 6,7 In the simplest form of the procedure, blood under pressure passes down one side of a highly permeable membrane allowing both water and substances up to a molecular weight of about 20,000 to pass across the membrane by convective flow, as in glomerular filtration. During hemofiltration, in contrast to hemodialysis, urea, creatinine, and phosphate are cleared at similar rates, and profound hypophosphatemia may develop unless the s phosphate intake is supplemented. Larger molecules such as heparin, insulin, myoglobin, and vancomycin, which are cleared from the blood in only negligible quantities in a dialyzer, are cleared efficiently by the hemofilter. In the kidney, the glomerular filtrate is selectively reabsorbed by the renal tubules, a process too complex to be artificially reproduced with current technology. Instead, during hemofiltration, the filtrate is discarded and the receives infusions (usually through the distal part of the hemofiltration circuit) of a solution in which the major crystalloid components of the plasma are at physiologic levels (the typical composition of hemofiltration is shown in Table 1). If there is no need for the removal of from the, the rate at which the is administered is matched exactly with the rate of production of hemofiltrate. Usually, however, there is a need to remove, because of either overload or the clinical need to adminis- Volume 336 Number
2 The New England Journal of Medicine Hemodialysis To From Dialysis Dialysate Replacement Na + H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O Na + To H 2 O H 2 O Na + Na + H 2 O H 2 O From Hemofiltrate Figure 1. Hemodialysis and. The arrows that cross the membrane indicate the predominant direction of movement of each solute through the membrane; the relative size of the arrows indicates the net amounts of the solute transferred. Other arrows indicate the direction of flow. ter s to a with oliguria. A net loss of extracellular is achieved by replacing less through infusion than is removed by hemofiltration. It is important to recognize that certain physical constraints affect hemofiltration as they do glomerular filtration. In both processes, the plasma component of the blood flowing through the circuit represents the sole source of the salt and water that are the principal constituents of the filtrate. therefore inevitably leads to an increase in the concentration of both red cells and plasma protein in the blood of the extracorporeal circuit 8 ; there is thus a tendency to produce viscous blood of high hematocrit and high colloid oncotic pressure at the distal end of the hemofilter. It is therefore generally unwise to induce a filtration rate that is more than 1304 May 1, 1997
3 TABLE 1. TYPICAL COMPOSITION OF HEMOFILTRATION REPLACEMENT FLUID.* COMPONENT VALUE mmol/ liter Sodium 140 Potassium 0 Calcium 1.6 Magnesium 0.75 Chloride 101 Lactate 45 Glucose 11 *The values shown are for Gambro Hemofiltrasol 22. Potassium chloride is added to the solution immediately before use in concentrations of up to 4 mmol per liter, depending on the serum potassium concentration. To convert the value for calcium to milligrams per deciliter, divide by 0.25; to convert the value for magnesium to milliequivalents per liter, divide by 0.5; and to convert the value for glucose to milligrams per deciliter, divide by percent of the blood-flow rate. Keeping the ratio between the two rates under 25 percent minimizes the unwanted effect. An alternative approach, known as predilution, circumvents the problem by administering the proximal to the hemofilter. This rarely used procedure reduces the efficiency and increases the cost of hemofiltration because a proportion of the generated filtrate is actually. As hemofiltration became an increasingly popular form of renal- therapy in the intensive care unit, a number of variants were developed (Table 2). These are outlined below. CONTINUOUS ARTERIOVENOUS HEMOFILTRATION Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration is the original and simplest form of the technique. 4,9 The femoral artery and vein are cannulated, and blood passes through the hemofilter under the influence of arterial pressure alone (Fig. 2). Because the pressure in the system exceeds the atmospheric pressure, there is no possibility of air being drawn into the circuit and no precautions need to be taken to prevent this from occurring. However, the simplicity of the system is offset by several disadvantages. First, a disconnection or leak in the circuit can result in rapid loss of blood. Second, the efficiency of hemofiltration depends on the arterial pressure, which is frequently low or unstable in s with acute renal failure. The effectiveness of the system is therefore determined mainly by factors outside the direct control of the physician. Low blood flow is associated with frequent clotting of the extracorporeal circuit, and the prolonged arterial cannulation typically used carries a risk of complications at the puncture site. Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration often results in clearance rates as low as 10 to 15 ml per minute even in normotensive s; clearance rates may drop to below 10 ml per minute if a has marked hypotension. CONTINUOUS ARTERIOVENOUS HEMODIALYSIS WITH FILTRATION The recognition of the inadequacy of continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration when used alone led to the addition of a dialysis circuit to the hemofilter. 10,11 TABLE 2. TYPES OF RENAL-REPLACEMENT THERAPY FOR ACUTE RENAL FAILURE. COAGULANT THERAPY RISK OF HEMORRHAGE RISK OF INFECTION ANTI- EXTRA- CELLULAR-FLUID VOLUME CONTROL USE IN HYPO- TENSION TYPE COMPLEXITY EFFICIENCY COST Peritoneal dialysis Low Moderate Moderate No Low High Moderate Yes Intermittent hemodialysis Moderate High Low Yes Moderate Low Intermittent No Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration Continuous arteriovenous hemodialysis with filtration Continuous venovenous hemofiltration Continuous venovenous hemodialysis with filtration Moderate Low and variable Moderate Yes Moderate Low Good No High Moderate High Yes Moderate Low Good Variable and variable Moderate High Moderate Yes Moderate Low Good Yes High High High Yes Moderate Low Good Yes Volume 336 Number
4 The New England Journal of Medicine Continuous Venovenous Hemodialysis with Filtration Continuous Venovenous Dialysis Bubble-trap air detector Occlusive pump Occlusive pump Hemofiltrate and dialysate Hemofiltrate Continuous Arteriovenous Hemodialysis with Filtration Continuous Arteriovenous Dialysis Hemofiltrate and dialysate Hemofiltrate Figure 2. The Mechanisms of and Hemodialysis with Filtration. No attempt has been made in this diagram to represent the automatic control of the rates of filtration and infusion of May 1, 1997
5 In such a system, although a minor fraction of the circulating blood is cleared by the filter, the remainder undergoes dialysis, which results in an important improvement in the clearance of at least the smaller molecules that accumulate in renal failure. The inefficiency of arteriovenous hemofiltration alone is thus overcome at the price of a considerable increase in the complexity of the equipment, and the other disadvantages of continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration are not eliminated. CONTINUOUS VENOVENOUS HEMOFILTRATION The incorporation of an occlusive pump into the filtration circuit, together with the use of a femoral, subclavian, or internal jugular vein as the source of blood for the extracorporeal circuit, allows for control of the blood flow and the filtration rate without the limitations imposed by relying on the arterial pressure to move the blood. 7,12,13 The use of a pump also averts the problems associated with cannulation of the femoral artery. This type of blood circuit, called venovenous hemofiltration, also incorporates safety devices to detect low inflow pressure and the presence of air in the circuit. Filtration rates in excess of 100 ml per minute can be achieved, though such rates are rarely required in the treatment of acute renal failure. The clear advantages of this system over simple arteriovenous hemofiltration have led to its widespread use in intensive care units. CONTINUOUS VENOVENOUS HEMODIALYSIS WITH FILTRATION Yet another system adds hemodialysis to venovenous hemofiltration in the same way that dialysis was added to continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration. 14,15 There is no doubt that higher clearance rates of small solutes are achieved at any given blood flow by this modification, but it is questionable whether there are any advantages over continuous venovenous hemofiltration alone unless one wishes to shorten treatment and make it intermittent. If a continuous mode of treatment is appropriate, more than adequate clearance rates are possible with the simpler and cheaper system of continuous venovenous hemofiltration alone. With more than 6000 days of treatment in our unit, we have never had a situation in which continuous venovenous hemofiltration alone was incapable of achieving metabolic control. PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF CONTINUOUS VENOVENOUS HEMOFILTRATION In continuous venovenous hemofiltration, vascular access is achieved by the insertion of a doublelumen catheter into a great vein. The blood pump is typically set to deliver approximately 125 ml per minute, and the most common hemofiltration rate is 25 ml per minute; this rate is controlled by an occlusive pump on the hemofiltrate line. In automated systems, the hemofiltrate is collected in bags that are suspended on a strain gauge and weighed continuously. The bags of, suspended on a second strain gauge, are similarly weighed. A servomechanism drives the - pump at a rate computed either to balance the inflow and loss of or to maintain a predetermined rate of loss. Anticoagulation of the extracorporeal circuit is almost always undertaken with a heparin infusion (200 to 1600 units per hour) through the inflow side of the circuit. Although heparin-induced thrombocytopenia can develop in s who receive continuous heparin therapy, this syndrome is not a common problem. 16 If thrombocytopenia should develop or if there is excessive bleeding for any reason, it is sometimes possible to continue treatment and either withhold anticoagulation or substitute epoprostenol (prostacyclin) for heparin. Care must be taken if epoprostenol is used in critically ill s, because of the drug s systemic effects. 17,18 Epoprostenol is also much more expensive than heparin (approximately $176 per 24-hour course of therapy, as compared with $3 for heparin). removes virtually all ions from the plasma, including calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate (Fig. 1); these must be replaced appropriately. Since it is impossible to manufacture a stable solution that contains the appropriate concentrations of these ions, a variety of anions have been substituted for bicarbonate in. The anion most commonly used in is lactate, because it is assumed that lactate will be converted to bicarbonate. This assumption is valid for most s, although not for those with lactic acidosis. In s with lactic acidosis, the exogenous lactate load from the, coupled with the continued removal of bicarbonate ions by the hemofilter, merely increases the plasma lactate concentration and reduces the arterial ph. Under such conditions, use of the hemofilter actually worsens the s acidosis. If hemofiltration is undertaken in these circumstances, bicarbonate ions must be provided directly. In our unit, this is done by infusing a mixture of isotonic sodium chloride and isotonic sodium bicarbonate in a ratio determined by the severity of the acidosis. 19,20 Because of the incompatibility of calcium salts with such a - mixture, calcium salts are infused together with magnesium salts at a separate part of the circuit. HEMOFILTRATION FOR ACUTE RENAL FAILURE It is probably the continuous nature of hemofiltration, more than any other feature, that makes the technique so beneficial in the treatment of s Volume 336 Number
6 The New England Journal of Medicine with acute renal failure in intensive care units (where most such s have multiorgan failure) Such s frequently receive more than 2 liters of a day, much of which represents nutrition. In s with a robust circulation, intermittent hemodialysis can correct biochemical abnormalities and remove, in a short time, the extracellular accumulated over 24 hours, although there is usually a degree of hypovolemia and hypokalemia associated with the process. In the more common situation of a with acute renal failure and compromised circulation, hemodialysis may lead to serious hypotension or cardiac arrhythmia. This fact may limit possible treatment; restriction of the s intake may be attempted, usually with a concomitant restriction of nutrition. With continuous hemofiltration, however, almost any quantity of can easily be removed over a 24-hour period. In computing the energy needs of a with acute renal failure who is receiving nutritional support, due allowance should be made for the calorific value of the lactate content of regular hemofiltration. At a filtration rate of 25 ml per minute, the net contribution of lactate to nutrition is approximately 500 kcal per day. It is frequently pointed out that mortality due to acute renal failure remains high despite recent improvements in treatment. 24 It may therefore be questioned whether continuous hemofiltration, despite its advantages, has been of any real benefit. In our experience, there has been a substantial improvement in survival coincident with the use of continuous hemofiltration among s with similar characteristics. 25,26 The question whether such an improvement would have resulted from other advances in intensive care had s continued to be treated by intermittent hemodialysis alone has not been answered unambiguously. No large-scale randomized trial comparing continuous hemofiltration and intermittent hemodialysis has been reported, although data from several small series suggest that hemofiltration may be preferable. 27,28 COSTS OF HEMOFILTRATION For treatment lasting an average of 9.3 days, with of the extracorporeal circuit every 2.5 days, the cost of consumables (hemofilter, blood and lines, and ) for each episode of acute renal failure in our unit is $1,614; the cost of ($880) is the most important single item. The equivalent cost for treatment with intermittent hemodialysis is $672, assuming 10 daily treatments. Labor costs are less easy to calculate because they depend to a large extent on local practice. In our intensive care unit, the supervision of hemofiltration is incorporated into the duties of the nurse responsible for the ; the treatment entails no additional labor costs. Hemodialysis with filtration, if undertaken so as to achieve plasma values for urea or creatinine similar to those achieved with hemofiltration alone, increases costs markedly because the combination process has a smaller effect per unit of consumed. CONCLUSIONS Continuous hemofiltration is a highly effective system for the of renal function in s with acute renal failure. The control of biochemical characteristics is constant, and the need never have any unwanted alterations of extracellular- volume, even if large quantities of are administered (for nutritional or other purposes). The use of hemofiltration has coincided with a substantial reduction in mortality. does not cure acute renal failure, but it is a safe and efficient way of replacing renal function while the kidneys recover from disease or injury. REFERENCES 1. Wing AJ, Broyer M, Brunner FP, et al. Combined report on regular dialysis and transplantation in Europe, XIII, Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc 1983;20: Brady HR, Singer GG. Acute renal failure. Lancet 1995;346: Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med 1996;334: Kramer P, Wigger W, Rieger J, Matthaei D, Scheler F. Arteriovenous haemofiltration: a new and simple method for treatment of over-hydrated s resistant to diuretics. Klin Wochenschr 1977;55: Olbricht CJ, Frei U, Koch KM. Haemodialysis, complications during haemodialysis, and adequacy of haemodialysis. In: Cameron S, Davison AM, Grünfeld J-P, Kerr D, Ritz E, eds. Oxford textbook of clinical nephrology. Vol. 2. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1992: Sieberth H-G. Continuous renal therapy in acute renal failure (haemofiltration and dialysis). In: Cameron S, Davison AM, Grünfeld J-P, Kerr D, Ritz E, eds. Oxford textbook of clinical nephrology. Vol. 2. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1992: Barton IK, Hilton PJ. Veno-venous haemofiltration in the intensive care unit. Clin Intensive Care 1993;4: Ronco C. Continuous renal therapies for the treatment of acute renal failure in intensive care s. Clin Nephrol 1993;40: Lauer A, Saccaggi A, Ronco C, Belledonne M, Glabman S, Bosch JP. Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in the critically ill : clinical use and operational characteristics. Ann Intern Med 1983;99: Geronemus R, Schneider N. Continuous arteriovenous hemodialysis: a new modality for treatment of acute renal failure. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 1984;30: van Geelen JA, Vincent HH, Schalekamp MADH. Continuous arteriovenous haemofiltration and haemodiafiltration in acute renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1988;3: Wendon J, Smithies M, Sheppard M, Bullen K, Tinker J, Bihari D. Continuous high volume venous-venous haemofiltration in acute renal failure. Intensive Care Med 1989;15: Macias WL, Mueller BA, Scarim SK, Robinson M, Rudy DW. Continuous venovenous hemofiltration: an alternative to continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration in acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 1991;18: Schäfer GE, Döring C, Sodemann K, Russ A, Schroder HM. Continuous arteriovenous and venovenous hemodialysis in critically ill s. Contrib Nephrol 1991;93: Bellomo R, Boyce N. Acute continuous hemodiafiltration: a prospective study of 110 s and a review of the literature. Am J Kidney Dis 1993;21: Miller LC, Hall JC, Crow JW, Cato AE, Edson JR, Scheinman JI. Hemodialysis in heparin-associated thrombocytopenia: epoprostenol (PGI 2 ) as sole anticoagulant. Dial Transplant 1985;14: Swartz RD, Flamenbaum W, Dubrow A, Hall JC, Crow JW, Cato A May 1, 1997
7 Epoprostenol (PGI 2, prostacyclin) during high-risk hemodialysis: preventing further bleeding complications. J Clin Pharmacol 1988;28: Journois D, Chanu D, Pouard P, Mauriat P, Safran D. Assessment of standardized ultrafiltrate production rate using prostacyclin in continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Contrib Nephrol 1991;93: Barton IK, Hilton PJ, Treacher DF, Bradley RD. Treatment of combined acute renal failure and lactic acidosis by hemofiltration. Clin Intensive Care 1992;3: Barton IK, Streather CP, Hilton PJ, Bradley RD. Successful treatment of severe lactic acidosis by haemofiltration using a bicarbonate-based. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1991;6: Price CA. Continuous renal therapy: the treatment of choice for acute renal failure. Anna J 1991;18: Kierdorf H. Continuous versus intermittent treatment: clinical results in acute renal failure. Contrib Nephrol 1991;93: Clark WR, Mueller BA, Alaka KJ, Macias WL. A comparison of metabolic control by continuous and intermittent therapies in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 1994;4: Chertow GM, Christiansen CL, Cleary PD, Munro C, Lazarus JM. Prognostic stratification in critically ill s with acute renal failure requiring dialysis. Arch Intern Med 1995;155: Barton IK, Hilton PJ, Taub NA, et al. Acute renal failure treated by haemofiltration: factors affecting outcome. Q J Med 1993;86: [Erratum, Q J Med 1993;86:283.] 26. Forni LG, Wright DA, Hilton PJ, Carr P, Taub HA, Warburton F. Prognostic stratification in acute renal failure. Arch Intern Med 1996;156: 1023, McDonald BR, Mehta RL. Decreased mortality in s with acute renal failure undergoing continuous arteriovenous hemodialysis. Contrib Nephrol 1991;93: van Bommel EFH, Bouvy ND, So KL, et al. Acute dialytic support for the critically ill: intermittent hemodialysis versus continuous arteriovenous hemodiafiltration. Am J Nephrol 1995;15: Volume 336 Number
UNDERSTANDING THE CRRT MACHINE
 UNDERSTANDING THE CRRT MACHINE Helen Dickie Renal Sister Critical Care Unit Guy s and St.Thomas NHS Foundation Trust 18.10.14 RRT options - IHD vs CRRT (1) Intermittent HaemoDialysis e.g. 4hrs daily or
UNDERSTANDING THE CRRT MACHINE Helen Dickie Renal Sister Critical Care Unit Guy s and St.Thomas NHS Foundation Trust 18.10.14 RRT options - IHD vs CRRT (1) Intermittent HaemoDialysis e.g. 4hrs daily or
Solute clearances during continuous venovenous haemofiltration at various ultrafiltration flow rates using Multiflow-100 and HF1000 filters
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18: 961 966 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg055 Original Article Solute clearances during continuous venovenous haemofiltration at various ultrafiltration flow rates using Multiflow-100
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18: 961 966 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg055 Original Article Solute clearances during continuous venovenous haemofiltration at various ultrafiltration flow rates using Multiflow-100
Management of the patient with established AKI. Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital
 Management of the patient with established AKI Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital Medical management Medical management Respiratory- pulmonary oedema, repositioning- upright, oxygen
Management of the patient with established AKI Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital Medical management Medical management Respiratory- pulmonary oedema, repositioning- upright, oxygen
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 1 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) S Sarkar Citation S Sarkar. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT). The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 1 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) S Sarkar Citation S Sarkar. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT). The Internet Journal
Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure
 CHAPTER 82 Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure R. Deshpande Introduction Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as an abrupt decrease in renal function sufficient to result in retention of nitrogenous
CHAPTER 82 Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Renal Failure R. Deshpande Introduction Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as an abrupt decrease in renal function sufficient to result in retention of nitrogenous
Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018
 Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018 Objectives By the end of this session the learner will
Implementing therapy-delivery, dose adjustments and fluid balance. Eileen Lischer MA, BSN, RN, CNN University of California San Diego March 6, 2018 Objectives By the end of this session the learner will
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test. AKI & CRRT Conference 2018
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test AKI & CRRT Conference 2018 Question 1 Which ONE of the following statements regarding solute clearance in CRRT is MOST correct? A. Convective and diffusive solute
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test AKI & CRRT Conference 2018 Question 1 Which ONE of the following statements regarding solute clearance in CRRT is MOST correct? A. Convective and diffusive solute
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test. AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
ECMO & Renal Failure Epidemeology Renal failure & effect on out come
 ECMO Induced Renal Issues Transient renal dysfunction Improvement in renal function ECMO & Renal Failure Epidemeology Renal failure & effect on out come With or Without RRT Renal replacement Therapy Utilizes
ECMO Induced Renal Issues Transient renal dysfunction Improvement in renal function ECMO & Renal Failure Epidemeology Renal failure & effect on out come With or Without RRT Renal replacement Therapy Utilizes
Renal Replacement Therapy in ICU. Dr. Sunil Sharma Senior Resident Dept of Pulmonary Medicine
 Renal Replacement Therapy in ICU Dr. Sunil Sharma Senior Resident Dept of Pulmonary Medicine Introduction Need for RRT in patients with ARF is a common & increasing problem in ICUs Leading cause of ARF
Renal Replacement Therapy in ICU Dr. Sunil Sharma Senior Resident Dept of Pulmonary Medicine Introduction Need for RRT in patients with ARF is a common & increasing problem in ICUs Leading cause of ARF
Recent advances in CRRT
 Recent advances in CRRT JAE IL SHIN, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children s Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Pediatric AKI epidemiology and demographics
Recent advances in CRRT JAE IL SHIN, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children s Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Pediatric AKI epidemiology and demographics
Continuous renal replacement therapy. David Connor
 Continuous renal replacement therapy David Connor Overview Classification of AKI Indications Principles Types of CRRT Controversies RIFL criteria Stage GFR Criteria Urine Output Criteria Risk Baseline
Continuous renal replacement therapy David Connor Overview Classification of AKI Indications Principles Types of CRRT Controversies RIFL criteria Stage GFR Criteria Urine Output Criteria Risk Baseline
higher dose with progress in technical equipment. Continuous Dialysis: Dose and Antikoagulation. prescribed and delivered
 1 2 Continuous Dialysis: Dose and Antikoagulation higher dose with progress in technical equipment Comparison of pump-driven and spontaneous continuous haemofiltration in postoperative acute renal failure.
1 2 Continuous Dialysis: Dose and Antikoagulation higher dose with progress in technical equipment Comparison of pump-driven and spontaneous continuous haemofiltration in postoperative acute renal failure.
UAB CRRT Primer Ashita Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham
 UAB CRRT Primer 2018 Ashita Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 1 CRRT Primer Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) is a "catch all" term used for all the continuous modes of renal
UAB CRRT Primer 2018 Ashita Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 1 CRRT Primer Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) is a "catch all" term used for all the continuous modes of renal
CRRT. Principles and Methods Of Anticoagulation in CRRT Ravindra L Mehta MD. FACP. Citrate Anticoagulation. Overview Practical Issues Sample Orders
 Principles and Methods Of Anticoagulation in CRRT Ravindra L Mehta MD. FACP. Educational Objectives: 1. Define the goals of anticoagulation in CRRT and identify the factors which affect anticoagulant choice
Principles and Methods Of Anticoagulation in CRRT Ravindra L Mehta MD. FACP. Educational Objectives: 1. Define the goals of anticoagulation in CRRT and identify the factors which affect anticoagulant choice
Dialysis in the Acute Setting
 Dialysis in the Acute Setting medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/dialysis-in-the-acute-setting/ October 8, 2015 Kunal Malhotra, MD Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Missouri School
Dialysis in the Acute Setting medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/dialysis-in-the-acute-setting/ October 8, 2015 Kunal Malhotra, MD Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Missouri School
- SLED Sustained Low-Efficiency Dialysis
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms - SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms - SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Technical Considerations for Renal Replacement Therapy in Children
 Technical Considerations for Renal Replacement Therapy in Children Timothy E. Bunchman, MD,* Patrick D. Brophy, MD, and Stuart L. Goldstein, MD Summary: Provision of renal replacement therapy to the critically
Technical Considerations for Renal Replacement Therapy in Children Timothy E. Bunchman, MD,* Patrick D. Brophy, MD, and Stuart L. Goldstein, MD Summary: Provision of renal replacement therapy to the critically
Kidney Failure. Haemodialysis
 Kidneys & Kidney Failure 2 Haemodialysis This booklet will help you to know the process of Haemodialysis in detail. It will also tell you about the disposables of Haemodialysis. In the end the advantages
Kidneys & Kidney Failure 2 Haemodialysis This booklet will help you to know the process of Haemodialysis in detail. It will also tell you about the disposables of Haemodialysis. In the end the advantages
Accelerated Venovenous Hemofiltration: Early Technical and Clinical Experience
 Accelerated Venovenous Hemofiltration: Early Technical and Clinical Experience Casey N. Gashti, MD, Susana Salcedo, MD, Virginia Robinson, RN, and Roger A. Rodby, MD Background: Renal replacement therapies
Accelerated Venovenous Hemofiltration: Early Technical and Clinical Experience Casey N. Gashti, MD, Susana Salcedo, MD, Virginia Robinson, RN, and Roger A. Rodby, MD Background: Renal replacement therapies
Nurse-Pharmacist Collaboration in the Delivery of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
 Cedarville University DigitalCommons@Cedarville Pharmacy Faculty Presentations School of Pharmacy 2-23-2012 Nurse-Pharmacist Collaboration in the Delivery of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jeb Ballentine
Cedarville University DigitalCommons@Cedarville Pharmacy Faculty Presentations School of Pharmacy 2-23-2012 Nurse-Pharmacist Collaboration in the Delivery of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Jeb Ballentine
PICANet Custom Audit Definitions Renal Dataset
 PICANet Custom Audit s Renal Dataset Version 1.0 (July 2016) PICANet Renal Custom Audit Data s Manual Version 1.0 July 2016 Renal Dataset Contents PICANet Custom Audit s... 1 Renal Dataset... 1 Version
PICANet Custom Audit s Renal Dataset Version 1.0 (July 2016) PICANet Renal Custom Audit Data s Manual Version 1.0 July 2016 Renal Dataset Contents PICANet Custom Audit s... 1 Renal Dataset... 1 Version
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in PICU: explanation/definitions/rationale/background
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in PICU: explanation/definitions/rationale/background Index: 1. Introduction Pg. 1 1.1 Definitions Pg. 2 1.2 Renal replacement therapy principles Pg. 2 2. Continuous
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in PICU: explanation/definitions/rationale/background Index: 1. Introduction Pg. 1 1.1 Definitions Pg. 2 1.2 Renal replacement therapy principles Pg. 2 2. Continuous
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT
 Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Section 3: Prevention and Treatment of AKI
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 KDIGO Summary of ommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 8 12; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.7 Section 2: AKI Definition 2.1.1: AKI is defined
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 KDIGO Summary of ommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 8 12; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.7 Section 2: AKI Definition 2.1.1: AKI is defined
RENAL FAILURE IN ICU. Jo-Ann Vosloo Department Critical Care SBAH
 RENAL FAILURE IN ICU Jo-Ann Vosloo Department Critical Care SBAH DEFINITION: RIFLE criteria Criteria for initiation of RRT Modes of RRT (options) CRRT = continuous renal replacement therapy SCUF : Ultra-filtration
RENAL FAILURE IN ICU Jo-Ann Vosloo Department Critical Care SBAH DEFINITION: RIFLE criteria Criteria for initiation of RRT Modes of RRT (options) CRRT = continuous renal replacement therapy SCUF : Ultra-filtration
Metabolismo del citrato nei pazienti critici. Filippo MARIANO Dipartimento di Area Medica, SCDO di Nefrologia e Dialisi Ospedale CTO, Torino
 Metabolismo del citrato nei pazienti critici Filippo MARIANO Dipartimento di Area Medica, SCDO di Nefrologia e Dialisi Ospedale CTO, Torino Regional citrate anticoagulation: the history First in hemodialysis
Metabolismo del citrato nei pazienti critici Filippo MARIANO Dipartimento di Area Medica, SCDO di Nefrologia e Dialisi Ospedale CTO, Torino Regional citrate anticoagulation: the history First in hemodialysis
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD 1 Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Effects of different doses in continuous veno-venous haemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: a prospective randomised trial
 Effects of different doses in continuous veno-venous haemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: a prospective randomised trial Claudio Ronco, Rinaldo Bellomo, Peter Homel, Alessandra Brendolan,
Effects of different doses in continuous veno-venous haemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: a prospective randomised trial Claudio Ronco, Rinaldo Bellomo, Peter Homel, Alessandra Brendolan,
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Gregory M. Susla, Pharm.D., F.C.C.M. Associate Director, Medical Information MedImmune, LLC Gaithersburg, MD Definition of Terms SCUF - Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration
Continuous renal replacement therapy Gulzar Salman Amlani Aga Khan University, School of Nursing, Karachi.
 Special Communication Continuous renal replacement therapy Gulzar Salman Amlani Aga Khan University, School of Nursing, Karachi. Abstract Acute renal failure refers to sudden deterioration in biochemical
Special Communication Continuous renal replacement therapy Gulzar Salman Amlani Aga Khan University, School of Nursing, Karachi. Abstract Acute renal failure refers to sudden deterioration in biochemical
Drug Use in Dialysis
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
PICANet Custom Audit Definitions Renal Dataset
 PICANet Custom Audit s Renal Dataset Version 2.0 (March 2017) PICANet Renal Custom Audit Data s Manual Version 2.0 29/03/2017 Renal Dataset Contents PICANet Custom Audit s... 1 Renal Dataset... 1 Version
PICANet Custom Audit s Renal Dataset Version 2.0 (March 2017) PICANet Renal Custom Audit Data s Manual Version 2.0 29/03/2017 Renal Dataset Contents PICANet Custom Audit s... 1 Renal Dataset... 1 Version
Aquarius Study Day Adult Pre-Reading Study Pack
 Aquarius Study Day Adult Pre-Reading Study Pack An Introduction to CRRT (Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy) Name Date. Hospital.. Please take the opportunity to read this booklet prior to attending
Aquarius Study Day Adult Pre-Reading Study Pack An Introduction to CRRT (Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy) Name Date. Hospital.. Please take the opportunity to read this booklet prior to attending
Decision making in acute dialysis
 Decision making in acute dialysis Geoffrey Bihl MB.BCh M.MED FCP(SA) Nephrologist and Director Winelands Kidney and Dialysis Centre Somerset West South Africa Important questions in AKI What is the cause?
Decision making in acute dialysis Geoffrey Bihl MB.BCh M.MED FCP(SA) Nephrologist and Director Winelands Kidney and Dialysis Centre Somerset West South Africa Important questions in AKI What is the cause?
CRRT. Sustained low efficiency daily dialysis, SLEDD. Sustained low efficiency daily diafiltration, SLEDD-f. inflammatory cytokine IL-1 IL-6 TNF-
 RRT, renal replacement therapy IHDCRRT CRRT 24 CRRT Sustained low efficiency daily dialysis, SLEDD 6 ~ 12 300 Sustained low efficiency daily diafiltration, SLEDD-f inflammatory cytokine IL-1 IL-6 TNF-
RRT, renal replacement therapy IHDCRRT CRRT 24 CRRT Sustained low efficiency daily dialysis, SLEDD 6 ~ 12 300 Sustained low efficiency daily diafiltration, SLEDD-f inflammatory cytokine IL-1 IL-6 TNF-
James Beck ECS 8 November 2014 Citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy
 Citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy Clinical Problem A 73 year old female patient presented to the Accident and Emergency Department (A&E) with a profound anaemia, acute kidney
Citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy Clinical Problem A 73 year old female patient presented to the Accident and Emergency Department (A&E) with a profound anaemia, acute kidney
Active UMMC Protocols
 UMMC CRRT 2018 Active UMMC Protocols 1. Standard CRRT Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with Fixed Ratio Regional Citrate Anticoagulation 2. No Anticoagulation Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with
UMMC CRRT 2018 Active UMMC Protocols 1. Standard CRRT Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with Fixed Ratio Regional Citrate Anticoagulation 2. No Anticoagulation Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with
Renal Physiology Intro to CRRT Concepts. Catherine Jones September 2017
 Renal Physiology Intro to CRRT Concepts Catherine Jones September 2017 Learning Outcomes To revise anatomy & physiology of kidney in health: To understand basic principles of continuous renal replacement
Renal Physiology Intro to CRRT Concepts Catherine Jones September 2017 Learning Outcomes To revise anatomy & physiology of kidney in health: To understand basic principles of continuous renal replacement
Renal Replacement Therapies
 Renal Replacement Therapies M I H Á L Y T A P O L Y A I, M D, F A S N, F A C P A s s o c i a t e P r o f e s s o r D e p a r t m e n t o f N e p h r o l o g y L o u i s i a n a S t a t e U n i v e r s
Renal Replacement Therapies M I H Á L Y T A P O L Y A I, M D, F A S N, F A C P A s s o c i a t e P r o f e s s o r D e p a r t m e n t o f N e p h r o l o g y L o u i s i a n a S t a t e U n i v e r s
Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis. Outline. Solute Removal Mechanisms in RRT
 Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis Jordan M. Symons, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital Outline Physical principles of mass transfer Hemodialysis
Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis Jordan M. Symons, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital Outline Physical principles of mass transfer Hemodialysis
Karen Mak R.N. (Team Leader) Renal Dialysis Centre Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital
 Karen Mak R.N. (Team Leader) Renal Dialysis Centre Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital - Renal Transplantation - Peritoneal Dialysis - Extracorporeal Therapy Extracorporeal Therapy It is the procedure in
Karen Mak R.N. (Team Leader) Renal Dialysis Centre Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital - Renal Transplantation - Peritoneal Dialysis - Extracorporeal Therapy Extracorporeal Therapy It is the procedure in
ACUTE HEMOFILTRATION IN INTENSIVE CARE SETTING
 ACUTE HEMOFILTRATION IN INTENSIVE CARE SETTING K N Lai F Mac-Moune Lai S C Cheng J Valiance -Owen Department of Medicine Chinese University of Hong Kong Prince of Wales Hospital Shantin, New Territories
ACUTE HEMOFILTRATION IN INTENSIVE CARE SETTING K N Lai F Mac-Moune Lai S C Cheng J Valiance -Owen Department of Medicine Chinese University of Hong Kong Prince of Wales Hospital Shantin, New Territories
Acute Kidney Injury- What Is It and How Do I Treat It?
 Acute Kidney Injury- What Is It and How Do I Treat It? Jayant Kumar, MD Renal Medicine Assoc., Albuquerque, NM Incidence of ARF in ICU Causes of ARF Non -ICU ICU 1 KDIGO criteria for AKI Increase in serum
Acute Kidney Injury- What Is It and How Do I Treat It? Jayant Kumar, MD Renal Medicine Assoc., Albuquerque, NM Incidence of ARF in ICU Causes of ARF Non -ICU ICU 1 KDIGO criteria for AKI Increase in serum
Excretory System Workbook
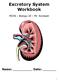 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
A quick reference guide to haemofiltration and renal failure
 A quick reference guide to haemofiltration and renal failure March 2004 Alison Bradshaw 1 Page 3 Acute Renal Failure Page 4 Normal Kidney Function Page 5 Nephron Function Page 6 Definitions of Key Words
A quick reference guide to haemofiltration and renal failure March 2004 Alison Bradshaw 1 Page 3 Acute Renal Failure Page 4 Normal Kidney Function Page 5 Nephron Function Page 6 Definitions of Key Words
MODALITIES of Renal Replacement Therapy in AKI
 MODALITIES of Renal Replacement Therapy in AKI Jorge Cerdá, MD, MS, FACP, FASN Clinical Professor of Medicine Albany Medical College Albany, NY, USA cerdaj@mail.amc.edu In AKI, RRT is a multidimensional
MODALITIES of Renal Replacement Therapy in AKI Jorge Cerdá, MD, MS, FACP, FASN Clinical Professor of Medicine Albany Medical College Albany, NY, USA cerdaj@mail.amc.edu In AKI, RRT is a multidimensional
Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
 Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Farahnak Assadi Fatemeh Ghane Sharbaf Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Principles and Practice Farahnak Assadi, M.D. Professor Emeritus Department
Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Farahnak Assadi Fatemeh Ghane Sharbaf Pediatric Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Principles and Practice Farahnak Assadi, M.D. Professor Emeritus Department
Fundamentals of DIALYSIS
 Fundamentals of DIALYSIS Knowing Your Kidneys Healthy Kidneys are the body s cleaning crew These are twin bean shaped organs, of the size of fist They make up a filter system for the blood & reabsorb almost
Fundamentals of DIALYSIS Knowing Your Kidneys Healthy Kidneys are the body s cleaning crew These are twin bean shaped organs, of the size of fist They make up a filter system for the blood & reabsorb almost
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test Answers. AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test Answers AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test Answers AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling
Commentary Recent evolution of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill patient Claudio Ronco
 Commentary Recent evolution of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill patient Claudio Ronco Department of Nephrology, St Bortolo Hospital, Vicenza, Italy Corresponding author: Claudio Ronco, cronco@goldnet.it
Commentary Recent evolution of renal replacement therapy in the critically ill patient Claudio Ronco Department of Nephrology, St Bortolo Hospital, Vicenza, Italy Corresponding author: Claudio Ronco, cronco@goldnet.it
[1] Levy [3] (odds ratio) 5.5. mannitol. (renal dose) dopamine 1 µg/kg/min atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
![[1] Levy [3] (odds ratio) 5.5. mannitol. (renal dose) dopamine 1 µg/kg/min atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) [1] Levy [3] (odds ratio) 5.5. mannitol. (renal dose) dopamine 1 µg/kg/min atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)](/thumbs/92/109602349.jpg) [1] Levy [3] 183 174 (odds ratio) 5.5 Woodrow [1] 1956 1989 mannitol (renal dose) dopamine 1 µg/kg/min atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) McCarthy [2] 1970 1990 insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) ANP 92
[1] Levy [3] 183 174 (odds ratio) 5.5 Woodrow [1] 1956 1989 mannitol (renal dose) dopamine 1 µg/kg/min atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) McCarthy [2] 1970 1990 insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) ANP 92
Objectives. Peritoneal Dialysis vs. Hemodialysis 02/27/2018. Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
End-Stage Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology
 End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
CRRT for the Experience User 1. Claudio Ronco, M.D. David Selewski, M.D. Rolando Claure-Del Granado, M.D. AKI & CRRT Conference March, 2018
 CRRT for the Experience User 1 Claudio Ronco, M.D. David Selewski, M.D. Rolando Claure-Del Granado, M.D. AKI & CRRT Conference March, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
CRRT for the Experience User 1 Claudio Ronco, M.D. David Selewski, M.D. Rolando Claure-Del Granado, M.D. AKI & CRRT Conference March, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
A safe citrate anticoagulation protocol with variable treatment efficacy and excellent control of the acid base status*
 A safe citrate anticoagulation protocol with variable treatment efficacy and excellent control of the acid base status* Stanislao Morgera, MD; Michael Schneider, MD; Torsten Slowinski, MD; Ortrud Vargas-Hein,
A safe citrate anticoagulation protocol with variable treatment efficacy and excellent control of the acid base status* Stanislao Morgera, MD; Michael Schneider, MD; Torsten Slowinski, MD; Ortrud Vargas-Hein,
Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are
 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Effects of lactate-buffered and lactate-free dialysate in CAVHD patients with and without liver dysfunction
 Kidney International, Vol. 58 (2000), pp. 1765 1772 Effects of lactate-buffered and lactate-free dialysate in CAVHD patients with and without liver dysfunction ADAM G. MCLEAN, ANDREW DAVENPORT, DOMINIC
Kidney International, Vol. 58 (2000), pp. 1765 1772 Effects of lactate-buffered and lactate-free dialysate in CAVHD patients with and without liver dysfunction ADAM G. MCLEAN, ANDREW DAVENPORT, DOMINIC
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Symposium. Principles of Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically ill children- Indian Perspective
 Symposium DOI- 10.21304/2018.0502.00376 in Critically ill children- Indian Perspective Sidharth Kumar Sethi *, Aliza Mittal**, Rupesh Raina***, Manindar Dhaliwal**** * Senior Consultant, Pediatric Nephrology
Symposium DOI- 10.21304/2018.0502.00376 in Critically ill children- Indian Perspective Sidharth Kumar Sethi *, Aliza Mittal**, Rupesh Raina***, Manindar Dhaliwal**** * Senior Consultant, Pediatric Nephrology
EFFECT OF ONLINE HAEMODIAFILTRATION ON ALL- CAUSE MORTALITY AND CARDIOVASCULAR OUTCOMES Ercan Ok, Izmir, Turkey
 EFFECT OF ONLINE HAEMODIAFILTRATION ON ALL- CAUSE MORTALITY AND CARDIOVASCULAR OUTCOMES Ercan Ok, Izmir, Turkey Chair: Walter H. Hörl, Vienna, Austria Wojciech Zaluska, Lublin, Poland Prof Ercan Ok Division
EFFECT OF ONLINE HAEMODIAFILTRATION ON ALL- CAUSE MORTALITY AND CARDIOVASCULAR OUTCOMES Ercan Ok, Izmir, Turkey Chair: Walter H. Hörl, Vienna, Austria Wojciech Zaluska, Lublin, Poland Prof Ercan Ok Division
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
Ultrafiltration rate as a dose surrogate in pre-dilution hemofiltration
 The International Journal of Artificial Organs / Vol. 30 / no. 2, 2007 / pp. 124-132 Artificial Kidney and Dialysis Ultrafiltration rate as a dose surrogate in pre-dilution hemofiltration Z. HUANG 1, J.J.
The International Journal of Artificial Organs / Vol. 30 / no. 2, 2007 / pp. 124-132 Artificial Kidney and Dialysis Ultrafiltration rate as a dose surrogate in pre-dilution hemofiltration Z. HUANG 1, J.J.
Haemofiltration: Experience in a Local Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2004;9:37-43 Haemofiltration: Experience in a Local Paediatric Intensive Care Unit BCB WU, WKY CHAN, TY MIU, GLH CHAN Abstract Key words We report 17 children who were admitted
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2004;9:37-43 Haemofiltration: Experience in a Local Paediatric Intensive Care Unit BCB WU, WKY CHAN, TY MIU, GLH CHAN Abstract Key words We report 17 children who were admitted
egfr 34 ml/min egfr 130 ml/min Am J Kidney Dis 2002;39(suppl 1):S17-S31
 Update on Renal Therapeutics Caroline Ashley Lead Pharmacist Renal Services UCL Centre for Nephrology, Royal Free Hospital, London Kongress für Arzneimittelinformation January 2011 What are we going to
Update on Renal Therapeutics Caroline Ashley Lead Pharmacist Renal Services UCL Centre for Nephrology, Royal Free Hospital, London Kongress für Arzneimittelinformation January 2011 What are we going to
ST. DOMINIC-JACKSON MEMORIAL HOSPITAL JACKSON, MISSISSIPPI. CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT) HEPARIN ANTICOAGULATION Page 1 of 5
 HEPARIN ANTICOAGULATION Page 1 of 5 Pharmacy Mnemonic: CRRTHEP1 PATIENT DATA: DIAGNOSIS: AKI ESRD Other: WEIGHT: Today: kg Admission Weight:: kg Dry Weight: kg Access TYPE: Temporary Dialysis Catheter
HEPARIN ANTICOAGULATION Page 1 of 5 Pharmacy Mnemonic: CRRTHEP1 PATIENT DATA: DIAGNOSIS: AKI ESRD Other: WEIGHT: Today: kg Admission Weight:: kg Dry Weight: kg Access TYPE: Temporary Dialysis Catheter
Enhancement of convective transport by internal filtration in a modified experimental hemodialyzer Technical Note
 Kidney International, Vol. 54 (1998), pp. 979 985 Enhancement of convective transport by internal filtration in a modified experimental hemodialyzer Technical Note CLAUDIO RONCO, GIANCARLO ORLANDINI, ALESSANDRA
Kidney International, Vol. 54 (1998), pp. 979 985 Enhancement of convective transport by internal filtration in a modified experimental hemodialyzer Technical Note CLAUDIO RONCO, GIANCARLO ORLANDINI, ALESSANDRA
Modes of Extracorporeal Therapies For ESRD Patients
 Modes of Extracorporeal Therapies For ESRD Patients Suhail, MD Extracorporeal Therapies: Dialytic Therapies Dialysis: Movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane (Bi-directional) Movement of
Modes of Extracorporeal Therapies For ESRD Patients Suhail, MD Extracorporeal Therapies: Dialytic Therapies Dialysis: Movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane (Bi-directional) Movement of
Package leaflet: information for the user. Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration
 Package leaflet: information for the user Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Calcium chloride dihydrate/ magnesium chloride hexahydrate/ glucose monohydrate/ lactic
Package leaflet: information for the user Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Calcium chloride dihydrate/ magnesium chloride hexahydrate/ glucose monohydrate/ lactic
What is renal failure?
 What is renal failure? The kidney is a very important organ, and cannot be restored to health once it fails. However, it is possible to avoid or retard the deterioration of its functionality if therapy
What is renal failure? The kidney is a very important organ, and cannot be restored to health once it fails. However, it is possible to avoid or retard the deterioration of its functionality if therapy
404FM.2 CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT) USING CITRATE Target Audience: Hospital only ICU. (Based on Gambro and Kalmar Hospital protocols)
 404FM.2 CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT) USING CITRATE Target Audience: Hospital only ICU (Based on Gambro and Kalmar Hospital protocols) CRRT using regional citrate anticoagulation This is
404FM.2 CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT) USING CITRATE Target Audience: Hospital only ICU (Based on Gambro and Kalmar Hospital protocols) CRRT using regional citrate anticoagulation This is
Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2011.26.1.68 Regional Anticoagulation with Citrate is Superior to Systemic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ιll Patients Undergoing Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2011.26.1.68 Regional Anticoagulation with Citrate is Superior to Systemic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ιll Patients Undergoing Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? Modalities of Dialysis
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? A common condition in ICU patients Associated with high mortality and morbidity Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) is the cornerstone
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) How Wise is Early Dialysis in Critically Ill Patients? A common condition in ICU patients Associated with high mortality and morbidity Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) is the cornerstone
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (1996) 11 [Suppl 2]: 75-80 Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Recirculation and the post-dialysis rebound J. E. Tattersall, P. Chamney, C. Aldridge and R. N. Greenwood Lister Hospital,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (1996) 11 [Suppl 2]: 75-80 Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Recirculation and the post-dialysis rebound J. E. Tattersall, P. Chamney, C. Aldridge and R. N. Greenwood Lister Hospital,
CRRT: The Technical Questions Modality & Dose. Ashita J. Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 2018
 CRRT: The Technical Questions Modality & Dose Ashita J. Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 2018 Case A 24YOM with HTN and OSA presents with acute pancreatitis. Despite aggressive fluid
CRRT: The Technical Questions Modality & Dose Ashita J. Tolwani, MD, MSc University of Alabama at Birmingham 2018 Case A 24YOM with HTN and OSA presents with acute pancreatitis. Despite aggressive fluid
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in Dogs and Cats
 Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in Dogs and Cats Mark J. Acierno, MBA, DVM KEYWORDS Continuous renal replacement therapy CRRT Acute kidney injury Dialysis In the early 1900s, a young pharmacologist
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy in Dogs and Cats Mark J. Acierno, MBA, DVM KEYWORDS Continuous renal replacement therapy CRRT Acute kidney injury Dialysis In the early 1900s, a young pharmacologist
Acid base homeostasis with the high convective dialysis treatments
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 7]: vii26 vii30 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1075 Acid base homeostasis with the high convective dialysis treatments Mariano Feriani Department of Nephrology and Dialysis,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 7]: vii26 vii30 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1075 Acid base homeostasis with the high convective dialysis treatments Mariano Feriani Department of Nephrology and Dialysis,
oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators
 oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators Heparin-grafted for reduced thrombogenicity Supports renal function POWERED
oxiris A single CRRT set with multiple benefits for managing critically ill patients with AKI Adsorption of inflammatory mediators Heparin-grafted for reduced thrombogenicity Supports renal function POWERED
Calcium (Ca 2+ ) mg/dl
 Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
multibic potassium-free multibic 2 mmol/l potassium multibic 3 mmol/l potassium multibic 4 mmol/l potassium
 FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE Deutschland GmbH Name(s) of the medicinal product(s): -free 2 mmol/l 3 mmol/l 4 mmol/l Pharmaceutical form: Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Procedure number(s): DE/H/0388/001-004/II/030/G
FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE Deutschland GmbH Name(s) of the medicinal product(s): -free 2 mmol/l 3 mmol/l 4 mmol/l Pharmaceutical form: Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Procedure number(s): DE/H/0388/001-004/II/030/G
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PRISMASOL and PHOXILLUM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PRISMASOL and
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PRISMASOL and PHOXILLUM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PRISMASOL and
Hemodiafiltration in Europe : Trends, Practices, Outcomes & Perspectives
 Hemodiafiltration in Europe : Trends, Practices, Outcomes & Perspectives Prof. Bernard Canaud Nephrology, Dialysis and Intensive Care Lapeyronie Hospital CHRU Montpellier - France Opening remarks and special
Hemodiafiltration in Europe : Trends, Practices, Outcomes & Perspectives Prof. Bernard Canaud Nephrology, Dialysis and Intensive Care Lapeyronie Hospital CHRU Montpellier - France Opening remarks and special
Citrate vs. heparin for anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration: a prospective randomized study
 Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:260 265 DOI 10.1007/s00134-003-2047-x ORIGINAL Mehran Monchi Denis Berghmans Didier Ledoux Jean-Luc Canivet Bernard Dubois Pierre Damas Citrate vs. heparin for anticoagulation
Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:260 265 DOI 10.1007/s00134-003-2047-x ORIGINAL Mehran Monchi Denis Berghmans Didier Ledoux Jean-Luc Canivet Bernard Dubois Pierre Damas Citrate vs. heparin for anticoagulation
Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury
 Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury ASCIM 2014 Dr Adrian Plunkett Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Aims of the presentation Important topic: AKI
Renal replacement therapy in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury ASCIM 2014 Dr Adrian Plunkett Consultant Paediatric Intensivist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Aims of the presentation Important topic: AKI
Duosol. Bicarbonate-buffered solution for hemofiltration. Avitum
 Duosol Bicarbonate-buffered solution for hemofiltration Avitum Duosol Knowledge serving health As a supplier of dialysis and apheresis systems, B. Braun possesses a wealth of experience in the field of
Duosol Bicarbonate-buffered solution for hemofiltration Avitum Duosol Knowledge serving health As a supplier of dialysis and apheresis systems, B. Braun possesses a wealth of experience in the field of
Keywords acidosis, alkalosis, bicarbonate, hemofiltration, hemodialysis, renal replacement therapy
 Review Bench-to-bedside review: Treating acid base abnormalities in the intensive care unit the role of renal replacement therapy Toshio Naka 1 and Rinaldo Bellomo 2 1 Research Fellow, Department of Intensive
Review Bench-to-bedside review: Treating acid base abnormalities in the intensive care unit the role of renal replacement therapy Toshio Naka 1 and Rinaldo Bellomo 2 1 Research Fellow, Department of Intensive
THERAPEUTIC PLASMA EXCHANGE
 THERAPEUTIC PLASMA EXCHANGE DIRECTORATE OF NEPHROLOGY AND TRANSPLANTATION Background and Indications Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) is an extracorporeal blood purification technique in which plasma
THERAPEUTIC PLASMA EXCHANGE DIRECTORATE OF NEPHROLOGY AND TRANSPLANTATION Background and Indications Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) is an extracorporeal blood purification technique in which plasma
Self-Learning Packet 2008
 Principles of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Self-Learning Packet 2008 This self-learning packet is approved for 2 contact hours for the following professionals: 1. Registered Nurse CRRT Table of
Principles of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Self-Learning Packet 2008 This self-learning packet is approved for 2 contact hours for the following professionals: 1. Registered Nurse CRRT Table of
HYPOVOLEMIA AND HEMORRHAGE UPDATE ON VOLUME RESUSCITATION HEMORRHAGE AND HYPOVOLEMIA DISTRIBUTION OF BODY FLUIDS 11/7/2015
 UPDATE ON VOLUME RESUSCITATION HYPOVOLEMIA AND HEMORRHAGE HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OPERATES WITH A SMALL VOLUME AND A VERY EFFICIENT VOLUME RESPONSIVE PUMP. HOWEVER THIS PUMP FAILS QUICKLY WITH VOLUME
UPDATE ON VOLUME RESUSCITATION HYPOVOLEMIA AND HEMORRHAGE HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OPERATES WITH A SMALL VOLUME AND A VERY EFFICIENT VOLUME RESPONSIVE PUMP. HOWEVER THIS PUMP FAILS QUICKLY WITH VOLUME
Continuous renal replacement therapy: Does technique influence electrolyte and bicarbonate control?
 The International Journal of Artificial Organs / Vol. 26 / no. 4, 2003 / pp. 289-296 Artificial Kidney and Dialysis Continuous renal replacement therapy: Does technique influence electrolyte and bicarbonate
The International Journal of Artificial Organs / Vol. 26 / no. 4, 2003 / pp. 289-296 Artificial Kidney and Dialysis Continuous renal replacement therapy: Does technique influence electrolyte and bicarbonate
Effectiveness of Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration for Patients with. Refractory heart failure
 Clinical Studies Effectiveness of Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration for Patients with Refractory Heart Failure Teruo INOUE, M.D., Shigenori MOROOKA, M.D., Terumi HAYASHI, M.D., Kan TAKAYANAGI, M.D.,
Clinical Studies Effectiveness of Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration for Patients with Refractory Heart Failure Teruo INOUE, M.D., Shigenori MOROOKA, M.D., Terumi HAYASHI, M.D., Kan TAKAYANAGI, M.D.,
Dialysis Dose Prescription and Delivery. William Clark, M.D. Claudio Ronco, M.D. Rolando Claure-Del Granado, M.D. CRRT Conference February 15, 2012
 Dialysis Dose Prescription and Delivery William Clark, M.D. Claudio Ronco, M.D. Rolando Claure-Del Granado, M.D. CRRT Conference February 15, 2012 Dose in RRT: Key concepts Dose definition Quantifying
Dialysis Dose Prescription and Delivery William Clark, M.D. Claudio Ronco, M.D. Rolando Claure-Del Granado, M.D. CRRT Conference February 15, 2012 Dose in RRT: Key concepts Dose definition Quantifying
Therapeutic apheresis (introduction) Orieji Illoh, MD November 21, 2006
 Therapeutic apheresis (introduction) Orieji Illoh, MD November 21, 2006 Apheresis Removal of blood Separation into component parts One component is retained and remainder is returned History First tried
Therapeutic apheresis (introduction) Orieji Illoh, MD November 21, 2006 Apheresis Removal of blood Separation into component parts One component is retained and remainder is returned History First tried
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Timing, Dosing and Selecting of modality of RRT for AKI - the ERBP position statement
 Timing, Dosing and Selecting of modality of RRT for AKI - the ERBP position statement Prof. Dr. Achim Jörres Dept. of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care Charité University Hospital Campus Virchow Klinikum
Timing, Dosing and Selecting of modality of RRT for AKI - the ERBP position statement Prof. Dr. Achim Jörres Dept. of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care Charité University Hospital Campus Virchow Klinikum
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1
 ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
